Michaelskirche (München) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
St. Michael's is a
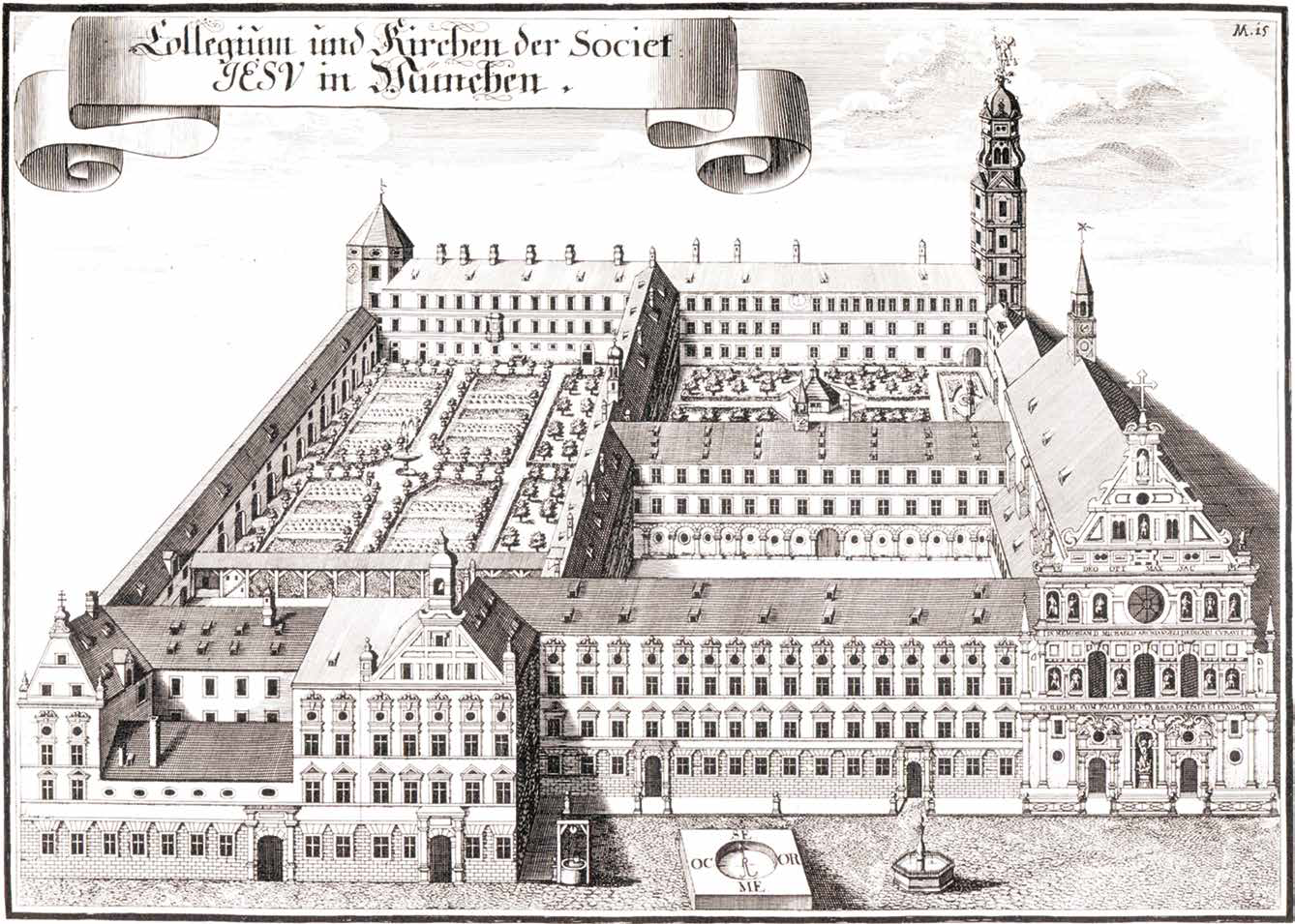
 The church was built by William V, Duke of Bavaria between 1583–97 as a spiritual center for the
The church was built by William V, Duke of Bavaria between 1583–97 as a spiritual center for the
Jesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders = ...
church in Munich, southern Germany, the largest Renaissance church north of the Alps. The style of the building had an enormous influence on Southern German early Baroque architecture
Baroque architecture is a highly decorative and theatrical style which appeared in Italy in the early 17th century and gradually spread across Europe. It was originally introduced by the Catholic Church, particularly by the Jesuits, as a means ...
.
History
In 1556,Albert V, Duke of Bavaria
Albert V (German: ''Albrecht V.'') (29 February 1528 – 24 October 1579) was Duke of Bavaria from 1550 until his death. He was born in Munich to William IV and Maria Jacobäa of Baden.
Early life
Albert was educated at Ingolstadt by Catholic ...
granted the Society of Jesus (Jesuits) permission to establish what is now Wilhelmsgymnasium in Munich, thus establishing the order's presence in the city. The collegiate church In Christianity, a collegiate church is a church where the daily office of worship is maintained by a college of canons: a non-monastic or "secular" community of clergy, organised as a self-governing corporate body, which may be presided over by ...
was only established during the reign of his son William V, Duke of Bavaria, also known as "the Pious". who was a supporter of the Jesuits' Counter Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also called the Catholic Reformation () or the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to the Protestant Reformation. It began with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) a ...
tenets.
The church was finally consecrated in 1597, after fourteen years of construction. When the Jesuits were suppressed and banned from most Catholic territories in Europe, the church came into possession of the Bavarian Royal Family and eventually the State of Bavaria, when Germany became a republic.
Architecture

 The church was built by William V, Duke of Bavaria between 1583–97 as a spiritual center for the
The church was built by William V, Duke of Bavaria between 1583–97 as a spiritual center for the Counter Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also called the Catholic Reformation () or the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to the Protestant Reformation. It began with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) a ...
.Munich City of the Arts by Hans Nohbauer, pp. 26, 115 The foundation stone was laid in 1585.''Germany'' by Joanna Egert-Romanowska and Małgorzata Omilanowska, p. 202
In order to realise his ambitious plans for the church and the adjoining college
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') is an educational institution or a constituent part of one. A college may be a degree-awarding tertiary educational institution, a part of a collegiate or federal university, an institution offering ...
, Duke William had 87 houses in the best location pulled down, ignoring the protests of the citizens. The church was erected in two stages. In the first stage (1583–88), the church was built by the model of Il Gesù in Rome and given a barrel-vault
A barrel vault, also known as a tunnel vault, wagon vault or wagonhead vault, is an architectural element formed by the extrusion of a single curve (or pair of curves, in the case of a pointed barrel vault) along a given distance. The curves are ...
ed roof by an unknown architect, the vault being the largest in the world apart from that of St Peter's Basilica in Rome, spanning freely more than 20 meters.
When the church was built, there were doubts about the stability of the vaulting. But it was the tower that collapsed in 1590, destroying the just completed quire. Duke William V took it as a bad omen and so planned to build a much larger church. The second phase of construction continued until the consecration of the church in 1597. Friedrich Sustris
Friedrich Sustris (c. 1540, in Padua – 1599, in Munich) was an Italian-Dutch painter, decorator and architect. He was a son of the artist Lambert Sustris, who worked in Italy.
Sustris got his training from his father Lambert in Venice and Pad ...
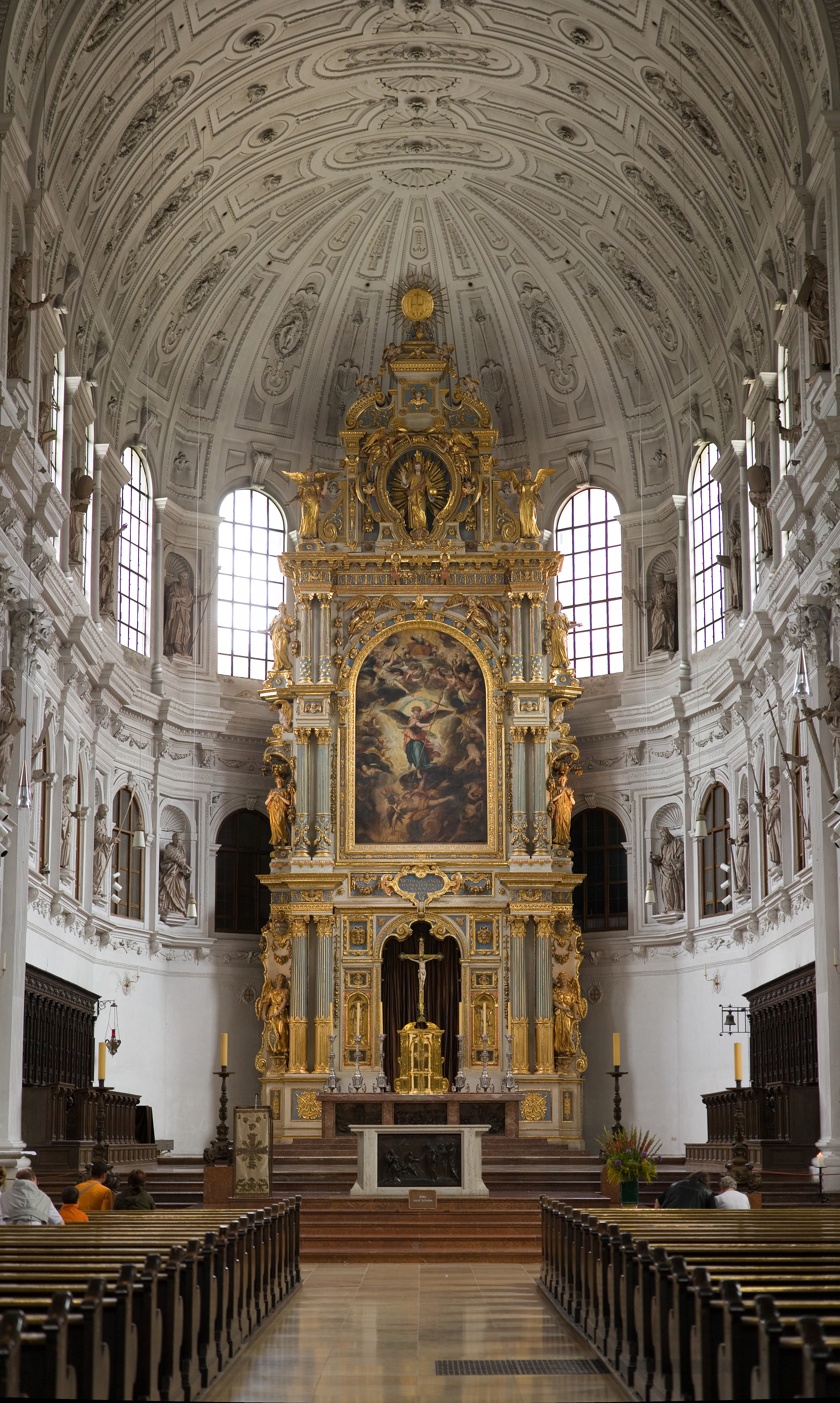
built on to the undamaged nave a new quire and a transept and a magnificent facade. The church is 78.2 meters long, 20.3 meters wide and 28.2 meters high.
The facade is impressive and contains standing statues of Duke Wilhelm and earlier rulers of the Bavarian Wittelsbach dynasty, cast in bronze, in the form of a family tree.
Hubert Gerhard
Hubert Gerhards (c. 1540/1550–1620; born 's-Hertogenbosch) was a Dutch sculptor. Like many of his contemporaries, he may have left the Netherlands in order to escape the religious conflicts and iconoclasm of the 1566–1567 era. He trained in Flo ...
's large bronze statue between the two entrances shows the Archangel Michael
Michael (; he, מִיכָאֵל, lit=Who is like El od, translit=Mīḵāʾēl; el, Μιχαήλ, translit=Mikhaḗl; la, Michahel; ar, ميخائيل ، مِيكَالَ ، ميكائيل, translit=Mīkāʾīl, Mīkāl, Mīkhāʾīl), also ...
fighting for the Faith and killing the Evil in the shape of a humanoid demon.
The interior is a representation of the triumph of Roman Catholicism in Bavaria during the Counter-Reformation. The heavily indented chancel arch as well as the short side aisles and even the side chapels are designed as a triumphal arch to ancient model. A very deep choir room adjoins the mighty nave. The stucco decoration of the nave represents the life of Jesus Christ. The altarpiece "Annunciation" was created by Peter Candid
Peter de Witte, known in Italy as Pietro Candido and in Bavaria as Peter Candid (c. 1548 – 1628) was a Flemish-born Mannerist painter, tapestry designer and draughtsman active in Italy and Bavaria.Second World War, the church was restored in 1946–48. Finally, between 1980 and 1983, the stucco-work was restored. The spire which lost its steepletop in World War II is situated further north next to the former convent.

 The church crypt contains the tomb of
The church crypt contains the tomb of
Photo spread of St Michael's Church/Michaelskirche
360° Panorama View
{{DEFAULTSORT:Saint Michael's Church, Munich Roman Catholic churches completed in 1597 16th-century Roman Catholic church buildings in Germany Michael's Church Renaissance architecture in Munich Jesuit churches in Germany Tourist attractions in Munich Burial sites of the House of Beauharnais Burial sites of the House of Wittelsbach Cultural heritage monuments in Munich
Burial places

Eugène de Beauharnais
Eugène Rose de Beauharnais, Duke of Leuchtenberg (; 3 September 1781 – 21 February 1824) was a French nobleman, statesman, and military commander who served during the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars.
Through the second ma ...
. A monument was erected by Bertel Thorwaldsen
Bertel Thorvaldsen (; 19 November 1770 – 24 March 1844) was a Danish and Icelandic sculptor medalist of international fame, who spent most of his life (1797–1838) in Italy. Thorvaldsen was born in Copenhagen into a working-class Danish ...
in 1830 in the church. Eugène was the son of Josephine de Beauharnais, Napoleon's wife and her first husband, general Alexandre de Beauharnais. He married a daughter of King Maximilian I Joseph of Bavaria
Maximilian I Joseph (german: Maximilian I. Joseph; 27 May 1756 – 13 October 1825) was Duke of Zweibrücken from 1795 to 1799, prince-elector of Bavaria (as Maximilian IV Joseph) from 1799 to 1806, then King of Bavaria (as Maximilian I Joseph ...
in 1806 and was created Duke of Leuchtenberg
Duke of Leuchtenberg was a title created twice by the monarchs of Bavaria for their relatives. The first creation was awarded by Maximilian I, Elector of Bavaria to his son Maximilian Philipp Hieronymus, upon whose death without children the land ...
in 1817. In the right transept, there is a cross monument of Giovanni da Bologna.
The crypt
A crypt (from Latin ''crypta'' "vault") is a stone chamber beneath the floor of a church or other building. It typically contains coffins, sarcophagi, or religious relics.
Originally, crypts were typically found below the main apse of a chur ...
contains among others the tombs of these members of the Wittelsbach dynasty:
* William V, Duke of Bavaria, (reg. 1579–1597)
* Maximilian I, Elector of Bavaria, (reg. 1597–1651)
* Charles II August, Duke of Zweibrücken
Charles II August Christian (german: Karl II. August Christian; 29 October 1746 – 1 April 1795) was Duke of Zweibrücken from 1775 to 1795. A member of the Palatine House of Zweibrücken-Birkenfeld, a branch of the House of Wittelsbach, he was ...
* King Ludwig II of Bavaria
Ludwig II (Ludwig Otto Friedrich Wilhelm; 25 August 1845 – 13 June 1886) was King of Bavaria from 1864 until his death in 1886. He is sometimes called the Swan King or ('the Fairy Tale King'). He also held the titles of Count Palatine of t ...
, (reg. 1864–1886)
* King Otto of Bavaria, (reg. 1886–1913), Ludwig's younger brother
* Prince Leopold of Bavaria
Prince Leopold of Bavaria (Leopold Maximilian Joseph Maria Arnulf; 9 February 1846 – 28 September 1930) was born in Munich, the son of Prince Regent Luitpold of Bavaria (1821–1912) and his wife Archduchess Augusta of Austria (1825–1864). H ...
, titular King of Greece.
* Archduchess Gisela of Austria
Archduchess Gisela Louise Marie of Austria (12 July 1856 – 27 July 1932) was the second daughter and eldest surviving child of Emperor Franz Joseph I and Empress Elisabeth of Austria.
Although christened ''Gisella'', she only ever wrot ...
, eldest surviving child of Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother (emp ...
Franz Joseph I of Austria and Empress Elisabeth
See also
* Saint Michael: Roman Catholic traditions and views * List of Jesuit sitesReferences
Sources
* *External links
Photo spread of St Michael's Church/Michaelskirche
360° Panorama View
{{DEFAULTSORT:Saint Michael's Church, Munich Roman Catholic churches completed in 1597 16th-century Roman Catholic church buildings in Germany Michael's Church Renaissance architecture in Munich Jesuit churches in Germany Tourist attractions in Munich Burial sites of the House of Beauharnais Burial sites of the House of Wittelsbach Cultural heritage monuments in Munich