Mombasa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mombasa ( ; ) is a coastal city in southeastern
. Cia.gov. Retrieved on 17 August 2013. after the capital
 Vasco da Gama was the first known European to visit Mombasa, receiving a chilly reception in 1498. Two years later, the town was sacked by the Portuguese. In 1502, the
Vasco da Gama was the first known European to visit Mombasa, receiving a chilly reception in 1498. Two years later, the town was sacked by the Portuguese. In 1502, the
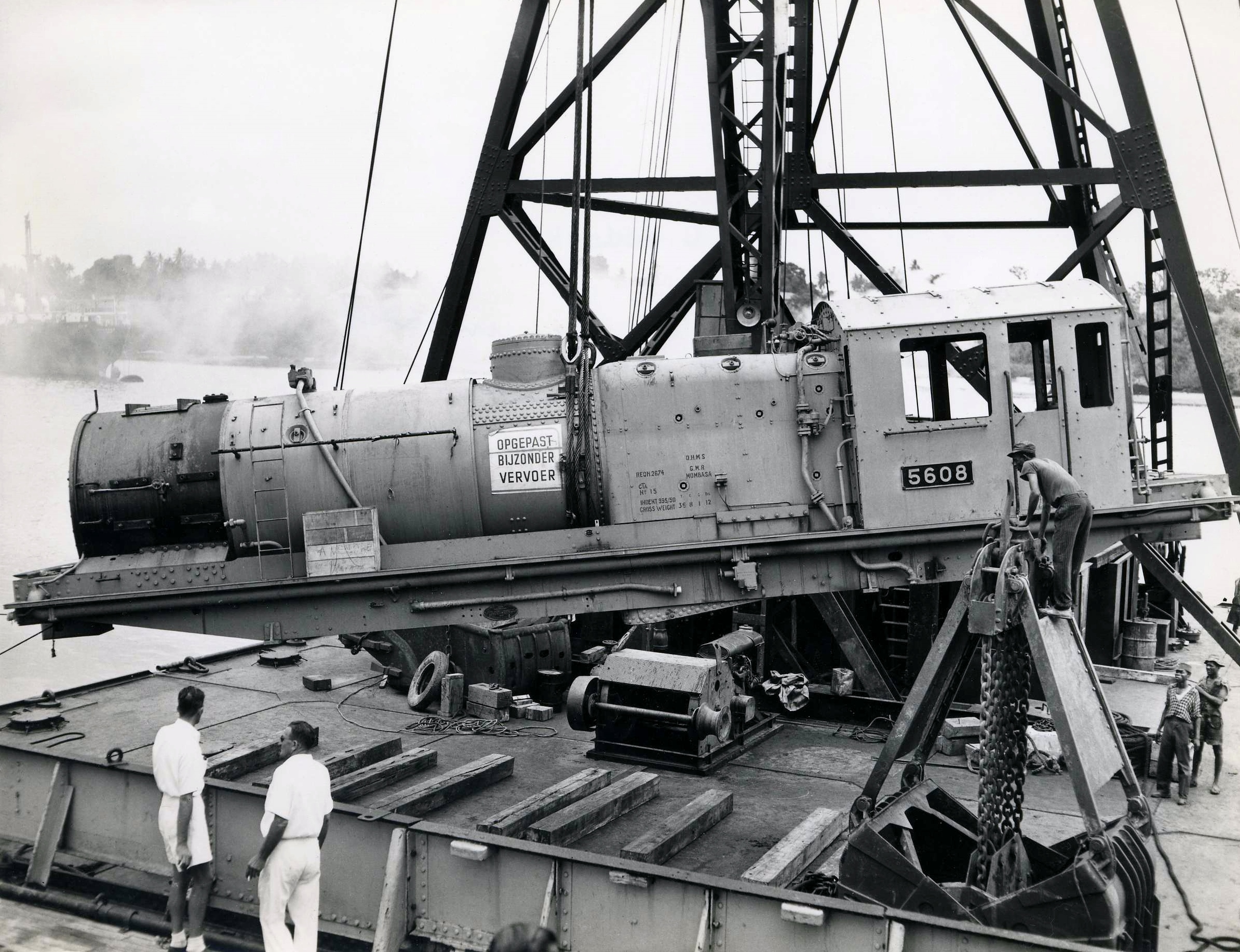 From 9 February 1824 to 25 July 1826, there was a
From 9 February 1824 to 25 July 1826, there was a
 Being a coastal town, Mombasa is characterised by a flat topography. The town of Mombasa is centred on Mombasa Island, but extends to the mainland. The island is separated from the mainland by two creeks, Port Reitz in the south and
Being a coastal town, Mombasa is characterised by a flat topography. The town of Mombasa is centred on Mombasa Island, but extends to the mainland. The island is separated from the mainland by two creeks, Port Reitz in the south and
 Mombasa CBD
Mombasa CBD
 Kizingo: Considered the prime residential area of Mombasa. The State House of Mombasa, Provincial Headquarters, The Mombasa Law Courts, and the Municipal Council are located in Kizingo. The Aga Khan Academy, Aga Khan High School, Serani Primary School, Serani High School, Santokben Nursery School, Coast Academy, Jaffery Academy, Mombasa Primary School, Loreto Convent, Mama Ngina Girls' High School and the Government Training Institute (GTI) Mombasa are all in Kizingo as well.
Central Business District: The Mombasa central business district across the TSS building roundabout, Moi Avenue, and Nyerere Avenue is densely populated. Organizations such as the Kenya Revenue Authority (KRA) and businesses such as Banks (ABSA, I&M Ltd, Bank of India Ltd), Insurance Firms (Nomura Insurance Brokers, Masumali Meghji Insurance), and Audit Firms (Anant Bhatt LLP, Pricewaterhouse Coopers LLP, Mazars LLP, Deloitte LLP, and PKF LLP) are located here.
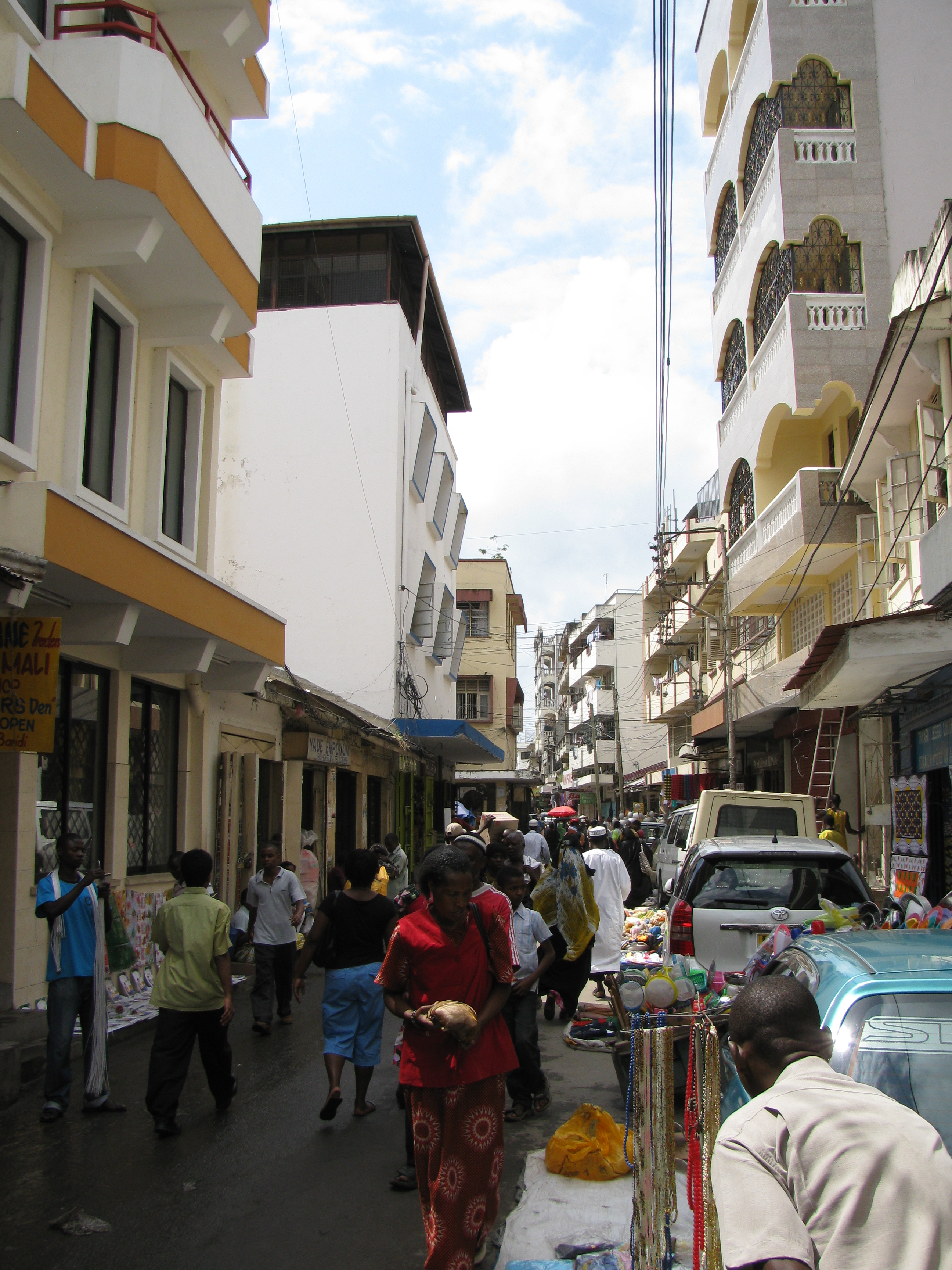
Kibokoni: Part of Old Town with Swahili architecture. Fort Jesus is in Baghani.
Englani: Part of Old town between Kibokoni and Makadara.
Kuze: Part of Old Town with Swahili culture and architecture. Originally flourishing with Swahili people but currently becoming a more cosmopolitan neighbourhood.
Makadara: Part of Old Town consisting of a high number of descendants of Baluchi former soldiers who settled within this area before it developed into a town. The name is derived from the Arabic words "Qadru r-Rahman" meaning "Decree of (God) the Merciful".
Ganjoni: Primarily a middle class residential, home of second biggest dry dock of Africa after the one in South Africa.
Tudor: Another middle class residential area with homes and shops. The
Kizingo: Considered the prime residential area of Mombasa. The State House of Mombasa, Provincial Headquarters, The Mombasa Law Courts, and the Municipal Council are located in Kizingo. The Aga Khan Academy, Aga Khan High School, Serani Primary School, Serani High School, Santokben Nursery School, Coast Academy, Jaffery Academy, Mombasa Primary School, Loreto Convent, Mama Ngina Girls' High School and the Government Training Institute (GTI) Mombasa are all in Kizingo as well.
Central Business District: The Mombasa central business district across the TSS building roundabout, Moi Avenue, and Nyerere Avenue is densely populated. Organizations such as the Kenya Revenue Authority (KRA) and businesses such as Banks (ABSA, I&M Ltd, Bank of India Ltd), Insurance Firms (Nomura Insurance Brokers, Masumali Meghji Insurance), and Audit Firms (Anant Bhatt LLP, Pricewaterhouse Coopers LLP, Mazars LLP, Deloitte LLP, and PKF LLP) are located here.
Kibokoni: Part of Old Town with Swahili architecture. Fort Jesus is in Baghani.
Englani: Part of Old town between Kibokoni and Makadara.
Kuze: Part of Old Town with Swahili culture and architecture. Originally flourishing with Swahili people but currently becoming a more cosmopolitan neighbourhood.
Makadara: Part of Old Town consisting of a high number of descendants of Baluchi former soldiers who settled within this area before it developed into a town. The name is derived from the Arabic words "Qadru r-Rahman" meaning "Decree of (God) the Merciful".
Ganjoni: Primarily a middle class residential, home of second biggest dry dock of Africa after the one in South Africa.
Tudor: Another middle class residential area with homes and shops. The
 Likoni: is a lower income and lower-middle-class neighbourhood connected to Mombasa Island by ferry. It is south of Mombasa Island and made up of mostly Swahili and non-Swahili Bantu tribes. The ferry was the target of the Likoni Riots of 1997.
Diani Beach: a beach resort area situated over the Likoni Ferry on the south coast of Mombasa. It is located some 36 km (22 miles) south of Mombasa city on the mainland coast and is a prime resort for many local and international tourists. Diani Beach has an airport at Ukunda town to cater for tourists who fly there directly from Nairobi Wilson or any other airports and airfields in the country.
Likoni: is a lower income and lower-middle-class neighbourhood connected to Mombasa Island by ferry. It is south of Mombasa Island and made up of mostly Swahili and non-Swahili Bantu tribes. The ferry was the target of the Likoni Riots of 1997.
Diani Beach: a beach resort area situated over the Likoni Ferry on the south coast of Mombasa. It is located some 36 km (22 miles) south of Mombasa city on the mainland coast and is a prime resort for many local and international tourists. Diani Beach has an airport at Ukunda town to cater for tourists who fly there directly from Nairobi Wilson or any other airports and airfields in the country.
 Magongo: is an outlying township 20 minutes driving distance northwest of Mombasa Island, situated on the Nairobi Highway. This fringe community lacks any effective electricity, water or sewer systems, with a general lack of infrastructure. Poverty, lack of sanitation, and unemployment continue to be the greatest issues for the Mikindani Township, which have ensured low health and safety standards for its residents. Poor, lower class housing is widespread, ranging from simple stone, two-storey structures to mud and earth homes fitted with corrugated iron roofs. Much of the community works outside of the township, within Mombasa Island itself as there is a lack of employment and industry. There are number of small health clinics, shops, and a few public primary schools: Nazarene primary is one school, which is known in particular as being staffed by a revolving volunteer teacher base from Western, and predominately English speaking nations. This small town serves as a link between the city and Moi International Airport. Magongo is also home to the Akamba Handicraft Cooperative.
Magongo: is an outlying township 20 minutes driving distance northwest of Mombasa Island, situated on the Nairobi Highway. This fringe community lacks any effective electricity, water or sewer systems, with a general lack of infrastructure. Poverty, lack of sanitation, and unemployment continue to be the greatest issues for the Mikindani Township, which have ensured low health and safety standards for its residents. Poor, lower class housing is widespread, ranging from simple stone, two-storey structures to mud and earth homes fitted with corrugated iron roofs. Much of the community works outside of the township, within Mombasa Island itself as there is a lack of employment and industry. There are number of small health clinics, shops, and a few public primary schools: Nazarene primary is one school, which is known in particular as being staffed by a revolving volunteer teacher base from Western, and predominately English speaking nations. This small town serves as a link between the city and Moi International Airport. Magongo is also home to the Akamba Handicraft Cooperative.
 Mombasa city has a population of 1,208,333 per the 2019 census.
Mombasa has a cosmopolitan population, with the Swahili people and Mijikenda predominant. Other communities include the Akamba and Taita Bantus as well as a significant population of
Mombasa city has a population of 1,208,333 per the 2019 census.
Mombasa has a cosmopolitan population, with the Swahili people and Mijikenda predominant. Other communities include the Akamba and Taita Bantus as well as a significant population of

 Mombasa is an important economic centre in Kenya. In addition to the coffee trade, the food and chemical industries, there is a steel mill, an aluminum rolling mill, an oil refinery and a cement plant. The city is home to the most important seaport in East Africa, Kilindini Harbor, which is also used by the neighboring countries Tanzania and Uganda for their imports and exports.
''Kilindini'' is an old Swahili term meaning "deep". The port is so-called because the channel is naturally very deep. Kilindini Harbour is an example of a natural geographic phenomenon called a
Mombasa is an important economic centre in Kenya. In addition to the coffee trade, the food and chemical industries, there is a steel mill, an aluminum rolling mill, an oil refinery and a cement plant. The city is home to the most important seaport in East Africa, Kilindini Harbor, which is also used by the neighboring countries Tanzania and Uganda for their imports and exports.
''Kilindini'' is an old Swahili term meaning "deep". The port is so-called because the channel is naturally very deep. Kilindini Harbour is an example of a natural geographic phenomenon called a
. Abarrelfull.wikidot.com (8 December 2012). Retrieved on 17 August 2013. and a cement factory capable of producing over 1.1 million tons per year. The major intercontinental undersea telecom cables reach shore next to Mombasa, connecting the
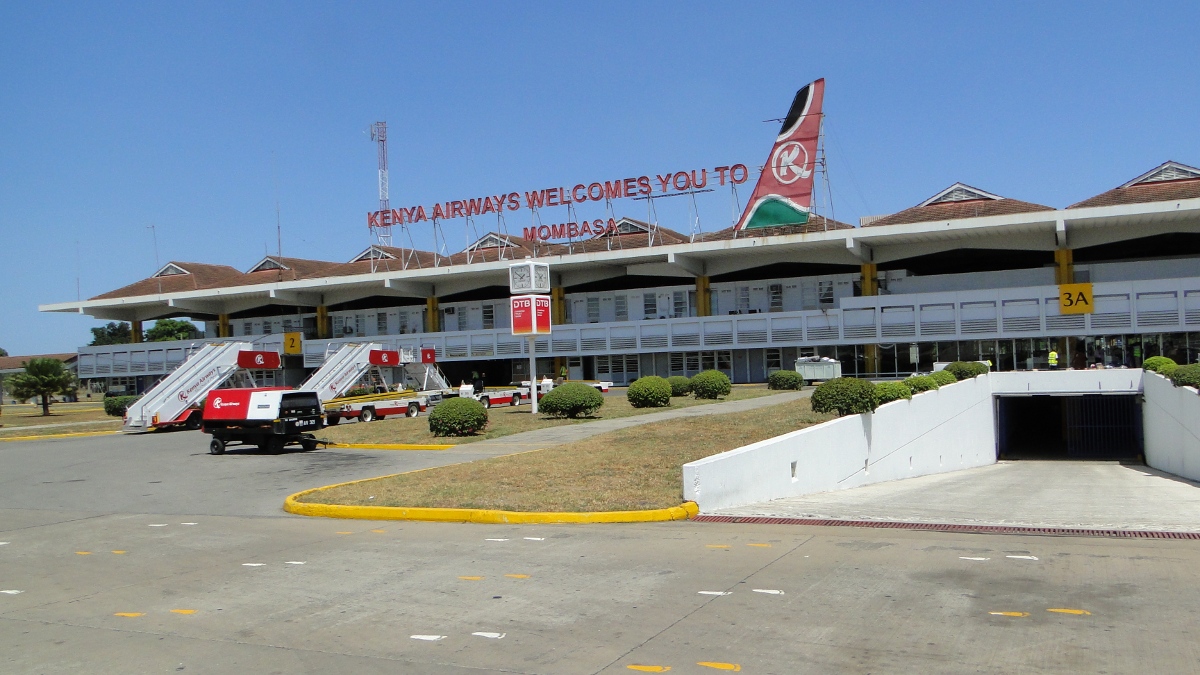 Moi International Airport is located in the city of Mombasa, and is the second largest airport in Kenya with daily flights to Nairobi and other Kenyan, European and Middle Eastern destinations. The airport also handles a large amount of air cargo through its freight terminal.
Moi International Airport is located in the city of Mombasa, and is the second largest airport in Kenya with daily flights to Nairobi and other Kenyan, European and Middle Eastern destinations. The airport also handles a large amount of air cargo through its freight terminal.



. Kpa.co.ke. Retrieved on 17 August 2013. The port is connected by rail and road to the interior. At present there is little or no scheduled passenger service from the port, however, international cruise ships frequent the port. The port is part of the
. KPA. Retrieved on 17 August 2013.
 There is no bridge between Mombasa Island and the south coast, instead the route is served by
There is no bridge between Mombasa Island and the south coast, instead the route is served by
 Mombasa has places of worship serving needs of the city's diverse communities. Christian denominations represented in the city include:
* Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Mombasa with Holy Ghost Cathedral, Mombasa as the main church
*
Mombasa has places of worship serving needs of the city's diverse communities. Christian denominations represented in the city include:
* Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Mombasa with Holy Ghost Cathedral, Mombasa as the main church
*
 A major cultural hub in
A major cultural hub in
. Worldmusic.nationalgeographic.com (17 October 2002). Retrieved on 17 August 2013. Styles of music native to Mombasa include the smooth and mellow Bango, fast-paced
File:Mombasa Building.jpg, Mombasa CBD Building
File:Mombasa beach sunrise.jpg, Mombasa beach sunrise
File:Port of Mombasa.jpg, Port of Mombasa
File:Mombasa old town view.JPG, View of the old town
File:New Dwarikadham Temple, Nyali.JPG, New Dwarikadham
Mombasa County Government
{{Authority control Populated coastal places in Kenya Populated places in Coast Province County capitals in Kenya Former British colonies and protectorates in Africa Former Portuguese colonies Mombasa County Port cities in Africa Port cities and towns of the Indian Ocean Swahili city-states 1824 establishments in the British Empire
Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
...
along the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by t ...
. It was the first capital of the British East Africa
East Africa Protectorate (also known as British East Africa) was an area in the African Great Lakes occupying roughly the same terrain as present-day Kenya from the Indian Ocean inland to the border with Uganda in the west. Controlled by Bri ...
, before Nairobi was elevated to capital city status. It now serves as the capital of Mombasa County
)
, pushpin_map = Kenya
, mapsize =
, map_caption = Location of Mombasa County
, seat_type = Capital
, seat = Mombasa
, subdiv ...
. The town is known as "the white and blue city" in Kenya. It is the country's oldest (circa 900 AD) and second-largest city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
The World Factbook. Cia.gov. Retrieved on 17 August 2013. after the capital
Nairobi
Nairobi ( ) is the capital and largest city of Kenya. The name is derived from the Maasai phrase ''Enkare Nairobi'', which translates to "place of cool waters", a reference to the Nairobi River which flows through the city. The city proper h ...
, with a population of about 1,208,333 people according to the 2019 census. Its metropolitan region is the second-largest in the country, and has a population of 3,528,940 people.
Mombasa's location on the Indian Ocean made it a historical trading centre, and it has been controlled by many countries because of its strategic location. Kenyan school history books place the founding of Mombasa as 900 A.D. It must have been already a prosperous trading town in the 12th century, as the Arab geographer al-Idrisi mentions it in 1151. The oldest stone mosque in Mombasa, Mnara, was built 1300. The Mandhry Mosque, built in 1570, has a minaret that contains a regionally specific ogee arch.
In the late pre-colonial period, it was the metropolis of a plantation society, which became dependent on slave labour based around the ivory trade. Throughout the early modern period, Mombasa was a key node in the complex and far reaching Indian Ocean trading networks; its key exports then were ivory, millet, sesamum and coconuts.
Today, Mombasa is a tourism-based town, home to one of the state houses, with an extra-large port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as H ...
and an international airport.
History
Ancient and medieval
The founding of Mombasa is associated with two rulers: Mwana Mkisi and Shehe Mvita. According to legend, Mwana Mkisi is the original ancestor of Mombasa's oldest lineages within ''Thenashara Taifa'' (or Twelve Nations). Families associated with the Twelve Nations are still considered the original inhabitants of the city. Mwana Mkisi was a queen from the pre-Islamic era, who founded Kongowea, the original urban settlement on Mombasa Island. Significantly, the names of both the queen and the city have linguistic and spiritual connections with Central Africa. "Mkisi" is considered the personification of ''"ukisi"'', which means "the holy" inkiKongo
Kongo or Kikongo is one of the Bantu languages spoken by the Kongo people living in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, Gabon and Angola. It is a tonal language. It was spoken by many of those who were taken from th ...
. "Kongowea" can similarly be interpreted as the Swahili locative of ''"kongo"'', which denotes the essence of civilizational order in central Africa. These legends can be read as an acknowledgment of the Bantu-speaking origins of the Swahili people.
Shehe Mvitaff superseded the dynasty of Mwana Mkisi and established the first permanent stone mosque on Mombasa Island. Mombasa's oldest extant stone mosque, Mnara, was built c. 1300. Shehe Mvita is remembered as a Muslim of great learning and so is connected more directly with the present ideals of Swahili culture that people identify with Mombasa. The ancient history associated with Mwana Mkisi and Shehe Mvita and the founding of an urban settlement on Mombasa Island is still linked to present-day peoples living in Mombasa. The Thenashara Taifa (or Twelve Nations) Swahili lineages recount this ancient history today and are the keepers of local Swahili traditions.
Most of the early information on Mombasa comes from the writings of Portuguese chroniclers
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
in the 16th century.
The famous Moroccan scholar and traveller Ibn Battuta (13041368/1369) visited the area during his travels to the Swahili Coast. He noted the city, although he stayed only one night. He wrote that the people of Mombasa were Shafi‘i
The Shafii ( ar, شَافِعِي, translit=Shāfiʿī, also spelled Shafei) school, also known as Madhhab al-Shāfiʿī, is one of the four major traditional schools of religious law (madhhab) in the Sunnī branch of Islam. It was founded by ...
Muslims, religious people, trustworthy and righteous. Their mosques were made of wood, expertly built.
The exact founding date of the city is unknown, but it has a long history. Kenyan school history books place the founding of Mombasa as 900 A.D. It must have been already a prosperous trading town in the 12th century, as the Arab geographer al-Idrisi mentions it in 1151. The oldest stone mosque in Mombasa, Mnara, was built 1300. The Mandhry Mosque, built in 1570, has a minaret that contains a regionally specific ogee arch. This suggests that Swahili architecture was an indigenous African product rather than being adopted from non-African Muslims who brought stone architecture to the Swahili Coast.
During the pre-modern period, Mombasa was an important centre for the trade in spices, gold, and ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals i ...
. Its trade links reached as far as India and China. Oral historians today can still recount this period of local history. Indian history shows that there were trade links between Mombasa and Cholas of South India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union territ ...
. Throughout the early modern period, Mombasa was a key node in the complex and far-reaching Indian Ocean trading networks, its key exports then were ivory, millet, sesamum and coconuts.
Ivory caravans remained a major source of economic prosperity. Mombasa became the major port city of pre-colonial Kenya in the Middle Ages and was used to trade with other African port cities, the Persian Empire, the Arabian Peninsula, India and China.
Sixteenth-century Portuguese voyager Duarte Barbosa
Duarte Barbosa (c. 14801 May 1521) was a Portuguese writer and officer from Portuguese India (between 1500 and 1516). He was a Christian pastor and scrivener in a '' feitoria'' in Kochi, and an interpreter of the local language, Malayalam. Barbo ...
wrote,
" ombasais a place of great traffic and has a good harbour in which there are always moored small craft of many kinds and also great ships, both of which are bound from Sofala and others which come from Cambay and Melinde and others which sail to the island ofZanzibar Zanzibar (; ; ) is an insular semi-autonomous province which united with Tanganyika in 1964 to form the United Republic of Tanzania. It is an archipelago in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of the mainland, and consists of many small islan ...."
Portuguese domination
 Vasco da Gama was the first known European to visit Mombasa, receiving a chilly reception in 1498. Two years later, the town was sacked by the Portuguese. In 1502, the
Vasco da Gama was the first known European to visit Mombasa, receiving a chilly reception in 1498. Two years later, the town was sacked by the Portuguese. In 1502, the sultanate
This article includes a list of successive Islamic states and Muslim dynasties beginning with the time of the Islamic prophet Muhammad (570–632 CE) and the early Muslim conquests that spread Islam outside of the Arabian Peninsula, and continuin ...
became independent from Kilwa Kisiwani and was renamed as Mvita (in Swahili) or Manbasa (Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
).
The Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
had since had encounters with the city several times; first under Tristão da Cunha in 1506, later under Afonso de Albuquerque in 1522 to quell an attempted mutiny by the sultan's nephew in Pemba and Zanzibar, and finally the destruction of the city under Nuno da Cunha
Nuno da Cunha (c. 1487 – March 5, 1539) was a Portuguese admiral who was governor of Portuguese possessions in India from 1529 to 1538. He was the governor of Portuguese Asia that ruled for more time in the sixteenth century in a total of nine y ...
again in 1528 after the Malindi sultan failed to pay tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conqu ...
.
In 1585, a joint military expedition between the Somalis
The Somalis ( so, Soomaalida 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒆𐒖, ar, صوماليون) are an ethnic group native to the Horn of Africa who share a common ancestry, culture and history. The Lowland East Cushitic Somali language is the shared ...
of Ajuran Empire
The Ajuran Sultanate ( so, Saldanadda Ajuuraan, ar, سلطنة الأجورانية), also natively referred-to as Ajuuraan, and often simply Ajuran, was a Somali Empire in the Middle Ages in the Horn of Africa that dominated the trade in th ...
and the Turks of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, led by Emir 'Ali Bey, successfully captured Mombasa, and other coastal cities in Southeast Africa from the Portuguese. However, Malindi
Malindi is a town on Malindi Bay at the mouth of the Sabaki River, lying on the Indian Ocean coast of Kenya. It is 120 kilometres northeast of Mombasa. The population of Malindi was 119,859 as of the 2019 census. It is the largest urban cent ...
remained loyal to Portugal. The Zimba overcame the towns of Sena and Tete on the Zambezi, and in 1587 they took Kilwa, killing 3,000 people. At Mombasa, the Zimba slaughtered the Muslim inhabitants, but they were halted at Malindi by the Bantu-speaking Segeju and went home. This stimulated the Portuguese to take over Mombasa a third time in 1589, and four years later they built Fort Jesus to administer the region. Between Lake Malawi and the Zambezi mouth, Kalonga Mzura made an alliance with the Portuguese in 1608 and fielded 4,000 warriors to help defeat their rival Zimba, who were led by chief Lundi.
After the building of Fort Jesus
Fort Jesus (Portuguese: ''Forte Jesus de Mombaça, Spanish: Fuerte de Jesús'') is a fort located on Mombasa Island. Designed by Italian Giovanni Battista Cairati, it was built between 1593 and 1596 by order of King Felipe II of Castille, ...
, Mombasa was put by the Portuguese under the rule of members of the ruling family of Malindi. In 1631 Dom Jeronimo the ruler of Mombasa slaughtered the Portuguese garrison in the city and defeated the relief force sent by the Portuguese. In 1632 Dom Jeronimo left Mombasa and became a pirate. That year the Portuguese returned and established direct rule over Mombasa.
Omani rule
With the capture of Fort Jesus in 1698, the town came under the influence of theImamate of Oman
The Imamate of Oman ( ar, إِمَامَة عُمَان, Imāmat ʿUmān, links=no) refers to a historical state within the ''Oman proper'' ( ar, عُمَان ٱلْوُسْطَى, ʿUmān al-Wusṭā) in the present-day Al Hajar Mountains in ...
, subordinate to the Omani rulers on the island of Unguja
Unguja (also referred to as "Zanzibar Island" or simply "Zanzibar", in grc, Μενουθιάς, Menuthias – as mentioned in The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'') is the largest and most populated island of the Zanzibar archipelago, in Tanza ...
, prompting regular local rebellions. Oman appointed three consecutive Governors (Wali in Arabic, Liwali in Swahili):
*12 December 1698 – December 1698: Imam Sa'if ibn Sultan
*December 1698 – 1728: Nasr ibn Abdallah al-Mazru'i
*1728–12 March 1728: Shaykh Rumba
Mombasa was briefly returned to Portuguese rule by captain-major Álvaro Caetano de Melo Castro (12 March 1728 – 21 September 1729), then four new Omani Liwali until 1746, when the last of them made it independent again (disputed by Oman), as the first of its recorded Sultans:
*1746–1755: 'Ali ibn Uthman al-Mazru'i
*1755–1773: Masud ibn Nasr al-Mazru'i
*1773–1782: Abdallah ibn Muhammad al-Mazru'i
*1782–1811: Ahmad ibn Muhammad al-Mazru'i (born 17–died 1814)
*1812–1823: 'Abdallah ibn Ahmad al-Mazru'i (died 1823)
*1823–1826: Sulayman ibn 'Ali al-Mazru'i
 From 9 February 1824 to 25 July 1826, there was a
From 9 February 1824 to 25 July 1826, there was a British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its int ...
over Mombasa, represented by governors. Omani rule was restored in 1826; seven where appointed. On 24 June 1837, it was nominally annexed by Said bin Sultan of Muscat and Oman
The Sultanate of Muscat and Oman ( ar, سلطنة مسقط وعمان, Salṭanat Masqaṭ wa-‘Umān), also known briefly as the State of Muscat and Oman () during the rule of Taimur bin Feisal, was a sovereign state that encompassed the prese ...
.
British rule and independence
On 25 May 1887 Mombasa was relinquished to the British East Africa Association, later theImperial British East Africa Company
The Imperial British East Africa Company (IBEAC) was a commercial association founded to develop African trade in the areas controlled by the British Empire. The company was incorporated in London on 18 April 1888 and granted a royal charter by Q ...
. It came under British administration in 1895.
It soon became the capital of the British East Africa Protectorate and the sea terminal of the Uganda Railway
The Uganda Railway was a metre-gauge railway system and former British state-owned railway company. The line linked the interiors of Uganda and Kenya with the Indian Ocean port of Mombasa in Kenya. After a series of mergers and splits, the li ...
, construction of which was started in 1896. Many workers were brought in from British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
to build the railway, and the city's fortunes revived. The Sultan of Zanzibar
The sultans of Zanzibar ( ar, سلاطين زنجبار) were the rulers of the Sultanate of Zanzibar, which was created on 19 October 1856 after the death of Said bin Sultan, who had ruled Oman and Zanzibar as the sultan of Oman since 1804. Th ...
formally presented the town to the British in 1898.
Mombasa became the capital of the Kenya Colony Protectorate of Kenya, sometime between 1887 and around 1906. The capital was later moved because medical officers warned that the ground was swampy, and urged Sir James Hayes Sadler
Colonel Sir James Hayes Sadler (21 May 1827 – 9 January 1910) was a British diplomat and civil servant.
Early life and education
Sadler was born to the Reverend James-Hayes Sadler (5 January 1785 – 26 August 1845) and Anne Sadler (née Ric ...
, then Commissioner of the East Africa Protectorate, to plead with London to move the town elsewhere to mitigate potential disease. Nairobi
Nairobi ( ) is the capital and largest city of Kenya. The name is derived from the Maasai phrase ''Enkare Nairobi'', which translates to "place of cool waters", a reference to the Nairobi River which flows through the city. The city proper h ...
has since been Kenya's capital to date.
The Mombasa tusks
The Mombasa tusks, also referred to as Mapemba ya Ndovu or Pembe za Ndovu ( Swahili for ''elephant tusks''), form a monument over Moi Avenue, a major thoroughfare in Mombasa, Kenya. Built in the 1950s to commemorate visits by the British royal f ...
, one of the city's best-known monuments, were originally constructed in 1952 by the British administration of the Kenya Colony
The Colony and Protectorate of Kenya, commonly known as British Kenya or British East Africa, was part of the British Empire in Africa. It was established when the former East Africa Protectorate was transformed into a British Crown colony in ...
, commemorating the visit of Queen Elizabeth II to the city.
In 2018, as part of an effort to increase tourism, Mombasa County Governor Hassan Joho issued a directive requiring that all buildings in the Old Town and the Central Business District be painted white with Egyptian blue
Egyptian blue, also known as calcium copper silicate (CaCuSi4O10 or CaOCuO(SiO2)4 (calcium copper tetrasilicate)) or cuprorivaite, is a pigment that was used in ancient Egypt for thousands of years. It is considered to be the first synthetic pi ...
trim and banned all signs from their walls or canopies. Transport, Infrastructure and Public Works County Executive Tawfiq Balala stated that the city wanted to be "the most photographed in Africa."
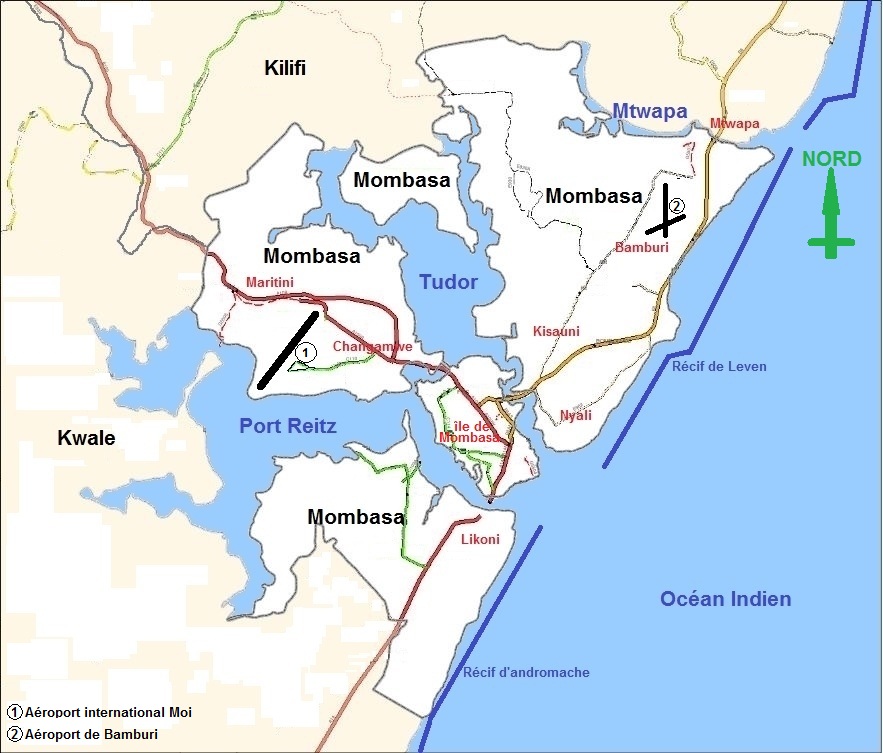
Geography
 Being a coastal town, Mombasa is characterised by a flat topography. The town of Mombasa is centred on Mombasa Island, but extends to the mainland. The island is separated from the mainland by two creeks, Port Reitz in the south and
Being a coastal town, Mombasa is characterised by a flat topography. The town of Mombasa is centred on Mombasa Island, but extends to the mainland. The island is separated from the mainland by two creeks, Port Reitz in the south and Tudor Creek
Tudor Creek is one of two main water bodies separating Mombasa Island (and the city of Mombasa) from the Kenyan mainland (the other body being Kilindini Harbour).
Before the estuary into the Indian Ocean, the tidal creek passes under the Ny ...
in the north.
Climate
Mombasa has atropical wet and dry climate
Tropical savanna climate or tropical wet and dry climate is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification categories ''Aw'' (for a dry winter) and ''As'' (for a dry summer). The driest month has less than of p ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
: ''As''). The amount of rainfall essentially depends on the season. The rainiest months are April and May, while rainfall is minimal between January and February.
Located near the equator, Mombasa has only a slight seasonal temperature variation, with high temperatures ranging .
As a seaport, Mombasa is subject to detrimental consequences of a fluctuating climate. In October 2006, Mombasa experienced a large flood that affected 60,000 people.
Like the rest of Kenya, climate change is already creating challenges for the city: coastal erosion
Coastal erosion is the loss or displacement of land, or the long-term removal of sediment and rocks along the coastline due to the action of waves, currents, tides, wind-driven water, waterborne ice, or other impacts of storms. The landwa ...
has become a problem for infrastructure in Mombasa. Due to rising sea levels, the coastline has been eroding at per year. This has increased the number of annual floods.
Suburbs
Mombasa is located onMombasa Island
Mombasa Island is a coral outcrop located on Kenya's coast on the Indian Ocean, which is connected to the mainland by a causeway. Part of the city of Mombasa is located on the island, including the Old Town.
History
The old town of Mombasa is ...
and sprawls to the surrounding mainlands. The island is separated from the mainland by two creeks: Tudor Creek
Tudor Creek is one of two main water bodies separating Mombasa Island (and the city of Mombasa) from the Kenyan mainland (the other body being Kilindini Harbour).
Before the estuary into the Indian Ocean, the tidal creek passes under the Ny ...
and Kilindini Harbour
Kilindini Harbour is a large, natural deep-water inlet extending inland from Mombasa, Kenya. It is at its deepest center, although the controlling depth is the outer channel in the port approaches with a dredged depth of . It serves as the harbo ...
. It is connected to the mainland to the north by the Nyali Bridge, to the south by the Likoni Ferry, and to the west by the Makupa Causeway, alongside which runs the Kenya-Uganda Railway
The Uganda Railway was a metre-gauge railway system and former British state-owned railway company. The line linked the interiors of Uganda and Kenya with the Indian Ocean port of Mombasa in Kenya. After a series of mergers and splits, the lin ...
. The port serves both Kenya and countries of the interior, linking them to the ocean. The city is served by Moi International Airport located in the northwest mainland suburb of Chaani.
Mombasa Island
 Mombasa CBD
Mombasa CBD
 Kizingo: Considered the prime residential area of Mombasa. The State House of Mombasa, Provincial Headquarters, The Mombasa Law Courts, and the Municipal Council are located in Kizingo. The Aga Khan Academy, Aga Khan High School, Serani Primary School, Serani High School, Santokben Nursery School, Coast Academy, Jaffery Academy, Mombasa Primary School, Loreto Convent, Mama Ngina Girls' High School and the Government Training Institute (GTI) Mombasa are all in Kizingo as well.
Central Business District: The Mombasa central business district across the TSS building roundabout, Moi Avenue, and Nyerere Avenue is densely populated. Organizations such as the Kenya Revenue Authority (KRA) and businesses such as Banks (ABSA, I&M Ltd, Bank of India Ltd), Insurance Firms (Nomura Insurance Brokers, Masumali Meghji Insurance), and Audit Firms (Anant Bhatt LLP, Pricewaterhouse Coopers LLP, Mazars LLP, Deloitte LLP, and PKF LLP) are located here.
Kibokoni: Part of Old Town with Swahili architecture. Fort Jesus is in Baghani.
Englani: Part of Old town between Kibokoni and Makadara.
Kuze: Part of Old Town with Swahili culture and architecture. Originally flourishing with Swahili people but currently becoming a more cosmopolitan neighbourhood.
Makadara: Part of Old Town consisting of a high number of descendants of Baluchi former soldiers who settled within this area before it developed into a town. The name is derived from the Arabic words "Qadru r-Rahman" meaning "Decree of (God) the Merciful".
Ganjoni: Primarily a middle class residential, home of second biggest dry dock of Africa after the one in South Africa.
Tudor: Another middle class residential area with homes and shops. The
Kizingo: Considered the prime residential area of Mombasa. The State House of Mombasa, Provincial Headquarters, The Mombasa Law Courts, and the Municipal Council are located in Kizingo. The Aga Khan Academy, Aga Khan High School, Serani Primary School, Serani High School, Santokben Nursery School, Coast Academy, Jaffery Academy, Mombasa Primary School, Loreto Convent, Mama Ngina Girls' High School and the Government Training Institute (GTI) Mombasa are all in Kizingo as well.
Central Business District: The Mombasa central business district across the TSS building roundabout, Moi Avenue, and Nyerere Avenue is densely populated. Organizations such as the Kenya Revenue Authority (KRA) and businesses such as Banks (ABSA, I&M Ltd, Bank of India Ltd), Insurance Firms (Nomura Insurance Brokers, Masumali Meghji Insurance), and Audit Firms (Anant Bhatt LLP, Pricewaterhouse Coopers LLP, Mazars LLP, Deloitte LLP, and PKF LLP) are located here.
Kibokoni: Part of Old Town with Swahili architecture. Fort Jesus is in Baghani.
Englani: Part of Old town between Kibokoni and Makadara.
Kuze: Part of Old Town with Swahili culture and architecture. Originally flourishing with Swahili people but currently becoming a more cosmopolitan neighbourhood.
Makadara: Part of Old Town consisting of a high number of descendants of Baluchi former soldiers who settled within this area before it developed into a town. The name is derived from the Arabic words "Qadru r-Rahman" meaning "Decree of (God) the Merciful".
Ganjoni: Primarily a middle class residential, home of second biggest dry dock of Africa after the one in South Africa.
Tudor: Another middle class residential area with homes and shops. The Technical University of Mombasa
Technical University of Mombasa (TUM) is a public university located in the coastal city of Mombasa, Kenya Tudor, along Tom Mboya avenue. It is amongst the oldest institution of higher learning in Kenya. It is one of the National Polytechnics ...
(TUM) is situated in this neighbourhood.
North Coast
Nyali
Nyali is a residential area and Sub-County within Mombasa City, located on the mainland north of Mombasa County. It is connected to Mombasa Island by the New Nyali Bridge.
Nyali is known for its many high-class hotels and residential houses, m ...
, also considered a prime and up-market residential area, it is on the mainland north of the island and is linked by the New Nyali Bridge. It has numerous beach front hotels in the area known as the "North Coast". Nyali has two distinct sections – the upmarket Old Nyali and the upcoming New Nyali. For many residents, Nyali has now become a self-contained residential area, with two Nakumatts, a multiplex cinema, shopping malls, banks, schools and post offices. This often eliminates the need for residents to cross the bridge and to go into the congested Mombasa city centre. Nyali is home for the Nyali Cinemax complex, Mamba Village, the Nyali Golf Club, and some of the most prestigious academic institutions of the Coast Province.
Kongowea is a densely populated area with 15 villages, two sub-locations and an estimated population of 106,180 residents. Kongowea is a cosmopolitan settlement mainly inhabited by people from mainland who migrated into the city in search of employment, mainly in service and manufacturing sector. The area is adjacent to the rich suburb of Nyali which employs a portion of the village residents. They are mainly hired as cheap labour as watchmen, gardeners, masons for up coming houses and house help. The most well known villages inside Kongowea include Kisumu Ndogo, Shauri Yako and Mnazi Mmoja, despite being located in this prime area, many residents live under extreme conditions – poor sanitation, high crime rate and lack of basic essential amenities like schools, hospitals and tap water. Kongowea is also home to one of the largest open-air markets in the African Great Lakes.
Bamburi is an outlying township (fifteen minutes drive) along the Malindi road. It is home to Bamburi Cement factory, the largest cement plant in the East African region. Other notable features in the area are the Jomo Kenyatta public beach, commonly known as Pirates, and Haller Park, a nature trail and wildlife conservatory. Kiembeni Estate, also in the Bamburi area, hosts around 100,000 residents. The estate has its own supermarket, several retail shops, salons and boutiques, and a number of licensed drinking dens. The establishments include The Shilla Bar, Turkey Base, Stars Garden and Sensera pub. Kiembeni is arguably the largest estate in Mombasa, and growing even faster.
Other areas include, Shanzu, Mkomani, Bombolulu, Kisauni and, across the Mtwapa creek, the popular area of Mtwapa, which is already located in Kilifi county.
The North Coast has an entertainment industry which attracts locals and tourists.
South Coast
 Likoni: is a lower income and lower-middle-class neighbourhood connected to Mombasa Island by ferry. It is south of Mombasa Island and made up of mostly Swahili and non-Swahili Bantu tribes. The ferry was the target of the Likoni Riots of 1997.
Diani Beach: a beach resort area situated over the Likoni Ferry on the south coast of Mombasa. It is located some 36 km (22 miles) south of Mombasa city on the mainland coast and is a prime resort for many local and international tourists. Diani Beach has an airport at Ukunda town to cater for tourists who fly there directly from Nairobi Wilson or any other airports and airfields in the country.
Likoni: is a lower income and lower-middle-class neighbourhood connected to Mombasa Island by ferry. It is south of Mombasa Island and made up of mostly Swahili and non-Swahili Bantu tribes. The ferry was the target of the Likoni Riots of 1997.
Diani Beach: a beach resort area situated over the Likoni Ferry on the south coast of Mombasa. It is located some 36 km (22 miles) south of Mombasa city on the mainland coast and is a prime resort for many local and international tourists. Diani Beach has an airport at Ukunda town to cater for tourists who fly there directly from Nairobi Wilson or any other airports and airfields in the country.
Mombasa Mainland
 Magongo: is an outlying township 20 minutes driving distance northwest of Mombasa Island, situated on the Nairobi Highway. This fringe community lacks any effective electricity, water or sewer systems, with a general lack of infrastructure. Poverty, lack of sanitation, and unemployment continue to be the greatest issues for the Mikindani Township, which have ensured low health and safety standards for its residents. Poor, lower class housing is widespread, ranging from simple stone, two-storey structures to mud and earth homes fitted with corrugated iron roofs. Much of the community works outside of the township, within Mombasa Island itself as there is a lack of employment and industry. There are number of small health clinics, shops, and a few public primary schools: Nazarene primary is one school, which is known in particular as being staffed by a revolving volunteer teacher base from Western, and predominately English speaking nations. This small town serves as a link between the city and Moi International Airport. Magongo is also home to the Akamba Handicraft Cooperative.
Magongo: is an outlying township 20 minutes driving distance northwest of Mombasa Island, situated on the Nairobi Highway. This fringe community lacks any effective electricity, water or sewer systems, with a general lack of infrastructure. Poverty, lack of sanitation, and unemployment continue to be the greatest issues for the Mikindani Township, which have ensured low health and safety standards for its residents. Poor, lower class housing is widespread, ranging from simple stone, two-storey structures to mud and earth homes fitted with corrugated iron roofs. Much of the community works outside of the township, within Mombasa Island itself as there is a lack of employment and industry. There are number of small health clinics, shops, and a few public primary schools: Nazarene primary is one school, which is known in particular as being staffed by a revolving volunteer teacher base from Western, and predominately English speaking nations. This small town serves as a link between the city and Moi International Airport. Magongo is also home to the Akamba Handicraft Cooperative.
Mikindani
Mikindani (''Mji wa kale wa Mikindani'' in Swahili) is a historic coastal town located in Mtwara-Mikindani District of Mtwara Region in Tanzania. The name comes from the Swahili word ''mikinda'' which means "young coconut trees". Therefore the ...
, a suburban area: This is an outlying township on the mainland along the Nairobi Highway. It is built in the heavy industrial sections of Changamwe
Changamwe is a suburb of Mombasa, in Mombasa County, in the former Coast Province of Kenya.
Geography
The area is primarily industrial, with a number of modern concrete tower blocks housing residents. Industries include refineries and various ...
and mainly accommodate the working class who either work in the industries, the town centre on the Island and the Port at Kilindini harbour.
Miritini
Miritini is a suburb of Mombasa, Kenya. Located in the Changamwe Constituency, it had a population of 31,485 in data from 1999.
External linksMaplandia
Populated places in Coast Province
Mombasa County
{{CoastKE-geo-stub ...
: outlying township on the Mombasa Nairobi Highway which is first growing as a suburban area.
Changamwe
Changamwe is a suburb of Mombasa, in Mombasa County, in the former Coast Province of Kenya.
Geography
The area is primarily industrial, with a number of modern concrete tower blocks housing residents. Industries include refineries and various ...
: Industrial area which contains the Kipevu power generation projects, the Kenya Oil Refinery Company facility and housing estates such as Chaani and is the gateway to the Moi International Airport. The area has administrative offices of the D.O and the chiefs who serve the administrative division.
Migadini & Chaani: They are two adjacent estate that are located east of Airport road and east of Kenya Port Authority
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
. They are bordered by Port Reitz, Magongo and KPA
Port Reitz: Is a suburb on the mainland which contains a beach, oil refineries, housing estates etc. Moi International Airport and the Port Reitz District Hospital
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
are in Port Reitz.
Demography
 Mombasa city has a population of 1,208,333 per the 2019 census.
Mombasa has a cosmopolitan population, with the Swahili people and Mijikenda predominant. Other communities include the Akamba and Taita Bantus as well as a significant population of
Mombasa city has a population of 1,208,333 per the 2019 census.
Mombasa has a cosmopolitan population, with the Swahili people and Mijikenda predominant. Other communities include the Akamba and Taita Bantus as well as a significant population of Luo Luo may refer to:
Luo peoples and languages
*Luo peoples, an ethno-linguistic group of eastern and central Africa
**Luo people of Kenya and Tanzania or Joluo, an ethnic group in western Kenya, eastern Uganda, and northern Tanzania.
*** Luoland, th ...
and Luhya. Gusii, Agikuyu, peoples from Western Kenya. The major religions practised in the city are Christianity and Islam. Over the centuries, many immigrants and traders have settled in Mombasa, particularly from the Middle East and South Asia.
Economy

 Mombasa is an important economic centre in Kenya. In addition to the coffee trade, the food and chemical industries, there is a steel mill, an aluminum rolling mill, an oil refinery and a cement plant. The city is home to the most important seaport in East Africa, Kilindini Harbor, which is also used by the neighboring countries Tanzania and Uganda for their imports and exports.
''Kilindini'' is an old Swahili term meaning "deep". The port is so-called because the channel is naturally very deep. Kilindini Harbour is an example of a natural geographic phenomenon called a
Mombasa is an important economic centre in Kenya. In addition to the coffee trade, the food and chemical industries, there is a steel mill, an aluminum rolling mill, an oil refinery and a cement plant. The city is home to the most important seaport in East Africa, Kilindini Harbor, which is also used by the neighboring countries Tanzania and Uganda for their imports and exports.
''Kilindini'' is an old Swahili term meaning "deep". The port is so-called because the channel is naturally very deep. Kilindini Harbour is an example of a natural geographic phenomenon called a ria
A ria (; gl, ría) is a coastal inlet formed by the partial submergence of an unglaciated river valley. It is a drowned river valley that remains open to the sea.
Definitions
Typically rias have a dendritic, treelike outline although they ca ...
, formed at the end of the last glacial period when the sea level rose and engulfed a river that was flowing from the mainland.
Mombasa is a centre of coastal tourism in Kenya. Mombasa Island itself is not a main attraction, although many people visit the Old Town and Fort Jesus
Fort Jesus (Portuguese: ''Forte Jesus de Mombaça, Spanish: Fuerte de Jesús'') is a fort located on Mombasa Island. Designed by Italian Giovanni Battista Cairati, it was built between 1593 and 1596 by order of King Felipe II of Castille, ...
. The Nyali
Nyali is a residential area and Sub-County within Mombasa City, located on the mainland north of Mombasa County. It is connected to Mombasa Island by the New Nyali Bridge.
Nyali is known for its many high-class hotels and residential houses, m ...
, Bamburi, and Shanzu beaches are located north of the city. The Shelly, Tiwi, and Diani beaches are located south of Mombasa. Several luxury hotels exist on these beaches, while the less expensive hotels are located further away.
Mombasa's northern shoreline is renowned for its vibrant 24-hour entertainment offers, including both family entertainment (water parks, cinemas, bowling
Bowling is a target sport and recreational activity in which a player rolls a ball toward pins (in pin bowling) or another target (in target bowling). The term ''bowling'' usually refers to pin bowling (most commonly ten-pin bowling), thou ...
, etc.), sports (watersports
Water sports or aquatic sports are sport activities conducted on waterbodies, and can be categorized according to the degree of immersion by the participants.
On the water
* Boat racing, the use of powerboats to participate in races
* Boatin ...
, mountain biking and gokarting), culinary offers (restaurants offering a wide range of specialties from Kenya, China, Japan, India, Italy, Germany and other countries) and nightlife (bars, pubs, clubs, discothèques, etc.).
Other local industries include an oil refinery
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refined into useful products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, asphalt base, fuel oils, heating oil, kerosene, lique ...
with a capacity of a day,Mombasa Refinery – A Barrel Full. Abarrelfull.wikidot.com (8 December 2012). Retrieved on 17 August 2013. and a cement factory capable of producing over 1.1 million tons per year. The major intercontinental undersea telecom cables reach shore next to Mombasa, connecting the
African Great Lakes
The African Great Lakes ( sw, Maziwa Makuu; rw, Ibiyaga bigari) are a series of lakes constituting the part of the Rift Valley lakes in and around the East African Rift. They include Lake Victoria, the second-largest fresh water lake in th ...
to the rest of the world and supporting a fast-growing call centre
A call centre ( Commonwealth spelling) or call center ( American spelling; see spelling differences) is a managed capability that can be centralised or remote that is used for receiving or transmitting a large volume of enquiries by telephon ...
business in the area. The estimated real GDP growth for Kenya in 2016 is 5.7-6.0%. This growth will be in response to the construction of a railway system from Nairobi to Mombasa which will aid in trade and transportation between Kenya's two major cities.
Mombasa will become a Special Economic Zone (SEZ) in which certain industries such as tea, garments, and footwear will be exempt from certain taxes to promote domestic growth. This is in response to the deficiencies in Export Processing Zones (EPZ).
The Kenyan Dock Worker's Union is situated in Mombasa and has roughly 5,000 members.
President Kenyatta has made it a priority to deepen economic ties with Asia at the onset of his presidency. Japan has played a role in financially sponsoring the expansion of the Mombasa port in phase one and two of the expansion project.
At 44%, the rate of youth unemployment in Mombasa is more than double the national average of 21% (2016).
Transport
Air
 Moi International Airport is located in the city of Mombasa, and is the second largest airport in Kenya with daily flights to Nairobi and other Kenyan, European and Middle Eastern destinations. The airport also handles a large amount of air cargo through its freight terminal.
Moi International Airport is located in the city of Mombasa, and is the second largest airport in Kenya with daily flights to Nairobi and other Kenyan, European and Middle Eastern destinations. The airport also handles a large amount of air cargo through its freight terminal.



Rail
Mombasa currently has a modern railway station on the Mombasa–Nairobi Standard Gauge Railway that replaced thenarrow-gauge
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge narrower than standard . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and .
Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with tighter curves, smaller structu ...
Uganda Railway
The Uganda Railway was a metre-gauge railway system and former British state-owned railway company. The line linked the interiors of Uganda and Kenya with the Indian Ocean port of Mombasa in Kenya. After a series of mergers and splits, the li ...
completed in 1901 under British colonial rule. Completed in 2017 and located at Miritini
Miritini is a suburb of Mombasa, Kenya. Located in the Changamwe Constituency, it had a population of 31,485 in data from 1999.
External linksMaplandia
Populated places in Coast Province
Mombasa County
{{CoastKE-geo-stub ...
, the Mombasa Terminus
Mombasa Terminus is a terminus of the Mombasa–Nairobi Standard Gauge Railway in Kenya located in Miritini, a suburb of Mombasa. The station building is made up of concentric circles and a central tower, representing a ripple in the ocean.
Tw ...
station links Mombasa to Nairobi. The station, situated about 20 kilometers from the city centre, is accessible through the newly built (2018) highway, being the first phase of the Dongo Kundu bypass. Kenya Railways transports passengers and cargo through the Standard Gauge Railway between Nairobi to Mombasa.
Road
Driving in Mombasa is straightforward and the majority of the roads are tarmacked. The Mombasa–Nairobi Expressway connects Mombasa to the capital city Nairobi. Within Mombasa, most local people use ''matatu
In Kenya matatu or matatus (known as mathree in Sheng) are privately owned minibuses used as share taxis. Often decorated, many ''matatu'' feature portraits of famous people or slogans and sayings. Likewise, the music they play is also aimed ...
s'' (mini-buses) which are extremely common in Kenya, to move around the city and its suburbs. The ''tuk-tuk
An auto rickshaw is a motorized version of the pulled rickshaw or cycle rickshaw. Most have three wheels and do not tilt. They are known by many terms in various countries including auto, auto rickshaw, baby taxi, mototaxi, pigeon, jonnybee, bajaj ...
''—a motor vehicle with three wheels—is widely used as transport around the city and its suburbs. No more than three passengers may be carried. A ''boda-boda
Boda bodas are bicycles and motorcycle taxis commonly found in East Africa. While motorcycle taxis like boda bodas are present throughout Africa and beyond, the term ''boda boda'' is specific to East Africa. In Kenya, they are more frequently c ...
'' is originally a bicycle taxi but have long since been replaced by motorcycles.
Sea
The port of Mombasa is the largest in East Africa, with 19 deep water berths with two additional berths nearing completion and two oil terminals.Home. Kpa.co.ke. Retrieved on 17 August 2013. The port is connected by rail and road to the interior. At present there is little or no scheduled passenger service from the port, however, international cruise ships frequent the port. The port is part of the
21st Century Maritime Silk Road
The 21st Century Maritime Silk Road (Chinese: 21世纪海上丝绸之路), commonly just Maritime Silk Road (MSR), is the sea route part of the Belt and Road Initiative which is a Chinese strategic initiative to increase investment and foster coll ...
that runs from the Chinese coast to the Upper Adriatic region. In connection with the Silk Road Initiative, China has started infrastructure development projects in Kenya and is building roads, railways and public buildings on credit.KPA. KPA. Retrieved on 17 August 2013.
Ferry
ferries
A ferry is a ship, watercraft or amphibious vehicle used to carry passengers, and sometimes vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A passenger ferry with many stops, such as in Venice, Italy, is sometimes called a water bus or water tax ...
operated by the Kenya Ferry Service from Kilindini and Mtongwe to Likoni in the south coast of Mombasa. The last major accident occurred in 1994 when a ferry serving Mtongwe route sank killing more than 270 people.
As a result of the increase in more luxurious hotels along the south coast and a lack of a direct bridge linking with Mombasa island, visiting tourists have the option of flying directly from Nairobi into the South Coast airstrip at Ukunda.
The Dongo Kundu Bypass Highway is currently (2018) under construction. With a total of three bridges, it will finally connect the mainland to the south coast easing the burden on the ferry services. Mombasa Gate Bridge will connect the mainland to likoni,this will eliminate the usage of the unsafe ferry which has claimed hundreds of lives.
Education
The major university in the island is theTechnical University of Mombasa
Technical University of Mombasa (TUM) is a public university located in the coastal city of Mombasa, Kenya Tudor, along Tom Mboya avenue. It is amongst the oldest institution of higher learning in Kenya. It is one of the National Polytechnics ...
.
The city has a campus of Kenyatta University
Kenyatta University (KU) is a public research university with its main campus in Nairobi County, Kenya. It acquired the status of university in 1985, being the third university after University of Nairobi (1970) and Moi University (1984). As of ...
.
Other major university campuses include University of Nairobi-Mombasa campus, Mount Kenya University-Mombasa campus, JKUAT-Mombasa, Shanzu Teachers Training College, Mombasa Technical College, Bandari college, Utalii college, and ICS college Mombasa.
Places of worship
Anglican Church of Kenya
The Anglican Church of Kenya (ACK) is a province of the Anglican Communion, and it is composed by 41 dioceses. The current Primate and Archbishop of Kenya is Jackson Ole Sapit. The Anglican Church of Kenya claims 5 million total members. Accordi ...
(Anglican Communion
The Anglican Communion is the third largest Christian communion after the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches. Founded in 1867 in London, the communion has more than 85 million members within the Church of England and other ...
), with Mombasa Anglican Cathedral Church as the main church
*Presbyterian Church of East Africa
Presbyterian Church of East Africa (PCEA) is a Presbyterian denomination headquartered in Nairobi, Kenya. In Kenya, 10% of the population is Presbyterian. It was started by missionaries from Scotland, most notable of whom was Dr John Arthur. I ...
*(World Communion of Reformed Churches
The World Communion of Reformed Churches (WCRC) is the largest association of Calvinist churches in the world. It has 230 member denominations in 108 countries, together claiming an estimated 80 million people, thus being the fourth-largest Chris ...
),
* Baptist Convention of Kenya (Baptist World Alliance
The Baptist World Alliance (BWA) is the largest international Baptist organization with an estimated 51 million people in 2022 with 246 member bodies in 128 countries and territories. A voluntary association of Baptist churches, the BWA account ...
),
* Assemblies of God.
There are also many Hindu Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
temples and Muslim mosques.
A large number of Hindus visit Mombasa to pray at a number of naturally formed Lingam
A lingam ( sa, लिङ्ग , lit. "sign, symbol or mark"), sometimes referred to as linga or Shiva linga, is an abstract or aniconic representation of the Hindu god Shiva in Shaivism. It is typically the primary '' murti'' or devotional ...
that have formed in the Nyali
Nyali is a residential area and Sub-County within Mombasa City, located on the mainland north of Mombasa County. It is connected to Mombasa Island by the New Nyali Bridge.
Nyali is known for its many high-class hotels and residential houses, m ...
beach Gombeshwar Caves. According to local folklore, the cave-temple was found a long time ago when a group of local herders were puzzled after they noticed that one of their cows regularly released all of her milk at a specific yet random spot on the hills. They are then said to have approached some Hindu families living in the area to ask if they had any idea behind the strange behaviour by the cow. The group then teamed up, made their way to the spot and started digging. That is how they ended up stumbling into the cave where they found a 'Shiva Lingam
A lingam ( sa, लिङ्ग , lit. "sign, symbol or mark"), sometimes referred to as linga or Shiva linga, is an abstract or aniconic representation of the Hindu god Shiva in Shaivism. It is typically the primary '' murti'' or devotional ...
' – an abstract representation of the Hindu God Lord Shiva, whose vehicle is Nandi (mythology)
Nandi ( sa, नन्दि), also known as Nandikeshwara or Nandideva, is the bull vahana of the Hindu god Shiva. He is also the guardian deity of Kailash, the abode of Shiva. Almost all Shiva temples display stone-images of a seated Nandi, ...
. Hindus worship Lord Shiva by offering milk to a Lingam
A lingam ( sa, लिङ्ग , lit. "sign, symbol or mark"), sometimes referred to as linga or Shiva linga, is an abstract or aniconic representation of the Hindu god Shiva in Shaivism. It is typically the primary '' murti'' or devotional ...
.
List of Hindu Temples in Mombasa:
*Hindu Union of Mombasa
The Hindu Union of Mombasa is one of Kenya's oldest Hindu organisation, which is based out of the port city of Mombasa.
History
The Hindu Union was formed in 1899 after a group of emigrated Gujarati Indians decided to walk village-to-village ...
- Shivalaay (Makadara)
*Hindu Union of Mombasa
The Hindu Union of Mombasa is one of Kenya's oldest Hindu organisation, which is based out of the port city of Mombasa.
History
The Hindu Union was formed in 1899 after a group of emigrated Gujarati Indians decided to walk village-to-village ...
- Gombeshwar (Nyali)
*Shree Ganesha Temple - Nyali
*Shree Ramdev Pir Temple - Nyali
*Shree Dwarikadham Hare Krishna Temple (ISKON) - Nyali
*Shree BAPS Swaminarayan Temple - Mombasa Mainland
*Shree Gayatri Brahm Samaj Temple - Mombasa Mainland
*Shree Cutch Satsang Swaminarayan Temple - Mombasa Mainland
*Shree Radhe-Krishna Makupa Temple - Mombasa Mainland
*Shree Vishwakarma Temple - Mombasa Mainland
Other temples within Mombasa include the Sikh Shree Guru Gobind Singh Sabha Temple, and the Shree Parshva Vallabh Jain Temple
Culture
 A major cultural hub in
A major cultural hub in Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
...
and the African Great Lakes
The African Great Lakes ( sw, Maziwa Makuu; rw, Ibiyaga bigari) are a series of lakes constituting the part of the Rift Valley lakes in and around the East African Rift. They include Lake Victoria, the second-largest fresh water lake in th ...
, Mombasa's proximity to Zanzibar
Zanzibar (; ; ) is an insular semi-autonomous province which united with Tanganyika in 1964 to form the United Republic of Tanzania. It is an archipelago in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of the mainland, and consists of many small islan ...
, Nairobi
Nairobi ( ) is the capital and largest city of Kenya. The name is derived from the Maasai phrase ''Enkare Nairobi'', which translates to "place of cool waters", a reference to the Nairobi River which flows through the city. The city proper h ...
and the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
, as well as its large shipping and maritime industries gives it a diverse mosaic of cultures. Music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspe ...
is a main feature of Mombasa's culture.
Music
Taarab
Taarab is a music genre popular in Tanzania and Kenya. It is influenced by the musical traditions of the African Great Lakes, North Africa, the Middle East, and the Indian subcontinent. Taarab rose to prominence in 1928 with the advent of the ...
music, which originates from Zanzibar
Zanzibar (; ; ) is an insular semi-autonomous province which united with Tanganyika in 1964 to form the United Republic of Tanzania. It is an archipelago in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of the mainland, and consists of many small islan ...
, has a prominent local presence.Taraab Music : National Geographic World Music. Worldmusic.nationalgeographic.com (17 October 2002). Retrieved on 17 August 2013. Styles of music native to Mombasa include the smooth and mellow Bango, fast-paced
Chakacha Chakacha is a traditional music and dance style (a ''ngoma'') of the Swahili people of coastal Kenya and Tanzania, originally associated with weddings and performed and watched by women. In the late 20th century, musical groups such as Mombasa Root ...
and traditional Mwanzele.
Musicians of note are Mombasa Roots, Safari Sounds, Them Mushrooms
Them Mushrooms is a musical band from Kenya, playing mostly Chakacha, some Benga and also some reggae. They are most famous for the Swahili 1982 song ''Jambo Bwana''. The band is composed of Teddy Kalanda, Henry Ndenge Saha and Ben Mutwiwa. T ...
, Prof Juma Bhalo, Maulidi Juma, Zuhura Swaleh, Zein Alabdin and Princess Farida. Mombasa has been the home or base for former greats like Fundi Konde, known for his song "Tausi"; Fadhili Williams and Grand Charo, famous for the song "Malaika"; Sal Davies; Malika Mohammed; Stara Butte; Juma Bhalo. Contemporary hip-hop fusion artistes are Susumila, Majizee, Nyota Ndogo, Cannibal (musician), Sharama and Ukoo Flani super group which once could boast up to 40 rappers.
Recently, hip hop, reggae
Reggae () is a music genre that originated in Jamaica in the late 1960s. The term also denotes the modern popular music of Jamaica and its diaspora. A 1968 single by Toots and the Maytals, " Do the Reggay" was the first popular song to use ...
, soul
In many religious and philosophical traditions, there is a belief that a soul is "the immaterial aspect or essence of a human being".
Etymology
The Modern English noun '' soul'' is derived from Old English ''sāwol, sāwel''. The earliest atte ...
, blues, salsa and (among the Indian community) bhangra have become popular, especially amongst the youth. Mombasa is mainly a tourism centre populated by hundreds of entertainment spots of all categories from night clubs, bars, hotels, fancy restaurants and many more. It has the most vibrant night life in Kenya catering to the mainly tourist population.
Sports
Currently, Mombasa is represented in theKenyan Premier League
The Kenyan Premier League (KPL), officially known as the FKF Premier League and as the BetKing Premier League (BPL) for sponsorship reasons, is a professional league for men's association football clubs in Kenya. Standing at the top of the Kenyan ...
by Bandari F.C, which plays at the Mbaraki Sports Grounds. Also, the Congo United FC, Promoted and dropped in 2011, are in the second tier Nationwide Super League with 4 other hometown clubs – Admiral F.C.; Magongo Rangers; Sparki Youth and Coast United. Derbies between Mombasa teams have become intriguing affairs recently. Another team, Coast Stars
Coast Stars is a Kenyan football club based in Mombasa. The club was founded in 1998. They are a member of the top division in Kenyan football. Their home stadium is Mombasa Municipal Stadium. They played the 2004/05 season under the name Dubai ...
, were relegated several years ago from the league. The only Mombasa-based team to win the league is Feisal F.C., the 1965 champions. Kiziwi leopards was a popular team in the 1980s as was Mombasa Wanderers decades before. There are several cricket teams in Mombasa; one is Mombasa Sports Club
Mombasa Sports Club (MSC) is multi-sport club based in Mombasa, Kenya. It also owns sporting facilities. The club was established in 1896, and it is among the oldest sporting clubs in Kenya.
Cricket
Mombasa Sports Club has a cricket team takin ...
(MSC), whose ground was given ODI status in 2006. MSC has also a rugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand. In it ...
team playing in the Kenya Cup
The Kenya Cup is the top tier club rugby union competition in Kenya organized by the Kenya Rugby Union. For the 2019-2020 season, twelve teams are divided into two pools of six, Each team plays home and away against each team in its pool and on ...
League, the premier rugby competition in Kenya. Mvita XI men and MSC ladies represent Mombasa in Kenyan field hockey leagues.
Mombasa is represented in the nationwide rugby league by Mombasa RFC. The city is also host to a leg of the national rugby sevens circuit, being one of only six city hosts. The Mombasa leg is referred to as the Driftwood sevens, and the annual tournament is extremely popular, attracting thousands of fans from across the country.
The 2007 World Cross Country Championships were held in Mombasa. Mombasa Marathon
The Mombasa International Marathon (formerly known as the Mombasa Marathon) is an annual marathon hosted in Mombasa, Kenya. Currently sponsored by County Government of Mombasa and Safaricom
Safaricom PLC is a listed Kenyan mobile network ope ...
is competed annually in Mombasa. The town also hosts the biennial classic edition of Safari Rally
The Safari Rally is a rally held in Kenya. It was first held in 1953 as a celebration of the coronation of Queen Elizabeth II. The event was part of the World Rally Championship from 1973 until 2002, before returning in 2021. It is historically r ...
and annually a Kenya National Rally Championship round.
Scuba diving takes place mostly within the Mombasa Marine National Park and Reserve, which is managed and maintained by Kenya Wildlife Service
Kenya Wildlife Service is a state corporation under the Ministry of Tourism and Wildlife established by an act of Parliament; Wildlife Conservation and Management Act CAP 376, of 1989, now repealed and replaced by the Wildlife Conservation and Ma ...
. The park has a length of about .
Twin towns – sister cities
Mombasa is twinned with: *Durban
Durban ( ) ( zu, eThekwini, from meaning 'the port' also called zu, eZibubulungwini for the mountain range that terminates in the area), nicknamed ''Durbs'',Ishani ChettyCity nicknames in SA and across the worldArticle on ''news24.com'' from ...
, South Africa (2012)
* Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kon ...
, China (2018)
* Honolulu
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the island ...
, United States (2008)
* Long Beach
Long Beach is a city in Los Angeles County, California. It is the 42nd-most populous city in the United States, with a population of 466,742 as of 2020. A charter city, Long Beach is the seventh-most populous city in California.
Incorporate ...
, United States (2007)
* Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in both the state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest regio ...
, United States (1981)
Notable people
During its history, Mombasa was visited by numerous pioneers of the maritime exploration, such as the Arabs Al Idrissi (1151) and Ibn Battuta (1330) or the Portuguese Vasco da Gama (1498),Pedro Álvares Cabral
Pedro Álvares Cabral ( or ; born Pedro Álvares de Gouveia; c. 1467 or 1468 – c. 1520) was a Portuguese nobleman, military commander, navigator and explorer regarded as the European discoverer of Brazil. He was the first human in ...
(1500) João da Nova
João da Nova ( gl, Xoán de Novoa, Joam de Nôvoa; es, Juan de Nova; ; born c. 1460 in Maceda, Ourense, Galicia; died July 16, 1509 in Kochi, India) was a Portuguese-Galician explorer of the Atlantic and Indian Oceans at the service of Portuga ...
(1505) and Afonso de Albuquerque (1507).
* Abdilatif Abdalla, writer, university professor and political protestor
* Karen Blixen, Danish novelist
* Mercedes Iman Diamond, drag queen and contestant on the eleventh season of ''RuPaul's Drag Race
''RuPaul's Drag Race'' is an American reality competition television series, the first in the ''Drag Race'' franchise, produced by World of Wonder for Logo TV (season 1–8), WOW Presents Plus, VH1 (season 9–14) and, beginning with the f ...
''
* Timothy R. McClanahan, marine ecologist who lived and has worked in Mombasa since 1991
* Swaleh Nguru, Arab businessman, conservationist and philanthropist
* Thomas Risley Odhiambo, entomologist
* Ayub Ogada, musician, singer and composer known for having composed two songs for the movie ''The Constant Gardener
''The Constant Gardener'' is a 2001 novel by British author John le Carré. The novel tells the story of Justin Quayle, a British diplomat whose activist wife is murdered. Believing there is something behind the murder, he seeks to uncover the t ...
''
* Fadhili William, musician, singer, and composer
Gallery
Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
temple in Nyali
File:Tusks in City of Mombasa.jpg, The Mombasa tusks
The Mombasa tusks, also referred to as Mapemba ya Ndovu or Pembe za Ndovu ( Swahili for ''elephant tusks''), form a monument over Moi Avenue, a major thoroughfare in Mombasa, Kenya. Built in the 1950s to commemorate visits by the British royal f ...
, on Moi Avenue
In popular culture
Mombasa is the subject of the popular song and music video of the same name, "Mombasa" by '' Jabali Afrika'' feat. ''Jason Dunford
Jason Edward Dunford, OGW, OLY (born 28 November 1986), also known as Samaki Mkuu, is a Kenyan Olympic swimmer, media personality, rapper and entrepreneur. During his swimming career he was predominantly a butterfly and freestyle sprinter winni ...
'' aka Samaki Mkuu released on July 17, 2020.
In the film ''Out of Africa
''Out of Africa'' is a memoir by the Danish author Karen Blixen. The book, first published in 1937, recounts events of the seventeen years when Blixen made her home in Kenya, then called British East Africa. The book is a lyrical meditation on ...
'', Mombasa is the train destination as the seaport for voyages to Europe via the Suez Canal, and Mombasa is indicated as downriver ("This water must go home to Mombasa").
Mombasa is a pivotal setting in the highly popular ''Halo
Halo, halos or haloes usually refer to:
* Halo (optical phenomenon)
* Halo (religious iconography), a ring of light around the image of a head
HALO, halo, halos or haloes may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Video games
* ''Halo'' (franch ...
'' video game series. Mombasa appears as a major setting in ''Halo 2
''Halo 2'' is a 2004 first-person shooter game developed by Bungie and published by Microsoft Game Studios for the Xbox console. ''Halo 2'' is the second installment in the ''Halo'' franchise and the sequel to 2001's critically acclaimed '' ...
'', and the entirety of '' Halo 3: ODST'' takes place in Mombasa. The science fiction games are set in the year 2552, and the city has been divided into "Old Mombasa" and "New Mombasa" (a prosperous section filled with futuristic skyscrapers and an iconic orbital elevator
A space elevator, also referred to as a space bridge, star ladder, and orbital lift, is a proposed type of planet-to-space transportation system, often depicted in science fiction. The main component would be a cable (also called a tether) anc ...
). It is the capital of the fictional East Africa Protectorate. The city comes under attack by humanity's alien adversaries, " The Covenant", who focus their planetary invasion in and around Mombasa in search of a massive, technologically advanced artifact buried nearby.
Mombasa is featured in the 2010 movie, ''Inception
''Inception'' is a 2010 science fiction action film written and directed by Christopher Nolan, who also produced the film with Emma Thomas, his wife. The film stars Leonardo DiCaprio as a professional thief who steals information by infi ...
'', where Cobb meets Eames and Yusuf before the job takes place.
In the Warren Zevon
Warren William Zevon (; January 24, 1947 – September 7, 2003) was an American rock singer, songwriter, and musician.
Zevon's most famous compositions include "Werewolves of London", " Lawyers, Guns and Money", and " Roland the Headless Th ...
song " Roland the Headless Thompson Gunner", Mombasa is one of the key locales related to the protagonist's quest.
The Finnish pop hit "Mombasa
Mombasa ( ; ) is a coastal city in southeastern Kenya along the Indian Ocean. It was the first capital of the British East Africa, before Nairobi was elevated to capital city status. It now serves as the capital of Mombasa County. The town is ...
" (by Taiska) is about the city.
In the US, the Walt Disney World
The Walt Disney World Resort, also called Walt Disney World or Disney World, is an entertainment resort complex in Bay Lake and Lake Buena Vista, Florida, United States, near the cities of Orlando and Kissimmee. Opened on October 1, 1971, ...
resort recreated a Kenyan village in the Africa section of the Disney's Animal Kingdom theme park named "Harambe", which is modelled after Mombasa. The village features a store called the "Mombasa Marketplace".
In the Indian movie '' Mr. India'', Mombasa is mentioned in the popular song "Hawa Hawaii".
The Indian Bollywood movie Company was partly shot in Mombasa.
Most of the events in the 2017 story "Consummation in Mombasa" (by Andrei Gusev
Andrei Evgenievich Gusev (russian: link=no, Андрей Евгеньевич Гусев, born 27 October 1952) is a Russian writer and journalist. He is the author of 10 inventions, 23 published scientific works. One of his co-authors is a winne ...
) take place in Mombasa and in the nearest district Mtwapa.
'' One-Way Ticket to Mombasa (Menolippu Mombasaan)'' is a 2002 Finnish film directed by Hannu Tuomainen.
Popular blackgaze band Deafheaven
Deafheaven is an American post-metal band formed in 2010. Originally based in San Francisco, the group began as a two-piece with singer George Clarke and guitarist Kerry McCoy, who recorded and self-released a demo album together. Following i ...
titled the last song of its 2021 album, '' Infinite Granite'', with the name of the city. The lyrics make reference to the beaches and general uplifting scenery of Mombasa.
See also
* Ngomongo VillagesReferences
Bibliography
External links
Mombasa County Government
{{Authority control Populated coastal places in Kenya Populated places in Coast Province County capitals in Kenya Former British colonies and protectorates in Africa Former Portuguese colonies Mombasa County Port cities in Africa Port cities and towns of the Indian Ocean Swahili city-states 1824 establishments in the British Empire