The militia of the
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, as defined by the
U.S. Congress, has changed over time.
[Spitzer, Robert J.: ''The Politics of Gun Control'', Page 36. Chatham House Publishers, Inc., 1995.] During
colonial America
The colonial history of the United States covers the period of European colonization of North America from the late 15th century until the unifying of the Thirteen British Colonies and creation of the United States in 1776, during the Re ...
, all able-bodied men of a certain age range were members of the
militia
A militia ( ) is a military or paramilitary force that comprises civilian members, as opposed to a professional standing army of regular, full-time military personnel. Militias may be raised in times of need to support regular troops or se ...
, depending on each colony's rule. Individual towns formed local independent militias for their own defense. The year before the
U.S. Constitution was
ratified
Ratification is a principal's legal confirmation of an act of its agent. In international law, ratification is the process by which a state declares its consent to be bound to a treaty. In the case of bilateral treaties, ratification is usuall ...
, ''
The Federalist Papers
''The Federalist Papers'' is a collection of 85 articles and essays written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay under the collective pseudonym "Publius" to promote the ratification of the Constitution of the United States. The ...
'' detailed the
Founding Fathers' paramount vision of the militia in 1787. The new Constitution empowered Congress to "organize, arm, and discipline" this national military force, leaving significant control in the hands of
each state government.
Today, as defined by the
Militia Act of 1903, the term "militia" is used to describe two classes within the United States:
* Organized militia – consisting of the
National Guard
National guard is the name used by a wide variety of current and historical uniformed organizations in different countries. The original National Guard was formed during the French Revolution around a cadre of defectors from the French Guards.
...
and
Naval Militia.
* Unorganized militia – comprising the reserve militia: every able-bodied man of at least 17 and under 45 years of age, who are not members of the National Guard or the Naval Militia. These are militia that are under control of the State
Governors
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the ...
.
Congress chose to organize militias for the interests of organizing reserve military units which were not limited in deployment by the strictures of its power over the constitutional militia, which can be called forth only "to execute the laws of the Union, suppress insurrections and repel invasions." Most modern organizations calling themselves militias are illegal private paramilitary organizations without the official sanctioning of a state government.
Etymology
The term "militia" derives from Old English ''milite'' meaning soldiers (plural), ''militisc'' meaning military and also classical Latin ''milit-, miles'' meaning soldier.
The Modern English term ''militia'' dates to the year 1590, with the original meaning now obsolete: "the body of soldiers in the service of a sovereign or a state". Subsequently, since approximately 1665, ''militia'' has taken the meaning "a military force raised from the civilian population of a country or region, especially to supplement a regular army in an emergency, frequently as distinguished from mercenaries or professional soldiers". The
U.S. Supreme Court adopted the following definition for "active militia" from an
Illinois Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of Illinois is the state supreme court, the highest court of the judiciary of Illinois. The court's authority is granted in Article VI of the current Illinois Constitution, which provides for seven justices elected from the fiv ...
case of 1879: " 'a body of citizens trained to military duty, who may be called out in certain cases, but may not be kept on service like standing armies, in times of peace'. . . when not engaged at stated periods . . . they return to their usual avocations . . . and are subject to call when public exigencies demand it."
The spelling ''millitia'' is often observed in written and printed materials from the 17th century through the 19th century.
History
Early-mid Colonial era (1607–1754)

The early colonists of America considered the militia an important social institution, necessary to provide defense and public safety.
[ Wills, Garry (1999). ''A Necessary Evil, A History of American Distrust of Government'' Page 27. New York, NY; Simon & Schuster. ]
On August 29, 1643, the
Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony (sometimes spelled Plimouth) was the first permanent English colony in New England from 1620 and the third permanent English colony in America, after Newfoundland and the Jamestown Colony. It was settled by the passengers on t ...
Court allowed and established a military discipline to be erected and maintained.
French and Indian War (1754–1763)

During the
French and Indian Wars, town militia formed a recruiting pool for the Provincial Forces. The legislature of the colony would authorize a certain force level for the season's campaign and set recruitment quotas for each local militia. In theory, militia members could be drafted by lot if there were inadequate forces for the Provincial Regulars; however, the draft was rarely resorted to because provincial regulars were highly paid (more highly paid than their regular British Army counterparts) and rarely engaged in combat.
In September 1755,
George Washington
George Washington (, 1799) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the first president of the United States, serving from 1789 to 1797. As commander of the Continental Army, Washington led Patriot (American Revoluti ...
, then
adjutant-general of the Virginia militia, upon a frustrating and futile attempt to call up the militia to respond to a frontier Indian attack:
[Sparks, Jared: ''"The Life of George Washington"'', page 70. F. Andrews, 1853.]
... he experienced all the evils of insubordination among the troops, perverseness in the militia, inactivity in the officers, disregard of orders, and reluctance in the civil authorities to render a proper support. And what added to his mortification was, that the laws gave him no power to correct these evils, either by enforcing discipline, or compelling the indolent and refractory to their duty ... The militia system was suited for only to times of peace. It provided for calling out men to repel invasion; but the powers granted for effecting it were so limited, as to be almost inoperative.
See
New Hampshire Provincial Regiment for a history of a Provincial unit during the French and Indian War.
Pre-American Revolutionary War era (1763–1775)
Just prior to the
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
, on October 26, 1774, the Massachusetts Provincial Congress, observing the British military buildup, deemed their militia resources to be insufficient: the troop strength, "including the sick and absent, amounted to about seventeen thousand men ... this was far short of the number wanted, that the council recommended an immediate application to the New England governments to make up the deficiency":
[Sparks, Jared: ''"The Life of George Washington"'', page 134–135. F. Andrews, 1853.]
... they recommended to the militia to form themselves into companies of minute-men, who should be equipped and prepared to march at the shortest notice. These minute-men were to consist of one quarter of the whole militia, to be enlisted under the direction of the field-officers, and divide into companies, consisting of at least fifty men each. The privates were to choose their captains and subalterns, and these officers were to form the companies into battalions, and chose the field-officers to command the same. Hence the minute-men became a body distinct from the rest of the militia, and, by being more devoted to military exercises, they acquired skill in the use of arms. More attention than formerly was likewise bestowed on the training and drilling of militia.
American Revolutionary War (1775–1783)

The American Revolutionary War began near Boston, Massachusetts with the
Battles of Lexington and Concord
The Battles of Lexington and Concord on April 19, 1775 were the first major military actions of the American Revolutionary War between the Kingdom of Great Britain and Patriot (American Revolution), Patriot militias from America's Thirteen Co ...
, in which a group of local militias constituted the American side (the "
Patriots"). On April 19, 1775, a British force 800 strong marched out of Boston to Concord intending to destroy patriot arms and ammunition. At 5:00 in the morning at Lexington, they met about 70 armed militiamen whom they ordered to disperse, but the militiamen refused. Firing ensued; it is not clear which side opened fire. This became known as "the shot heard round the world". Eight militiamen were killed and ten wounded, whereupon the remainder took flight. The British continued on to Concord and were unable to find most of the arms and ammunition of the patriots. As the British marched back toward Boston, patriot militiamen assembled along the route, taking cover behind stone walls, and sniped at the British. At Meriam's Corner in Concord, the British columns had to close in to cross a narrow bridge, exposing themselves to concentrated, deadly fire. The British retreat became a rout. It was only with the help of an additional detachment of 900 troops that the British force managed to return to Boston. This marked the beginning of the war. It was "three days after the affair of Lexington and Concord that any movement was made towards embodying a regular army".
[Sparks, Jared: ''The Life of George Washington'', page 135. F. Andrews, 1853.]
In 1777, the Second
Continental Congress
The Continental Congress was a series of legislature, legislative bodies, with some executive function, for the Thirteen Colonies of British America, Great Britain in North America, and the newly declared United States before, during, and after ...
adopted the
Articles of Confederation
The Articles of Confederation, officially the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, was an agreement and early body of law in the Thirteen Colonies, which served as the nation's first Constitution, frame of government during the Ameri ...
, which contained a provision for raising a confederal militia that consent would be required from nine of the 13 States. Article VI of the Articles of Confederation states,
... every State shall always keep up a well-regulated and disciplined militia, sufficiently armed and accoutered, and shall provide and constantly have ready for use, in public stores, a due number of field pieces and tents, and a proper quantity of arms, ammunition and camp equipage.
Some militia units appeared without adequate arms, as evidenced in this letter from John Adams to his wife, dated August 26, 1777:
The militia are turning out with great alacrity both in Maryland and Pennsylvania. They are distressed for want of arms. Many have none, we shall rake and scrape enough to do Howe's business, by favor of the Heaven.
The initial enthusiasm of Patriot militiamen in the beginning days of the war soon waned. The historian Garry Wills explains,
The fervor of the early days in the reorganized militias wore off in the long grind of an eight-year war. Now the right to elect their own officers was used to demand that the men not serve away from their state. Men evaded service, bought substitutes to go for them as in the old days, and had to be bribed with higher and higher bounties to join the effort – which is why Jefferson and Samuel Adams
Samuel Adams (, 1722 – October 2, 1803) was an American statesman, Political philosophy, political philosopher, and a Founding Father of the United States. He was a politician in Province of Massachusetts Bay, colonial Massachusetts, a le ...
called them so expensive. As wartime inflation devalued the currency, other pledges had to be offered, including land grants and the promise of "a healthy slave" at the end of the war. Some men would take a bounty and not show up. Or they would show up for a while, desert, and then, when they felt the need for another bounty, sign up again in a different place. ... This practice was common enough to have its own technical term – "bounty jumping".
The burden of waging war passed to a large extent to the standing army, the
Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies representing the Thirteen Colonies and later the United States during the American Revolutionary War. It was formed on June 14, 1775, by a resolution passed by the Second Continental Co ...
. The stay-at-home militia tended then to perform the role of the internal police to keep order. British forces sought to disrupt American communities by instigating slave rebellions and Indian raids. The militia fended off these threats. Militias also spied on Loyalists in the American communities. In Albany County, New York, the militia established a
Committee for Detecting and Defeating Conspiracies to look out for and investigate people with suspicious allegiances.
Confederation period (1783–1787)
Politically, the militia was highly popular during the postwar period, though to some extent, based more on pride of victory in the recent war than on the realities.
This skepticism of the actual value of relying upon the militia for national defense, versus a trained regular army was expressed by
Gouverneur Morris
Gouverneur Morris ( ; January 31, 1752 – November 6, 1816) was an American statesman, a Founding Father of the United States, and a signatory to the Articles of Confederation and the United States Constitution. He wrote the Preamble to the ...
:
An overweening vanity leads the fond many, each man against the conviction of his own heart, to believe or affect to believe, that militia can beat veteran troops in the open field and even play of battle. This idle notion, fed by vaunting demagogues, alarmed us for our country, when in the course of that time and chance, which happen to all, she should be at war with a great power.
Robert Spitzer, citing Daniel Boorstin, describes this political dichotomy of the public popularity of the militia versus the military value:
While the reliance upon militias was politically satisfying, it proved to be an administrative and military nightmare. State detachments could not be easily combined into larger fighting units; soldiers could not be relied on to serve for extended periods, and desertions were common; officers were elected, based on popularity rather than experience or training; discipline and uniformity were almost nonexistent.
General George Washington defended the militia in public, but in correspondence with Congress expressed his opinion of the militia quite to the contrary:
To place any dependence on the Militia, is, assuredly, resting upon a broken staff. Men just dragged from the tender Scenes of domestic life; unaccustomed to the din of Arms; totally unacquainted with every kind of military skill, which being followed by a want of confidence in themselves, when opposed to Troops regularly trained, disciplined, and appointed, superior in knowledge and superior in Arms, makes them timid, and ready to fly from their own shadows ... if I was called upon to declare upon Oath, whether the Militia have been most serviceable or hurtful upon the whole, I should subscribe to the latter.
At the end of the Revolutionary War, a political atmosphere developed at the local level where the militia was seen with fondness, despite their spotty record on the battlefield. Typically, when the militia did act well was when the battle came into the locale of the militia, and local inhabitants tended to exaggerate the performance of the local militia versus the performance of the Continental Army. The Continental Army was seen as the protector of the States, though it also was viewed as a dominating force over the local communities.
Joseph Reed, president of Pennsylvania viewed this jealousy between the militia forces and the standing army as similar to the prior frictions between the militia and the British Regular Army a generation before during the
French and Indian War
The French and Indian War, 1754 to 1763, was a colonial conflict in North America between Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of France, France, along with their respective Native Americans in the United States, Native American ...
. Tensions came to a head at the end of the war when the Continental Army officers demanded pensions and set up the
Society of the Cincinnati
The Society of the Cincinnati is a lineage society, fraternal, hereditary society founded in 1783 to commemorate the American Revolutionary War that saw the creation of the United States. Membership is largely restricted to descendants of milita ...
to honor their own wartime deeds. The local communities did not want to pay national taxes to cover the Army pensions, when the local militiamen received none.
Constitution and Bill of Rights (1787–1789)
The delegates of the Constitutional Convention (the Founding Fathers/Framers of the
U.S. Constitution) under Article 1; section 8, clauses 15 and 16 of the federal constitution, granted Congress the power to "provide for organizing, arming, and disciplining the Militia", as well as, and in distinction to, the power to raise an army and a navy. The U.S. Congress is granted the power to use the militia of the U.S. for three specific missions, as described in Article 1, section 8, clause 15: "To provide for the calling of the militia to execute the laws of the Union, suppress insurrections, and repel invasions." The
Militia Act of 1792 clarified whom the militia consists of:
Civilian control of a peacetime army
At the time of the drafting of the Constitution, and the Bill of Rights, a political sentiment existed in the newly formed United States involving suspicion of peacetime armies not under civilian control. This political belief has been identified as stemming from the memory of the abuses of the standing army of
Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English statesman, politician and soldier, widely regarded as one of the most important figures in British history. He came to prominence during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, initially ...
and King
James II, in Great Britain in the prior century, which led to the
Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution, also known as the Revolution of 1688, was the deposition of James II and VII, James II and VII in November 1688. He was replaced by his daughter Mary II, Mary II and her Dutch husband, William III of Orange ...
and resulted in placing the standing army under the control of Parliament.
During the Congressional debates,
James Madison
James Madison (June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison was popularly acclaimed as the ...
discussed how a militia could help defend liberty against tyranny and oppression. (Source I Annals of Congress 434, June 8, 1789) However, during his presidency, after enduring the failures of the militia in the
War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the Uni ...
, Madison came to favor the maintenance of a strong standing army.
Shift from states' power to federal power
A major concern of the various delegates during the constitutional debates over the U.S. Constitution and the
Second Amendment to the Constitution revolved around the issue of transferring militia power held by the states (under the existing
Articles of Confederation
The Articles of Confederation, officially the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, was an agreement and early body of law in the Thirteen Colonies, which served as the nation's first Constitution, frame of government during the Ameri ...
) to federal control.
Political debate regarding compulsory militia service for pacifists
Records of the constitutional debate over the early drafts of the language of the Second Amendment included significant discussion of whether service in the militia should be compulsory for all able bodied men, or should there be an exemption for the "religiously scrupulous" conscientious objector.
The concern about risks of a "religiously scrupulous" exemption clause within the second amendment to the Federal Constitution was expressed by
Elbridge Gerry of Massachusetts (from 1 Annals of Congress at 750, 17 August 1789):
The "religiously scrupulous" clause was ultimately stricken from the final draft of second amendment to the Federal Constitution though the militia clause was retained. The Supreme Court of the United States has upheld a right to conscientious objection to military service.
Concern over select militias
William S. Fields and David T. Hardy write:
While in The Federalist No. 46, Madison argued that a standing army of 25,000 to 30,000 men would be offset by "a militia amounting to near a half million of citizens with arms in their hands, officered by men chosen from among themselves ..." 19The Antifederalists were not persuaded by these arguments, in part because of the degree of control over the militia given to the national government by the proposed constitution. The fears of the more conservative opponents centered upon the possible phasing out of the general militia in favor of a smaller, more readily corrupted, select militia. Proposals for such a select militia already had been advanced by individuals such as Baron Von Steuben, Washington's Inspector General, who proposed supplementing the general militia with a force of 21,000 men given government- issued arms and special training. 20An article in the Connecticut Journal expressed the fear that the proposed constitution might allow Congress to create such select militias: " is looks too much like Baron Steuben's militia, by which a standing army was meant and intended." 21In Pennsylvania, John Smiley told the ratifying convention that "Congress may give us a select militia which will in fact be a standing army", and worried that, .34with this force in hand, "the people in general may be disarmed". 22Similar concerns were raised by Richard Henry Lee in Virginia. In his widely-read pamphlet, Letters from the Federal Farmer to the Republican, Lee warned that liberties might be undermined by the creation of a select militia that " ouldanswer to all the purposes of an army", and concluded that "the Constitution ought to secure a genuine and guard against a select militia by providing that the militia shall always be kept well organized, armed, and disciplined, and include, according to the past and general usage of the states, all men capable of bearing arms."
Note: In Federalist Paper 29 Hamilton argued the inability to train the whole Militia made select corps inevitable and, like Madison, paid it no concern.
Federalist period (1789–1801)
In 1794, a militia numbering approximately 13,000 was raised and personally led by President George Washington to quell the
Whiskey Rebellion in Pennsylvania. From this experience, a major weakness of a States-based citizen militia system was found to be the lack of systematic army organization, and a lack of training for engineers and officers. George Washington repeatedly warned of these shortcomings up until his death in 1799. Two days before his death, in a letter to General Alexander Hamilton, George Washington wrote: "The establishment of a Military Academy upon a respectable and extensive basis has ever been considered by me as an object of primary importance to this country; and while I was in the chair of government, I omitted no proper opportunity of recommending it in my public speeches, and otherwise to the attention of the legislature."
[Cullum, George and Wood, Eleazer:''Campaigns of the War of 1812–1815, Against Great Britain: Sketched and Criticized.''. J. Miller, 1879.]
Early republic (1801–1812)
In 1802, the federal military academy at
West Point
The United States Military Academy (USMA), commonly known as West Point, is a United States service academies, United States service academy in West Point, New York that educates cadets for service as Officer_(armed_forces)#United_States, comm ...
was established, in part to rectify the failings of irregular training inherent in a States-based militia system.
War of 1812 (1812–1815)
In the
War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the Uni ...
, the United States Militia were at times routed if they fought conventionally on the battle in the open as they were undisciplined, untrained, and underfunded. For example, at the
Battle of Bladensburg, the militia were set up in linear formation with little to no entrenchments and very little help from the Regular Army. Thus the Militia were routed easily and fled from the battlefield in large numbers, allowing the smaller British force to successfully raid and destroy the White House in Washington D.C.
American militias were very effective when fighting in unconventional guerrilla warfare such as the defense of Hampton Village on June 25, 1813, where American militia conducted a few devastating ambushes, conducted harassing fire behind cover, and fought some hit-and-run engagements. Although the militia were routed and withdrew with 7 killed, 12 wounded, and 12 missing, the British suffered 120 killed and at least 95 wounded. American militia as horse-mounted raiders were very effective at conducting incursions or raids into British Canada. For instance, Duncan McArthur led a successful
mounted raid into Canada with an almost entirely militia force. William Henry Harrison led an incursion into
Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after th ...
with an almost entirely Kentucky mounted militia force which captured an entire British army, eliminated Tecumseh, and suffered very few casualties.
Militias fared better and proved more reliable when protected behind defensive entrenchments and fixed fortifications, using guerrilla tactics such as firing from behind cover, being reinforced with Regular armed forces, or a little bit of all those factors. In the
Battle of Plattsburgh, the American militia dug entrenchments, fixed fortifications, disguised the roads with camouflage, and felled trees across the road. The Regulars and militia harassed the British army by firing at them from behind stone fences, trees, and whatever cover they could find before retreating to their entrenched fortified defense. As the British lost the naval engagement of the Plattsburgh battle, they continued to face heavy fire from the militia. Facing increased casualties, the British withdrew, making the Americans the victors.
The American militia failed if they were poorly led, had bad logistics, were not trained properly or were misused. But they could be a potent force if there was a good competent leader, better logistics, used carefully, better trained, or a combination of all those factors. However, the U.S. government still believed militia were inadequate, and the desire for a professional regular army prevailed. Military budgets were greatly increased at this time and a smaller, standing federal army, rather than States' militias, was deemed better for the national defense.
Antebellum era (1815–1861)
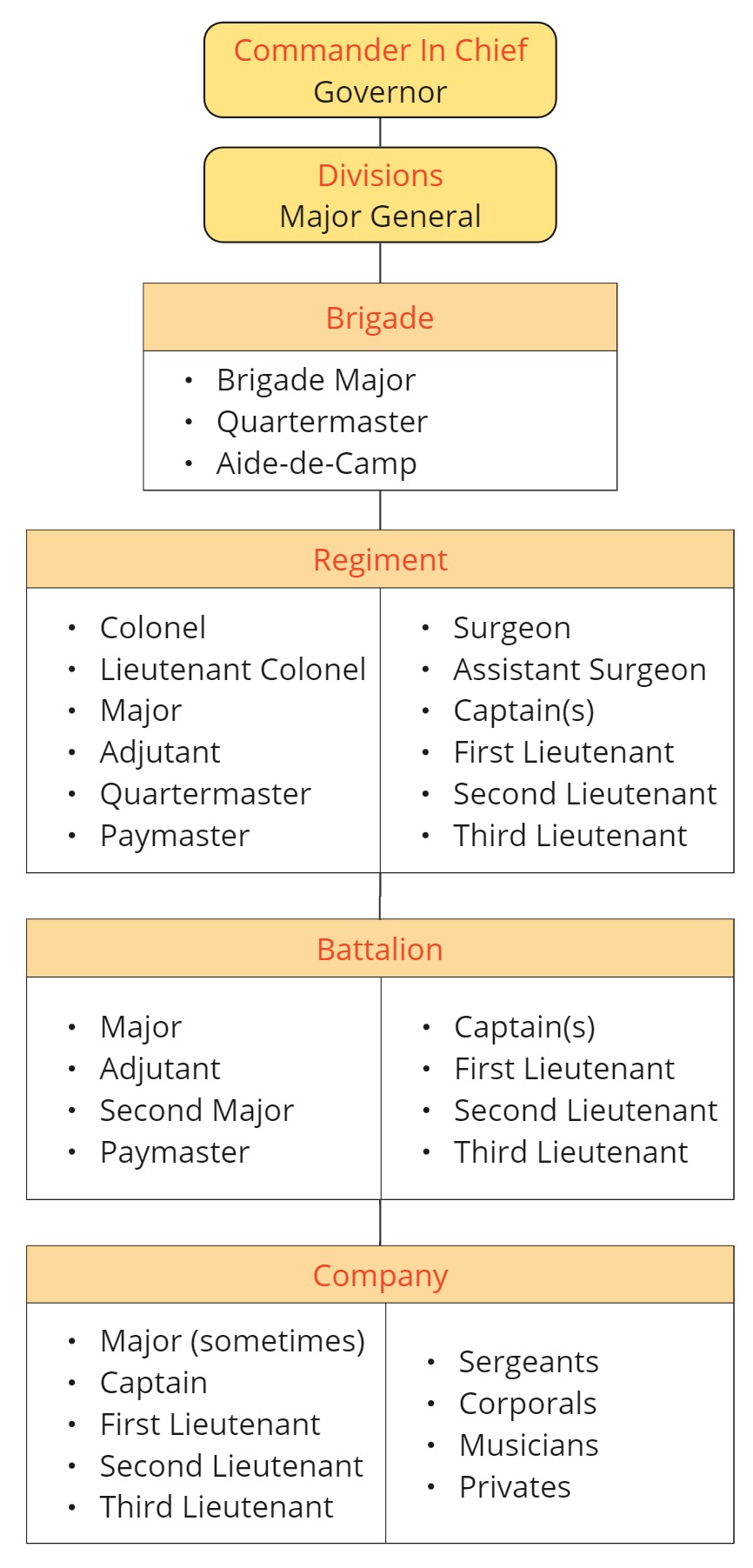
By the 1830s, the
American frontier
The American frontier, also known as the Old West, and popularly known as the Wild West, encompasses the Geography of the United States, geography, History of the United States, history, Folklore of the United States, folklore, and Cultur ...
expanded westwards, with the
Indian Wars in the eastern U.S. ending. Many states let their unorganized militia lapse in favor of volunteer militia units such as
city guards who carried on in functions such as assisting local law enforcement, providing troops for ceremonies and parades or as a social club. The groups of
company
A company, abbreviated as co., is a Legal personality, legal entity representing an association of legal people, whether Natural person, natural, Juridical person, juridical or a mixture of both, with a specific objective. Company members ...
size were usually uniformed and armed through their own contributions. Volunteer units of sufficient size could elect their own officers and apply for a state charter under names that they themselves chose.
The states' militia continued service, notably, in the slave-holding states, to maintain public order by performing slave patrols to round up fugitive slaves. A Mississippi town history described their militia of the 1840s: "The company musters of the citizen soldiers were held four times a year...After a brief parade, which consisted in a blundering execution of unwarlike antics, these men would start drinking and usually several fights occurred."
Responding to criticisms of failures of the militia, Adjutant General William Sumner wrote an analysis and rebuttal in a letter to John Adams, May 3, 1823:
The disasters of the militia may be ascribed chiefly, to two causes, of which the failure to train the men is a principle one; but, the omission to train the officers is as so much greater, that I think the history of its conduct, where it has been unfortunate, will prove that its defects are attributable, more to their want of knowledge or the best mode of applying the force under their authority to their attainment of their object than to all others. It may almost be stated, as an axiom, that the larger the body of undisciplined men is, the less is its chance of success; ...
During this inter-war period of the nineteenth century, the states' militia tended towards being disorderly and unprepared.
The demoralizing influences even of our own militia drills has long been notorious to a proverb. It has been a source of general corruptions to the community, and formed habits of idleness, dissipation and profligacy ... musterfields have generally been scenes or occasions of gambling, licentiousness, and almost every vice. ... An eye-witness of a New England training, so late as 1845, says, "beastly drunkenness, and other immoralities, were enough to make good men shudder at the very name of a muster".
Joseph Story
Joseph Story (September18, 1779September10, 1845) was an American lawyer, jurist, and politician who served as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1812 to 1845. He is most remembered for his opinions in ''Martin ...
lamented in 1842 how the militia had fallen into serious decline:
And yet, though this truth would seem so clear, and the importance of a well regulated militia would seem so undeniable, it cannot be disguised, that among the American people there is a growing indifference to any system of militia discipline, and a strong disposition, from a sense of its burdens, to be rid of all regulations. How it is practicable to keep the people duly armed without some organization, it is difficult to see. There is certainly no small danger, that indifference may lead to disgust, and disgust to contempt; and thus gradually undermine all the protection intended by this clause of our National Bill of Rights.
Due to rising tensions between Latter-day Saints and their Missourian neighbors, in 1838, General
David R. Atchison, the commander of the state militia of Northwestern Missouri, ordered
Samuel Bogart to "prevent, if possible, any invasion of Ray County by persons in arms whatever". Bogart, who had participated in former anti-Mormon
vigilante groups, proceeded to disarm resident Latter-day Saints and forced them to leave the county. In response
David W. Patten led the Caldwell County militia to rescue Latter-day Saint residents from what they believed was a "mob". The confrontation between these two county militias (Ray and Caldwell) became known as the
Battle of Crooked River and is a primary cause for Governor
Lilburn Boggs issuing
Missouri Executive Order 44. This order, often called the "Extermination Order", told the commander of the Missouri State Militia, General
John Bullock Clark, that, "The Mormons must be treated as enemies, and must be exterminated or driven from the state if necessary for the public pease—their outrages are beyond description." In the following days, Missouri militia killed 17 Latter-day Saints at
Haun's Mill, laid siege to
Far West, Missouri and jailed Latter-day Saint church leaders, including
Joseph Smith
Joseph Smith Jr. (December 23, 1805June 27, 1844) was an American religious and political leader and the founder of Mormonism and the Latter Day Saint movement. Publishing the Book of Mormon at the age of 24, Smith attracted tens of thou ...
. The Mormons would later relocate to
Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its ...
and form their own state-authorized militia, the
Nauvoo Legion. After conflicts again rose between the Mormons and the other residents of Illinois, the Mormons migrated west to
Utah
Utah is a landlocked state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is one of the Four Corners states, sharing a border with Arizona, Colorado, and New Mexico. It also borders Wyoming to the northea ...
and attempted to start their own nation. The
Utah Territorial Militia, the subsequent successor of the Nauvoo Legion, fought against U.S. federal troops in the
Utah War in 1857 and 1858 over control of government territory.
During the
violent political confrontations in the
Kansas Territory
The Territory of Kansas was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 30, 1854, until January 29, 1861, when the eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the United States, Union as the Slave and ...
involving anti-slavery
Free-Staters and pro-slavery "
Border Ruffian
Border ruffians were Proslavery thought, proslavery raiders who crossed into the Kansas Territory from Missouri during the mid-19th century to help ensure the territory entered the United States as a Slave states and free states, slave state. ...
s" elements, the militia was called out to enforce order on several occasions, notably during the incidents referred to as the
Wakarusa War.
During
John Brown's raid on Harpers Ferry, local militia companies from villages within a 30-mile radius of Harpers Ferry cut off Brown's escape routes and trapped Brown's men in the armory.
American Civil War
At the beginning of the
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
, neither the North or the South was nearly well enough prepared for war, and few people imagined the demands and hardships the war would bring. Just prior to the war the total peacetime army consisted of a paltry 16,000 men. Both sides issued an immediate call to forces from the militia, followed by the immediate awareness of an acute shortage of weapons, uniforms, and trained officers. State militia regiments were of uneven quality, and none had anything resembling combat training. The typical militia drilling at the time amounted to, at best, parade-ground marching. The militia units, from local communities, had never drilled together as a larger regiment, and thus lacked the extremely important skill, critically necessary for the war style of the time, of maneuvering from a marching line into a fighting line. Yet both sides were equally unready, and rushed to prepare.
Confederate militia
Union militia

Following South Carolina's declaration of secession, the Battle of
Fort Sumter
Fort Sumter is a historical Coastal defense and fortification#Sea forts, sea fort located near Charleston, South Carolina. Constructed on an artificial island at the entrance of Charleston Harbor in 1829, the fort was built in response to the W ...
, and the beginning of the Civil War, President
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln (February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was the 16th president of the United States, serving from 1861 until Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War ...
called up
75,000 state militiamen to retake the former U.S. federal fort and found that the militia "strength was far short of what the Congressional statute provided and required".
In the summer of 1861, military camps circled around Washington, D.C. composed of new three-year army volunteers and 90-day militia units. The generals in charge of this gathering had never handled large bodies of men before, and the men were simply inexperienced civilians with arms having little discipline and less understanding of the importance of discipline.
In the West, Union state and territorial militias existed as active forces in defense of settlers there.
California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
especially had
many active militia companies at the beginning of the war that rose in number until the end of the war. It provided the most volunteers from west of the Rocky Mountains: eight regiments and two battalions of infantry, two regiments and a battalion of cavalry. It also provided most of the men for the infantry regiment from
Washington Territory
The Washington Territory was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 2, 1853, until November 11, 1889, when the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Washington. It was created from the ...
.
Oregon
Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while t ...
raised an infantry and a cavalry regiment.
Colorado Territory
The Territory of Colorado was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from February 28, 1861, until August 1, 1876, when it was admitted to the Union as the 38th State of Colorado.
The territory was organized ...
militias were organized to resist both the Confederacy and any civil disorder caused by secessionists,
Copperheads,
Mormons
Mormons are a Religious denomination, religious and ethnocultural group, cultural group related to Mormonism, the principal branch of the Latter Day Saint movement started by Joseph Smith in upstate New York during the 1820s. After Smith's d ...
, or most particularly the native tribes.
The
Colorado Volunteers participated in the
Battle of Glorieta Pass
The Battle of Glorieta Pass was fought March 26–28, 1862, in the northern New Mexico Territory, by Union Army, Union and Confederate States Army, Confederate forces during the American Civil War. While not the largest battle of the New Mexic ...
, turning back a Confederate invasion of
New Mexico Territory
The Territory of New Mexico was an organized incorporated territory of the United States from September 9, 1850, until January 6, 1912. It was created from the U.S. provisional government of New Mexico, as a result of '' Nuevo México'' becomi ...
. Later they initiated the
Colorado War with the
Plains Indians and committed the
Sand Creek massacre. The
California Volunteers of the
California Column were sent east across the southern deserts to drive the Confederates out of southern Arizona, New Mexico, and west
Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
around
El Paso
El Paso (; ; or ) is a city in and the county seat of El Paso County, Texas, United States. The 2020 United States census, 2020 population of the city from the United States Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau was 678,815, making it the List of ...
, then fought the
Navajo
The Navajo or Diné are an Indigenous people of the Southwestern United States. Their traditional language is Diné bizaad, a Southern Athabascan language.
The states with the largest Diné populations are Arizona (140,263) and New Mexico (1 ...
and
Apache
The Apache ( ) are several Southern Athabaskan language-speaking peoples of the Southwestern United States, Southwest, the Southern Plains and Northern Mexico. They are linguistically related to the Navajo. They migrated from the Athabascan ho ...
until 1866. They also were sent to guard the
Overland Trail, keep the
Mormons
Mormons are a Religious denomination, religious and ethnocultural group, cultural group related to Mormonism, the principal branch of the Latter Day Saint movement started by Joseph Smith in upstate New York during the 1820s. After Smith's d ...
under observation by the establishment of
Fort Douglas in
Salt Lake City
Salt Lake City, often shortened to Salt Lake or SLC, is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Utah. It is the county seat of Salt Lake County, the most populous county in the state. The city is the core of the Salt Lake Ci ...
, and fought a campaign against the
Shoshone
The Shoshone or Shoshoni ( or ), also known by the endonym Newe, are an Native Americans in the United States, Indigenous people of the United States with four large cultural/linguistic divisions:
* Eastern Shoshone: Wyoming
* Northern Shoshon ...
culminating in the
Battle of Bear River.
In Nevada, Oregon and
Idaho Territory, California,
Oregon
Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while t ...
and
Washington Territorial Volunteers tried to protect the settlers and pacified tribes, fighting the
Goshute,
Paiute,
Ute and hostile
Snake Indians
Snake Indians is a collective name given to the Northern Paiute, Bannock, and Shoshone Native American tribes.
The term was used as early as 1739 by French trader and explorer Pierre Gaultier de Varennes, Sieur de la Verendrye when he descr ...
in the
Snake War from 1864 until 1866. In California, volunteer forces fought the
Bald Hills War in the northwestern forests until 1864 and also the
Owens Valley Indian War in 1862–1863.
Reconstruction era
With passage of federal
reconstruction laws between 1866 and 1870 the U.S. Army took control of the former rebel states and ordered elections to be held. These elections were the first in which African Americans could vote. Each state (except Virginia) elected Republican governments, which organized militia units.
[Singletary, Otis (1957). ''Negro militia and Reconstruction''. Austin: University of Texas Press. ] The majority of militiamen were black. Racial tension and conflict, sometimes intense, existed between the Negro
freedmen
A freedman or freedwoman is a person who has been released from slavery, usually by legal means. Historically, slaves were freed by manumission (granted freedom by their owners), emancipation (granted freedom as part of a larger group), or self- ...
and the ex-Confederate whites.
In parts of the South, white paramilitary groups and rifle clubs formed to counter this black militia, despite the laws prohibiting drilling, organizing, or parading except for duly authorized militia. In Reconstruction Louisiana, the Knights of the White Camelia, the Ku Klux Klan, Swamp Fox Rangers, and a couple other paramilitary groups sought to counter official governments. These groups engaged in a prolonged series of retaliatory, vengeful, and hostile acts against this black militia.
... the militia companies were composed almost entirely of Negroes and their marching and counter-marching through the country drove the white people to frenzy. Even a cool-headed man like General George advised the Democrats to form military organizations that should be able to maintain a front against the negro militia. Many indications pointed to trouble. A hardware merchant of Vicksburg reported that with the exceptions of the first year of the war his trade had never been so brisk. It was said that 10,000 Spencer rifles had been brought into the State.
The activity of the official black militia, and the unofficial illegal white rifle clubs, typically peaked in the autumn surrounding elections. This was the case in the race riot of
Clinton, Mississippi
Clinton is a List of cities in Mississippi, city in Hinds County, Mississippi, United States. Situated in the Jackson, Mississippi metropolitan area, Jackson metropolitan area, it is the List of municipalities in Mississippi, 10th most populous c ...
in September 1875, and the following month in
Jackson, Mississippi
Jackson is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Mississippi, most populous city of the U.S. state of Mississippi. The city sits on the Pearl River (Mississippi–Louisiana), Pearl River and is locate ...
. An eyewitness account:
I found the town in great excitement; un-uniformed militia were parading the streets, both white and colored. I found that the white people—democrats—were very much excited in consequence of the governor organizing the militia force of the state. ... I found that these people were determined to resist his marching the militia (to Clinton) with arms, and they threatened to kill his militiamen.
Outright war between the state militia and the white rifle clubs was avoided only by the complete surrender of one of the belligerents, though tensions escalated in the following months leading to a December riot in
Vicksburg, Mississippi resulting in the deaths of two whites and thirty-five black people. Reaction to this riot was mixed, with the local Democrats upset at the influx of federal troops that followed, and the Northern press expressing outrage: "Once more, as always, it is the Negroes that are slaughtered while the whites escape."
Great Railroad Strike of 1877
The
Great Railroad Strike of 1877
The Great Railroad Strike of 1877, sometimes referred to as the Great Upheaval, began on July 14 in Martinsburg, West Virginia, after the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) cut wages for the third time in a year. The Great Railroad Strike of 187 ...
, beginning in July 1877 in
Martinsburg, West Virginia and spreading to 15 other states across the Midwest, was the first national labor strike in United States history. West Virginia Governor
Henry M. Mathews was the first state commander-in-chief to call up militia units to suppress the strike, and this action has been viewed in retrospect as an action that would transform the
National Guard
National guard is the name used by a wide variety of current and historical uniformed organizations in different countries. The original National Guard was formed during the French Revolution around a cadre of defectors from the French Guards.
...
by revealing the shortcomings of the state militias. In all, approximately 45,000 militiamen were called out nationwide.
Posse Comitatus Act
In 1878, Congress passed the
Posse Comitatus Act intended to prohibit federal troops and federal-controlled militia from supervising elections. This act substantially limits the powers of the Federal government to use the military serving on active duty under
Title 10 for law enforcement, but does not preclude governors from using their National Guard in a law enforcement role as long as the guardsmen are serving under
Title 32 or on state active duty.
Spanish–American War
Despite a lack of initial readiness, training, and supplies, the militias of the United States fought and achieved victory in the
Spanish–American War
The Spanish–American War (April 21 – August 13, 1898) was fought between Restoration (Spain), Spain and the United States in 1898. It began with the sinking of the USS Maine (1889), USS ''Maine'' in Havana Harbor in Cuba, and resulted in the ...
.
Ludlow massacre
In 1914, in
Ludlow, Colorado, the militia was called out to calm the situation during a coal mine strike, but the sympathies of the militia leaders allied with company management and resulted in the deaths of roughly 19 to 25 people.
The state National Guard was originally called out, but the company was allowed to organize an additional private militia consisting of Colorado Fuel & Iron Company (CF&I) guards in National Guard uniforms augmented by non-uniformed mine guards.
The
Ludlow massacre was an attack by the Colorado National Guard and Colorado Fuel & Iron Company camp guards on a tent colony of 1,200 striking coal miners and their families at Ludlow, Colorado on April 20, 1914.
In retaliation for Ludlow, the miners armed themselves and attacked dozens of mines over the next ten days, destroying property and engaging in several skirmishes with the Colorado National Guard along a 40-mile front from Trinidad to Walsenburg. The entire strike cost between 69 and 199 lives. Thomas Franklin Andrews described it as the "deadliest strike in the history of the United States".
Mexican Revolution
American organized and unorganized militias fought in the
Mexican Revolution
The Mexican Revolution () was an extended sequence of armed regional conflicts in Mexico from 20 November 1910 to 1 December 1920. It has been called "the defining event of modern Mexican history". It saw the destruction of the Federal Army, its ...
. Some campaigned in Mexico as
insurgent
An insurgency is a violent, armed rebellion by small, lightly armed bands who practice guerrilla warfare against a larger authority. The key descriptive feature of insurgency is its asymmetric nature: small irregular forces face a large, well ...
forces and others fought in battles such as
Ambos Nogales and
Columbus in defense of the interests of United States.
World War I
#The Plattsburg Movement
Preparedness Movement. The Hays Law.
Twentieth century and current
Organized militia
Each state and most territories have two mandatory forces, namely the Army National Guard and the Air National Guard. Many states also have state defense forces and a naval militia, which assist, support and augment National Guard forces.
National Guard
The National Guard (or National Guard of a State) differs from the
National Guard of the United States; however, the two do go hand-in-hand.
The National Guard is a militia force organized by each of the 50 states, the
U.S. federal capital district, and three of the five populated
U.S. territories. Established under
Title 10 and
Title 32 of the
U.S. Code
The United States Code (formally The Code of Laws of the United States of America) is the official Codification (law), codification of the general and permanent Law of the United States#Federal law, federal statutes of the United States. It ...
, the state
National Guard
National guard is the name used by a wide variety of current and historical uniformed organizations in different countries. The original National Guard was formed during the French Revolution around a cadre of defectors from the French Guards.
...
serves as part of the first-line defense for the United States. A state or territorial National Guard is divided up into units stationed within their borders and operates under their respective state governor or territorial government.
The National Guard may be called up for active duty by the state governors or
territorial commanding generals to help respond to domestic emergencies and disasters, such as those caused by hurricanes, floods, and earthquakes.
The National Guard of the United States is a
military reserve force
A military reserve force is a military organization whose members (reservists) have military and civilian occupations. They are not normally kept under arms, and their main role is to be available when their military requires additional ma ...
composed of state National Guard members or units under federally recognized active or inactive
armed force
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily Weapon, armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable ...
service for the United States.
Created by the 1933 amendments to the
National Defense Act of 1916, the National Guard of the United States is a joint
reserve component of the
United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary Land warfare, land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of th ...
and the
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Air force, air service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is one of the six United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Tracing its ori ...
. The National Guard of the United States maintains two subcomponents: the
Army National Guard of the United States for the Army and the Air Force's
Air National Guard of the United States
The Air National Guard (ANG), also known as the Air Guard, is a Reserve components of the United States Armed Forces, federal military reserve force of the United States Air Force, as well as the air militia (United States), militia of each U.S. ...
.
The current
United States Code
The United States Code (formally The Code of Laws of the United States of America) is the official Codification (law), codification of the general and permanent Law of the United States#Federal law, federal statutes of the United States. It ...
, Title 10 (Armed forces), section 246 (Militia: Composition and Classes), paragraph (a) states: "The militia of the United States consists of all able-bodied males at least 17 years of age and, except as provided in section 313 of title 32, under 45 years of age who are, or who have made a declaration of intention to become, citizens of the United States and of female citizens of the United States who are members of the National Guard." Section 313 of Title 32 refers to persons with prior military experience. ("Sec. 313. Appointments and enlistments: age limitation
(a) To be eligible for original enlistment in the National Guard, a person must be at least 17 years of age and under 45, or under 64 years of age and a former member of the Regular Army, Regular Navy, Regular Air Force, or Regular Marine Corps. To be eligible for reenlistment, a person must be under 64 years of age. (b) To be eligible for appointment as an officer of the National Guard, a person must – (1) be a citizen of the United States; and (2) be at least 18 years of age and under 64.")
These persons remain members of the militia until age 64. Paragraph (b) further states, "The classes of the militia are: (1) the organized militia, which consists of the National Guard and the Naval Militia; and (2) the unorganized militia, which consists of the members of the militia who are not members of the National Guard or the Naval Militia."
The National Guard of the United States is the largest of the organized federal reserve military forces in the United States. The National Guard of the United States is classified (under title 10, United States Code (see above)) as the organized federal
reserve military force. Under federal control, the National Guard of the United States can be called up for active duty by the
President of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal government of t ...
. Since the
2003 invasion of Iraq, many National Guard units have served overseas – under the
Total Force Policy of 1973 which effectively combined the National Guard with the federal Reserve Components of the armed forces, making them regular troops. This can lead to problems for states that also face internal emergencies while the Guard is deployed overseas. To address such issues, many of the states, such as
New York and
Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
also have organized state "militia" forces or state guards which are under the control of the governor of a state; however, many of these "militia" also act as a reserve for the National Guard and are thus a part of it (this varies from state to state depending on individual state statutory laws). New York and Ohio also have active
naval militias, and a few other states have on-call or proposed ones. In 1990, the United States Supreme Court ruled in the case of
Perpich v. Department of Defense
''Perpich v. Department of Defense'', 496 U.S. 334 (1990), was a case decided by the United States Supreme Court concerning the Militia Clauses of Article One of the United States Constitution#Section 8: Powers of Congress, Article I, Section 8, o ...
that the federal government has plenary power over the National Guard, greatly reducing (to the point of nonexistence) the state government's ability to withhold consent to federal deployments and training missions of the National Guard.
State defense forces
Since the Militia Act of 1903, many states have created and maintained a reserve military force known as
state defense force
In the United States, state defense forces (SDFs) are military units that operate under the sole authority of a State governments of the United States, state government. State defense forces are authorized by state and federal law and are unde ...
s; some states refer to them as state military reserves or state guards. They were created to assist, support, and augment National Guard forces during peacetime conditions. During the call-up of National Guard forces for wartime deployments, state defense forces can be used to assume the full military responsibilities of the state. Their mission includes the defense of the state and the enforcement of military orders when ordered by their Governor.
Throughout the 20th century, state defense forces were used in every major war. New York Guard soldiers patrolled and secured the water aqueduct of New York and mass transit areas, and were even deployed to France to assist in logistical operations in World War I. The Texas State Guard's soldiers suppressed a riot and maintained peace and order in Texas throughout World War II.
Today state defense forces continue to assist, support, and augment the National Guard of the state. They provide logistical, administrative, medical, transportation, security, and ceremonial assistance. Some states have provided additional support, such as the New York State Defense Force (New York Guard) providing its soldiers to support and augment the National Guard CERFP Team. The California State Military Reserve provides the National Guard with soldiers to assist with military police training, and the Alaska State Defense Force constantly provides armed military police troops to assist with the security of that state. One of the major roles of the Mississippi State Guard is providing operational support during natural disasters such as hurricane relief operations.
Unorganized militia
All able-bodied men 17 to 45 of age who are not part of the organized militia are known as the unorganized militia (10 USC). Able-bodied men who are not eligible for inclusion in the reserve militia pool are those aliens not having declared their intent to become citizens of the United States (10 USC 246).
All female citizens who are members of National Guard units are also included in the reserve militia pool ().
Other persons who are exempt from call to duty () and are therefore not required to be in the reserve militia pool include:
* Former regular component veterans of the armed forces who have reached the age of 64 (32 USC 313). See Standby Reserve, and Individual Ready Reserve regarding status of veterans younger than 64 years.
* The Vice President (also constitutionally the President of the Senate, that body which confirms the appointment of senior armed forces officers made by the Commander in Chief).
* The judicial and executive officers of the United States, the several States and Territories, and Puerto Rico.
* Members of the armed forces, except members who are not on active duty.
* Customhouse clerks.
* Persons employed by the United States in the transmission of mail.
* Workmen employed in armories, arsenals, and naval shipyards of the United States.
* Pilots on navigable waters.
* Mariners in the sea service of a citizen of, or a merchant in, the United States.
At the time of formation of the Republic, each state was the authority commanding unorganized militias of their residents, as contrasted with organized military units subject to inclusion to the Continental Army.
Many individual states have additional statutes describing their residents as part of the state militia. For example
Washington law specifies all able-bodied citizens or intended citizens over the age of eighteen as members of the state militia, as explicitly distinct from the National Guard and Washington State Guard. In states such as Texas, the state constitution classifies male citizens between the ages of 17 and 45 to belong to the "Unorganized Reserve Militia". The Texas constitution also grants
county sheriffs and the state governor the authority to call upon the unorganized reserve militia to uphold the peace, repel invasion, and suppress rebellion, similar to the early "
Texas Rangers".
Private militias and the modern citizen-militia movement
Laws authorizing the state governments to officially make privately organized militias part of the state's official military force vary;
Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a landlocked state in the Western United States. It borders Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the seventh-most extensive, th ...
, for example, allows
the governor to "issue licenses to bodies of persons to organize, drill and bear arms as volunteer military companies or volunteer military organizations," whereas
South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
prohibits any group from being enlisted into
its state guard. States with military histories that date back to the
American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
may officially recognize militias from that era that continue to exist and operate independently;
Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
law explicitly makes the
National Lancers part of its organized militia and protects the right of the
Ancient and Honorable Artillery Company of Massachusetts to exist and operate as a private organization,
while Rhode Island recognizes a number of
independent chartered militias as a separate part of its overall military force. During World War II,
Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
authorized several private paramilitary militias to operate, including the
Businessmen's Military Training Corps and the
Hawaii Air Depot Volunteer Corps.
Since approximately 1992, there have been a number of state- and regional-level private organizations in the United States that call themselves militia or unorganized militia, some of which have been tied to
domestic terrorism and extremist views, which operate without any official sanctioning or licensing by their state governments.
Barbara MacQuade argues these paramilitary groups calling themselves militia are unconstitutional as is the 'insurrection theory' that many of these paramilitaries claim justifies their existence.
The 2000s and 2010s also saw the formation of several national-level private militia organizations, the largest of which were the
Oath Keepers and
Three Percenters.
List of legislated militia in the United States
U.S. federal militia forces
*
United States National Guard
The National Guard is a U.S. state, state-based military force that becomes part of the United States Armed Forces, U.S. military's reserve components of the United States Armed Forces, reserve components of the United States Army, U.S. Army a ...
U.S. states' militia forces
*
State defense force
In the United States, state defense forces (SDFs) are military units that operate under the sole authority of a State governments of the United States, state government. State defense forces are authorized by state and federal law and are unde ...
s
**
Naval militia
See also
*
Colonial American military history
*
Social history of soldiers and veterans in the United States
*
Irregular military
Irregular military is any military component distinct from a country's regular armed forces, representing non-standard militant elements outside of conventional governmental backing. Irregular elements can consist of militias, private armie ...
*
List of United States militia units in the American Revolutionary War
*
Nauvoo Legion
*
State Guard Association of the United States
References
Sources
Historic documents
*
Anti-Federalist Papers
*
Federalist Papers
*
Militia Act of 1792
*
Militia Act of 1903
*
National Defense Act of 1916
* National Guard Mobilization Act of 1933
*
Total Force Policy of 1973
Further reading
* Anderson, Fred. "A People’s Army: Provincial Military Service in Massachusetts during the Seven Years’ War" ''William and Mary Quarterly'' 40#4 (1983), pp. 500–27
online* Boucher, Ronald L. "The Colonial Militia As a Social Institution: Salem, Massachusetts 1764-1775." ''Military Affairs'' 37#4 (1973), pp. 125–30
online* Brundage, Lyle D. "The Organization, Administration, and Training of the United States Ordinary and Volunteer Militia, 1792-1861" (PhD dissertation, University of Michigan; ProQuest Dissertations & Theses, 1959. 5903913).
*
*
* Ferling, John. "Soldiers for Virginia: Who Served in the French and Indian War?" ''Virginia Magazine of History and Biography'' 94#3 (1986), pp. 307–2
online*
* Kreidberg, Marvin A., and Merton G. Henry. ''History of Military Mobilization in the United States Army 1775-1945'' (US Army, 1955
online not copyright because it is a government publication.
* Mahon, John K. "Bibliographic Essay on Research into the History of the Militia and the National Guard." ''Military Affairs'' 48#2 (1984) pp. 74–77
online*
*
*
* Radabaugh, Jack S. "The Militia of Colonial Massachusetts" ''Military Affairs'' 18#1 (1954), pp. 1–18
online* Selesky, Harold E. ''War and Society in Colonial Connecticut'' (Yale UP 1990)
* Shy, John W. ''A people numerous and armed: Reflections on the military struggle for American independence'' (U of Michigan Press, 1990
online
* Singletary, Otis. ''Negro militia and Reconstruction'', Austin: University of Texas Press. (1957)
* Smith, Joshua M. "The Yankee Soldier's Might: The District of Maine and the Reputation of the Massachusetts Militia, 1800–1812," ''New England Quarterly'' 84#2 (June 2011), 234–264.
* Stentiford, Barry M. "The Meaning of a Name: The Rise of the National Guard and the End of a Town Militia," ''Journal of Military History,'' July 2008, Vol. 72 Issue 3, pp 727–754
* Stentiford, Barry M. ''The American Home Guard: The State Militia in the Twentieth Century'' (Williams-Ford Texas A&M University Military History Series)"
{{Authority control
Gun politics in the United States
Military history of the United States
*
 The early colonists of America considered the militia an important social institution, necessary to provide defense and public safety. Wills, Garry (1999). ''A Necessary Evil, A History of American Distrust of Government'' Page 27. New York, NY; Simon & Schuster.
On August 29, 1643, the
The early colonists of America considered the militia an important social institution, necessary to provide defense and public safety. Wills, Garry (1999). ''A Necessary Evil, A History of American Distrust of Government'' Page 27. New York, NY; Simon & Schuster.
On August 29, 1643, the  During the French and Indian Wars, town militia formed a recruiting pool for the Provincial Forces. The legislature of the colony would authorize a certain force level for the season's campaign and set recruitment quotas for each local militia. In theory, militia members could be drafted by lot if there were inadequate forces for the Provincial Regulars; however, the draft was rarely resorted to because provincial regulars were highly paid (more highly paid than their regular British Army counterparts) and rarely engaged in combat.
In September 1755,
During the French and Indian Wars, town militia formed a recruiting pool for the Provincial Forces. The legislature of the colony would authorize a certain force level for the season's campaign and set recruitment quotas for each local militia. In theory, militia members could be drafted by lot if there were inadequate forces for the Provincial Regulars; however, the draft was rarely resorted to because provincial regulars were highly paid (more highly paid than their regular British Army counterparts) and rarely engaged in combat.
In September 1755,  The American Revolutionary War began near Boston, Massachusetts with the
The American Revolutionary War began near Boston, Massachusetts with the  By the 1830s, the
By the 1830s, the  Following South Carolina's declaration of secession, the Battle of
Following South Carolina's declaration of secession, the Battle of