Mongol conquests on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the
 The Mongols conquered, by battle or voluntary surrender, the areas of present-day Iran, Iraq, the
The Mongols conquered, by battle or voluntary surrender, the areas of present-day Iran, Iraq, the
 Genghis Khan and his descendants launched progressive
Genghis Khan and his descendants launched progressive 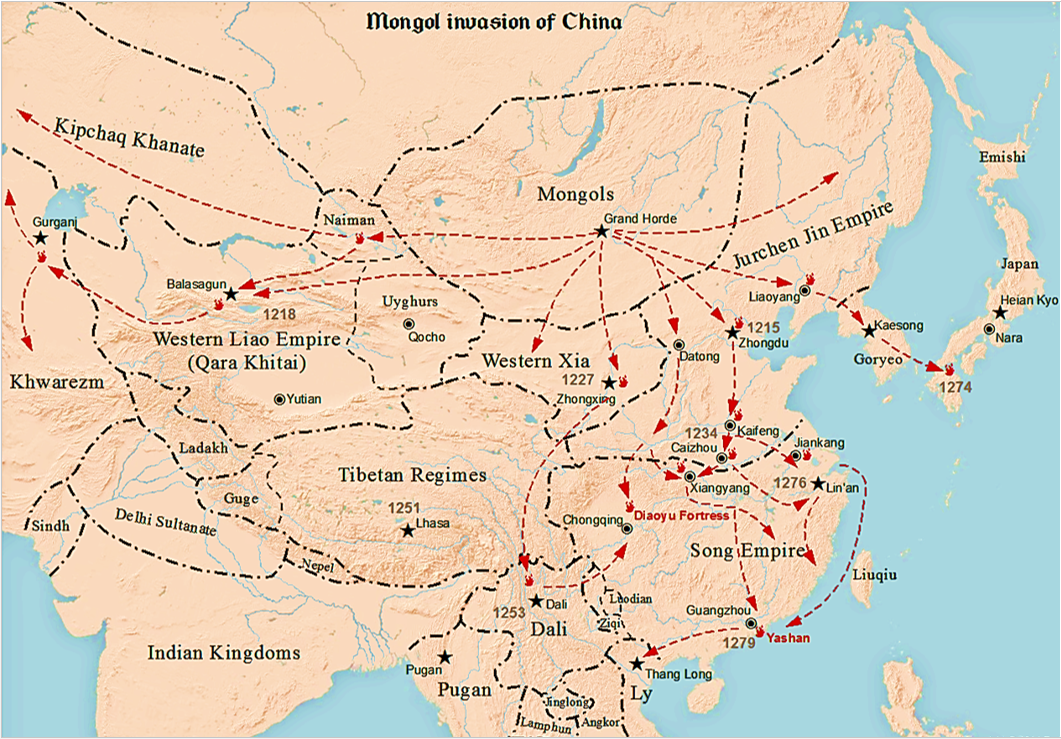 The Mongols' greatest triumph was when
The Mongols' greatest triumph was when

 The Mongols invaded and destroyed
The Mongols invaded and destroyed
p. 112.Woodside 1971
p. 8. The Mongol invasions played an indirect role in the establishment of major Tai states in the region by recently migrated Tais, who originally came from Southern China, in the early centuries of the second millennium. Major Tai states such as


 * 1207–1210 invasion of Western Xia
* 1207 conquest of Siberia
* 1211–1234 conquest of Jin dynasty
* 1216–1220 conquest of Central Asia and Eastern Persia
** 1216–1218 conquest of the Qara Khitai
** 1219–1220 conquest of Khwarazm
** 1256 capture of Alamut
* 1220–1223, 1235–1330 invasions of Georgia and the Caucasus
* 1220–1224 invasion of the Cumans
* 1222–1327 Mongol invasions of India
* 1223–1236 invasion of Volga Bulgaria
* 1225–1227 conquest of Western Xia
* 1231–1259 invasion of Korea
* 1233 conquest of Eastern Xia
* 1235–1279 conquest of Song dynasty
* 1222, 1236–1242 Mongol invasion of Europe
** 1236–1242 invasion of Rus
*** 1237–1238 invasion of eastern and northern Rus'
*** 1239–1240 invasion of southern and western Rus'
**1237–1242 invasion of Cumania
***1241–1242 invasion of Moldavia and Wallachia
** 1238–1239 invasion of Circassia
** 1238–1239 invasion of Chechnya
** 1241 invasion of Poland and Bohemia;
*** 1241 Battle of Legnica
** 1241 invasion of Hungary
*** 1241 Battle of Mohi
** 1241 invasion of Austria and Northeast Italy
**1241–1242 invasion of Croatia
** 1242 invasion of Bulgaria and Serbia
* 1240–1241 invasion of Tibet
* 1241–1244 invasion of Anatolia
* 1244–1265 invasion of
* 1207–1210 invasion of Western Xia
* 1207 conquest of Siberia
* 1211–1234 conquest of Jin dynasty
* 1216–1220 conquest of Central Asia and Eastern Persia
** 1216–1218 conquest of the Qara Khitai
** 1219–1220 conquest of Khwarazm
** 1256 capture of Alamut
* 1220–1223, 1235–1330 invasions of Georgia and the Caucasus
* 1220–1224 invasion of the Cumans
* 1222–1327 Mongol invasions of India
* 1223–1236 invasion of Volga Bulgaria
* 1225–1227 conquest of Western Xia
* 1231–1259 invasion of Korea
* 1233 conquest of Eastern Xia
* 1235–1279 conquest of Song dynasty
* 1222, 1236–1242 Mongol invasion of Europe
** 1236–1242 invasion of Rus
*** 1237–1238 invasion of eastern and northern Rus'
*** 1239–1240 invasion of southern and western Rus'
**1237–1242 invasion of Cumania
***1241–1242 invasion of Moldavia and Wallachia
** 1238–1239 invasion of Circassia
** 1238–1239 invasion of Chechnya
** 1241 invasion of Poland and Bohemia;
*** 1241 Battle of Legnica
** 1241 invasion of Hungary
*** 1241 Battle of Mohi
** 1241 invasion of Austria and Northeast Italy
**1241–1242 invasion of Croatia
** 1242 invasion of Bulgaria and Serbia
* 1240–1241 invasion of Tibet
* 1241–1244 invasion of Anatolia
* 1244–1265 invasion of
online reviewexcerpt and text search
* Morgan, David. ''The Mongols'' (2nd ed. 2007) * Rossabi, Morris. ''The Mongols: A Very Short Introduction'' (Oxford University Press, 2012) * Saunders, J. J. ''The History of the Mongol Conquests'' (2001
excerpt and text search
* Turnbull, Stephen. ''Genghis Khan and the Mongol Conquests 1190–1400'' (2003
excerpt and text search
* Bayarsaikhan Dashdondog
The Mongols and the Armenians (1220–1335)
BRILL (2010)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mongol Invasions and Conquests 13th-century conflicts 14th-century conflicts Expeditionary warfare
Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
( 1206-1368
Year 1368 ( MCCCLXVIII) was a leap year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
January–December
* January 23 – The Hongwu Emperor (Zhu Yuanzhang) establishes the Ming Dynasty ...
), which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
. Historians regard the Mongol devastation as one of the deadliest episodes in history. In addition, Mongol expeditions may have spread the bubonic plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of plague caused by the plague bacterium ('' Yersinia pestis''). One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting, as wel ...
across much of Eurasia, helping to spark the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
of the 14th century.
The Mongol Empire developed in the course of the 13th century through a series of victorious campaigns throughout Asia, reaching Eastern Europe by the 1240s. In contrast with later "empires of the sea" such as European colonial powers
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their reli ...
, the Mongol Empire was a land power, fueled by the grass-foraging Mongol cavalry and cattle. Thus most Mongol conquest and plundering took place during the warmer seasons, when there was sufficient grazing for their herds. The rise of the Mongols was preceded by 15 years of wet and warm weather conditions from 1211 to 1225 that allowed favourable conditions for the breeding of horses, which greatly assisted their expansion.
As the Mongol Empire began to fragment from 1260, conflict between the Mongols and Eastern European polities continued for centuries. Mongols continued to rule China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
into the 14th century under the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fif ...
, while Mongol rule in Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
persisted into the 15th century under the Timurid Empire
The Timurid Empire ( chg, , fa, ), self-designated as Gurkani (Chagatai language, Chagatai: کورگن, ''Küregen''; fa, , ''Gūrkāniyān''), was a PersianateB.F. Manz, ''"Tīmūr Lang"'', in Encyclopaedia of Islam, Online Edition, 2006 Tu ...
. In India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
, the later Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
survived into the 19th century.
Central Asia

Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; ; xng, Temüjin, script=Latn; ., name=Temujin – August 25, 1227) was the founder and first Great Khan (Emperor) of the Mongol Empire, which became the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in history a ...
forged the initial Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
in Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
, starting with the unification of the nomadic tribes Merkits, Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different Turki ...
, in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different Turki ...
Keraites
The Keraites (also ''Kerait, Kereit, Khereid''; ; ) were one of the five dominant Mongol or Turkic tribal confederations ( khanates) in the Altai-Sayan region during the 12th century. They had converted to the Church of the East ( Nestorianism) ...
, Turks, Naimans and Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
. The Uighur Buddhist Qocho Kingdom surrendered and joined the empire. He then continued expansion via conquest of the Qara Khitai and the Khwarazmian dynasty
The Anushtegin dynasty or Anushteginids (English: , fa, ), also known as the Khwarazmian dynasty ( fa, ) was a Persianate C. E. BosworthKhwarazmshahs i. Descendants of the line of Anuštigin In Encyclopaedia Iranica, online ed., 2009: ''" ...
.
Large areas of Islamic Central Asia and northeastern Persia were seriously depopulated, as every city or town that resisted the Mongols was destroyed. Each soldier was given a quota of enemies to execute according to circumstances. For example, after the conquest of Urgench, each Mongol warrior – in an army of perhaps two tumens (20,000 troops) – was required to execute 24 people, or nearly half a million people per said army.
Against the Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
and the Cumans
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many so ...
(Kipchaks
The Kipchaks or Qipchaks, also known as Kipchak Turks or Polovtsians, were a Turkic nomadic people and confederation that existed in the Middle Ages, inhabiting parts of the Eurasian Steppe. First mentioned in the 8th century as part of the ...
), the Mongols used divide-and-conquer tactics by first warning the Cumans to end their support of the Alans, whom they then defeated, before rounding on the Cumans. Alans were recruited into the Mongol forces with one unit called "Right Alan Guard" which was combined with "recently surrendered" soldiers. Mongols and Chinese soldiers stationed in the area of the former Kingdom of Qocho and in Besh Balikh established a Chinese military colony led by Chinese general Qi Kongzhi (Ch'i Kung-chih).
During the Mongol attack on the Mamluks in the Middle East, most of the Mamluk military was composed of Kipchaks, and the Golden Horde's supply of Kipchak fighters replenished the Mamluk armies and helped them fight off the Mongols.
Hungary became a refuge for fleeing Cumans.
The decentralized, stateless Kipchaks only converted to Islam after the Mongol conquest, unlike the centralized Karakhanid entity comprising the Yaghma, Qarluqs, and Oghuz who converted earlier to world religions.
The Mongol conquest of the Kipchaks led to a merged society with a Mongol ruling class over a Kipchak-speaking populace which came to be known as Tatar, and which eventually absorbed Armenians, Italians, Greeks, and Goths on the Crimean peninsula to form the modern day Crimean Tatar people.
West Asia
 The Mongols conquered, by battle or voluntary surrender, the areas of present-day Iran, Iraq, the
The Mongols conquered, by battle or voluntary surrender, the areas of present-day Iran, Iraq, the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historica ...
, and parts of Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
and Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
, with further Mongol raids reaching southwards into Palestine as far as Gaza in 1260 and 1300. The major battles were the Siege of Baghdad (1258)
The siege of Baghdad was a siege that took place in Baghdad in 1258, lasting for 13 days from January 29, 1258 until February 10, 1258. The siege, laid by Ilkhanate Mongol forces and allied troops, involved the investment, capture, and sac ...
, when the Mongols sacked the city which had been the center of Islamic power for 500 years, and the Battle of Ain Jalut
The Battle of Ain Jalut (), also spelled Ayn Jalut, was fought between the Bahri Mamluks of Egypt and the Mongol Empire on 3 September 1260 (25 Ramadan 658 AH) in southeastern Galilee in the Jezreel Valley near what is known today as the S ...
in 1260 in south-eastern Galilee
Galilee (; he, הַגָּלִיל, hagGālīl; ar, الجليل, al-jalīl) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon. Galilee traditionally refers to the mountainous part, divided into Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and Lower Gali ...
, when the Muslim Bahri Mamluks were able to defeat the Mongols and decisively hault their advance for the first time. One thousand northern Chinese engineer squads accompanied the Mongol Hulagu Khan
Hulagu Khan, also known as Hülegü or Hulegu ( mn, Хүлэгү/ , lit=Surplus, translit=Hu’legu’/Qülegü; chg, ; Arabic: fa, هولاکو خان, ''Holâku Khân;'' ; 8 February 1265), was a Mongol ruler who conquered much of We ...
during his conquest of the Middle East.
East Asia
 Genghis Khan and his descendants launched progressive
Genghis Khan and his descendants launched progressive invasions of China
An invasion is a military offensive in which large numbers of combatants of one geopolitical entity aggressively enter territory owned by another such entity, generally with the objective of either: conquering; liberating or re-establishing c ...
, subjugating the Western Xia
The Western Xia or the Xi Xia (), officially the Great Xia (), also known as the Tangut Empire, and known as ''Mi-nyak''Stein (1972), pp. 70–71. to the Tanguts and Tibetans, was a Tangut-led Buddhist imperial dynasty of China tha ...
in 1209 before destroying them in 1227, defeating the Jin dynasty in 1234 and defeating the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the res ...
in 1279. They made the Kingdom of Dali
The Dali Kingdom, also known as the Dali State (; Bai: Dablit Guaif), was a state situated in modern Yunnan province, China from 937 until 1253. In 1253, it was conquered by the Mongols but members of its former ruling dynasty continued to a ...
into a vassal state in 1253 after the Dali King Duan Xingzhi defected to the Mongols and helped them conquer the rest of Yunnan, forced Korea to capitulate through nine invasions, but failed in their attempts to invade Japan, their fleets scattered by ''kamikaze
, officially , were a part of the Japanese Special Attack Units of military aviators who flew suicide attacks for the Empire of Japan against Allied naval vessels in the closing stages of the Pacific campaign of World War II, intending ...
'' storms.
 The Mongols' greatest triumph was when
The Mongols' greatest triumph was when Kublai Khan
Kublai ; Mongolian script: ; (23 September 1215 – 18 February 1294), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shizu of Yuan and his regnal name Setsen Khan, was the founder of the Yuan dynasty of China and the fifth khagan-emperor of ...
established the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fif ...
in China in 1271. The dynasty created a "Han Army" (漢軍) out of defected Jin troops and an army of defected Song troops called the "Newly Submitted Army" (新附軍).
The Mongol force which invaded southern China was far greater than the force they sent to invade the Middle East in 1256.
The Yuan dynasty established the top-level government agency Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs __NOTOC__
The Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs, or Xuanzheng Yuan () was a government agency of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty of China to handle Buddhist affairs across the empire in addition to managing the territory of Tibet. It was origi ...
to govern Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, ...
, which was conquered by the Mongols and put under Yuan rule. The Mongols also invaded Sakhalin Island between 1264 and 1308. Likewise, Korea (Goryeo
Goryeo (; ) was a Korean kingdom founded in 918, during a time of national division called the Later Three Kingdoms period, that unified and ruled the Korean Peninsula until 1392. Goryeo achieved what has been called a "true national unificat ...
) became a semi-autonomous vassal state of the Yuan dynasty for about 80 years.
North Asia
By 1206,Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; ; xng, Temüjin, script=Latn; ., name=Temujin – August 25, 1227) was the founder and first Great Khan (Emperor) of the Mongol Empire, which became the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in history a ...
had conquered all Mongol and Turkic tribes in Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million ...
and southern Siberia. In 1207 his eldest son Jochi
Jochi Khan ( Mongolian: mn, Зүчи, ; kk, Жошы, Joşy جوشى; ; crh, Cuçi, Джучи, جوچى; also spelled Juchi; Djochi, and Jöchi c. 1182– February 1227) was a Mongol army commander who was the eldest son of Temüjin (aka G ...
subjugated the Siberian forest people, the Uriankhai, the Oirats
Oirats ( mn, Ойрад, ''Oirad'', or , Oird; xal-RU, Өөрд; zh, 瓦剌; in the past, also Eleuths) are the westernmost group of the Mongols whose ancestral home is in the Altai region of Siberia, Xinjiang and western Mongolia.
Histor ...
, Barga, Khakas
The Khakas (also spelled Khakass; Khakas: , ''khakas'', , ''tadar'', , ''khakastar'', , ''tadarlar'') are a Turkic indigenous people of Siberia, who live in the republic of Khakassia, Russia. They speak the Khakas language.
The Khakhassi ...
, Buryats
The Buryats ( bua, Буряад, Buryaad; mn, Буриад, Buriad) are a Mongolic ethnic group native to southeastern Siberia who speak the Buryat language. They are one of the two largest indigenous groups in Siberia, the other being the ...
, Tuvans
The Tuvans ( tyv, Тывалар, Tıvalar) are a TurkicOtto Maenchen-Helfen, Journey to Tuva, p. 169 ethnic group indigenous to Siberia who live in Russia ( Tuva), Mongolia, and China. They speak Tuvan, a Siberian Turkic language. They are a ...
, Khori-Tumed, and Yenisei Kyrgyz
The Yenisei Kyrgyz ( otk, 𐰶𐰃𐰺𐰴𐰕:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, Qyrqyz bodun), were an ancient Turkic people who dwelled along the upper Yenisei River in the southern portion of the Minusinsk Depression from the 3rd century BCE to the 13th ...
. He then organized the Siberians into three tumens. Genghis Khan gave the Telengit
Telengits or Telengut are a Turkic ethnic group primarily found in the Altai Republic, Russia. Telengits mainly live in a territory of Kosh-Agach District of the Altai Republic. They are part of a larger cultural group of Southern Altaians. T ...
and Tolos along the Irtysh River
The Irtysh ( otk, 𐰼𐱅𐰾:𐰇𐰏𐰕𐰏, Ertis ügüzüg, mn, Эрчис мөрөн, ''Erchis mörön'', "erchleh", "twirl"; russian: Иртыш; kk, Ертіс, Ertis, ; Chinese: 额尔齐斯河, pinyin: ''É'ěrqísī hé'', Xiao'e ...
to an old companion, Qorchi. While the Barga, Tumed, Buriats, Khori, Keshmiti, and Bashkirs
, native_name_lang = bak
, flag = File:Bashkirs of Baymak rayon.jpg
, flag_caption = Bashkirs of Baymak in traditional dress
, image =
, caption =
, population = approx. 2 million
, popplace ...
were organized in separate thousands, the Telengit, Tolos, Oirats and Yenisei Kirghiz were numbered into the regular tumens Genghis created a settlement of Chinese craftsmen and farmers at Kem-kemchik after the first phase of the Mongol conquest of the Jin dynasty. The Great Khans favored gyrfalcon
The gyrfalcon ( or ) (), the largest of the falcon species, is a bird of prey. The abbreviation gyr is also used. It breeds on Arctic coasts and tundra, and the islands of northern North America and the Eurosiberian region. It is mainly a resid ...
s, furs, women, and Kyrgyz horses for tribute.
Western Siberia came under the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragmen ...
. The descendants of Orda Khan
Orda Ichen ( Mongolian: c. 1206 – 1251) was a Mongol Khan and military strategist who ruled the eastern part of the Golden Horde (division of the Mongol Empire) during the 13th century.
First Khan of the White Horde
Orda Ichen (-1251 ...
, the eldest son of Jochi, directly ruled the area. In the swamps of western Siberia, dog sled
A dog sled or dog sleigh is a sled pulled by one or more sled dogs used to travel over ice and through snow. Numerous types of sleds are used, depending on their function. They can be used for dog sled racing. Traditionally in Greenland and th ...
Yam stations were set up to facilitate collection of tribute.
In 1270, Kublai Khan
Kublai ; Mongolian script: ; (23 September 1215 – 18 February 1294), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shizu of Yuan and his regnal name Setsen Khan, was the founder of the Yuan dynasty of China and the fifth khagan-emperor of ...
sent a Chinese official, with a new batch of settlers, to serve as judge of the Kyrgyz and Tuvan basin areas ( 益蘭州 and 謙州). Ogedei's grandson Kaidu
Kaidu (Middle Mongol: , Modern Mongol: / , ; ; c. 1230 – 1301) was a grandson of the Mongol khagan Ögedei (1185–1241) and thus leader of the House of Ögedei and the ''de facto'' khan of the Chagatai Khanate, a division of the Mongol Em ...
occupied portions of Central Siberia from 1275 on. The Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fif ...
army under Kublai's Kipchak general Tutugh reoccupied the Kyrgyz lands in 1293. From then on the Yuan dynasty controlled large portions of Central and Eastern Siberia.
Eastern and Central Europe

 The Mongols invaded and destroyed
The Mongols invaded and destroyed Volga Bulgaria
Volga Bulgaria or Volga–Kama Bulgaria, was a historic Bulgar state that existed between the 7th and 13th centuries around the confluence of the Volga and Kama River, in what is now European Russia. Volga Bulgaria was a multi-ethnic state ...
and Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas o ...
, before invading Poland, Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Cr ...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
, and other territories. Over the course of three years (1237–1240), the Mongols razed all the major cities of Russia with the exceptions of Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( rus, links=no, Великий Новгород, t=Great Newtown, p=vʲɪˈlʲikʲɪj ˈnovɡərət), also known as just Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the ...
and Pskov
Pskov ( rus, Псков, a=pskov-ru.ogg, p=pskof; see also names in other languages) is a city in northwestern Russia and the administrative center of Pskov Oblast, located about east of the Estonian border, on the Velikaya River. Population ...
.
Giovanni da Pian del Carpine, the Pope's envoy to the Mongol Great Khan, traveled through Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Ky ...
in February 1246 and wrote:
The Mongol invasions displaced populations on a scale never seen before in central Asia or eastern Europe. Word of the Mongol hordes' approach spread terror and panic. The violent character of the invasions acted as a catalyst for further violence between Europe's elites and sparked additional conflicts. The increase in violence in the affected eastern European regions correlates with a decrease in the elite's numerical skills, and has been postulated as a root of the Great Divergence.
South Asia
From 1221 to 1327, the Mongol Empire launched several invasions into theIndian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
. The Mongols occupied parts of Punjab region for decades. However, they failed to penetrate past the outskirts of Delhi and were repelled from the interior of India. Centuries later, the Mughals
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
, whose founder Babur
Babur ( fa, , lit= tiger, translit= Bābur; ; 14 February 148326 December 1530), born Mīrzā Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad, was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through hi ...
had Mongol roots, established their own empire in India.
Southeast Asia
Kublai Khan's Yuan dynasty invaded Burma between 1277 and 1287, resulting in the capitulation and disintegration of thePagan Kingdom
The Kingdom of Pagan ( my, ပုဂံခေတ်, , ; also known as the Pagan Dynasty and the Pagan Empire; also the Bagan Dynasty or Bagan Empire) was the first Burmese kingdom to unify the regions that would later constitute modern-da ...
. However, the invasion of 1301 was repulsed by the Burmese Myinsaing Kingdom
, conventional_long_name = Myinsaing Kingdom
, common_name = Myinsaing Kingdom
, era = Warring states
, status = Regency
, event_pre =
, date_pre = 1277–87
, event_start =
, year_start ...
. The Mongol invasions of Vietnam (Đại Việt
Đại Việt (, ; literally Great Việt), often known as Annam ( vi, An Nam, Chữ Hán: 安南), was a monarchy in eastern Mainland Southeast Asia from the 10th century AD to the early 19th century, centered around the region of present-day H ...
) and Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
resulted in defeat for the Mongols, although much of Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
agreed to pay tribute to avoid further bloodshed.Gunn 2011p. 112.Woodside 1971
p. 8. The Mongol invasions played an indirect role in the establishment of major Tai states in the region by recently migrated Tais, who originally came from Southern China, in the early centuries of the second millennium. Major Tai states such as
Lan Na
The Lan Na Kingdom ( nod, , , "Kingdom of a Million Rice Fields"; th, อาณาจักรล้านนา, , ), also known as Lannathai, and most commonly called Lanna or Lanna Kingdom, was an Indianized state centered in present-day ...
, Sukhothai, and Lan Xang
existed as a unified kingdom from 1353 to 1707.
For three and a half centuries, Lan Xang was one of the largest kingdoms in Southeast Asia. The meaning of the kingdom's name alludes to the power of the kingship and formidable war machine of the ea ...
appeared around this time.
Death toll
Due to the lack of contemporary records, estimates of the violence associated with the Mongol conquests vary considerably. Not including the mortality fromthe Plague
Plague or The Plague may refer to:
Agriculture, fauna, and medicine
*Plague (disease), a disease caused by ''Yersinia pestis''
* An epidemic of infectious disease (medical or agricultural)
* A pandemic caused by such a disease
* A swarm of pes ...
in Europe, West Asia, or China it is possible that between 20 and 57 million people were killed between 1206 and 1405 during the various campaigns of Genghis Khan, Kublai Khan, and Timur. The havoc included battles, sieges, early biological warfare, and massacres.Halperin, C. J. (1987). ''Russia and the Golden Horde: the Mongol impact on medieval Russian history'' (Vol. 445). Indiana University Press.
Timeline
 * 1207–1210 invasion of Western Xia
* 1207 conquest of Siberia
* 1211–1234 conquest of Jin dynasty
* 1216–1220 conquest of Central Asia and Eastern Persia
** 1216–1218 conquest of the Qara Khitai
** 1219–1220 conquest of Khwarazm
** 1256 capture of Alamut
* 1220–1223, 1235–1330 invasions of Georgia and the Caucasus
* 1220–1224 invasion of the Cumans
* 1222–1327 Mongol invasions of India
* 1223–1236 invasion of Volga Bulgaria
* 1225–1227 conquest of Western Xia
* 1231–1259 invasion of Korea
* 1233 conquest of Eastern Xia
* 1235–1279 conquest of Song dynasty
* 1222, 1236–1242 Mongol invasion of Europe
** 1236–1242 invasion of Rus
*** 1237–1238 invasion of eastern and northern Rus'
*** 1239–1240 invasion of southern and western Rus'
**1237–1242 invasion of Cumania
***1241–1242 invasion of Moldavia and Wallachia
** 1238–1239 invasion of Circassia
** 1238–1239 invasion of Chechnya
** 1241 invasion of Poland and Bohemia;
*** 1241 Battle of Legnica
** 1241 invasion of Hungary
*** 1241 Battle of Mohi
** 1241 invasion of Austria and Northeast Italy
**1241–1242 invasion of Croatia
** 1242 invasion of Bulgaria and Serbia
* 1240–1241 invasion of Tibet
* 1241–1244 invasion of Anatolia
* 1244–1265 invasion of
* 1207–1210 invasion of Western Xia
* 1207 conquest of Siberia
* 1211–1234 conquest of Jin dynasty
* 1216–1220 conquest of Central Asia and Eastern Persia
** 1216–1218 conquest of the Qara Khitai
** 1219–1220 conquest of Khwarazm
** 1256 capture of Alamut
* 1220–1223, 1235–1330 invasions of Georgia and the Caucasus
* 1220–1224 invasion of the Cumans
* 1222–1327 Mongol invasions of India
* 1223–1236 invasion of Volga Bulgaria
* 1225–1227 conquest of Western Xia
* 1231–1259 invasion of Korea
* 1233 conquest of Eastern Xia
* 1235–1279 conquest of Song dynasty
* 1222, 1236–1242 Mongol invasion of Europe
** 1236–1242 invasion of Rus
*** 1237–1238 invasion of eastern and northern Rus'
*** 1239–1240 invasion of southern and western Rus'
**1237–1242 invasion of Cumania
***1241–1242 invasion of Moldavia and Wallachia
** 1238–1239 invasion of Circassia
** 1238–1239 invasion of Chechnya
** 1241 invasion of Poland and Bohemia;
*** 1241 Battle of Legnica
** 1241 invasion of Hungary
*** 1241 Battle of Mohi
** 1241 invasion of Austria and Northeast Italy
**1241–1242 invasion of Croatia
** 1242 invasion of Bulgaria and Serbia
* 1240–1241 invasion of Tibet
* 1241–1244 invasion of Anatolia
* 1244–1265 invasion of Dali Kingdom
The Dali Kingdom, also known as the Dali State (; Bai: Dablit Guaif), was a state situated in modern Yunnan province, China from 937 until 1253. In 1253, it was conquered by the Mongols but members of its former ruling dynasty continued to a ...
* 1251–1259 invasion of Persia, Syria and Mesopotamia
* 1253–1256 invasion of Yunnan
* 1253–1256 Mongol campaign against the Nizaris
* 1257, 1284, 1287 invasions of Vietnam
* 1258 invasion of Baghdad
* 1258–1260 invasion of Halych-Volhynia, Lithuania and Poland
** Sack of Sandomierz
* 1260 Battle of Ain Jalut
* 1260 Mongol raid against Syria
* 1264–1265 raid against Bulgaria and Thrace
* 1264–1308 invasion of Sakhalin Island
* 1271 raid against Syria
* 1274, 1281 invasions of Japan
*1274 raid against Bulgaria
* 1275, 1277 raids against Lithuania
* 1277 battle of Abulustayn
* 1277 invasion of Myanmar
* 1281 invasion of Syria
* 1284–1285 invasion of Hungary
*1285 raid against Bulgaria
*1283 invasion of Khmer Empire
* 1287 invasion of Myanmar
* 1287–1288 invasion of Poland
* 1293 invasion of Java
* 1299 invasion of Syria
* 1300 Mongol invasion of Myanmar
* 1300 Mongol invasion of Syria
* 1303 Invasion of Syria
* 1307 Mongol invasion of Gilan
*1312 Mongol invasion of Syria
* 1324, 1337 Tatar raids against Thrace
* 1337, 1340 Ruthenian-Tatar raids against Poland
See also
*Battle of the Kalka River
The Battle of the Kalka River (russian: Битва на реке Калке; uk, Битва на річці Калка) was fought between the Mongol Empire, whose armies were led by Jebe and Subutai, and a coalition of several Rus' principalit ...
* Political divisions and vassals of the Mongol Empire
* Division of the Mongol Empire
* List of conflicts in Eastern Europe during Turco-Mongol rule
* Mongol invasion of Europe
From the 1220s into the 1240s, the Mongols conquered the Turkic states of Volga Bulgaria, Cumania, Alania, and the Kievan Rus' federation. Following this, they began their invasion into heartland Europe by launching a two-pronged invasion of ...
* Mongol military tactics and organization
* List of conflicts in Europe during Turco-Mongol rule
* Destruction under the Mongol Empire
* List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll
References
Notes
References
Further reading
* Boyle, J.A. ''The Mongol World Enterprise, 1206–1370'' (London 1977) *Hildinger, Erik. ''Warriors of the Steppe: A Military History of Central Asia, 500 B.C. to A.D. 1700 '' * May, Timothy. ''The Mongol Conquests in World History'' (London: Reaktion Books, 2011online review
* Morgan, David. ''The Mongols'' (2nd ed. 2007) * Rossabi, Morris. ''The Mongols: A Very Short Introduction'' (Oxford University Press, 2012) * Saunders, J. J. ''The History of the Mongol Conquests'' (2001
excerpt and text search
* Turnbull, Stephen. ''Genghis Khan and the Mongol Conquests 1190–1400'' (2003
excerpt and text search
* Bayarsaikhan Dashdondog
The Mongols and the Armenians (1220–1335)
BRILL (2010)
Primary sources
* Rossabi, Morris. ''The Mongols and Global History: A Norton Documents Reader'' (2011)External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mongol Invasions and Conquests 13th-century conflicts 14th-century conflicts Expeditionary warfare