Misery index (economics) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The misery index is an
The misery index is an
 Political economists Jonathan Nitzan and Shimshon Bichler found a negative correlation between a similar "stagflation index" and corporate amalgamation (i.e.
Political economists Jonathan Nitzan and Shimshon Bichler found a negative correlation between a similar "stagflation index" and corporate amalgamation (i.e.
U3
and the
CPI-U
from the
The current and historical Misery Index
The Misery Index by President
The Misery Index By Year
Cato Publications Commentary
Correlations of Misery Index and Consumer Sentiment
{{Poverty Political science theories Economic indicators Unemployment Inflation
 The misery index is an
The misery index is an economic indicator
An economic indicator is a statistic about an economic activity. Economic indicators allow analysis of economic performance and predictions of future performance. One application of economic indicators is the study of business cycles. Economic ...
, created by economist Arthur Okun. The index helps determining how the average citizen is doing economically and it is calculated by adding the seasonally adjusted unemployment rate
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the refere ...
to the annual inflation rate
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reductio ...
. It is assumed that both a higher rate of unemployment and a worsening of inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduct ...
create economic and social costs for a country.
Misery index by US presidential administration
Variations
Harvard EconomistRobert Barro
Robert Joseph Barro (born September 28, 1944) is an American macroeconomist and the Paul M. Warburg Professor of Economics at Harvard University. Barro is considered one of the founders of new classical macroeconomics, along with Robert Lucas, J ...
created what he dubbed the "Barro Misery Index" (BMI), in 1999. The BMI takes the sum of the inflation and unemployment rates, and adds to that the interest rate, plus (minus) the shortfall (surplus) between the actual and trend rate of GDP growth.
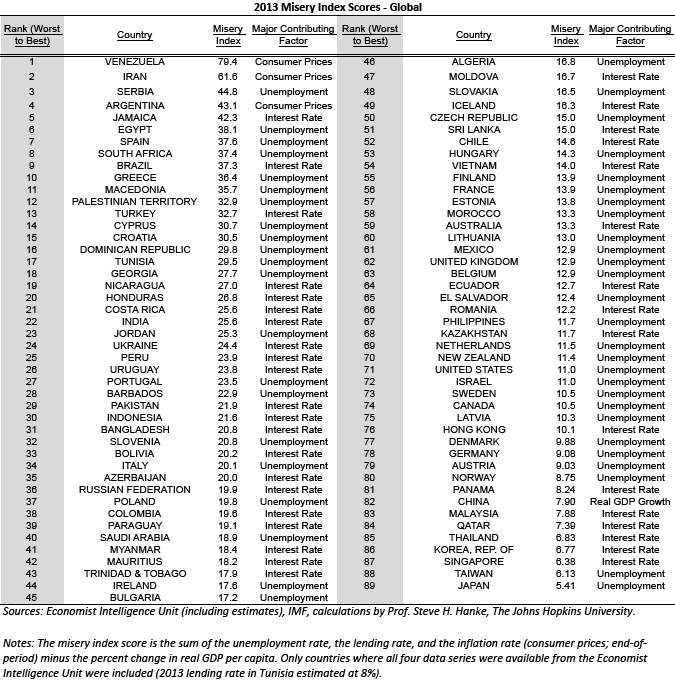
In the late 2000s, Johns Hopkins economist Steve Hanke built upon Barro's misery index and began applying it to countries beyond the United States. His modified misery index is the sum of the interest, inflation, and unemployment rates, minus the year-over-year percent change in per-capita GDP growth.
Hanke has recently constructed a World Table of Misery Index Scores by exclusively relying on data reported by the Economist Intelligence Unit. This table includes a list of 89 countries, ranked from worst to best, with data as of December 31, 2013 (see table below).
 Political economists Jonathan Nitzan and Shimshon Bichler found a negative correlation between a similar "stagflation index" and corporate amalgamation (i.e.
Political economists Jonathan Nitzan and Shimshon Bichler found a negative correlation between a similar "stagflation index" and corporate amalgamation (i.e. mergers and acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are business transactions in which the ownership of companies, other business organizations, or their operating units are transferred to or consolidated with another company or business organization. As an aspec ...
) in the United States since the 1930s. In their theory, stagflation is a form of political economic sabotage employed by corporations to achieve differential accumulation, in this case as an alternative to amalgamation when merger and acquisition opportunities have run out.
Hanke's 2020 Misery Index
Criticism
A 2001 paper looking at large-scale surveys in Europe and the United States concluded that unemployment more heavily influences unhappiness than inflation. This implies that the basic misery index underweights the unhappiness attributable to the unemployment rate: "the estimates suggest that people would trade off a 1-percentage-point increase in the employment rate for a 1.7-percentage-point increase in the inflation rate."Misery and crime
Some economists posit that the components of the Misery Index drive the crime rate to a degree. Using data from 1960 to 2005, they have found that the Misery Index and the crime rate correlate strongly and that the Misery Index seems to lead the crime rate by a year or so. In fact, the correlation is so strong that the two can be said to be cointegrated, and stronger than correlation with either the unemployment rate or inflation rate alone.Data sources
The data for the misery index is obtained fromunemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the refe ...
data published by the U.S. Department of Labor
The United States Department of Labor (DOL) is one of the United States federal executive departments, executive departments of the federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government. It is responsible for the administration of fede ...
U3
and the
Inflation Rate
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reductio ...
CPI-U
from the
Bureau of Labor Statistics
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics and statistics and serves as a principal agency of ...
. The exact methods used for measuring unemployment and inflation have changed over time, although past data is usually normalized so that past and future metrics are comparable.
See also
* Elder IndexReferences
External links
The current and historical Misery Index
The Misery Index by President
The Misery Index By Year
Cato Publications Commentary
Correlations of Misery Index and Consumer Sentiment
{{Poverty Political science theories Economic indicators Unemployment Inflation