Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' (MRO) is a

 On August 12, 2005, MRO was launched aboard an Atlas V-401 rocket from
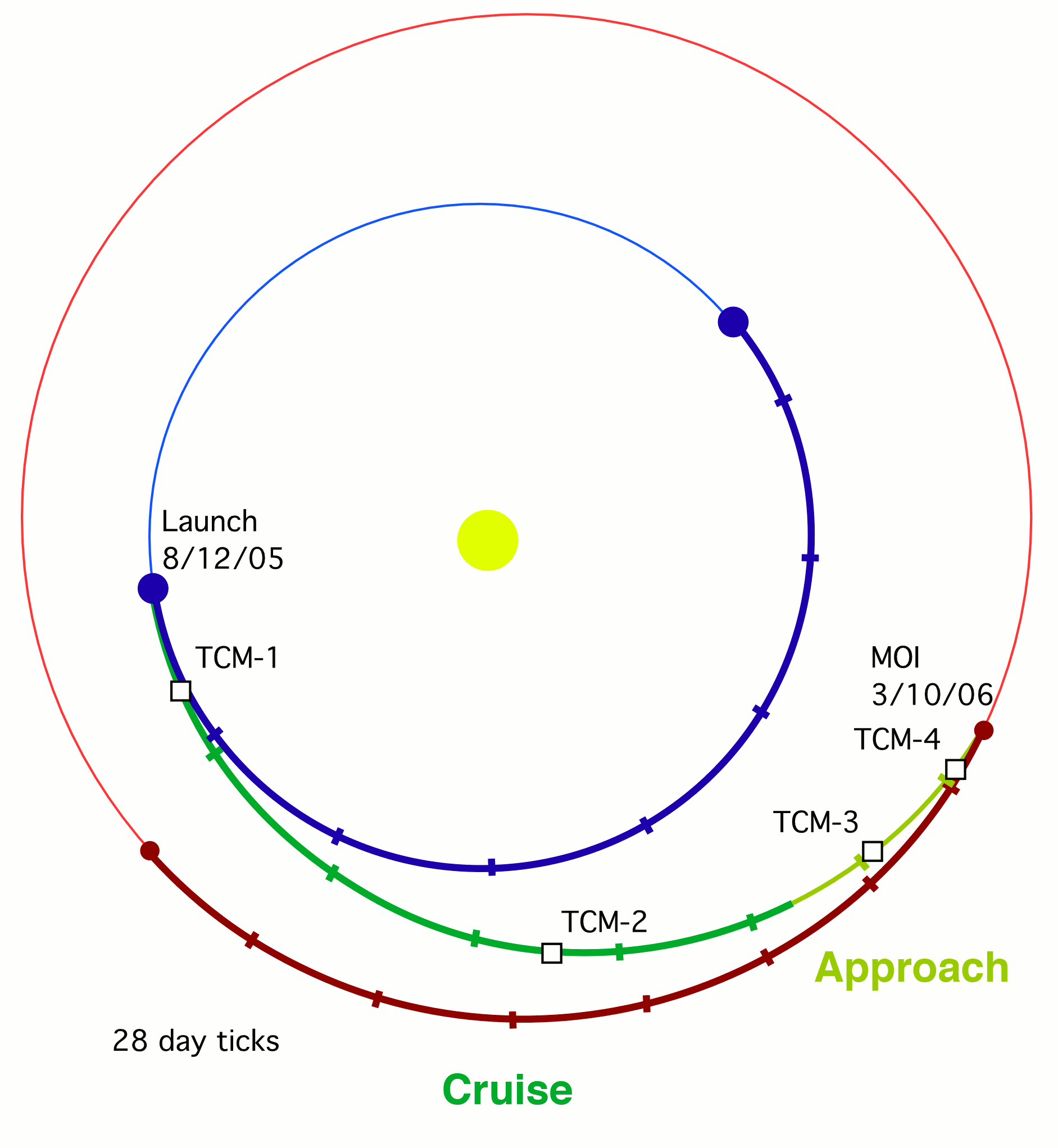
On August 12, 2005, MRO was launched aboard an Atlas V-401 rocket from  MRO began orbital insertion by approaching Mars on March 10, 2006, and passing above its southern hemisphere at an altitude of . All six of MRO's main engines burned for 27 minutes to slow the probe by . The helium pressurization tank was colder than expected, which reduced the pressure in the fuel tank by about . The reduced pressure caused the engine thrust to be diminished by 2%, but MRO automatically compensated by extending the burn time by 33 seconds.
Completion of the orbital insertion placed the orbiter in a highly elliptical polar orbit with a period of approximately 35.5 hours. Shortly after insertion, the periapsis – the point in the orbit closest to Mars – was from the surface ( from the planet's center). The apoapsis – the point in the orbit farthest from Mars – was from the surface ( from the planet's center).
When MRO entered orbit, it joined five other active spacecraft that were either in orbit or on the planet's surface: ''
MRO began orbital insertion by approaching Mars on March 10, 2006, and passing above its southern hemisphere at an altitude of . All six of MRO's main engines burned for 27 minutes to slow the probe by . The helium pressurization tank was colder than expected, which reduced the pressure in the fuel tank by about . The reduced pressure caused the engine thrust to be diminished by 2%, but MRO automatically compensated by extending the burn time by 33 seconds.
Completion of the orbital insertion placed the orbiter in a highly elliptical polar orbit with a period of approximately 35.5 hours. Shortly after insertion, the periapsis – the point in the orbit closest to Mars – was from the surface ( from the planet's center). The apoapsis – the point in the orbit farthest from Mars – was from the surface ( from the planet's center).
When MRO entered orbit, it joined five other active spacecraft that were either in orbit or on the planet's surface: '' On March 30, 2006, MRO began the process of aerobraking, a three-step procedure that cuts in half the fuel needed to achieve a lower, more circular orbit with a shorter period. First, during its first five orbits of the planet (one Earth week), MRO used its thrusters to drop the periapsis of its orbit into aerobraking altitude. This altitude depends on the thickness of the
On March 30, 2006, MRO began the process of aerobraking, a three-step procedure that cuts in half the fuel needed to achieve a lower, more circular orbit with a shorter period. First, during its first five orbits of the planet (one Earth week), MRO used its thrusters to drop the periapsis of its orbit into aerobraking altitude. This altitude depends on the thickness of the
 On September 29, 2006 (
On September 29, 2006 ( HiRISE continues to return images that have enabled discoveries regarding the geology of Mars. Foremost among these is the announcement of banded terrain observations indicating the presence and action of liquid
HiRISE continues to return images that have enabled discoveries regarding the geology of Mars. Foremost among these is the announcement of banded terrain observations indicating the presence and action of liquid
 The High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera is a
The High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera is a
 The Mars Color Imager (MARCI) is a wide-angle, relatively low-resolution camera that views the surface of Mars in five visible and two
The Mars Color Imager (MARCI) is a wide-angle, relatively low-resolution camera that views the surface of Mars in five visible and two
 The Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) instrument is a visible and
The Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) instrument is a visible and
 MRO's Shallow Subsurface Radar (SHARAD) experiment is designed to probe the internal structure of the Martian polar
MRO's Shallow Subsurface Radar (SHARAD) experiment is designed to probe the internal structure of the Martian polar
 MRO gets all of its electrical power from two
MRO gets all of its electrical power from two
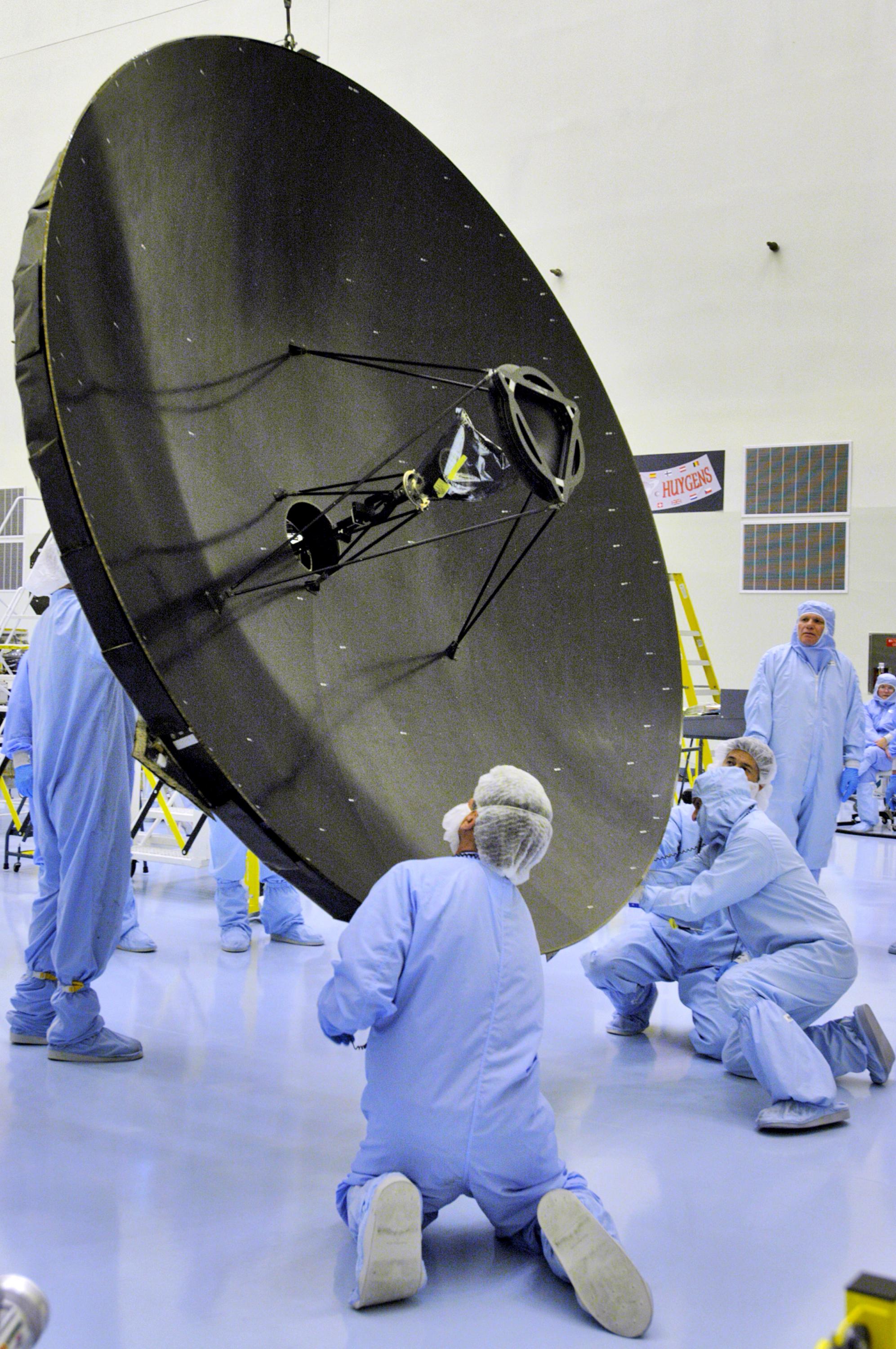 The Telecom Subsystem on MRO is the best digital communication system sent into deep space so far, and for the first time used capacity-approaching
The Telecom Subsystem on MRO is the best digital communication system sent into deep space so far, and for the first time used capacity-approaching 
 An article in the journal ''Science'' in September 2009, reported that some new craters on Mars have excavated relatively pure water ice. After being exposed, the ice gradually fades as it sublimates away. These new craters were found and dated by the CTX camera, and the identification of the ice was confirmed with the Compact Imaging Spectrometer (CRISM) on board the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter''. The ice was found in a total of five locations. Three of the locations are in the
An article in the journal ''Science'' in September 2009, reported that some new craters on Mars have excavated relatively pure water ice. After being exposed, the ice gradually fades as it sublimates away. These new craters were found and dated by the CTX camera, and the identification of the ice was confirmed with the Compact Imaging Spectrometer (CRISM) on board the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter''. The ice was found in a total of five locations. Three of the locations are in the
Iceincraterscomparison.jpg, Two pictures from HiRISE showing how ice disappeared over time in a crater. The crater on the left is before ice disappeared. The crater is 6 meters in diameter and located in
 Radar results from SHARAD suggested that features termed
Radar results from SHARAD suggested that features termed
 Using data from ''Mars Global Surveyor'', ''Mars Odyssey'', and the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'', scientists have found widespread deposits of chloride minerals. Evidence suggests that the deposits were formed from the evaporation of mineral enriched waters. The research suggests that lakes may have been scattered over large areas of the Martian surface. Usually chlorides are the last minerals to come out of solution. Carbonates, sulfates, and silica should precipitate out ahead of them. Sulfates and silica have been found by the Mars rovers on the surface. Places with chloride minerals may have once held various life forms. Furthermore, such areas could preserve traces of ancient life.
Using data from ''Mars Global Surveyor'', ''Mars Odyssey'', and the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'', scientists have found widespread deposits of chloride minerals. Evidence suggests that the deposits were formed from the evaporation of mineral enriched waters. The research suggests that lakes may have been scattered over large areas of the Martian surface. Usually chlorides are the last minerals to come out of solution. Carbonates, sulfates, and silica should precipitate out ahead of them. Sulfates and silica have been found by the Mars rovers on the surface. Places with chloride minerals may have once held various life forms. Furthermore, such areas could preserve traces of ancient life.
Four Martian avalanches, 2008.jpg, Martian avalanche and debris falls (HiRISE 2008)
Mars Avalanche with Scale.jpg , A photo with scale demonstrates the size of the avalanche.
Descent of Phoenix with a crater in the background taken by Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.jpg, Image of '' Phoenix'' landing on Mars, as seen by HiRISE. Although in the image it appears to be descending into the crater, ''Phoenix'' actually landed away from it.
Phoenix Lander from HiRISE.JPG, The ''Phoenix'' lander and its heatshield as seen by HiRISE
Opportunity Tracks.jpg, Tracks of the rover ''
NASA's ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' page
MRO Mars Arrival Press Kit (2006)
* ttps://www.planetary.org/blogs/blog-archive.html?keywords=mars-reconnaissance-orbiter Planetary Society coverage of the MRO mission
HiRISE Website
SHARAD Website
CRISM Website
HiRISE Image Catalog
''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' images at the JPL Photojournal
Multimedia gallery
by Seán Doran based on HiRISE photos
Multimedia gallery
by Seán Doran based on CTX photos
Multimedia gallery
by Kevin Gill based on HiRISE photos {{Good article Mars Exploration Program
spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, ...
designed to study the geology and climate of Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
, provide reconnaissance of future landing sites, and relay data from surface missions back to Earth. It was launched on August 12, 2005, and reached Mars on March 10, 2006. In November 2006, after five months of aerobraking, it entered its final science orbit and began its primary science phase. The cost to develop and operate MRO through the end of its prime mission in 2010 was .
The spacecraft continues to operate at Mars, far beyond its intended design life. Due to its critical role as a high-speed data-relay for ground missions, NASA intends to continue the mission as long as possible, at least through the late 2020s.
Pre-launch
After the twin failures of the ''Mars Climate Orbiter
The ''Mars Climate Orbiter'' (formerly the Mars Surveyor '98 Orbiter) was a robotic space probe launched by NASA on December 11, 1998, to study the Martian climate, Martian atmosphere, and surface changes and to act as the communications re ...
'' and the Mars Polar Lander
The Mars Polar Lander, also known as the Mars Surveyor '98 Lander, was a 290-kilogram robotic spacecraft lander launched by NASA on January 3, 1999, to study the soil and climate of Planum Australe, a region near the south pole on Mars. It form ...
missions in 1999, NASA reorganized and replanned its Mars Exploration Program. In October 2000, NASA announced its reformulated Mars plans, which reduced the number of planned missions and introduced a new theme: "follow the water". The plans included a newly christened ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' to launch in 2005.
On October 3, 2001, NASA chose Lockheed Martin
The Lockheed Martin Corporation is an American aerospace, arms, defense, information security, and technology corporation with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta in March 1995. It ...
as the primary contractor for the spacecraft's fabrication. By the end of 2001 all of the mission's instruments were selected. There were no major setbacks during MRO's construction, and the spacecraft was shipped to John F. Kennedy Space Center
The John F. Kennedy Space Center (KSC, originally known as the NASA Launch Operations Center), located on Merritt Island, Florida, is one of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) ten field centers. Since December 1968, ...
on May 1, 2005, to prepare it for launch.
Mission objectives
MRO has both scientific and "mission support" objectives. The prime science mission was designed to last from November 2006 to November 2008, and the mission support phase from November 2006 – November 2010. Both missions have been extended. The formal science objectives of MRO are to: * observe the present climate, particularly its atmospheric circulation and seasonal variations; * search for signs of water, both past and present, and understand how it altered the planet's surface; * map and characterize the geological forces that shaped the surface. The two mission support objectives for MRO are to: * provide data relay services from ground missions back to Earth; * characterize the safety and feasibility of potential future landing sites andMars rover
A Mars rover is a motor vehicle designed to travel on the surface of Mars. Rovers have several advantages over stationary landers: they examine more territory, they can be directed to interesting features, they can place themselves in sunny pos ...
traverses.
MRO played a key role in choosing safe landing sites for the ''Phoenix'' lander (2007), ''Mars Science Laboratory
Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) is a robotic space probe mission to Mars launched by NASA on November 26, 2011, which successfully landed ''Curiosity'', a Mars rover, in Gale Crater on August 6, 2012. The overall objectives include investigati ...
'' / ''Curiosity
Curiosity (from Latin '' cūriōsitās'', from ''cūriōsus'' "careful, diligent, curious", akin to ''cura'' "care") is a quality related to inquisitive thinking such as exploration, investigation, and learning, evident by observation in human ...
'' rover (2012), ''InSight
Insight is the understanding of a specific cause and effect within a particular context. The term insight can have several related meanings:
*a piece of information
*the act or result of understanding the inner nature of things or of seeing intui ...
'' lander (2018), and the ''Mars 2020
Mars 2020 is a Mars rover mission forming part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program that includes the rover '' Perseverance'', the small robotic, coaxial helicopter '' Ingenuity'', and associated delivery vehicles. Mars 2020 was launched from ...
'' / ''Perseverance'' rover (2021).
Launch and orbital insertion


 On August 12, 2005, MRO was launched aboard an Atlas V-401 rocket from
On August 12, 2005, MRO was launched aboard an Atlas V-401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41
Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41), previously Launch Complex 41 (LC-41), is an active launch site at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. As of 2020, the site is used by United Launch Alliance (ULA) for Atlas V launches. Previously, it had been use ...
at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida.
Headquartered at the nearby Patrick Space Force Base, the statio ...
. The Centaur upper stage of the rocket completed its burns over a fifty-six-minute period and placed MRO into an interplanetary transfer orbit towards Mars.
MRO cruised through interplanetary space for seven and a half months before reaching Mars. While en route most of the scientific instruments and experiments were tested and calibrated. To ensure proper orbital insertion
Orbit insertion is the spaceflight operation of adjusting a spacecraft’s momentum, in particular to allow for entry into a stable orbit around a planet, moon, or other celestial body. This maneuver involves either deceleration from a speed in ex ...
upon reaching Mars, four trajectory
A trajectory or flight path is the path that an object with mass in motion follows through space as a function of time. In classical mechanics, a trajectory is defined by Hamiltonian mechanics via canonical coordinates; hence, a complete tr ...
correction maneuvers were planned and a fifth emergency maneuver was discussed. However, only three trajectory correction maneuvers were necessary, which saved of fuel that would be usable during MRO's extended mission.
 MRO began orbital insertion by approaching Mars on March 10, 2006, and passing above its southern hemisphere at an altitude of . All six of MRO's main engines burned for 27 minutes to slow the probe by . The helium pressurization tank was colder than expected, which reduced the pressure in the fuel tank by about . The reduced pressure caused the engine thrust to be diminished by 2%, but MRO automatically compensated by extending the burn time by 33 seconds.
Completion of the orbital insertion placed the orbiter in a highly elliptical polar orbit with a period of approximately 35.5 hours. Shortly after insertion, the periapsis – the point in the orbit closest to Mars – was from the surface ( from the planet's center). The apoapsis – the point in the orbit farthest from Mars – was from the surface ( from the planet's center).
When MRO entered orbit, it joined five other active spacecraft that were either in orbit or on the planet's surface: ''
MRO began orbital insertion by approaching Mars on March 10, 2006, and passing above its southern hemisphere at an altitude of . All six of MRO's main engines burned for 27 minutes to slow the probe by . The helium pressurization tank was colder than expected, which reduced the pressure in the fuel tank by about . The reduced pressure caused the engine thrust to be diminished by 2%, but MRO automatically compensated by extending the burn time by 33 seconds.
Completion of the orbital insertion placed the orbiter in a highly elliptical polar orbit with a period of approximately 35.5 hours. Shortly after insertion, the periapsis – the point in the orbit closest to Mars – was from the surface ( from the planet's center). The apoapsis – the point in the orbit farthest from Mars – was from the surface ( from the planet's center).
When MRO entered orbit, it joined five other active spacecraft that were either in orbit or on the planet's surface: ''Mars Global Surveyor
''Mars Global Surveyor'' (MGS) was an American robotic space probe developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and launched November 1996. MGS was a global mapping mission that examined the entire planet, from the ionosphere down through t ...
'', ''Mars Express
''Mars Express'' is a space exploration mission being conducted by the European Space Agency (ESA). The ''Mars Express'' mission is exploring the planet Mars, and is the first planetary mission attempted by the agency. "Express" originally ref ...
'', ''2001 Mars Odyssey
''2001 Mars Odyssey'' is a robotic spacecraft orbiting the planet Mars. The project was developed by NASA, and contracted out to Lockheed Martin, with an expected cost for the entire mission of US$297 million. Its mission is to use ...
'', and the two Mars Exploration Rover
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover (MER) mission was a robotic space mission involving two Mars rovers, '' Spirit'' and '' Opportunity'', exploring the planet Mars. It began in 2003 with the launch of the two rovers to explore the Martian surface ...
s ('' Spirit'' and ''Opportunity
Opportunity may refer to:
Places
* Opportunity, Montana, an unincorporated community, United States
* Opportunity, Nebraska, an unincorporated community, United States
* Opportunity, Washington, a former census-designated place, United States
* ...
''). This set a new record for the most operational spacecraft in the immediate vicinity of Mars. ''Mars Global Surveyor'' and the rovers ''Spirit'' and ''Opportunity'' have since ceased to function. , ''2001 Mars Odyssey'', ''Mars Express'' and MRO remain operational and have been joined by ''Mars Orbiter Mission
The Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), also called ''Mangalyaan'', was a space probe orbiting Mars since 24 September 2014. It was launched on 5 November 2013 by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). It was India's first interplanetary mis ...
'', '' MAVEN'' and '' ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter'', the Emirates ''Hope'' orbiter and the Chinese '' Tianwen-1'' orbiter in orbit, and ''Curiosity
Curiosity (from Latin '' cūriōsitās'', from ''cūriōsus'' "careful, diligent, curious", akin to ''cura'' "care") is a quality related to inquisitive thinking such as exploration, investigation, and learning, evident by observation in human ...
, Perseverance'', ''InSight
Insight is the understanding of a specific cause and effect within a particular context. The term insight can have several related meanings:
*a piece of information
*the act or result of understanding the inner nature of things or of seeing intui ...
'' and '' Zhurong'' on the surface, raising the record to twelve active spacecraft.
 On March 30, 2006, MRO began the process of aerobraking, a three-step procedure that cuts in half the fuel needed to achieve a lower, more circular orbit with a shorter period. First, during its first five orbits of the planet (one Earth week), MRO used its thrusters to drop the periapsis of its orbit into aerobraking altitude. This altitude depends on the thickness of the
On March 30, 2006, MRO began the process of aerobraking, a three-step procedure that cuts in half the fuel needed to achieve a lower, more circular orbit with a shorter period. First, during its first five orbits of the planet (one Earth week), MRO used its thrusters to drop the periapsis of its orbit into aerobraking altitude. This altitude depends on the thickness of the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A ...
because Martian atmospheric density changes with its seasons. Second, while using its thrusters to make minor corrections to its periapsis altitude, MRO maintained aerobraking altitude for 445 planetary orbits (about five Earth months) to reduce the apoapsis of the orbit to . This was done in such a way so as to not heat the spacecraft too much, but also dip enough into the atmosphere to slow the spacecraft down. After the process was complete, MRO used its thrusters to move its periapsis out of the edge of the Martian atmosphere on August 30, 2006.
In September 2006 MRO fired its thrusters twice more to fine-tune its final, nearly circular orbit to approximately above the Martian surface, with a period of about 112 minutes. The SHARAD radar antennas were deployed on September 16. All of the scientific instruments were tested and most were turned off prior to the solar conjunction
Solar conjunction generally occurs when a planet or other Solar System object is on the opposite side of the Sun from the Earth. From an Earth reference, the Sun will pass between the Earth and the object. Communication with any spacecraft in sol ...
that occurred from October 7 to November 6, 2006. After the conjunction ended the "primary science phase" began.
On November 17, 2006, NASA announced the successful test of the MRO as an orbital communications relay. Using the NASA rover '' Spirit'' as the point of origin for the transmission, the MRO acted as a relay for transmitting data back to Earth.
Timeline
 On September 29, 2006 (
On September 29, 2006 (sol
Sol or SOL may refer to:
Astronomy
* The Sun
Currency
* SOL Project, a currency project in France
* French sol, or sou
* Argentine sol
* Bolivian sol, the currency of Bolivia from 1827 to 1864
* Peruvian sol, introduced in 1991
* Peruvian sol ...
), MRO took its first high resolution image from its science orbit. This image is said to resolve items as small as 90 cm (3 feet) in diameter. On October 6, NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
released detailed pictures from the MRO of Victoria crater along with the ''Opportunity'' rover on the rim above it. In November, problems began to surface in the operation of two MRO spacecraft instruments. A stepping mechanism in the Mars Climate Sounder (MCS) skipped on multiple occasions resulting in a field of view that is slightly out of position. By December normal operations of the instrument was suspended, although a mitigation strategy allows the instrument to continue making most of its intended observations. Also, an increase in noise and resulting bad pixels
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the sm ...
has been observed in several CCDs of the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction o ...
(HiRISE). Operation of this camera with a longer warm-up time has alleviated the issue. However, the cause is still unknown and may return.
 HiRISE continues to return images that have enabled discoveries regarding the geology of Mars. Foremost among these is the announcement of banded terrain observations indicating the presence and action of liquid
HiRISE continues to return images that have enabled discoveries regarding the geology of Mars. Foremost among these is the announcement of banded terrain observations indicating the presence and action of liquid carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
(CO2) or water on the surface of Mars in its recent geological past. HiRISE was able to photograph the ''Phoenix'' lander during its parachuted descent to Vastitas Borealis on May 25, 2008 (sol ).
The orbiter continued to experience recurring problems in 2009, including four spontaneous resets, culminating in a four-month shut-down of the spacecraft from August to December. While engineers have not determined the cause of the recurrent resets, they have created new software to help troubleshoot the problem should it recur.
On March 3, 2010, the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' passed another significant milestone, having transmitted over 100 terabits of data back to Earth, which was more than all other interplanetary probes sent from Earth combined.
On August 6, 2012 (sol ), the orbiter passed over Gale crater, the landing site of the Mars Science Laboratory
Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) is a robotic space probe mission to Mars launched by NASA on November 26, 2011, which successfully landed ''Curiosity'', a Mars rover, in Gale Crater on August 6, 2012. The overall objectives include investigati ...
mission, during its EDL phase. It captured an image via the HiRISE camera of the ''Curiosity'' Rover descending with its backshell and supersonic parachute.
NASA reported that the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'', as well as the Mars Odyssey Orbiter and '' MAVEN'' orbiter had a chance to study the Comet Siding Spring flyby on October 19, 2014.
On July 29, 2015, the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' was placed into a new orbit to provide communications support during the anticipated arrival of the ''InSight
Insight is the understanding of a specific cause and effect within a particular context. The term insight can have several related meanings:
*a piece of information
*the act or result of understanding the inner nature of things or of seeing intui ...
'' Mars lander mission in September 2016. The maneuver's engine burn lasted for 75 seconds. ''InSight'' was delayed and missed the 2016 launch window
In the context of spaceflight, launch period is the collection of days and launch window is the time period on a given day during which a particular rocket must be launched in order to reach its intended target. If the rocket is not launched wi ...
, but was successfully launched during the next window on May 5, 2018, and landed on November 26, 2018.
Instruments
Three cameras, two spectrometers and a radar are included on the orbiter along with two "science-facility instruments", which use data from engineering subsystems to collect science data. Three technology experiments will test and demonstrate new equipment for future missions. It is expected MRO will obtain about 5,000 images per year.HiRISE (camera)

 The High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera is a
The High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera is a reflecting telescope
A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is a telescope that uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century by Isaac Newton as an alternati ...
, the largest ever carried on a deep space mission, and has a resolution of 1 microradian
The radian, denoted by the symbol rad, is the unit of angle in the International System of Units (SI) and is the standard unit of angular measure used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly an SI supplementary unit (before that ...
(μrad), or from an altitude of . In comparison, satellite images of Earth are generally available with a resolution of , and satellite images on Google Maps
Google Maps is a web mapping platform and consumer application offered by Google. It offers satellite imagery, aerial photography, street maps, 360° interactive panoramic views of streets (Street View), real-time traffic conditions, and rou ...
are available to . HiRISE collects images in three color bands, 400 to 600 nm (blue–green or B–G), 550 to 850 nm (red) and 800 to 1,000 nm (near infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from arou ...
or NIR).
Red color images are 20,264 pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the ...
s across ( wide), and B–G and NIR are 4,048 pixels across ( wide). HiRISE's onboard computer reads these lines in time with the orbiter's ground speed
Ground speed is the horizontal speed of an aircraft relative to the Earth’s surface. It is vital for accurate navigation that the pilot has an estimate of the ground speed that will be achieved during each leg of a flight.
An aircraft diving ve ...
, and images are potentially unlimited in length. Practically however, their length is limited by the computer's 28 Gigabit
The bit is the most basic unit of information in computing and digital communications. The name is a portmanteau of binary digit. The bit represents a logical state with one of two possible values. These values are most commonly represented ...
(Gb) memory capacity, and the nominal maximum size is 20,000 × 40,000 pixels (800 megapixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the ...
s) and 4,000 × 40,000 pixels (160 megapixels) for B–G and NIR images. Each 16.4 Gb image is compressed to 5 Gb before transmission and release to the general public on the HiRISE website in JPEG 2000
JPEG 2000 (JP2) is an image compression standard and coding system. It was developed from 1997 to 2000 by a Joint Photographic Experts Group committee chaired by Touradj Ebrahimi (later the JPEG president), with the intention of superseding th ...
format. To facilitate the mapping of potential landing sites, HiRISE can produce stereo pairs of images from which topography can be calculated to an accuracy of .
HiRISE was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp.
CTX (camera)
The Context Camera (CTX) providesgrayscale
In digital photography, computer-generated imagery, and colorimetry, a grayscale image is one in which the value of each pixel is a single sample representing only an ''amount'' of light; that is, it carries only intensity information. Graysc ...
images (500 to 800 nm) with a pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the ...
resolution up to about . CTX is designed to provide context maps for the targeted observations of HiRISE and CRISM, and is also used to mosaic large areas of Mars, monitor a number of locations for changes over time, and to acquire stereo (3D) coverage of key regions and potential future landing sites. The optics of CTX consist of a focal length
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system converges light, while a negative foc ...
Maksutov Cassegrain Cassegrain may refer to
* Cassegrain reflector, a design used in telescopes
* Cassegrain antenna, a type of parabolic antenna
* Cassegrain (crater), on the Moon
* a Belgian canned vegetables producer now part of Bonduelle S.A.
People :
* Guillau ...
telescope with a 5,064 pixel wide line array CCD. The instrument takes pictures wide and has enough internal memory to store an image long before loading it into the main computer. The camera was built, and is operated by Malin Space Science Systems
Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS) is a San Diego, California-based private technology company that designs, develops, and operates instruments and technical equipment to fly on unmanned spacecraft. MSSS is headed by chief scientist and CEO Mich ...
. CTX mapped 50% of Mars by February 2010. In 2012 it found the impacts of six 55-pound (25-kilogram) entry ballast masses from Mars Science Laboratory
Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) is a robotic space probe mission to Mars launched by NASA on November 26, 2011, which successfully landed ''Curiosity'', a Mars rover, in Gale Crater on August 6, 2012. The overall objectives include investigati ...
's landing of ''Curiosity'' rover.
MARCI (camera)
 The Mars Color Imager (MARCI) is a wide-angle, relatively low-resolution camera that views the surface of Mars in five visible and two
The Mars Color Imager (MARCI) is a wide-angle, relatively low-resolution camera that views the surface of Mars in five visible and two ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
bands. Each day, MARCI collects about 84 images and produces a global map with pixel resolutions of . This map provides a weekly weather report for Mars, helps to characterize its seasonal and annual variations, and maps the presence of water vapor and ozone in its atmosphere. The camera was built and is operated by Malin Space Science Systems
Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS) is a San Diego, California-based private technology company that designs, develops, and operates instruments and technical equipment to fly on unmanned spacecraft. MSSS is headed by chief scientist and CEO Mich ...
. It has a 180-degree fisheye lens with the seven color filters bonded directly on a single CCD sensor.
CRISM (spectrometer)
 The Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) instrument is a visible and
The Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) instrument is a visible and near infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from arou ...
(VNIR
The visible and near-infrared (VNIR) portion of the electromagnetic spectrum has wavelengths between approximately 400 and 1100 nanometers (nm). It combines the full visible spectrum with an adjacent portion of the infrared spectrum up to the ...
) spectrometer
A spectrometer () is a scientific instrument used to separate and measure spectral components of a physical phenomenon. Spectrometer is a broad term often used to describe instruments that measure a continuous variable of a phenomenon where the ...
that is used to produce detailed maps of the surface mineralogy
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifacts. Specific studies within mineralogy include the proce ...
of Mars. It operates from 370 to 3920 nm, measures the spectrum in 544 channels (each 6.55 nm wide), and has a resolution of at an altitude of . CRISM is being used to identify minerals and chemicals indicative of the past or present existence of water on the surface of Mars. These materials include iron, oxides
An oxide () is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the E ...
, phyllosilicates
Silicate minerals are rock-forming minerals made up of silicate groups. They are the largest and most important class of minerals and make up approximately 90 percent of Earth's crust.
In mineralogy, silica (silicon dioxide, ) is usually consid ...
, and carbonates, which have characteristic patterns in their visible-infrared energy. The CRISM instrument will be shut down during the 6th extended mission from 2022 to 2025, as the cryocooler was lost, forcing the shutdown of one of the two spectrometers.
Mars Climate Sounder
The Mars Climate Sounder (MCS) looks both down and horizontally through theatmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A ...
in order to quantify the global atmosphere's vertical variations. It is a spectrometer with one visible/near infrared channel (0.3 to 3.0 μm) and eight far infrared
Far infrared (FIR) is a region in the infrared spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. Far infrared is often defined as any radiation with a wavelength of 15 micrometers (μm) to 1 mm (corresponding to a range of about 20 THz to ...
(12 to 50 μm) channels selected for the purpose. MCS observes the atmosphere on the horizon of Mars (as viewed from MRO) by breaking it up into vertical slices and taking measurements within each slice in increments. These measurements are assembled into daily global weather maps to show the basic variables of Martian weather: temperature, pressure, humidity, and dust density.
This instrument, supplied by NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
's Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a Federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center and NASA field center in the City of La Cañada Flintridge, California, La Cañada Flintridge, California ...
, Pasadena, California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
, utilizes technological advances to achieve the measurement objectives of a heavier, larger instrument originally developed at JPL for the 1992 '' Mars Observer'' and 1998 ''Mars Climate Orbiter
The ''Mars Climate Orbiter'' (formerly the Mars Surveyor '98 Orbiter) was a robotic space probe launched by NASA on December 11, 1998, to study the Martian climate, Martian atmosphere, and surface changes and to act as the communications re ...
'' missions.
SHARAD (radar)
 MRO's Shallow Subsurface Radar (SHARAD) experiment is designed to probe the internal structure of the Martian polar
MRO's Shallow Subsurface Radar (SHARAD) experiment is designed to probe the internal structure of the Martian polar ice cap
In glaciology, an ice cap is a mass of ice that covers less than of land area (usually covering a highland area). Larger ice masses covering more than are termed ice sheets.
Description
Ice caps are not constrained by topographical feat ...
s. It also gathers planet-wide information about underground layers of ice, rock and possibly liquid water that might be accessible from the surface. SHARAD uses HF radio waves between 15 and 25 MHz, a range that allows it to resolve layers as thin as to a maximum depth of . It has a horizontal resolution of . SHARAD is designed to operate in conjunction with the Mars Express
''Mars Express'' is a space exploration mission being conducted by the European Space Agency (ESA). The ''Mars Express'' mission is exploring the planet Mars, and is the first planetary mission attempted by the agency. "Express" originally ref ...
MARSIS, which has lower resolution but penetrates to a much greater depth. Both SHARAD and MARSIS were made by the Italian Space Agency
The Italian Space Agency ( it, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana; ASI) is a government agency established in 1988 to fund, regulate and coordinate space exploration activities in Italy. The agency cooperates with numerous national and international enti ...
.
Engineering instruments
In addition to its imaging equipment, MRO carries a variety of engineering instruments. The Gravity Field Investigation Package measures variations in the Martian gravitational field through variations in the spacecraft's velocity. Velocity changes are detected by measuringdoppler shift
The Doppler effect or Doppler shift (or simply Doppler, when in context) is the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It is named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler, who ...
s in MRO's radio signals received on Earth. The package also includes sensitive onboard accelerometers used to deduce the ''in situ'' atmospheric density of Mars during aerobraking.
The Electra
Electra (; grc, Ήλέκτρα) is one of the most popular mythological characters in tragedies.Evans (1970), p. 79 She is the main character in two Greek tragedies, '' Electra'' by Sophocles and '' Electra'' by Euripides. She is also the centra ...
communications package is a UHF
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter (on ...
software-defined radio
Software-defined radio (SDR) is a radio communication system where components that have been traditionally implemented in analog hardware (e.g. mixers, filters, amplifiers, modulators/demodulators, detectors, etc.) are instead implemented by ...
(SDR) that provides a flexible platform for evolving relay capabilities. It is designed to communicate with other spacecraft as they approach, land, and operate on Mars. In addition to protocol controlled inter-spacecraft data links of 1 kbit/s to 2 Mbit/s, Electra also provides Doppler data collection, open loop recording and a highly accurate timing service based on a 5e−13 ultra-stable oscillator. Doppler information for approaching vehicles can be used for final descent targeting or descent and landing trajectory recreation. Doppler information on landed vehicles will also enable scientists to accurately determine the surface location of Mars landers and rovers. The two Mars Exploration Rover
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover (MER) mission was a robotic space mission involving two Mars rovers, '' Spirit'' and '' Opportunity'', exploring the planet Mars. It began in 2003 with the launch of the two rovers to explore the Martian surface ...
spacecraft currently on Mars utilize an earlier generation UHF relay radio providing similar functions through the Mars Odyssey orbiter. The Electra radio has proven its functionality by relaying information to and from the MER spacecraft, ''Phoenix'' Mars lander and ''Curiosity'' Rover.
The Optical Navigation Camera images the Martian moons, Phobos and Deimos Deimos, a Greek word for ''dread'', may refer to:
* Deimos (deity), one of the sons of Ares and Aphrodite in Greek mythology
* Deimos (moon), the smaller and outermost of Mars' two natural satellites
* Elecnor Deimos, a Spanish aerospace company
* ...
, against background stars to precisely determine MRO's orbit. Although moon imaging is not mission critical, it was included as a technology test for future orbiting and landing of spacecraft. The Optical Navigation Camera was tested successfully in February and March 2006. There is a proposal to search for small moons, dust rings, and old orbiters with it.
Engineering data

Structure
Workers atLockheed Martin Space Systems
Lockheed Martin Space is one of the four major business divisions of Lockheed Martin. It has its headquarters in Littleton, Colorado, with additional sites in Valley Forge, Pennsylvania; Sunnyvale, California; Santa Cruz, California; Huntsvil ...
in Denver assembled the spacecraft structure and attached the instruments. Instruments were constructed at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the University of Arizona
The University of Arizona (Arizona, U of A, UArizona, or UA) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Tucson, Arizona. Founded in 1885 by the 13th Arizona Territorial Legislature, it was the first ...
Lunar and Planetary Laboratory in Tucson, Arizona
, "(at the) base of the black ill
, nicknames = "The Old Pueblo", "Optics Valley", "America's biggest small town"
, image_map =
, mapsize = 260px
, map_caption = Interactive map ...
, Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University (Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1876, Johns Hopkins is the oldest research university in the United States and in the western hemisphere. It consi ...
Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland
Laurel is a city in Maryland, United States, located midway between Washington and Baltimore on the banks of the Patuxent River. While the city limits are entirely in northern Prince George's County, outlying developments extend into Anne Arunde ...
, the Italian Space Agency
The Italian Space Agency ( it, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana; ASI) is a government agency established in 1988 to fund, regulate and coordinate space exploration activities in Italy. The agency cooperates with numerous national and international enti ...
in Rome, and Malin Space Science Systems
Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS) is a San Diego, California-based private technology company that designs, develops, and operates instruments and technical equipment to fly on unmanned spacecraft. MSSS is headed by chief scientist and CEO Mich ...
in San Diego.
The structure is made of mostly carbon composites and aluminum-honeycombed plates. The titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion i ...
fuel tank takes up most of the volume and mass of the spacecraft and provides most of its structural integrity. The spacecraft's total mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different ele ...
is less than with an unfueled dry mass less than .
Power systems
 MRO gets all of its electrical power from two
MRO gets all of its electrical power from two solar panel
A solar cell panel, solar electric panel, photo-voltaic (PV) module, PV panel or solar panel is an assembly of photovoltaic solar cells mounted in a (usually rectangular) frame, and a neatly organised collection of PV panels is called a photo ...
s, each of which can move independently around two axes (up-down, or left-right rotation). Each solar panel measures and has covered with 3,744 individual photovoltaic cells. Its high-efficiency triple junction solar cells are able to convert more than 26% of the Sun's energy directly into electricity and are connected together to produce a total output of 32 volts
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827).
Defini ...
. At Mars, each of the panels produces more than 1,000 watts of power; in contrast, the panels would generate 3,000 watts in a comparable Earth orbit by being closer to the Sun.
MRO has two rechargeable nickel-hydrogen batteries used to power the spacecraft when it is not facing the Sun. Each battery has an energy storage capacity of 50 ampere hour
An ampere hour or amp hour (symbol: A⋅h or A h; often simplified as Ah) is a unit of electric charge, having dimensions of electric current multiplied by time, equal to the charge transferred by a steady current of one ampere flowing for ...
s (180 kC). The full range of the batteries cannot be used due to voltage constraints on the spacecraft, but allows the operators to extend the battery life—a valuable capability, given that battery drain is one of the most common causes of long-term satellite failure. Planners anticipate that only 40% of the batteries' capacities will be required during the lifetime of the spacecraft.
Electronic systems
MRO's main computer is a 133 MHz, 10.4 milliontransistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
, 32-bit, RAD750
The RAD750 is a radiation-hardened single-board computer manufactured by BAE Systems Electronics, Intelligence & Support. The successor of the RAD6000, the RAD750 is for use in high-radiation environments experienced on board satellites and sp ...
processor. This processor is a radiation-hardened version of a PowerPC
PowerPC (with the backronym Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC – Performance Computing, sometimes abbreviated as PPC) is a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) created by the 1991 Apple– IBM– ...
750 or G3 processor with a specially built motherboard
A motherboard (also called mainboard, main circuit board, mb, mboard, backplane board, base board, system board, logic board (only in Apple computers) or mobo) is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expand ...
. The RAD750 is a successor to the RAD6000. This processor may seem underpowered in comparison to a modern PC processor, but it is extremely reliable, resilient, and can function in solar flare
A solar flare is an intense localized eruption of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other sol ...
-ravaged deep space. The operating system software is VxWorks
VxWorks is a real-time operating system (or RTOS) developed as proprietary software by Wind River Systems, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Aptiv. First released in 1987, VxWorks is designed for use in embedded systems requiring real-time, determi ...
and has extensive fault protection protocols and monitoring.
Data is stored in a 160 Gb (20 GB) flash memory module consisting of over 700 memory chips, each with a 256 Mbit
The megabit is a multiple of the unit bit for digital information. The prefix mega (symbol M) is defined in the International System of Units (SI) as a multiplier of 106 (1 million), and therefore
:1 megabit = = = 1000 kilobits.
The megabit ...
capacity. This memory capacity is not actually that large considering the amount of data to be acquired; for example, a single image from the HiRISE camera can be as large as 28 Gb.
Telecommunications system
 The Telecom Subsystem on MRO is the best digital communication system sent into deep space so far, and for the first time used capacity-approaching
The Telecom Subsystem on MRO is the best digital communication system sent into deep space so far, and for the first time used capacity-approaching turbo-code
In information theory, turbo codes (originally in French ''Turbocodes'') are a class of high-performance forward error correction (FEC) codes developed around 1990–91, but first published in 1993. They were the first practical codes to closely ...
s. The Electra
Electra (; grc, Ήλέκτρα) is one of the most popular mythological characters in tragedies.Evans (1970), p. 79 She is the main character in two Greek tragedies, '' Electra'' by Sophocles and '' Electra'' by Euripides. She is also the centra ...
communications package is a UHF
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter (on ...
software-defined radio
Software-defined radio (SDR) is a radio communication system where components that have been traditionally implemented in analog hardware (e.g. mixers, filters, amplifiers, modulators/demodulators, detectors, etc.) are instead implemented by ...
(SDR) that provides a flexible platform for evolving relay capabilities. It is designed to communicate with other spacecraft as they approach, land, and operate on Mars. The system consists of a very large () antenna, which is used to transmit data through the Deep Space Network
The NASA Deep Space Network (DSN) is a worldwide network of American spacecraft communication ground segment facilities, located in the United States (California), Spain (Madrid), and Australia (Canberra), that supports NASA's interplanetary ...
via X-band
The X band is the designation for a band of frequencies in the microwave radio region of the electromagnetic spectrum. In some cases, such as in communication engineering, the frequency range of the X band is rather indefinitely set at approxi ...
frequencies at 8 GHz, and it demonstrates the use of the at 32 GHz for higher data rates. Maximum transmission speed from Mars is projected to be as high as 6 Mbit/s, a rate ten times higher than previous Mars orbiters. The spacecraft carries two 100-watt X-band amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It may increase the power significantly, or its main effect may be to boost t ...
s (one of which is a backup), one 35-watt Ka-band amplifier, and two Small deep space transponder
The Small Deep Space Transponder is a transponder designed by JPL specifically for deep space probes. It unifies a number of communication functions -
receiver, command detector, telemetry modulator, exciters, beacon tone generator, and control f ...
s (SDSTs).
Two smaller low-gain antennas are also present for lower-rate communication during emergencies and special events, such as launch and Mars Orbit Insertion. These antennas do not have focusing dishes and can transmit and receive from any direction. They are an important backup system to ensure that MRO can always be reached, even if its main antenna is pointed away from the Earth.
The Ka-band subsystem was used for demonstration purposes. Due to lack of spectrum at 8.41 GHz X-band, future high-rate deep space missions will use 32 GHz Ka-band. NASA Deep Space Network (DSN) implemented Ka-band receiving capabilities at all three of its complexes (Goldstone, Canberra and Madrid) over its 34-m beam-waveguide (BWG) antenna subnet. During the cruise phase, spacecraft Ka-band telemetry was tracked 36 times by these antennas proving functionality at all antennas. Ka-band tests were also planned during the science phase, but during aerobraking a switch failed, limiting the X-band high gain antenna to a single amplifier. If this amplifier fails all high-speed X-band communications will be lost. The Ka downlink is the only remaining backup for this functionality, and since the Ka-band capability of one of the SDST transponders has already failed, (and the other might have the same problem) JPL decided to halt all Ka-band demonstrations and hold the remaining capability in reserve.
By November 2013, the MRO had passed 200 terabits in the amount of science data returned. The data returned by the mission is more than three times the total data returned via NASA's Deep Space Network for all the other missions managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory over the past 10 years.

Propulsion and attitude control
The spacecraft uses a fuel tank filled with ofhydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly toxic unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine ...
monopropellant
Monopropellants are propellants consisting of chemicals that release energy through exothermic chemical decomposition. The molecular bond energy of the monopropellant is released usually through use of a catalyst. This can be contrasted with bipro ...
. Fuel pressure is regulated by adding pressurized helium gas from an external tank. Seventy percent of the propellant was used for orbital insertion, and it has enough propellant to keep functioning into the 2030s.
MRO has twenty rocket engine thrusters on board. Six large thrusters each produce of thrust for a total of meant mainly for orbital insertion. These thrusters were originally designed for the Mars Surveyor 2001 Lander
The Mars Surveyor 2001 project was a multi-part Mars exploration mission intended as a follow-up to Mars Surveyor '98. After the two probes of the 1998 project, Mars Climate Orbiter and Mars Polar Lander, were both lost, NASA's "better, faste ...
. Six medium thrusters each produce of thrust for trajectory correction maneuvers and attitude control
Attitude control is the process of controlling the orientation of an aerospace vehicle with respect to an inertial frame of reference or another entity such as the celestial sphere, certain fields, and nearby objects, etc.
Controlling vehicle ...
during orbit insertion. Finally, eight small thrusters each produce of thrust for attitude control during normal operations.
Four reaction wheel
A reaction wheel (RW) is used primarily by spacecraft for three-axis attitude control, and does not require rockets or external applicators of torque. They provide a high pointing accuracy, and are particularly useful when the spacecraft must be ...
s are also used for precise attitude control during activities requiring a highly stable platform, such as high-resolution imaging, in which even small motions can cause blurring of the image. Each wheel is used for one axis of motion. The fourth (skewed) wheel is a backup in case one of the other three wheels fails. Each wheel weighs and can be spun as fast as 100 Hz or 6,000 rpm.
In order to determine the spacecraft's orbit and facilitate maneuvers, sixteen Sun sensors – eight primaries and eight backups – are placed around the spacecraft to calibrate solar direction relative to the orbiter's frame. Two star trackers, digital camera
A digital camera is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devices ...
s used to map the position of catalogued star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
s, provide NASA with full, three-axis knowledge of the spacecraft orientation and attitude
Attitude may refer to:
Philosophy and psychology
* Attitude (psychology), an individual's predisposed state of mind regarding a value
* Metaphysics of presence
* Propositional attitude, a relational mental state connecting a person to a propo ...
. A primary and backup Miniature Inertial Measurement Unit (MIMU), provided by Honeywell
Honeywell International Inc. is an American publicly traded, multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina. It primarily operates in four areas of business: aerospace, building technologies, performance ma ...
, measures changes to the spacecraft attitude as well as any non-gravitationally induced changes to its linear velocity. Each MIMU is a combination of three accelerometer
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acce ...
s and three ring-laser gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rot ...
s. These systems are all critically important to MRO, as it must be able to point its camera to a very high precision in order to take the high-quality pictures that the mission requires. It has also been specifically designed to minimize any vibrations on the spacecraft, so as to allow its instruments to take images without any distortions caused by vibrations.
Cost
The total cost of the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' through the end of its prime mission was . Of this amount, was spent on spacecraft development, approximately for its launch, and for 5 years of mission operations. Since 2011, MRO's annual operations costs are, on average, per year, when adjusted for inflation.Discoveries and photographs
Water ice in ice cap measured
Results published in 2009 of radar measurements of the north polar ice cap determined that the volume of water ice in the cap is , equal to 30% of the Earth's Greenland ice sheet.Ice exposed in new craters
 An article in the journal ''Science'' in September 2009, reported that some new craters on Mars have excavated relatively pure water ice. After being exposed, the ice gradually fades as it sublimates away. These new craters were found and dated by the CTX camera, and the identification of the ice was confirmed with the Compact Imaging Spectrometer (CRISM) on board the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter''. The ice was found in a total of five locations. Three of the locations are in the
An article in the journal ''Science'' in September 2009, reported that some new craters on Mars have excavated relatively pure water ice. After being exposed, the ice gradually fades as it sublimates away. These new craters were found and dated by the CTX camera, and the identification of the ice was confirmed with the Compact Imaging Spectrometer (CRISM) on board the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter''. The ice was found in a total of five locations. Three of the locations are in the Cebrenia quadrangle
The Cebrenia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the northeastern portion of Mars’ eastern hemisphere and ...
. These locations are ; ; and . Two others are in the Diacria quadrangle: and .
Cebrenia quadrangle
The Cebrenia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the northeastern portion of Mars’ eastern hemisphere and ...
.
Ice in lobate debris aprons
lobate debris apron
Lobate debris aprons (LDAs) are geological features on Mars, first seen by the Viking Orbiters, consisting of piles of rock debris below cliffs. These features have a convex topography and a gentle slope from cliffs or escarpments, which suggest fl ...
s (LDAs) contain large amounts of water ice. Of interest from the days of the Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
Orbiters, these LDA are aprons of material surrounding cliffs. They have a convex topography and a gentle slope; this suggests flow away from the steep source cliff. In addition, lobate debris aprons can show surface lineations just as rock glaciers on the Earth. SHARAD has provided strong evidence that the LDAs in Hellas Planitia are glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such a ...
s that are covered with a thin layer of debris (i.e. rocks and dust); a strong reflection from the top and base of LDAs was observed, suggesting that pure water ice makes up the bulk of the formation (between the two reflections). Based on the experiments of the ''Phoenix'' lander and the studies of the ''Mars Odyssey
''2001 Mars Odyssey'' is a robotic spacecraft orbiting the planet Mars. The project was developed by NASA, and contracted out to Lockheed Martin, with an expected cost for the entire mission of US$297 million. Its mission is to use spectro ...
'' from orbit, water ice is known to exist just under the surface of Mars in the far north and south (high latitudes).
Chloride deposits
Other Aqueous Minerals
In 2009, a group of scientists from the CRISM team reported on 9 to 10 different classes of minerals formed in the presence of water. Different types ofclays
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay par ...
(also called phyllosilicates) were found in many locations. The phyllosilicates identified included aluminum smectite, iron/magnesium smectite, kaolinite
Kaolinite ( ) is a clay mineral, with the chemical composition Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4. It is an important industrial mineral. It is a layered silicate mineral, with one tetrahedral sheet of silica () linked through oxygen atoms to one octahed ...
, prehnite, and chlorite
The chlorite ion, or chlorine dioxide anion, is the halite with the chemical formula of . A chlorite (compound) is a compound that contains this group, with chlorine in the oxidation state of +3. Chlorites are also known as salts of chlorou ...
. Rocks containing carbonate were found around the Isidis basin. Carbonates belong to one class in which life could have developed. Areas around Valles Marineris were found to contain hydrated silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
and hydrated sulfates. The researchers identified hydrated sulfates and ferric minerals in Terra Meridiani and in Valles Marineris. Other minerals found on Mars were jarosite
Jarosite is a basic hydrous sulfate of potassium and ferric iron (Fe-III) with a chemical formula of KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6. This sulfate mineral is formed in ore deposits by the oxidation of iron sulfides. Jarosite is often produced as a byproduct d ...
, alunite
Alunite is a hydroxylated aluminium potassium sulfate mineral, formula K Al3( S O4)2(O H)6. It was first observed in the 15th century at Tolfa, near Rome, where it was mined for the manufacture of alum. First called ''aluminilite'' by J.C. D ...
, hematite
Hematite (), also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of . ...
, opal
Opal is a hydrated amorphous form of silica (SiO2·''n''H2O); its water content may range from 3 to 21% by weight, but is usually between 6 and 10%. Due to its amorphous property, it is classified as a mineraloid, unlike crystalline form ...
, and gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywa ...
. Two to five of the mineral classes were formed with the right pH and sufficient water to permit life to grow.
Avalanches
The ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' CTX and HiRISE cameras have photographed a number of avalanches off the scarps of the northern polar cap as they were occurring.Other spacecraft
Opportunity
Opportunity may refer to:
Places
* Opportunity, Montana, an unincorporated community, United States
* Opportunity, Nebraska, an unincorporated community, United States
* Opportunity, Washington, a former census-designated place, United States
* ...
'', as seen by HiRISE. The white dots are places where the rover stopped to perform scientific observations or turned.
Opportunity Rover by HiRISE.jpg, ''Opportunity'' as seen by HiRISE on January 29, 2009. ''Opportunity'' is on its way to Endeavour Crater, away at this point.
MRO sees Curiosity landing.jpg, The ''Curiosity'' rover during atmospheric entry as seen by HiRISE on August 6, 2012. Supersonic parachute and backshell visible.
HiRISE Captured Perseverance During Descent to Mars.jpg, ''Perseverance'' rover parachute descend over the Jezero crater photographed by HiRISE on February 18, 2021.
Flowing salty water
On August 4, 2011 (sol ), NASA announced that MRO had detected what appeared to be flowing salty water on the surface or subsurface of Mars. On September 28, 2015, this finding was confirmed at a special NASA news conference.See also
* * * * * * * *References
Further reading
* * *External links
General
NASA's ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' page
MRO Mars Arrival Press Kit (2006)
* ttps://www.planetary.org/blogs/blog-archive.html?keywords=mars-reconnaissance-orbiter Planetary Society coverage of the MRO mission
Official instrument websites
HiRISE Website
SHARAD Website
CRISM Website
Images
HiRISE Image Catalog
''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' images at the JPL Photojournal
Multimedia gallery
by Seán Doran based on HiRISE photos
Multimedia gallery
by Seán Doran based on CTX photos
Multimedia gallery
by Kevin Gill based on HiRISE photos {{Good article Mars Exploration Program
Reconnaissance
In military operations, reconnaissance or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, terrain, and other activities.
Examples of reconnaissance include patrolling by troops ( skirmishe ...
Mars Reconnaissance
Reconnaissance
In military operations, reconnaissance or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, terrain, and other activities.
Examples of reconnaissance include patrolling by troops ( skirmishe ...
Mars Reconnaissance
Mars Reconnaissance
Spacecraft launched by Atlas rockets
2005 in Florida