Mauryan art on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mauryan art is the art produced during the period of the
 This period marked an imaginative and impressive step forward in Indian stone sculpture; much previous sculpture was probably in wood and has not survived. The elaborately carved animal capitals surviving on from some Pillars of Ashoka are the best known works, and among the finest, above all the
This period marked an imaginative and impressive step forward in Indian stone sculpture; much previous sculpture was probably in wood and has not survived. The elaborately carved animal capitals surviving on from some Pillars of Ashoka are the best known works, and among the finest, above all the
 The Pataliputra capital, dated to the 3rd century BCE, has been excavated at the Mauryan city of
The Pataliputra capital, dated to the 3rd century BCE, has been excavated at the Mauryan city of  Emperor Ashoka also erected religious pillars throughout India. These pillars were carved in two types of stone. Some were of the spotted red and white sandstone from the region of
Emperor Ashoka also erected religious pillars throughout India. These pillars were carved in two types of stone. Some were of the spotted red and white sandstone from the region of

 The work of local sculptors illustrates the popular art of the Mauryan period. This consisted of sculpture which probably was not commissioned by the emperor. The patrons of the popular art were the local governors and the more well-to-do subjects. It is represented by figures such as the female figure of Besnagar, the male figure of Parkham and the whisk-bearer from Didarganj (although its age is debated). Technically they are fashioned with less skill than the pillar capitals. They express a considerable earthiness and physical vitality.
The stone elephant at
The work of local sculptors illustrates the popular art of the Mauryan period. This consisted of sculpture which probably was not commissioned by the emperor. The patrons of the popular art were the local governors and the more well-to-do subjects. It is represented by figures such as the female figure of Besnagar, the male figure of Parkham and the whisk-bearer from Didarganj (although its age is debated). Technically they are fashioned with less skill than the pillar capitals. They express a considerable earthiness and physical vitality.
The stone elephant at
File:Female figure, northern India, Maurya period, c. 320-200 BCE, terracotta, HAA.JPG, Female
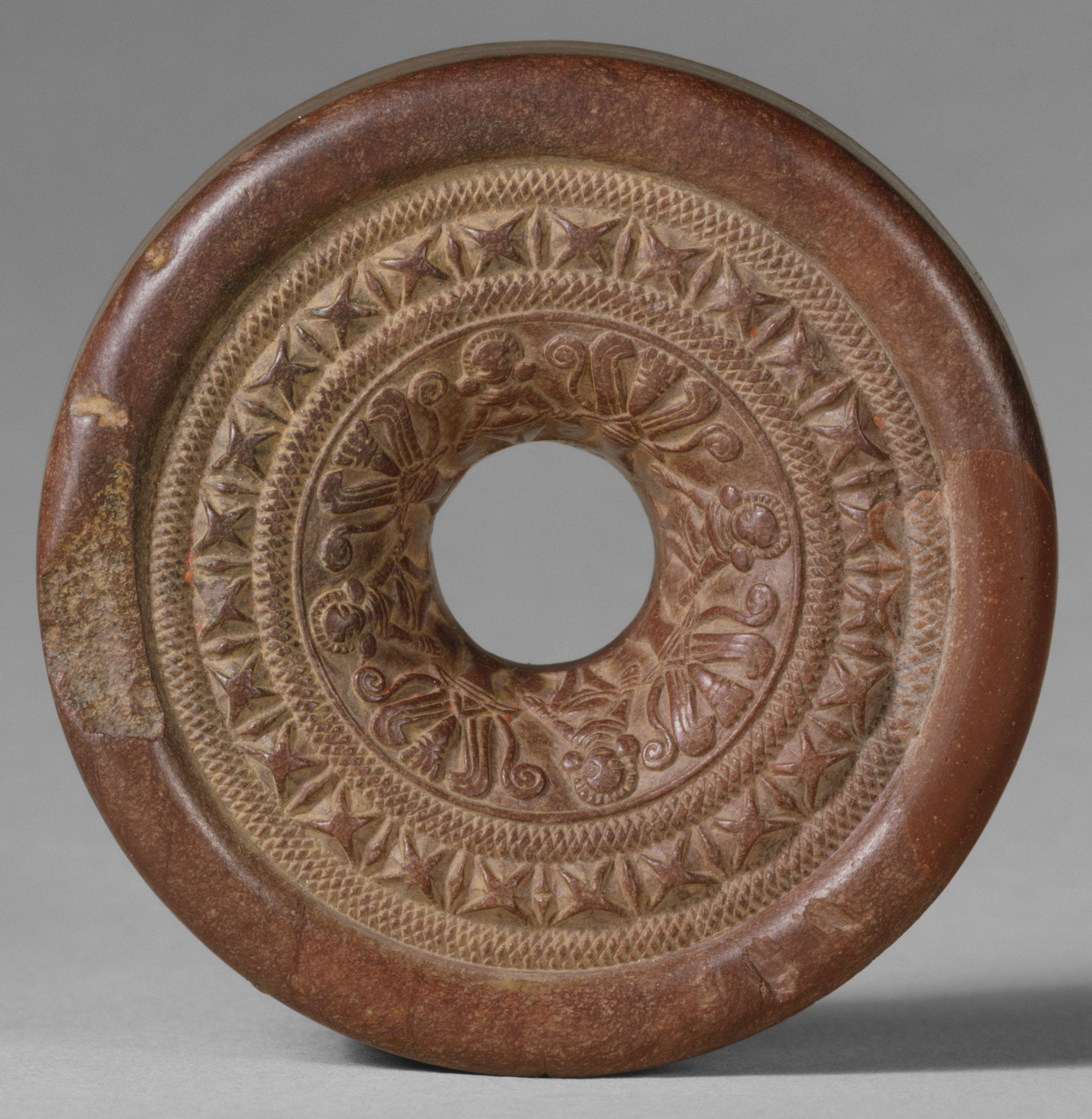

 The ringstone is a distinctive type of artefact and miniature sculpture made in India during the approximate period of the Mauryan Empire and the following Sunga Empire (187-78 BCE). They are usually dated to the 3rd or 2nd centuries BCE. They are shaped like a
The ringstone is a distinctive type of artefact and miniature sculpture made in India during the approximate period of the Mauryan Empire and the following Sunga Empire (187-78 BCE). They are usually dated to the 3rd or 2nd centuries BCE. They are shaped like a
 While the period marked a second transition to use of brick and stone, wood was still the material of choice.
While the period marked a second transition to use of brick and stone, wood was still the material of choice. 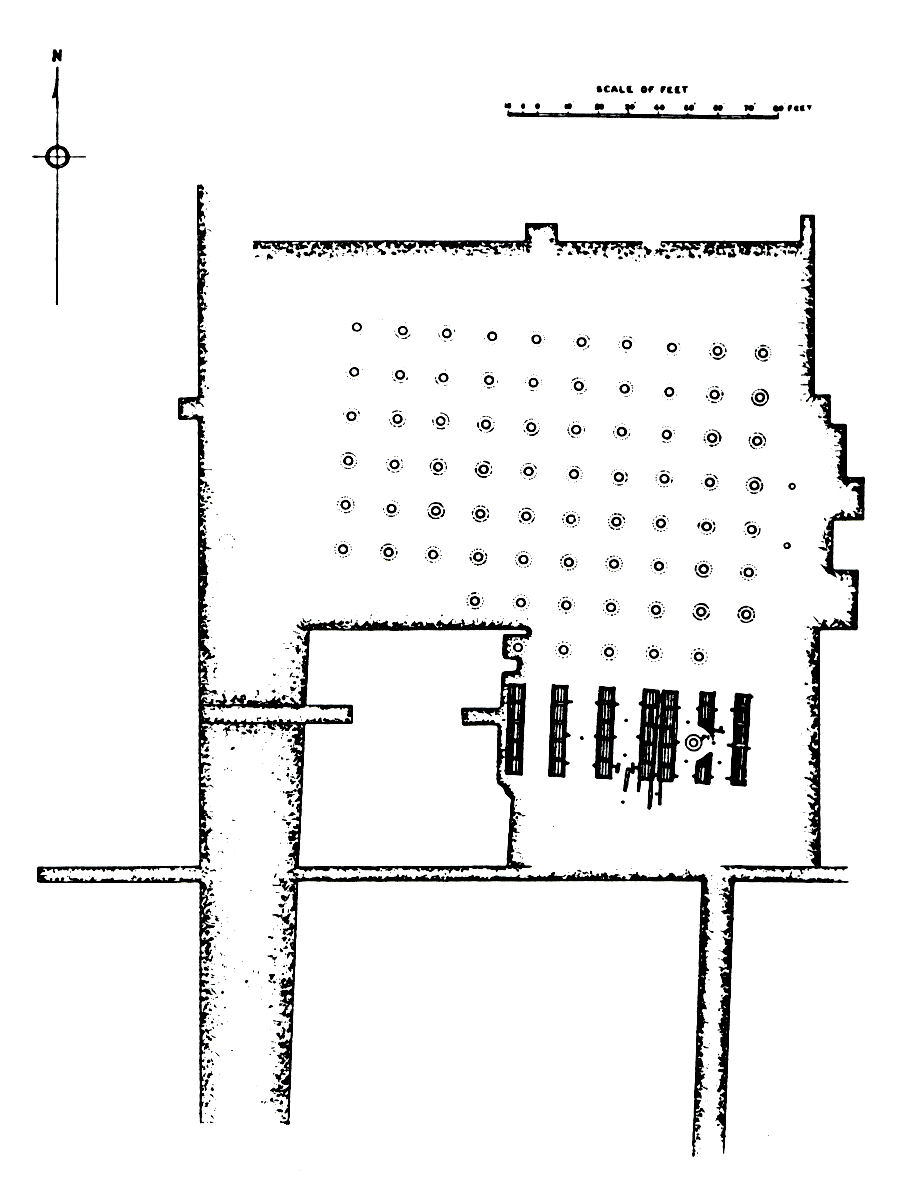 The Greek ambassador
The Greek ambassador
 The coins issued by the Mauryans are mostly silver and a few copper pieces of metal in various shapes, sizes and weights and which have one or more symbols punched on them. The most common symbols are the elephant, the tree in railing symbol and the mountain. The technique of producing such coins was generally that the metal was cut first and then the device was punched. These symbols are said to have either represented the Royal insignia or the symbol of the local guild that struck the coin. Some coins had ''Shroff'' (
The coins issued by the Mauryans are mostly silver and a few copper pieces of metal in various shapes, sizes and weights and which have one or more symbols punched on them. The most common symbols are the elephant, the tree in railing symbol and the mountain. The technique of producing such coins was generally that the metal was cut first and then the device was punched. These symbols are said to have either represented the Royal insignia or the symbol of the local guild that struck the coin. Some coins had ''Shroff'' (
File:Lohanipur torso.jpg, The
PDF
* 'The Culture and Civilisation of Ancient India in Historical outline' by D.D. Kosambi, 1964 reprinted in 1997, Vikas Publications, New Delhi, * *Lerner, Martin and Kossak, Steven, ''The Lotus Transcendent: Indian and Southeast Asian Art from the Samuel Eilenberg Collection'', 1991, Metropolitan Museum of Art (New York, N.Y.), , 9780870996139
google books
*"V&A"
"Ring stone"
in collection * *FocusCivil.onlin
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mauryan Art Mauryan art, Indian art art Cultural history of India
Mauryan Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until ...
, which was the first empire to rule over most of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
, between 322 and 185 BCE. It represented an important transition in Indian art from use of wood to stone. It was a royal art patronized by Mauryan kings especially Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, s ...
. Pillars, Stupas, caves are the most prominent survivals.
The most significant remains of monumental Mauryan art include the remains of the royal palace and the city of Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliputra at t ...
, a monolithic rail at Sarnath
Sarnath (Hindustani pronunciation: aːɾnaːtʰ also referred to as Sarangnath, Isipatana, Rishipattana, Migadaya, or Mrigadava) is a place located northeast of Varanasi, near the confluence of the Ganges and the Varuna rivers in Uttar Pr ...
, the Bodhimandala or the altar resting on four pillars at Bodhgaya, the rock-cut chaitya
A chaitya, chaitya hall, chaitya-griha, (Sanskrit:''Caitya''; Pāli: ''Cetiya'') refers to a shrine, sanctuary, temple or prayer hall in Indian religions. The term is most common in Buddhism, where it refers to a space with a stupa and a rounded ...
-halls in the Barabar Caves
The Barabar Hill Caves (Hindi बराबर, ''Barābar'') are the oldest surviving rock-cut caves in India, dating from the Maurya Empire (322–185 BCE), some with Ashokan inscriptions, located in the Makhdumpur region of Jehanabad distric ...
near Gaya including the Sudama cave bearing the inscription dated the 12th regnal year of Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, s ...
, the non-edict bearing and edict bearing pillars, the animal sculptures crowning the pillars with animal and vegetal reliefs decorating the abaci of the capitals and the front half of the representation of an elephant carved out in the round from a live rock at Dhauli.
Ananda Coomaraswamy
Ananda Kentish Muthu Coomaraswamy ( ta, ஆனந்த குமாரசுவாமி, ''Ānanda Kentiś Muthū Kumāraswāmī''; si, ආනන්ද කුමාරස්වාමි ''Ānanda Kumārasvāmī''; 22 August 1877 − 9 Septem ...
, writing in 1923, argued that the Mauryan art has three main phases. The first phase is found in some instances of the representation of the Vedic deities (the most significant examples are the reliefs of Surya
Surya (; sa, सूर्य, ) is the sun as well as the solar deity in Hinduism. He is traditionally one of the major five deities in the Smarta tradition, all of whom are considered as equivalent deities in the Panchayatana puja and a ...
and Indra
Indra (; Sanskrit: इन्द्र) is the king of the devas (god-like deities) and Svarga (heaven) in Hindu mythology. He is associated with the sky, lightning, weather, thunder, storms, rains, river flows, and war. volumes/ref> I ...
at the Bhaja Caves
Bhaja Caves is a group of 22 rock-cut caves dating back to the 2nd century BC located in the city of Pune, India. The caves are 400 feet above the village of Bhaja, on an important ancient trade route running from the Arabian Sea eastward into th ...
). However the art of the Bhaja Caves
Bhaja Caves is a group of 22 rock-cut caves dating back to the 2nd century BC located in the city of Pune, India. The caves are 400 feet above the village of Bhaja, on an important ancient trade route running from the Arabian Sea eastward into th ...
is now generally dated later than the Mauryan period, to the 2nd-1st centuries BCE. The second phase was the court art of Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, s ...
, typically found in the monolithic columns on which his edicts are inscribed and the third phase was the beginning of brick and stone architecture, as in the case of the original stupa
A stupa ( sa, स्तूप, lit=heap, ) is a mound-like or hemispherical structure containing relics (such as ''śarīra'' – typically the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns) that is used as a place of meditation.
In Buddhism, circum ...
at Sanchi
Sanchi is a Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometres from Raisen town, district headquarter and north-east of Bh ...
, the small monolithic rail at Sanchi and the Lomas Rishi Cave in the Barabar Caves
The Barabar Hill Caves (Hindi बराबर, ''Barābar'') are the oldest surviving rock-cut caves in India, dating from the Maurya Empire (322–185 BCE), some with Ashokan inscriptions, located in the Makhdumpur region of Jehanabad distric ...
, with its ornamented facade, reproducing the forms of wooden structure.
Most scholars agree that Mauryan art was influenced by Greek and Persian art
Persian art or Iranian art () has one of the richest art heritages in world history and has been strong in many media including architecture, painting, weaving, pottery, calligraphy, metalworking and sculpture. At different times, influences f ...
, especially in imperial sculpture and architecture. Political and cultural contacts between the Greek and Persian cultures and India were intensive and ran for a long period of time, encouraging the propagation of their advances in the area of sculpture.
Sculpture
 This period marked an imaginative and impressive step forward in Indian stone sculpture; much previous sculpture was probably in wood and has not survived. The elaborately carved animal capitals surviving on from some Pillars of Ashoka are the best known works, and among the finest, above all the
This period marked an imaginative and impressive step forward in Indian stone sculpture; much previous sculpture was probably in wood and has not survived. The elaborately carved animal capitals surviving on from some Pillars of Ashoka are the best known works, and among the finest, above all the Lion Capital of Ashoka
The Lion Capital of Ashoka is the capital, or head, of a column erected by the Mauryan emperor Ashoka in Sarnath, India, . Its crowning features are four life-sized lions set back to back on a drum-shaped abacus. The side of the abacus ...
from Sarnath
Sarnath (Hindustani pronunciation: aːɾnaːtʰ also referred to as Sarangnath, Isipatana, Rishipattana, Migadaya, or Mrigadava) is a place located northeast of Varanasi, near the confluence of the Ganges and the Varuna rivers in Uttar Pr ...
that is now the National Emblem of India
The State Emblem of India is the national emblem of the Republic of India and is used by the union government, many state governments, and other government agencies. The emblem is an adaptation of the Lion Capital of Ashoka, an ancient sculp ...
. Coomaraswamy distinguishes between court art and a more popular art during the Mauryan period. Court art is represented by the pillars and their capitals,Thapar, Romila (2001). '' and the Decline of the Mauryas'', New Delhi: Oxford University Press, , pp.267-70 and surviving popular art by some stone pieces, and many smaller works in terracotta
Terracotta, terra cotta, or terra-cotta (; ; ), in its material sense as an earthenware substrate, is a clay-based unglazed or glazed ceramic where the fired body is porous.
In applied art, craft, construction, and architecture, terra ...
.
The highly polished surface of court sculpture is often called Mauryan polish
Mauryan polish describes one of the frequent characteristics of architecture and sculptures of the Maurya Empire in India (325 to 185 BCE), which gives a very smooth and shiny surface to the stone material, generally of sandstone or granite.The ...
. However this seems not to be entirely reliable as a diagnostic tool for a Mauryan date, as some works from considerably later periods also have it. The Didarganj Yakshi
The Didarganj Yakshi (or Didarganj Chauri Bearer; hi, दीदारगंज यक्षी) is one of the finest examples of very early Indian stone statues. It used to be dated to the 3rd century BCE, as it has the fine Mauryan polish ass ...
, now most often thought to be from the 2nd century CE, is an example.
Pillars and their capitals
 The Pataliputra capital, dated to the 3rd century BCE, has been excavated at the Mauryan city of
The Pataliputra capital, dated to the 3rd century BCE, has been excavated at the Mauryan city of Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliputra at t ...
. It has been described as Perso- Ionic, with a strong Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
stylistic influence, including volute
A volute is a spiral, scroll-like ornament that forms the basis of the Ionic order, found in the capital of the Ionic column. It was later incorporated into Corinthian order and Composite column capitals. Four are normally to be found on an Ion ...
, bead and reel
Bead and reel is an architectural motif, usually found in sculptures, moldings and numismatics. It consists in a thin line where beadlike elements alternate with cylindrical ones. It is found throughout the modern Western world in architectural d ...
, meander
A meander is one of a series of regular sinuous curves in the channel of a river or other watercourse. It is produced as a watercourse erodes the sediments of an outer, concave bank ( cut bank) and deposits sediments on an inner, convex ban ...
or honeysuckle
Honeysuckles are arching shrubs or twining vines in the genus ''Lonicera'' () of the family Caprifoliaceae, native to northern latitudes in North America and Eurasia. Approximately 180 species of honeysuckle have been identified in both con ...
designs. This monumental piece of architecture tends to suggest the Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
and Hellenistic artistic influence at the Mauryan court from early on.
 Emperor Ashoka also erected religious pillars throughout India. These pillars were carved in two types of stone. Some were of the spotted red and white sandstone from the region of
Emperor Ashoka also erected religious pillars throughout India. These pillars were carved in two types of stone. Some were of the spotted red and white sandstone from the region of Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located approximately north of Agra, and south-east of Delhi; about from the town of Vrindavan, and from Govardhan. ...
, the others of buff-coloured fine grained hard sandstone usually with small black spots quarried in the Chunar
Chunar is a city located in Mirzapur district of Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is nearby Mirzapur city. The railway tracks passing through Chunar Junction railway station leads to major destinations of India, including Howrah, Delhi, T ...
near Varanasi
Varanasi (; ; also Banaras or Benares (; ), and Kashi.) is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.
*
*
*
* The city has a syncretic t ...
. The uniformity of style in the pillar capitals suggests that they were all sculpted by craftsmen from the same region. It would therefore seem, that stone transported from Mathura and Chunar to the various sites where the pillars have been found and here the stone was cut and carved by craftsmen They were given a fine polish characteristic of Mauryan sculpture.
These pillars were mainly erected in the Gangetic plains
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain encompassing northern regions of the Indian subcontinent, including most of northern and eastern India, around half of Pakistan, virtually all of Ba ...
. They were inscribed with edicts of Ashoka on Dhamma
Dharma (; sa, धर्म, dharma, ; pi, dhamma, italic=yes) is a key concept with multiple meanings in Indian religions, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism and others. Although there is no direct single-word translation for ' ...
or righteousness. The animal capital as a finely carved lifelike representation, noteworthy are the lion capital of Sarnath
Sarnath (Hindustani pronunciation: aːɾnaːtʰ also referred to as Sarangnath, Isipatana, Rishipattana, Migadaya, or Mrigadava) is a place located northeast of Varanasi, near the confluence of the Ganges and the Varuna rivers in Uttar Pr ...
, the bull capital of Rampurva and the lion capital of Lauria Nandangarh. Much speculation has been made about the similarity between these capitals and Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
works.
"Popular" sculpture

 The work of local sculptors illustrates the popular art of the Mauryan period. This consisted of sculpture which probably was not commissioned by the emperor. The patrons of the popular art were the local governors and the more well-to-do subjects. It is represented by figures such as the female figure of Besnagar, the male figure of Parkham and the whisk-bearer from Didarganj (although its age is debated). Technically they are fashioned with less skill than the pillar capitals. They express a considerable earthiness and physical vitality.
The stone elephant at
The work of local sculptors illustrates the popular art of the Mauryan period. This consisted of sculpture which probably was not commissioned by the emperor. The patrons of the popular art were the local governors and the more well-to-do subjects. It is represented by figures such as the female figure of Besnagar, the male figure of Parkham and the whisk-bearer from Didarganj (although its age is debated). Technically they are fashioned with less skill than the pillar capitals. They express a considerable earthiness and physical vitality.
The stone elephant at Dhauli
Dhauli or Dhauligiri is a hill located on the banks of the river Daya, 8 km south of Bhubaneswar in Odisha, India.
Significance
Dhauli known for "Dhauli Santi Stupa", a peace pagoda monument which witnesses the great Kalinga War built ...
was also probably carved by local craftsmen and not by the court-based artists who were responsible for the animal capitals. The image of the elephant emerging from the rock is a most impressive one, and its purpose was probably to draw attention to the inscription nearby.
Terracottas
Popularterracotta
Terracotta, terra cotta, or terra-cotta (; ; ), in its material sense as an earthenware substrate, is a clay-based unglazed or glazed ceramic where the fired body is porous.
In applied art, craft, construction, and architecture, terra ...
objects of various sizes have been found at Mauryan sites, and elsewhere, and are probably the most numerous Mauryan works of art. Made by local people who may not have been specialists, but for example potters with a sideline, they are very difficult to date if not recorded as coming from an identifiable archaeological context. Many are regarded as pre-Mauryan, but a continuation of the tradition of making mother-goddesses in clay, which dates back to the prehistoric period is revealed by the discovery of these objects at Mauryan levels during the excavations at Ahicchatra.
They are found more commonly from Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliputra at t ...
to Taxila
Taxila or Takshashila (; sa, तक्षशिला; pi, ; , ; , ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area a ...
. Many have stylized forms and technically they are more accomplished, in that they have a well-defined shape and clear ornamentation. Some appear to have been made from moulds, yet there is little duplication. Terracotas from Taxila consists of deity figures, votive reliefs with deities, toys, dice, ornaments and beads. Among the ornaments were round medallions, similar to the ''bullae'' worn by Roman boys. Terracotta images of folk gods and goddesses often have an earthy charm (some of them are perhaps dolls). Many animal figures are probably toys for children.
terracotta
Terracotta, terra cotta, or terra-cotta (; ; ), in its material sense as an earthenware substrate, is a clay-based unglazed or glazed ceramic where the fired body is porous.
In applied art, craft, construction, and architecture, terra ...
figure, northern India, c. 320-200 BCE
File:Indian - Head of an Indian Village Deity - Walters 2563 (cropped).jpg, Head of an Indian Village Deity, terracotta, 3rd century BCE
File:Indian - A Votive Figurine - Walters 25249 - Three Quarter Left (cropped).jpg, Mother goddess (terracotta) from Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located approximately north of Agra, and south-east of Delhi; about from the town of Vrindavan, and from Govardhan. ...
, 3rd century BCE
File:Elephant LACMA AC1994.233.2.jpg, Elephant (terracotta) from Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located approximately north of Agra, and south-east of Delhi; about from the town of Vrindavan, and from Govardhan. ...
, 3rd century BCE
File:Forepart of an Animal LACMA AC1994.233.1.jpg, Forepart of an animal (terracotta) from Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located approximately north of Agra, and south-east of Delhi; about from the town of Vrindavan, and from Govardhan. ...
, 3rd century BCE
File:Mathura, epoca maurya-sunga, scimmia, III-II sec ac. 02.JPG, Monkey (terracotta) from Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located approximately north of Agra, and south-east of Delhi; about from the town of Vrindavan, and from Govardhan. ...
, 3rd-2nd century BCE
Ringstones

 The ringstone is a distinctive type of artefact and miniature sculpture made in India during the approximate period of the Mauryan Empire and the following Sunga Empire (187-78 BCE). They are usually dated to the 3rd or 2nd centuries BCE. They are shaped like a
The ringstone is a distinctive type of artefact and miniature sculpture made in India during the approximate period of the Mauryan Empire and the following Sunga Empire (187-78 BCE). They are usually dated to the 3rd or 2nd centuries BCE. They are shaped like a doughnut
A doughnut or donut () is a type of food made from leavened fried dough. It is popular in many countries and is prepared in various forms as a sweet snack that can be homemade or purchased in bakeries, supermarkets, food stalls, and fra ...
, but with straighter sides, and flat and plain on the bottom. They are in stone, with the top side very finely carved in relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term '' relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that th ...
with several circular zones of decoration running around the hole in the centre. When complete, they are about 2.5 to 4 inches across.
The designs vary, but all examples are finely carved, despite their small size. A number of components appear in a variety of variations. Typically the innermost zone, which runs down the sloping sides of the hole, has standing female figures, often nude or nearly so, but with jewellery and elaborate hairstyles, with trees in between them. These may be called "goddesses", or "mother goddesses", and the trees, apparently of various species, as the tree of life
The tree of life is a fundamental archetype in many of the world's mythological, religious, and philosophical traditions. It is closely related to the concept of the sacred tree.Giovino, Mariana (2007). ''The Assyrian Sacred Tree: A Hist ...
, but these interpretations are not universally accepted.
Their purpose, and any practical function, remains unclear and "enigmatic". They may have a specific religious purpose, or a more general one promoting fertility, or been used to make jewellery by hammering metal foil over the designs. About 70 have been found, many only as fragments, with a 2014 find in Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
the first from outside the Indian subcontinent; it is assumed this was imported from India.
Painting
It is clear fromMegasthenes
Megasthenes ( ; grc, Μεγασθένης, c. 350 BCE– c. 290 BCE) was an ancient Greek historian, diplomat and Indian ethnographer and explorer in the Hellenistic period. He described India in his book '' Indica'', which is now lost, but ha ...
that the Mauryans had painting of some quality, but no examples have survived. Many centuries later, the paintings of the Ajanta Caves
The Ajanta Caves are approximately thirty rock-cut Buddhist cave monuments dating from the second century BCE to about 480 CE in the Aurangabad district of Maharashtra state in India. The caves include paintings and rock-cut sculptures de ...
, the oldest significant body of Indian painting, show there was a well-developed tradition, which may well stretch back to Mauryan times.
Architecture
 While the period marked a second transition to use of brick and stone, wood was still the material of choice.
While the period marked a second transition to use of brick and stone, wood was still the material of choice. Kautilya
Chanakya (Sanskrit: चाणक्य; IAST: ', ; 375–283 BCE) was an ancient Indian polymath who was active as a teacher, author, strategist, philosopher, economist, jurist, and royal advisor. He is traditionally identified as Kauṭilya o ...
in the Arthashastra
The ''Arthashastra'' ( sa, अर्थशास्त्रम्, ) is an Ancient Indian Sanskrit treatise on statecraft, political science, economic policy and military strategy. Kautilya, also identified as Vishnugupta and Chanakya, is ...
advises the use of brick and stone for their durability. Yet he devotes a large section to safeguards to be taken against conflagrations in wooden buildings indicating their popularity.
 The Greek ambassador
The Greek ambassador Megasthenes
Megasthenes ( ; grc, Μεγασθένης, c. 350 BCE– c. 290 BCE) was an ancient Greek historian, diplomat and Indian ethnographer and explorer in the Hellenistic period. He described India in his book '' Indica'', which is now lost, but ha ...
mentions that the capital city of Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliputra at t ...
was encircled by a massive timber-palisade, perforated by holes or slits through which archers could shoot. It had sixty-four gates and 570 towers. According to Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
, the gilded pillars of the palace were adorned with golden vines and silver birds. The palace stood in an extensive park studded with fish ponds. It was furnished with a great variety of ornamental trees and shrubs. Excavations carried out by Spooner and Waddell have brought to light remains of huge wooden palisades at Bulandi Bagh
Bulandi Bagh is an area of the archaeological site of Pataliputra (north of railway station of the modern city of Patna). It is mainly known for the discovery of the monumental Pataliputra capital, unearthed in 1895 by L.A. Waddell, as well as t ...
in Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliputra at t ...
. The remains of one of the buildings, an 80 pillared hall at Kumrahar
Kumhrar or Kumrahar is the area of Patna where remains of the ancient city of Pataliputra were excavated by the Archaeological Survey of India starting from 1913. It is located 5 km east of Patna Railway Station.
Archaeological remains of ...
are of particular significance. Out of 80 stone columns, that once stood on a wooden platform and supported a wooden roof, Spooner was able to discover the entire lower part of at least one in almost perfect conditions. It is more or less similar to an Ashokan pillar, smooth, polished and made of grey Chunar sandstone.Mahajan V.D. (1960, reprint 2007). ''Ancient India'', New Delhi: S.Chand, New Delhi, , p.349
Many stupas like those at Sanchi
Sanchi is a Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometres from Raisen town, district headquarter and north-east of Bh ...
, Sarnath
Sarnath (Hindustani pronunciation: aːɾnaːtʰ also referred to as Sarangnath, Isipatana, Rishipattana, Migadaya, or Mrigadava) is a place located northeast of Varanasi, near the confluence of the Ganges and the Varuna rivers in Uttar Pr ...
and possibly Amaravati Stupa
The Amarāvati ''Stupa'', is a ruined Buddhist '' stūpa'' at the village of Amaravathi, Palnadu district, Andhra Pradesh, India, probably built in phases between the third century BCE and about 250 CE. It was enlarged and new sculptures repla ...
were originally built as brick and masonry mounds during the reign of Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, s ...
. Most were renovated many times, which leaves us with hardly a clue of the original structures.
Pottery
Use of the potters wheel became universal. The pottery associated with the Mauryan period consists of many types of ware. But the most highly developed technique is seen in a special type of pottery known as theNorthern Black Polished Ware
The Northern Black Polished Ware culture (abbreviated NBPW or NBP) is an urban Iron Age Indian culture of the Indian Subcontinent, lasting c. 700–200 BCE (proto NBPW between 1200 and 700 BCE), succeeding the Painted Grey Ware culture and Blac ...
(NBP), which was the hallmark of the preceding and early Mauryan periods. The NBP ware is made of finely levigated alluvial clay, which when seen in section is usually of a grey and sometimes of a red hue. It has a brilliantly burnished dressing of the quality of a glaze which ranges from a jet black to a deep grey or a metallic steel blue. Occasionally small red-brown patches are apparent on the surface. It can be distinguished from other polished or graphite-coated red wares by its peculiar lustre and brilliance.
This ware was used largely for dishes and small bowls. It is found in abundance in the Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
valley. Although NBP was not very rare, it was obviously a more expensive ware than the other varieties, since potsherds of NBP were occasionally found riveted with copper pins indicating that even a cracked vessel in NBP ware had its value.Thapar, Romila (2001). '' and the Decline of the Mauryas'', New Delhi: Oxford University Press, , pp.239-49
Coins
money changer
A money changer is a person or organization whose business is the exchange of coins or currency of one country for that of another. This trade was a predecessor of modern banking.
The advent of paper money in the mid-17th century and the develop ...
) marks on them indicating that older coins were often re-issued.
The alloy content closely resembles that specified in the Arthashastra. Based on his identification of the symbols on the punch-marked coins with certain Mauryan rulers, Kosambi
Kosambi (Pali) or Kaushambi ( Sanskrit) was an important city in ancient India. It was the capital of the Vatsa kingdom, one of the sixteen mahajanapadas. It was located on the Yamuna River about southwest of its confluence with the Ganges ...
argued that the Mauryan punch-marked ''Karshapana
Karshapana ( sa, कार्षापण, IAST: ''Kārṣāpaṇa''), according to the Ashtadhyayi of Panini, refers to ancient Indian coins current during the 6th century BCE onwards, which were unstamped and stamped (''āhata'') metallic pi ...
'' after Chandragupta has the same weight as its predecessor, but much more copper, cruder fabric, and such a large variation in weight that the manufacture must have been hasty. This evidence of stress and unsatisfied currency demand is accompanied by debasement (inflation) plus vanishing of the reverse marks which denoted the ancient trade guilds. This in his opinion indicated that there was a fiscal crisis in the later Mauryan period. However his method of analysis and the chronological identification has been questioned.Thapar, Romila (2001). '' and the Decline of the Mauryas'', New Delhi: Oxford University Press, , p.289
Gallery
Lohanipur torso
The Lohanipur torso is a damaged statue of polished sandstone, dated to the 3rd century BCE ~ 2nd century CE, found in Lohanipur village, a central Division of Patna, ancient Pataliputra, Bihar, India. There are some claims however for a later d ...
.
File:Mauryan head.jpg, Head from Sarnath
Sarnath (Hindustani pronunciation: aːɾnaːtʰ also referred to as Sarangnath, Isipatana, Rishipattana, Migadaya, or Mrigadava) is a place located northeast of Varanasi, near the confluence of the Ganges and the Varuna rivers in Uttar Pr ...
,
File:Statue of Matrikas found near Agam Kuan, Patna, 1895.jpg, Statue of Matrikas
Matrikas (Sanskrit: मातृका (singular), IAST: mātṝkās, lit. "divine mothers") also called Matar or Matri, are a group of mother goddesses who are always depicted together in Hinduism. The Matrikas are often depicted in a group ...
found near Agam Kuan
Agam Kuan ( hi, अगम कुआं ,"unfathomable well") is an ancient well and archaeological site in Patna, India. It is said to date back to the period of Mauryan emperor, Ashoka (304–232 BCE). Circular in shape, the well is lined with ...
, Patna
Patna (
), historically known as Pataliputra, is the capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Patna had a population of 2.35 million, making it the 19th largest city in India. ...
File:MauryanStatuette2ndCenturyBCE.jpg, 2nd-century statuette
File:Sarnath1.jpg, Dharmek Stupa at Sarnath
Sarnath (Hindustani pronunciation: aːɾnaːtʰ also referred to as Sarangnath, Isipatana, Rishipattana, Migadaya, or Mrigadava) is a place located northeast of Varanasi, near the confluence of the Ganges and the Varuna rivers in Uttar Pr ...
Image:6thPillarOfAshoka.JPG, Fragment of the 6th Pillar Edict of Ashoka (238 BCE), in Brahmi
Brahmi (; ; ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system of ancient South Asia. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' o ...
, sandstone, British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docum ...
Image:AsokaKandahar.jpg, Kandahar Bilingual Rock Inscription (Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated i ...
) by king Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, s ...
, from Kandahar
Kandahar (; Kandahār, , Qandahār) is a city in Afghanistan, located in the south of the country on the Arghandab River, at an elevation of . It is Afghanistan's second largest city after Kabul, with a population of about 614,118. It is the c ...
. Kabul Museum.
File:Indian Stone Sphere with Scenes of Rites at the Shrine of a Yaksha, 3rd century BC.jpg, Stone Sphere with Scenes of Rites at the Shrine of a Yaksha
The yakshas ( sa, यक्ष ; pi, yakkha, i=yes) are a broad class of nature-spirits, usually benevolent, but sometimes mischievous or capricious, connected with water, fertility, trees, the forest, treasure and wilderness. They appear in ...
(male nature spirit) (Maurya period, 3rd century BCE)
File:Serpent Hood - Chunar Sandstone - Circa 3rd Century BCE - Rajgir - ACCN NS3-A24301 - Indian Museum - Kolkata 2014-02-14 9262.JPG, Serpent Hood (Chunar sandstone) from Rajgir, ca. 3rd century BCE
File:Patna griffin.jpg, Patna griffin.
File:Masarh_lion_sculpture.jpg, Masarh lion The Masarh lion is a stone sculpture found at Masarh, a village near Arrah town in the Bhojpur district in the Indian state of Bihar.Page 88: "It is carved out of Chunar sandstone and it also bears the typical Mauryan polish. But it is undoubtedly ...
.
Notes
References
* The Wonder that was India' by A.L Basham, Picador India, *Bennett, Anna (2019), "Suvarnabhumi, "Land of Gold"", in ''Suvarnabhumi, the Golden Land'', 2019, GISDA* 'The Culture and Civilisation of Ancient India in Historical outline' by D.D. Kosambi, 1964 reprinted in 1997, Vikas Publications, New Delhi, * *Lerner, Martin and Kossak, Steven, ''The Lotus Transcendent: Indian and Southeast Asian Art from the Samuel Eilenberg Collection'', 1991, Metropolitan Museum of Art (New York, N.Y.), , 9780870996139
google books
*"V&A"
"Ring stone"
in collection * *FocusCivil.onlin
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mauryan Art Mauryan art, Indian art art Cultural history of India