Military alliance on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

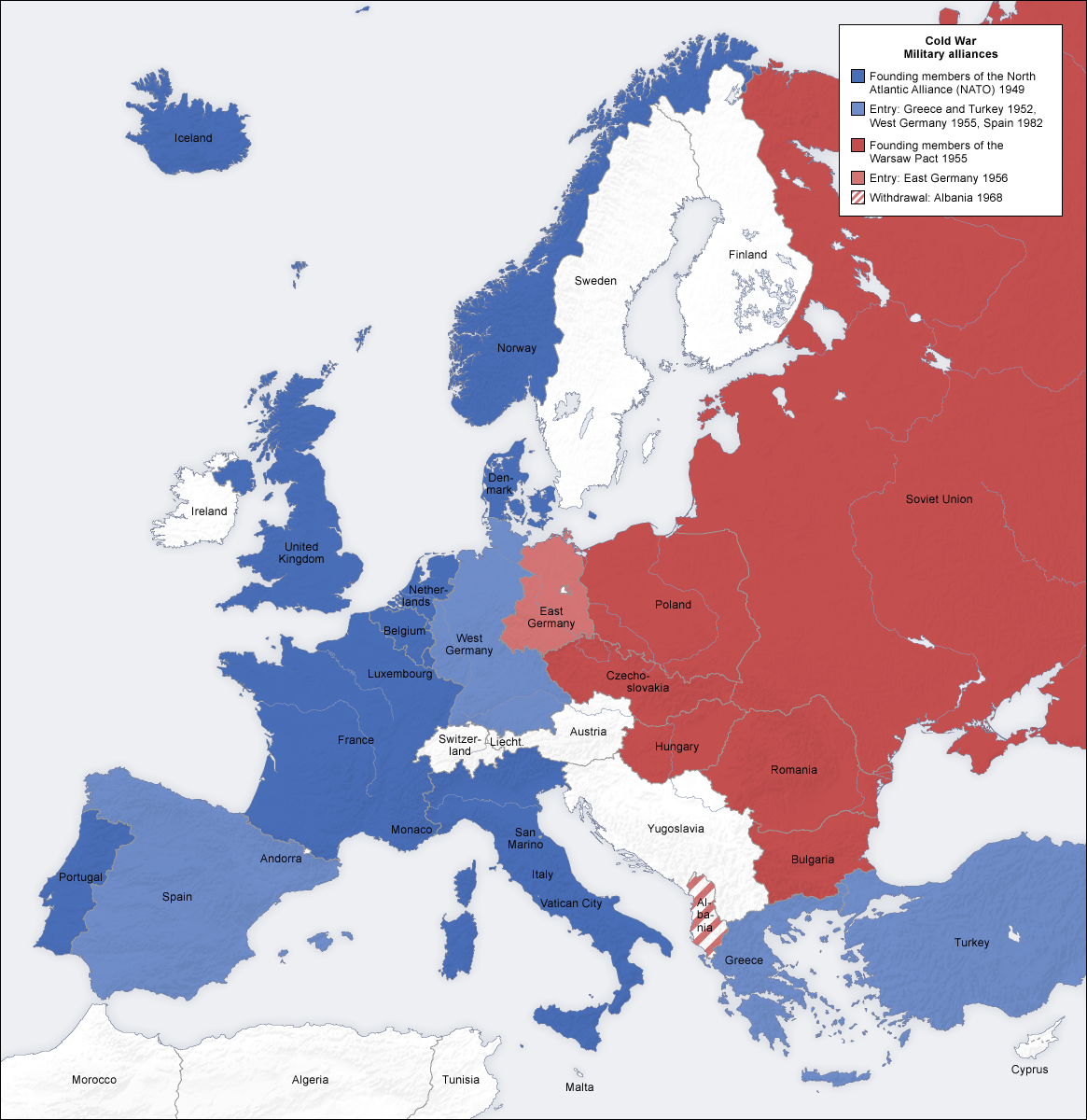 A military alliance is a formal agreement between nations that specifies mutual obligations regarding
A military alliance is a formal agreement between nations that specifies mutual obligations regarding
The Defense Cooperation Agreement Dataset (DCAD)
. ''Journal of Conflict Resolution''. 64 (4): 729–755. * * * * * * Weitsman, Patricia A. 2010. " Alliances and War." ''Oxford Research Encyclopedia of International Studies'', {{Authority control
 A military alliance is a formal agreement between nations that specifies mutual obligations regarding
A military alliance is a formal agreement between nations that specifies mutual obligations regarding national security
National security, or national defence (national defense in American English), is the security and Defence (military), defence of a sovereign state, including its Citizenship, citizens, economy, and institutions, which is regarded as a duty of ...
. In the event a nation is attacked, members of the alliance are often obligated to come to their defense regardless if attacked directly. Military alliances can be classified into defense pacts, non-aggression pact
A non-aggression pact or neutrality pact is a treaty between two or more states/countries that includes a promise by the signatories not to engage in military action against each other. Such treaties may be described by other names, such as a t ...
s, and ententes. Alliances may be covert (as was common from 1870 to 1916) or public.
According to a 2002 dataset of military alliances, there have been 538 alliance treaties from 1815 to 2003. The vast majority of the alliances involve commitments to come to the military support of one ally involved in war. The vast majority are defensive in nature. Since the end of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, military alliances have usually behaved less aggressively and act more as a deterrent.
Characteristics
Military alliances are related tocollective security
Collective security is arrangement between states in which the institution accepts that an attack on one state is the concern of all and merits a collective response to threats by all. Collective security was a key principle underpinning the Lea ...
systems but can differ in nature. An early 1950s memorandum from the United States Department of State
The United States Department of State (DOS), or simply the State Department, is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the U.S. federal government responsible for the country's foreign policy of the United State ...
explained the difference by noting that historically, alliances "were designed to advance the respective nationalistic interests of the parties, and provided for joint military action if one of the parties in pursuit of such objectives became involved in war." A collective security arrangement "is directed against no one; it is directed solely against aggression. It seeks not to influence any shifting 'balance of power' but to strengthen the 'balance of principle'."
The obvious motivation in states engaging in military alliances is to protect themselves against threats from other countries. However, states have also entered into alliances to improve ties with a particular nation or to manage conflict with a particular nation.
The nature of alliances, including their formation and cohesiveness (or lack thereof), is a subject of much academic study past and present. Influential works include those by Glenn Snyder, Stephen Walt
Stephen Martin Walt (born July 2, 1955) is an American political scientist serving as the Robert and Renee Belfer Professor of international relations at the Harvard Kennedy School. A member of the realist school of international relations, Walt ...
, and Kenneth Waltz
Kenneth Neal Waltz (; June 8, 1924 – May 12, 2013) was an American political scientist who was a member of the faculty at both the University of California, Berkeley, and Columbia University and one of the most prominent scholars in the field ...
. Kenneth Waltz
Kenneth Neal Waltz (; June 8, 1924 – May 12, 2013) was an American political scientist who was a member of the faculty at both the University of California, Berkeley, and Columbia University and one of the most prominent scholars in the field ...
outlined in his 1979 book '' Theory of International Politics'' a neorealist theory of international politics where he argued that balances of power tend to form in world politics. Alongside neoliberalism
Neoliberalism is a political and economic ideology that advocates for free-market capitalism, which became dominant in policy-making from the late 20th century onward. The term has multiple, competing definitions, and is most often used pe ...
, neorealism is one of the two most influential contemporary approaches to the study of military alliances in international relations; the two perspectives dominated international relations theory from the 1960s to the 1990s. Neorealism emerged from the North American discipline of political science
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and Power (social and political), power, and the analysis of political activities, political philosophy, political thought, polit ...
, and reformulates the understanding of military alliances in the classical realist tradition of E. H. Carr, Hans Morgenthau
Hans Joachim Morgenthau (February 17, 1904 – July 19, 1980) was a German-American jurist and political scientist who was one of the major 20th-century figures in the study of international relations. Morgenthau's works belong to the tradition ...
, George Kennan
George Frost Kennan (February 16, 1904 – March 17, 2005) was an American diplomat and historian. He was best known as an advocate of a policy of containment of Soviet expansion during the Cold War. He lectured widely and wrote scholarly hist ...
and Reinhold Niebuhr
Karl Paul Reinhold Niebuhr (June 21, 1892 – June 1, 1971) was an American Reformed theologian, ethicist, commentator on politics and public affairs, and professor at Union Theological Seminary for more than 30 years. Niebuhr was one of Ameri ...
. Neorealism is subdivided into defensive
Defense or defence may refer to:
Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups
* Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare
* Civil defense, the organizing of civilians to deal with emergencies or enemy attacks
* Defense indust ...
and offensive neorealism.
During peace-time, according to a 2019 study, almost all alliances from 1870 to 1916 may have been covert or implied. In other time periods, covert alliances have been rare. The study argues that from 1870 to 1916, the unusual amount of covert alliances was incentivized by other covert alliances. The creation of public alliances would signal to the covert ally that the public alliance was more valuable. According to Ronald Krebs, pre-WWII alliances were generally "relatively simple, short-lived affairs."
Common problems for alliances revolve around free-riding and burden-sharing. Members of an alliance have incentives not to contribute to the alliance while simultaneously benefiting on the public goods
In economics, a public good (also referred to as a social good or collective good)Oakland, W. H. (1987). Theory of public goods. In Handbook of public economics (Vol. 2, pp. 485–535). Elsevier. is a goods, commodity, product or service that ...
provided by the alliance. According to Mancur Olson
Mancur Lloyd Olson Jr. (; January 22, 1932 – February 19, 1998) was an American economist and political scientist who taught at the University of Maryland, College Park. His most influential contributions were to new institutional economics, ...
and Richard Zeckhauser's classic study of alliances, small states frequently free-ride on the large state's contributions to an alliance. Small allies that are militarily vulnerable are less likely to free-ride, whereas strategically important small allies are most likely to free-ride. Alliances may also lead to moral hazard whereby allies behave more aggressively and recklessly if they believe that the alliance will aid them in any conflict. On the whole, alliances do deter aggression on net.
Military alliances can incentivize the kinds of military capabilities that member states develop. Rather than duplicate similar capabilities across allies, alliances can incentivize member states to specialize in certain capabilities that they have an advantage in and under-produce other capabilities that they have a disadvantage in producing. This can enhance the capabilities of the alliance as a whole.
Within alliances, actors may fear entrapment or abandonment. Entrapment means that allies get dragged into a conflict over one ally's interests that the other allies do not share. Scholars have disputed the prevalence of entrapment, with Stephen Brooks and William Wohlforth writing "it is nearly impossible to find a clear case of entrapment actually occurring." Abandonment means that allies do not come to the rescue of a fellow ally. Strong commitments to an alliance can reduce the bargaining power of that ally vis-a-vis the other allies. However, an ally whose commitment to the alliance is in doubt has greater bargaining leverage. Weak alliance commitments can make it easier for the ally to realign the alliance if a fellow ally is considered unsatisfactory. Strong alliance commitments may strengthen the adversary's alliance, as the adversary may face a greater threat.
The failure of a strong ally to come to the rescue of a weaker ally (abandonment) may jeopardize the strong ally's other alliances. However, it may also strengthen the other alliances, as the other allies may sometimes prefer that the strong ally abandons a weak ally if it is likely to raise the risks of military escalation for the other allies.
Great powers may engage in coercive actions, in particular covert action, against allies when there are doubts about allies’ future alignment.
European historiography
In the European historical context, a military alliance can be viewed as a league between independent states, defined by treaty, for the purpose of combined action, defensive or offensive, or both. The oldest such alliance in the world today is the Anglo-Portuguese Alliance, dating back to 1373 where the then Kingdoms ofEngland
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
and Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
pledged to "perpetual friendship" between the two countries. This remains in action today
Today (archaically to-day) may refer to:
* The current day and calendar date
** Today is between and , subject to the local time zone
* Now, the time that is perceived directly, present
* The current, present era
Arts, entertainment and m ...
between the current United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
and Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
, and the two have never fought against each other in any military campaign. Alliances have often been directed to specific objects carefully defined in the treaties. Thus the Triple Alliance of 1668 between Great Britain, Sweden and the Netherlands, and the Grand Alliance of 1689 between the Holy Roman Empire, Holland, England, Spain and Saxony, were both directed against the power of Louis XIV of France
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
. The Quadruple or Grand Alliance of 1814, defined in the Treaty of Chaumont, between Great Britain, Austria, Russia and Prussia, had for its object the overthrow of Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
and his dynasty, and the confining of France within her traditional boundaries. The Triple Alliance of 1882 between Germany, Austria and Italy was ostensibly directed to the preservation of European peace against any possible aggressive action of France or Russia; and this led in turn, some ten years later, to the Dual Alliance between Russia and France, for mutual support in case of any hostile action of the other powers.
Occasionally, however, attempts have been made to give alliances a more general character. Thus the Holy Alliance
The Holy Alliance (; ), also called the Grand Alliance, was a coalition linking the absolute monarchist great powers of Austria, Prussia, and Russia, which was created after the final defeat of Napoleon at the behest of Emperor Alexander I of Rus ...
of 26 September 1815 was an attempt, inspired by the religious idealism of the Emperor Alexander I of Russia
Alexander I (, ; – ), nicknamed "the Blessed", was Emperor of Russia from 1801, the first king of Congress Poland from 1815, and the grand duke of Finland from 1809 to his death in 1825. He ruled Russian Empire, Russia during the chaotic perio ...
, to find in the "sacred precepts of the Gospel", a common basis for a general league of the European governments, its object being, primarily, the preservation of peace. So, too, by Article VI of the Quadruple Treaty signed at Paris on 20 November 1815 – which renewed that of Chaumont and was again renewed, in 1818, at Aix-la-Chapelle – the scope of the Grand Alliance was extended to objects of common interest not specifically stated in the treaties. The article runs: "In order to consolidate the intimate tie which unites the four sovereigns for the happiness of the world, the High Contracting Powers have agreed to renew at fixed intervals, either under their own auspices or by their respective ministers, meetings consecrated to great common objects and to the examination of such measures as at each one of these epochs shall be judged most salutary for the peace and prosperity of the nations and the maintenance of the tranquility of Europe".
It was this article of the treaty of the 20 November 1815, rather than the Holy Alliance, that formed the basis of the serious effort made by the great powers, between 1815 and 1822, to govern Europe in concert. In general it proved that an alliance, to be effective, must be clearly defined as to its objects, and that in the long run the treaty in which these objects are defined must – to quote Otto von Bismarck
Otto, Prince of Bismarck, Count of Bismarck-Schönhausen, Duke of Lauenburg (; born ''Otto Eduard Leopold von Bismarck''; 1 April 1815 – 30 July 1898) was a German statesman and diplomat who oversaw the unification of Germany and served as ...
's somewhat cynical dictum – "be reinforced by the interests" of the parties concerned. Yet the "moral alliance" of Europe, as Count Karl Nesselrode
Karl Robert Reichsgraf von Nesselrode-Ehreshoven, also known as Charles de Nesselrode (; 14 December 1780 – 23 March 1862), was a Foreign policy of the Russian Empire, Russian diplomat of German nobility, German noble descent. For 40 years ( ...
called it, though it failed to secure the permanent harmony of the powers, was an effective instrument for peace during the years immediately following the downfall of Napoleon; and it set the precedent for those periodical meetings of the representatives of the powers, for the discussion and settlement of questions of international importance, which, though cumbrous and inefficient for constructive work, contributed much to the preservation of the general peace during much of the nineteenth century.
See also
*List of military alliances
A military alliance is a legally binding treaty between two or more parties in which the contracting parties agree to mutually protect one another militarily in case of an armed conflict. Military alliances differ from Coalition#Military, coaliti ...
* Multinational force A multinational force is a multinational operation which may be defensive, offensive, or for peacekeeping purposes. In multinational operations, many countries form an alliance to carry them out.
Multinational forces include:
* Supreme Headquar ...
* Coercion (international relations)
In international relations, coercion refers to the imposition of costs by a state on other states and non-state actors to prevent them from taking an action ( deterrence) or to compel them to take an action ( compellence). Coercion frequently tak ...
Notes
References
* *Further reading
* Elias, Barbara. 2020. '' Why Allies Rebel: Defiant Local Partners in Counterinsurgency Wars''. Cambridge University Press. *Kinne, Brandon J. (2020).The Defense Cooperation Agreement Dataset (DCAD)
. ''Journal of Conflict Resolution''. 64 (4): 729–755. * * * * * * Weitsman, Patricia A. 2010. " Alliances and War." ''Oxford Research Encyclopedia of International Studies'', {{Authority control