Millbank Prison on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
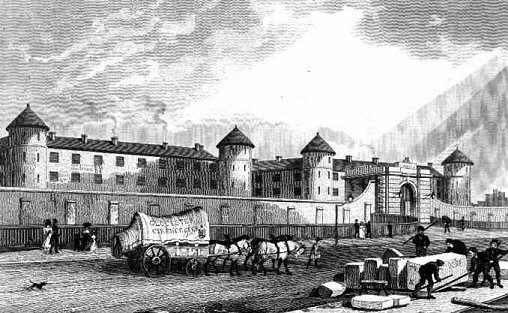 Millbank Prison or Millbank Penitentiary was a prison in
Millbank Prison or Millbank Penitentiary was a prison in
 The site at Millbank was originally purchased in 1799 from the
The site at Millbank was originally purchased in 1799 from the

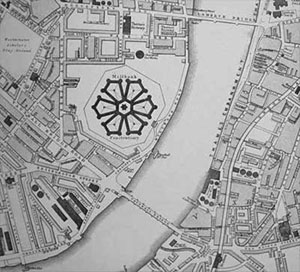 The plan of the prison comprised a circular chapel at the centre of the site, surrounded by a three-storey hexagon made up of the governor's quarters, administrative offices and laundries, surrounded in turn by six pentagons of cell blocks. The buildings of each pentagon were set around a cluster of five small courtyards (with a
The plan of the prison comprised a circular chapel at the centre of the site, surrounded by a three-storey hexagon made up of the governor's quarters, administrative offices and laundries, surrounded in turn by six pentagons of cell blocks. The buildings of each pentagon were set around a cluster of five small courtyards (with a
 As the prison was progressively demolished its site was redeveloped. The principal new buildings erected were the National Gallery of British Art (now
As the prison was progressively demolished its site was redeveloped. The principal new buildings erected were the National Gallery of British Art (now

 A large circular
A large circular
Collection of Victorian references
- the penitentiary is the distinctive six-pointed building near the bottom
Millbank Estate today
{{Prisons in London 1816 establishments in England Defunct prisons in London Former buildings and structures in the City of Westminster Demolished buildings and structures in London Buildings and structures demolished in 1903 19th century in London 1890 disestablishments in England Millbank Demolished prisons
 Millbank Prison or Millbank Penitentiary was a prison in
Millbank Prison or Millbank Penitentiary was a prison in Millbank
Millbank is an area of central London in the City of Westminster. Millbank is located by the River Thames, east of Pimlico and south of Westminster. Millbank is known as the location of major government offices, Burberry headquarters, the ...
, Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster.
The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, B ...
, London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
, originally constructed as the National Penitentiary, and which for part of its history served as a holding facility for convicted prisoners
A prisoner (also known as an inmate or detainee) is a person who is deprived of liberty against their will. This can be by confinement, captivity, or forcible restraint. The term applies particularly to serving a prison sentence in a prison.
...
before they were transported to Australia
Between 1788 and 1868, about 162,000 convicts were transported from Britain and Ireland to various penal colonies in Australia.
The British Government began transporting convicts overseas to American colonies in the early 18th century. When ...
. It was opened in 1816 and closed in 1890.
Construction
 The site at Millbank was originally purchased in 1799 from the
The site at Millbank was originally purchased in 1799 from the Marquess of Salisbury
Marquess of Salisbury is a title in the Peerage of Great Britain. It was created in 1789 for the 7th Earl of Salisbury. Most of the holders of the title have been prominent in British political life over the last two centuries, particularly th ...
for £12,000 by the philosopher Jeremy Bentham
Jeremy Bentham (; 15 February 1748 ld Style and New Style dates, O.S. 4 February 1747– 6 June 1832) was an English philosopher, jurist, and social reformer regarded as the founder of modern utilitarianism.
Bentham defined as the "fundam ...
, acting on behalf of the Crown
The Crown is the state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, overseas territories, provinces, or states). Legally ill-defined, the term has differ ...
, for the erection of his proposed panopticon
The panopticon is a type of institutional building and a system of control designed by the English philosopher and social theorist Jeremy Bentham in the 18th century. The concept of the design is to allow all prisoners of an institution to be o ...
prison as Britain's new National Penitentiary. After various changes in circumstance, the Panopticon plan was abandoned in 1812. Proposals for the National Penitentiary continued, however, and were given a legislative basis in the Penitentiary House, etc. Act of 1812 (52 Geo. 3 c. 44). An architectural competition for a new prison building on the Millbank site attracted 43 entrants: the winning design was that of William Williams, drawing master at the Royal Military College, Sandhurst
The Royal Military College (RMC), founded in 1801 and established in 1802 at Great Marlow and High Wycombe in Buckinghamshire, England, but moved in October 1812 to Sandhurst, Berkshire, was a British Army military academy for training infant ...
. Williams' basic plan was adapted by a practising architect, Thomas Hardwick
Thomas Hardwick (1752–1829) was an English architect and a founding member of the Architects' Club in 1791.
Early life and career
Hardwick was born in Brentford, Middlesex the son of a master mason turned architect also named Thomas Hard ...
, who began construction in the same year.
The marshy site on which the prison stood meant that the builders experienced problems of subsidence
Subsidence is a general term for downward vertical movement of the Earth's surface, which can be caused by both natural processes and human activities. Subsidence involves little or no horizontal movement, which distinguishes it from slope mov ...
from the outset, and explains the succession of architects. it was to consist of a hexagonal central courtyard with an elongated pentagonal courtyard on each outer wall of the central courtyard; the three outer corners of the pentagonal courtyards each had a tower one storey higher than the three floors of the rest of the building. When the boundary wall reached a height of about six feet high it began to tilt and crack. After 18 months, with £26,000 spent on it, Hardwick resigned in 1813, and John Harvey took over the role. Harvey was dismissed in turn in 1815, and replaced by Robert Smirke, who brought the project to completion in 1821. Further legislation was passed in the form of the Millbank Penitentiary Act of 1816 (56 Geo. 3 c. 63).
In February 1816 the first prisoners were admitted during the construction process, but the building creaked and several windows spontaneously shattered. Smirke and the engineer John Rennie the Elder
John Rennie FRSE FRS (7 June 1761 – 4 October 1821) was a Scottish civil engineer who designed many bridges, canals, docks and warehouses, and a pioneer in the use of structural cast-iron.
Early years
He was born the younger son of James Re ...
were called in, and they recommended demolition of three of the towers and the underpinning of the entire building with concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most wid ...
foundations, in form of a raft
A raft is any flat structure for support or transportation over water. It is usually of basic design, characterized by the absence of a hull. Rafts are usually kept afloat by using any combination of buoyant materials such as wood, sealed barrels ...
: the first known use of this material for foundations in Britain since the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
. However, this added considerably to the construction costs, which eventually totalled £500,000, more than twice the original estimate and equivalent to £500 per cell.
History
The first prisoners, all women, were admitted on 26 June 1816. The first men arrived in January 1817. The prison held 103 men and 109 women by the end of 1817, and 452 men and 326 women by late 1822. Sentences of five to ten years in the National Penitentiary were offered as an alternative totransportation
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land ( rail and road), water, cable, pipelin ...
to those thought most likely to reform.
In addition to the problems of construction, the marshy site fostered disease, to which the prisoners had little immunity owing to their extremely poor diet. In 1818 the authorities engaged Dr Alexander Copland Hutchison
Alexander Copland (or Copeland) Hutchison FRSE (1786–1840) was a British surgeon and medical author remembered for his book ''Practical Observations in Surgery'' (1811).
In 1818 he made an interesting observation that navy personnel suffered e ...
of Westminster Dispensary as Medical Supervisor, to oversee the health of the inmates. In 1822–23 an epidemic swept through the prison, which seems to have comprised a mixture of dysentery
Dysentery (UK pronunciation: , US: ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications ...
, scurvy
Scurvy is a deficiency disease, disease resulting from a lack of vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Early symptoms of deficiency include weakness, feeling tired and sore arms and legs. Without treatment, anemia, decreased red blood cells, gum disease, ch ...
, depression and other disorders. The decision was eventually taken to evacuate the buildings for several months: the female prisoners were released, and the male prisoners temporarily transferred to the prison hulks
A prison ship, often more accurately described as a prison hulk, is a current or former seagoing vessel that has been modified to become a place of substantive detention for convicts, prisoners of war or civilian internees. While many nation ...
at Woolwich
Woolwich () is a district in southeast London, England, within the Royal Borough of Greenwich.
The district's location on the River Thames led to its status as an important naval, military and industrial area; a role that was maintained thr ...
, where their health improved.
The design of Millbank also turned out to be unsatisfactory. The network of corridors was so labyrinthine that even the warders got lost; and the ventilation system allowed sound to carry, so that prisoners could communicate between cells. The annual running costs turned out to be an unsupportable £16,000.
In view of these problems, the decision was eventually taken to build a new "model prison" at Pentonville
Pentonville is an area on the northern fringe of Central London, in the London Borough of Islington. It is located north-northeast of Charing Cross on the Inner Ring Road. Pentonville developed in the northwestern edge of the ancient parish ...
, which opened in 1842 and took over Millbank's role as the National Penitentiary. By an Act of Parliament of 1843, Millbank's status was downgraded, and it became a holding depot for convicts prior to transportation
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land ( rail and road), water, cable, pipelin ...
. Every person sentenced to transportation was sent to Millbank first, where they were held for three months before their final destination was decided. By 1850, around 4,000 people were condemned annually to transportation from the UK. Prisoners awaiting transportation were kept in solitary confinement and restricted to silence for the first half of their sentence.
Large-scale transportation ended in 1853 (although the practice continued on a reduced scale until 1867); and Millbank then became an ordinary local prison, and from 1870 a military prison. By 1886 it had ceased to hold inmates, and it closed in 1890. Demolition began in 1892, and continued sporadically until 1903.
Description
 The plan of the prison comprised a circular chapel at the centre of the site, surrounded by a three-storey hexagon made up of the governor's quarters, administrative offices and laundries, surrounded in turn by six pentagons of cell blocks. The buildings of each pentagon were set around a cluster of five small courtyards (with a
The plan of the prison comprised a circular chapel at the centre of the site, surrounded by a three-storey hexagon made up of the governor's quarters, administrative offices and laundries, surrounded in turn by six pentagons of cell blocks. The buildings of each pentagon were set around a cluster of five small courtyards (with a watchtower
A watchtower or watch tower is a type of fortification used in many parts of the world. It differs from a regular tower in that its primary use is military and from a turret in that it is usually a freestanding structure. Its main purpose is to ...
at the centre) used as airing-yards, and in which prisoners undertook labour. The three outer angles of each pentagon were distinguished by tall circular towers, described in 1862 as " Martello-like": these served in part as watchtowers, but their primary purpose was to contain staircases and water-closets.Mayhew and Binny 1862. The third and fourth pentagons (those to the north-west, furthest from the entrance) were used to house female prisoners, and the remaining four for male prisoners.
In the ''Handbook of London'' in 1850 the prison was described as follows:
Each cell had a single window (looking into the pentagon courtyard), and was equipped with a washing tub, a wooden stool, a hammock and bedding, and books including a Bible, a prayer-book, a hymn-book, an arithmetic-book, a work entitled ''Home and Common Things'', and publications of the Society for Promoting Christian Knowledge
The Society for Promoting Christian Knowledge (SPCK) is a UK-based Christian charity. Founded in 1698 by Thomas Bray, it has worked for over 300 years to increase awareness of the Christian faith in the UK and across the world.
The SPCK is t ...
.
Irish republican
Irish republicanism ( ga, poblachtánachas Éireannach) is the political movement for the unity and independence of Ireland under a republic. Irish republicans view British rule in any part of Ireland as inherently illegitimate.
The developm ...
prisoner Michael Davitt
Michael Davitt (25 March 184630 May 1906) was an Irish republican activist for a variety of causes, especially Home Rule and land reform. Following an eviction when he was four years old, Davitt's family migrated to England. He began his caree ...
, who was held briefly at Millbank in 1870, described the experience:
Later development of the site
 As the prison was progressively demolished its site was redeveloped. The principal new buildings erected were the National Gallery of British Art (now
As the prison was progressively demolished its site was redeveloped. The principal new buildings erected were the National Gallery of British Art (now Tate Britain
Tate Britain, known from 1897 to 1932 as the National Gallery of British Art and from 1932 to 2000 as the Tate Gallery, is an art museum on Millbank in the City of Westminster in London, England. It is part of the Tate network of galleries in ...
), which opened in 1897; the Royal Army Medical College
The Royal Army Medical College (RAMC) was located on a site south of the Tate Gallery (now known as Tate Britain) on Millbank, in Westminster, London, overlooking the River Thames. The college moved from the site in 1999 and the buildings are now ...
, the buildings of which were adapted in 2005 to become the Chelsea College of Art & Design
Chelsea College of Arts is a constituent college of the University of the Arts London based in London, United Kingdom, and is a leading British art and design institution with an international reputation.
It offers further education, further ...
; andusing the original bricks of the prisonthe Millbank Estate, a housing estate built by the London County Council
London County Council (LCC) was the principal local government body for the County of London throughout its existence from 1889 to 1965, and the first London-wide general municipal authority to be directly elected. It covered the area today kn ...
(LCC) between 1897 and 1902. The estate comprises 17 buildings, each named after a distinguished painter, and is Grade II listed
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern I ...
.
Surviving remains

 A large circular
A large circular bollard
A bollard is a sturdy, short, vertical post. The term originally referred to a post on a ship or quay used principally for mooring boats. It now also refers to posts installed to control road traffic and posts designed to prevent automotive ...
stands by the river with the inscription: "Near this site stood Millbank Prison which was opened in 1816 and closed in 1890. This buttress stood at the head of the river steps from which, until 1867, prisoners sentenced to transportation embarked on their journey to Australia."
Part of the perimeter ditch of the prison survives running between Cureton Street and John Islip Street. It is now used as a clothes-drying area for residents of Wilkie House.
Archaeological investigations in the late 1990s and early 2000s on the sites of Chelsea College of Art and Design and Tate Britain recorded significant remains of the foundations of the external pentagon walls of the prison, of parts of the inner hexagon, of two of the courtyard watchtowers, of drainage culvert
A culvert is a structure that channels water past an obstacle or to a subterranean waterway. Typically embedded so as to be surrounded by soil, a culvert may be made from a pipe, reinforced concrete or other material. In the United Kingdo ...
s, and of Smirke's concrete raft.
The granite gate piers at the entrance of Purbeck House, High Street, Swanage
Swanage () is a coastal town and civil parish in the south east of Dorset, England. It is at the eastern end of the Isle of Purbeck and one of its two towns, approximately south of Poole and east of Dorchester. In the 2011 census the civi ...
in Dorset, and a granite bollard next to the gate, are thought by Historic England
Historic England (officially the Historic Buildings and Monuments Commission for England) is an executive non-departmental public body of the British Government sponsored by the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport. It is tasked w ...
to be possibly from Millbank Prison.
Cultural references
Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian er ...
describes the prison in chapter 52 ("Obstinacy") of his novel, ''Bleak House
''Bleak House'' is a novel by Charles Dickens, first published as a 20-episode serial between March 1852 and September 1853. The novel has many characters and several sub-plots, and is told partly by the novel's heroine, Esther Summerson, and ...
'' (1852–3). One of the characters is put into custody there, and other characters go to visit him. Esther Summerson, one of the book's narrators, gives a brief description of its layout.
In Henry James
Henry James ( – ) was an American-British author. He is regarded as a key transitional figure between literary realism and literary modernism, and is considered by many to be among the greatest novelists in the English language. He was the ...
's realist novel '' The Princess Casamassima'' (1886) the prison is the "primal scene" of Hyacinth Robinson's life: the visit to his mother, dying in the infirmary, is described in chapter 3. James visited Millbank on 12 December 1884 to gain material.
Sir Arthur Conan Doyle
Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle (22 May 1859 – 7 July 1930) was a British writer and physician. He created the character Sherlock Holmes in 1887 for ''A Study in Scarlet'', the first of four novels and fifty-six short stories about Ho ...
in chapter 8 of ''The Sign of Four
''The Sign of the Four'' (1890), also called ''The Sign of Four'', is the second novel featuring Sherlock Holmes by British writer Sir Arthur Conan Doyle. Doyle wrote four novels and 56 short stories featuring the fictional detective.
Pl ...
'' (1890) refers to Holmes
Holmes may refer to:
Name
* Holmes (surname)
* Holmes (given name)
* Baron Holmes, noble title created twice in the Peerage of Ireland
* Chris Holmes, Baron Holmes of Richmond (born 1971), British former swimmer and life peer
Places
In the Uni ...
and Watson
Watson may refer to:
Companies
* Actavis, a pharmaceutical company formerly known as Watson Pharmaceuticals
* A.S. Watson Group, retail division of Hutchison Whampoa
* Thomas J. Watson Research Center, IBM research center
* Watson Systems, make ...
crossing the Thames from the house of Mordecai Smith and landing by the Millbank Penitentiary.
In chapter 8 of Conan Doyle's '' The Lost World'' (1912), Professor Challenger says that he dislikes walking along the Thames as it is always sad to see one's final destination. Challenger means that he expects to be buried at Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the United ...
, but his rival Professor Summerlee responds sardonically that he understands that Millbank Prison has been demolished.
The prison is a key location within Sarah Waters' novel '' Affinity'' (1999).
The prison, Bentham's philosophy surrounding it, and a fictionalized account of Smirke's role in its construction play a key part in the plot of horror fiction podcast ''The Magnus Archives
''The Magnus Archives'' is a horror fiction podcast written by Jonathan Sims, directed by Alexander J. Newall, and distributed by Rusty Quill. Sims narrated the podcast in-character as the main character, Jonathan Sims, the newly appointed Hea ...
'' by Jonathan Sims.
See also
*List of demolished buildings and structures in London
This list of demolished buildings and structures in London includes buildings, structures and urban scenes of particular architectural and historical interest, scenic buildings which are preserved in old photographs, prints and paintings, but whic ...
*Convicts in Australia
Between 1788 and 1868, about 162,000 convicts were transported from Britain and Ireland to various penal colonies in Australia.
The British Government began transporting convicts overseas to American colonies in the early 18th century. When ...
*Penal transportation
Penal transportation or transportation was the relocation of convicted criminals, or other persons regarded as undesirable, to a distant place, often a colony, for a specified term; later, specifically established penal colonies became thei ...
*Separate system
The separate system is a form of prison management based on the principle of keeping prisoners in solitary confinement. When first introduced in the early 19th century, the objective of such a prison or "penitentiary" was that of penance by the p ...
Notes
Bibliography
* * * * * * * (Chapter 5). * ''The Nuttall Encyclopaedia
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the ...
'', "Millbank Prison".
*
External links
Collection of Victorian references
- the penitentiary is the distinctive six-pointed building near the bottom
Millbank Estate today
{{Prisons in London 1816 establishments in England Defunct prisons in London Former buildings and structures in the City of Westminster Demolished buildings and structures in London Buildings and structures demolished in 1903 19th century in London 1890 disestablishments in England Millbank Demolished prisons