Maxim machine gun on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Maxim gun is a
 The Maxim gun featured one of the earliest
The Maxim gun featured one of the earliest
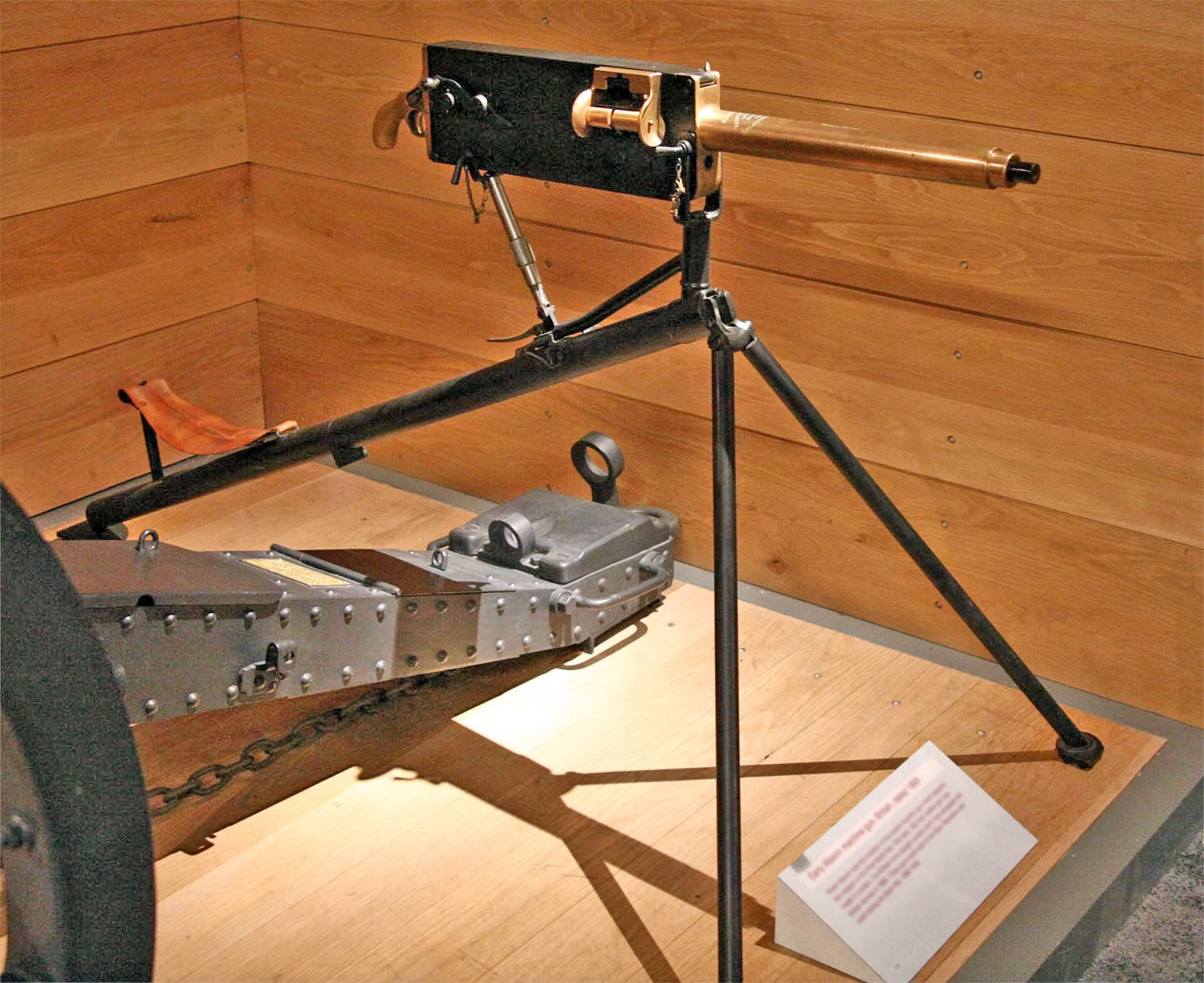
 A prototype of the Maxim gun was given by Hiram Maxim to the Emin Pasha Relief Expedition in 1886–1890, under the leadership of
A prototype of the Maxim gun was given by Hiram Maxim to the Emin Pasha Relief Expedition in 1886–1890, under the leadership of
File:BASA-1221K-1-61-14.jpg, Austro-Hungarian soldiers with a trophy Maxim machine gun in the High Alps, c. 1916
File:Red army soldiers, end of 1920s-beginning of 1930s.jpg, Red Army soldiers with a Maxim machine gun, c. 1930
 The
The
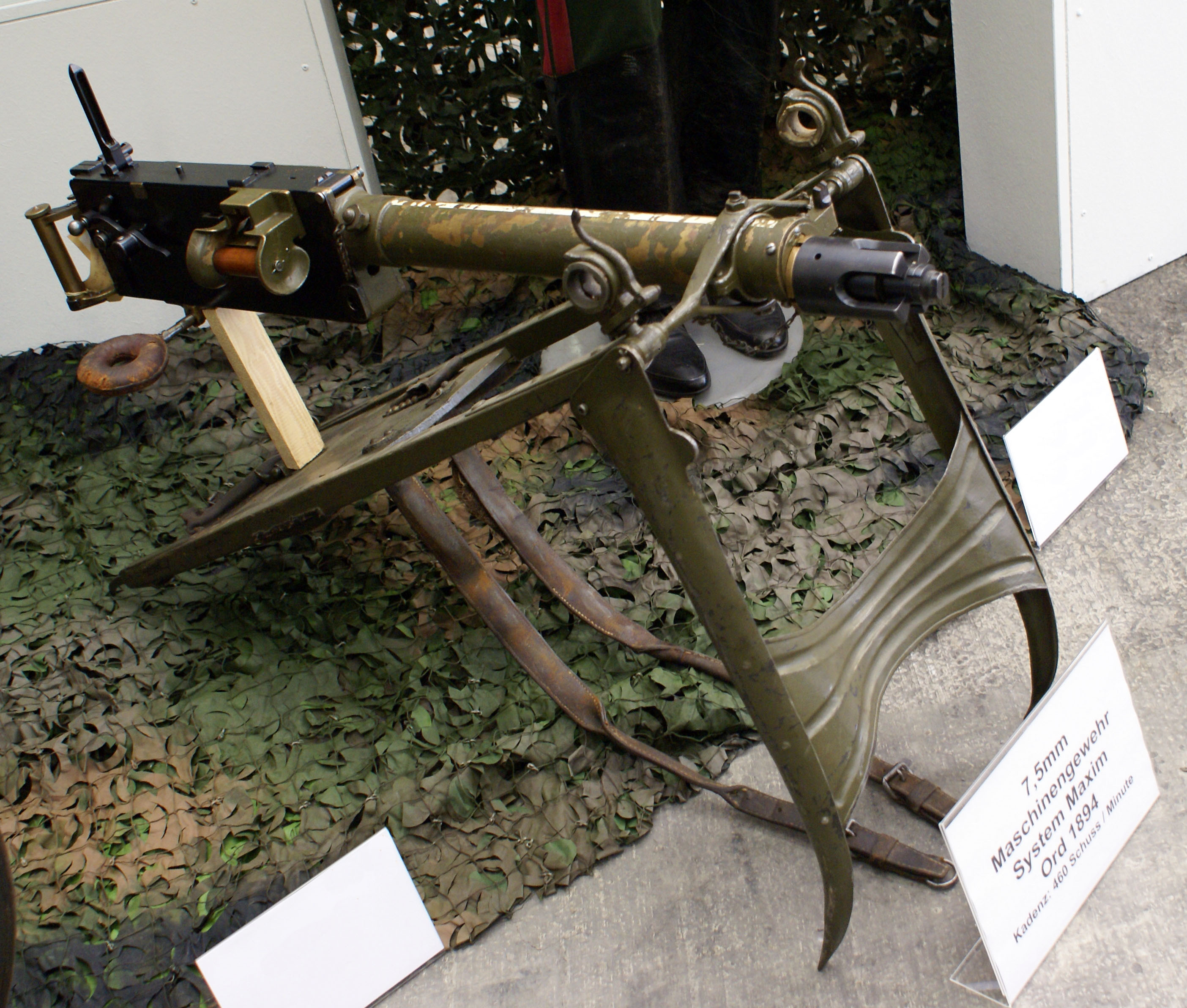 * Maxim five-barrel machine gun, fed from overhead inserted magazines and later belt-fed.
*
* Maxim five-barrel machine gun, fed from overhead inserted magazines and later belt-fed.
*
''Handbook of the Maxim Automatic Machine Gun, caliber .30, model of 1904, with pack outfits and accessories''. US War Department, July 1916
The Maxim Machine Gun Systems Blueprints by 1906
Animation of Maxim's prototype machine gun, 1884
Animation of Maxim's second prototype machine gun 1885
Animation of Maxim's transitional machine gun 1885
{{WWI British Empire small arms Early machine guns Machine guns of the United Kingdom Short recoil firearms Victorian-era weapons of the United Kingdom Weapons and ammunition introduced in 1886 Weapons of the Ottoman Empire World War I infantry weapons of the United States World War I infantry weapons World War I machine guns
recoil-operated
Recoil operation is an operating mechanism used to implement locked breech, autoloading firearms. Recoil operated firearms use the energy of recoil to cycle the action, as opposed to gas operation or blowback operation using the pressure of the ...
machine gun
A machine gun is a fully automatic, rifled autoloading firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles (including assault rifles and battle rifles ...
invented in 1884 by Hiram Stevens Maxim
Sir Hiram Stevens Maxim (5 February 1840 – 24 November 1916) was an American- British inventor
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, ...
. It was the first fully automatic machine gun in the world.
The Maxim gun has been called "the weapon most associated with imperial conquest" by historian Martin Gilbert, and was heavily used by colonial powers
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their relig ...
during the "Scramble for Africa
The Scramble for Africa, also called the Partition of Africa, or Conquest of Africa, was the invasion, annexation, division, and colonization of most of Africa by seven Western European powers during a short period known as New Imperialism ...
". Afterwards, Maxim guns also saw extensive usage by different armies during the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
, the First and Second World Wars
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, as well as by insurgent
An insurgency is a violent, armed rebellion against authority waged by small, lightly armed bands who practice guerrilla warfare from primarily rural base areas. The key descriptive feature of insurgency is its asymmetric nature: small irre ...
groups in contemporary conflicts.
The Maxim gun was greatly influential in the development of machine guns, and it has multiple variants and derivatives.
Design
 The Maxim gun featured one of the earliest
The Maxim gun featured one of the earliest recoil
Recoil (often called knockback, kickback or simply kick) is the rearward thrust generated when a gun is being discharged. In technical terms, the recoil is a result of conservation of momentum, as according to Newton's third law the force r ...
-operated firing systems in history. Energy from recoil acting on the breech block is used to eject each spent cartridge and insert the next one. Maxim's earliest designs used a 360-degree rotating cam to reverse the movement of the block, but this was later simplified to a toggle lock. This made it vastly more efficient and less labor-intensive than previous rapid-firing guns, such as the manually cranked Mitrailleuse, Gatling
The Gatling gun is a rapid-firing multiple-barrel firearm invented in 1861 by Richard Jordan Gatling. It is an early machine gun and a forerunner of the modern electric motor-driven rotary cannon.
The Gatling gun's operation centered on a ...
, Gardner, or Nordenfelt
The Nordenfelt gun was a multiple-barrel organ gun that had a row of up to twelve barrels. It was fired by pulling a lever back and forth and ammunition was gravity fed through chutes for each barrel. It was produced in a number of different c ...
.
The Maxim gun was water cooled, allowing it to sustain its rate of fire far longer than air-cooled guns. The extra weight and complexity this added, however, made it heavier and less flexible in use.
Trials demonstrated that the Maxim could fire 600 rounds per minute. Compared to modern machine guns, the Maxim was heavy, bulky, and awkward. A lone soldier could fire the weapon, but it was usually operated by a team of men, usually 4 to 6. Apart from the gunner, other crew were needed to speed reload, spot targets, and carry and ready ammunition and water. Several men were needed to move or mount the heavy weapon.
Production company
Maxim established the Maxim Gun Company with financing from , son of steel entrepreneurEdward Vickers
Edward Vickers (1804-1897) was the founder of Naylor Vickers & Co. which became Vickers Limited.
Career
Vickers was a successful miller who invested his money in the railway industry. In 1828 he gained control of his father-in-law's steel foundry ...
. A blue plaque
A blue plaque is a permanent sign installed in a public place in the United Kingdom and elsewhere to commemorate a link between that location and a famous person, event, or former building on the site, serving as a historical marker. The term ...
on the Factory where Maxim invented and produced the gun is to be found in Hatton Garden
Hatton Garden is a street and commercial zone in the Holborn district of the London Borough of Camden, abutting the narrow precinct of Saffron Hill which then abuts the City of London. It takes its name from Sir Christopher Hatton, a favouri ...
at the junction with Clerkenwell Road in London.
Albert Vickers became the company's chairman, and it later joined hands with a Swedish competitor, Nordenfelt
The Nordenfelt gun was a multiple-barrel organ gun that had a row of up to twelve barrels. It was fired by pulling a lever back and forth and ammunition was gravity fed through chutes for each barrel. It was produced in a number of different c ...
, to become Maxim Nordenfelt Guns and Ammunition Company
The Maxim-Nordenfelt Guns and Ammunition Company was the result of a takeover by Hiram Maxim of Thorsten Nordenfelt's Nordenfelt Guns and Ammunition Company in 1888. Rothschild issued £1.9 million of shares to finance the merger. Nathan Rothsc ...
. ''The Post Office Directory of trades in London'' of 1895 lists its office at 32 Victoria Street SW (London) on page 1579.
Finally, the company was absorbed into the mother Vickers
Vickers was a British engineering company that existed from 1828 until 1999. It was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by Edward Vickers and his father-in-law, and soon became famous for casting church bells. The company went public i ...
company, leading first to the Maxim-Vickers gun and then, after Vickers' redesign, the Vickers machine gun
The Vickers machine gun or Vickers gun is a water-cooled .303 British (7.7 mm) machine gun produced by Vickers Limited, originally for the British Army. The gun was operated by a three-man crew but typically required more men to move and o ...
.
History
Development (1883–1884)
Maxim's first British patents relating to the development of the Maxim gun were granted in June and July 1883. The first prototype was demonstrated to invited guests in October 1884.Use in colonial warfare (1886–1914)

 A prototype of the Maxim gun was given by Hiram Maxim to the Emin Pasha Relief Expedition in 1886–1890, under the leadership of
A prototype of the Maxim gun was given by Hiram Maxim to the Emin Pasha Relief Expedition in 1886–1890, under the leadership of Henry Morton Stanley
Sir Henry Morton Stanley (born John Rowlands; 28 January 1841 – 10 May 1904) was a Welsh-American explorer, journalist, soldier, colonial administrator, author and politician who was famous for his exploration of Central Africa and his sear ...
. More a publicity stunt than a serious military contribution, in view of the main financier of the expedition, William Mackinnon, "merely exhibiting" the gun was likely to "prove a great peace-preserver". The weapon was used on several occasions, especially during the expedition's retreat from central Africa, not because of its devastating effects, but as an effective means to scare off attackers. One of the first uses of the Maxim gun by British Forces was in the 1887 Yoni Expedition. The same prototype used by Stanley was brought back to central Africa by Frederick Lugard
Frederick John Dealtry Lugard, 1st Baron Lugard (22 January 1858 – 11 April 1945), known as Sir Frederick Lugard between 1901 and 1928, was a British soldier, mercenary, explorer of Africa and colonial administrator. He was Governor of Hong ...
, where it played an instrumental role in the establishment of the Uganda Protectorate
The Protectorate of Uganda was a protectorate of the British Empire from 1894 to 1962. In 1893 the Imperial British East Africa Company transferred its administration rights of territory consisting mainly of the Kingdom of Buganda to the Bri ...
.
The first unit in the world to receive the Maxim was the expeditionary force led by Hermann Wissmann
Hermann Wilhelm Leopold Ludwig Wissmann, after 1890 Hermann von Wissmann (4 September 1853 – 15 June 1905), was a German explorer and administrator in Africa.
Early life
Born in Frankfurt an der Oder, Wissmann was enlisted in the Army in 18 ...
which was sent in 1888 by the German Imperial government to its colonies in East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historica ...
to suppress the Abushiri Revolt
The Abushiri revolt, also known as the slave trader revolt (german: Sklavenhändlerrevolte), was an insurrection in 1888–1889 by the Arab and Swahili population of the areas of the coast of East Africa that were granted, under protest, to G ...
. Wissmann was issued one of the first Maxim guns which had reached Germany and used it successfully in his capture of Pangani
Pangani Town is a historic Swahili settlement located on the south eastern shore of Tanga Region, Tanzania. The town lies south of the city of Tanga, at the mouth of the Pangani River. It is the headquarters of the Pangani District. Admin ...
.
The Singapore Volunteer Corps
The Singapore Volunteer Corps or the Singapore Special Constabulary, was a militia unit established in 1854 as the Singapore Volunteer Rifle Corps. The Corps underwent several reorganisations and was known by various names throughout its histor ...
received a Maxim gun in 1889, but it was never used. This was a civilian volunteer defence unit on the British colony.
The Maxim gun was first used extensively in an African conflict during the First Matabele War
The First Matabele War was fought between 1893 and 1894 in modern-day Zimbabwe. It pitted the British South Africa Company against the Ndebele (Matabele) Kingdom. Lobengula, king of the Ndebele, had tried to avoid outright war with the compa ...
in Rhodesia
Rhodesia (, ), officially from 1970 the Republic of Rhodesia, was an unrecognised state in Southern Africa from 1965 to 1979, equivalent in territory to modern Zimbabwe. Rhodesia was the ''de facto'' successor state to the British colony of So ...
. During the Battle of the Shangani
The Battle of the Shangani took place on 25 October 1893 during the First Matabele War in what is now Zimbabwe. A British column was attacked during night by a large force of Matabele warriors. The British repulsed them with a heavy loss of lif ...
, 700 soldiers fought off 5,000 Matabele warriors with just five Maxim guns. It played an important role in the "Scramble for Africa
The Scramble for Africa, also called the Partition of Africa, or Conquest of Africa, was the invasion, annexation, division, and colonization of most of Africa by seven Western European powers during a short period known as New Imperialism ...
" in the late 19th century. The extreme lethality was employed to devastating effect against obsolete charging tactics, when African opponents could be lured into pitched battle
A pitched battle or set-piece battle is a battle in which opposing forces each anticipate the setting of the battle, and each chooses to commit to it. Either side may have the option to disengage before the battle starts or shortly thereafter. A ...
s in open terrain. As it was put by Hilaire Belloc
Joseph Hilaire Pierre René Belloc (, ; 27 July 187016 July 1953) was a Franco-English writer and historian of the early twentieth century. Belloc was also an orator, poet, sailor, satirist, writer of letters, soldier, and political activist. ...
, in the words of the figure "Blood" in his poem "The Modern Traveller":
However, the destructive power of the Maxim gun in colonial warfare has often been embellished by popular myth. Modern historical accounts suggest that, while it was effective in pitched battles, as in the Matabele wars or the Battle of Omdurman
The Battle of Omdurman was fought during the Anglo-Egyptian conquest of Sudan between a British–Egyptian expeditionary force commanded by British Commander-in-Chief ( sirdar) major general Horatio Herbert Kitchener and a Sudanese army of the ...
, its significance owed much to its psychological impact.
A larger-calibre version of the Maxim, firing a one-pound shell, was built by Maxim-Nordenfeldt. This was known in the Second Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the So ...
(in South Africa) as the Pom-Pom
A pom-pom – also spelled pom-pon, pompom or pompon – is a decorative ball or tuft of fibrous material.
The term may refer to large tufts used by cheerleaders, or a small, tighter ball attached to the top of a hat, also known as a ...
from its sound. The Boers' "one-pounder" Maxim-Nordenfeldt was a large caliber, belt-fed, water-cooled "auto cannon" that fired explosive rounds (smokeless ammunition) at 450 rounds per minute.
The Maxim gun was also used in the Anglo-Aro War
The Anglo-Aro War (1901–1902) was a conflict between the Aro Confederacy in present-day Eastern Nigeria, and the British Empire. The war began after increasing tension between Aro leaders and the British after years of failed negotiations.
...
(in present-day Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
) of 1901–1902.
National and military authorities were reluctant to adopt the weapon, and Maxim's company initially had some trouble convincing European governments of the weapon's efficiency. Soldiers generally held a great mistrust of machine guns due to their tendency to jam. In the 1906 version of his book ''Small Wars'', Charles Callwell says of machine guns: "The older forms are not suitable as a rule... they jammed at Ulundi
Ulundi, also known as Mahlabathini, is a town in the Zululand District Municipality. At one time the capital of Zulu Kingdom in South Africa and later the capital of the Bantustan of KwaZulu, Ulundi now lies in KwaZulu-Natal Province (of which, ...
, they jammed at Dogali, they jammed at Abu Klea and Tofrek, in some cases with unfortunate results." However, the Maxim was far more reliable than its contemporaries.''Small Wars''. 1906. Callwell, p. 559. A more immediate problem was that, initially, its position was easily given away by the clouds of smoke that the gun produced (although the same was true of artillery pieces and units of troops that the machine gun was intended to replace or supplement, so this wasn't viewed as a particular drawback by the early users). The advent of smokeless powder
Finnish smokeless powderSmokeless powder is a type of propellant used in firearms and artillery that produces less smoke and less fouling when fired compared to gunpowder ("black powder"). The combustion products are mainly gaseous, compared t ...
(developed by, among others, Hiram's brother Hudson Maxim), helped to change this.
The weapon was adopted by the British Army under the guidance of Sir Garnet Wolseley
Field marshal (United Kingdom), Field Marshal Garnet Joseph Wolseley, 1st Viscount Wolseley, (4 June 183325 March 1913), was an Anglo-Irish officer in the British Army. He became one of the most influential and admired British generals after a s ...
, who had been appointed Commander-in-Chief of the British Army in 1888. In October that year, he placed an order of 120 rifle-calibre Maxims using the same .577/450 ammunition as the Martini–Henry
The Martini–Henry is a breech-loading single-shot rifle with a lever action that was used by the British Army. It first entered service in 1871, eventually replacing the Snider–Enfield, a muzzle-loader converted to the cartridge system ...
rifles. Wolseley had previously led military expeditions in Africa (the Ashanti war
The Anglo-Ashanti wars were a series of five conflicts that took place between 1824 and 1900 between the Ashanti Empire—in the Akan interior of the Gold Coast—and the British Empire and its African allies. Though the Ashanti emerged victori ...
and the Gordon Relief Expedition
The Nile Expedition, sometimes called the Gordon Relief Expedition (1884–85), was a British mission to relieve Major-General Charles George Gordon at Khartoum, Sudan. Gordon had been sent to the Sudan to help Egyptians evacuate from Sudan ...
in 1884–85) and had a reputation for being a strong subscriber to military innovation and reform, which he demonstrated in Africa. There he used machine guns, explored other unconventional ideas, and founded an Egyptian camel corps.
The gun's design was also purchased and used by several other European countries.
Russo-Japanese War
In 1895, theImperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emper ...
purchased a number of Maxims but later decided to standardize on the Hotchkiss machine gun
The Hotchkiss machine gun was any of a line of products developed and sold by Hotchkiss et Cie, (full name Société Anonyme des Anciens Etablissements Hotchkiss et Cie), established by United States gunsmith Benjamin B. Hotchkiss. Hotchkiss moved ...
. The Imperial Russian Army
The Imperial Russian Army (russian: Ру́сская импера́торская а́рмия, tr. ) was the armed land force of the Russian Empire, active from around 1721 to the Russian Revolution of 1917. In the early 1850s, the Russian Ar ...
likewise purchased 58 Maxim machine guns in 1899 and contracted with Vickers in 1902 to manufacture the design in Russia, although manufacturing did not start until 1910., p. 225. During the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
of 1904–1905, the Russian Army employed the Maxim in combat and placed a rush order for another 450 units from overseas suppliers, which were mostly delivered to front-line troops before the end of the war.
World War I (1914–1918)
ByWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, many armies had moved on to improved machine guns. The British Vickers machine gun
The Vickers machine gun or Vickers gun is a water-cooled .303 British (7.7 mm) machine gun produced by Vickers Limited, originally for the British Army. The gun was operated by a three-man crew but typically required more men to move and o ...
was an improved and redesigned Maxim, introduced into the British Army in 1912 and remaining in service until 1968. Production took place at Erith in Kent, and some models were fitted to early biplanes also fabricated there. The German Army's Maschinengewehr 08
The ''Maschinengewehr'' 08, or MG 08, was the German Army's standard machine gun in World War I and is an adaptation of Hiram S. Maxim's original 1884 Maxim gun. It was produced in a number of variants during the war. The MG 08 served during W ...
and the Russian Pulemyot Maxim were both more or less direct copies of the Maxim.
It also saw use during the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
, which followed the Revolution
In political science, a revolution (Latin: ''revolutio'', "a turn around") is a fundamental and relatively sudden change in political power and political organization which occurs when the population revolts against the government, typically due ...
in 1917. A picture of the period depicts a Maxim gun mounted on a tachanka, a horse-drawn carriage, along with the gunner, firing backwards at a pursuing White Army
The White Army (russian: Белая армия, Belaya armiya) or White Guard (russian: Бѣлая гвардія/Белая гвардия, Belaya gvardiya, label=none), also referred to as the Whites or White Guardsmen (russian: Бѣлогв� ...
regiment. Anarchist
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that is skeptical of all justifications for authority and seeks to abolish the institutions it claims maintain unnecessary coercion and hierarchy, typically including, though not necessar ...
s attribute this mobile setup to Nestor Makhno
Nestor Ivanovych Makhno, The surname "Makhno" ( uk, Махно́) was itself a corruption of Nestor's father's surname "Mikhnenko" ( uk, Міхненко). ( 1888 – 25 July 1934), also known as Bat'ko Makhno ("Father Makhno"),; According to ...
.
American use
 The
The United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, ...
had shown interest in the Maxim machine gun since 1887. Model 1889 and Model 1900 Maxims were used for testing, which lasted for years but not continuously. The gun was finally adopted in 1904 as the Maxim Machine Gun, Caliber .30, Model of 1904 as the first rifle-caliber heavy machine gun for standard service in the U.S. Army. The design was characteristic for its visually distinctive cage-like muzzle recoil booster
A muzzle booster or recoil booster is a device fixed to the muzzle of a firearm, intended to harness the energy of the escaping propellant to augment the force of recoil on portions of the firearm. In spite of its name, a muzzle booster does not ...
.
The first 50 guns and tripods were made by Vickers, Sons & Maxim in the U.K. chambered for .30-03. Colt's Manufacturing Company
Colt's Manufacturing Company, LLC (CMC, formerly Colt's Patent Firearms Manufacturing Company) is an American firearms manufacturer, founded in 1855 by Samuel Colt and is now a subsidiary of Czech holding company Colt CZ Group. It is the suc ...
was selected to produce it domestically, but challenges with schematics and specifications delayed its introduction. By the time Colt began production in 1908 (which was also the last year orders were placed for the guns), a total of 90 M1904s were made by Vickers. Colt made their machine guns for the new .30-06 caliber, and the ones made by Vickers were re-chambered for the new round. A total of 287 M1904 Maxims were manufactured. The U.S. procured other machine guns after M1904 production ended, including the M1909 Benét–Mercié, the Colt–Vickers M1915, and the Browning M1917
The M1917 Browning machine gun is a heavy machine gun used by the United States armed forces in World War I, World War II, the Korean War, and the Vietnam War; it has also been used by other nations. It was a crew-served, belt-fed, water-cool ...
.
M1904 Maxims were issued to infantry companies and cavalry. Each company had four guns with associated tripods, ammunition, and 20 mule
The mule is a domestic equine hybrid between a donkey and a horse. It is the offspring of a male donkey (a jack) and a female horse (a mare). The horse and the donkey are different species, with different numbers of chromosomes; of the two po ...
s to transport the heavy guns. The M1904 was deployed in operations in the Philippines, Hawaii, Mexico, and Central and South America, but never saw much combat use. During World War I, it remained in the U.S. for training.
Russo-Ukrainian War
The Maxim, in the form of thePM M1910
The Pulemyot Maxima PM1910 (PM M1910) (Russian: Пулемёт Максима образца 1910 года, ''Pulemyot Maxima obraztsa 1910 goda'' – "Maxim's machine gun Model 1910") is a Heavy machine gun that was used by the Imperial Russian ...
, saw use by both sides during the 2022 Russo-Ukrainian War
The Russo-Ukrainian War; uk, російсько-українська війна, rosiisko-ukrainska viina. has been ongoing between Russia (alongside Russian separatists in Ukraine) and Ukraine since February 2014. Following Ukraine's Rev ...
, introducing modifications to the century-old machine gun that redefined its intended use. These changes included its inclusion on Technicals and the introduction of Red dot sight
A red dot sight is a common classification for a type of non- magnifying reflector (or reflex) sight for firearms, and other devices that require aiming, that gives the user a point of aim in the form of an illuminated red dot. A standard desig ...
s.
Variants and derivatives
 * Maxim five-barrel machine gun, fed from overhead inserted magazines and later belt-fed.
*
* Maxim five-barrel machine gun, fed from overhead inserted magazines and later belt-fed.
* Vickers machine gun
The Vickers machine gun or Vickers gun is a water-cooled .303 British (7.7 mm) machine gun produced by Vickers Limited, originally for the British Army. The gun was operated by a three-man crew but typically required more men to move and o ...
: earlier Maxims had been chambered for earlier British service cartridges, but the Vickers was produced for export available in most of the different calibres and cartridges used by countries around the world, and including a large caliber (.50 inch) as used on Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
warships. The machine gun was lighter and had been tested by the Army in 1909.
* Maschinengewehr 01, made by Deutsche Waffen und Munitionsfabriken
''Deutsche Waffen- und Munitionsfabriken Aktiengesellschaft'' (German Weapons and Munitions public limited company), known as DWM, was an arms company in Imperial Germany created in 1896 when '' Ludwig Loewe & Company'' united its weapons and am ...
(DWM)
* MG 08
The ''Maschinengewehr'' 08, or MG 08, was the German Army's standard machine gun in World War I and is an adaptation of Hiram S. Maxim's original 1884 Maxim gun. It was produced in a number of variants during the war. The MG 08 served during Wo ...
** Derivatives (e.g., MG08/15)
* Chinese Type 24 Heavy Machine Gun (Copies of the Maschinengewehr 1908)
* Maschinengewehr Modell 1911, made by Waffenfabrik Bern
''Waffenfabrik Bern'' (Weapons Factory Bern), also known as W+F Bern, was an arms manufacturer in Bern, Switzerland, which was a government-owned corporation producing firearms for the Swiss Armed Forces.
List of W+F weapons
*Vetterli rifle
*S ...
* Russian/Soviet Pulemyot Maxima PM1910 and lighter variants Maxim–Tokarev
The Maxim–Tokarev was the first domestic Soviet light machine gun accepted for service. It was developed from the Maxim machine gun M1910 by Fedor Tokarev
History
During World War I and the Russian Civil War, the Soviet army was equipped w ...
and PV-1 machine gun
PV-1 (''Pulemet Vozdushny'', airborne machine gun) is a Soviet air-cooled version of the Russian M1910 Maxim for mounting on aircraft. It was designed between 1926 and 1927. The first prototypes were produced and accepted into service in 1928.Ш� ...
* Finnish Maxim M09/21 and Maxim M/32-33
* American M1904
* Romanian-made 6.5 mm version, at least 8–12 were produced and were used by the Romanian Danube Flotilla during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
* MG 18 TuF
The ''Maschinengewehr 18 Tank und Flieger'' or MG 18 TuF, is a German dual-purpose heavy machine gun that was designed to fill both anti-tank and anti-aircraft roles. Developed at the end of the First World War, it fired the same 13.25 × 92mm SR ...
Anti-tank & Anti-aircraft gun
Users
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * :By 1912 the army had 12 maxims; 50 more were ordered during the Balkan wars but it is not know if they arrived in time * * * * (1918–1940, .303 and other versions) * * * Used in the Battle of Namasique against the forces of Honduran GeneralManuel Bonilla
General Manuel Bonilla Chirinos (7 June 1849 – 21 March 1913) was President of Honduras from 13 April 1903 to 25 February 1907, and again from 1 February 1912 to 21 March 1913. He had previously served as Vice President of Honduras from 189 ...
Jowett, Phillip, Latin American Wars 1900-1941: Osprey Publishing (2018)
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
See also
*Caldwell machine gun
The Caldwell machine gun is a machine gun of Australian origin developed by Thomas Frederick Caldwell in 1915.
History
The Caldwell machine gun was designed by Thomas F. Caldwell of Melbourne, who moved to the United Kingdom to bring his inventio ...
* Fittipaldi machine gun
The Fittipaldi machine gun is a recoil-operated machine gun designed by Rafael Fittipaldi (an Italian immigrant to Argentina) and patented as USPTO number 1,099,245, of June 9, 1914.
Description
The Fittipaldi machine gun uses the barrel of the ...
* Hotchkiss machine gun
The Hotchkiss machine gun was any of a line of products developed and sold by Hotchkiss et Cie, (full name Société Anonyme des Anciens Etablissements Hotchkiss et Cie), established by United States gunsmith Benjamin B. Hotchkiss. Hotchkiss moved ...
* Kjellman machine gun
The Kjellman LMG was a machine gun produced in Sweden. It is notable for being one of the first fully automatic weapons ever conceived (if not produced) and one of the first light machine guns as well.
Although the patent dated back to 1870, and ...
* M1917 Browning machine gun
The M1917 Browning machine gun is a heavy machine gun used by the United States armed forces in World War I, World War II, the Korean War, and the Vietnam War; it has also been used by other nations. It was a crew-served, belt-fed, water-cool ...
* Nordenfelt gun
The Nordenfelt gun was a multiple-barrel organ gun that had a row of up to twelve barrels. It was fired by pulling a lever back and forth and ammunition was gravity fed through chutes for each barrel. It was produced in a number of different ...
* Perino Model 1908
* QF 1-pounder pom-pom
* St. Étienne Mle 1907
The French St. Étienne Mle 1907 (french: Mitrailleuse Mle 1907 T) was a gas operated air-cooled machine gun in 8mm Lebel which was widely used in the early years of the First World War. The "St.Etienne Mle 1907" was not derived from the Hotchkiss ...
Citations
General sources
* Anon., ''Vickers, Sons and Maxim Limited: Their Works and Manufactures. (Reprinted from 'Engineering')'' London (1898). It gives plates showing the mechanism of the Vickers Maxim gun and numerous plates showing the variety of mounts available at the end of the 19th century. It also includes numerous plates of the factories in which they were made. * This is a reprint of the 1906 version. * (See chapter 3: "Hiram Maxim Changes War") * * * * *External links
''Handbook of the Maxim Automatic Machine Gun, caliber .30, model of 1904, with pack outfits and accessories''. US War Department, July 1916
The Maxim Machine Gun Systems Blueprints by 1906
Animation of Maxim's prototype machine gun, 1884
Animation of Maxim's second prototype machine gun 1885
Animation of Maxim's transitional machine gun 1885
{{WWI British Empire small arms Early machine guns Machine guns of the United Kingdom Short recoil firearms Victorian-era weapons of the United Kingdom Weapons and ammunition introduced in 1886 Weapons of the Ottoman Empire World War I infantry weapons of the United States World War I infantry weapons World War I machine guns