Mu (letter) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mu (uppercase Μ, lowercase μ; 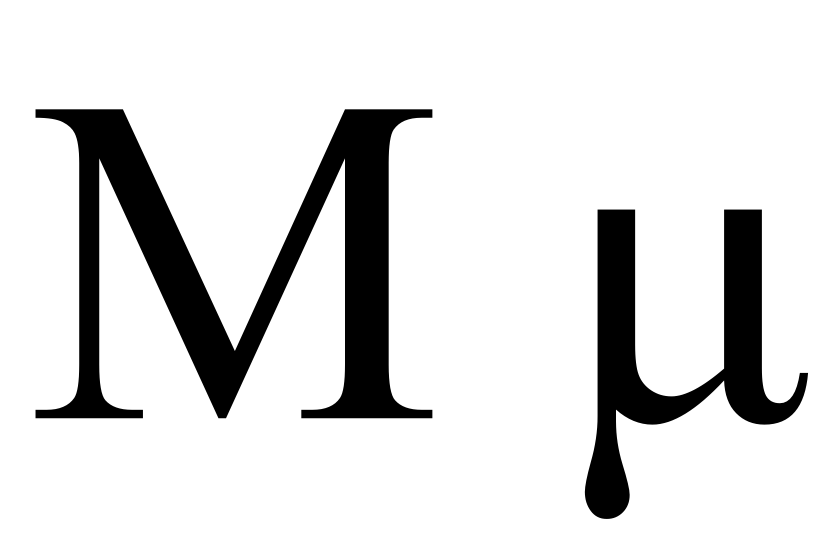
Greek and Coptic (Range: 0370-03FF)
/ref> * Mathematical Mu These characters are used only as mathematical symbols. Stylized Greek text should be encoded using the normal Greek letters, with markup and formatting to indicate text style.
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
, ell, μι or μυ—both ) is the 12th letter
Letter, letters, or literature may refer to:
Characters typeface
* Letter (alphabet), a character representing one or more of the sounds used in speech; any of the symbols of an alphabet.
* Letterform, the graphic form of a letter of the alphabe ...
of the Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BCE. It is derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and was the earliest known alphabetic script to have distinct letters for vowels as w ...
, representing the voiced bilabial nasal . In the system of Greek numerals
Greek numerals, also known as Ionic, Ionian, Milesian, or Alexandrian numerals, are a system of writing numbers using the letters of the Greek alphabet. In modern Greece, they are still used for ordinal numbers and in contexts similar to tho ...
it has a value of 40. Mu was derived from the Egyptian hieroglyphic symbol for water, which had been simplified by the Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
ns and named after their word for water, to become 𐤌 (mem). Letters that derive from mu include the Roman M and the Cyrillic М.
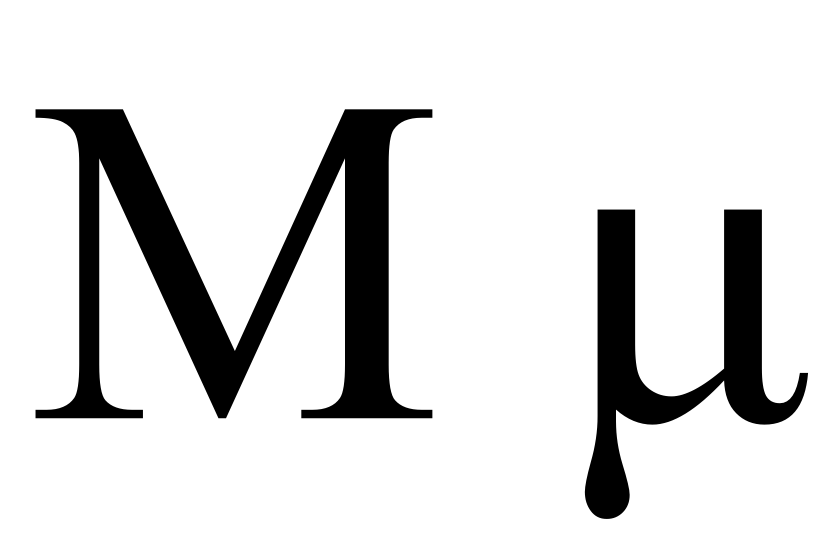
Names
Ancient Greek
In Ancient Greek, the name of the letter was written and pronouncedModern Greek
InModern Greek
Modern Greek (, , or , ''Kiní Neoellinikí Glóssa''), generally referred to by speakers simply as Greek (, ), refers collectively to the dialects of the Greek language spoken in the modern era, including the official standardized form of the ...
, the letter is spelled and pronounced . In polytonic orthography, it is written with an acute accent: .
Use as symbol
The lowercase letter mu (μ) is used as a special symbol in manyacademic field
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, f ...
s. Uppercase mu is not used, because it appears identical to Latin M.
Measurement
*the SI prefix ''micro-
''Micro'' (Greek letter μ ( U+03BC) or the legacy symbol µ (U+00B5)) is a unit prefix in the metric system denoting a factor of 10−6 (one millionth). Confirmed in 1960, the prefix comes from the Greek ('), meaning "small".
The symbol for ...
'', which represents one millionth, or 10−6. Lowercase letter "u" is often substituted for "μ" when the Greek character is not typographically available; for example the unit "micro farad", correctly "μF", is often rendered as "uF" or "ufarad" in technical documents.
*the micron "μ", an old unit now named the micrometre
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Unit ...
and denoted "μm"
Mathematics
"μ" is conventionally used to denote certain things; however, any Greek letter or other symbol may be used freely as a variable name. *a measure in measure theory * minimalization in computability theory andRecursion theory
Computability theory, also known as recursion theory, is a branch of mathematical logic, computer science, and the theory of computation that originated in the 1930s with the study of computable functions and Turing degrees. The field has sinc ...
*the integrating factor in ordinary differential equations
*the degree of membership
Member may refer to:
* Military jury, referred to as "Members" in military jargon
* Element (mathematics), an object that belongs to a mathematical set
* In object-oriented programming, a member of a class
** Field (computer science), entries in ...
in a fuzzy set
In mathematics, fuzzy sets (a.k.a. uncertain sets) are sets whose elements have degrees of membership. Fuzzy sets were introduced independently by Lotfi A. Zadeh in 1965 as an extension of the classical notion of set.
At the same time, defined ...
*the Möbius function
The Möbius function is a multiplicative function in number theory introduced by the German mathematician August Ferdinand Möbius (also transliterated ''Moebius'') in 1832. It is ubiquitous in elementary and analytic number theory and most of ...
in number theory
Number theory (or arithmetic or higher arithmetic in older usage) is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers and integer-valued functions. German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777–1855) said, "Mat ...
*the population mean or expected value in probability
Probability is the branch of mathematics concerning numerical descriptions of how likely an event is to occur, or how likely it is that a proposition is true. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1, where, roughly speakin ...
and statistics
*the Ramanujan–Soldner constant
Physics and engineering
In classical physics andengineering
Engineering is the use of scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more speciali ...
:
*the coefficient of friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:
*Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of t ...
(also used in aviation as braking coefficient (see Braking action)
*reduced mass
In physics, the reduced mass is the "effective" inertial mass appearing in the two-body problem of Newtonian mechanics. It is a quantity which allows the two-body problem to be solved as if it were a one-body problem. Note, however, that the mass ...
in the two-body problem
* Standard gravitational parameter in celestial mechanics
*linear density
Linear density is the measure of a quantity of any characteristic value per unit of length. Linear mass density (titer in textile engineering, the amount of mass per unit length) and linear charge density (the amount of electric charge per unit ...
, or mass per unit length, in strings and other one-dimensional objects
* permeability in electromagnetism
*the magnetic dipole moment of a current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
-carrying coil
* dynamic viscosity in fluid mechanics
*the amplification factor or voltage gain of a triode vacuum tube
*the electrical mobility of a charged particle
*the rotor advance ratio, the ratio of aircraft airspeed
In aviation, airspeed is the speed of an aircraft relative to the air. Among the common conventions for qualifying airspeed are:
* Indicated airspeed ("IAS"), what is read on an airspeed gauge connected to a Pitot-static system;
* Calibrated ...
to rotor-tip speed in rotorcraft
A rotorcraft or rotary-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air aircraft with rotary wings or rotor blades, which generate lift by rotating around a vertical mast. Several rotor blades mounted on a single mast are referred to as a rotor. The Internat ...
*the pore water pressure in saturated soil
In particle physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) an ...
:
*the elementary particles called the muon and antimuon
*the proton-to-electron mass ratio
In thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws of th ...
:
*the chemical potential of a system or component of a system
Computer science
Inevolutionary algorithm
In computational intelligence (CI), an evolutionary algorithm (EA) is a subset of evolutionary computation, a generic population-based metaheuristic optimization algorithm. An EA uses mechanisms inspired by biological evolution, such as reproduct ...
s:
* μ, population size from which in each generation λ offspring will generate (the terms μ and λ originate from evolution strategy
In computer science, an evolution strategy (ES) is an optimization technique based on ideas of evolution. It belongs to the general class of evolutionary computation or artificial evolution methodologies.
History
The 'evolution strategy' optimizat ...
notation)
In type theory
In mathematics, logic, and computer science, a type theory is the formal presentation of a specific type system, and in general type theory is the academic study of type systems. Some type theories serve as alternatives to set theory as a fou ...
:
* Used to introduce a recursive data type
In computer programming languages, a recursive data type (also known as a recursively-defined, inductively-defined or inductive data type) is a data type for values that may contain other values of the same type. Data of recursive types are usuall ...
. For example, is the type of lists with elements of type (a type variable): a sum of unit
Unit may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* UNIT, a fictional military organization in the science fiction television series ''Doctor Who''
* Unit of action, a discrete piece of action (or beat) in a theatrical presentation
Music
* ''Unit'' (a ...
, representing , with a pair of a and another (represented by ). In this notation, is a binding form, where the variable () introduced by is bound within the following term () to the term itself. Via substitution and arithmetic, the type expands to , an infinite sum of ever-increasing products
Product may refer to:
Business
* Product (business), an item that serves as a solution to a specific consumer problem.
* Product (project management), a deliverable or set of deliverables that contribute to a business solution
Mathematics
* Produ ...
of (that is, a is any -tuple of values of type for any ). Another way to express the same type is .
Chemistry
In chemistry: *the prefix given inIUPAC
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is ...
nomenclature for a bridging ligand
Biology
Inbiology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary i ...
:
*the mutation rate
In genetics, the mutation rate is the frequency of new mutations in a single gene or organism over time. Mutation rates are not constant and are not limited to a single type of mutation; there are many different types of mutations. Mutation rates ...
in population genetics
* A class of Immunoglobulin heavy chain that defines IgM
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is one of several isotypes of antibody (also known as immunoglobulin) that are produced by vertebrates. IgM is the largest antibody, and it is the first antibody to appear in the response to initial exposure to an antig ...
type Antibodies
Pharmacology
In pharmacology: *an important opiate receptorOrbital mechanics
Inorbital mechanics
Orbital mechanics or astrodynamics is the application of ballistics and celestial mechanics to the practical problems concerning the motion of rockets and other spacecraft. The motion of these objects is usually calculated from Newton's laws of ...
:
* Standard gravitational parameter of a celestial body, the product of the gravitational constant ''G'' and the mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different eleme ...
''M''
*planetary discriminant, represents an experimental measure of the actual degree of cleanliness
Cleanliness is both the state of being clean and free from germs, dirt, trash, or waste, and the habit of achieving and maintaining that state. Cleanliness is often achieved through cleaning. Culturally, cleanliness is usually a good quality, as ...
of the orbital zone, a criterion for defining a planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a you ...
. The value of μ is calculated by dividing the mass of the candidate body by the total mass of the other objects that share its orbital zone.
Music
* Mu chord *Electronic musicianMike Paradinas
Michael Paradinas (born 26 September 1971), better known by his stage name μ-Ziq (pronounced "music" or mu-zik), is an English electronic musician from Wimbledon, London. He was associated with the electronic style intelligent dance music (ID ...
runs the label Planet Mu which utilizes the letter as its logo, and releases music under the pseudonym μ-Ziq, pronounced "music"
*Used as the name of the school idol group μ's, pronounced "muse", consisting of nine singing idols in the anime Love Live! School Idol Project
is a Japanese multimedia project co-developed by ASCII Media Works' ''Dengeki G's Magazine'', music label Lantis, and animation studio Sunrise. It is the first multimedia project in the ''Love Live!'' franchise. The project revolves aro ...
*Official fandom name
Many fandoms in popular culture have their own names that distinguish them from other fan communities. These names are popular with singers, music groups, films, authors, television shows, books, games, sports teams, and actors. Some of the te ...
of Kpop group f(x), appearing as either MeU or 'μ'
*Hip-hop artist Muonboy has taken inspiration from the particle for his stage name and his first EP named Mu uses the letter as its title.
Cameras
The Olympus Corporation manufactures a series of digital cameras called Olympus μ (known as Olympus Stylus in North America)Linguistics
Inphonology
Phonology is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages or dialects systematically organize their sounds or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a ...
:
* mora
In syntax:
* μP (mu phrase) can be used as the name for a functional projection.
In Celtic linguistics:
* /μ/ can represent an Old Irish
Old Irish, also called Old Gaelic ( sga, Goídelc, Ogham script: ᚌᚑᚔᚇᚓᚂᚉ; ga, Sean-Ghaeilge; gd, Seann-Ghàidhlig; gv, Shenn Yernish or ), is the oldest form of the Goidelic/Gaelic language for which there are extensive writt ...
nasalized labial fricative
A fricative is a consonant produced by forcing air through a narrow channel made by placing two articulators close together. These may be the lower lip against the upper teeth, in the case of ; the back of the tongue against the soft palate in t ...
of uncertain articulation, the ancestor of the sound represented by Modern Irish ''mh''.
Character encodings
* Greek Mu / Coptic MuUnicode Code ChartsGreek and Coptic (Range: 0370-03FF)
/ref> * Mathematical Mu These characters are used only as mathematical symbols. Stylized Greek text should be encoded using the normal Greek letters, with markup and formatting to indicate text style.
Image list for readers with font problems
#See also
*Greek letters used in mathematics, science, and engineering
Greek letters are used in mathematics, science, engineering, and other areas where mathematical notation is used as symbols for constants, special functions, and also conventionally for variables representing certain quantities. In these conte ...
* Fraser alphabet#Consonants
References
{{Reflist Greek letters