Mental Foramen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The mental foramen is one of two foramina (openings) located on the anterior surface of the
The mental foramen is one of two foramina (openings) located on the anterior surface of the
File:Gray188.png, Side view of the skull.
File:Foramen mentale.PNG, The skull from the front.
File:Gray778.png, Distribution of the maxillary and mandibular nerves, and the submaxillary ganglion.
File:Gray781.png, Mandibular division of the trifacial nerve.
File:Gray1003.png, The permanent teeth, viewed from the right.
Diagram at uni-mainz.de
Foramina of the skull {{musculoskeletal-stub
 The mental foramen is one of two foramina (openings) located on the anterior surface of the
The mental foramen is one of two foramina (openings) located on the anterior surface of the mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
. It is part of the mandibular canal. It transmits the terminal branches of the inferior alveolar nerve
The inferior alveolar nerve (IAN) (also the inferior dental nerve) is a branch of the mandibular nerve, which is itself the third branch of the trigeminal nerve. The inferior alveolar nerves supply sensation to the lower teeth.
Structure
The inf ...
and the mental vessels.
Structure
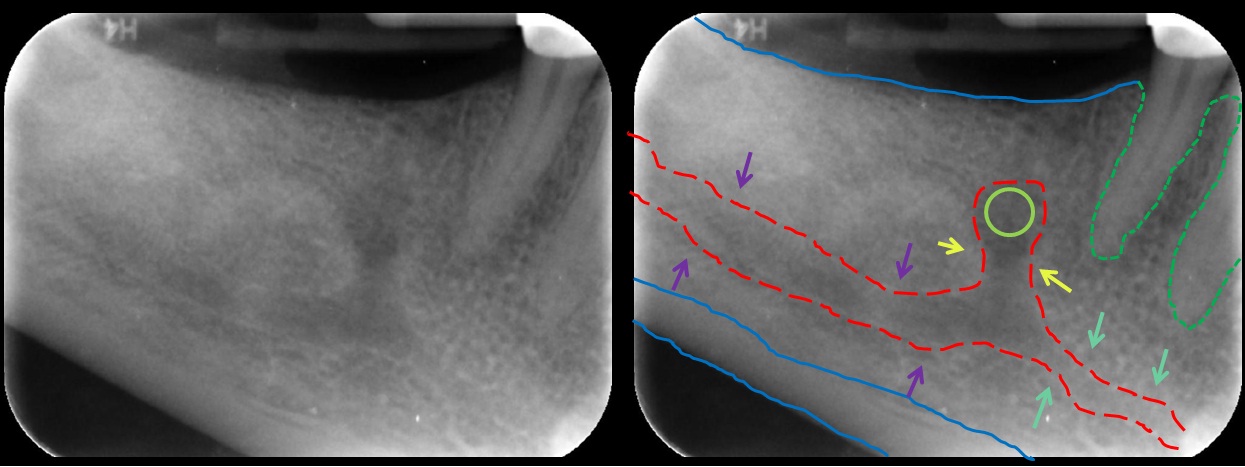
The mental foramen is located on the anterior surface of themandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
. It is directly below the commisure of the lips, and the tendon of depressor labii inferioris muscle. It is at the end of the mandibular canal, which begins at the mandibular foramen on the posterior surface of the mandible. It transmits the terminal branches of the inferior alveolar nerve
The inferior alveolar nerve (IAN) (also the inferior dental nerve) is a branch of the mandibular nerve, which is itself the third branch of the trigeminal nerve. The inferior alveolar nerves supply sensation to the lower teeth.
Structure
The inf ...
(the mental nerve), the mental artery
The inferior alveolar artery (inferior dental artery) is an artery of the face. It is a branch of the first portion of the maxillary artery.
Structure
It descends with the inferior alveolar nerve to the mandibular foramen on the medial surface of ...
, and the mental vein.
Variation
The mental foramen descends slightly in toothless individuals. The mental foramen is in line with the longitudinal axis of the 2ndpremolar
The premolars, also called premolar teeth, or bicuspids, are transitional teeth located between the canine and molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per quadrant in the permanent set of teeth, making eight premolars total in the mouth ...
in 63% of people. It generally lies at the level of the vestibular fornix and about a finger's breadth above the inferior border of the mandible.
In the general population, 17% of mandibles have an additional mental foramen or foramina on at least one side, while 4% of the mandibles show multiple mental foramina on both sides. Most are unequal in size, often with a single large foramen while any others are smaller. An incisive mental foramen is observed in 1% of the side of the mandible.
Clinical significance
The mental nerve may be anaesthetized as it leaves the mental foramen. This causes loss of sensation to the lower lip andchin
The chin is the forward pointed part of the anterior mandible ( mental region) below the lower lip. A fully developed human skull has a chin of between 0.7 cm and 1.1 cm.
Evolution
The presence of a well-developed chin is considered to be one ...
on the same side.
Additional images
See also
* Mandibular foramenReferences
External links
* ()Diagram at uni-mainz.de
Foramina of the skull {{musculoskeletal-stub