Master's Mate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Master's mate is an obsolete rating which was used by the
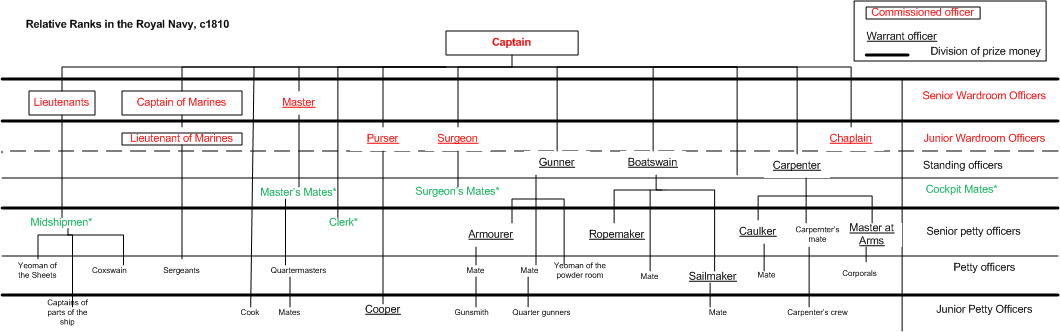
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
, United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
and merchant services in both countries for a senior petty officer
A petty officer (PO) is a non-commissioned officer in many navies and is given the NATO rank denotation OR-5 or OR-6. In many nations, they are typically equal to a sergeant in comparison to other military branches. Often they may be super ...
who assisted the master
Master or masters may refer to:
Ranks or titles
* Ascended master, a term used in the Theosophical religious tradition to refer to spiritually enlightened beings who in past incarnations were ordinary humans
*Grandmaster (chess), National Master ...
. Master's mates evolved into the modern rank of Sub-Lieutenant
Sub-lieutenant is usually a junior officer rank, used in armies, navies and air forces.
In most armies, sub-lieutenant is the lowest officer rank. However, in Brazil, it is the highest non-commissioned rank, and in Spain, it is the second hig ...
in the Royal Navy, while in the merchant service they evolved into the numbered mates or officers.
Royal Navy
Originally, a master's mate was an experienced petty officer who assisted themaster
Master or masters may refer to:
Ranks or titles
* Ascended master, a term used in the Theosophical religious tradition to refer to spiritually enlightened beings who in past incarnations were ordinary humans
*Grandmaster (chess), National Master ...
but was not in line for promotion to lieutenant
A lieutenant ( , ; abbreviated Lt., Lt, LT, Lieut and similar) is a commissioned officer rank in the armed forces of many nations.
The meaning of lieutenant differs in different militaries (see comparative military ranks), but it is often ...
. By the mid-eighteenth century, he was far more likely to be a superior midshipman, still waiting to pass his examination for lieutenant or to receive his commission, but taking rather more responsibility aboard ship. Six master's mates were allowed on a first rate
In the rating system of the British Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a first rate was the designation for the largest ships of the line. Originating in the Jacobean era with the designation of Ships Royal capable of carrying at ...
, three on a third rate, and two on most frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat.
The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed an ...
s.

Duties
Master's mates were experienced seamen, and were usually selected from the ranks of the quartermasters, who they supervised, or from the ranks of midshipmen who wanted more responsibility aboard ship; they were less commonly selected from other mates of warrant officers andable seamen
An able seaman (AB) is a seaman and member of the deck department of a merchant ship with more than two years' experience at sea and considered "well acquainted with his duty". An AB may work as a watchstander, a day worker, or a combination ...
. Master's mates were allowed to command vessels, walk the quarterdeck, and mess in the gunroom
A gunroom is the junior officers' mess on a naval vessel. It was occupied by the officers below the rank of lieutenant. In the wooden sailing ships it was on the lower deck, and was originally the quarters of the gunner, but in its form as a mess ...
with the other warrant officers.
Master's mates were responsible for fitting out the ship, and making sure they had all the sailing supplies necessary for the voyage. They hoisted and lowered the anchor, and docked and undocked the ship. They would examine the ship daily, notifying the master if there were problems with the sails, masts, ropes, or pulleys. They executed the orders of the master, and would command in his place if he was sick or absent.
Normally master's mates worked on a three-watch system, with the lieutenants, so that one served as the deputy to the lieutenant on each watch. Master's mates generally assisted the master in navigating the ship and directly supervised the quartermasters
Quartermaster is a military term, the meaning of which depends on the country and service. In land armies, a quartermaster is generally a relatively senior soldier who supervises stores or barracks and distributes supplies and provisions. In ...
in steering the ship. The master's mate with the highest seniority was appointed the head of the midshipman's berth and was responsible for teaching mathematics, navigation, and sailing lore. Master's mates had to keep detailed logs similar to midshipmen. They were also responsible for the division of the crew that included the petty officers.
Second master
Second master was a rating introduced in 1753 that indicated a deputy master on3rd rate
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Numbers
* 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3
* , a fraction of one third
* 1⁄60 of a ''second'', or 1⁄3600 of a ''minute''
Places
* 3rd Street (disambiguation)
* Third Avenue (disambiguation)
* Hi ...
ships of the line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactic known as the line of battle, which depended on the two colu ...
or larger. Master's mates also acted as Second Master of vessels too small to be allocated a warranted Master. They were paid significantly more than master's mates, £5 5s per month. A second master was generally a master's mate who had passed his examination for master and was deemed worthy of being master of a vessel. Second masters were given the first opportunity for master vacancies as they occurred.
Mate
Passed midshipmen awaiting promotion often elected to become master's mates. Though formally the rating did not lead to promotion to lieutenant, master's mates were paid more than any other rating and were the only ratings allowed to command any sort of vessel. A midshipman who became master's mate earned an increase in pay from £1 13s 6p to £3 16s per month, but initially reduced his chances at a commission. Over time, however, an appointment of master's mate became considered a normal part of the path to a commission; the situation caused some confusion during the last part of the 18th century, when two parallel roles - master's mates trying to become masters, and former midshipmen working toward a commission - held the same title and responsibilities aboard ship. By the first years of the nineteenth century, the prefix "master's" was dropped for passed midshipman, to distinguish them from master's mates in the navigator's branch. In 1824 two further grades were also introduced, consisting of master's assistants and second-class volunteers. These corresponded to midshipmen and first-class volunteers respectively in the executive line. From this point, passed midshipmen had the rating master's mate, abbreviated as mate, and prospective masters had the rating master's assistant. These changes helped eliminate the confusion caused by the mingling of midshipmen in the navigator's branch. In 1838 a Royal Commission, presided over by theDuke of Wellington
Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, (1 May 1769 – 14 September 1852) was an Anglo-Irish soldier and Tory statesman who was one of the leading military and political figures of 19th-century Britain, serving twice as prime minister ...
, recommended the institution of the rank of mate as an official step between midshipman and lieutenant.
By 1840 there were two completely separate "ladders" for promotion:
Renaming and later use
In 1861 mate was abolished in favor of sub-lieutenant. This made no practical difference to the officers in question since they continued to receive the same pay as before. But the new title was more distinctive; it brought them into line with their opposite numbers in the Army and established them as commissioned officers. In 1867, master was renamed navigating lieutenant, so at the same time second master was renamed navigating sub-lieutenant and the master's assistant was renamed navigating midshipman. Mate was revived in 1913 for the accelerated promotion of promising ratings, and mates ranked with sub-lieutenants but messed separately. In 1931 the title was abandoned again, and mates were re-mustered as sub-lieutenants.US Navy
As a warrant officer
In the U.S. Navy, the rank of master's mate was established 1797 as a warrant officer rank, but it was disestablished in 1813. After 1843 no more warrants were issued but those who had been appointed continued to hold their office and received their pay. In 1865, it was replaced by the rating mate. By an act of theUnited States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is Bicameralism, bicameral, composed of a lower body, the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, and an upper body, ...
in 1906, the mates on the U.S. Navy retired list were promoted to the next higher grade if they had creditable American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
service, which most of them had. They were given warrant rank and rated with the lowest grade of warrant officer.
As a seaman
Master's mate was re-established in 1838 as a rating for experienced seamen, and was not considered a warrant rank. At the same time sailing master was renamed master, master commandant was renamedcommander
Commander (commonly abbreviated as Cmdr.) is a common naval officer rank. Commander is also used as a rank or title in other formal organizations, including several police forces. In several countries this naval rank is termed frigate captain. ...
, and some masters were commissioned as officers, formally "Master in line for Promotion" to distinguish them from the warrant masters who would not be promoted.
In 1865, "master's mate" was changed to "mate", and the United States Secretary of the Navy
The secretary of the Navy (or SECNAV) is a statutory officer () and the head (chief executive officer) of the Department of the Navy, a military department (component organization) within the United States Department of Defense.
By law, the se ...
was authorized to increase their pay and to rate them from Seaman
Seaman may refer to:
* Sailor, a member of a marine watercraft's crew
* Seaman (rank), a military rank in some navies
* Seaman (name) (including a list of people with the name)
* ''Seaman'' (video game), a 1999 simulation video game for the Seg ...
to Ordinary Seaman
__NOTOC__
An ordinary seaman (OS) is a member of the deck department of a ship. The position is an apprenticeship to become an able seaman, and has been for centuries. In modern times, an OS is required to work on a ship for a specific amount ...
who had enlisted in the naval service for not less than two years. The act of 15 July 1870 gave formal recognition to mates as part of the naval forces and their pay was fixed at $900 when at sea, $700 on shore duty, and $500 on leave or awaiting orders.
The quota of mates in the Navy was not fixed, but there was maximum of about 842 on 1 January 1865, during the Civil War. The Navy stopped making appointments to the rank of mate in 1870 but allowed those in serving in the position to remain in service. The U.S. Navy Register of Commissioned Officers of 1871 shows there were 130 mates on active duty as of January 1. The number gradually diminished until 1 July 1894 when there were only 27 remaining.This occurred because the U.S. Navy shrank during the long period of peace between the Civil War and the Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (clock ...
and that there were no appointments to the rank of mate during that time period.
The Navy resumed appointing mates in 1897 in limited quantities. The 1899 Register shows a total of 34 mates on active duty with 12 being appointed in 1870 or earlier, 6 in 1897 and 16 in 1898. The revival of the rank of mate was only temporary as most of the remaining mates were promoted to the warrant officer rank of Boatswain in 1899. In the Navy Register of 1903 only 7 mates were listed as being on active duty. The Navy started appointing mates that year and by January 1, 1907, there were 39 on active duty. The revival was short lived as by January 1, 1908, there were no mates on active duty.U.S. Navy Register of Commissioned Officers, January 1, 1908.
Retirement and pensions
Before 1 August 1894 there had been no authority for retirement of these men, but on that date a law was passed increasing the pay of those in the Navy and providing that they should have the same benefits of retirement as warrant officers. One purpose of the act was to make the retired pay of mates large enough to induce them to retire. By an act of Congress in 1906, the mates on the U.S. Navy retired list were promoted to the next higher grade if they had creditable Civil War service, which most of them had. They were given warrant rank and rated with the lowest grade of warrant officer. They were still called mates, but whether they were officers or enlisted men apparently was not clear. A year after the passage of this act theAttorney General of the United States
The United States attorney general (AG) is the head of the United States Department of Justice, and is the chief law enforcement officer of the federal government of the United States. The attorney general serves as the principal advisor to the ...
published the legal opinion that mates "occupy the status of both officers in the Navy and enlisted men".
Merchant service
In the merchant service, master's mates were the officers immediately subordinate to the master and frequently divided by seniority into first, second, third (etc.) mate which evolved into the modern termsFirst Mate
A chief mate (C/M) or chief officer, usually also synonymous with the first mate or first officer, is a licensed mariner and head of the deck department of a merchant ship. The chief mate is customarily a watchstander and is in charge of the shi ...
, Second Mate and Third Mate. Since the 1930s, there has been a tendency in the merchant service to replace mate with officer (e.g. First Officer).
See also
* Master (naval) *Midshipman
A midshipman is an officer of the lowest rank, in the Royal Navy, United States Navy, and many Commonwealth navies. Commonwealth countries which use the rank include Canada (Naval Cadet), Australia, Bangladesh, Namibia, New Zealand, South Af ...
*Sub-lieutenant
Sub-lieutenant is usually a junior officer rank, used in armies, navies and air forces.
In most armies, sub-lieutenant is the lowest officer rank. However, in Brazil, it is the highest non-commissioned rank, and in Spain, it is the second hig ...
*Warrant Officer
Warrant officer (WO) is a rank or category of ranks in the armed forces of many countries. Depending on the country, service, or historical context, warrant officers are sometimes classified as the most junior of the commissioned ranks, the mo ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Master's Mate Naval ranks Military ranks of the Royal Navy Military ranks of the United States Navy