New Guinea on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern
 The island has been known by various names:
The name ''Papua'' was used to refer to parts of the island before contact with the West. Its etymology is unclear; one theory states that it derived from Tidore, the language used by the Sultanate of Tidore. An expedition by the Sultan of Tidore, together with Sahmardan, the ''Sangaji'' of Patani, and the Papuan Gurabesi, managed to conquer some areas in New Guinea, which was then reorganised to form ''Korano Ngaruha'' ("Four Kings") or Raja Ampat, ''Papoua Gam Sio'' ( "The Papua Nine ''Negeri''"), and ''Mafor Soa Raha'' ( The Mafor "Four ''Soa''"). The name comes from the words ''papo'' ("to unite") and ''ua'' (negation), which means "not united", i.e. an outlying possession of Tidore.
Anton Ploeg reports that the word ''papua'' is often said to be derived from the Malay word or , meaning "frizzly-haired", referring to the very curly hair of the island's inhabitants. However Sollewijn Gelpke in 1993 considered this unlikely as it had been used earlier, and he instead derived it from the Biak phrase , which means "the land below he sunset, and refers to the Raja Ampat Islands.
When Portuguese and Spanish explorers arrived via the Spice Islands, they also used the name ''Papua''. However, Westerners, beginning with Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez in 1545, used the name ''New Guinea'', due to the resemblance between the indigenous peoples of the island and Africans of the Guinea region. The name is one of several toponyms sharing similar etymologies, ultimately meaning "land of the blacks" or similar meanings.
The Dutch, who arrived later under Jacob Le Maire and Willem Schouten, called it ''Schouten island''. They later used this name only to refer to islands off the north coast of Papua proper, the Schouten Islands or Biak Island. When the Dutch colonized the main island as part of the
The island has been known by various names:
The name ''Papua'' was used to refer to parts of the island before contact with the West. Its etymology is unclear; one theory states that it derived from Tidore, the language used by the Sultanate of Tidore. An expedition by the Sultan of Tidore, together with Sahmardan, the ''Sangaji'' of Patani, and the Papuan Gurabesi, managed to conquer some areas in New Guinea, which was then reorganised to form ''Korano Ngaruha'' ("Four Kings") or Raja Ampat, ''Papoua Gam Sio'' ( "The Papua Nine ''Negeri''"), and ''Mafor Soa Raha'' ( The Mafor "Four ''Soa''"). The name comes from the words ''papo'' ("to unite") and ''ua'' (negation), which means "not united", i.e. an outlying possession of Tidore.
Anton Ploeg reports that the word ''papua'' is often said to be derived from the Malay word or , meaning "frizzly-haired", referring to the very curly hair of the island's inhabitants. However Sollewijn Gelpke in 1993 considered this unlikely as it had been used earlier, and he instead derived it from the Biak phrase , which means "the land below he sunset, and refers to the Raja Ampat Islands.
When Portuguese and Spanish explorers arrived via the Spice Islands, they also used the name ''Papua''. However, Westerners, beginning with Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez in 1545, used the name ''New Guinea'', due to the resemblance between the indigenous peoples of the island and Africans of the Guinea region. The name is one of several toponyms sharing similar etymologies, ultimately meaning "land of the blacks" or similar meanings.
The Dutch, who arrived later under Jacob Le Maire and Willem Schouten, called it ''Schouten island''. They later used this name only to refer to islands off the north coast of Papua proper, the Schouten Islands or Biak Island. When the Dutch colonized the main island as part of the
 New Guinea is an island to the north of the Australian mainland, south of the equator. It is isolated by the Arafura Sea to the west, and the Torres Strait and
New Guinea is an island to the north of the Australian mainland, south of the equator. It is isolated by the Arafura Sea to the west, and the Torres Strait and  The shape of New Guinea is often compared to that of a bird-of-paradise (indigenous to the island), and this results in the usual names for the two extremes of the island: the Bird's Head Peninsula in the northwest (''Vogelkop'' in Dutch, ''Kepala Burung'' in Indonesian; also known as the Doberai Peninsula), and the Bird's Tail Peninsula in the southeast (also known as the Papuan Peninsula).
A spine of east–west mountains, the New Guinea Highlands, dominates the geography of New Guinea, stretching over across the island, with many mountains over . The western half of the island contains the highest mountains in
The shape of New Guinea is often compared to that of a bird-of-paradise (indigenous to the island), and this results in the usual names for the two extremes of the island: the Bird's Head Peninsula in the northwest (''Vogelkop'' in Dutch, ''Kepala Burung'' in Indonesian; also known as the Doberai Peninsula), and the Bird's Tail Peninsula in the southeast (also known as the Papuan Peninsula).
A spine of east–west mountains, the New Guinea Highlands, dominates the geography of New Guinea, stretching over across the island, with many mountains over . The western half of the island contains the highest mountains in 
 Another major habitat feature is the vast southern and northern lowlands. Stretching for hundreds of kilometres, these include lowland rainforests, extensive wetlands, savanna grasslands, and some of the largest expanses of mangrove forest in the world. The southern lowlands are the site of Lorentz National Park, a
Another major habitat feature is the vast southern and northern lowlands. Stretching for hundreds of kilometres, these include lowland rainforests, extensive wetlands, savanna grasslands, and some of the largest expanses of mangrove forest in the world. The southern lowlands are the site of Lorentz National Park, a
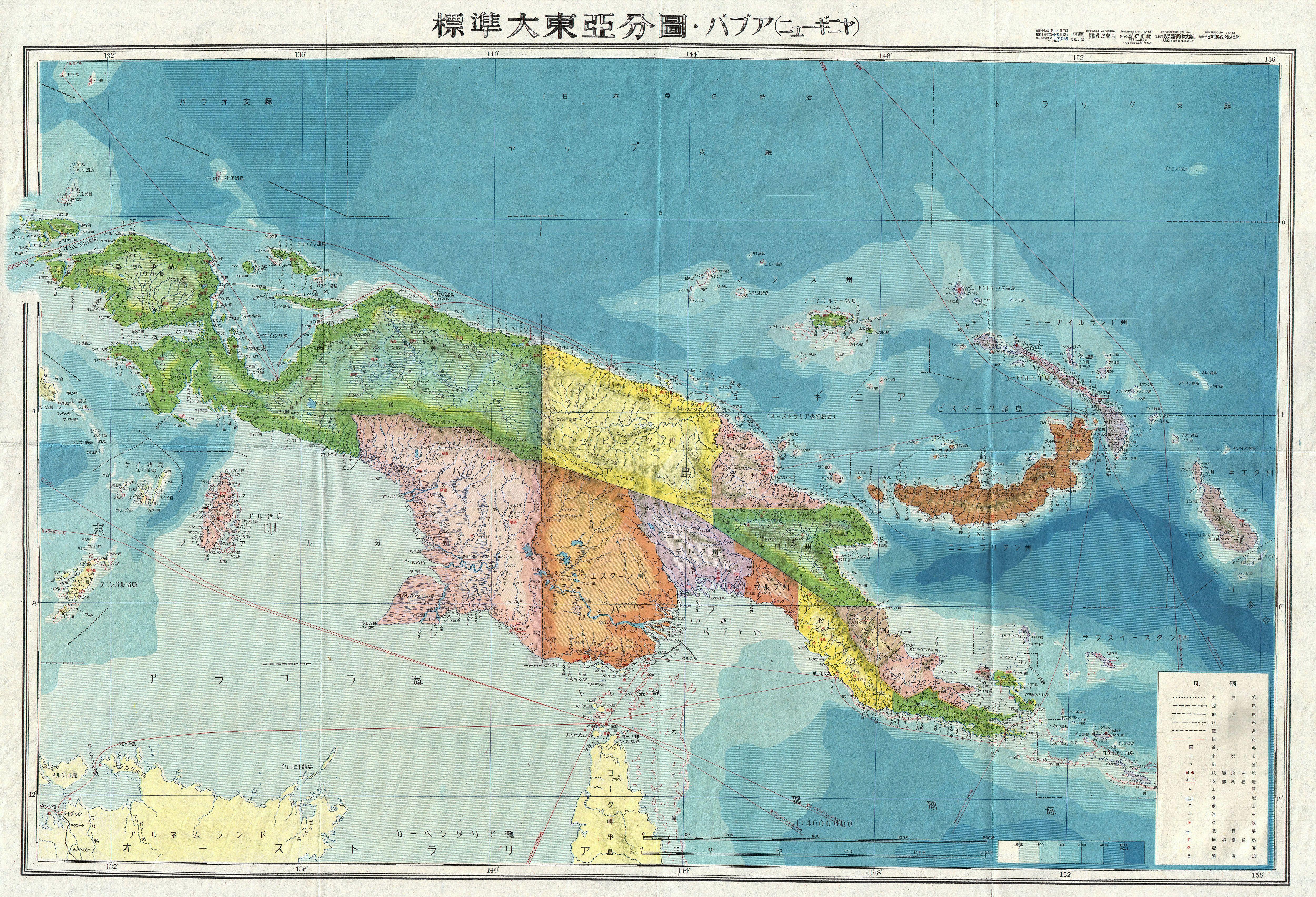
 The island of New Guinea is divided politically into roughly equal halves across a north–south line:
* The western portion of the island located west of 141°E longitude (except for a small section of territory to the east of the Fly River which belongs to Papua New Guinea) was formerly a Dutch colony, part of the
The island of New Guinea is divided politically into roughly equal halves across a north–south line:
* The western portion of the island located west of 141°E longitude (except for a small section of territory to the east of the Fly River which belongs to Papua New Guinea) was formerly a Dutch colony, part of the
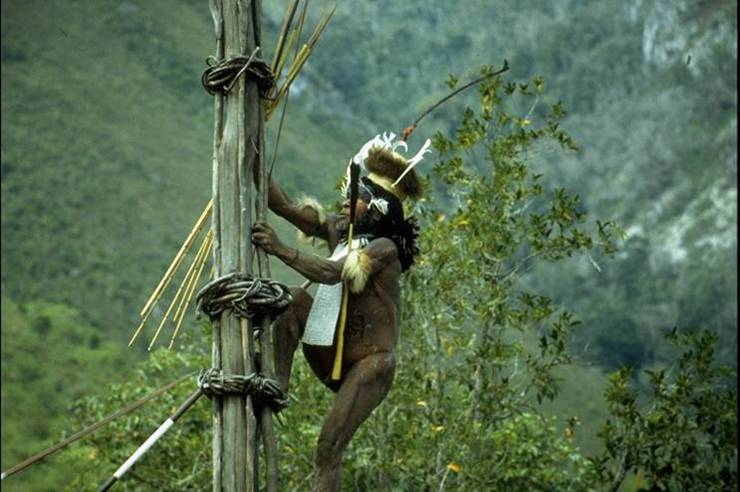 Current evidence indicates that the Papuans (who constitute the majority of the island's peoples) are descended from the earliest human inhabitants of New Guinea. These original inhabitants first arrived in New Guinea during the Last Glacial Period when the island was connected to the Australian continent via a land bridge, forming the landmass of Sahul. These peoples had made the (shortened) sea-crossing from the islands of Wallacea and Sundaland (the present Malay Archipelago) by at least 40,000 years ago.
Current evidence indicates that the Papuans (who constitute the majority of the island's peoples) are descended from the earliest human inhabitants of New Guinea. These original inhabitants first arrived in New Guinea during the Last Glacial Period when the island was connected to the Australian continent via a land bridge, forming the landmass of Sahul. These peoples had made the (shortened) sea-crossing from the islands of Wallacea and Sundaland (the present Malay Archipelago) by at least 40,000 years ago.
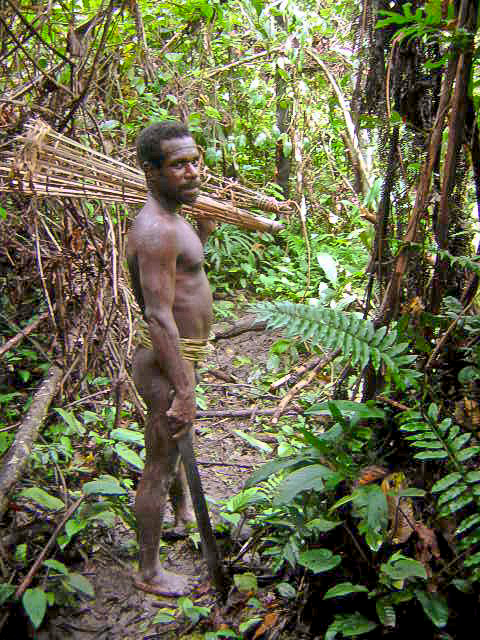 The ancestral Austronesian peoples are believed to have arrived considerably later, approximately 3,500 years ago, as part of a gradual seafaring migration from
The ancestral Austronesian peoples are believed to have arrived considerably later, approximately 3,500 years ago, as part of a gradual seafaring migration from

 Biogeographically, New Guinea is part of
Biogeographically, New Guinea is part of  As of 2020, the Western portion of New Guinea, Papua and West Papua, accounts for 54% of the island's primary forest and about 51% of the island's total tree cover, according to satellite data.
As of 2020, the Western portion of New Guinea, Papua and West Papua, accounts for 54% of the island's primary forest and about 51% of the island's total tree cover, according to satellite data.
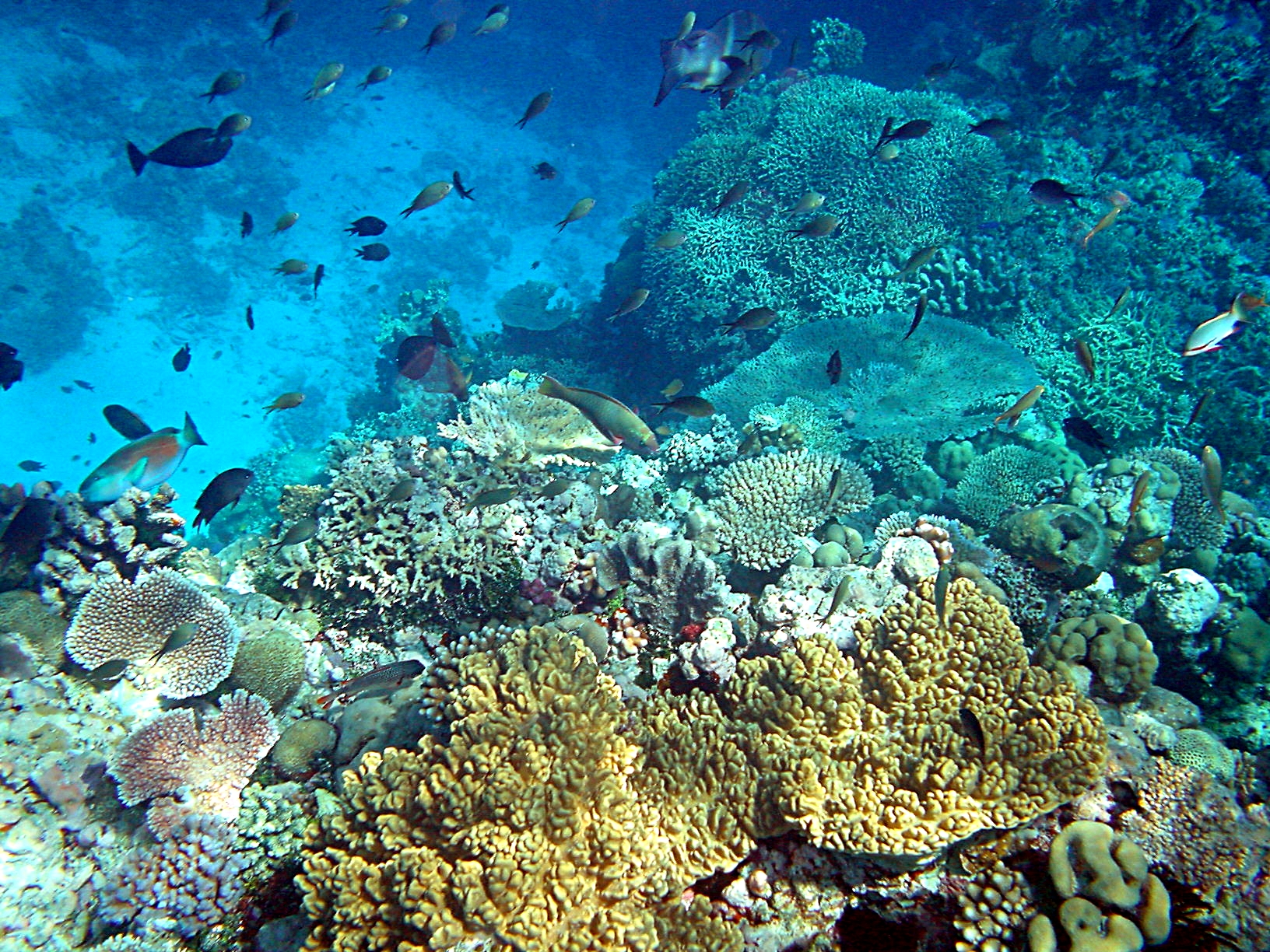

 Archaeological evidence indicates that humans arrived on New Guinea perhaps 60,000 years ago, although this is under debate. They came probably by sea from
Archaeological evidence indicates that humans arrived on New Guinea perhaps 60,000 years ago, although this is under debate. They came probably by sea from
 Netherlands New Guinea and the Australian territories (the eastern half ) were invaded in 1942 by the Japanese. The Netherlands were defeated by that stage and did not put up a fight, and the western section was not of any strategic value to either side, so they did not battle there. The Japanese invaded the north shore of the Australia territories and were aiming to move south and take the southern shore too. The highlands, northern and eastern parts of the island became key battlefields in the South West Pacific Theatre of
Netherlands New Guinea and the Australian territories (the eastern half ) were invaded in 1942 by the Japanese. The Netherlands were defeated by that stage and did not put up a fight, and the western section was not of any strategic value to either side, so they did not battle there. The Japanese invaded the north shore of the Australia territories and were aiming to move south and take the southern shore too. The highlands, northern and eastern parts of the island became key battlefields in the South West Pacific Theatre of
 During the 1950s, the Dutch government began to prepare Netherlands New Guinea for full independence and allowed elections in 1959; the partial elected New Guinea Council took office on 5 April 1961. The Council decided on the name of West Papua (''Papua Barat'') for the territory, along with an emblem,
During the 1950s, the Dutch government began to prepare Netherlands New Guinea for full independence and allowed elections in 1959; the partial elected New Guinea Council took office on 5 April 1961. The Council decided on the name of West Papua (''Papua Barat'') for the territory, along with an emblem,
Autonomy isn't independence; Indonesian democracy stops in Papua
Le Monde Diplomatique, June 2010 both through civil disobedience (such as publicly raising the Morning Star flag) and via the formation of the Organisasi Papua Merdeka (OPM, or Free Papua Movement) in 1965. From 1971, the name Papua New Guinea was used for the Australian territory. On 16 September 1975, Australia granted full independence to Papua New Guinea. In 2000, Irian Jaya was formally renamed "The Province of Papua" and a Law on Special Autonomy was passed in 2001. The Law established a (MRP) with representatives of the different indigenous cultures of Papua. The MRP was empowered to protect the rights of Papuans, raise the status of women in Papua, and to ease religious tensions in Papua; block grants were given for the implementation of the Law as much as $266 million in 2004. The Indonesian courts' enforcement of the Law on Special Autonomy blocked further creation of subdivisions of Papua: although President Megawati Sukarnoputri was able to create a separate West Papua province in 2003 as a
From 1971, the name Papua New Guinea was used for the Australian territory. On 16 September 1975, Australia granted full independence to Papua New Guinea. In 2000, Irian Jaya was formally renamed "The Province of Papua" and a Law on Special Autonomy was passed in 2001. The Law established a (MRP) with representatives of the different indigenous cultures of Papua. The MRP was empowered to protect the rights of Papuans, raise the status of women in Papua, and to ease religious tensions in Papua; block grants were given for the implementation of the Law as much as $266 million in 2004. The Indonesian courts' enforcement of the Law on Special Autonomy blocked further creation of subdivisions of Papua: although President Megawati Sukarnoputri was able to create a separate West Papua province in 2003 as a
Facsimile of material from "The Discovery of New Guinea" by George Collingridge
Scientists hail discovery of hundreds of new species in remote New Guinea
PapuaWeb official website
* {{Authority control Islands of the Pacific Ocean International islands Geography of Melanesia Islands of Indonesia Islands of Papua New Guinea Former Spanish colonies
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
, the island is separated from Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
by the wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf, and were united during episodes of low sea level in the Pleistocene glaciations as the combined landmass of Sahul. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The island's name was given by Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez during his maritime expedition of 1545 due to the perceived resemblance of the indigenous peoples of the island to those in the African region of Guinea.
The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the nation of Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean n ...
. The western half, known as Western New Guinea, forms a part of Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
and is organized as the provinces of Papua, Central Papua, Highland Papua
Highland Papua () is a provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia, which roughly follows the borders of the Papuan customary region of Lano-Pago (often shortened to La Pago). It covers an area of and had a population of 1,467,050 according to ...
, South Papua, Southwest Papua, and West Papua. The two major cities on the island are Port Moresby and Jayapura.
Names
 The island has been known by various names:
The name ''Papua'' was used to refer to parts of the island before contact with the West. Its etymology is unclear; one theory states that it derived from Tidore, the language used by the Sultanate of Tidore. An expedition by the Sultan of Tidore, together with Sahmardan, the ''Sangaji'' of Patani, and the Papuan Gurabesi, managed to conquer some areas in New Guinea, which was then reorganised to form ''Korano Ngaruha'' ("Four Kings") or Raja Ampat, ''Papoua Gam Sio'' ( "The Papua Nine ''Negeri''"), and ''Mafor Soa Raha'' ( The Mafor "Four ''Soa''"). The name comes from the words ''papo'' ("to unite") and ''ua'' (negation), which means "not united", i.e. an outlying possession of Tidore.
Anton Ploeg reports that the word ''papua'' is often said to be derived from the Malay word or , meaning "frizzly-haired", referring to the very curly hair of the island's inhabitants. However Sollewijn Gelpke in 1993 considered this unlikely as it had been used earlier, and he instead derived it from the Biak phrase , which means "the land below he sunset, and refers to the Raja Ampat Islands.
When Portuguese and Spanish explorers arrived via the Spice Islands, they also used the name ''Papua''. However, Westerners, beginning with Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez in 1545, used the name ''New Guinea'', due to the resemblance between the indigenous peoples of the island and Africans of the Guinea region. The name is one of several toponyms sharing similar etymologies, ultimately meaning "land of the blacks" or similar meanings.
The Dutch, who arrived later under Jacob Le Maire and Willem Schouten, called it ''Schouten island''. They later used this name only to refer to islands off the north coast of Papua proper, the Schouten Islands or Biak Island. When the Dutch colonized the main island as part of the
The island has been known by various names:
The name ''Papua'' was used to refer to parts of the island before contact with the West. Its etymology is unclear; one theory states that it derived from Tidore, the language used by the Sultanate of Tidore. An expedition by the Sultan of Tidore, together with Sahmardan, the ''Sangaji'' of Patani, and the Papuan Gurabesi, managed to conquer some areas in New Guinea, which was then reorganised to form ''Korano Ngaruha'' ("Four Kings") or Raja Ampat, ''Papoua Gam Sio'' ( "The Papua Nine ''Negeri''"), and ''Mafor Soa Raha'' ( The Mafor "Four ''Soa''"). The name comes from the words ''papo'' ("to unite") and ''ua'' (negation), which means "not united", i.e. an outlying possession of Tidore.
Anton Ploeg reports that the word ''papua'' is often said to be derived from the Malay word or , meaning "frizzly-haired", referring to the very curly hair of the island's inhabitants. However Sollewijn Gelpke in 1993 considered this unlikely as it had been used earlier, and he instead derived it from the Biak phrase , which means "the land below he sunset, and refers to the Raja Ampat Islands.
When Portuguese and Spanish explorers arrived via the Spice Islands, they also used the name ''Papua''. However, Westerners, beginning with Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez in 1545, used the name ''New Guinea'', due to the resemblance between the indigenous peoples of the island and Africans of the Guinea region. The name is one of several toponyms sharing similar etymologies, ultimately meaning "land of the blacks" or similar meanings.
The Dutch, who arrived later under Jacob Le Maire and Willem Schouten, called it ''Schouten island''. They later used this name only to refer to islands off the north coast of Papua proper, the Schouten Islands or Biak Island. When the Dutch colonized the main island as part of the Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies (; ), was a Dutch Empire, Dutch colony with territory mostly comprising the modern state of Indonesia, which Proclamation of Indonesian Independence, declared independence on 17 Au ...
, they called it ''Nieuw Guinea''.
The name was used in the Indonesian language to refer to the island and Indonesian province, as (West Irian) Province and later Province. The name Irian was suggested during a tribal committee meeting in Tobati, Jayapura, formed by Soegoro Atmoprasodjo under governor JP van Eechoed, to decide on a new name because of the negative association of ''Papua''. Frans Kaisiepo, the committee leader, suggested the name from Mansren Koreri myths, from the Biak language of Biak Island, meaning "hot land" (referring to the climate), but also from ''Iryan'' which means heated process as a metaphor for a land that is entering a new era. In Serui ''Iri-an'' ( "land-nation") means "pillar of nation", while in Merauke ''Iri-an'' ( "placed higher-nation") means "rising spirit" or "to rise". The name was promoted in 1945 by Marcus Kaisiepo, brother of Frans Kaisiepo. The name was politicized later by Corinus Krey, Marthen Indey, Silas Papare, and others with the Indonesian backronym ("Join the Republic of Indonesia Oppose the Netherlands"). ''Irian'' was used somewhat in 1972. The name was used until 2001, when ''Papua'' was again used for the island and the province. The name ''Irian'', which was originally favored by natives, is now considered to be a name imposed by the Indonesian government.
Geography
Coral Sea
The Coral Sea () is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific off the northeast coast of Australia, and classified as an Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia, interim Australian bioregion. The Coral Sea extends down t ...
to the east. Sometimes considered to be the easternmost island of the Indonesian archipelago, it lies north of Australia's Top End, the Gulf of Carpentaria
The Gulf of Carpentaria is a sea off the northern coast of Australia. It is enclosed on three sides by northern Australia and bounded on the north by the eastern Arafura Sea, which separates Australia and New Guinea. The northern boundary ...
and Cape York Peninsula, and west of the Bismarck Archipelago and the Solomon Islands archipelago.
Politically, the western half of the island comprises six provinces of Indonesia: Papua, Central Papua, Highland Papua
Highland Papua () is a provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia, which roughly follows the borders of the Papuan customary region of Lano-Pago (often shortened to La Pago). It covers an area of and had a population of 1,467,050 according to ...
, South Papua, West Papua and Southwest Papua. The eastern half forms the mainland of the country of Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean n ...
.
 The shape of New Guinea is often compared to that of a bird-of-paradise (indigenous to the island), and this results in the usual names for the two extremes of the island: the Bird's Head Peninsula in the northwest (''Vogelkop'' in Dutch, ''Kepala Burung'' in Indonesian; also known as the Doberai Peninsula), and the Bird's Tail Peninsula in the southeast (also known as the Papuan Peninsula).
A spine of east–west mountains, the New Guinea Highlands, dominates the geography of New Guinea, stretching over across the island, with many mountains over . The western half of the island contains the highest mountains in
The shape of New Guinea is often compared to that of a bird-of-paradise (indigenous to the island), and this results in the usual names for the two extremes of the island: the Bird's Head Peninsula in the northwest (''Vogelkop'' in Dutch, ''Kepala Burung'' in Indonesian; also known as the Doberai Peninsula), and the Bird's Tail Peninsula in the southeast (also known as the Papuan Peninsula).
A spine of east–west mountains, the New Guinea Highlands, dominates the geography of New Guinea, stretching over across the island, with many mountains over . The western half of the island contains the highest mountains in Oceania
Oceania ( , ) is a region, geographical region including Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Outside of the English-speaking world, Oceania is generally considered a continent, while Mainland Australia is regarded as its co ...
, with its highest point, Puncak Jaya, reaching an elevation of 4,884 m (16,023 ft). The tree line is around elevation, and the tallest peaks contain equatorial glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
s—which have been retreating since at least 1936. Various other smaller mountain ranges occur both north and west of the central ranges. Except in high elevations, most areas possess a warm humid climate throughout the year, with some seasonal variation associated with the northeast monsoon season.

UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
. The northern lowlands are drained principally by the Mamberamo River and its tributaries on the western side, and by the Sepik on the eastern side. The more extensive southern lowlands are drained by a larger number of rivers, principally the Digul in the west and the Fly in the east. The largest island offshore, Dolak, lies near the Digul estuary, separated by a strait so narrow it has been named a "creek".
New Guinea contains many of the world's ecosystem types: glacial, alpine tundra, savanna, montane and lowland rainforest, mangroves, wetlands, lake and river ecosystems, seagrasses, and some of the richest coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in group ...
s on the planet.
The entire length of the New Guinea Highlands system passes through New Guinea as a vast watershed. The northern rivers flow into the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
, the southern rivers into the Arafura Sea and the Gulf of Papua. On the north side, the largest rivers are the Mamberamo, Sepik and Ramu.
Mamberamo was born from the confluence of two large inland rivers. Tariku comes from the west to the east and Taritatu from the east. These rivers meander through swamps with huge internal descents and then merge. The Mamberamo thus formed reaches the ocean by breaking through the Coastal Mountains. Mamberamo River is navigable to Marine Falls. The Sepik is a much more important river. Similarly, it collects water from a spacious pool. It is 1,100 kilometers from the Victor Emanuel Range to the estuary, making it the longest river in New Guinea. The winding, muddy, sluggish river can be navigated for 500 km. Ramu is a 650 km long river. Its lower section is navigable, but its upper flow is high-falling, fast-flowing. The energy of the river is used by a power plant near the city of Kainantu.
On the south side, the most significant rivers are Pulau, Digul, Fly, Kikori and Purari. The largest river in the western part of the island is Digul. It originates from the Star Mountains, which rise to an altitude of 4,700 m. The coastal plain is bordered by a swamp world hundreds of kilometers wide. Digul is the main transport route to the fertile hills and mountains within the island. The river Fly is born near the eastern branches of the Digul. It is named after one of the ships of the English Royal Fleet, which first sailed into the mouth of the river in 1845. The total length of the river is 1,050 km. Smaller boats can sail 900 km on the river. The estuary section, which decomposes into islands, is 70 km wide. The tide of the sea can have an effect of up to 300 kilometers. Strickland, a tributary of the Fly, reaches the Papuan Plain through wild gorges. Fly and Strickland together form the largest river in New Guinea. The many rivers flowing into the Gulf of Papua form a single delta complex. The rivers of the island are extremely rich in water due to the annual rainfall of 2,000–10,000 mm. According to a modest calculation, the New Guinea River carries about of water into the sea. Fly alone carries more water than all the rivers in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
combined.
Relation to surroundings
The island of New Guinea lies to the east of the Malay Archipelago, with which it is sometimes included as part of a greater Indo-Australian Archipelago. Geologically it is a part of the same tectonic plate as Australia. When world sea levels were low, the two shared shorelines (which now lie 100 to 140 metres below sea level), and combined with lands now inundated into the tectonic continent of Sahul, also known as Greater Australia. The two landmasses became separated when the area now known as the Torres Strait flooded after the end of the last glacial period. Anthropologically, New Guinea is considered part of Melanesia. New Guinea is differentiated from its drier, flatter, and less fertile southern counterpart, Australia, by its much higher rainfall and its active volcanic geology. Yet the two land masses share a similar animal fauna, with marsupials, including wallabies andpossums
Possum may refer to:
Animals
* Didelphimorphia, or (o)possums, an order of marsupials native to the Americas
** Didelphis, a genus of marsupials within Didelphimorphia
*** Common opossum, native to Central and South America
*** Virginia opossum, ...
, and the egg-laying monotreme, the echidna. Other than bats and some two dozen indigenous rodent genera, there are no pre-human indigenous placental mammals. Pigs, several additional species of rats, and the ancestor of the New Guinea singing dog were introduced with human colonization.
Prior to the 1970s, archaeologists called the single Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
landmass by the name ''Australasia'', although this word is most often used for a wider region that includes lands, such as New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
, which are not on the same continental shelf. In the early 1970s, they introduced the term ''Greater Australia'' for the Pleistocene continent. Then, at a 1975 conference and consequent publication, they extended the name ''Sahul'' from its previous use for just the Sahul Shelf to cover the continent.
Political divisions
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies (; ), was a Dutch Empire, Dutch colony with territory mostly comprising the modern state of Indonesia, which Proclamation of Indonesian Independence, declared independence on 17 Au ...
. After the West New Guinea dispute it is now six Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
n provinces:
** West Papua with Manokwari as its capital.
** Papua with the city of Jayapura as its capital.
** Highland Papua
Highland Papua () is a provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia, which roughly follows the borders of the Papuan customary region of Lano-Pago (often shortened to La Pago). It covers an area of and had a population of 1,467,050 according to ...
with Jayawijaya Regency as its capital.
** Central Papua with Nabire Regency as its capital.
** South Papua with Merauke Regency as its capital.
** Southwest Papua with Sorong as its capital
* The eastern part forms the mainland of Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean n ...
, which has been an independent country since 1975. It was formerly the Territory of Papua and New Guinea governed by Australia, consisting of the Trust Territory of New Guinea (northeastern quarter, formerly German New Guinea
German New Guinea () consisted of the northeastern part of the island of New Guinea and several nearby island groups, and was part of the German colonial empire. The mainland part of the territory, called , became a German protectorate in 188 ...
), and the Territory of Papua (southeastern quarter). Three of Papua New Guinea's four regions are parts of New Guinea island:
** Southern, consisting of Western, Gulf, Central, Oro (Northern) and Milne Bay
Milne Bay is a large bay in Milne Bay Province, south-eastern Papua New Guinea. More than long and over wide, Milne Bay is a sheltered deep-water harbor accessible via Ward Hunt Strait. It is surrounded by the heavily wooded Stirling Range (Papu ...
provinces.
** Highlands, consisting of Southern Highlands, Hela Province, Jiwaka Province, Enga Province, Western Highlands, Simbu and Eastern Highlands provinces.
** Momase, consisting of Morobe, Madang, East Sepik and Sandaun (West Sepik) provinces.
Demographics
10 largest cities and towns in New Guinea (Papua) by population
* *People
The current population of the island of New Guinea is about fifteen million. Archaeological evidence indicates that humans may have inhabited the island continuously since 50,000 BCE, and first settlement possibly dating back to 60,000 years ago has been proposed. The island is presently populated by almost a thousand different tribal groups and a near-equivalent number of separate languages, which makes New Guinea the most linguistically diverse area in the world. Ethnologue's 14th edition lists 826 languages ofPapua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean n ...
and 257 languages of Western New Guinea, total 1073 languages, with 12 languages overlapping. They can be divided into two groups, the Austronesian languages, and all the others placed in the catch-all category of Papuan languages
The Papuan languages are the non- Austronesian languages spoken on the western Pacific island of New Guinea, as well as neighbouring islands in Indonesia, Solomon Islands, and East Timor. It is a strictly geographical grouping, and does not imply ...
, most of which are unrelated.
The separation is not merely linguistic; warfare
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of State (polity), states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or betwe ...
among societies was a factor in the evolution of the ''men's house'': separate housing for groups of adult men, away from the single-family houses of women and children. Pig-based trade between groups and pig-based feasts form a common tradition with the other peoples of southeast Asia and Oceania. Most Papuan societies practice agriculture, supplemented by hunting and gathering.
 Current evidence indicates that the Papuans (who constitute the majority of the island's peoples) are descended from the earliest human inhabitants of New Guinea. These original inhabitants first arrived in New Guinea during the Last Glacial Period when the island was connected to the Australian continent via a land bridge, forming the landmass of Sahul. These peoples had made the (shortened) sea-crossing from the islands of Wallacea and Sundaland (the present Malay Archipelago) by at least 40,000 years ago.
Current evidence indicates that the Papuans (who constitute the majority of the island's peoples) are descended from the earliest human inhabitants of New Guinea. These original inhabitants first arrived in New Guinea during the Last Glacial Period when the island was connected to the Australian continent via a land bridge, forming the landmass of Sahul. These peoples had made the (shortened) sea-crossing from the islands of Wallacea and Sundaland (the present Malay Archipelago) by at least 40,000 years ago.
 The ancestral Austronesian peoples are believed to have arrived considerably later, approximately 3,500 years ago, as part of a gradual seafaring migration from
The ancestral Austronesian peoples are believed to have arrived considerably later, approximately 3,500 years ago, as part of a gradual seafaring migration from Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
, possibly originating in Taiwan. Austronesian-speaking peoples colonized many of the offshore islands to the north and east of New Guinea, such as New Ireland and New Britain, with settlements also on the coastal fringes of the main island in places. Human habitation of New Guinea over tens of thousands of years has led to a great deal of diversity, which was further increased by the later arrival of the Austronesians and the more recent history of European and Asian settlement through events like transmigration.
Large areas of New Guinea are yet to be explored by scientists and anthropologists. The Indonesian province of West Papua is home to an estimated 44 uncontacted tribal groups.
Biodiversity and ecology
With some 786,000 km2 of tropical land—less than one-half of one percent (0.5%) of the Earth's surface—New Guinea has an immensebiodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
, containing between 5 and 10 percent of the total species on the planet. This percentage is about the same amount as that found in the United States or Australia. A high percentage of New Guinea's species are endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
, and thousands are still unknown to science: probably well over 200,000 species of insect, between 11,000 and 20,000 plant species, and over 650 resident bird species. Most of these species are shared, at least in their origin, with the continent of Australia, which was until fairly recent geological times part of the same landmass (see Australia-New Guinea for an overview). The island is so large that it is considered 'nearly a continent' in terms of its biological distinctiveness.
In the period from 1998 to 2008, conservationists identified 1,060 new species in New Guinea, including 218 plants, 43 reptiles, 12 mammals, 580 invertebrates, 134 amphibians, 2 birds and 71 fish. Between 2011 and 2017, researchers described 465 previously undocumented plant species in New Guinea. As of 2019, the Indonesian portion of New Guinea and the Maluku Islands is estimated to have 9,518 species of vascular plants, of which 4,380 are endemic. In 2020, an international study conducted by a team of 99 experts cataloged 13,634 species representing 1,742 genera and 264 families of vascular plants for New Guinea and its associated islands ( Aru Islands, Bismarck Archipelago, D'Entrecasteaux Islands, Louisiade Archipelago), making it the world's most floristically diverse island, surpassing Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
(11,488), Borneo (11,165), Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
(4,598), and the Philippines (9,432).

 Biogeographically, New Guinea is part of
Biogeographically, New Guinea is part of Australasia
Australasia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising Australia, New Zealand (overlapping with Polynesia), and sometimes including New Guinea and surrounding islands (overlapping with Melanesia). The term is used in a number of different context ...
rather than the Indomalayan realm, although New Guinea's flora has many more affinities with Asia than its fauna, which is overwhelmingly Australian. Botanically, New Guinea is considered part of Malesia, a floristic region that extends from the Malay Peninsula across Indonesia to New Guinea and the East Melanesian Islands. The flora of New Guinea is a mixture of many tropical rainforest species with origins in Asia, together with typically Australasian flora. Typical Southern Hemisphere flora include the conifer
Conifers () are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a sin ...
s ''Podocarpus
''Podocarpus'' () is a genus of conifers, the most numerous and widely distributed of the podocarp family, the Podocarpaceae. ''Podocarpus'' species are evergreen shrubs or trees, usually from tall, known to reach at times. The cones have ...
'' and the rainforest emergents '' Araucaria'' and '' Agathis,'' as well as tree ferns and several species of ''Eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of more than 700 species of flowering plants in the family Myrtaceae. Most species of ''Eucalyptus'' are trees, often Mallee (habit), mallees, and a few are shrubs. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalyp ...
''.
New Guinea has 284 species and six orders of mammals: monotremes, three orders of marsupials, rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and Mandible, lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal specie ...
s and bats; 195 of the mammal species (69%) are endemic. New Guinea has 578 species of breeding birds, of which 324 species are endemic. The island's frogs are one of the most poorly known vertebrate groups, totalling 282 species, but this number is expected to double or even triple when all species have been documented. New Guinea has a rich diversity of coral life and 1,200 species of fish have been found. Also about 600 species of reef-building coral—the latter equal to 75 percent of the world's known total. The entire coral area covers 18 million hectares off a peninsula in northwest New Guinea.
Ecoregions
Terrestrial
According to the WWF, New Guinea can be divided into twelve terrestrial ecoregions: * Central Range montane rain forests * Central Range sub-alpine grasslands * Huon Peninsula montane rain forests * New Guinea mangroves * Northern New Guinea lowland rain and freshwater swamp forests * Northern New Guinea montane rain forests * Southeastern Papuan rain forests * Southern New Guinea freshwater swamp forests * Southern New Guinea lowland rain forests * Trans-Fly savanna and grasslands * Vogelkop montane rain forests * Vogelkop-Aru lowland rain forestsFreshwater
The WWF and Nature Conservancy divide New Guinea into five freshwater ecoregions: * Vogelkop–Bomberai * New Guinea North Coast * New Guinea Central Mountains * Southwest New Guinea–Trans-Fly Lowland * Papuan PeninsulaMarine
The WWF and Nature Conservancy identify several marine ecoregions in the seas bordering New Guinea: * Papua * Arafura Sea * Bismarck Sea * Solomon Sea * Southeast Papua New Guinea * Gulf of PapuaHistory
Early history
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
during the Last Glacial Period, when the sea was lower and distances between islands shorter.
The first inhabitants Indigenous people of New Guinea, from whom the Papuan people are probably descended, adapted to the range of ecologies and, in time, developed one of the earliest known agricultures. Remains of this agricultural system, in the form of ancient irrigation systems in the highlands of Papua New Guinea, are being studied by archaeologists. Research indicates that the highlands were an early and independent center of agriculture, with evidence of irrigation going back at least 10,000 years. Sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
was cultivated in New Guinea around 6000 BCE.
The gardens of the New Guinea Highlands are ancient, intensive permacultures, adapted to high population densities, very high rainfalls (as high as 10,000 mm per year (400 in/yr)), earthquakes, hilly land, and occasional frost. Complex mulches, crop rotations and tillages are used in rotation on terraces with complex irrigation systems. Western agronomists still do not understand all of the practices, and it has been noted that native gardeners are as, or even more, successful than most scientific farmers in raising certain crops. There is evidence that New Guinea gardeners invented crop rotation well before western Europeans. A unique feature of New Guinea permaculture is the silviculture
Silviculture is the practice of controlling the growth, composition/structure, as well as quality of forests to meet values and needs, specifically timber production.
The name comes from the Latin ('forest') and ('growing'). The study of forests ...
of '' Casuarina oligodon'', a tall, sturdy native ironwood tree, suited to use for timber and fuel, with root nodules that fix nitrogen. Pollen studies show that it was adopted during an ancient period of extreme deforestation.
In more recent millennia, another wave of people arrived on the shores of New Guinea. These were the Austronesian people, who had spread down from Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
, through the South-east Asian archipelago, colonising many of the islands on the way. The Austronesian people had technology and skills extremely well adapted to ocean voyaging and Austronesian language speaking people are present along much of the coastal areas and islands of New Guinea. They also introduced pigs and dogs. These Austronesian migrants are considered the ancestors of most people in insular Southeast Asia, from Sumatra
Sumatra () is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the list of islands by area, sixth-largest island in the world at 482,286.55 km2 (182,812 mi. ...
and Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
to Borneo and Sulawesi
Sulawesi ( ), also known as Celebes ( ), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the List of islands by area, world's 11th-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Min ...
, as well as coastal new Guinea.
Precolonial history
The western part of the island was in contact with kingdoms in other parts of modern-day Indonesia. The ''Negarakertagama
The ''Nagarakretagama'' or ''Nagarakṛtāgama'', also known in Bali as ''Desawarnana'' or ''Deśavarṇana'', is an Old Javanese eulogy to Hayam Wuruk, a Javanese king of the Majapahit Empire. It was written on lontar as a '' kakawin'' ...
'' mentioned the region of Wanin and Sran, in eastern Nusantara as part of Majapahit's tributary. This 'Wanin' has been identified with the Onin Peninsula, part of the Bomberai Peninsula near the city of Fakfak. while ' Sran' had been identified as region of Kowiai, just south of Onin peninsula. The sultans of Tidore, in the Maluku Islands
The Maluku Islands ( ; , ) or the Moluccas ( ; ) are an archipelago in the eastern part of Indonesia. Tectonics, Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone. Geographically they are located in West ...
, claimed sovereignty over various coastal parts of the island. During Tidore's rule, the main exports of the island during this period were resins, spices, slaves and the highly priced feathers of the bird-of-paradise. In a period of constant conflict called 'hongi wars', in which rival villages or kingdoms would invoke the name of Tidore Sultan, rightly, for punitive expeditions for not fulfilling their tributary obligations, or opportunitively for competitions over resources and prestige. Sultan Nuku, one of the most famous Tidore sultans who rebelled against Dutch colonization, called himself "Sultan of Tidore and Papua", during his revolt in 1780s. He commanded loyalty from both Moluccan and Papuan chiefs, especially those of Raja Ampat Islands, from his base in Gebe. Following Tidore's subjugation as Dutch tributary, much of the territory it claimed in western part of New Guinea came under Dutch rule as part of Dutch East Indies.
European contact
The first known European contact with New Guinea was by Portuguese and Spanish sailors in the 16th century. In 1526–27, Portuguese explorer Jorge de Menezes saw the western tip of New Guinea and named it ''ilhas dos Papuas''. In 1528, the Spanish navigator Álvaro de Saavedra also recorded its sighting when trying to return from Tidore to New Spain. In 1545, Spaniard Íñigo Ortíz de Retes sailed along the north coast of New Guinea as far as the Mamberamo River, near which he landed on 20 June, naming the island 'Nueva Guinea'. The first known map of the island was made by F. Hoeiu in 1600 and shows it as 'Nova Guinea'. In 1606, Luís Vaz de Torres explored the southern coast of New Guinea fromMilne Bay
Milne Bay is a large bay in Milne Bay Province, south-eastern Papua New Guinea. More than long and over wide, Milne Bay is a sheltered deep-water harbor accessible via Ward Hunt Strait. It is surrounded by the heavily wooded Stirling Range (Papu ...
to the Gulf of Papua including Orangerie Bay, which he named ''Bahía de San Lorenzo''. His expedition also discovered Basilaki Island naming it ''Tierra de San Buenaventura'', which he claimed for Spain in July 1606.Translation of Torres' report to the king in Collingridge, G. (1895) ''Discovery of Australia'' p.229-237. Golden Press Edition 1983, Gladesville, NSW. On 18 October, his expedition reached the western part of the island in present-day Indonesia, and also claimed the territory for the King of Spain.
A successive European claim occurred in 1828, when the Netherlands formally claimed the western half of the island as Netherlands New Guinea. Dutch colonial authority built Fort Du Bus an administrative and trading post established near Lobo, Triton Bay, but by 1835 had been abandoned. Considering that New Guinea had little economic value for them, the Dutch promoted Tidore as suzerain of Papua. By 1849, Tidore's borders had been extended to the proximity of the current international border between Indonesia and Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean n ...
, as it formed extensive trade pact and custom of ''Uli-Siwa'' ( federation of nine ).
In 1883, following a short-lived French annexation of New Ireland, the British colony of Queensland
Queensland ( , commonly abbreviated as Qld) is a States and territories of Australia, state in northeastern Australia, and is the second-largest and third-most populous state in Australia. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Austr ...
annexed south-eastern New Guinea. However, the Queensland government's superiors in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
revoked the claim, and (formally) assumed direct responsibility in 1884, when Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
claimed north-eastern New Guinea as the protectorate of German New Guinea
German New Guinea () consisted of the northeastern part of the island of New Guinea and several nearby island groups, and was part of the German colonial empire. The mainland part of the territory, called , became a German protectorate in 188 ...
(also called Kaiser-Wilhelmsland).
The first Dutch government posts were established in 1898 and in 1902: Manokwari on the north coast, Fak-Fak in the west and Merauke in the south at the border with British New Guinea. The German, Dutch and British colonial administrators each attempted to suppress the still-widespread practices of inter-village warfare and headhunting within their respective territories.
In 1905, the British government transferred some administrative responsibility over southeast New Guinea to Australia (which renamed the area " Territory of Papua"); and, in 1906, transferred all remaining responsibility to Australia. During World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, Australian forces seized German New Guinea, which in 1920 became the Territory of New Guinea, to be administered by Australia under a League of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace ...
mandate. The territories under Australian administration became collectively known as The Territories of Papua and New Guinea (until February 1942).
Before about 1930, European maps showed the highlands as uninhabited forests. When first flown over by aircraft, numerous settlements with agricultural terraces and stockades were observed. The most startling discovery took place on 4 August 1938, when Richard Archbold discovered the Grand Valley of the Baliem River, which had 50,000 yet-undiscovered Stone Age farmers living in orderly villages. The people, known as the Dani, were the last society of its size to make first contact with the rest of the world. A 1930 expedition led by the prospector Michael Lehay also encountered an indigenous group in the highlands. The inhabitants, believing themselves to be the only people in the world and, having never seen Europeans before, initially believed the explorers to be spirits of the dead due to the local belief that a person's skin turned white when they died and crossed into the land of the dead.

World War II
 Netherlands New Guinea and the Australian territories (the eastern half ) were invaded in 1942 by the Japanese. The Netherlands were defeated by that stage and did not put up a fight, and the western section was not of any strategic value to either side, so they did not battle there. The Japanese invaded the north shore of the Australia territories and were aiming to move south and take the southern shore too. The highlands, northern and eastern parts of the island became key battlefields in the South West Pacific Theatre of
Netherlands New Guinea and the Australian territories (the eastern half ) were invaded in 1942 by the Japanese. The Netherlands were defeated by that stage and did not put up a fight, and the western section was not of any strategic value to either side, so they did not battle there. The Japanese invaded the north shore of the Australia territories and were aiming to move south and take the southern shore too. The highlands, northern and eastern parts of the island became key battlefields in the South West Pacific Theatre of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. Notable battles were for Port Moresby (the naval battle is known as the Battle of the Coral Sea), Milne Bay
Milne Bay is a large bay in Milne Bay Province, south-eastern Papua New Guinea. More than long and over wide, Milne Bay is a sheltered deep-water harbor accessible via Ward Hunt Strait. It is surrounded by the heavily wooded Stirling Range (Papu ...
and for the Kokoda track. Papuans often gave vital assistance to the Allies, fighting alongside Australian troops, and carrying equipment and injured men across New Guinea. Approximately 216,000 Japanese, Australian and U.S. soldiers, sailors and airmen died during the New Guinea Campaign.
Since World War II
Following the return to civil administration after World War II, the Australian section was known as the Territory of Papua-New Guinea from 1945 to 1949 and then as Territory of Papua and New Guinea. Although the rest of the Dutch East Indies achieved independence as Indonesia on 27 December 1949, the Netherlands regained control of western New Guinea. During the 1950s, the Dutch government began to prepare Netherlands New Guinea for full independence and allowed elections in 1959; the partial elected New Guinea Council took office on 5 April 1961. The Council decided on the name of West Papua (''Papua Barat'') for the territory, along with an emblem,
During the 1950s, the Dutch government began to prepare Netherlands New Guinea for full independence and allowed elections in 1959; the partial elected New Guinea Council took office on 5 April 1961. The Council decided on the name of West Papua (''Papua Barat'') for the territory, along with an emblem, flag
A flag is a piece of textile, fabric (most often rectangular) with distinctive colours and design. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design employed, and fla ...
, and anthem to complement those of the Netherlands. On 1 October 1962, after some military interventions and negotiations, the Dutch handed over the territory to the United Nations Temporary Executive Authority, until 1 May 1963, when Indonesia took control. The territory was renamed West Irian () and then Irian Jaya. In 1969, Indonesia, under the 1962 New York Agreement, organised a referendum named the Act of Free Choice, in which the military hand picked Papuan tribal elders to vote for integration with Indonesia.
There has been significant reported resistance to Indonesian integration and occupation,Philippe Pataud CelerierAutonomy isn't independence; Indonesian democracy stops in Papua
Le Monde Diplomatique, June 2010 both through civil disobedience (such as publicly raising the Morning Star flag) and via the formation of the Organisasi Papua Merdeka (OPM, or Free Papua Movement) in 1965.
Amnesty International
Amnesty International (also referred to as Amnesty or AI) is an international non-governmental organization focused on human rights, with its headquarters in the United Kingdom. The organization says that it has more than ten million members a ...
has estimated more than 100,000 Papuans, one-sixth of the population, have died as a result of government-sponsored violence against West Papuans. Reports published by TRT World and De Gruyter Oldenbourg have put the number of killed Papuans since the start of the conflict at roughly 500,000.
 From 1971, the name Papua New Guinea was used for the Australian territory. On 16 September 1975, Australia granted full independence to Papua New Guinea. In 2000, Irian Jaya was formally renamed "The Province of Papua" and a Law on Special Autonomy was passed in 2001. The Law established a (MRP) with representatives of the different indigenous cultures of Papua. The MRP was empowered to protect the rights of Papuans, raise the status of women in Papua, and to ease religious tensions in Papua; block grants were given for the implementation of the Law as much as $266 million in 2004. The Indonesian courts' enforcement of the Law on Special Autonomy blocked further creation of subdivisions of Papua: although President Megawati Sukarnoputri was able to create a separate West Papua province in 2003 as a
From 1971, the name Papua New Guinea was used for the Australian territory. On 16 September 1975, Australia granted full independence to Papua New Guinea. In 2000, Irian Jaya was formally renamed "The Province of Papua" and a Law on Special Autonomy was passed in 2001. The Law established a (MRP) with representatives of the different indigenous cultures of Papua. The MRP was empowered to protect the rights of Papuans, raise the status of women in Papua, and to ease religious tensions in Papua; block grants were given for the implementation of the Law as much as $266 million in 2004. The Indonesian courts' enforcement of the Law on Special Autonomy blocked further creation of subdivisions of Papua: although President Megawati Sukarnoputri was able to create a separate West Papua province in 2003 as a fait accompli
Many words in the English vocabulary are of French language, French origin, most coming from the Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman spoken by the upper classes in England for several hundred years after the Norman conquest of England, Norman ...
, plans for a third province on western New Guinea were blocked by the courts. Critics argue that the Indonesian government has been reluctant to establish or issue various government implementing regulations so that the legal provisions of special autonomy could be put into practice, and as a result special autonomy in Papua has "failed".
In 2022, the Indonesian government split Papua Province into four provinces. In addition to Papua Province proper (capital Jayapura), the three new provinces are South Papua (capital Merauke), Central Papua (capital Nabire) and Highland Papua
Highland Papua () is a provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia, which roughly follows the borders of the Papuan customary region of Lano-Pago (often shortened to La Pago). It covers an area of and had a population of 1,467,050 according to ...
(capital Jayawijaya). Furthermore, Southwest Papua (capital Sorong) was split from West Papua (capital Manokwari).
The culture of inter-tribal warfare and animosity between the neighboring tribes are still present in New Guinea.
Notes
References
Further reading
* Jared Diamond, '' Guns, Germs and Steel: A Short History of Everybody for the last 13,000 Years'', 1997. *External links
Facsimile of material from "The Discovery of New Guinea" by George Collingridge
Scientists hail discovery of hundreds of new species in remote New Guinea
PapuaWeb official website
* {{Authority control Islands of the Pacific Ocean International islands Geography of Melanesia Islands of Indonesia Islands of Papua New Guinea Former Spanish colonies