Neon Discharge Tube on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A gas-filled tube, also commonly known as a discharge tube or formerly as a Plücker tube, is an arrangement of
A gas-filled tube, also commonly known as a discharge tube or formerly as a Plücker tube, is an arrangement of
"The Evolution of the Hydrogen Thyratron"
Marconi Applied Technologies Ltd, Chelmsford, U.K.

/ref> The electrodes undergo damage by high-velocity ions. The neutral atoms of the gas slow the ions down by collisions, and reduce the energy transferred to the electrodes by the ion impact. Gases with high atomic weight, e.g. xenon, protect the electrodes better than lighter ones, e.g. neon.
Lamptech.co.uk. Retrieved on 2011-05-17. *
by John Dakin, Robert G. W. Brown, p. 52, CRC Press, 2006 Mercury is used in
 *
*
 The fundamental mechanism is the Townsend discharge, which is the sustained multiplication of electron flow by ion impact when a critical value of electric field strength for the density of the gas is reached. As the electric field is increased various phases of discharge are encountered as shown in the accompanying plot. The gas used dramatically influences the parameters of the tube. The breakdown voltage depends on the gas composition and electrode distance; the dependencies are described by
The fundamental mechanism is the Townsend discharge, which is the sustained multiplication of electron flow by ion impact when a critical value of electric field strength for the density of the gas is reached. As the electric field is increased various phases of discharge are encountered as shown in the accompanying plot. The gas used dramatically influences the parameters of the tube. The breakdown voltage depends on the gas composition and electrode distance; the dependencies are described by
by Wendy Middleton, Mac E. Van Valkenburg, pp. 16–42, Newnes, 2002
Chapter 2: The construction of a gas-discharge tube
''1964 Philips Gas-Discharge Tubes book''
Chapter 8: Special tubes
''1964 Philips Gas-Discharge Tubes book'' *Mercury pool tubes ** Excitron, a mercury pool tube ** Gusetron or gausitron, a mercury arc pool tube **
Pulse Power Switching Devices – An Overview (both vacuum and gas-filled switching tubes)
{{Authority control Electrical components Glass applications cs:Výbojka hi:गैस नली lv:Gazotrons
 A gas-filled tube, also commonly known as a discharge tube or formerly as a Plücker tube, is an arrangement of
A gas-filled tube, also commonly known as a discharge tube or formerly as a Plücker tube, is an arrangement of electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or a gas). In electrochemical cells, electrodes are essential parts that can consist of a varie ...
s in a gas
Gas is a state of matter that has neither a fixed volume nor a fixed shape and is a compressible fluid. A ''pure gas'' is made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon) or molecules of either a single type of atom ( elements such as ...
within an insulating, temperature-resistant envelope
An envelope is a common packaging item, usually made of thin, flat material. It is designed to contain a flat object, such as a letter (message), letter or Greeting card, card.
Traditional envelopes are made from sheets of paper cut to one o ...
. Gas-filled tubes exploit phenomena related to electric discharge in gases
Electric discharge in gases occurs when electric current flows through a gaseous medium due to ionization of the gas. Depending on several factors, the discharge may radiate visible light. The properties of electric discharges in gases are studied ...
, and operate by ionizing the gas with an applied voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), ...
sufficient to cause electrical conduction
Electrical resistivity (also called volume resistivity or specific electrical resistance) is a fundamental specific property of a material that measures its electrical resistance or how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity i ...
by the underlying phenomena of the Townsend discharge
In electromagnetism, the Townsend discharge or Townsend avalanche is an ionisation process for gases where free electrons are accelerated by an electric field, collide with gas molecules, and consequently free additional electrons. Those electr ...
. A gas-discharge lamp
Gas-discharge lamps are a family of artificial light sources that generate light by sending an electric discharge through an ionization, ionized gas, a plasma (physics), plasma.
Typically, such lamps use a
noble gas (argon, neon, krypton, and x ...
is an electric light
Electric light is an artificial light source powered by electricity.
Electric Light may also refer to:
* Light fixture, a decorative enclosure for an electric light source
* Electric Light (album), ''Electric Light'' (album), a 2018 album by James ...
using a gas-filled tube; these include fluorescent lamp
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, to produce ultraviolet and make a phosphor ...
s, metal-halide lamps, sodium-vapor lamps, and neon lights. Specialized gas-filled tubes such as krytron
The krytron is a cold-cathode gas-filled tube intended for use as a very high-speed switch, somewhat similar to the thyratron. It consists of a sealed glass tube with four electrodes. A small triggering pulse on the control grid, grid electrode s ...
s, thyratron
A thyratron is a type of gas-filled tube used as a high-power electrical switch and controlled rectifier. Thyratrons can handle much greater currents than similar hard-vacuum tubes. Electron multiplication occurs when the gas becomes ionized, pro ...
s, and ignitron
An ignitron is a type of gas-filled tube used as a controlled rectifier and dating from the 1930s. Invented by Joseph Slepian while employed by Westinghouse Electric Corporation, Westinghouse, Westinghouse was the original manufacturer and owned tr ...
s are used as switching devices in electric devices.
The voltage required to initiate and sustain discharge is dependent on the pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and eve ...
and composition of the fill gas and geometry of the tube. Although the envelope is typically glass, power tubes often use ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcela ...
s, and military tubes often use glass-lined metal. Both hot cathode
In vacuum tubes and gas-filled tubes, a hot cathode or thermionic cathode is a cathode electrode which is heated to make it emit electrons due to thermionic emission. This is in contrast to a cold cathode, which does not have a heating element ...
and cold cathode
A cold cathode is a cathode that is not electrically heated by a Electrical filament, filament.A negatively charged electrode emits electrons or is the positively charged terminal. For more, see field emission. A cathode may be considered "cold" ...
type devices are encountered.
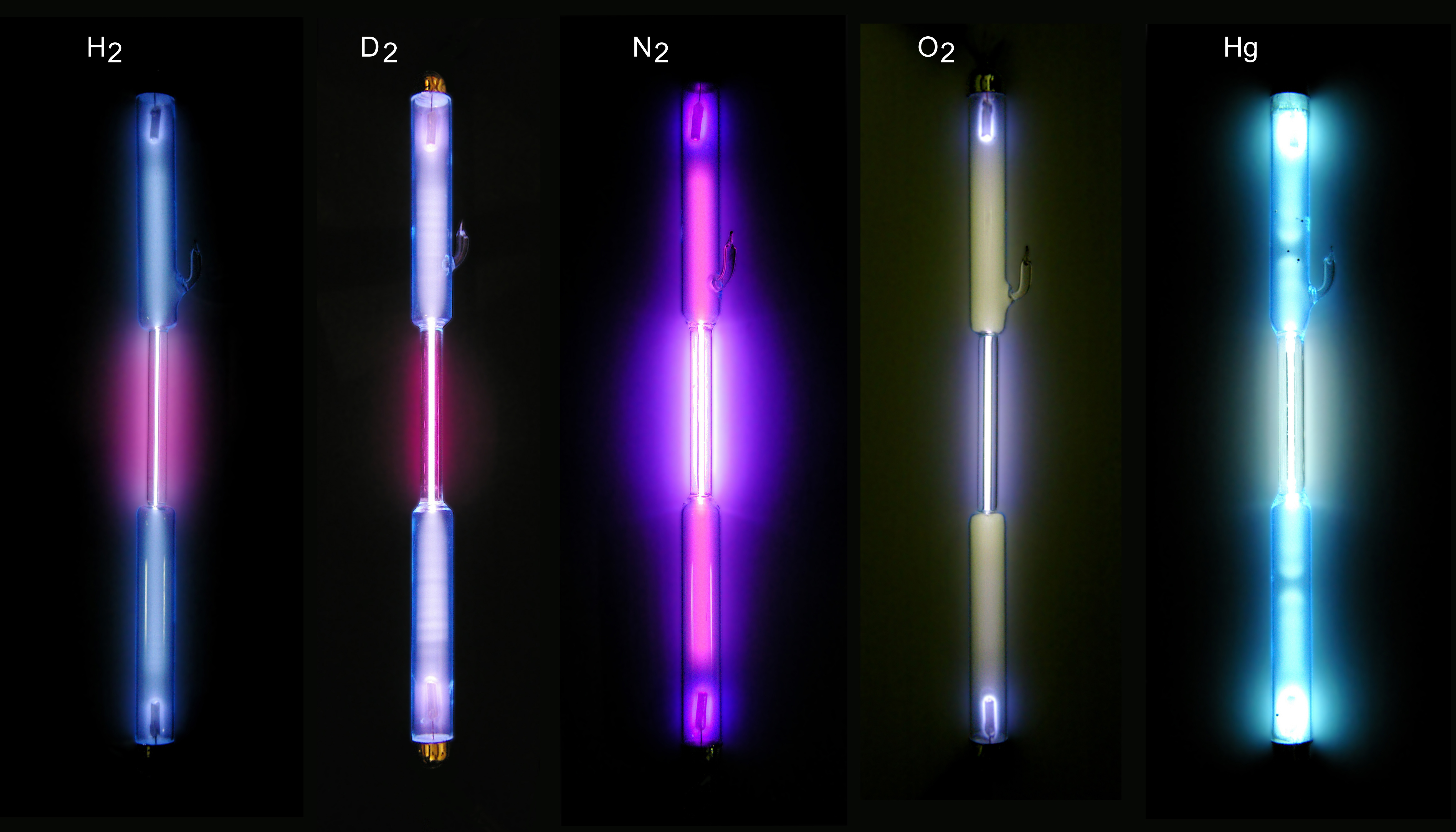
Gases in use
Hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
is used in tubes used for very fast switching, e.g. some thyratron
A thyratron is a type of gas-filled tube used as a high-power electrical switch and controlled rectifier. Thyratrons can handle much greater currents than similar hard-vacuum tubes. Electron multiplication occurs when the gas becomes ionized, pro ...
s, dekatron
In electronics, a Dekatron (or Decatron, or generically three-phase gas counting tube or glow-transfer counting tube or cold cathode tube) is a gas-filled decade counting tube. Dekatrons were used in computers, calculators, and other counti ...
s, and krytron
The krytron is a cold-cathode gas-filled tube intended for use as a very high-speed switch, somewhat similar to the thyratron. It consists of a sealed glass tube with four electrodes. A small triggering pulse on the control grid, grid electrode s ...
s, where very steep edges are required. The build-up and recovery times of hydrogen are much shorter than in other gases. Hydrogen thyratrons are usually hot-cathode. Hydrogen (and deuterium) can be stored in the tube in the form of a metal hydride
In chemistry, a hydride is formally the anion of hydrogen (H−), a hydrogen ion with two electrons. In modern usage, this is typically only used for ionic bonds, but it is sometimes (and has been more frequently in the past) applied to all che ...
, heated with an auxiliary filament; hydrogen by heating such storage element can be used to replenish cleaned-up gas, and even to adjust the pressure as needed for a thyratron operation at a given voltage.C. A. Pirrie and H. Menow"The Evolution of the Hydrogen Thyratron"
Marconi Applied Technologies Ltd, Chelmsford, U.K.
Deuterium
Deuterium
Deuterium (hydrogen-2, symbol H or D, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen; the other is protium, or hydrogen-1, H. The deuterium nucleus (deuteron) contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more c ...
is used in ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
lamps for ultraviolet spectroscopy
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of th ...
, in neutron generator
Neutron generators are neutron source devices which contain compact linear particle accelerators and that produce neutrons by fusing isotopes of hydrogen together. The nuclear fusion, fusion reactions take place in these devices by acceleratin ...
tubes, and in special tubes (e.g. crossatron
In electronics, a crossatron is a high-power pulsed modulator device that consists of a cold cathode gas-filled tube that combines features of thyratrons, vacuum tubes, and power semiconductor switches. This switch is capable of operating with vo ...
). It has higher breakdown voltage than hydrogen. In fast switching tubes it is used instead of hydrogen where high voltage operation is required. For a comparison, the hydrogen-filled CX1140 thyratron has anode voltage rating of 25 kV, while the deuterium-filled and otherwise identical CX1159 has 33 kV. Also, at the same voltage the pressure of deuterium can be higher than of hydrogen, allowing higher rise rates of current before it causes excessive anode dissipation. Significantly higher peak powers are achievable. Its recovery time is however about 40% slower than for hydrogen.
Noble gases

Noble gas
The noble gases (historically the inert gases, sometimes referred to as aerogens) are the members of Group (periodic table), group 18 of the periodic table: helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), radon (Rn) and, in some ...
es are frequently used in tubes for many purposes, from lighting to switching. Pure noble gases are employed in switching tubes. Noble-gas-filled thyratrons have better electrical parameters than mercury-based ones."Pulse Power Switching Devices – An Overview"/ref> The electrodes undergo damage by high-velocity ions. The neutral atoms of the gas slow the ions down by collisions, and reduce the energy transferred to the electrodes by the ion impact. Gases with high atomic weight, e.g. xenon, protect the electrodes better than lighter ones, e.g. neon.
Lamptech.co.uk. Retrieved on 2011-05-17. *
Helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is ...
is used in helium–neon laser
A helium–neon laser or He–Ne laser is a type of gas laser whose high energetic gain medium consists of a mixture of helium and neon (ratio between 5:1 and 10:1) at a total pressure of approximately 1 Torr (133.322 Pa) inside a small electr ...
s and in some thyratrons rated for high currents and high voltages. Helium provides about as short deionization time as hydrogen, but can withstand lower voltage, so it is used much less often.
*Neon
Neon is a chemical element; it has symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is the second noble gas in the periodic table. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with approximately two-thirds the density of ...
has low ignition voltage and is frequently used in low-voltage tubes. Discharge in neon emits relatively bright red light; neon-filled switching tubes therefore also act as indicators, shining red when switched on. This is exploited in the decatron tubes, which act as both counters and displays. Its red light is exploited in neon signage. Used in fluorescent tube
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, to produce ultraviolet and make a phosphor ...
s with high power and short length, e.g. industrial lighting tubes. Has higher voltage drop in comparison with argon and krypton. Its low atomic mass provides only a little protection to the electrodes against accelerated ions; additional screening wires or plates can be used for prolonging the anode lifetime. In fluorescent tubes it is used in combination with mercury.
*Argon
Argon is a chemical element; it has symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as abu ...
was the first gas used in fluorescent tubes and is still frequently used due to its low cost, high efficiency, and very low striking voltage. In fluorescent tubes it is used in combination with mercury. It was also used in early rectifier tubes; first thyratrons were derived from such argon-filled tubes.
*Krypton
Krypton (from 'the hidden one') is a chemical element; it has symbol (chemistry), symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a colorless, odorless noble gas that occurs in trace element, trace amounts in the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere and is of ...
can be used in fluorescent lamps instead of argon; in that application it reduces the total energy losses on electrodes from about 15% to 7%. The voltage drop per lamp length is however lower than with argon, which can be compensated by smaller tube diameter. Krypton-filled lamps also require higher starting voltage; this can be alleviated by using e.g. 25%–75% argon-krypton mixture. In fluorescent tubes it is used in combination with mercury.
*Xenon
Xenon is a chemical element; it has symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
in pure state has high breakdown voltage, making it useful in higher-voltage switching tubes. Xenon is also used as a component of gas mixtures when production of ultraviolet radiation is required, e.g. in plasma display
A plasma display panel is a type of flat-panel display that uses small cells containing Plasma (physics), plasma: Ionization, ionized gas that responds to electric fields. Plasma televisions were the first large (over diagonal) flat-panel displ ...
s, usually to excite a phosphor
A phosphor is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence; it emits light when exposed to some type of radiant energy. The term is used both for fluorescent or phosphorescent substances which glow on exposure to ultraviolet or ...
. The wavelength produced is longer than with argon and krypton and penetrates the phosphors better. To lower the ionization voltage, neon-xenon or helium-xenon are used; above , helium has lower breakdown voltage than neon and vice versa. At concentrations of 1% and less of xenon, the Penning effect becomes significant in such mixtures, as most of xenon ionization occurs by collision with excited atoms of the other noble gas; at more than few percents of xenon, the discharge ionizes xenon directly due to most energy of the electrons being spent on direct ionization of xenon.
* Penning mixtures are used where lower ionization voltage is required, e.g. in the neon lamp
A neon lamp (also neon glow lamp) is a miniature gas-discharge lamp. The lamp typically consists of a small glass capsule that contains a mixture of neon and other gases at a low pressure and two electrodes (an anode and a cathode). When suffi ...
s, Geiger–Müller tube
The Geiger–Müller tube or G–M tube is the sensing element of the Geiger counter instrument used for the detection of ionizing radiation. It is named after Hans Geiger, who invented the principle in 1908, and Walther Müller, who collaborate ...
s and other gas-filled particle detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing elementary particle, particles, such as t ...
s. A classical combination is about 98–99.5% of neon with 0.5–2% of argon, used in, e.g. neon bulbs and in monochrome plasma display
A plasma display panel is a type of flat-panel display that uses small cells containing Plasma (physics), plasma: Ionization, ionized gas that responds to electric fields. Plasma televisions were the first large (over diagonal) flat-panel displ ...
s.
Elemental vapors (metals and nonmetals)
* Mercury vapors are used for applications with high current, e.g. lights,mercury-arc valve
A mercury-arc valve or mercury-vapor rectifier or (UK) mercury-arc rectifier is a type of electrical rectifier used for converting high-voltage or high- current alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). It is a type of cold cathode gas-f ...
s, ignitron
An ignitron is a type of gas-filled tube used as a controlled rectifier and dating from the 1930s. Invented by Joseph Slepian while employed by Westinghouse Electric Corporation, Westinghouse, Westinghouse was the original manufacturer and owned tr ...
s. Mercury is used because of its high vapor pressure and low ionization potential. Mercury mixed with an inert gas is used where the energy losses in the tube have to be low and the tube lifetime should be long. In mercury-inert gas mixtures, the discharge is initially carried primarily by the inert gas; the released heat then serves to evaporate enough mercury to reach the desired vapor pressure. Low-voltage (hundreds volts) rectifiers use saturated mercury vapor in combination with a small amount of inert gas, allowing cold start of the tubes. High-voltage (kilovolts and more) rectifiers use pure mercury vapor at low pressure, requiring maintenance of maximum temperature of the tube. The liquid mercury serves as a reservoir of mercury, replenishing the vapors that are used up during the discharge. Unsaturated mercury vapor can be used, but as it can not be replenished, the lifetime of such tubes is lower. The strong dependence of vapor pressure on mercury temperature limits the environments the mercury-based tubes can operate in. In low-pressure mercury lamps, there is an optimum mercury pressure for the highest efficiency. Photons emitted by ionized mercury atoms can be absorbed by nearby nonionized atoms and either reradiated or the atom is deexcited nonradiatively, too high mercury pressure therefore causes losses of light. Too low mercury pressure leads to too few atoms present to get ionized and radiate photons. The optimum temperature for low-pressure mercury lamps is at about 42 °C, when the saturated vapor pressure of mercury (present as a drop of about 1 mg of liquid mercury in the tube, as a reservoir compensating for losses by clean-up) reaches this optimum. In lamps intended for operation at higher ambient temperatures, and at a wider temperature range, mercury is present in the form of an amalgam with e.g. bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element; it has symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs nat ...
and indium
Indium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol In and atomic number 49. It is a silvery-white post-transition metal and one of the softest elements. Chemically, indium is similar to gallium and thallium, and its properties are la ...
; the vapor pressure above amalgam is lower than above liquid mercury.''Handbook of optoelectronics'', Volume 1by John Dakin, Robert G. W. Brown, p. 52, CRC Press, 2006 Mercury is used in
fluorescent tube
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, to produce ultraviolet and make a phosphor ...
s as a source of visible and ultraviolet light for exciting the phosphor
A phosphor is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence; it emits light when exposed to some type of radiant energy. The term is used both for fluorescent or phosphorescent substances which glow on exposure to ultraviolet or ...
; in that application it is usually used together with argon, or in some cases with krypton or neon. Mercury ions deionize slowly, limiting the switching speed of mercury-filled thyratrons. Ion bombardment with mercury ions of even relatively low energies also gradually destroys oxide-coated cathodes.
*Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
vapors are used in sodium-vapor lamps.
*Sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms ...
vapors are used in sulfur lamps.
*Vapors of many metals, alone or together with a noble gas, are used in many laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
s.
Other gases
 *
*Air
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
can be used in some low-demanding applications.
*Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
at relatively high pressure tends to be used in surge arresters, due to its short build-up time, giving the tubes fast response time to voltage surges.
*Halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and the radioactive elements astatine (At) and tennessine (Ts), though some authors would ...
s and alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
vapors absorb ultraviolet radiation and have high electron affinity. When added to inert gases, they quench the discharge; this is exploited in e.g. Geiger–Müller tube
The Geiger–Müller tube or G–M tube is the sensing element of the Geiger counter instrument used for the detection of ionizing radiation. It is named after Hans Geiger, who invented the principle in 1908, and Walther Müller, who collaborate ...
s.
Insulating gases
In special cases (e.g., high-voltage switches), gases with good dielectric properties and very high breakdown voltages are needed. Highlyelectronegative
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the d ...
elements, e.g., halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and the radioactive elements astatine (At) and tennessine (Ts), though some authors would ...
s, are favored as they rapidly recombine with the ions present in the discharge channel. One of the most popular choices is sulfur hexafluoride
Sulfur hexafluoride or sulphur hexafluoride ( British spelling) is an inorganic compound with the formula SF6. It is a colorless, odorless, non-flammable, and non-toxic gas. has an octahedral geometry, consisting of six fluorine atoms attache ...
, used in special high-voltage applications. Other common options are dry pressurized nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
and halocarbon
Halocarbon compounds are chemical compounds in which one or more carbon atoms are linked by covalent bonds with one or more halogen atoms (fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine – ) resulting in the formation of organofluorine compounds, or ...
s.
Gas-tube physics and technology
Paschen's law
Paschen's law is an equation that gives the breakdown voltage, that is, the voltage necessary to start a discharge or electric arc, between two electrodes in a gas as a function of pressure and gap length. It is named after Friedrich Paschen who ...
.
Gas pressure
The gas pressure may range between ; most commonly, pressures between 1–10 torr are used. The gas pressure influences the following factors: *breakdown voltage
The breakdown voltage of an insulator (electrical), insulator is the minimum voltage that causes a portion of an insulator to experience electrical breakdown and become electrically Conductor (material), conductive.
For diodes, the breakdown vo ...
(also called ignition voltage)
*current density
In electromagnetism, current density is the amount of charge per unit time that flows through a unit area of a chosen cross section. The current density vector is defined as a vector whose magnitude is the electric current per cross-sectional ...
*operating voltage
*backfire voltage
*tube lifetime (lower pressure tubes tend to have shorter lifetimes due to using up of the gas)
*cathode sputtering
In physics, sputtering is a phenomenon in which microscopic particles of a solid material are ejected from its surface, after the material is itself bombarded by energetic particles of a plasma or gas. It occurs naturally in outer space, and c ...
, reduced at higher pressures
Above a certain value, the higher the gas pressure, the higher the ignition voltage. High-pressure lighting tubes can require a few kilovolts impulse for ignition when cold, when the gas pressure is low. After warming up, when the volatile compound used for light emission is vaporized and the pressure increases, reignition of the discharge requires either significantly higher voltage or reducing the internal pressure by cooling down the lamp. For example, many sodium vapor lamps cannot be re-lit immediately after being shut off; they must cool down before they can be lit up again.
The gas tends to be used up during the tube operation, by several phenomena collectively called clean-up. The gas atoms or molecules are adsorbed on the surfaces of the electrodes. In high voltage tubes, the accelerated ions can penetrate into the electrode materials. New surfaces, formed by sputtering of the electrodes and deposited on e.g. the inner surfaces of the tube, also readily adsorb gases. Non-inert gases can also chemically react with the tube components. Hydrogen may diffuse through some metals.
For removal of gas in vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, thermionic valve (British usage), or tube (North America) is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. It ...
s, getter
A getter is a deposit of reactive material that is placed inside a vacuum system to complete and maintain the vacuum. When gas molecules strike the getter material, they combine with it chemically or by adsorption. Thus the getter removes small ...
s are used. For resupplying gas for gas-filled tubes, replenishers are employed. Most commonly, replenishers are used with hydrogen; a filament made from a hydrogen-absorbing metal (e.g. zirconium or titanium) is present in the tube, and by controlling its temperature the ratio of absorbed and desorbed hydrogen is adjusted, resulting in controlling of the hydrogen pressure in the tube. The metal filament acts as a hydrogen storage. This approach is used in e.g. hydrogen thyratrons or neutron tubes. Usage of saturated mercury vapor allows using a pool of liquid mercury as a large storage of material; the atoms lost by clean-up are automatically replenished by evaporation of more mercury. The pressure in the tube is however strongly dependent on the mercury temperature, which has to be controlled carefully.
Large rectifiers use saturated mercury vapor with a small amount of an inert gas. The inert gas supports the discharge when the tube is cold.
The mercury arc valve current-voltage characteristics are highly dependent on the temperature of the liquid mercury. The voltage drop in forward bias decreases from about 60 volts at 0 °C to somewhat above 10 volts at 50 °C and then stays constant; the reverse bias breakdown ("arc-back") voltage drops dramatically with temperature, from 36 kV at 60 °C to 12 kV at 80 °C to even less at higher temperatures. The operating range is therefore usually between 18–65 °C.''Reference Data for Engineers: Radio, Electronics, Computers and Communications''by Wendy Middleton, Mac E. Van Valkenburg, pp. 16–42, Newnes, 2002
Gas purity
The gas in the tube has to be kept pure to maintain the desired properties; even small amount of impurities can dramatically change the tube values. The presence of non-inert gases generally increases the breakdown and burning voltages. The presence of impurities can be observed by changes in the glow color of the gas. Air leaking into the tube introduces oxygen, which is highly electronegative and inhibits the production of electron avalanches. This makes the discharge look pale, milky, or reddish. Traces of mercury vapors glow bluish, obscuring the original gas color. Magnesium vapor colors the discharge green. To preventoutgassing
Outgassing (sometimes called offgassing, particularly when in reference to indoor air quality) is the release of a gas that was dissolved, trapped, frozen, or absorbed in some material. Outgassing can include sublimation and evaporation (whic ...
of the tube components during operation, a bake-out
Bake-out, in several areas of technology and fabrication, and in building construction, refers to the process of using high heat temperature (heat), and possibly vacuum, to remove volatile compounds from materials and objects before placing th ...
is required before filling with gas and sealing. Thorough degassing is required for high-quality tubes; even as little as 10−8 torr (≈1 μPa) of oxygen is sufficient for covering the electrodes with monomolecular oxide layer in few hours. Non-inert gases can be removed by suitable getter
A getter is a deposit of reactive material that is placed inside a vacuum system to complete and maintain the vacuum. When gas molecules strike the getter material, they combine with it chemically or by adsorption. Thus the getter removes small ...
s. For mercury-containing tubes, getters that do not form amalgams with mercury (e.g. zirconium
Zirconium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Zr and atomic number 40. First identified in 1789, isolated in impure form in 1824, and manufactured at scale by 1925, pure zirconium is a lustrous transition metal with a greyis ...
, but not barium
Barium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in group 2 and is a soft, silvery alkaline earth metal. Because of its high chemical reactivity, barium is never found in nature as a free element.
Th ...
) have to be used. Cathode sputtering may be used intentionally for gettering non-inert gases; some reference tubes use molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mo (from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'') and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals hav ...
cathodes for this purpose.
Pure inert gases are used where the difference between the ignition voltage and the burning voltage has to be high, e.g. in switching tubes. Tubes for indication and stabilization, where the difference has to be lower, tend to be filled with Penning mixtures; the lower difference between ignition and burning voltages allows using lower power supply voltages and smaller series resistances.Hajo Lorens van der HorstChapter 2: The construction of a gas-discharge tube
''1964 Philips Gas-Discharge Tubes book''
Lighting and display gas-filled tubes
Fluorescent lighting
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, to produce ultraviolet and make a phosphor ...
, CFL lamps, mercury and sodium discharge lamps and HID lamps are all gas-filled tubes used for lighting.
Neon lamp
A neon lamp (also neon glow lamp) is a miniature gas-discharge lamp. The lamp typically consists of a small glass capsule that contains a mixture of neon and other gases at a low pressure and two electrodes (an anode and a cathode). When suffi ...
s and neon signage (most of which is not neon based these days) are also low-pressure gas-filled tubes.
Specialized historic low-pressure gas-filled tube devices include the Nixie tube
A Nixie tube ( ), or cold cathode display, is an electronics, electronic device used for display device, displaying numerals or other information using glow discharge.
The glass tube contains a wire-mesh anode and multiple cathodes, shaped like ...
(used to display numerals) and the Decatron (used to count or divide pulses, with display as a secondary function).
Xenon flash lamp
A flashtube (flashlamp) produces an electrostatic discharge with an extremely intense, incoherent, full-spectrum white light for a very short time. A flashtube is a glass tube with an electrode at each end and is filled with a gas that, when tr ...
s are gas-filled tubes used in camera
A camera is an instrument used to capture and store images and videos, either digitally via an electronic image sensor, or chemically via a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. As a pivotal technology in the fields of photograp ...
s and strobe light
A strobe light or stroboscopic lamp, commonly called a strobe, is a device used to produce regular flashes of light. It is one of a number of devices that can be used as a stroboscope. The word originated from the Ancient Greek ('), meaning ...
s to produce bright flashes of light.
The recently developed sulfur lamps are also gas-filled tubes when hot.
Gas-filled tubes in electronics
Since the ignition voltage depends on the ion concentration which may drop to zero after a long period of inactivity, many tubes are primed for ion availability: * optically, by ambient light or by a 2-watt incandescent lamp, or by a glow discharge in the same envelope, * radioactively, by addingtritium
Tritium () or hydrogen-3 (symbol T or H) is a rare and radioactive isotope of hydrogen with a half-life of ~12.33 years. The tritium nucleus (t, sometimes called a ''triton'') contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus of the ...
to the gas, or by coating the envelope inside,
* electrically, with a ''keep-alive'' or ''primer'' electrode
Power devices
Some important examples include thethyratron
A thyratron is a type of gas-filled tube used as a high-power electrical switch and controlled rectifier. Thyratrons can handle much greater currents than similar hard-vacuum tubes. Electron multiplication occurs when the gas becomes ionized, pro ...
, krytron
The krytron is a cold-cathode gas-filled tube intended for use as a very high-speed switch, somewhat similar to the thyratron. It consists of a sealed glass tube with four electrodes. A small triggering pulse on the control grid, grid electrode s ...
, and ignitron
An ignitron is a type of gas-filled tube used as a controlled rectifier and dating from the 1930s. Invented by Joseph Slepian while employed by Westinghouse Electric Corporation, Westinghouse, Westinghouse was the original manufacturer and owned tr ...
tubes, which are used to switch high-voltage currents. A specialized type of gas-filled tube called a Gas Discharge Tube (GDT) is fabricated for use as surge protector
A surge protector, spike suppressor, surge suppressor, surge diverter, surge protection device (SPD), transient voltage suppressor (TVS) or transient voltage surge suppressor (TVSS) is an appliance or device intended to protect Electronics, ele ...
s, to limit voltage surges in electrical and electronic circuits.
Computing tubes
TheSchmitt trigger
In electronics, a Schmitt trigger is a comparator circuit with hysteresis implemented by applying positive feedback to the noninverting input of a comparator or differential amplifier. It is an passivity (engineering), active circuit which con ...
effect of the negative differential resistance-region can be exploited to realize timers, relaxation oscillators and digital circuits
Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. It deals with the relationship between binary inputs and outputs by passing electrical signals through ...
with neon lamp
A neon lamp (also neon glow lamp) is a miniature gas-discharge lamp. The lamp typically consists of a small glass capsule that contains a mixture of neon and other gases at a low pressure and two electrodes (an anode and a cathode). When suffi ...
s, ''trigger tubes'', ''relay tubes'', dekatron
In electronics, a Dekatron (or Decatron, or generically three-phase gas counting tube or glow-transfer counting tube or cold cathode tube) is a gas-filled decade counting tube. Dekatrons were used in computers, calculators, and other counti ...
s and nixie tube
A Nixie tube ( ), or cold cathode display, is an electronics, electronic device used for display device, displaying numerals or other information using glow discharge.
The glass tube contains a wire-mesh anode and multiple cathodes, shaped like ...
s.
Thyratrons can also be used as triode
A triode is an electronic amplifier, amplifying vacuum tube (or ''thermionic valve'' in British English) consisting of three electrodes inside an evacuated glass envelope: a heated Electrical filament, filament or cathode, a control grid, grid ...
s by operating them below their ignition voltage, allowing them to amplify analog signals as a self-quenching superregenerative detector in radio control
Radio control (often abbreviated to RC) is the use of control signals transmitted by radio to remotely operate a device. Examples of simple radio control systems are garage door openers and keyless entry systems for vehicles, in which a small ha ...
receivers.
Indicators
There were special neon lamps besides nixie tubes: *''Tuneon'' early tuning indicator, a glass tube with a short wire anode and a long wire cathode that glows partially; the glow length is proportional to the tube current *Phosphor
A phosphor is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence; it emits light when exposed to some type of radiant energy. The term is used both for fluorescent or phosphorescent substances which glow on exposure to ultraviolet or ...
ed neon lamp
*Luminescent trigger tube, used as latching indicators, or pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, p ...
s of dot-matrix display
A dot-matrix display is a low-cost electronic digital display device that displays information on machines such as clocks, watches, calculators, and many other devices requiring a simple alphanumeric (and/or graphic) display device of limited res ...
s
**Direct-glow trigger tube
**Phosphored trigger tube
Noise diodes
Hot-cathode, gas-discharge noise diodes were available in normal radio tube glass envelopes for frequencies up toUHF
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter ...
, and as long, thin glass tubes with a normal bayonet light bulb mount for the filament and an anode top cap, for SHF frequencies and diagonal insertion into a waveguide
A waveguide is a structure that guides waves by restricting the transmission of energy to one direction. Common types of waveguides include acoustic waveguides which direct sound, optical waveguides which direct light, and radio-frequency w ...
.
They were filled with a pure inert gas such as neon
Neon is a chemical element; it has symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is the second noble gas in the periodic table. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with approximately two-thirds the density of ...
because mixtures made the output temperature-dependent. Their burning voltage was under 200 V, but they needed optical priming by an incandescent 2-watt lamp and a voltage surge in the 5-kV range for ignition.
One miniature thyratron
A thyratron is a type of gas-filled tube used as a high-power electrical switch and controlled rectifier. Thyratrons can handle much greater currents than similar hard-vacuum tubes. Electron multiplication occurs when the gas becomes ionized, pro ...
found an additional use as a noise source, when operated as a diode in a transverse magnetic field.
Voltage-regulator tubes
In the mid-20th century,voltage-regulator tube
A voltage-regulator tube (VR tube) is an Electronics, electronic component used as a voltage regulator#Shunt regulators, shunt regulator to hold a voltage constant at a predetermined level.
Physically, these devices resemble vacuum tubes, but th ...
s were commonly used.
Elapsed-time measurement
Cathode sputtering is taken advantage of in the ''Time Totalizer'', a metal-vaporcoulometer
A voltameter or coulometer is a scientific instrument used for measuring instrument, measuring electric charge (quantity of electricity) through electrolytic action. The International System of Units, SI unit of electric charge is the coulomb.
T ...
-based elapsed time meter where the sputtered metal is deposited on a collector element whose resistance therefore decreases slowly.
List of -tron tubes
Hajo Lorens van der HorsChapter 8: Special tubes
''1964 Philips Gas-Discharge Tubes book'' *Mercury pool tubes ** Excitron, a mercury pool tube ** Gusetron or gausitron, a mercury arc pool tube **
Ignitron
An ignitron is a type of gas-filled tube used as a controlled rectifier and dating from the 1930s. Invented by Joseph Slepian while employed by Westinghouse Electric Corporation, Westinghouse, Westinghouse was the original manufacturer and owned tr ...
, a mercury pool tube
** Sendytron, a mercury pool tube
* Trignitron, a trade name for a mercury pool tube used in electric welders
** Capacitron, a mercury pool tube
* Corotron, a trade name for a gas-filled shunt regulator, usually contains small quantities of radioactive materials to set the regulated voltage
*Crossatron
In electronics, a crossatron is a high-power pulsed modulator device that consists of a cold cathode gas-filled tube that combines features of thyratrons, vacuum tubes, and power semiconductor switches. This switch is capable of operating with vo ...
, a modulator tube
* Kathetron or cathetron, a hot cathode gas-filled triode
A triode is an electronic amplifier, amplifying vacuum tube (or ''thermionic valve'' in British English) consisting of three electrodes inside an evacuated glass envelope: a heated Electrical filament, filament or cathode, a control grid, grid ...
with grid outside of the tube
* Neotron, a pulse generator
* Permatron, a hot cathode rectifier with anode current controlled by magnetic field
* Phanotron, a rectifier
* Plomatron, a grid-controlled mercury-arc rectifier
* Strobotron, a cold cathode tube designed for high current narrow pulses, used in high-speed photography
High-speed photography is the science of taking pictures of very fast phenomena. In 1948, the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) defined high-speed photography as any set of photographs captured by a camera capable of 69 ...
* Takktron, a cold cathode rectifier for low currents at high voltages
*Thyratron
A thyratron is a type of gas-filled tube used as a high-power electrical switch and controlled rectifier. Thyratrons can handle much greater currents than similar hard-vacuum tubes. Electron multiplication occurs when the gas becomes ionized, pro ...
, a hot cathode switching tube
*Trigatron
A trigatron is a type of triggerable spark gap switch designed for high current and high voltage (usually 10–100 kV and 20–100 kA, though devices in the mega-ampere range exist as well). It has very simple construction and in many cases is the ...
, a high-current switch similar to a spark gap
* Alphatron, a form of ionization tube for measuring vacuum
*Dekatron
In electronics, a Dekatron (or Decatron, or generically three-phase gas counting tube or glow-transfer counting tube or cold cathode tube) is a gas-filled decade counting tube. Dekatrons were used in computers, calculators, and other counti ...
, a counting tube (see also nixie tube
A Nixie tube ( ), or cold cathode display, is an electronics, electronic device used for display device, displaying numerals or other information using glow discharge.
The glass tube contains a wire-mesh anode and multiple cathodes, shaped like ...
and neon light)
* Plasmatron, a hot cathode tube with controlled anode current
* Tacitron, a low-noise thyratron with interruptible current flow
*Krytron
The krytron is a cold-cathode gas-filled tube intended for use as a very high-speed switch, somewhat similar to the thyratron. It consists of a sealed glass tube with four electrodes. A small triggering pulse on the control grid, grid electrode s ...
, a fast cold-cathode switching tube
References
External links
Pulse Power Switching Devices – An Overview (both vacuum and gas-filled switching tubes)
{{Authority control Electrical components Glass applications cs:Výbojka hi:गैस नली lv:Gazotrons