Nuclear Import on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Nuclear transport refers to the mechanisms by which molecules move across the
 G-proteins are
G-proteins are
Myospreader improves gene editing in skeletal muscle by myonuclear propagation
''Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.'' (2024). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2321438121. Protein shuttling can be assessed using a ''
Nuclear Transport animations
Nuclear Transport illustrations
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090207214312/http://sspatel.googlepages.com/nuclearporecomplex2 , date=2009-02-07 Cell biology
nuclear membrane
The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer polar membrane, membranes that in eukaryotic cells surround the Cell nucleus, nucleus, which encloses the genome, genetic material.
The nuclear envelope con ...
of a cell. The entry and exit of large molecules from the cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (; : nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have #Anucleated_cells, ...
is tightly controlled by the nuclear pore complex
The nuclear pore complex (NPC), is a large protein complex giving rise to the nuclear pore. A great number of nuclear pores are studded throughout the nuclear envelope that surrounds the eukaryote cell nucleus. The pores enable the nuclear tra ...
es (NPCs). Although small molecules can enter the nucleus without regulation, macromolecules such as RNA and proteins require association with transport factors known as nuclear transport receptors, like karyopherin
Karyopherins are protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme c ...
s called importin
Importin is a type of karyopherin that transports protein molecules from the Eukaryotic Cell, cell's cytoplasm to the cell nucleus, nucleus. It does so by binding to specific recognition sequences, called nuclear localization sequences (NLS).
I ...
s to enter the nucleus and exportin
Karyopherins are proteins involved in transporting molecules between the cytoplasm and the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. The inside of the nucleus is called the karyoplasm (or nucleoplasm). Generally, karyopherin-mediated transport occurs through ...
s to exit.
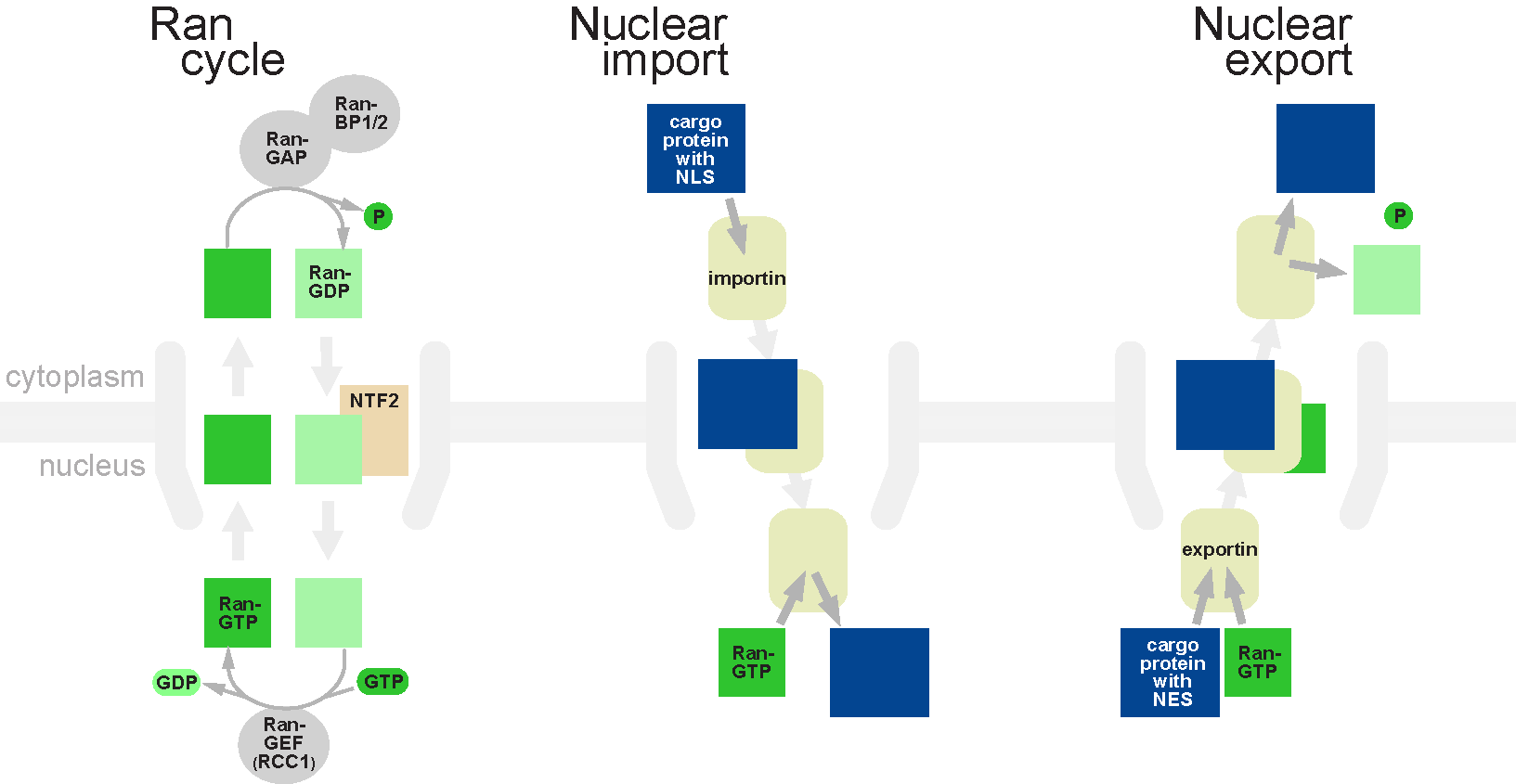
Nuclear import
Protein that must be imported to the nucleus from the cytoplasm carrynuclear localization signal
A nuclear localization signal ''or'' sequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysin ...
s (NLS) that are bound by importins. An NLS is a sequence of amino acids that acts as a tag. They are most commonly hydrophilic
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.
In contrast, hydrophobes are n ...
sequences containing lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. Lysine contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form when the lysine is dissolved in water at physiological pH), an α-carboxylic acid group ( ...
and arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidinium, guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) a ...
residues, although diverse NLS sequences have been documented. Proteins, transfer RNA
Transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA), formerly referred to as soluble ribonucleic acid (sRNA), is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes). In a cell, it provides the physical link between the gene ...
, and assembled ribosomal
Ribosomes () are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA molecules to fo ...
subunits are exported from the nucleus due to association with exportins, which bind signaling sequences called nuclear export signal
A nuclear export signal (NES) is a short target peptide containing 4 hydrophobic residues in a protein that targets it for export from the cell nucleus to the cytoplasm through the nuclear pore complex using nuclear transport. It has the opposit ...
s (NES). The ability of both importins and exportins to transport their cargo is regulated by the Ran
RAN may refer to:
* Radio access network, a part of a mobile telecommunication system
* Rainforest Action Network
* Ran (gene) (RAs-related Nuclear protein), also known as GTP-binding nuclear protein Ran, a protein that in humans is encoded by t ...
small G-protein
Small GTPases (), also known as small G-proteins, are a family of hydrolase enzymes that can bind and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP). They are a type of G-protein found in the cytosol that are homologous to the alpha subunit of heterotrim ...
.  G-proteins are
G-proteins are GTPase
GTPases are a large family of hydrolase enzymes that bind to the nucleotide guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and hydrolyze it to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The GTP binding and hydrolysis takes place in the highly conserved P-loop "G domain", a ...
enzymes that bind to a molecule called guanosine triphosphate
Guanosine-5'-triphosphate (GTP) is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It is one of the building blocks needed for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process. Its structure is similar to that of the guanosine nucleoside, the only di ...
(GTP) which they then hydrolyze
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis ...
to create guanosine diphosphate (GDP) and release energy. The RAN enzymes exist in two nucleotide-bound forms: GDP-bound and GTP-bound. In its GTP-bound state, Ran is capable of binding importins and exportins. Importins release cargo upon binding to RanGTP, while exportins must bind RanGTP to form a ternary complex with their export cargo. The dominant nucleotide binding state of Ran depends on whether it is located in the nucleus (RanGTP) or the cytoplasm (RanGDP).
Nuclear export
Nuclear export roughly reverses the import process; in the nucleus, the exportin binds the cargo and Ran-GTP and diffuses through the pore to the cytoplasm, where the complex dissociates. Ran-GTP binds GAP and hydrolyzes GTP, and the resulting Ran-GDP complex is restored to the nucleus where it exchanges its bound ligand for GTP. Hence, whereas importins depend on RanGTP to dissociate from their cargo, exportins require RanGTP in order to bind to their cargo. A specialized mRNA exporter protein moves mature mRNA to the cytoplasm after post-transcriptional modification is complete. This translocation process is actively dependent on the Ran protein, although the specific mechanism is not yet well understood. Some particularly commonly transcribed genes are physically located near nuclear pores to facilitate the translocation process. Export of tRNA is also dependent on the various modifications it undergoes, thus preventing export of improperly functioning tRNA. This quality control mechanism is important due to tRNA's central role in translation, where it is involved in adding amino acids to a growing peptide chain. The tRNA exporter in vertebrates is called ''exportin-t''. Exportin-t binds directly to its tRNA cargo in the nucleus, a process promoted by the presence of RanGTP. Mutations that affect tRNA's structure inhibit its ability to bind to exportin-t, and consequentially, to be exported, providing the cell with another quality control step. As described above, once the complex has crossed the envelope it dissociates and releases the tRNA cargo into the cytosol.Protein shuttling
Many proteins are known to have both NESs and NLSs and thus shuttle constantly between the nucleus and the cytosol. In certain cases one of these steps (i.e., nuclear import or nuclear export) is regulated, often bypost-translational modifications
In molecular biology, post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent process of changing proteins following protein biosynthesis. PTMs may involve enzymes or occur spontaneously. Proteins are created by ribosomes, which translation (biolog ...
.
Nuclear import limits the propagation of large proteins expressed in skeletal muscle fibers and possibly other syncytial tissues, maintaining localized gene expression in certain nuclei. Combining both NESs and NLSs promotes propagation of large proteins to more distant nuclei in muscle fibers.Kiril K. Poukalov, M. Carmen Valero , Derek R. Muscato, Leanne M. Adams, Heejae Chun, Young il Lee, Nadja S. Andrade, Zane Zeier, H. Lee Sweeney, and Eric T. Wang Myospreader improves gene editing in skeletal muscle by myonuclear propagation
''Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.'' (2024). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2321438121. Protein shuttling can be assessed using a ''
heterokaryon
In biology, a heterokaryon is a multinucleate cell that contains genetically different nuclei. This is a special type of syncytium. This can occur naturally, such as in the mycelium of fungi during sexual reproduction, or artificially as formed b ...
fusion assay''.
References
External links
Nuclear Transport animations
Nuclear Transport illustrations
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090207214312/http://sspatel.googlepages.com/nuclearporecomplex2 , date=2009-02-07 Cell biology