Multilink Suspension on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A multi-link suspension is a type of
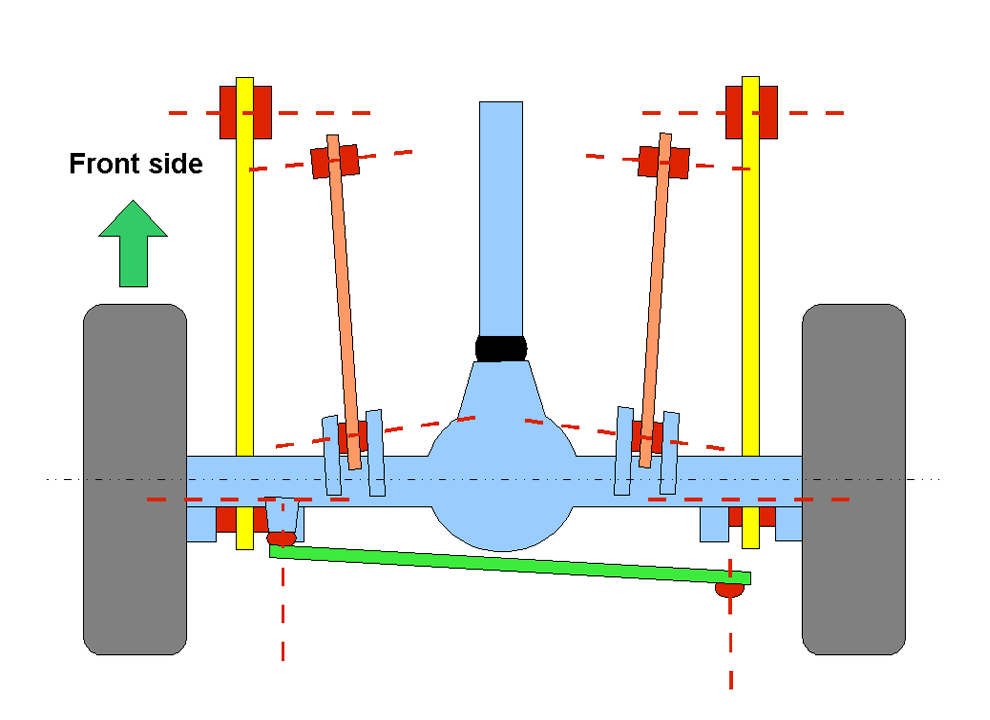
File:5link-rear1-small.gif, 5-link rear wheel suspension mechanism (front view)
File:5link-rear2-small.gif, 5-link rear wheel suspension mechanism (top view)
File:5link-steer front view.gif, 5-link suspension mechanism with rack-and-pinion steering input (front view)
File:5link-steer top view.gif, 5-link suspension mechanism with rack-and-pinion steering input (top view)
"What is: Multilink suspension?" from CarPoint Australia
1998 technical paper on the design of multilink suspensions
2002 technical paper on the design and analysis of five-link suspensions
{{Use dmy dates, date=March 2018 Automotive suspension technologies
vehicle suspension
Suspension is the system of tires, tire air, springs, shock absorbers and linkages that connects a vehicle to its wheels and allows relative motion between the two. Suspension systems must support both road holding/handling and ride qua ...
with one or more longitudinal arms. A wider definition can consider any independent suspensions having three control links or more multi-link suspensions. These arms do not have to be of equal length, and may be angled away from their "obvious" direction. It was first introduced in the late 1960s on the Mercedes-Benz C111 and later on their W201 and W124 series.
Typically each arm has a spherical joint (ball joint) or rubber bushing at each end. Consequently, they react to loads along their own length, in tension and compression, but not in bending. Some multi-links do use a trailing arm
A (semi) trailing-arm suspension, sometimes referred to as (semi) trailing-link is a vehicle axle or wheel suspension design in which one or more horizontal arms (or "links"), perpendicular to and forward of the axle, are connecting the axle or ...
, control arm or wishbone, which has two bushings at one end.
On a front suspension one of the lateral arms is replaced by the tie-rod
A tie rod or tie bar (also known as a hanger rod if vertical) is a slender structural unit used as a tie and (in most applications) capable of carrying tensile loads only.
It is any rod or bar-shaped structural member designed to prevent the separa ...
, which connects the rack or steering box to the wheel hub.
The solid axle multi-link system is another variation of the same concept, and offers some advantages over independent multi-link, as it is significantly cheaper and less complex to build, offering good mechanical resistance and excellent reliability with very similar benefits.
Layout
In order to simplify understanding, it is usual to consider the function of the arms in each of three orthogonal planes: *Top view: The arms have to control toe/steer and lateral compliance. This needs a pair of arms longitudinally separated. *Front view: The arms have to control camber, particularly the way that the camber changes as the wheel moves up (into jounce, or bump) and down into rebound or droop. *Side view: The arms have to transmit traction and braking loads, usually accomplished via a longitudinal link. They also have to controlcaster
A caster (or castor) is an undriven wheel that is designed to be attached to the bottom of a larger object (the "vehicle") to enable that object to be moved.
Casters are used in numerous applications, including shopping carts, office chairs, ...
. Note that brake torques also have to be reacted - either by a second longitudinal link, or by rotating the hub, which forces the lateral arms out of plane, so allowing them to react 'spin' forces, or by rigidly fixing the longitudinal link to the hub.
;Solid axle suspension:When used in a solid axle suspension the multi-link system use the lower arms to control forward and backward motion, and the upper arms to control forward and backward rotation. This rotation is present under acceleration and braking.

Advantages
Multi-link suspension allows the auto designer the ability to incorporate both good ride and goodhandling
Handling may refer to:
* Automobile handling, the turning characteristics of land vehicles
* Handling of stolen goods, a statutory offence in England and Wales and Northern Ireland
People
* Adam Handling (born 1988), British chef and restaura ...
in the same vehicle.
In its simplest form, multi-link suspension is orthogonal—i.e., it is possible to alter one parameter in the suspension at a time, without affecting anything else. This is in direct contrast to a double wishbone
A double wishbone suspension is an independent suspension design for automobiles using two (occasionally parallel) wishbone-shaped arms to locate the wheel. Each wishbone or arm has two mounting points to the chassis and one joint at the knuck ...
suspension, where moving a hardpoint or changing a bushing compliance will affect two or more parameters.
Advantages also extend to off-road driving. A multi-link suspension allows the vehicle to flex more; this means simply that the suspension is able to move more easily to conform to the varying angles of off-road driving. Multi-link-equipped vehicles are ideally suited for sports such as desert racing
Desert racing is the act of racing through the desert in a two- or four-wheeled off-road vehicle. Races, which generally consist of two or more loops around a course covering up to , can take the form of Hare and Hound or Hare scramble style ev ...
. In desert racing, the use of a good sway bar is needed to counter body roll.
The benefit of the triangulated and double-triangulated arrangement is that they do not need a panhard bar. The benefits of this are increased articulation and potential ease of installation.
Multi-link for solid axle offers a benefit over the independent multi-link in that it is significantly cheaper and much less complex to build.
Disadvantages
Multilink suspension is costly and complex. It is also difficult to tune the geometry without a full 3Dcomputer aided design
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or ) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve c ...
analysis. Compliance under load can have an important effect and must be checked using a multibody simulation software.
Gallery
Source:See also
* Automotive suspension designReferences
*Adams, H. (1993). ''Chassis Engineering''. New York, New York, Penguin Putnam. *Milliken, W.F., Milliken, D. (2002). ''Chassis Design: Principles and Dynamics'', SAE International.External links
"What is: Multilink suspension?" from CarPoint Australia
1998 technical paper on the design of multilink suspensions
2002 technical paper on the design and analysis of five-link suspensions
{{Use dmy dates, date=March 2018 Automotive suspension technologies