The wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo'') is an
upland ground bird native to
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
, one of two extant species of
turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
and the heaviest member of the order
Galliformes
Galliformes is an order of heavy-bodied ground-feeding birds that includes turkeys, chickens, quail, and other landfowl. Gallinaceous birds, as they are called, are important in their ecosystems as seed dispersers and predators, and are ofte ...
. It is the ancestor to the
domestic turkey
The domestic turkey (Meleagris gallopavo domesticus) is a large fowl, one of the two species in the genus '' Meleagris'' and the same species as the wild turkey. Although turkey domestication was thought to have occurred in central Mesoamerica ...
, which was originally derived from a southern Mexican
subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics ( morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all specie ...
of wild turkey (not the related
ocellated turkey
The ocellated turkey (''Meleagris ocellata'') is a species of turkey residing primarily in the Yucatán Peninsula, Mexico, as well as in parts of Belize and Guatemala. A relative of the North American wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo''), it was ...
).
Description
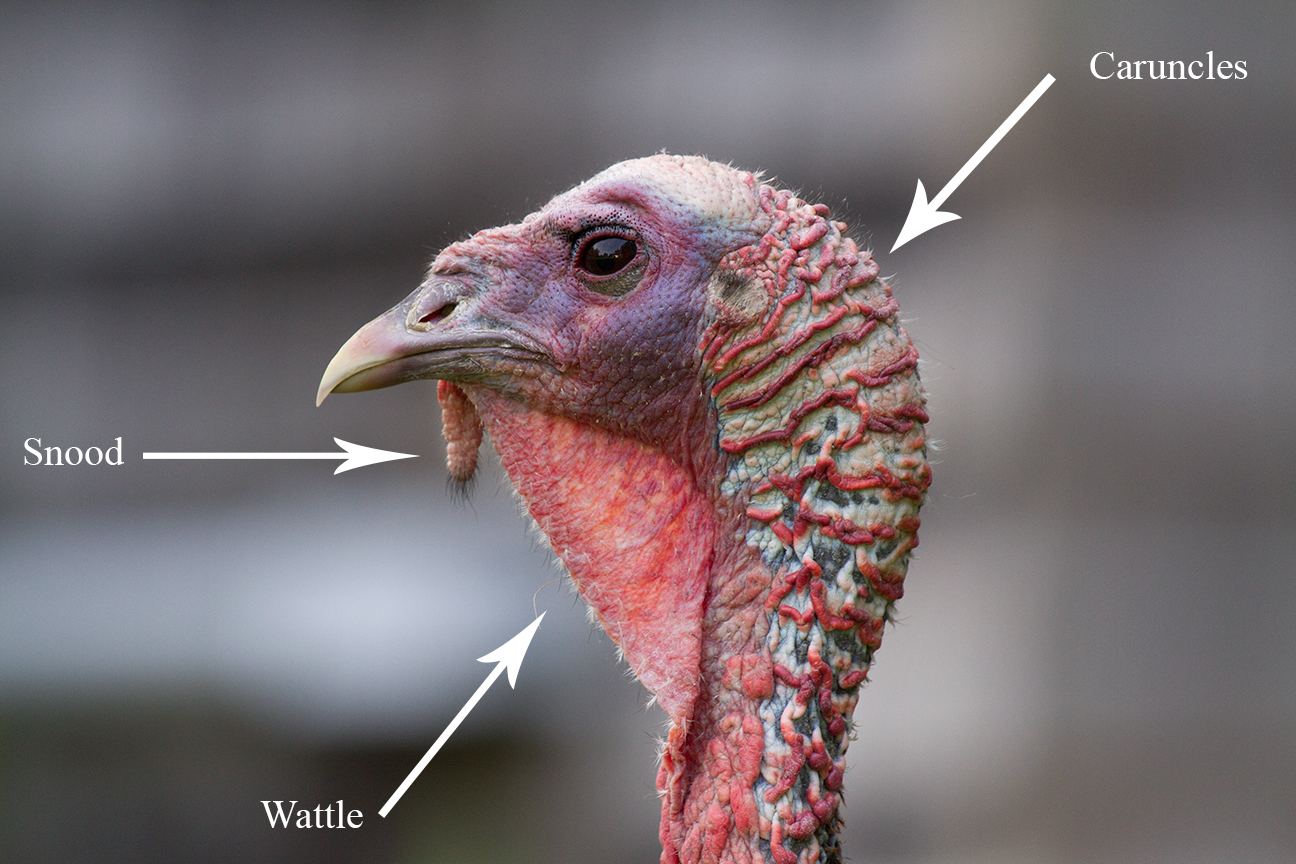
Adult wild turkeys have long reddish-yellow to grayish-green legs. The body feathers are generally blackish and dark, sometimes grey brown overall with a coppery sheen that becomes more complex in adult males. Adult males, called toms or gobblers, have a large, featherless, reddish head, red throat, and red
wattles on the throat and neck. The head has fleshy growths called
caruncles. Juvenile males are called jakes; the difference between an adult male and a juvenile is that the jake has a very short beard and his tail fan has longer feathers in the middle. The adult male's tail fan feathers will be all the same length. When males are excited, a fleshy flap on the bill (called a
snood) expands, and this, the wattles and the bare skin of the head and neck all become engorged with blood. Each foot has three toes in front, with a shorter, rear-facing toe in back; males have a spur behind each of their lower legs.

Male turkeys have a long, dark, fan-shaped tail and glossy bronze wings. As with many other species of the
Galliformes
Galliformes is an order of heavy-bodied ground-feeding birds that includes turkeys, chickens, quail, and other landfowl. Gallinaceous birds, as they are called, are important in their ecosystems as seed dispersers and predators, and are ofte ...
, turkeys exhibit strong
sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most an ...
. The male is substantially larger than the female, and his feathers have areas of red, purple, green, copper, bronze, and gold
iridescence
Iridescence (also known as goniochromism) is the phenomenon of certain surfaces that appear to gradually change color as the angle of view or the angle of illumination changes. Examples of iridescence include soap bubbles, feathers, butterfl ...
. The preen gland (
uropygial gland
The uropygial gland, informally known as the preen gland or the oil gland, is a bilobed sebaceous gland possessed by the majority of birds used to distribute the gland's oil through the plumage by means of preening. It is located dorsally at th ...
) is also larger in male turkeys compared to female ones. In contrast to the majority of other birds, they are colonized by bacteria of unknown function (''
Corynebacterium uropygiale'').
Females, called hens, have feathers that are duller overall, in shades of brown and gray. Parasites can dull coloration of both sexes; in males, coloration may serve as a signal of health. The primary wing feathers have white bars. Turkeys have 5000 to 6000 feathers.
Tail feathers are of the same length in adults, different lengths in juveniles. Males typically have at least one "beard", a tuft of coarse hair-like filaments (
mesofiloplumes), growing from the center of the breast.
Beards grow continuously during the turkey's lifespan
and a one-year-old male has a beard up to long.
Approximately 10% of females have a beard, usually shorter and thinner than that of the male.
The adult male (or "tom") normally weighs from and measures in length. The adult female (or "hen") is typically much smaller at and is long. Per two large studies, the average weight of adult males is and the average weight of adult females is .
[''CRC Handbook of Avian Body Masses'' by John B. Dunning Jr. (Editor). CRC Press (1992), .][''CRC Handbook of Avian Body Masses, 2nd Edition'' by John B. Dunning Jr. (Editor). CRC Press (2008), .] The wings are relatively small, as is typical of the galliform order, and the wingspan ranges from . The
wing chord is only . The
bill
Bill(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
* Banknote, paper cash (especially in the United States)
* Bill (law), a proposed law put before a legislature
* Invoice, commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer
* Bill, a bird or animal's beak
Pla ...
is also relatively small, as adults measure in
culmen length. The
tarsus of the wild turkey is quite long and sturdy, measuring from . The tail is also relatively long, ranging from .
The record-sized adult male wild turkey, according to the
National Wild Turkey Federation, weighed , with records of tom turkeys weighing over uncommon but not rare. While it is usually rather lighter than the waterfowl, after the
trumpeter swan
The trumpeter swan (''Cygnus buccinator'') is a species of swan found in North America. The heaviest living bird native to North America, it is also the largest extant species of waterfowl, with a wingspan of 185 to 250 cm (6 ft 2 in to 8 ft 2 ...
(''Cygnus buccinator''), the turkey has the second heaviest maximum weight of any North American bird. Going on average mass, several other birds on the continent, including the
American white pelican
The American white pelican (''Pelecanus erythrorhynchos'') is a large Aquatic animal, aquatic soaring bird from the order (biology), order Pelecaniformes. It breeds in interior North America, moving south and to the coasts, as far as Central Amer ...
(''Pelecanus erythrorhynchos''), the
tundra swan
The tundra swan (''Cygnus columbianus'') is a small swan of the Holarctic. The two taxa within it are usually regarded as conspecific, but are also sometimes split into two species: Bewick's swan (''Cygnus bewickii'') of the Palaearctic and th ...
(''Cygnus columbianus columbianus'') and the very rare
California condor
The California condor (''Gymnogyps californianus'') is a New World vulture and the largest North American land bird. It became extinct in the wild in 1987 when all remaining wild individuals were captured, but has since been reintroduced to nort ...
(''Gymnogyps californianus'') and
whooping crane
The whooping crane (''Grus americana'') is the tallest North American bird, named for its whooping sound. It is an endangered crane species. Along with the sandhill crane (''Antigone canadensis''), it is one of only two crane species native to ...
(''Grus americana'') surpass the mean weight of turkeys.
Habitat

Wild turkeys prefer
hardwood
Hardwood is wood from dicot trees. These are usually found in broad-leaved temperate and tropical forests. In temperate and boreal latitudes they are mostly deciduous, but in tropics and subtropics mostly evergreen. Hardwood (which comes from ...
and mixed
conifer
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All ext ...
-hardwood forests with scattered openings such as
pasture
Pasture (from the Latin ''pastus'', past participle of ''pascere'', "to feed") is land used for grazing. Pasture lands in the narrow sense are enclosed tracts of farmland, grazed by domesticated livestock, such as horses, cattle, sheep, or sw ...
s,
fields,
orchard
An orchard is an intentional plantation of trees or shrubs that is maintained for food production. Orchards comprise fruit- or nut-producing trees which are generally grown for commercial production. Orchards are also sometimes a feature of ...
s and seasonal
marsh
A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p Marshes can often be found ...
es. They seemingly can adapt to virtually any dense native plant community as long as coverage and openings are widely available. Open, mature forest with a variety of interspersion of tree species appear to be preferred. In the Northeast of North America, turkeys are most profuse in hardwood timber of
oak-
hickory
Hickory is a common name for trees composing the genus ''Carya'', which includes around 18 species. Five or six species are native to China, Indochina, and India (Assam), as many as twelve are native to the United States, four are found in Mex ...
(''
Quercus
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' (; Latin "oak tree") of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 500 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably ...
''-''
Carya
Hickory is a common name for trees composing the genus ''Carya'', which includes around 18 species. Five or six species are native to China, Indochina, and India (Assam), as many as twelve are native to the United States, four are found in Mexi ...
'') and forests of red oak (''
Quercus rubra
''Quercus rubra'', the northern red oak, is an oak tree in the red oak group (''Quercus'' section ''Lobatae''). It is a native of North America, in the eastern and central United States and southeast and south-central Canada. It has been intro ...
''), beech (''
Fagus grandifolia
''Fagus grandifolia'', the American beech or North American beech, is a species of beech tree native to the eastern United States and extreme southeast of Canada.
Description
''Fagus grandifolia'' is a large deciduous tree growing to tall, w ...
''), cherry (''
Prunus serotina'') and white ash (''
Fraxinus americana
''Fraxinus americana'', the white ash or American ash, is a species of ''ash tree'' native to eastern and central North America.
The species is native to mesophytic hardwood forests from Nova Scotia west to Minnesota, south to northern Florida, ...
''). Best ranges for turkeys in the
Coastal Plain
A coastal plain is flat, low-lying land adjacent to a sea coast. A fall line commonly marks the border between a coastal plain and a piedmont area. Some of the largest coastal plains are in Alaska and the southeastern United States. The Gulf Co ...
and
Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
sections have an interspersion of clearings, farms, and plantations with preferred habitat along principal rivers and in cypress (''
Taxodium distichum
''Taxodium distichum'' (bald cypress, swamp cypress; french: cyprès chauve;
''cipre'' in Louisiana) is a deciduous conifer in the family Cupressaceae. It is native to the southeastern United States. Hardy and tough, this tree adapts to a wide r ...
'') and tupelo (''
Nyssa sylvatica
''Nyssa sylvatica'', commonly known as tupelo, black tupelo, black gum or sour gum, is a medium-sized deciduous tree native to eastern North America from the coastal Northeastern United States and southern Ontario south to central Florida and e ...
'') swamps.
In
Appalachian and
Cumberland plateau
The Cumberland Plateau is the southern part of the Appalachian Plateau in the Appalachian Mountains of the United States. It includes much of eastern Kentucky and Tennessee, and portions of northern Alabama and northwest Georgia. The terms " Al ...
s, birds occupy mixed forest of oaks and pines on southern and western slopes, also hickory with diverse understories. Bald cypress and sweet gum (''
Liquidambar styraciflua
American sweetgum (''Liquidambar styraciflua''), also known as American storax, hazel pine, bilsted, redgum, satin-walnut, star-leaved gum, alligatorwood, or simply sweetgum, is a deciduous tree in the genus ''Liquidambar'' native to warm temper ...
'') swamps of s.
Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and ...
; also hardwood of ''
Cliftonia'' (a heath) and oak in north-central Florida.
Lykes Fisheating Creek
Fisheating Creek is a stream that flows into Lake Okeechobee in Florida. It is the only remaining free-flowing water course feeding into the lake, and the second-largest natural source for the lake. Most of the land surrounding the stream is eithe ...
area of s. Florida has up to 51% cypress, 12% hardwood hammocks, 17% glades of short grasses with isolated live oak (''
Quercus virginiana
''Quercus virginiana'', also known as the southern live oak, is an evergreen oak tree endemic to the Southeastern United States. Though many other species are loosely called live oak, the southern live oak is particularly iconic of the Old Sou ...
''); nesting in neighboring prairies. Original habitat here was mainly longleaf pine (''
Pinus palustris
The longleaf pine (''Pinus palustris'') is a pine species native to the Southeastern United States, found along the coastal plain from East Texas to southern Virginia, extending into northern and central Florida. In this area it is also known as ...
'') with turkey oak (''
Quercus laevis
''Quercus laevis'', the turkey oak, is a member of the red oak group of oaks. It is native to the southeastern United States. The name turkey oak derives from the resemblance of the leaves to a turkey's foot. A Turkish and southern European sp ...
'') and slash pine (''
Pinus caribaea
The Caribbean pine (''Pinus caribaea'') is a hard pine species native to Central America and the northern West Indies (in Cuba, the Bahamas, and the Turks and Caicos Islands). It belongs to subsection '' Australes'' in subgenus ''Pinus''. It inha ...
'') "flatwoods," now mainly replaced by slash pine plantations.
Behavior
Flight


Despite their weight, wild turkeys, unlike their
domesticated counterparts, are agile, fast fliers. In ideal habitat of open woodland or wooded grasslands, they may fly beneath the canopy top and find perches. They usually fly close to the ground for no more than 400 m (a quarter mile).
Wild turkeys have very good eyesight, but their vision is very poor at night. They will generally not see a predator until it is too late. At twilight most turkeys will head for the trees and roost well off the ground: it is safer to sleep there in numbers than to risk being victim to predators who hunt by night. Because wild turkeys don't migrate, in snowier parts of the species's habitat like the Northeast, Rockies, much of Canada, and the Midwest, it is very important for this bird to learn to select large conifer trees where they can fly onto the branches and shelter from blizzards.
Vocalizations
Wild turkeys have many calls: gobbles, plain yelp, cluck & purr, clucks, cutting, excited hen, fly down, tree yelp, old hen, kee kee, putts. In early spring, males older than a year old (called gobblers or toms) and, occasionally to a lesser extent, males younger than a year old (called "jakes") gobble to announce their presence to females and competing males. The gobble of a wild turkey can be heard up to a mile away. Males also emit a low-pitched "drumming" sound, produced by the movement of air in the
air sac in the chest, similar to the booming of a
prairie chicken. In addition they produce a sound known as the "spit" which is a sharp expulsion of air from this air sac.
Foraging

Wild turkeys are
omnivorous
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nut ...
, foraging on the ground or climbing shrubs and small trees to feed. They prefer eating
acorn
The acorn, or oaknut, is the nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera '' Quercus'' and '' Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains one seed (occasionally
two seeds), enclosed in a tough, leathery shell, and b ...
s,
nuts and other hard
mast
Mast, MAST or MASt may refer to:
Engineering
* Mast (sailing), a vertical spar on a sailing ship
* Flagmast, a pole for flying a flag
* Guyed mast, a structure supported by guy-wires
* Mooring mast, a structure for docking an airship
* Radio mas ...
of various trees, including
hazel
The hazel (''Corylus'') is a genus of deciduous trees and large shrubs native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. The genus is usually placed in the birch family Betulaceae,Germplasmgobills Information Network''Corylus''Rushforth, K. (1999). ...
,
chestnut
The chestnuts are the deciduous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Castanea'', in the beech family Fagaceae. They are native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere.
The name also refers to the edible nuts they produce.
The unrel ...
,
hickory
Hickory is a common name for trees composing the genus ''Carya'', which includes around 18 species. Five or six species are native to China, Indochina, and India (Assam), as many as twelve are native to the United States, four are found in Mex ...
, and
pinyon pine
The pinyon or piñon pine group grows in southwestern North America, especially in New Mexico, Arizona, and Utah. The trees yield edible nuts, which are a staple food of Native Americans, and widely eaten as a snack and as an ingredient in ...
as well as various
seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosper ...
s,
berries
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone or pit, although many pips or seeds may be present. Common examples are strawberries, ras ...
such as
juniper
Junipers are coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Juniperus'' () of the cypress family Cupressaceae. Depending on the taxonomy, between 50 and 67 species of junipers are widely distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere, from the Arc ...
and
bearberry
Bearberries ( indigenous kinnickinnick) are three species of dwarf shrubs in the genus ''Arctostaphylos''. Unlike the other species of ''Arctostaphylos'' (see manzanita), they are adapted to Arctic and Subarctic climates, and have a circumpolar ...
,
bud
In botany, a bud is an undeveloped or embryonic shoot and normally occurs in the axil of a leaf or at the tip of a stem. Once formed, a bud may remain for some time in a dormant condition, or it may form a shoot immediately. Buds may be spec ...
s,
leaves
A leaf ( : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, st ...
,
fern fronds,
roots and
insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three pa ...
s. Turkeys also occasionally consume
amphibian
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arbo ...
s such as
salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All t ...
s
and small
reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates ( lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalia ...
s such as
lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia altho ...
s and small
snake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more ...
s. Poults have been observed eating insects, berries, and seeds. Wild turkeys often feed in cow
pasture
Pasture (from the Latin ''pastus'', past participle of ''pascere'', "to feed") is land used for grazing. Pasture lands in the narrow sense are enclosed tracts of farmland, grazed by domesticated livestock, such as horses, cattle, sheep, or sw ...
s, sometimes visit backyard bird feeders, and favor croplands after harvest to scavenge seeds on the ground. Turkeys are also known to eat a wide variety of
grass
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns a ...
es.
Turkey populations can reach large numbers in small areas because of their ability to forage for different types of food. Early morning and late afternoon are the desired times for eating.
Social structure and mating

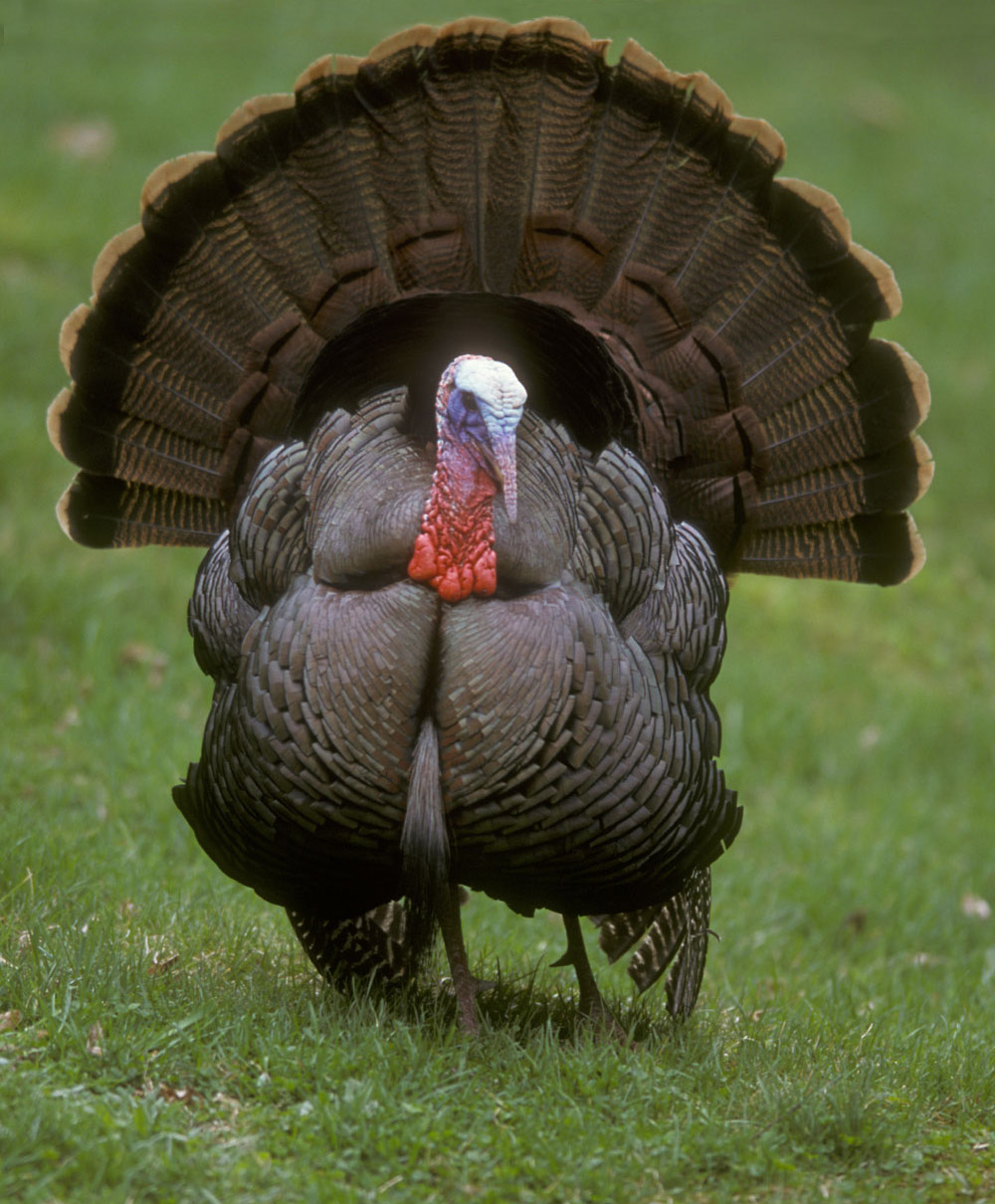
Males are
polygamous
Crimes
Polygamy (from Late Greek (') "state of marriage to many spouses") is the practice of marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, sociologists call this polygyny. When a woman is marri ...
, mating with as many hens as they can. Male wild turkeys
display for females by puffing out their feathers, spreading out their tails and dragging their wings. This behavior is most commonly referred to as strutting. Their heads and necks are colored brilliantly with red, white, and blue. The color can change with the turkey's mood, with a solid white head and neck being the most excited. They use gobbling, drumming/booming and spitting as signs of social dominance, and to attract females. Courtship begins during the months of March and April, which is when turkeys are still flocked together in winter areas.

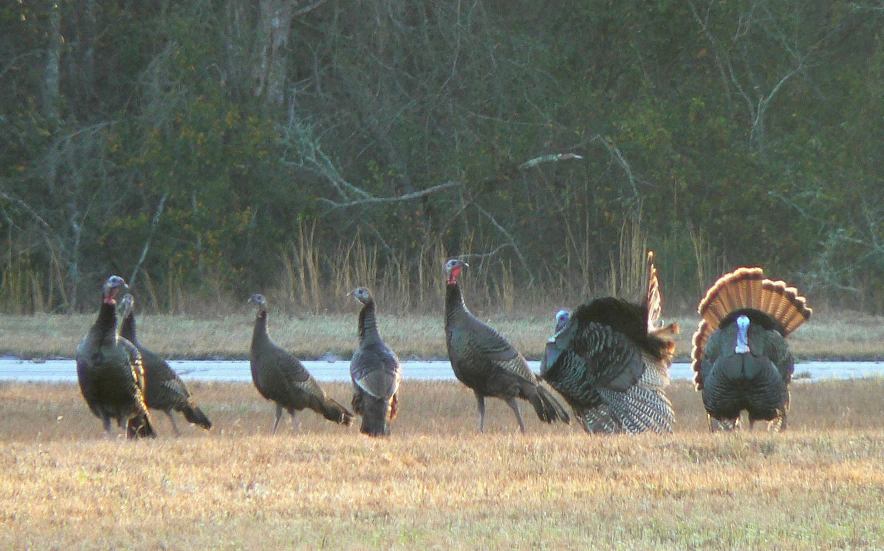
Males may be seen courting in groups, often with the dominant male gobbling, spreading his tail feathers (strutting), drumming/booming and spitting. In a study, the average dominant male that courted as part of a pair of males fathered six more eggs than males that courted alone. Genetic analysis of pairs of males courting together shows that they are close relatives, with half of their genetic material being identical. The theory behind the team-courtship is that the less dominant male would have a greater chance of passing along shared genetic material than if it were courting alone.
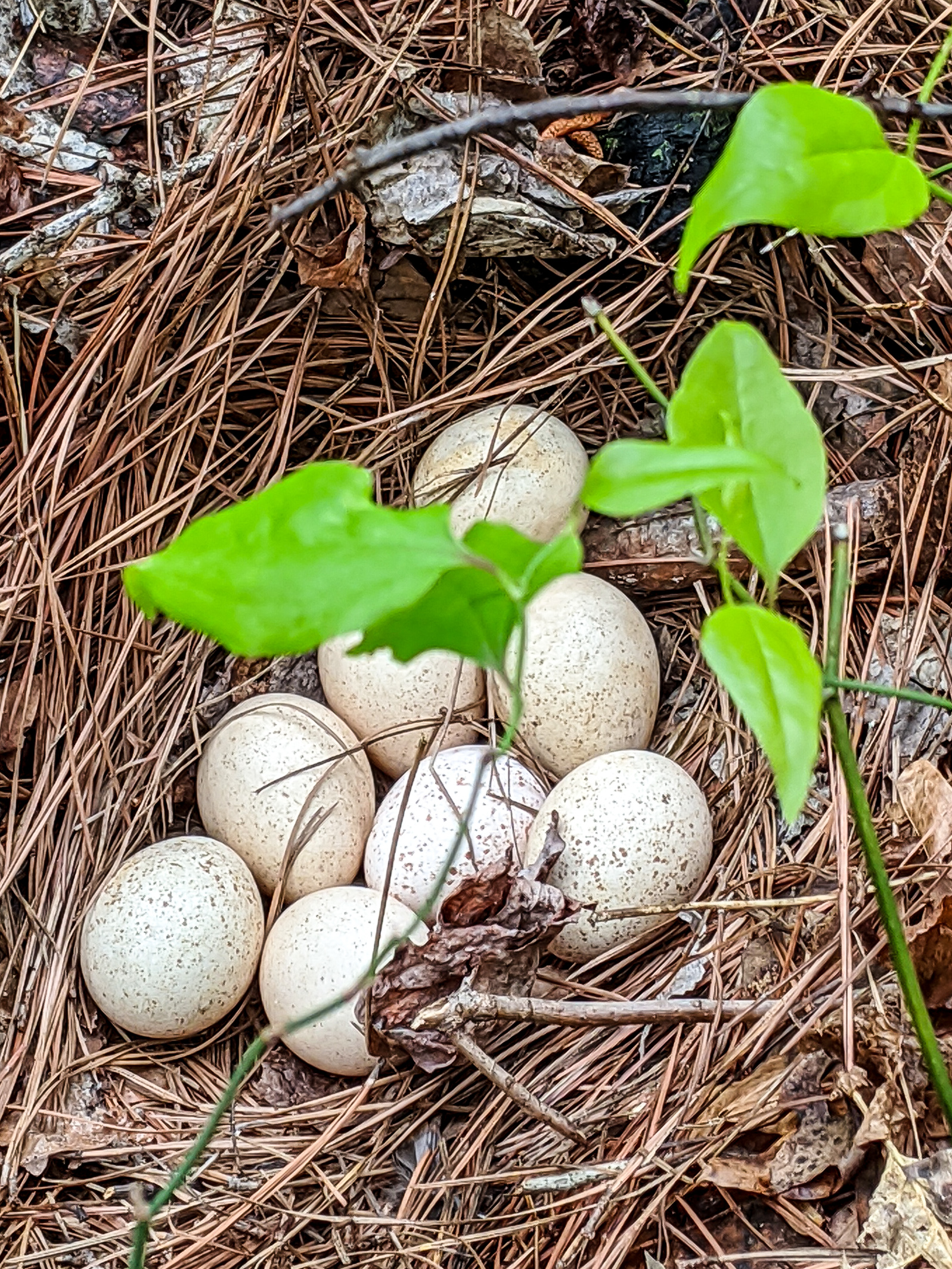
When mating is finished, females search for nest sites. Nests are shallow dirt depressions engulfed with woody vegetation. Hens lay a clutch of 10–14 eggs, usually one per day. The eggs are incubated for at least 28 days. The poults are
precocial
In biology, altricial species are those in which the young are underdeveloped at the time of birth, but with the aid of their parents mature after birth. Precocial species are those in which the young are relatively mature and mobile from the mome ...
and
nidifugous
In biology, nidifugous ( , ) organisms are those that leave the nest shortly after hatching or birth. The term is derived from Latin ''nidus'' for "nest" and ''fugere'', meaning "to flee". The terminology is most often used to describe birds and ...
, leaving the nest in about 12–24 hours.
Positive relationships with other wild species
Turkey are known to occasionally forage with deer and squirrels, and may even play with them. By foraging together, each can help the other watch for predators with their different senses: the deer with their improved olfactory sense, the turkey with its superior sight, and squirrels providing an additional set of eyes from the air.
Predators
Predators of eggs and nestlings include
raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the common raccoon to distinguish it from other species, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest of the procyonid family, having a body length of , and a body weight of ...
s (''Procyon lotor''),
Virginia opossum
The Virginia opossum (''Didelphis virginiana''), also known as the North American opossum, is the only opossum living north of Mexico, its range extending south into Central America. It is the northernmost marsupial in the world. In the United S ...
s (''Didelphis virginiana''),
striped skunks (''Mephitis mephitis''),
gray fox
The gray fox (''Urocyon cinereoargenteus''), or grey fox, is an omnivorous mammal of the family Canidae, widespread throughout North America and Central America. This species and its only congener, the diminutive island fox (''Urocyon littor ...
es (''Urocyon citnereoargenteus''),
groundhog
The groundhog (''Marmota monax''), also known as a woodchuck, is a rodent of the family Sciuridae, belonging to the group of large ground squirrels known as marmots.
The groundhog is a lowland creature of North America; it is found through mu ...
s (''Marmota monax''), other
rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are n ...
s and
spotted skunk
The genus ''Spilogale'' includes all skunks commonly known as spotted skunks. Currently, there are four accepted extant species: ''S. gracilis'', ''S. putorius'', ''S. pygmaea'', and ''S. angustifrons''. New research, however, proposes that ther ...
s (''Spilogale'' ssp.). Predators of poults in addition to nestlings and eggs also include several species of snake, namely
rat snake
Rat snakes are members – along with kingsnakes, milk snakes, vine snakes and indigo snakes – of the subfamily Colubrinae of the family Colubridae. They are medium to large constrictors and are found throughout much of the Northern Hemi ...
s (''Elaphe'' ssp.),
gopher snakes (''Pituophis catenifer'') and
pinesnakes (''Pituophis'' ssp.).
Avian predators of poults include
raptors such as
bald eagles (''Haliaeetus leucocephalus''),
barred owl
The barred owl (''Strix varia''), also known as the northern barred owl, striped owl or, more informally, hoot owl, is a North American large species of owl. A member of the true owl family, Strigidae, they belong to the genus '' Strix'', whic ...
(''Strix varia''),
red-shouldered (''Buteo lineatus''),
red-tailed (''Buteo jamaicensis''),
white-tailed (''Geranoaetus albicaudatus''), and
Harris's hawks (''Parabuteo unicinctus'')—and the smallish
Cooper's hawk
Cooper's hawk (''Accipiter cooperii'') is a medium-sized hawk native to the North American continent and found from southern Canada to Mexico. This species is a member of the genus ''Accipiter'', sometimes referred to as true hawks, which are f ...
(''Accipiter cooperii'') and
broad-winged hawk
The broad-winged hawk (''Buteo platypterus'') is a medium-sized hawk of the genus ''Buteo''. During the summer, some subspecies are distributed over eastern North America, as far west as British Columbia and Texas; they then migrate south to win ...
(''Buteo platypterus'') (both likely of very small poults). Mortality of poults is greatest in the first 14 days of life, especially of those roosting on the ground, decreasing most notably after half a year, when they attain near adult sizes.

In addition to poults, hens and adult-sized fledglings (but not, as far as is known, adult male toms) are vulnerable to predation by
great horned owl
The great horned owl (''Bubo virginianus''), also known as the tiger owl (originally derived from early naturalists' description as the "winged tiger" or "tiger of the air"), or the hoot owl, is a large owl native to the Americas. It is an extre ...
s (''Bubo virginianus''),
northern goshawk (''Accipiter gentilis''),
domestic dogs (''Canis familiaris''),
domestic cats (''Felis catus''), and
red foxes (''Vulpes vulpes''). Predators of both adults and poults include
coyotes (''Canis latrans''),
gray wolves (''Canis lupus''),
bobcats (''Lynx rufus''),
cougars (''Puma concolor''),
Canada lynx
The Canada lynx (''Lynx canadensis''), or Canadian lynx, is a medium-sized North American lynx that ranges across Alaska, Canada, and northern areas of the contiguous United States. It is characterized by its long, dense fur, triangular ears ...
''(Lynx canadensis),''
golden eagle
The golden eagle (''Aquila chrysaetos'') is a bird of prey living in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the most widely distributed species of eagle. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. They are one of the best-known birds of ...
s (''Aquila chrysaetos''), and possibly
American black bears (''Ursus americanus''), which also will eat the eggs if they find them. The
American alligator
The American alligator (''Alligator mississippiensis''), sometimes referred to colloquially as a gator or common alligator, is a large crocodilian reptile native to the Southeastern United States. It is one of the two extant species in the gen ...
(''Alligator mississippiensis)'' is a predator to all turkeys of all ages in the Southeast and will eat them if they get too close to water. Humans are now the leading predator of adult turkeys. When approached by potential predators, turkeys and their poults usually run away rather than fly away from potential predators, though they may also fly short distances if pressed.
Occasionally, if cornered, adult turkeys may try to fight off predators and large male toms can be especially aggressive in self-defense. When fighting off predators, turkeys may kick with their legs, using the spurs on their back of the legs as a weapon, bite with their beak and ram with their relatively large bodies and may be able to deter predators up to the size of mid-sized mammals. Hen turkeys have been seen to chase off at least two species of hawks in flight when their poults are threatened.
Wild turkeys are not usually aggressive towards humans, but can be frightened or provoked to behave with aggression. They are most likely to attack if startled, cornered or harassed, or if approached too closely. They also have been seen to chase off humans as well. However, attacks and potential injuries can usually be avoided by giving wild turkeys a respectful amount of space and keeping outdoor spaces clean and undisturbed. Also, turkeys that are habituated to seeing people, at places like parks or campgrounds, can be very tame and will even feed from the hands of people. Male toms occasionally will attack parked cars and reflective surfaces, thinking they see another turkey and must defend their territory, but starting a car engine and moving the car is typically enough to scare it away.
Range and population
The wild turkey in the United States in 1957 ranged from
Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
to southeastern
Oklahoma and thence through
Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
,
West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the B ...
,
New York, and
Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
, and south to
Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and ...
and
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
. It formerly ranged north to southeastern
South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota and Dakota Sioux Native American tribes, who comprise a large porti ...
, southern
Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
, and southwestern
Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and ...
. The A.O.U. Checklist also described
Upper Pliocene fossils in
Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to th ...
, and
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
fossils widely from
New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ke ...
to
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
and
Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and ...
. The Californian turkey (''Meleagris californica'') is an extinct species of
turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
indigenous to the
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
and early
Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
of
California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
. It became extinct about 10,000 years ago. The present Californian wild turkey population derives from wild birds re-introduced during the 1960s and 70s from other areas by game officials. They proliferated after 2000 to become an everyday sight in the East
Bay Area by 2015.
At the beginning of the 20th century the range and numbers of wild turkeys had plummeted due to hunting and loss of habitat. When Europeans arrived in the New World, they were found from Canada to Mexico in the millions. Europeans and their successors knew nothing about the life cycle of the bird and ecology itself as a science would come too late, not even in its infancy until the end of the 19th century whereas heavy hunting began in the 17th century. Deforestation destroyed trees turkeys need to roost in. Destruction of subtypes of environment like prairie grassland in the Midwest, canebrakes in the Southeast, and pine in the desert highlands made them easy prey for predators as there was nowhere to hide or lay eggs.
Game managers estimate that the entire population of wild turkeys in the United States was as low as 30,000 by the late 1930s. By the 1940s, it was almost totally extirpated from
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
and had become localized in pockets in the United States, in the north-east effectively restricted to the
Appalachians
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
, only as far north as central Pennsylvania. Early attempts used hand reared birds, a practice that failed miserably as the birds were unable to survive in the wild at all and many had imprinted far too much on people to effectively survive. Game officials later made efforts to protect and encourage the breeding of the surviving wild population. They would wait for numbers to grow, catch the surplus birds with a device that would have a projectile net that would ensnare the creature, move it to another unoccupied territory, and repeat the cycle. Over time this included some in the western states where it was not native. There is evidence that the bird does well when near farmland, which provides grain and also berry-bearing shrubs at its edges. As wild turkey numbers rebounded, hunting became legal in 49 U.S. states (excluding
Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S. ...
). In 1973, the total U.S. population was estimated to be 1.3 million, and current estimates place the entire wild turkey population at 7 million individuals. Since the 1980s, "trap and transfer" projects have reintroduced wild turkeys to several provinces of Canada as well, sometimes from across the border in the United States. They appear to be very successful as of 2018 as wild turkeys have multiplied rapidly and flourished in places where they were not expected to survive by Canadian scientists, often quite far north of their original expected range.
Attempts to introduce the wild turkey to
Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
as a game bird in the 18th century were not successful.
George II George II or 2 may refer to:
People
* George II of Antioch (seventh century AD)
* George II of Armenia (late ninth century)
* George II of Abkhazia (916–960)
* Patriarch George II of Alexandria (1021–1051)
* George II of Georgia (1072–1089) ...
is said to have had a flock of a few thousand in
Richmond Park
Richmond Park, in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames, is the largest of London's Royal Parks, and is of national and international importance for wildlife conservation. It was created by Charles I in the 17th century as a deer park ...
near London, but they were too easy for local
poachers
Poaching has been defined as the illegal hunting or capturing of wild animals, usually associated with land use rights.
Poaching was once performed by impoverished peasants for subsistence purposes and to supplement meager diets. It was set a ...
to destroy, and the fights with poachers became too dangerous for the
gamekeeper
A gamekeeper (often abbreviated to keeper), or in case of those dealing with deer (deer-)stalker, is a person who manages an area of countryside (e.g. areas of woodland, moorland, waterway or farmland) to make sure there is enough game for s ...
s. They were hunted with dogs and then shot out of trees where they took refuge. Several other populations, introduced or escaped, have survived for periods elsewhere in Britain and
Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
, but seem to have died out, perhaps from a combination of lack of winter feed and poaching. Small populations, probably descended from farm as well as wild stock, in the
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
and
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
have been more successful, and there are wild populations of some size following introductions in
Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state ...
and
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
.
Subspecies
There are subtle differences in the coloration, habitat, and behavior of the different subspecies of wild turkeys. The six subspecies are:

Eastern wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo silvestris'') ( Viellot, 1817)
This was the turkey subspecies Europeans first encountered in the wild: by the
Puritan
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to purify the Church of England of Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become more Protestant. ...
s, the founders of
Jamestown, the Dutch who lived in New York, and by the
Acadians. Its range is one of the largest of all subspecies, covering the entire eastern half of the United States from
Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and ...
in the north to northern
Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and ...
and extending as far west as
Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
,
Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rockf ...
, and into
Missouri
Missouri is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee): Iowa to the north, Illinois, Kentucky and Tennessee to the east, Arkansas t ...
. In Canada, its range extends into Southeastern
Manitoba
, image_map = Manitoba in Canada 2.svg
, map_alt = Map showing Manitoba's location in the centre of Southern Canada
, Label_map = yes
, coordinates =
, capital = Winn ...
,
Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
, Southwestern
Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
(including
Pontiac, Quebec and the lower half of the
Western Quebec Seismic Zone), and the
Maritime Provinces
The Maritimes, also called the Maritime provinces, is a region of Eastern Canada consisting of three provinces: New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. The Maritimes had a population of 1,899,324 in 2021, which makes up 5.1% of Ca ...
. They number from 5.1 to 5.3 million birds. They were first named 'forest turkey' in 1817, and can grow up to tall. The upper tail coverts are tipped with chestnut brown. Males can reach in weight. The eastern wild turkey is heavily hunted in the Eastern USA and is the most hunted wild turkey subspecies.
Osceola wild turkey or Florida wild turkey (''M. g. osceola'') (Scott, 1890)
Most common in the
Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and ...
peninsula, they number from 80,000 to 100,000 birds. This bird is named for the famous
Seminole
The Seminole are a Native American people who developed in Florida in the 18th century. Today, they live in Oklahoma and Florida, and comprise three federally recognized tribes: the Seminole Nation of Oklahoma, the Seminole Tribe of Florida, ...
leader
Osceola
Osceola (1804 – January 30, 1838, Asi-yahola in Muscogee language, Creek), named Billy Powell at birth in Alabama, became an influential leader of the Seminole people in Florida. His mother was Muscogee, and his great-grandfather was a S ...
, and was first described in 1890. It is smaller and darker than the eastern wild turkey. The wing feathers are very dark with smaller amounts of the white barring seen on other subspecies. Their overall body feathers are an
iridescent green-purple color. They are often found in scrub patches of palmetto and occasionally near swamps, where amphibian prey is abundant. Osceola turkeys are the smallest subspecies weighing .

Rio Grande wild turkey (''M. g. intermedia'') (Sennett, 1879)
The Rio Grande wild turkey ranges through
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
to
Oklahoma,
Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to th ...
,
New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ke ...
,
Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
,
Oregon
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. T ...
,
Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
, and was introduced to central and western
California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
, as well as parts of a few northeastern states. It was also introduced to
Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state ...
in the late 1950s. Population estimates for this subspecies are around 1,000,000. This subspecies, native to the central plain states, was first described in 1879, and has relatively long legs, better adapted to a prairie habitat. Its body feathers often have a green-coppery sheen. The tips of the tail and lower back feathers are a buff-to-very light tan color. Its habitats are brush areas next to streams, rivers or
mesquite
Mesquite is a common name for several plants in the genus '' Prosopis'', which contains over 40 species of small leguminous trees. They are native to dry areas in the Americas.
They have extremely long roots to seek water from very far under gr ...
,
pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden accepts ...
and scrub oak forests. The Rio Grande turkey is
gregarious.
Merriam's wild turkey (''M. g. merriami'') (Nelson
Nelson may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Nelson'' (1918 film), a historical film directed by Maurice Elvey
* ''Nelson'' (1926 film), a historical film directed by Walter Summers
* ''Nelson'' (opera), an opera by Lennox Berkeley to a lib ...
, 1900)
The Merriam's wild turkey ranges through the
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico ...
and the neighboring
prairie
Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the ...
s of
Wyoming
Wyoming () is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the southwest, and Colorado to the s ...
,
Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columb ...
and
South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota and Dakota Sioux Native American tribes, who comprise a large porti ...
, as well as much of the high mesa country of
New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ke ...
,
Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
, southern
Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
and The
Navajo Nation
The Navajo Nation ( nv, Naabeehó Bináhásdzo), also known as Navajoland, is a Native American reservation in the United States. It occupies portions of northeastern Arizona, northwestern New Mexico, and southeastern Utah; at roughly , the ...
, with number from 334,460 to 344,460 birds. The subspecies has also been introduced into
Oregon
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. T ...
. The initial releases of Merriam's turkeys in 1961 resulted in establishing a remnant population of Merriam's turkeys along the east-slope of Mt. Hood and natural immigration of turkeys from Idaho has established Merriam's flocks along the eastern border of Oregon. Merriam's wild turkeys live in
ponderosa pine
''Pinus ponderosa'', commonly known as the ponderosa pine, bull pine, blackjack pine, western yellow-pine, or filipinus pine is a very large pine tree species of variable habitat native to mountainous regions of western North America. It is the ...
and mountainous regions. The subspecies was named in 1900 in honor of
Clinton Hart Merriam
Clinton Hart Merriam (December 5, 1855 – March 19, 1942) was an American zoologist, mammalogist, ornithologist, entomologist, ecologist, ethnographer, geographer, naturalist and physician. He was commonly known as the 'father of mammalogy', a ...
, the first chief of the
U.S. Biological Survey. The tail and lower back feathers have white tips and purple and bronze reflections.
Gould's wild turkey (''M. g. mexicana'') ( Gould, 1856)

Native from the central valleys to the northern mountains of
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
and the southernmost parts of
Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
and
New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ke ...
. Gould's wild turkeys are heavily protected and regulated. The subspecies was first described in 1856. They exist in small numbers in the U.S. but are abundant in northwestern portions of Mexico. A small population has been established in southern Arizona. Gould's are the largest of the six subspecies. They have longer legs, larger feet, and longer tail feathers. The main colors of the body feathers are copper and greenish-gold. This subspecies is heavily protected owing to its skittish nature and threatened status.
South Mexican wild turkey (''M. g. gallopavo'') (Linnaeus, 1758)
The south Mexican wild turkey is considered the
nominate subspecies, and the only one that is not found in the United States or Canada. In central Mexico, archaeological ''M. gallopavo'' bones have been identified at sites dating to 800–100 BC
0 1 It is unclear whether these early specimens represent wild or domestic individuals, but domestic turkeys were likely established in central Mexico by the first half of the Classic Period (c. AD 200–1000). Late Preclassic (300 BC–AD 100) turkey remains identified at the archaeological site of El Mirador (Petén, Guatemala) represent the earliest evidence of the export of the south Mexican wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo gallopavo'') to the ancient Maya world. The south
Mexican wild subspecies, ''M. g. gallopavo'', was
domesticated
Domestication is a sustained multi-generational relationship in which humans assume a significant degree of control over the reproduction and care of another group of organisms to secure a more predictable supply of resources from that group. A ...
either in Mexico or by Preclassic peoples in
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica ...
, giving rise to the
domestic turkey
The domestic turkey (Meleagris gallopavo domesticus) is a large fowl, one of the two species in the genus '' Meleagris'' and the same species as the wild turkey. Although turkey domestication was thought to have occurred in central Mesoamerica ...
(''M. g. domesticus''). The Spaniards brought this tamed subspecies back to Europe with them in the mid-16th century; from Spain it spread to France and later Britain as a farmyard animal, usually becoming the centerpiece of a feast for the well-to-do. By 1620 it was common enough so that Pilgrim settlers of Massachusetts could bring turkeys with them from
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
, unaware that it had a larger close relative already occupying the forests of Massachusetts. It is one of the smallest subspecies and is best known in Spanish from its Aztec-derived name, ''guajolote''. This wild turkey subspecies is thought to be critically endangered, as of 2010.

Benjamin Franklin and the myth of U.S. national bird suggestion
The idea that
Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading inte ...
preferred the turkey as the national bird of the United States comes from a letter he wrote to his daughter Sarah Bache on 26 January 1784. The main subject of the letter is a criticism of the
Society of the Cincinnati, which he likened to a
chivalric order
An order of chivalry, order of knighthood, chivalric order, or equestrian order is an order (distinction), order of knights, typically founded during or inspired by the original Catholic Military order (religious society), military orders of the ...
, which contradicted the ideals of the newly founded American
republic.
In one section of the letter, Franklin remarked on the appearance of the
bald eagle on the Society's crest:
Franklin never publicly voiced opposition to the bald eagle as a national symbol, nor did he ever publicly suggest the turkey as a national symbol.
[
]
Significance to Native Americans
 The wild turkey, throughout its range, plays a significant role in the cultures of many
The wild turkey, throughout its range, plays a significant role in the cultures of many Native American tribe
In the United States, an American Indian tribe, Native American tribe, Alaska Native village, tribal nation, or similar concept is any extant or historical clan, tribe, band, nation, or other group or community of Native Americans in the Unit ...
s all over North America. Outside of the Thanksgiving feast, it is a favorite meal in eastern tribes. Eastern Native American tribes consumed both the eggs and meat, sometimes turning the latter into a type of jerky to preserve it and make it last through cold weather. They provided habitat by burning down portions of forests to create meadows which would attract mating birds, and thus give a clear shot to hunters. The feathers of turkeys also often made their way into the rituals and headgear of many tribes. Many leaders, such as Catawba Catawba may refer to:
*Catawba people, a Native American tribe in the Carolinas
*Catawba language, a language in the Catawban languages family
*Catawban languages
Botany
*Catalpa, a genus of trees, based on the name used by the Catawba and other N ...
chiefs, traditionally wore turkey feather headdresses.
Significant peoples of several tribes, including Muscogee Creek and Wampanoag
The Wampanoag , also rendered Wôpanâak, are an Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands based in southeastern Massachusetts and historically parts of eastern Rhode Island,Salwen, "Indians of Southern New England and Long Island," p. 1 ...
, wore turkey feather cloaks. The turkey clan is one of the three Lenape clans. Movements of wild turkeys inspired the Caddo tribe's turkey dance."Caddo Nation Today."
''Texas Beyond History.'' (retrieved 28 Dec 2010) The
Navajo people of Northeastern Arizona, New Mexico and Utah call the turkey ''Tązhii'' and relate the bird to the corn and seeds which The Turkey in Navajo folklore brought from the Third Navajo World. It is one of the Navajos' sacred birds, with the Navajo people using the feathers and parts in multiple traditional ceremonies.
See also
*
Heritage turkey
*
Turkey calls
The term turkey call can refer to either the different vocalizations of the Turkey (bird), turkey or devices designed and used to imitate these sounds.
Bird vocalization, Vocalizations of wild turkeys include "gubles", "clucks", "putts", "purrs", ...
*
Turkeypox virus
''Turkeypox virus'' is a virus of the family ''Poxviridae'' and the genus '' Avipoxvirus'' that causes turkeypox. It is one of the most common diseases in the wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo'') population. Turkeypox, like all avipoxviruses, is ...
Notes
References
* Dickson, James G., ''The Wild Turkey: Biology and Management'' (A National Wild Turkey Federation and USDA Forest Service book), 1992, Stackpole Books, , 9780811718592
google books* Pritzker, Barry M. ''A Native American Encyclopedia: History, Culture, and Peoples.'' Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2000. .
External links
Turkey as U.S. national bird
*View the ttp://www.ensembl.org/Meleagris_gallopavo/Info/Index/ turkey genomein Ensembl
Ensembl genome database project is a scientific project at the European Bioinformatics Institute, which provides a centralized resource for geneticists, molecular biologists and other researchers studying the genomes of our own species and other v ...
*
*
{{Authority control
Wild Turkey
The wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo'') is an upland ground bird native to North America, one of two extant species of turkey and the heaviest member of the order Galliformes. It is the ancestor to the domestic turkey, which was originally d ...
Birds described in 1758
Birds of Canada
Game birds
Native American cuisine
Hunting in the United States
Birds of the United States
Birds of Mexico
Wild Turkey
The wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo'') is an upland ground bird native to North America, one of two extant species of turkey and the heaviest member of the order Galliformes. It is the ancestor to the domestic turkey, which was originally d ...
Symbols of Alabama
nv:Tązhii
 Adult wild turkeys have long reddish-yellow to grayish-green legs. The body feathers are generally blackish and dark, sometimes grey brown overall with a coppery sheen that becomes more complex in adult males. Adult males, called toms or gobblers, have a large, featherless, reddish head, red throat, and red wattles on the throat and neck. The head has fleshy growths called caruncles. Juvenile males are called jakes; the difference between an adult male and a juvenile is that the jake has a very short beard and his tail fan has longer feathers in the middle. The adult male's tail fan feathers will be all the same length. When males are excited, a fleshy flap on the bill (called a snood) expands, and this, the wattles and the bare skin of the head and neck all become engorged with blood. Each foot has three toes in front, with a shorter, rear-facing toe in back; males have a spur behind each of their lower legs.
Adult wild turkeys have long reddish-yellow to grayish-green legs. The body feathers are generally blackish and dark, sometimes grey brown overall with a coppery sheen that becomes more complex in adult males. Adult males, called toms or gobblers, have a large, featherless, reddish head, red throat, and red wattles on the throat and neck. The head has fleshy growths called caruncles. Juvenile males are called jakes; the difference between an adult male and a juvenile is that the jake has a very short beard and his tail fan has longer feathers in the middle. The adult male's tail fan feathers will be all the same length. When males are excited, a fleshy flap on the bill (called a snood) expands, and this, the wattles and the bare skin of the head and neck all become engorged with blood. Each foot has three toes in front, with a shorter, rear-facing toe in back; males have a spur behind each of their lower legs.
 Male turkeys have a long, dark, fan-shaped tail and glossy bronze wings. As with many other species of the
Male turkeys have a long, dark, fan-shaped tail and glossy bronze wings. As with many other species of the 
 Despite their weight, wild turkeys, unlike their domesticated counterparts, are agile, fast fliers. In ideal habitat of open woodland or wooded grasslands, they may fly beneath the canopy top and find perches. They usually fly close to the ground for no more than 400 m (a quarter mile).
Wild turkeys have very good eyesight, but their vision is very poor at night. They will generally not see a predator until it is too late. At twilight most turkeys will head for the trees and roost well off the ground: it is safer to sleep there in numbers than to risk being victim to predators who hunt by night. Because wild turkeys don't migrate, in snowier parts of the species's habitat like the Northeast, Rockies, much of Canada, and the Midwest, it is very important for this bird to learn to select large conifer trees where they can fly onto the branches and shelter from blizzards.
Despite their weight, wild turkeys, unlike their domesticated counterparts, are agile, fast fliers. In ideal habitat of open woodland or wooded grasslands, they may fly beneath the canopy top and find perches. They usually fly close to the ground for no more than 400 m (a quarter mile).
Wild turkeys have very good eyesight, but their vision is very poor at night. They will generally not see a predator until it is too late. At twilight most turkeys will head for the trees and roost well off the ground: it is safer to sleep there in numbers than to risk being victim to predators who hunt by night. Because wild turkeys don't migrate, in snowier parts of the species's habitat like the Northeast, Rockies, much of Canada, and the Midwest, it is very important for this bird to learn to select large conifer trees where they can fly onto the branches and shelter from blizzards.
 Wild turkeys are
Wild turkeys are  Males are
Males are  Males may be seen courting in groups, often with the dominant male gobbling, spreading his tail feathers (strutting), drumming/booming and spitting. In a study, the average dominant male that courted as part of a pair of males fathered six more eggs than males that courted alone. Genetic analysis of pairs of males courting together shows that they are close relatives, with half of their genetic material being identical. The theory behind the team-courtship is that the less dominant male would have a greater chance of passing along shared genetic material than if it were courting alone.
When mating is finished, females search for nest sites. Nests are shallow dirt depressions engulfed with woody vegetation. Hens lay a clutch of 10–14 eggs, usually one per day. The eggs are incubated for at least 28 days. The poults are
Males may be seen courting in groups, often with the dominant male gobbling, spreading his tail feathers (strutting), drumming/booming and spitting. In a study, the average dominant male that courted as part of a pair of males fathered six more eggs than males that courted alone. Genetic analysis of pairs of males courting together shows that they are close relatives, with half of their genetic material being identical. The theory behind the team-courtship is that the less dominant male would have a greater chance of passing along shared genetic material than if it were courting alone.
When mating is finished, females search for nest sites. Nests are shallow dirt depressions engulfed with woody vegetation. Hens lay a clutch of 10–14 eggs, usually one per day. The eggs are incubated for at least 28 days. The poults are  In addition to poults, hens and adult-sized fledglings (but not, as far as is known, adult male toms) are vulnerable to predation by
In addition to poults, hens and adult-sized fledglings (but not, as far as is known, adult male toms) are vulnerable to predation by 
 Native from the central valleys to the northern mountains of
Native from the central valleys to the northern mountains of 
 The wild turkey, throughout its range, plays a significant role in the cultures of many
The wild turkey, throughout its range, plays a significant role in the cultures of many