methohexital on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Methohexital or methohexitone (marketed under the brand names Brevital and Brietal) is a drug which is a
barbiturate
Barbiturates are a class of depressant drugs that are chemically derived from barbituric acid. They are effective when used medically as anxiolytics, hypnotics, and anticonvulsants, but have physical and psychological addiction potential a ...
derivative. It is classified as short-acting, and has a rapid onset of action. It is similar in its effects to sodium thiopental, a drug with which it competed in the market for anaesthetics
An anesthetic (American English) or anaesthetic (British English; see spelling differences) is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into two ...
.
Pharmacology
Methohexital binds to a distinct site which is associated with Cl−ionophore
In chemistry, an ionophore () is a chemical species that reversibly binds ions. Many ionophores are lipid-soluble entities that transport ions across the cell membrane. Ionophores catalyze ion transport across hydrophobic membranes, such as liq ...
s at GABAA receptors. This increases the length of time which the Cl− ionopores are open, thus causing an inhibitory effect.
Metabolism of methohexital is primarily hepatic via demethylation and oxidation. Side-chain oxidation is the primary means of metabolism involved in the termination of the drug's biological activity
In pharmacology, biological activity or pharmacological activity describes the beneficial or adverse effects of a drug on living matter. When a drug is a complex chemical mixture, this activity is exerted by the substance's active ingredient or ...
.
Indications
Methohexital is primarily used to induceanesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), ...
, and is generally provided as a sodium salt (i.e. methohexital sodium). It is only used in hospital
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment with specialized health science and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emergen ...
or similar settings, under strict supervision. It has been commonly used to induce deep sedation or general anesthesia for surgery and dental procedures. Unlike many other barbiturates, methohexital actually lowers the seizure threshold, a property that makes it particularly useful when anesthesia is provided for an electroconvulsive therapy
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a psychiatric treatment where a generalized seizure (without muscular convulsions) is electrically induced to manage refractory mental disorders.Rudorfer, MV, Henry, ME, Sackeim, HA (2003)"Electroconvulsive th ...
(ECT). Its rapid recovery rate with consciousness being gained within three to seven minutes after induction and full recovery within 30 minutes is a major advantage over other ECT barbiturates.
Synthesis
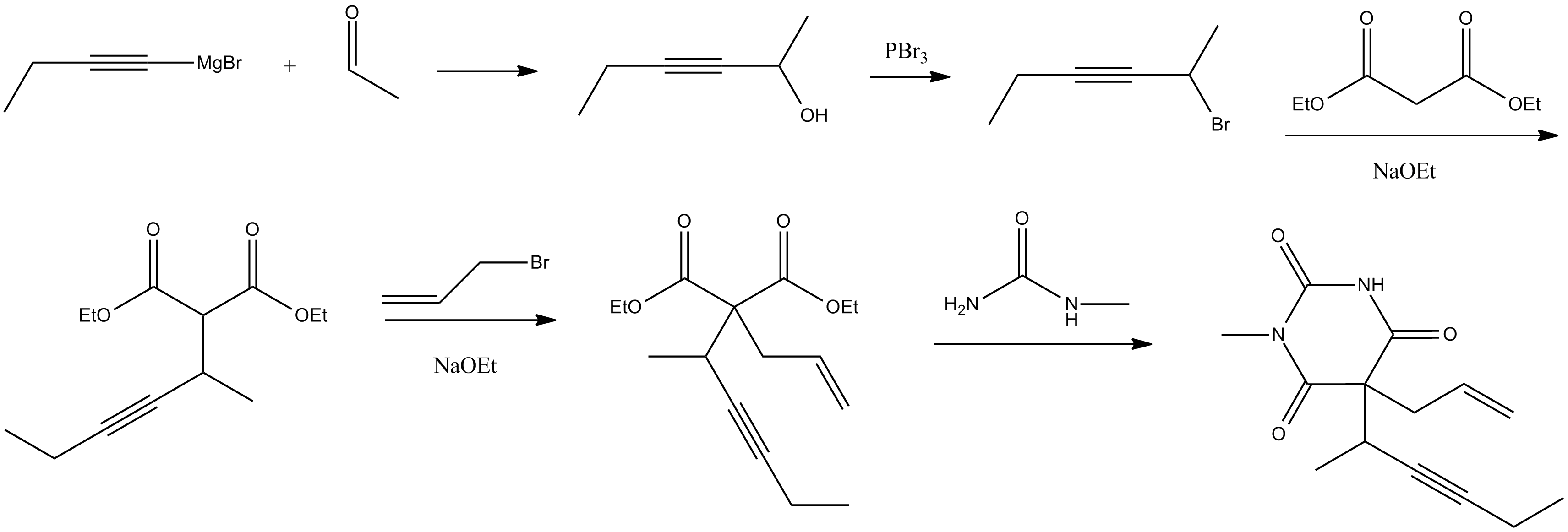
Methohexital can be synthesized in the classic manner of making barbituric acid derivatives, in particular by the reaction of malonic ester derivatives with derivatives ofurea
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid.
Urea serves an important ...
. The resulting allyl-(1-methyl-2-pentynyl) malonic ester is synthesized by subsequent alkylation of the malonic ester itself, beginning with 2-bromo-3-hexyne, which gives (1-methyl-2-pentynyl)malonic ester, and then by allylbromide. In the final step, reaction of the disubstituted malonic ester with ''N''-methylurea gives methohexital.
:
References
External links
* * {{Authority control Barbiturates General anesthetics Allyl compounds Alkyne derivatives GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators