network externality on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
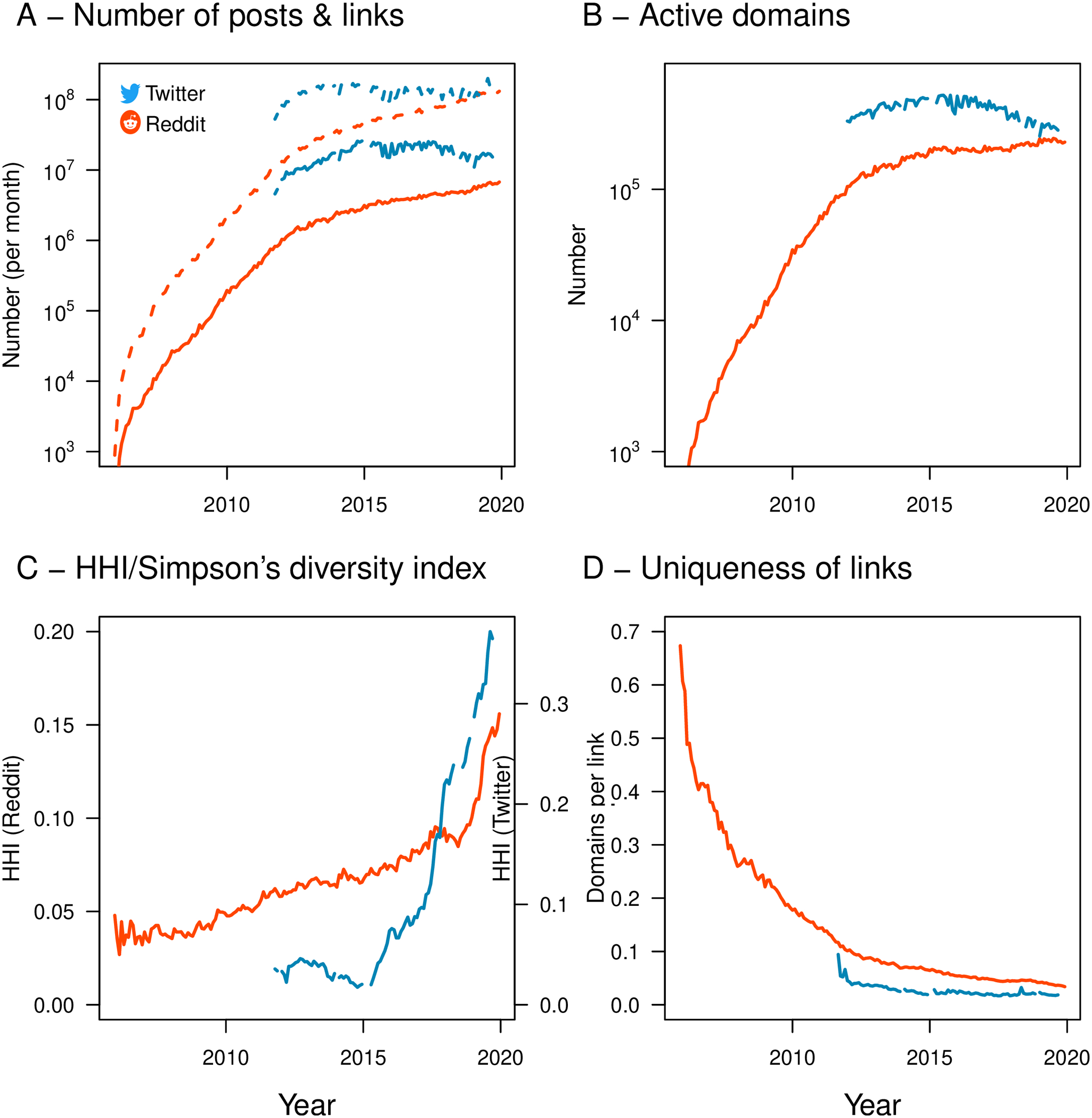 While the diversity of sources is in decline, there is a countervailing force of continually increasing functionality with new services, products and applications — such as music
While the diversity of sources is in decline, there is a countervailing force of continually increasing functionality with new services, products and applications — such as music
 There are strong network effects in the initial choice of
There are strong network effects in the initial choice of
Coordination and Lock-In: Competition with Switching Costs and Network Effects
Joseph Farrell and Paul Klemperer.
S. J. Liebowitz, Stephen E. Margolis.
Arun Sundararajan.
The Economics of Networks
Nicholas Economides.
Network Economics: An Introduction
by Anna Nagurney of the Isenberg School of Management at
Supply chain network economics
by Anna Nagurney {{authority control Business models Economics effects Monopoly (economics) Networks Technological change Transport economics
economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interac ...
, a network effect (also called network externality or demand-side economies of scale) is the phenomenon by which the value or utility
In economics, utility is a measure of a certain person's satisfaction from a certain state of the world. Over time, the term has been used with at least two meanings.
* In a normative context, utility refers to a goal or objective that we wish ...
a user derives from a good
In most contexts, the concept of good denotes the conduct that should be preferred when posed with a choice between possible actions. Good is generally considered to be the opposite of evil. The specific meaning and etymology of the term and its ...
or service
Service may refer to:
Activities
* Administrative service, a required part of the workload of university faculty
* Civil service, the body of employees of a government
* Community service, volunteer service for the benefit of a community or a ...
depends on the number of users of compatible products. Network effects are typically positive feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop where the outcome of a process reinforces the inciting process to build momentum. As such, these forces can exacerbate the effects ...
systems, resulting in users deriving more and more value from a product as more users join the same network. The adoption of a product by an additional user can be broken into two effects: an increase in the value to all other users (''total effect'') and also the enhancement of other non-users' motivation for using the product (''marginal effect'').
Network effects can be direct or indirect. Direct network effects arise when a given user's utility increases with the number of other users of the same product or technology, meaning that adoption of a product by different users is complementary. This effect is separate from effects related to price, such as a benefit to existing users resulting from price decreases as more users join. Direct network effects can be seen with social networking service
A social networking service (SNS), or social networking site, is a type of online social media platform which people use to build social networks or social relationships with other people who share similar personal or career content, interest ...
s, including Twitter
Twitter, officially known as X since 2023, is an American microblogging and social networking service. It is one of the world's largest social media platforms and one of the most-visited websites. Users can share short text messages, image ...
, Facebook
Facebook is a social media and social networking service owned by the American technology conglomerate Meta Platforms, Meta. Created in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with four other Harvard College students and roommates, Eduardo Saverin, Andre ...
, Airbnb
Airbnb, Inc. ( , an abbreviation of its original name, "Air Bed and Breakfast") is an American company operating an online marketplace for short-and-long-term homestays, experiences and services in various countries and regions. It acts as a ...
, Uber
Uber Technologies, Inc. is an American multinational transportation company that provides Ridesharing company, ride-hailing services, courier services, food delivery, and freight transport. It is headquartered in San Francisco, California, a ...
, and LinkedIn
LinkedIn () is an American business and employment-oriented Social networking service, social network. It was launched on May 5, 2003 by Reid Hoffman and Eric Ly. Since December 2016, LinkedIn has been a wholly owned subsidiary of Microsoft. ...
; telecommunications
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of ...
devices like the telephone
A telephone, colloquially referred to as a phone, is a telecommunications device that enables two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most ...
; and instant messaging
Instant messaging (IM) technology is a type of synchronous computer-mediated communication involving the immediate ( real-time) transmission of messages between two or more parties over the Internet or another computer network. Originally involv ...
services such as MSN, AIM or QQ. Indirect (or cross-group) network effects arise when there are "at least two different customer groups that are interdependent, and the utility of at least one group grows as the other group(s) grow". For example, hardware may become more valuable to consumers with the growth of compatible software.
Network effects are commonly mistaken for economies of scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of Productivity, output produced per unit of cost (production cost). A decrease in ...
, which describe decreasing average production costs in relation to the total volume of units produced. Economies of scale are a common phenomenon in traditional industries such as manufacturing, whereas network effects are most prevalent in new economy
The New Economy refers to the ongoing development of the American economic system. It evolved from the notions of the classical economy via the transition from a manufacturing-based economy to a service-based economy, and has been driven by ...
industries, particularly information and communication technologies
Information and communications technology (ICT) is an extensional term for information technology (IT) that stresses the role of unified communications and the integration of telecommunications (telephone lines and wireless signals) and compute ...
. Network effects are the demand side counterpart of economies of scale, as they function by increasing a customer's willingness to pay due rather than decreasing the supplier's average cost.
Upon reaching critical mass, a bandwagon effect
The bandwagon effect is a psychological phenomenon where people adopt certain behaviors, styles, or attitudes simply because others are doing so. More specifically, it is a cognitive bias by which public opinion or behaviours can alter due to ...
can result. As the network continues to become more valuable with each new adopter, more people are incentivised to adopt, resulting in a positive feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop where the outcome of a process reinforces the inciting process to build momentum. As such, these forces can exacerbate the effects ...
loop. Multiple equilibria and a market monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek language, Greek and ) is a market in which one person or company is the only supplier of a particular good or service. A monopoly is characterized by a lack of economic Competition (economics), competition to produce ...
are two key potential outcomes in markets that exhibit network effects. Consumer expectations are key in determining which outcomes will result.
Origins
Network effects were a central theme in the arguments ofTheodore Vail
Theodore Newton Vail (July 16, 1845 – April 16, 1920) was an American businessman who served as the general manager of the Bell Telephone Company from 1878 to 1887 and became the founding president of American Telephone and Telegraph Company ...
, the first post-patent president of Bell Telephone, in gaining a monopoly on US telephone services. In 1908, when he presented the concept in Bell's annual report, there were over 4,000 local and regional telephone exchanges, most of which were eventually merged into the Bell System
The Bell System was a system of telecommunication companies, led by the Bell Telephone Company and later by the AT&T Corporation, American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T), that dominated the telephone services industry in North America fo ...
.
Network effects were popularized by Robert Metcalfe
Robert "Bob" Melancton Metcalfe (born April 7, 1946) is an American engineer and entrepreneur who contributed to the development of the internet in the 1970s. He co-invented Ethernet, co-founded 3Com, and formulated Metcalfe's law, which desc ...
, stated as Metcalfe's law
Metcalfe's law states that the financial value or influence of a telecommunications network is proportional to the square of the number of connected users of the system (2). The law is named after Robert Metcalfe and was first proposed in 1980 ...
. Metcalfe was one of the co-inventors of Ethernet
Ethernet ( ) is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 198 ...
and a co-founder of the company 3Com. In selling the product, Metcalfe argued that customers needed Ethernet cards to grow above a certain critical mass
In nuclear engineering, critical mass is the minimum mass of the fissile material needed for a sustained nuclear chain reaction in a particular setup. The critical mass of a fissionable material depends upon its nuclear properties (specific ...
if they were to reap the benefits of their network. According to Metcalfe, the rationale behind the sale of networking cards was that the cost of the network was directly proportional to the number of cards installed, but the value of the network was proportional to the square of the number of users. This was expressed algebraically as having a cost of N, and a value of N2. While the actual numbers behind this proposition were never firm, the concept allowed customers to share access to expensive resources like disk drives and printers, send e-mail, and eventually access the Internet.
The economic theory of the network effect was advanced significantly between 1985 and 1995 by researchers Michael L. Katz, Carl Shapiro, Joseph Farrell, and Garth Saloner. Author, high-tech entrepreneur Rod Beckstrom presented a mathematical model for describing networks that are in a state of positive network effect at BlackHat and Defcon in 2009 and also presented the ''inverse network effect'' with an economic model for defining it as well. Because of the positive feedback often associated with the network effect, system dynamics
System dynamics (SD) is an approach to understanding the nonlinear behaviour of complex systems over time using stocks, flows, internal feedback loops, table functions and time delays.
Overview
System dynamics is a methodology and mathematical ...
can be used as a modelling method to describe the phenomena. Word of mouth
Word of mouth is the passing of information from person to person using oral communication, which could be as simple as telling someone the time of day. Storytelling is a common form of word-of-mouth communication where one person tells others a ...
and the Bass diffusion model are also potentially applicable. The next major advance occurred between 2000 and 2003 when researchers Geoffrey G Parker, Marshall Van Alstyne, Jean-Charles Rochet and Jean Tirole
Jean Tirole (born 9 August 1953) is a French economist who is currently a professor of economics at Toulouse 1 Capitole University. He focuses on industrial organization, game theory, banking and finance, and psychology. In particular, he focus ...
independently developed the two-sided market
In mathematics, specifically in topology of manifolds, a compact codimension-one submanifold F of a manifold M is said to be 2-sided in M when there is an embedding
::h\colon F\times 1,1to M
with h(x,0)=x for each x\in F and
::h(F\times ...
literature showing how network externalities
In economics, an externality is an indirect cost (external cost) or indirect benefit (external benefit) to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effect of another party's (or parties') activity. Externalities can be considered as unpriced ...
that cross distinct groups can lead to free pricing for one of those groups.
Evidence and consequences
 While the diversity of sources is in decline, there is a countervailing force of continually increasing functionality with new services, products and applications — such as music
While the diversity of sources is in decline, there is a countervailing force of continually increasing functionality with new services, products and applications — such as music streaming services
A streaming media service (also simply called a streaming service) is an online platform that allows users to watch or listen to content, such as film, movies, Television show, TV shows, music, or podcasts, over the internet. Instead of downloadi ...
(Spotify), file sharing
File sharing is the practice of distributing or providing access to digital media, such as computer programs, multimedia (audio, images and video), documents or electronic books. Common methods of storage, transmission and dispersion include ...
programs (Dropbox) and messaging platforms (Messenger, WhatsApp and Snapchat). Another major finding was the dramatic increase in the ''infant mortality'' rate of websites — with the dominant players in each functional niche - once established guarding their turf more staunchly than ever.
On the other hand, growing network effect does not always bring proportional increase in returns. Whether additional users bring more value depends on the commoditization of supply, the type of incremental user and the nature of substitutes. For example, social networks can hit an inflection point, after which additional users do not bring more value. This could be attributed to the fact that as more people join the network, its users are less willing to share personal content and the site becomes more focused on news and public content.
Economics
Network economics refers to business economics that benefit from the network effect. This is when the value of a good or service increases when others buy the same good or service. Examples are website such asEBay
eBay Inc. ( , often stylized as ebay) is an American multinational e-commerce company based in San Jose, California, that allows users to buy or view items via retail sales through online marketplaces and websites in 190 markets worldwide. ...
, or iVillage where the community comes together and shares thoughts to help the website become a better business organization.
In sustainability
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): env ...
, network economics refers to multiple professionals (architects, designers, or related businesses) all working together to develop sustainable products and technologies. The more companies are involved in environmentally friendly production, the easier and cheaper it becomes to produce new sustainable products. For instance, if no one produces sustainable products, it is difficult and expensive to design a sustainable house with custom materials and technology. But due to network economics, the more industries are involved in creating such products, the easier it is to design an environmentally sustainable building.
Another benefit of network economics in a certain field is improvement that results from competition and networking within an industry.
Adoption and competition
Critical mass
In the early phases of a network technology, incentives to adopt the new technology are low. After a certain number of people have adopted the technology, network effects become significant enough that adoption becomes adominant strategy
In game theory, a strategy ''A'' dominates another strategy ''B'' if ''A'' will always produce a better result than ''B'', regardless of how any other player plays. Some very simple games (called straightforward games) can be solved using domi ...
. This point is called critical mass. At the critical mass point, the value obtained from the good or service is greater than or equal to the price paid for the good or service.
When a product reaches critical mass, network effects will drive subsequent growth until a stable balance is reached. Therefore, a key business concern must then be how to attract users prior to reaching critical mass. Critical quality is closely related to consumer expectations, which will be affected by price and quality of products or services, the company's reputation and the growth path of the network. Thus, one way is to rely on extrinsic motivation, such as a payment, a fee waiver, or a request for friends to sign up. A more natural strategy is to build a system that has enough value ''without'' network effects, at least to early adopters. Then, as the number of users increases, the system becomes even more valuable and is able to attract a wider user base.
Limits to growth
Network growth is generally not infinite, and tends to plateau when it reachesmarket saturation
In economics, market saturation is a situation in which a Product (business), product has become Diffusion_(business), diffused (distributed) within a Market (economics), market; the actual level of saturation can depend on consumer purchasing p ...
(all customers have already joined) or diminishing returns
In economics, diminishing returns means the decrease in marginal (incremental) output of a production process as the amount of a single factor of production is incrementally increased, holding all other factors of production equal ('' ceter ...
make acquisition of the last few customers too costly.
Networks can also stop growing or collapse if they do not have enough capacity to handle growth. For example, an overloaded phone network that has so many customers that it becomes congested, leading to busy signals, the inability to get a dial tone
A dial tone (dialling tone in the UK) is a telephony signal sent by a telephone exchange or private branch exchange (PBX) to a terminating device, such as a telephone, when an off-hook condition is detected. It indicates that the exchange is ...
, and poor customer support
Customer support is a range of services to assist customers in making cost effective and correct use of a product. It includes assistance in planning, installation, training, troubleshooting, maintenance, upgrading, and disposal of a product. Rega ...
. This creates a risk that customers will defect to a rival network because of the inadequate capacity of the existing system. After this point, each additional user decreases the value obtained by every other user.
Peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the network, forming a peer-to-peer network of Node ...
(P2P) systems are networks designed to distribute load among their user pool. This theoretically allows P2P networks to scale indefinitely. The P2P based telephony service Skype
Skype () was a proprietary telecommunications application operated by Skype Technologies, a division of Microsoft, best known for IP-based videotelephony, videoconferencing and voice calls. It also had instant messaging, file transfer, ...
benefits from this effect and its growth is limited primarily by market saturation.
Market tipping
Network effects give rise to the potential outcome of market tipping, defined as "the tendency of one system to pull away from its rivals in popularity once it has gained an initial edge". Tipping results in a market in which only one good or service dominates and competition is stifled, and can result in amonopoly
A monopoly (from Greek language, Greek and ) is a market in which one person or company is the only supplier of a particular good or service. A monopoly is characterized by a lack of economic Competition (economics), competition to produce ...
. This is because network effects tend to incentivise users to coordinate their adoption of a single product. Therefore, tipping can result in a natural form of market concentration in markets that display network effects. However, the presence of network effects does not necessarily imply that a market will tip; the following additional conditions must be met:
# The utility derived by users from network effects must exceed the utility they derive from differentiation
# Users must have high costs of multihoming
Multihoming is the practice of connecting a Host (network), host or a computer network to more than one network. This can be done in order to increase reliability or performance.
A typical host or end-user network is connected to just one networ ...
(i.e. adopting more than one competing networks)
# Users must have high switching costs
If any of these three conditions are not satisfied, the market may fail to tip and multiple products with significant market shares may coexist. One such example is the U.S. instant messaging market, which remained an oligopoly despite significant network effects. This can be attributed to the low multi-homing and switching costs faced by users.
Market tipping does not imply permanent success in a given market. Competition can be reintroduced into the market due to shocks such as the development of new technologies. Additionally, if the price is raised above customers' willingness to pay, this may reverse market tipping.
Multiple equilibria and expectations
Networks effects often result in multiple potential market equilibrium outcomes. The key determinant in which equilibrium will manifest are the expectations of the market participants, which are self-fulfilling. Because users are incentivised to coordinate their adoption, user will tend to adopt the product that they expect to draw the largest number of users. These expectations may be shaped by path dependence, such as a perceivedfirst-mover advantage
In marketing strategy, first-mover advantage (FMA) is the competitive advantage gained by the initial ("first-moving") significant occupant of a market segment. First-mover advantage enables a company or firm to establish strong brand recogniti ...
, which can result in lock-in. The most commonly cited example of path dependence is the QWERTY
QWERTY ( ) is a keyboard layout for Latin-script alphabets. The name comes from the order of the first six Computer keyboard keys#Types, keys on the top letter row of the keyboard: . The QWERTY design is based on a layout included in the Sh ...
keyboard, which owes its ubiquity to its establishment of an early lead in the keyboard layout industry and high switching costs, rather than any inherent advantage over competitors. Other key influences of adoption expectations can be reputational (e.g. a firm that has previously produced high quality products may be favoured over a new firm).
Markets with network effects may result in inefficient equilibrium outcomes. With simultaneous adoption, users may fail to coordinate towards a single agreed-upon product, resulting in splintering among different networks, or may coordinate to lock-in to a different product than the one that is best for them.
Technology lifecycle
If some existing technology or company whose benefits are largely based on network effects starts to lose market share against a challenger such as a disruptive technology oropen standards
An open standard is a standard that is openly accessible and usable by anyone. It is also a common prerequisite that open standards use an open license that provides for extensibility. Typically, anybody can participate in their development due to ...
based competition, the benefits of network effects will reduce for the incumbent, and increase for the challenger. In this model, a tipping point is eventually reached at which the network effects of the challenger dominate those of the former incumbent, and the incumbent is forced into an accelerating decline, whilst the challenger takes over the incumbent's former position.
Sony's Betamax and Victor Company of Japan (JVC)'s video home system (VHS) can both be used for video cassette recorders (VCR), but the two technologies are not compatible. Therefore, the VCR that is suitable for one type of cassette cannot fit in another. VHS's technology gradually surpassed Betamax in the competition. In the end, Betamax lost its original market share and was replaced by VHS.
Negative network externalities
Negative network externalities, in the mathematical sense, are those that have a negative effect compared to normal (positive) network effects. Just as positive network externalities (network effects) causepositive feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop where the outcome of a process reinforces the inciting process to build momentum. As such, these forces can exacerbate the effects ...
and exponential growth
Exponential growth occurs when a quantity grows as an exponential function of time. The quantity grows at a rate directly proportional to its present size. For example, when it is 3 times as big as it is now, it will be growing 3 times as fast ...
, negative network externalities are also caused by positive feedback resulting in exponential decay
A quantity is subject to exponential decay if it decreases at a rate proportional to its current value. Symbolically, this process can be expressed by the following differential equation, where is the quantity and (lambda
Lambda (; uppe ...
. Negative network effect must not be confused with negative feedback. Negative feedback is the forces that pull towards equilibrium and are responsible for stability.
Therefore, congestion occurs when the efficiency of a network decreases as more people use it, and this reduces the value to people already using it. Traffic congestion
Traffic congestion is a condition in transport that is characterized by slower speeds, longer trip times, and increased vehicular queueing. Traffic congestion on urban road networks has increased substantially since the 1950s, resulting in m ...
that overloads the freeway and network congestion
Network congestion in data networking and queueing theory is the reduced quality of service that occurs when a network node or link is carrying more data than it can handle. Typical effects include queueing delay, packet loss or the blocking of ...
on connections with limited bandwidth both display negative network externalities.
Braess's paradox
Braess's paradox is the observation that adding one or more roads to a road network can slow down overall road traffic, traffic flow through it. The paradox was first discovered by Arthur Cecil Pigou, Arthur Pigou in 1920, and Stigler's law of ep ...
suggests that adding paths through a network can have a negative effect on performance of the network.
Interoperability
Interoperability
Interoperability is a characteristic of a product or system to work with other products or systems. While the term was initially defined for information technology or systems engineering services to allow for information exchange, a broader de ...
has the effect of making the network bigger and thus increases the external value of the network to consumers. Interoperability achieves this primarily by increasing potential connections and secondarily by attracting new participants to the network. Other benefits of interoperability include reduced uncertainty, reduced lock-in, commoditization and competition based on price.
Interoperability can be achieved through standardization
Standardization (American English) or standardisation (British English) is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organiza ...
or other cooperation. Companies involved in fostering interoperability face a tension between cooperating with their competitors to grow the potential market for products and competing for market share.
Compatibility and incompatibility
Product compatibility is closely related to network externalities in company's competition, which refers to two systems that can be operated together without changing. Compatible products are characterized by better matching with customers, so they can enjoy all the benefits of the network without having to purchase products from the same company. However, not only products of compatibility will intensify competition between companies, this will make users who had purchased products lose their advantages, but also proprietary networks may raise the industry entry standards. Compared to large companies with better reputation or strength, weaker companies or small networks will more inclined to choose compatible products. Besides, the compatibility of products is conducive to the company's increase in market share. For example, theWindows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
system is famous for its operating compatibility, thereby satisfying consumers' diversification of other applications. As the supplier of Windows systems, Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
benefits from indirect network effects, which cause the growing of the company's market share.
Incompatibility is the opposite of compatibility. Because incompatibility of products will aggravate market segmentation
In marketing, market segmentation or customer segmentation is the process of dividing a consumer or business market into meaningful sub-groups of current or potential customers (or consumers) known as ''segments''. Its purpose is to identify pr ...
and reduce efficiency, and also harm consumer interests and enhance competition. The result of the competition between incompatible networks depends on the complete sequential of adoption and the early preferences of the adopters. Effective competition determines the market share of companies, which is historically important. Since the installed base can directly bring more network profit and increase the consumers' expectations, which will have a positive impact on the smooth implementation of subsequent network effects.
Open versus closed standards
In communication and information technologies,open standard
An open standard is a standard that is openly accessible and usable by anyone. It is also a common prerequisite that open standards use an open license that provides for extensibility. Typically, anybody can participate in their development due to ...
s and interfaces are often developed through the participation of multiple companies and are usually perceived to provide mutual benefit. But, in cases in which the relevant communication protocols or interfaces are closed standards, the network effect can give the company controlling those standards monopoly power. The Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
corporation is widely seen by computer professionals as maintaining its monopoly through these means. One observed method Microsoft uses to put the network effect to its advantage is called Embrace, extend and extinguish
"Embrace, extend, and extinguish" (EEE), also known as "embrace, extend, and exterminate", is a phrase that the U.S. Department of Justice found was used internally by Microsoft to describe its strategy for entering product categories involving wi ...
.
Mirabilis is an Israeli start-up which pioneered instant messaging
Instant messaging (IM) technology is a type of synchronous computer-mediated communication involving the immediate ( real-time) transmission of messages between two or more parties over the Internet or another computer network. Originally involv ...
(IM) and was bought by America Online
AOL (formerly a company known as AOL Inc. and originally known as America Online) is an American web portal and online service provider based in New York City, and a brand marketed by Yahoo! Inc. (2017–present), Yahoo! Inc.
The service tra ...
. By giving away their ICQ product for free and preventing interoperability between their client software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
and other products, they were able to temporarily dominate the market for instant messaging. The IM technology has completed the use from the home to the workplace, because of its faster processing speed and simplified process characteristics. Because of the network effect, new IM users gained much more value by choosing to use the Mirabilis system (and join its large network of users) than they would use a competing system. As was typical for that era, the company never made any attempt to generate profits from its dominant position before selling the company.
Network effect as a competitive advantage
Network effect can significantly influence the competitive landscape of an industry. According to Michael E. Porter, strong network effect might decrease the threat of new entrants, which is one of the five major competitive forces that act on an industry. Persistent barriers to entry into a market may help incumbent companies to fend off competition and keep or increase theirmarket share
Market share is the percentage of the total revenue or sales in a Market (economics), market that a company's business makes up. For example, if there are 50,000 units sold per year in a given industry, a company whose sales were 5,000 of those ...
, while maintaining profitability and return on capital.
These attractive characteristics are one of the reasons that allowed platform companies like Amazon, Google or Facebook to grow rapidly and create shareholder value. On the other hand, network effect can result in high concentration of power in an industry, or even a monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek language, Greek and ) is a market in which one person or company is the only supplier of a particular good or service. A monopoly is characterized by a lack of economic Competition (economics), competition to produce ...
. This often leads to increased scrutiny from regulators that try to restore healthy competition, as is often the case with large technology companies.
Examples
Telephone
Network effects are the incremental benefit gained by each user for each new user that joins a network. An example of a direct network effect is thetelephone
A telephone, colloquially referred to as a phone, is a telecommunications device that enables two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most ...
. Originally when only a small number of people owned a telephone the value it provided was minimal. Not only did other people need to own a telephone for it to be useful, but it also had to be connected to the network through the users home. As technology advanced it became more affordable for people to own a telephone. This created more value and utility due to the increase in users. Eventually increased usage through exponential growth led to the telephone is used by almost every household adding more value to the network for all users. Without the network effect and technological advances the telephone would have nowhere near the amount of value or utility as it does today.
Financial exchanges
Transactions in the financial field may feature a network effect. As the number of sellers and buyers in the exchange, who have the symmetric information increases, liquidity increases, and transaction costs decrease. This then attracts a larger number of buyers and sellers to the exchange. The network advantage of financial exchanges is apparent in the difficulty that startup exchanges have in dislodging a dominant exchange. For example, theChicago Board of Trade
The Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT), is an American futures exchange, futures and options exchange that was founded in 1848. On July 12, 2007, the CBOT merged with the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) to form CME Group. CBOT and three other excha ...
has retained overwhelming dominance of trading in US Treasury bond futures despite the startup of Eurex
Eurex Exchange is a German derivatives exchange which primarily offers trading in European based derivatives. The products traded on this exchange vary from German and Swiss debt instruments to European stocks and various stock indexes. All tran ...
US trading of identical futures contracts. Similarly, the Chicago Mercantile Exchange
The Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) (often called "the Chicago Merc", or "the Merc") is an American derivatives marketplace based in Chicago and located at 20 S. Wacker Drive. The CME was founded in 1898 as the Chicago Butter and Egg Board ...
has maintained dominance in trading of Eurobond interest rate futures despite a challenge from Euronext.Liffe.
Cryptocurrencies and blockchains
Cryptocurrencies
A cryptocurrency (colloquially crypto) is a digital currency designed to work through a computer network that is not reliant on any central authority, such as a government or bank, to uphold or maintain it.
Individual coin ownership records ...
such as Bitcoin
Bitcoin (abbreviation: BTC; Currency symbol, sign: ₿) is the first Decentralized application, decentralized cryptocurrency. Based on a free-market ideology, bitcoin was invented in 2008 when an unknown entity published a white paper under ...
and smart contract blockchains such as Ethereum
Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain with smart contract functionality. Ether (abbreviation: ETH) is the native cryptocurrency of the platform. Among cryptocurrencies, ether is second only to bitcoin in market capitalization. It is open-s ...
also exhibit network effects.
Smart contract
A smart contract is a computer program or a Transaction Protocol Data Unit, transaction protocol that is intended to automatically execute, control or document events and actions according to the terms of a contract or an agreement. The objective ...
blockchains can produce network effects through the social network of individuals that uses a blockchain
The blockchain is a distributed ledger with growing lists of Record (computer science), records (''blocks'') that are securely linked together via Cryptographic hash function, cryptographic hashes. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of th ...
for securing its transactions. Public infrastructure networks such as Ethereum
Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain with smart contract functionality. Ether (abbreviation: ETH) is the native cryptocurrency of the platform. Among cryptocurrencies, ether is second only to bitcoin in market capitalization. It is open-s ...
and others can facilitate entities that do not explicitly trust one another to collaborate in meaningful way, incentivizing growth in the network. However, as of 2019, such networks grow more slowly due to missing particular requirements such as privacy
Privacy (, ) is the ability of an individual or group to seclude themselves or information about themselves, and thereby express themselves selectively.
The domain of privacy partially overlaps with security, which can include the concepts of a ...
and scalability
Scalability is the property of a system to handle a growing amount of work. One definition for software systems specifies that this may be done by adding resources to the system.
In an economic context, a scalable business model implies that ...
.
Software
The widely used computersoftware
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
benefits from powerful network effects. The software-purchase characteristic is that it is easily influenced by the opinions of others, so the customer base of the software is the key to realizing a positive network effect. Although customers' motivation for choosing software is related to the product itself, media interaction and word-of-mouth recommendations from purchased customers can still increase the possibility of software being applied to other customers who have not purchased it, thereby resulting in network effects.
In 2007 Apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
released the iPhone
The iPhone is a line of smartphones developed and marketed by Apple that run iOS, the company's own mobile operating system. The first-generation iPhone was announced by then–Apple CEO and co-founder Steve Jobs on January 9, 2007, at ...
followed by the app store
An app store, also called an app marketplace or app catalog, is a type of digital distribution platform for computer software called applications, often in a mobile context. Apps provide a specific set of functions which, by definition, do not i ...
. Most iPhone apps rely heavily on the existence of strong network effects. This enables the software to grow in popularity very quickly and spread to a large userbase with very limited marketing needed. The Freemium
Freemium, a portmanteau of the words "free" and "premium", is a pricing strategy by which a basic product or service is provided free of charge, but money (a premium) is charged for additional features, services, or virtual (online) or physical ( ...
business model has evolved to take advantage of these network effects by releasing a free version that will not limit the adoption or any users and then charge for premium features as the primary source of revenue. Furthermore, some software companies will launch free trial versions during the trial period to attract buyers and reduce their uncertainty. The duration of free time is related to the network effect. The more positive feedback the company received, the shorter the free trial time will be.
Software companies (for example Adobe
Adobe (from arabic: الطوب Attub ; ) is a building material made from earth and organic materials. is Spanish for mudbrick. In some English-speaking regions of Spanish heritage, such as the Southwestern United States, the term is use ...
or Autodesk
Autodesk, Inc. is an American multinational software corporation that provides software products and services for the architecture, engineering, construction, manufacturing, media, education, and entertainment industries. Autodesk is headquarte ...
) often give significant discounts to students. By doing so, they intentionally stimulate the network effect - as more students learn to use a particular piece of software, it becomes more viable for companies and employers to use it as well. And the more employers require a given skill, the higher the benefit that employees will receive from learning it. This creates a self-reinforcing cycle, further strengthening the network effect.
Web sites
Manyweb site
A website (also written as a web site) is any web page whose content is identified by a common domain name and is published on at least one web server. Websites are typically dedicated to a particular topic or purpose, such as news, education, ...
s benefit from a network effect. One example is web marketplaces and exchanges. For example, eBay
eBay Inc. ( , often stylized as ebay) is an American multinational e-commerce company based in San Jose, California, that allows users to buy or view items via retail sales through online marketplaces and websites in 190 markets worldwide. ...
would not be a particularly useful site if auction
An auction is usually a process of Trade, buying and selling Good (economics), goods or Service (economics), services by offering them up for Bidding, bids, taking bids, and then selling the item to the highest bidder or buying the item from th ...
s were not competitive. As the number of users grows on eBay, auctions grow more competitive, pushing up the prices of bids on items. This makes it more worthwhile to sell on eBay and brings more sellers onto eBay, which, in turn, drives prices down again due to increased supply. Increased supply brings even more buyers to eBay. Essentially, as the number of users of eBay grows, prices fall and supply increases, and more and more people find the site to be useful.
Network effects were used as justification in business model
A business model describes how a Company, business organization creates, delivers, and captures value creation, value,''Business Model Generation'', Alexander Osterwalder, Yves Pigneur, Alan Smith, and 470 practitioners from 45 countries, self-pub ...
s by some of the dot-com companies in the late 1990s. These firms operated under the belief that when a new market
Market is a term used to describe concepts such as:
*Market (economics), system in which parties engage in transactions according to supply and demand
*Market economy
*Marketplace, a physical marketplace or public market
*Marketing, the act of sat ...
comes into being which contains strong network effects, firms should care more about growing their market share
Market share is the percentage of the total revenue or sales in a Market (economics), market that a company's business makes up. For example, if there are 50,000 units sold per year in a given industry, a company whose sales were 5,000 of those ...
than about becoming profitable
In economics, profit is the difference between revenue that an economic entity has received from its outputs and total costs of its inputs, also known as surplus value. It is equal to total revenue minus total cost, including both explicit an ...
. The justification was that market share would determine which firm could set technical and marketing standards and giving these companies a first-mover advantage
In marketing strategy, first-mover advantage (FMA) is the competitive advantage gained by the initial ("first-moving") significant occupant of a market segment. First-mover advantage enables a company or firm to establish strong brand recogniti ...
.
Social networking
A social network is a social structure consisting of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), networks of Dyad (sociology), dyadic ties, and other Social relation, social interactions between actors. The social network per ...
websites are good examples. The more people register onto a social networking website, the more useful the website is to its registrants.
Google uses the network effect in its advertising business with its Google AdSense
Google AdSense is a program run by Google through which website publishers in the Google Display Network, Google Network of content sites serve text, images, video, or interactive media advertisements that are targeted advertising, targeted t ...
service. AdSense places ads on many small sites, such as blog
A blog (a Clipping (morphology), truncation of "weblog") is an informational website consisting of discrete, often informal diary-style text entries also known as posts. Posts are typically displayed in Reverse chronology, reverse chronologic ...
s, using Google technology to determine which ads are relevant to which blogs. Thus, the service appears to aim to serve as an exchange (or ad network) for matching many advertisers with many small sites. In general, the more blogs AdSense can reach, the more advertisers it will attract, making it the most attractive option for more blogs.
By contrast, the value of a news site is primarily proportional to the quality of the articles, not to the number of other people using the site. Similarly, the first generation of search engine
A search engine is a software system that provides hyperlinks to web pages, and other relevant information on World Wide Web, the Web in response to a user's web query, query. The user enters a query in a web browser or a mobile app, and the sea ...
s experienced little network effect, as the value of the site was based on the value of the search results. This allowed Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial ...
to win users away from Yahoo!
Yahoo (, styled yahoo''!'' in its logo) is an American web portal that provides the search engine Yahoo Search and related services including My Yahoo, Yahoo Mail, Yahoo News, Yahoo Finance, Yahoo Sports, y!entertainment, yahoo!life, and its a ...
without much trouble, once users believed that Google's search results were superior. Some commentators mistook the value of the Yahoo! brand (which does increase as more people know of it) for a network effect protecting its advertising business.
Rail gauge
rail gauge
In rail transport, track gauge is the distance between the two rails of a railway track. All vehicles on a rail network must have wheelsets that are compatible with the track gauge. Since many different track gauges exist worldwide, gauge dif ...
, and in gauge conversion decisions. Even when placing isolated rails not connected to any other lines, track layers usually choose a standard rail gauge so they can use off-the-shelf rolling stock. Although a few manufacturers make rolling stock that can adjust to different rail gauges, most manufacturers make rolling stock that only works with one of the standard rail gauges. This even applies to urban rail
Urban rail transit is a wide term for various types of local rail systems providing passenger service within and around urban or suburban areas. The set of urban rail systems can be roughly subdivided into the following categories, which som ...
systems where historically tram
A tram (also known as a streetcar or trolley in Canada and the United States) is an urban rail transit in which Rolling stock, vehicles, whether individual railcars or multiple-unit trains, run on tramway tracks on urban public streets; some ...
ways and to a lesser extent metros would come in a wide array of different gauges, nowadays virtually all new networks are built to a handful of gauges and overwhelmingly standard gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the ...
.
Credit cards
For credit cards that are now widely used, large-scale applications on the market are closely related to network effects. Credit card, as one of the currency payment methods in the current economy, which was originated in 1949. Early research on the circulation of credit cards at the retail level found that credit cardinterest rate
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, ...
s were not affected by macroeconomic interest rates and remained almost unchanged. Later, credit cards gradually entered the network level due to changes in policy priorities and became a popular trend in payment in the 1980s. Different levels of credit cards separate benefit from two types of network effects. The application of credit cards related to external network effects, which is because when this has become a payment method, and more people use credit cards. Each additional person uses the same credit card, the value of rest people who use the credit card will increase. Besides, the credit card system at the network level could be seen as a two-sided market
In mathematics, specifically in topology of manifolds, a compact codimension-one submanifold F of a manifold M is said to be 2-sided in M when there is an embedding
::h\colon F\times 1,1to M
with h(x,0)=x for each x\in F and
::h(F\times ...
. On the one hand, the number of cardholders attracts merchants to use credit cards as a payment method. On the other hand, an increasing number of merchants can also attract more new cardholders. In other words, the use of credit cards has increased significantly among merchants which leads to increased value. This can conversely increase the cardholder's credit card value and the number of users. Moreover, credit card services also display a network effect between merchant discounts and credit accessibility. When credit accessibility increases which greater sales can be obtained, merchants are willing to be charged more discounts by credit card issuers.
Visa has become a leader in the electronic payment industry through the network effect of credit cards as its competitive advantage. Till 2016, Visa's credit card market share
Market share is the percentage of the total revenue or sales in a Market (economics), market that a company's business makes up. For example, if there are 50,000 units sold per year in a given industry, a company whose sales were 5,000 of those ...
has risen from a quarter to as much as half in four years. Visa benefits from the network effect. Since every additional Visa cardholder is more attractive to merchants, and merchants can also attract more new cardholders through the brand. In other words, the popularity and convenience of Visa in the electronic payment market, lead more people and merchants choose to use Visa, which greatly increases the value of Visa.
See also
References
Further reading
*External links
Coordination and Lock-In: Competition with Switching Costs and Network Effects
Joseph Farrell and Paul Klemperer.
S. J. Liebowitz, Stephen E. Margolis.
Arun Sundararajan.
The Economics of Networks
Nicholas Economides.
Network Economics: An Introduction
by Anna Nagurney of the Isenberg School of Management at
University of Massachusetts Amherst
The University of Massachusetts Amherst (UMass Amherst) is a public land-grant research university in Amherst, Massachusetts, United States. It is the flagship campus of the University of Massachusetts system and was founded in 1863 as the ...
Supply chain network economics
by Anna Nagurney {{authority control Business models Economics effects Monopoly (economics) Networks Technological change Transport economics