MG 81 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The MG 81 was a German belt fed 7.92×57mm Mauser 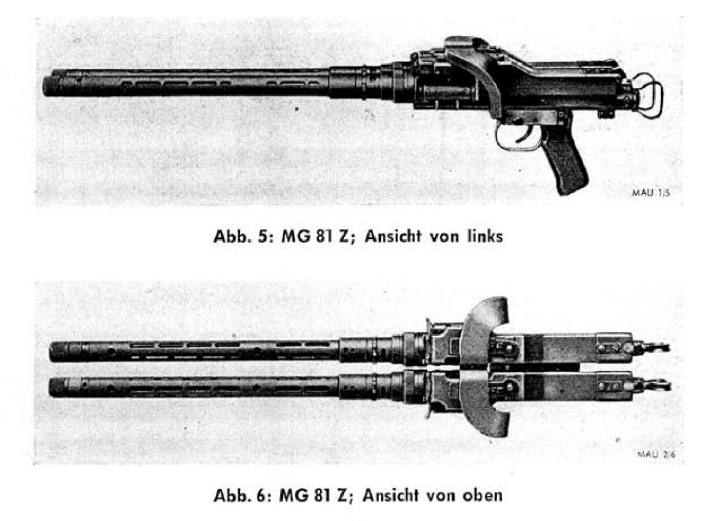
Airwar.ru (Russian language)
Full size images for the MG81
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mg 81 Machine Gun 7.92×57mm Mauser machine guns MG 017 machine gun Machine guns of Germany World War II infantry weapons of Germany Weapons and ammunition introduced in 1940
machine gun
A machine gun is a fully automatic, rifled autoloading firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles (including assault rifles and battle ri ...
which was used in flexible installations in World War II Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabtei ...
aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engine ...
, in which capacity it replaced the older drum magazine-fed MG 15
The MG 15 was a German 7.92 mm machine gun designed specifically as a hand-manipulated defensive gun for combat aircraft during the early 1930s. By 1941 it was replaced by other types and found new uses with ground troops.
History
The MG ...
.
The MG 81 was developed by Mauser
Mauser, originally Königlich Württembergische Gewehrfabrik ("Royal Württemberg Rifle Factory"), was a German arms manufacturer. Their line of bolt-action rifles and semi-automatic pistols has been produced since the 1870s for the German ar ...
as a derivative of their successful MG 34
The MG 34 (shortened from German: ''Maschinengewehr 34'', or "machine gun 34") is a German recoil-operated air-cooled general-purpose machine gun, first tested in 1929, introduced in 1934, and issued to units in 1936. It introduced an entirely n ...
general-purpose machine gun
A general-purpose machine gun (GPMG) is an air-cooled, usually belt-fed machine gun that can be adapted flexibly to various tactical roles for light and medium machine guns. A GPMG typically features a quick-change barrel design calibered for v ...
. Development focus was to reduce production cost and time and to optimize the machine gun for use in aircraft. Developed in 1938/1939, it was in production from 1940 to 1945.
A special twin-mount MG 81Z (the Z suffix stands for ''Zwilling'', meaning "twin") was introduced in 1942. It paired up two of the weapons on one mount to provide even more firepower with a maximum cyclic rate of fire of 3,200 rounds per minute without requiring much more space than a standard machine gun.
Towards the end of the war many specimens were delivered to the army and equipped for use in ground battles with shoulder rest and bipod.

Applications
The MG 81Z was found in many unique installations in Luftwaffe combat aircraft, such as a pair of MG 81Z (for a total of four guns) installed in the hollow tail cone of theDornier Do 217
The Dornier Do 217 was a bomber used by the German ''Luftwaffe'' during World War II as a more powerful development of the Dornier Do 17, known as the ''Fliegender Bleistift'' (German: "flying pencil"). Designed in 1937 and 1938 as a heavy bombe ...
. Designated R19 (R for Rüstsatz
''Rüstsätze'' were field modification kits produced for the German Luftwaffe during the Second World War. They were packaged in kit form, usually direct from the aircraft manufacturer, and allowed for field modifications of various German aircra ...
) as a factory designed field conversion/upgrade kit, it allowed the pilot of the Do 217 to shoot at pursuers.
Another application was the ''Gießkanne'' (Watering can), an externally mounted pod with three gun pairs, making a total of six guns and their ammunition. Able to fire at a cyclic rate of 9,000 rounds per minute, this was attached to Junkers Ju 87
The Junkers Ju 87 or Stuka (from ''Sturzkampfflugzeug'', "dive bomber") was a German dive bomber and ground-attack aircraft. Designed by Hermann Pohlmann, it first flew in 1935. The Ju 87 made its combat debut in 1937 with the Luftwaffe's Co ...
or Ju 88
The Junkers Ju 88 is a German World War II ''Luftwaffe'' twin-engined multirole combat aircraft. Junkers Aircraft and Motor Works (JFM) designed the plane in the mid-1930s as a so-called '' Schnellbomber'' ("fast bomber") that would be too fas ...
in an underwing mount and used to strafe ground targets.
Specifications
;MG 81 *Weight: *Length: ( with flash hider) *Muzzle velocity: (sS ball ammunition), , or , depending on ammo type *Rate of fire: 1,400–1,600 rpm (sS ball ammunition) *Rate of fire: 1,700–1,800 rpm *Rate of fire: 800 rpm (coaxial mount) ;MG 81Z *Weight: 12.9 kg (28.44 lb) *Length: 915 mm (965& mm with flash hider) *Muzzle velocity: (sS ball ammunition), , or , depending on ammo type *Rate of fire: 2,800–3,200 rpm (sS ball ammunition) *Rate of fire: 3,400–3,600 rpmSee also
*ShKAS
The ShKAS (Shpitalny-Komaritski Aviatsionny Skorostrelny, Shpitalny-Komaritski rapid fire for aircraft; Russian: ШКАС - Шпитального-Комарицкого Авиационный Скорострельный) is a 7.62 mm calibre ...
*Vickers K machine gun
The Vickers K machine gun, known as the Vickers Gas Operated (Vickers G.O.) or Gun, Machine, Vickers G.O. .303-inch in British service, was a rapid-firing machine gun developed and manufactured for use in aircraft by Vickers-Armstrongs. The hig ...
*List of firearms
This is an extensive list of small arms—including pistols, revolvers, submachine guns, shotguns, battle rifles, assault rifles, sniper rifles, machine guns, personal defense weapons, carbines, designated marksman rifles, flamethrowers, multi ...
* List of secondary and special-issue World War II infantry weapons
References
External links
Airwar.ru (Russian language)
Full size images for the MG81
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mg 81 Machine Gun 7.92×57mm Mauser machine guns MG 017 machine gun Machine guns of Germany World War II infantry weapons of Germany Weapons and ammunition introduced in 1940