Middle Egypt on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
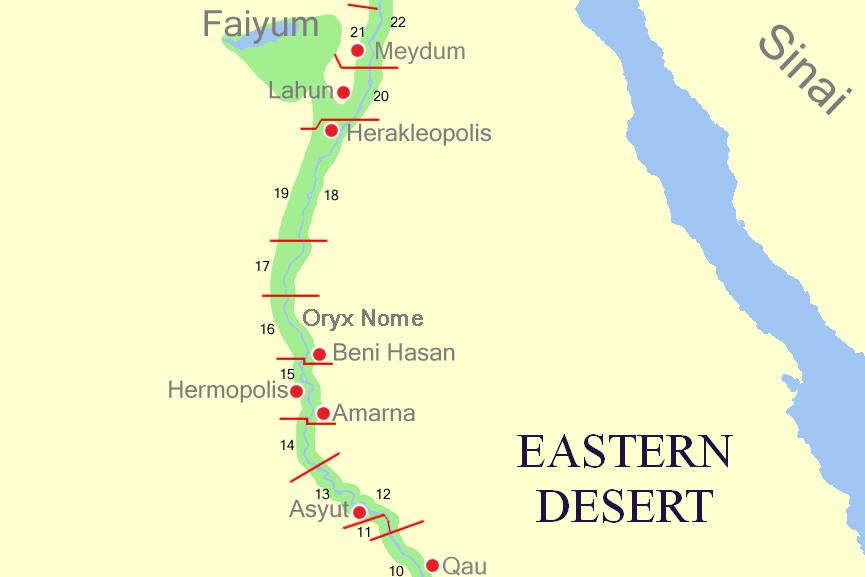 Middle Egypt () is the section of land between
Middle Egypt () is the section of land between
Heptanomide. 1.2. Vues de Gebel Abou Fedah et des environs; 3-5. Épures de chapiteaux tracées dans les hypogées de Gebel Abou Fedah; 6-8. Plans et détails de Gebel Cheykh el Harydy.
{{Regions of Africa *
 Middle Egypt () is the section of land between
Middle Egypt () is the section of land between Lower Egypt
Lower Egypt ( ar, مصر السفلى '; ) is the northernmost region of Egypt, which consists of the fertile Nile Delta between Upper Egypt and the Mediterranean Sea, from El Aiyat, south of modern-day Cairo, and Dahshur. Historically, ...
(the Nile Delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to ...
) and Upper Egypt
Upper Egypt ( ar, صعيد مصر ', shortened to , , locally: ; ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the lands on both sides of the Nile that extend upriver from Lower Egypt in the north to Nubia in the south.
In ancient E ...
, stretching upstream from Asyut
AsyutAlso spelled ''Assiout'' or ''Assiut'' ( ar, أسيوط ' , from ' ) is the capital of the modern Asyut Governorate in Egypt. It was built close to the ancient city of the same name, which is situated nearby. The modern city is located at ...
in the south to Memphis
Memphis most commonly refers to:
* Memphis, Egypt, a former capital of ancient Egypt
* Memphis, Tennessee, a major American city
Memphis may also refer to:
Places United States
* Memphis, Alabama
* Memphis, Florida
* Memphis, Indiana
* Memp ...
in the north. At the time, Ancient Egypt was divided into Lower and Upper Egypt, though Middle Egypt was technically a subdivision of Upper Egypt. It was not until the 19th century that archaeologists felt the need to divide Upper Egypt in two. As a result, they coined the term "Middle Egypt" for the stretch of river between Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metr ...
and the Qena Bend. It was also associated with a region termed "Heptanomis
Middle Egypt () is the section of land between Lower Egypt (the Nile Delta) and Upper Egypt, stretching upstream from Asyut in the south to Memphis in the north. At the time, Ancient Egypt was divided into Lower and Upper Egypt, though Middle ...
" (; Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
: , in Ptol. iv. 5. § 55; more properly or , in Dionysius Periegetes 251; and sometimes ; meaning "Seven Nomes", a " nome" being a subdivision of ancient Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
), generally as the district which separates the Thebaïd
The Thebaid or Thebais ( grc-gre, Θηβαΐς, ''Thēbaïs'') was a region in ancient Egypt, comprising the 13 southernmost nomes of Upper Egypt, from Abydos to Aswan.
Pharaonic history
The Thebaid acquired its name from its proximity t ...
from the Delta.
Middle Egypt today can be identified as the part of the Nile Valley that, while geographically part of Upper Egypt, is culturally closer to Lower Egypt. For instance, in terms of language, the Egyptian Arabic
Egyptian Arabic, locally known as Colloquial Egyptian ( ar, العامية المصرية, ), or simply Masri (also Masry) (), is the most widely spoken vernacular Arabic dialect in Egypt. It is part of the Afro-Asiatic language family, and ...
of people in Beni Suef
Beni Suef ( ar, بني سويف, Baniswēf the capital city of the Beni Suef Governorate in Egypt. Beni Suef is the location of Beni Suef University. An important agricultural trade centre on the west bank of the Nile River, the city is located ...
and northwards shares features with Cairene and particularly rural Delta Arabic rather than with the Sa'idi Arabic
A Ṣa‘īdī (, Coptic: ⲣⲉⲙⲣⲏⲥ ''Remris'') is a person from Upper Egypt (, Coptic: ⲙⲁⲣⲏⲥ ''Maris'').
Etymology
The word literally means "from Ṣa‘īd" (i.e. Upper Egypt), and can also refer to a form of music or ...
spoken further south, and are often not considered Sa'idi
A Ṣa‘īdī (, Coptic language, Coptic: ⲣⲉⲙⲣⲏⲥ ''Remris'') is a person from Upper Egypt (, Coptic language, Coptic: ⲙⲁⲣⲏⲥ ''Maris'').
Etymology
The word literally means "from Ṣa‘īd" (i.e. Upper Egypt), and can a ...
s.
Heptanomis
In the 19th century, "Heptanomis" was described generally as the district which separates theThebaïd
The Thebaid or Thebais ( grc-gre, Θηβαΐς, ''Thēbaïs'') was a region in ancient Egypt, comprising the 13 southernmost nomes of Upper Egypt, from Abydos to Aswan.
Pharaonic history
The Thebaid acquired its name from its proximity t ...
from the Delta. In as much, however, as the appellation of the Seven Nomes is political rather than territorial, it is not easy to define the actual boundaries of this region. The northern portion belonged to the kingdom of Lower Egypt, of which it contained the capital, Memphis
Memphis most commonly refers to:
* Memphis, Egypt, a former capital of ancient Egypt
* Memphis, Tennessee, a major American city
Memphis may also refer to:
Places United States
* Memphis, Alabama
* Memphis, Florida
* Memphis, Indiana
* Memp ...
; the southern appertained to the elder kingdom of Thebes, so long at least as there continued to be two monarchies in the Nile valley. It is not possible to determine at what period, if indeed at any, the Heptanomis was regarded as an integral third of Egypt. About the number of its nomes there can be no question; but which, at any given era, were the seven principal nomes, it is less easy to decide. They probably varied with the vicissitudes of local prosperity, war, commerce, or migration, from time to time, causing a superior nome to decline, and, on the contrary, raising an inferior nome to eminence. According to Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
and Agatharchides
Agatharchides or Agatharchus ( grc-gre, Ἀγαθαρχίδης or , ''Agatharchos'') of Cnidus was a Greek historian and geographer (flourished 2nd century BC).
Life
Agatharchides is believed to have been born at Cnidus, hence his appellation. A ...
(''De Rubr. Mar. ap.'' Photius
Photios I ( el, Φώτιος, ''Phōtios''; c. 810/820 – 6 February 893), also spelled PhotiusFr. Justin Taylor, essay "Canon Law in the Age of the Fathers" (published in Jordan Hite, T.O.R., & Daniel J. Ward, O.S.B., "Readings, Cases, Materia ...
''Biblioth.'' p. 1339. R.), both of whom wrote long after the original divisions had been modified, the Seven Nomes were the following: (1) Memphites; (2) Heracleopolites; (3) Crocodilopolites, renamed Arsinoites; (4) Aphroditopolites; (5) Oxyrhynchites; (6) Cynopolites; and (7) Hermopolites. The Greater and Lesser Lesser, from Eliezer (, "Help/Court of my God"), is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Adolf Lesser (1851–1926), German physician
* Aleksander Lesser (1814–1884), Polish painter and art critic
* Anton Lesser (born 1952), Br ...
Oases were always reckoned portions of the Heptanomis, and hence it must apparently have sent nine, and not seven, nomarchs to the general assembly in the Labyrinth
In Greek mythology, the Labyrinth (, ) was an elaborate, confusing structure designed and built by the legendary artificer Daedalus for King Minos of Crete at Knossos. Its function was to hold the Minotaur, the monster eventually killed by ...
. The capitals of the Nomes, whose names are sufficiently indicated by the respective appellations of the divisions themselves, ''e.g.'' Hermopolis
Hermopolis ( grc, Ἑρμούπολις ''Hermoúpolis'' "the City of Hermes", also ''Hermopolis Magna'', ''Hermoû pólis megálẽ'', egy, ḫmnw , Egyptological pronunciation: "Khemenu"; cop, Ϣⲙⲟⲩⲛ ''Shmun''; ar, الأشمون� ...
of the Nomos Hermopolites, ''etc.'', were also the chief towns of the Middle Land. This district comprised the three greatest works of Egyptian art and enterprise, e. g., the Pyramids, the Labyrinth, and the artificial district formed by the canal Bahr-Jusuf (Canal of Joseph), the Nomos Arsinoites or the Fayyum
Faiyum ( ar, الفيوم ' , borrowed from cop, ̀Ⲫⲓⲟⲙ or Ⲫⲓⲱⲙ ' from egy, pꜣ ym "the Sea, Lake") is a city in Middle Egypt. Located southwest of Cairo, in the Faiyum Oasis, it is the capital of the modern Faiyum ...
(Fyoum). The Heptanomis extended from latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north ...
27°4′ North to 30° north; its boundary to south was the castle of Hermopolis (), to the north the apex of the Delta and the town of Cercasorum, on the west the irregular line of the Libyan Desert
The Libyan Desert (not to be confused with the Libyan Sahara) is a geographical region filling the north-eastern Sahara Desert, from eastern Libya to the Western Desert of Egypt and far northwestern Sudan. On medieval maps, its use predates ...
, and on the east, the hills which confine the Nile, or the sinuous outline, the recesses and projections of the Arabian mountains. Thus, near Hermopolis at the southern extremity of this region, the eastern hills approach very near the river, while those on the western or left bank recede to a considerable distance from it. Again, in latitude 29° north, the Libyan hills retire from the vicinity of the Nile, bend toward northwest, and sharply return to it by a curve to east, embracing the province of Arsinoë (formerly Crocodilopolis
Faiyum ( ar, الفيوم ' , borrowed from cop, ̀Ⲫⲓⲟⲙ or Ⲫⲓⲱⲙ ' from egy, pꜣ ym "the Sea, Lake") is a city in Middle Egypt. Located southwest of Cairo, in the Faiyum Oasis, it is the capital of the modern Faiyum ...
, now the city of Al Fayyum
Faiyum ( ar, الفيوم ' , borrowed from cop, ̀Ⲫⲓⲟⲙ or Ⲫⲓⲱⲙ ' from egy, pꜣ ym "the Sea, Lake") is a city in Middle Egypt. Located southwest of Cairo, in the Faiyum Oasis, it is the capital of the modern Faiy ...
). Between the hills on which the Pyramids stand and the corresponding elevation of Gebel-el-Mokattam on the eastern bank of the river, the Heptanomis expands, until near Cercasorum it acquires almost the breadth of the subjacent Delta. The Heptanomis is remarkable for its quarries of stone and its rock-grottoes. Besides the Alabastrites, to the north of Antinoë the grottoes of Beni Hasan
Beni Hasan (also written as Bani Hasan, or also Beni-Hassan) ( ar, بني حسن) is an ancient Egyptian cemetery. It is located approximately to the south of modern-day Minya in the region known as Middle Egypt, the area between Asyut and Me ...
, the ''Speos Artemidos'' of the Greeks is found. Nine miles lower down are the grottoes of Kom el-Ahmar
Hebenu is an ancient Egyptian city. It was the early capital of the 16th Upper Egyptian Nome. The modern village of Kom el Ahmar ( Minya Governorate) is built on the site where the ancient city stood.
See also
* List of ancient Egyptian to ...
, and in the Arabian desert, on the east, quarries of the beautiful veined and white alabaster, which the Egyptians employed in their sarcophagi, and in the more delicate portions of their architecture. From the quarries of Tourah and Massarah, in the hills of Gebel-el-Mokattam, east of Memphis, they obtained the limestone used in casing the pyramids. The roads from these quarries may still be traced across the intervening plain. Under the Ptolemies
The Ptolemaic dynasty (; grc, Πτολεμαῖοι, ''Ptolemaioi''), sometimes referred to as the Lagid dynasty (Λαγίδαι, ''Lagidae;'' after Ptolemy I's father, Lagus), was a Macedonian Greek royal dynasty which ruled the Ptolemaic ...
, the Heptanomis was governed by an (viceroy / prefect), and by an officer of corresponding designation, procurator
Procurator (with procuracy or procuratorate referring to the office itself) may refer to:
* Procurator, one engaged in procuration, the action of taking care of, hence management, stewardship, agency
* ''Procurator'' (Ancient Rome), the title o ...
, under the Roman Caesars. The procurator described in inscriptions (Orelli, ''Inscr. Lat.'' n. 516) was described as ''procurator Augusti epistrategiae Septem Nomorum''. Under the later Caesars in the 3rd century, the five northern Nomes, Memphites, Heracleopolites, Arsinoites, Aphroditopolites, and Oxyrhyncites, together with the Nomos Leptopolites, constituted the province of Arcadia Ægypti, which subsequently became a metropolitan episcopal see
An episcopal see is, in a practical use of the phrase, the area of a bishop's ecclesiastical jurisdiction.
Phrases concerning actions occurring within or outside an episcopal see are indicative of the geographical significance of the term, mak ...
. The natural productions of the Heptanomis resemble those of Upper Egypt generally, and present a more tropical fauna and flora than those of the Delta. Its population also was less modified by Greek or Nubia
Nubia () ( Nobiin: Nobīn, ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile (just south of Aswan in southern Egypt) and the confluence of the Blue and White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sud ...
n admixture than that of either Lower or Upper Egypt; although, after the 4th century, the Heptanomis was overrun by Arabian
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
marauders, who considerably affected the native racial mix.
The capital cities of the Heptanomis were collectively called the "Heptapolis" ( grc, Ἑπταπολίς, meaning "Seven Cities"), and they were Memphis, Heracleopolis, Crocodilopolis
Faiyum ( ar, الفيوم ' , borrowed from cop, ̀Ⲫⲓⲟⲙ or Ⲫⲓⲱⲙ ' from egy, pꜣ ym "the Sea, Lake") is a city in Middle Egypt. Located southwest of Cairo, in the Faiyum Oasis, it is the capital of the modern Faiyum ...
(later Arsinoe), Aphroditopolis, Oxyrhynchos
Oxyrhynchus (; grc-gre, Ὀξύρρυγχος, Oxýrrhynchos, sharp-nosed; ancient Egyptian ''Pr-Medjed''; cop, or , ''Pemdje''; ar, البهنسا, ''Al-Bahnasa'') is a city in Middle Egypt located about 160 km south-southwest of Cair ...
, Cynopolis
Cynopolis ( gr, Κυνόπολις for "city of the dog") was the Hellenistic toponym for two cities in ancient Egypt. Both Cynopolis superior and Cynopolis inferior were bishoprics in Christian times.
Cynopolis superior
Cynopolis was the Gre ...
and Hermopolis
Hermopolis ( grc, Ἑρμούπολις ''Hermoúpolis'' "the City of Hermes", also ''Hermopolis Magna'', ''Hermoû pólis megálẽ'', egy, ḫmnw , Egyptological pronunciation: "Khemenu"; cop, Ϣⲙⲟⲩⲛ ''Shmun''; ar, الأشمون� ...
.
Major cities
*6th of October City
6th of October ( ar, السادس من أكتوبر, Al Sādis Min Uktōber; arz, ستة اكتوبر, Setta Oktōbar) is a city in Giza Governorate, a satellite town and part of the urban area of Cairo, Egypt, 32 km (20 miles) outside the ...
* Beni Suef
* Minya
* Giza
Giza (; sometimes spelled ''Gizah'' arz, الجيزة ' ) is the second-largest city in Egypt after Cairo and fourth-largest city in Africa after Kinshasa, Lagos and Cairo. It is the capital of Giza Governorate with a total population of 9.2 ...
* Fayoum
Faiyum ( ar, الفيوم ' , borrowed from cop, ̀Ⲫⲓⲟⲙ or Ⲫⲓⲱⲙ ' from egy, pꜣ ym "the Sea, Lake") is a city in Middle Egypt. Located southwest of Cairo, in the Faiyum Oasis, it is the capital of the modern Faiyum ...
See also
*Upper and Lower Egypt
In Egyptian history, the Upper and Lower Egypt period (also known as The Two Lands) was the final stage of prehistoric Egypt and directly preceded the unification of the realm. The conception of Egypt as the Two Lands was an example of the dual ...
* Geography of Egypt
References
External links
Heptanomide. 1.2. Vues de Gebel Abou Fedah et des environs; 3-5. Épures de chapiteaux tracées dans les hypogées de Gebel Abou Fedah; 6-8. Plans et détails de Gebel Cheykh el Harydy.
{{Regions of Africa *
Middle Egypt
Middle Egypt () is the section of land between Lower Egypt (the Nile Delta) and Upper Egypt, stretching upstream from Asyut in the south to Memphis in the north. At the time, Ancient Egypt was divided into Lower and Upper Egypt, though Middle ...
it:Geografia dell'antico Egitto#Medio Egitto