Monastic Habit on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A religious habit is a distinctive set of
 In
In
 The religious habits of Catholic nuns typically consist of the following elements:
* Tunic: This is the central piece of the habit. It is a loose dress made of
The religious habits of Catholic nuns typically consist of the following elements:
* Tunic: This is the central piece of the habit. It is a loose dress made of
 Historically, the religious habit of Catholic sisters was a visible sign of a woman's consecration to God. Different orders adhere to different styles of dress; these styles have changed over time. For example, in former times, the
Historically, the religious habit of Catholic sisters was a visible sign of a woman's consecration to God. Different orders adhere to different styles of dress; these styles have changed over time. For example, in former times, the
 Monks in the Catholic church wear a tunic, a
Monks in the Catholic church wear a tunic, a
File:Nun and novice discalced carmelites in Porto Alegre Brazil 20101129.jpeg, The religious habit of the
File:Jan Sezonow.jpg, Inner Rason worn by
Images of medieval monks and nuns in the dress of their Orders
(Public Domain images and text)
Catholic Sisters International Collection, University of Dayton Special Collections
(photographs of reproductions of over 130 religious habits) {{Authority control Asceticism Byzantine clothing Christian clothing Eastern Christian vestments Hesychasm History of clothing (Western fashion) History of clothing History of fashion Monasticism Religious clothing Religious practices Robes and cloaks Sacramentals
clothing
Clothing (also known as clothes, garments, dress, apparel, or attire) is any item worn on a human human body, body. Typically, clothing is made of fabrics or textiles, but over time it has included garments made from animal skin and other thin s ...
worn by members of a religious order
A religious order is a subgroup within a larger confessional community with a distinctive high-religiosity lifestyle and clear membership. Religious orders often trace their lineage from revered teachers, venerate their Organizational founder, ...
. Traditionally, some plain garb recognizable as a religious habit has also been worn by those leading the religious eremitic
A hermit, also known as an eremite (adjectival form: hermitic or eremitic) or solitary, is a person who lives in seclusion. Eremitism plays a role in a variety of religions.
Description
In Christianity, the term was originally applied to a Ch ...
and anchoritic life, although in their case without conformity to a particular uniform style.
Uniformity and distinctiveness by order often evolved and changed over time. Interpretation of terms for clothes in religious rules could change over centuries. Furthermore, every time new communities gained importance in a cultural area the need for visual separation increased for new as well as old communities. Thus, modern habits are rooted in historic forms, but do not necessarily resemble them in cut, color, material, detail or use.
In Christian monastic orders of the Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
and Anglican
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the ...
Churches, the habit often consists of a tunic
A tunic is a garment for the torso, usually simple in style, reaching from the shoulders to a length somewhere between the hips and the ankles. It might have arm-sleeves, either short or full-length. Most forms have no fastenings. The name deri ...
covered by a scapular
A scapular () is a Western Christian garment suspended from the shoulders. There are two types of scapulars, the monastic and devotional scapular; both forms may simply be referred to as "scapular". As an object of popular piety, a scapular ...
and cowl
A cowl is an item of clothing consisting of a long, hooded garment with wide sleeves, often worn by monks. It was developed during the Early Middle Ages. The term may have originally referred to the hooded portion of a cloak, though contempor ...
, with a hood for monk
A monk (; from , ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a man who is a member of a religious order and lives in a monastery. A monk usually lives his life in prayer and contemplation. The concept is ancient and can be seen in many reli ...
s or friar
A friar is a member of one of the mendicant orders in the Catholic Church. There are also friars outside of the Catholic Church, such as within the Anglican Communion. The term, first used in the 12th or 13th century, distinguishes the mendi ...
s and a veil
A veil is an article of clothing or hanging cloth that is intended to cover some part of the human head, head or face, or an object of some significance. Veiling has a long history in European, Asian, and African societies. The practice has be ...
for nun
A nun is a woman who vows to dedicate her life to religious service and contemplation, typically living under vows of poverty, chastity, and obedience in the enclosure of a monastery or convent.''The Oxford English Dictionary'', vol. X, page 5 ...
s; in apostolic orders it may be a distinctive form of cassock
The cassock, or soutane, is a Christian clerical clothing, clerical coat used by the clergy and Consecrated life, male religious of the Oriental Orthodox Churches, Eastern Orthodox Church and the Catholic Church, in addition to some clergy in ...
for men, or a distinctive habit and veil for women. Catholic Canon Law
Canon law (from , , a 'straight measuring rod, ruler') is a set of ordinances and regulations made by ecclesiastical jurisdiction, ecclesiastical authority (church leadership) for the government of a Christian organization or church and its membe ...
requires only that the garb of their members be in some way identifiable so that the person may serve as a witness of the Evangelical counsels
In Christianity, the three evangelical counsels, or counsels of perfection, are chastity, poverty (or perfect charity), and obedience. As stated by Jesus in the canonical gospels, they are counsels for those who desire to become "perfect" (, ).
...
.
In many orders, the conclusion of postulancy
A postulant (from , "to ask") was originally one who makes a request or demand; hence, a candidate. The use of the term is now generally restricted to those asking for admission into a Christian monastery or a religious order for the period precedi ...
and the beginning of the novitiate
The novitiate, also called the noviciate, is the period of training and preparation that a Christian ''novice'' (or ''prospective'') monastic, apostolic, or member of a religious order undergoes prior to taking vows in order to discern whether ...
is marked by a ceremony, in which the new novice is accepted as a novice and then clothed in the community's habit by the superior. In some cases the novice's habit will be somewhat different from the customary habit: for instance, in certain orders of women that use the veil
A veil is an article of clothing or hanging cloth that is intended to cover some part of the human head, head or face, or an object of some significance. Veiling has a long history in European, Asian, and African societies. The practice has be ...
, it is common for novices to wear a white veil while professed members wear black, or if the order generally wears white, the novice wears a grey veil. Among some Franciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related organizations in the Catholic Church, founded or inspired by the Italian saint Francis of Assisi. They include three independent Religious institute, religious orders for men (the Order of Friars Minor bei ...
communities of men, novices wear a sort of overshirt over their tunic; Carthusian
The Carthusians, also known as the Order of Carthusians (), are a Latin enclosed religious order of the Catholic Church. The order was founded by Bruno of Cologne in 1084 and includes both monks and nuns. The order has its own rule, called th ...
novices wear a black cloak over their white habit.
Buddhism
Kāṣāya (;Pali
Pāli (, IAST: pāl̤i) is a Classical languages of India, classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages, Middle Indo-Aryan language of the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pali Canon, Pāli Can ...
: kasāva; ), "chougu" ( Tibetan) are the robes of Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
monks
A monk (; from , ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a man who is a member of a religious order and lives in a monastery. A monk usually lives his life in prayer and contemplation. The concept is ancient and can be seen in many reli ...
and nuns
A nun is a woman who vows to dedicate her life to religious service and contemplation, typically living under vows of Evangelical counsels, poverty, chastity, and obedience in the Enclosed religious orders, enclosure of a monastery or convent.' ...
, named after a brown or saffron dye. In Sanskrit and Pali, these robes are also given the more general term ''cīvara'', which references the robes without regard to color.
Origin and construction
Buddhist kāṣāya are said to have originated inIndia
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
as set of robes for the devotees of Gautama Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha (),*
*
*
was a śramaṇa, wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist lege ...
. A notable variant has a pattern reminiscent of an Asian rice field. Original kāṣāya were constructed of discarded fabric
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, and different types of fabric. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is no ...
. These were stitched together to form three rectangular pieces of cloth, which were then fitted over the body in a specific manner. The three main pieces of cloth are the ''antarvāsa'', the ''uttarāsaṅga'', and the '. Together they form the "triple robe", or ''tricīvara''. The tricīvara is described more fully in the Theravāda
''Theravāda'' (; 'School of the Elders'; ) is Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school's adherents, termed ''Theravādins'' ( anglicized from Pali ''theravādī''), have preserved their version of the Buddha's teaching or '' Dhamma'' in ...
Vinaya
The Vinaya (Pali and Sanskrit: विनय) refers to numerous monastic rules and ethical precepts for fully ordained monks and nuns of Buddhist Sanghas (community of like-minded ''sramanas''). These sets of ethical rules and guidelines devel ...
(Vin 1:94 289).
Uttarāsaṅga
A robe covering the upper body. It is worn over the undergarment, or antarvāsa. In representations of the Buddha, the uttarāsaṅga rarely appears as the uppermost garment, since it is often covered by the outer robe, or saṃghāti.Saṃghāti
The saṃghāti is an outer robe used for various occasions. It comes over the upper robe ('), and the undergarment (''antarvāsa''). In representations of the Buddha, the saṃghāti is usually the most visible garment, with the undergarment or uttarāsaṅga protruding at the bottom. It is quite similar in shape to the Greekhimation
A himation ( , ) was a type of clothing, a mantle (clothing), mantle or Wrap (clothing), wrap worn by ancient Greek men and women from the Archaic Greece, Archaic period through the Hellenistic period ( BC). It was usually worn over a Chiton (gar ...
, and its shape and folds have been treated in Greek style in the Greco-Buddhist art
The Greco-Buddhist art or Gandhara art is the artistic manifestation of Greco-Buddhism, a cultural syncretism between Ancient Greek art and Buddhism. It had mainly evolved in the ancient region of Gandhara, located in the northwestern fringe of t ...
of Gandhāra.
Additions
Other items that may have been worn with the triple robe were: * a waist cloth, the kushalaka * a buckled belt, the samakaksikaKāṣāya in Indian Buddhism
In India, variations of the kāṣāya robe distinguished different types of monastics. These represented the different schools that they belonged to, and their robes ranged widely from red and ochre, to blue and black. Between 148 and 170 CE, theParthia
Parthia ( ''Parθava''; ''Parθaw''; ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Medes during the 7th century BC, was incorporated into the subsequent Achaemeni ...
n monk An Shigao
An Shigao (, Korean: An Sego, Japanese: An Seikō, Vietnamese: An Thế Cao) (fl. c. 148–180 CE) was an early Buddhist missionary to China, and the earliest known translator of Indian Buddhist texts into Chinese. According to legend, he was a p ...
came to China and translated a work which describes the color of monastic robes utilized in five major Indian Buddhist sects, called ''Dà Bǐqiū Sānqiān Wēiyí'' (Ch. ). Another text translated at a later date, the ''Śariputraparipṛcchā'', contains a very similar passage corroborating this information, but the colors for the Sarvāstivāda and Dharmaguptaka sects are reversed.
In traditions of Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism is a form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet, Bhutan and Mongolia. It also has a sizable number of adherents in the areas surrounding the Himalayas, including the Indian regions of Ladakh, Gorkhaland Territorial Administration, D ...
, which follow the Mūlasarvāstivāda Vinaya, red robes are regarded as characteristic of the Mūlasarvāstivādins. According to Dudjom Rinpoche from the tradition of Tibetan Buddhism, the robes of fully ordained Mahāsāṃghika monastics were to be sewn out of more than seven sections, but no more than twenty-three sections. The symbols sewn on the robes were the endless knot
file:Endless knot detail, from- Burmese-Pali Manuscript. Wellcome L0026495 (cropped).jpg, Endless knot in a Burmese Pali manuscript
The endless knot or eternal knot is a symbolic Knot (mathematics), knot and one of the Ashtamangala, Eight Au ...
(Skt. ) and the conch shell (Skt. ''śaṅkha''), two of the Eight Auspicious Signs in Buddhism.
Jiāshā in Chinese Buddhism
InChinese Buddhism
Chinese Buddhism or Han Buddhism ( zh, s=汉传佛教, t=漢傳佛教, first=t, poj=Hàn-thoân Hu̍t-kàu, j=Hon3 Cyun4 Fat6 Gaau3, p=Hànchuán Fójiào) is a Chinese form of Mahayana Buddhism. The Chinese Buddhist canonJiang Wu, "The Chin ...
, the kāṣāya is called ''gāsā'' (Ch. ). During the early period of Chinese Buddhism
Chinese Buddhism or Han Buddhism ( zh, s=汉传佛教, t=漢傳佛教, first=t, poj=Hàn-thoân Hu̍t-kàu, j=Hon3 Cyun4 Fat6 Gaau3, p=Hànchuán Fójiào) is a Chinese form of Mahayana Buddhism. The Chinese Buddhist canonJiang Wu, "The Chin ...
, the most common color was red. Later, the color of the robes came to serve as a way to distinguish monastics, just as they did in India. However, the colors of a Chinese Buddhist monastic's robes often corresponded to their geographical region rather than to any specific schools. By the maturation of Chinese Buddhism, only the Dharmaguptaka ordination lineage was still in use, and therefore the color of robes served no useful purpose as a designation for sects, the way that it had in India.
in Japanese Buddhism
 In
In Japanese Buddhism
Buddhism was first established in Japan in the 6th century CE. Most of the Japanese Buddhists belong to new schools of Buddhism which were established in the Kamakura period (1185-1333). During the Edo period (1603–1868), Buddhism was cont ...
, the is known as the . In Japan, during the Edo
Edo (), also romanized as Jedo, Yedo or Yeddo, is the former name of Tokyo.
Edo, formerly a (castle town) centered on Edo Castle located in Musashi Province, became the '' de facto'' capital of Japan from 1603 as the seat of the Tokugawa shogu ...
and Meiji period
The was an era of Japanese history that extended from October 23, 1868, to July 30, 1912. The Meiji era was the first half of the Empire of Japan, when the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonizatio ...
s, were sometimes pieced together from the theatrical kimono
The is a traditional Japanese garment and the national dress of Japan. The kimono is a wrapped-front garment with square sleeves and a rectangular body, and is worn Garment collars in hanfu#Youren (right lapel), left side wrapped over ri ...
used in Noh theatre
is a major form of classical Japanese dance-drama that has been performed since the 14th century. It is Japan's oldest major theater art that is still regularly performed today. Noh is often based on tales from traditional literature featuri ...
.
Christianity
Catholicism
Pope John Paul II
Pope John Paul II (born Karol Józef Wojtyła; 18 May 19202 April 2005) was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 16 October 1978 until Death and funeral of Pope John Paul II, his death in 2005.
In his you ...
in his post-apostolic Exhortation (1996) says concerning the religious habit of consecrated
Sacred describes something that is dedicated or set apart for the service or worship of a deity; is considered worthy of spiritual respect or devotion; or inspires awe or reverence among believers. The property is often ascribed to objects (a ...
persons:
Nuns
serge Serge may refer to:
*Serge (fabric), a type of twill fabric
*Serge (llama) (born 2005), a llama in the Cirque Franco-Italien and internet meme
*Serge (name), a masculine given name (includes a list of people with this name)
*Serge (post), a hitchi ...
fabric pleated at the neck and draping to the ground. It can be worn pinned up in the front or in the back to allow the nun to work.
* Scapular
A scapular () is a Western Christian garment suspended from the shoulders. There are two types of scapulars, the monastic and devotional scapular; both forms may simply be referred to as "scapular". As an object of popular piety, a scapular ...
: This symbolic apron hangs from both front and back; it is worn over the tunic, and Benedictine
The Benedictines, officially the Order of Saint Benedict (, abbreviated as O.S.B. or OSB), are a mainly contemplative monastic order of the Catholic Church for men and for women who follow the Rule of Saint Benedict. Initiated in 529, th ...
nuns also wear it over the belt, whereas some other orders wear it tied under the belt.
* Cincture: The habit is often secured around the waist with a belt of leather, wool or a lanyard. The cincture of the Franciscan orders has three (or four) knots standing for the vows.
* Coif
A coif () is a close fitting cap worn by both men and women that covers the top, back, and sides of the head.
History
Coifs date from the tenth century, but fell out of popularity with men in the fourteenth century."A New Look for Women." Arts ...
: This is the garment's headpiece and includes the white cotton cap secured by a bandeau
A bandeau ( ; ; diminutive of the French word meaning 'strip') is a garment comprising, in appearance, a strip of cloth. Today, the term frequently refers to a garment that wraps around a woman's breasts. It is usually part of a bikini in sports ...
and a white wimple
A wimple is a medieval form of female headcovering, formed of a large piece of cloth worn draped around the neck and chin, covering the top of the head; it was usually made from white linen or silk. Its use developed in early medieval Europe ...
(to cover the neck and cheeks) and guimpe (to cover the chest, similar to a short cape) of starched linen, cotton, or (today) polyester. It is sometimes covered by a thin layer of black crêpe
A crêpe or crepe ( or , , ) is a dish made from unleavened batter or dough that is cooked on a frying pan or a griddle. Crêpes are usually one of two varieties: ''sweet crêpes'' () or ''savoury galettes'' (). They are often served ...
.
* Veil
A veil is an article of clothing or hanging cloth that is intended to cover some part of the human head, head or face, or an object of some significance. Veiling has a long history in European, Asian, and African societies. The practice has be ...
: This element is worn pinned over the coif head coverings. Some veils can be worn down to cover the face or up to expose it. The veil sometimes includes a white underveil as well. The colour of the veil depends as well from the habit of the order and the status of the sister or nun (novices or postulants wear differently coloured veils than the professed sisters and nuns).
The coif and veil were common items of clothing for married women in medieval Europe.
Different orders adhere to different styles of dress; these styles have changed over time.
Sisters
 Historically, the religious habit of Catholic sisters was a visible sign of a woman's consecration to God. Different orders adhere to different styles of dress; these styles have changed over time. For example, in former times, the
Historically, the religious habit of Catholic sisters was a visible sign of a woman's consecration to God. Different orders adhere to different styles of dress; these styles have changed over time. For example, in former times, the Daughters of Charity of Saint Vincent de Paul
The Company of the Daughters of Charity of Saint Vincent de Paul (; abbreviated DC), commonly called the Daughters of Charity or Sisters of Charity of Saint Vincent de Paul, is a society of apostolic life for women within the Catholic Church. ...
wore a cornette
A cornette is a piece of headwear for religious sisters. It is essentially a type of wimple consisting of a large starched piece of white cloth that is folded upward in such a way as to create the resemblance of horns () on the wearer's head ...
instead of a veil. Due the ecclesiastical document , many congregations decided to simplify their habits, to conform to the attire of the culture they are working in, or to even discard their use entirely.
While styles vary, for those wearing the traditional habit, three pieces are consistently worn: tunic (robe), belt/cincture, veil. The habit of some Dominican Sisters consists of a tunic, belt (cincture), scapular, veil, rosary, and on formal occasions a cappa (mantle). Even for orders that have chosen not to wear a habit, these sisters often share a common appearance: calf-length skirt, blouse or sweater, visible cross necklace.
Monks
 Monks in the Catholic church wear a tunic, a
Monks in the Catholic church wear a tunic, a cincture
The cincture is a rope-like or ribbon-like article sometimes worn with certain Christian liturgical vestments, encircling the body around or above the waist. As usual with vestments, both the term and the object are taken from ordinary everyday ...
, a hooded scapular, and, for the Liturgy of the Hours
The Liturgy of the Hours (), Divine Office (), or ''Opus Dei'' ("Work of God") are a set of Catholic prayers comprising the canonical hours, often also referred to as the breviary, of the Latin Church. The Liturgy of the Hours forms the official ...
, a mantle (novices) or a cowl
A cowl is an item of clothing consisting of a long, hooded garment with wide sleeves, often worn by monks. It was developed during the Early Middle Ages. The term may have originally referred to the hooded portion of a cloak, though contempor ...
(professed monks).
Friars
Canons regular
Owing to the different traditions and origins that exist, there is no singular common habit worn by theCanons Regular
The Canons Regular of St. Augustine are Catholic priests who live in community under a rule ( and κανών, ''kanon'', in Greek) and are generally organised into Religious order (Catholic), religious orders, differing from both Secular clergy, ...
. Historically the common habit was the distinctive white cassock, with white fascia, over time some communities of Canons have changed to wearing the black cassock with black fascia. The only item of the habit that is common to all Canons is the linen rochet a mark of the canonical status.
In the Netherlands, some wore a ''cacullae'' (a small asymmetrical black cope
A cope ( ("rain coat") or ("cape")) is a liturgical long mantle or cloak, open at the front and fastened at the breast with a band or clasp. It may be of any liturgical colour.
A cope may be worn by any rank of the Catholic or Anglican clerg ...
of cloth or sheepskin.) Some communities of canons, notably in Austria and Switzerland wear a sarotium, coming from the Latin , 'the sacred rochet'. It is a thin band of linen worn over the cassock when not in choir. As part of their choir dress, some communities of Canons wear a mozzetta, either black or purple over the rochet.
Outdoors Canons wear a black cloak and hood, but again adaptations have been made to this in some of the communities. Canons also traditionally wore a biretta
The biretta () is a square cap with three or four peaks or horns, sometimes surmounted by a tuft. Traditionally the three-peaked biretta is worn by Christian clergy, especially Catholic Church hierarchy, Roman Catholic clergy, as well as some ...
.
Clergy
Usually, secular priests wear either a blackcassock
The cassock, or soutane, is a Christian clerical clothing, clerical coat used by the clergy and Consecrated life, male religious of the Oriental Orthodox Churches, Eastern Orthodox Church and the Catholic Church, in addition to some clergy in ...
or an ordinary men's garb in black or another dark color along with a white clerical collar
A clerical collar, Roman collar, clergy collar, or, informally, dog collar, is an item of Christian clerical clothing.
Overview
The clerical collar is almost always white and was originally made of cotton or linen but is now frequently made of pl ...
. White cassocks or clothes may be worn in hot climates. Also, a ferraiolo (a kind of cope) could be worn along with the cassock. Priests also traditionally wore a biretta
The biretta () is a square cap with three or four peaks or horns, sometimes surmounted by a tuft. Traditionally the three-peaked biretta is worn by Christian clergy, especially Catholic Church hierarchy, Roman Catholic clergy, as well as some ...
along with the cassock.
Deacons, priests, and bishops belonging to religious institute
In the Catholic Church, a religious institute is "a society in which members, according to proper law, pronounce public religious vows, vows, either perpetual or temporary which are to be renewed, however, when the period of time has elapsed, a ...
s wear the habit of their institute.
Abbot or cardinal
Latin Church
The Latin Church () is the largest autonomous () particular church within the Catholic Church, whose members constitute the vast majority of the 1.3 billion Catholics. The Latin Church is one of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical ...
clergy other than bishops, in particular any who are abbot
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the head of an independent monastery for men in various Western Christian traditions. The name is derived from ''abba'', the Aramaic form of the Hebrew ''ab'', and means "father". The female equivale ...
s or apostolic prefect
An apostolic prefect or prefect apostolic is a priest who heads what is known as an apostolic prefecture, a 'pre-diocesan' missionary jurisdiction where the Catholic Church is not yet sufficiently developed to have it made a diocese. Although it ...
s or ordinary of a personal ordinariate, may wear pontifical items. Mitre, crosier and ring are bestowed on an abbot at his blessing and the pectoral cross is a customary part of an abbatial habit.
Catholic habits gallery
Carmelite Order
The Order of the Brothers of the Blessed Virgin Mary of Mount Carmel (; abbreviated OCarm), known as the Carmelites or sometimes by synecdoche known simply as Carmel, is a mendicant order in the Catholic Church for both men and women. Histo ...
is brown and includes the Scapular of Our Lady of Mount Carmel (also known as Brown Scapular).
File:Francisco de Zurbarán 041.jpg, The religious habit of the Hieronymite enclosed monks and nuns is white and includes a brown scapular.
File:Maria Droste zu Vischering.jpg, The religious habit of the Sisters of the Good Shepherd (and also of the Sisters from the Order of Our Lady of Charity) is white, with a white scapular, a black veil and a large silver heart on the breast.
File:Mary of Jesus d'Oultremont.jpg, The religious habit of the Sisters of Mary Reparatrix is white, with a blue scapular, a white and blue veil and a large golden heart on the breast.
File:Pater Pax.jpg, The religious habit of the Franciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related organizations in the Catholic Church, founded or inspired by the Italian saint Francis of Assisi. They include three independent Religious institute, religious orders for men (the Order of Friars Minor bei ...
Order of Friars Minor
The Order of Friars Minor (commonly called the Franciscans, the Franciscan Order, or the Seraphic Order; postnominal abbreviation OFM) is a mendicant Catholic religious order, founded in 1209 by Francis of Assisi. The order adheres to the t ...
and Friars Minor Capuchin is usually brown or gray; the habit of the Order of Friars Minor Conventual
The Order of Friars Minor Conventual (O.F.M. Conv.) is a male religious fraternity in the Catholic Church and a branch of the Franciscan Order. Conventual Franciscan Friars are identified by the affix O.F.M. Conv. after their names. They are ...
and Third Order Regular is black, although the Order of Friars Minor Conventual is returning to the grey habit worldwide.
File:Kovelklein.JPG, The religious habit of the Benedictines
The Benedictines, officially the Order of Saint Benedict (, abbreviated as O.S.B. or OSB), are a mainly Christian mysticism, contemplative Christian monasticism, monastic Religious order (Catholic), order of the Catholic Church for men and f ...
is black (the style varies depending upon the monastery).
File:Nicolas Mignard 001.jpg, The religious habit of the Carthusians
The Carthusians, also known as the Order of Carthusians (), are a Latin enclosed religious order of the Catholic Church. The order was founded by Bruno of Cologne in 1084 and includes both monks and nuns. The order has its own rule, called the ...
is white. A similar habit is used by the Monastic Family of Bethlehem, of the Assumption of the Virgin and of Saint Bruno.
File:FrColl2.jpg, The religious habit of the Dominicans
Dominicans () also known as Quisqueyans () are an ethnic group, ethno-nationality, national people, a people of shared ancestry and culture, who have ancestral roots in the Dominican Republic.
The Dominican ethnic group was born out of a fusio ...
is black and white.
File:Cistersian priests in Szczyrzyc monastery.JPG, Cistercians
The Cistercians (), officially the Order of Cistercians (, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint Benedict, as well as the contri ...
in their religious habit (with the black scapular
A scapular () is a Western Christian garment suspended from the shoulders. There are two types of scapulars, the monastic and devotional scapular; both forms may simply be referred to as "scapular". As an object of popular piety, a scapular ...
).
File:Poor Clares sister.jpg, The religious habit of the Clarisses (also known as Poor Clares
The Poor Clares, officially the Order of Saint Clare (Latin language, Latin: ''Ordo Sanctae Clarae''), originally referred to as the Order of Poor Ladies, and also known as the Clarisses or Clarissines, the Minoresses, the Franciscan Clarist Or ...
) is brown, with a black veil.
File:St. Jeanne de Valois.jpg, The religious habit of the Sisters of the Annunciation is white, with a red scapular and a black veil.
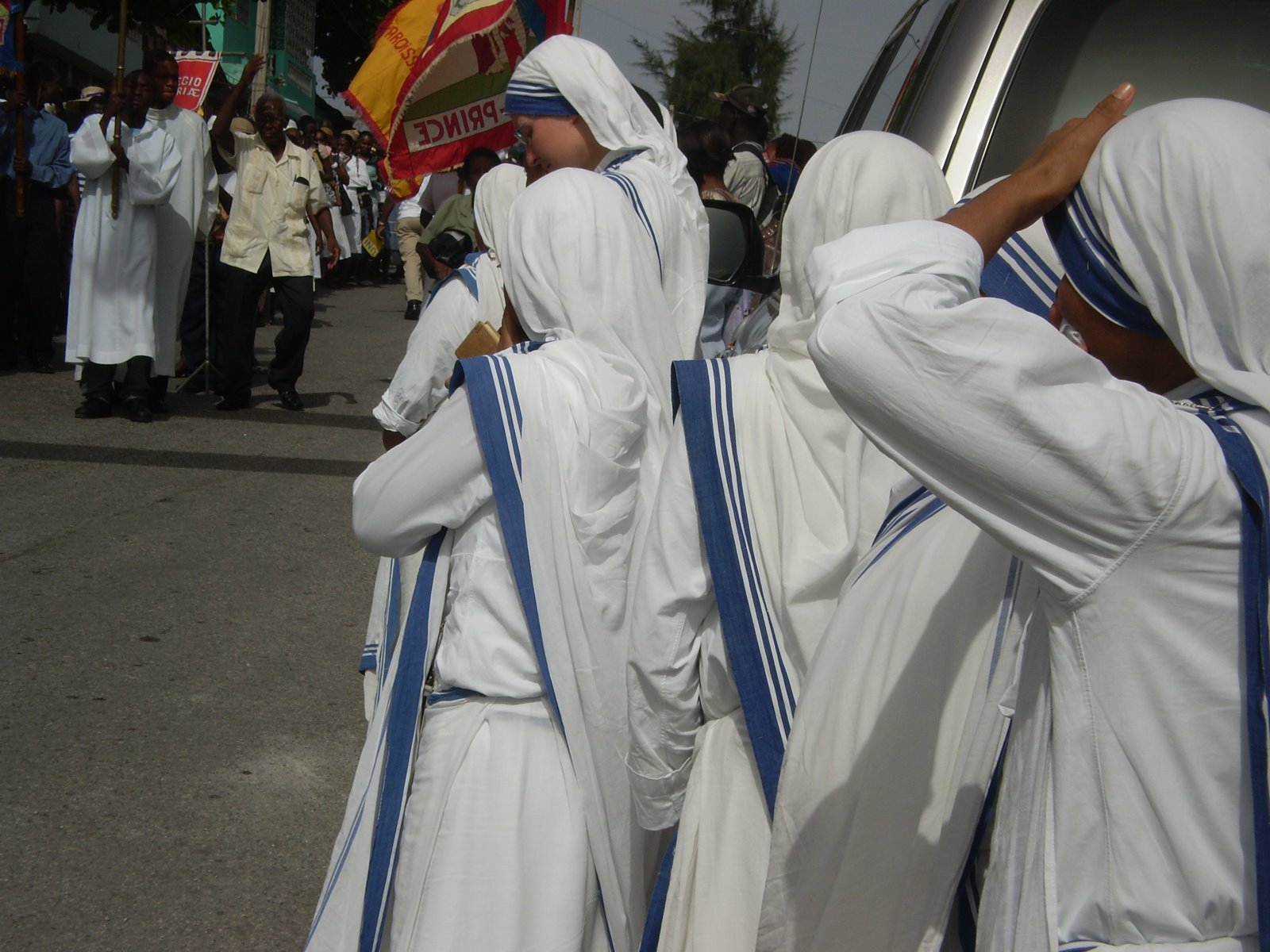
File:Sisters of Charity.jpg, The religious habit (based on the Indian sari
A sari (also called sharee, saree or sadi)The name of the garment in various regional languages include:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* is a drape (cloth) and a women's garment in the Indian subcontinent. It consists of an un-sti ...
) of the Missionaries of Charity
The Missionaries of Charity () is a Catholic centralised religious institute of consecrated life of Pontifical Right for women
established in 1950 by Mother Teresa, now known in the Catholic Church as Saint Teresa of Calcutta. , it consisted o ...
, founded by Mother Teresa of Calcutta
Mary Teresa Bojaxhiu (born Anjezë Gonxhe Bojaxhiu, ; 26 August 1910 – 5 September 1997), better known as Mother Teresa or Saint Mother Teresa, was an Albanian-Indian Catholic Church, Roman Catholic nun, founder of the Missionaries of ...
File:Jean de Matha Ordre de la Sainte Trinité.jpg, The religious habit of the Trinitarian Order is white with a distinctive cross with a blue horizontal bar and a red vertical bar.
File:Sister of the Incarnate Word.png, The religious habit of the Sisters of the Incarnate Word and Blessed Sacrament is white, with a red scapular and a black veil.
File:Perreyve, Henri.jpg, Oratorians wear roughly the same vestments as parish priests. The distinctive Oratorian clerical collar consists of white cloth that folds over the collar all around the neck.
File:Armand Gautier Nuns.gif, Sisters belonging to the Daughters of Charity with the cornette which used to be common
File:Trappist praying 2007-08-20 dti.jpg, Religious habit of a Trappist
The Trappists, officially known as the Order of Cistercians of the Strict Observance (, abbreviated as OCSO) and originally named the Order of Reformed Cistercians of Our Lady of La Trappe, are a Religious order (Catholic), Catholic religious o ...
monk
File:Rüti - Ortsmuseum - Kloster - Prämostratenser-Habit IMG 5172.JPG, Religious habit of a Premonstratensian
The Order of Canons Regular of Prémontré (), also known as the Premonstratensians, the Norbertines and, in Britain and Ireland, as the White Canons (from the colour of their habit), is a religious order of canons regular in the Catholic Chur ...
canon
File:Pius Przeździecki 1-R-613.jpg, Pauline Pius Przeździecki
File:Francisco de Zurbarán - Fray Pedro Machado - Google Art Project.jpg, The Mercedarians
The Royal, Celestial and Military Order of Our Lady of Mercy and the Redemption of the Captives (, abbreviated O. de M.), also known as the Mercedarians, is a Catholic mendicant order established in 1218 by Peter Nolasco in the city of Barcelo ...
wear white.
File:Giambattista Tiepolo - Estasi di San Francesco di Paola - Museo Paradiso - Piove di Sacco.jpg, The religious habit of a Minims friar. It consists of a black tunic, a scapular with a capuche and a black cincture with four knots (four vows).
Lutheranism
InLutheranism
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
, various religious order
A religious order is a subgroup within a larger confessional community with a distinctive high-religiosity lifestyle and clear membership. Religious orders often trace their lineage from revered teachers, venerate their Organizational founder, ...
s have a habit of a different colour. The Daughters of Mary wear a blue habit.
Anglicanism
Eastern Orthodoxy
TheEastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, and also called the Greek Orthodox Church or simply the Orthodox Church, is List of Christian denominations by number of members, one of the three major doctrinal and ...
does not have distinct religious orders such as those in the Catholic Church. The habit () is essentially the same throughout the world. The normal monastic color is black, symbolic of repentance and simplicity. The habits of monks and nuns are identical; additionally, nuns wear a scarf, called an apostolnik. The habit is bestowed in degrees, as the monk or nun advances in the spiritual life. There are three degrees: (1) the beginner, known as the Rassaphore ('robe bearer') (2) the intermediate, known as the Stavrophore ('cross bearer'), and (3) the Great Schema worn by Great Schema Monks or Nuns. Only the last, the Schemamonk or Schemanun, the monastic of the highest degree, wears the full habit.
The habit is formally bestowed upon monks and nuns at the ceremony known as the tonsure
Tonsure () is the practice of cutting or shaving some or all of the hair on the scalp as a sign of religious devotion or humility. The term originates from the Latin word ' (meaning "clipping" or "shearing") and referred to a specific practice in ...
(Greek ). The parts of the Eastern Orthodox habit are:
* Inner Rason (Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
: , or ; Slavonic: ): The inner rason (cassock) is the innermost garment. It is a long, collared garment coming to the feet, with narrow, tapered sleeves. Unlike the Roman cassock, it is double-breasted. The inner rason is the basic garment and is worn at all times, even when working. It is often given to novice
A novice is a person who has entered a religious order and is under probation, before taking vows. A ''novice'' can also refer to a person (or animal e.g. racehorse) who is entering a profession with no prior experience.
Religion Buddhism
...
s and seminarian
A seminary, school of theology, theological college, or divinity school is an educational institution for educating students (sometimes called seminarians) in scripture and theology, generally to prepare them for ordination to serve as clergy ...
s, though this differs from community to community. The inner rason is also worn by chanter
The chanter is the part of the bagpipe upon which the player creates the melody. It consists of a number of finger-holes, and in its simpler forms looks similar to a recorder. On more elaborate bagpipes, such as the Northumbrian bagpipes or ...
s, readers, and the married clergy. For monks and nuns, it symbolizes the vow
A vow ( Lat. ''votum'', vow, promise; see vote) is a promise or oath. A vow is used as a promise that is solemn rather than casual.
Marriage vows
Marriage vows are binding promises each partner in a couple makes to the other during a weddin ...
of poverty
Poverty is a state or condition in which an individual lacks the financial resources and essentials for a basic standard of living. Poverty can have diverse Biophysical environmen ...
.
* Belt (Greek: ; Slavonic: ): The belt worn by Orthodox monks and nuns is normally leather, though sometimes it is of cloth. In the Russian tradition, married clergy, as well as the higher monastic clergy, may wear a cloth belt that is finely embroidered
Embroidery is the art of decorating Textile, fabric or other materials using a Sewing needle, needle to stitch Yarn, thread or yarn. It is one of the oldest forms of Textile arts, textile art, with origins dating back thousands of years across ...
, especially on feast days
The calendar of saints is the traditional Christian method of organizing a liturgical year by associating each day with one or more saints and referring to the day as the feast day or feast of said saint. The word "feast" in this context does n ...
. The belt is symbolic of the vow of chastity
Chastity, also known as purity, is a virtue related to temperance. Someone who is ''chaste'' refrains from sexual activity that is considered immoral or from any sexual activity, according to their state of life. In some contexts, for exampl ...
.
* Paramand (Greek: ; Slavonic: ): The Paramand is a piece of cloth, approximately square which is attached by ribbons to a wooden cross. The cloth is embroidered with a cross and the Instruments of the Passion. The wooden cross is worn over the chest, then the ribbons pass over and under the arms, like a yoke
A yoke is a wooden beam used between a pair of oxen or other animals to enable them to pull together on a load when working in pairs, as oxen usually do; some yokes are fitted to individual animals. There are several types of yoke, used in dif ...
, and hold the square cloth centered on the back. The paramand is symbolic of the yoke of Christ (Matthew 11:29–30).
* Outer Rason (, Greek: or simply ; Slavonic: ): Among the Greeks it is worn by readers and all higher clerics; among the Russians it is worn only by monks, deacons, priests, and bishops.
* Analavos (Greek: ; Slavonic: ): The distinctive dress of the Great Schema is the analavos, and it is worn only by Schemamonks and Schemanuns. Traditionally made of either leather or wool, the analavos covers the shoulders, and then comes down in the front and back, forming a cross (see illustration, above right).
* Polystavrion (Greek: , lit. "many crosses"): The polystavrion is a long cord that has been plaited with numerous crosses forming a yoke that is worn over the analavos to hold it in place.
* Mantle (Greek: ; Slavonic: ): The Mantle is a long, full cape, joined at the neck which the monastic wears over the other parts of the habit.
* Kalymafki (a.k.a. '' Kalimavkion'', Greek: ; Slavonic: ): The distinctive headdress
Headgear, headwear, or headdress is any element of clothing which is worn on one's head, including hats, helmets, turbans and many other types. Headgear is worn for many purposes, including protection against the elements, decoration, or fo ...
of Eastern Orthodox monks and nuns is the kalymafki, a stiffened hat, something like a fez, only black and with straight sides, covered with a veil
A veil is an article of clothing or hanging cloth that is intended to cover some part of the human head, head or face, or an object of some significance. Veiling has a long history in European, Asian, and African societies. The practice has be ...
. The veil has lappets which hang down on each side of the head and a stylized hood falling down the back. For monastics of the Great Schema, the kalymafki takes a very distinctive shape, known as a koukoulion (cowl), and is embroidered with the Instruments of the Passion. The koukoulion is also worn by the Patriarchs of several local churches, regardless of whether or not he has been tonsured to that degree. In the Slavic tradition, the koukoulion will be in the form of a cloth hood, similar to that worn on the Western cowl. Outside church, monastics wear a soft hat known as a Skufia. Again, for Schemamonks and Schemanuns it is embroidered with the Instruments of the Passion.
The portions of the habit worn by the various degrees of monastics is as follows:
Eastern Orthodox habits gallery
Polish Orthodox Church
The Polish Autocephalous Orthodox Church (), commonly known as the Polish Orthodox Church, or Orthodox Church of Poland, is one of the autocephalous Eastern Orthodox churches in full communion. The church was established in 1924, to accommodate O ...
cleric
File:Dosifeya (Tarakanova).jpg
File:Unknown Monk (Skhimnik) at the Mount Athos, 1850s.jpg, Monk at the Mount Athos, 1850s
Hinduism
In Hinduism, religious clothing is a huge element of an individual’s life. Most Hindus are known to wear a religious pendant in their daily life to show their faith in God. Hindu women cover their heads with scarf as a sign of respect for not only religion but also their husbands. In India, most devoted Hindus are seen wearing a tilak and orange clothing depicting devotion to their religion. Most Hindu Pandits are either seen in a white or orange (kesari) religious clothing in India. Brahmin Hindus are most known for their devotion to the religion among all Hindus. They are seen wearing religious habits at various important moments in their life.Islam
Sunni in west asia before 19th century, religious clergy colloquially known as Mullah wore common clothes of their era with very small differences. later most Sunni mullahs in former territories of Ottoman empire started wearing long robes in black or other colours such as grey or blue, with a typical red fez and white turban which did not look as prominent as turbans of earlier eras. Shia meanwhile clothing of Shia mullahs was mainly based on common clothing of Qajar era with a typical common robe called Qaba which evolved from robes of Safavid and Mongol eras, and a large overcoat called Aba, which was sewn in a rectangle pattern without separate sleeves which was also common among other classes but with slight differences, and seyyids wore black turbans, the same clothing has been preserved till present day and spread to shia scholars outside Iran whore used to wear local clothing before 20th century; pattern of Qaba has been changed and slightly westernised with buttons added and sleeves sewn into the body rather than traditional straight sleeves, and they no more use a sash, and caps are not worn under turban. there has been also a newer design called Labbada with round collar instead of Qaba. before 20th century left side of Qaba covered the right side as it had originated from Ilkhanate but at least from second half of 20th century some Qaba and Labbada are produced in opposite manner. Mullahs used to have long preserved beards and usually shaved their head but after the revolution the trend is trimmed short beard and typical short hairstyles. Sunni in central asia Sunni mullahs in central asia continued wearing their traditional clothing which resembled common clothing, in case of Ethnicities which did not wear turban as daily wear (such as Turkmens and Kazakhs) the only difference of mullahs was wearing turbans which was in common with Sufi derwishes. largest centres of Islamic education in central education was in Turkestan which was also centre of Sufism and Bukhara which was the main destination of Turkmen mullahs before 20th century and such large cities. mullahs wore same robes as commoners with an overcoat called Chapan/Chakmen. from 20th century onwards islamic education declined in central asia under Soviet rule and after 1990's there was a rise in wahabism and fundamentalism rather than locally developed schools which also affected the clothing and modern day mullahs in central asia wear uniforms similar to west asian mullahs. Turkmen mullahs in Iran continued wearing traditional Chakmen till modern day but new uniforms have been introduced in official madrasahs which are cyan or grey robes with westernised designs and are tighter than shorter. turbans have also been made smaller than before. however old generation mullahs still wear Chakmen over white shirt rather the standardised uniforms. keeping a mustache was also more common in earlier times but modern mullahs either fully shave or trim the mustaches following fundamentalist trend.Jainism
Female ascetics andŚvetāmbara
The Śvetāmbara (; also spelled Shwetambara, Shvetambara, Svetambara or Swetambara) is one of the two main branches of Jainism, the other being the Digambara. ''Śvetāmbara'' in Sanskrit means "white-clad", and refers to its ascetics' practi ...
male monks always wear un-stitched or minimally stitched white clothes. Digambara
''Digambara'' (; "sky-clad") is one of the two major Jain schools and branches, schools of Jainism, the other being ''Śvetāmbara'' (white-clad). The Sanskrit word ''Digambara'' means "sky-clad", referring to their traditional monastic pract ...
Jain monks do not wear clothes. A loin cloth which reaches up to the shins is called a Cholapattak. Another cloth to cover the upper part of the body is called Pangarani (Uttariya Vastra). A cloth that passes over the left shoulder and covers the body up to a little above the ankle is called a Kïmli. Kïmli is a woolen shawl. They also carry a woolen bed sheet and a woolen mat to sit on. Those who wear clothes have a muhapati, which is a square or rectangular piece of cloth of a prescribed measurement, either in their hand or tied on their face covering the mouth. Śvetāmbara ascetics have an Ogho or Rajoharan (a broom of woolen threads) to clean insects around their sitting place or while they are walking. Digambara ascetics have a Morpichhi and a Kamandal in their hands. This practice may vary among different sects of Jains but essential principle remains the same to limit needs.
Shinto
In Japan, various types of very traditional dress are worn byShinto
, also called Shintoism, is a religion originating in Japan. Classified as an East Asian religions, East Asian religion by Religious studies, scholars of religion, it is often regarded by its practitioners as Japan's indigenous religion and as ...
priests, often dating to styles worn by nobles during the Nara period
The of the history of Japan covers the years from 710 to 794. Empress Genmei established the capital of Heijō-kyō (present-day Nara). Except for a five-year period (740–745), when the capital was briefly moved again, it remained the capita ...
or Heian period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kammu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-kyō (modern Kyoto). means in Japanese. It is a ...
.
are a type of traditional Japanese clothing, originally worn only by men, but today they are worn by both sexes. There are two types, divided and undivided . The ''umanori'' type have divided legs, similar to trousers
Trousers (British English), slacks, or pants ( American, Canadian and Australian English) are an item of clothing worn from the waist to anywhere between the knees and the ankles, covering both legs separately (rather than with cloth extending ...
, but both types appear similar. ''Hakama'' are tied at the waist and fall approximately to the ankles, and are worn over a kimono
The is a traditional Japanese garment and the national dress of Japan. The kimono is a wrapped-front garment with square sleeves and a rectangular body, and is worn Garment collars in hanfu#Youren (right lapel), left side wrapped over ri ...
(hakamashita), with the kimono then appearing like a shirt.
A is a garment worn in Japan by people attending religious ceremonies and activities, including Buddhist and Shinto related occasions. Not only Shinto
, also called Shintoism, is a religion originating in Japan. Classified as an East Asian religions, East Asian religion by Religious studies, scholars of religion, it is often regarded by its practitioners as Japan's indigenous religion and as ...
and Buddhist priests can be found wearing Jōe at rituals, but laymen as well, for example when participating in pilgrimage such as the Shikoku Pilgrimage. The garment is usually white or yellow and is made of linen or silk depending on its kind and use. The Shinto priest who wears the is attired in a peaked cap
A cap is a flat headgear, usually with a visor. Caps have crowns that fit very close to the head. They made their first appearance as early as 3200 BC. The origin of the word "cap" comes from the Old French word "chapeau" which means "head co ...
called , an outer tunic called the proper, an outer robe called , an undergarment called , ballooning trousers called or , and a girdle called .
See also
*Degrees of Eastern Orthodox monasticism
The degrees of Eastern Orthodox monasticism are the stages an Eastern Orthodox monk or nun passes through in their religious vocation.
In the Eastern Orthodox Church, the process of becoming a monk or nun is intentionally slow, as the monastic ...
* Religious dress
Religious clothing is clothing which is worn in accordance with religion, religious practice, tradition or significance to a faith group. It includes clerical clothing such as cassocks, and religious habit, robes, and other vestments. Accessories ...
* Tonsure
Tonsure () is the practice of cutting or shaving some or all of the hair on the scalp as a sign of religious devotion or humility. The term originates from the Latin word ' (meaning "clipping" or "shearing") and referred to a specific practice in ...
* Zucchetto
The zucchetto (, also ,"zucchetto"
(US) and ,< ...
(US) and ,< ...
References
Bibliography
* * * * * *Further reading
*External links
Images of medieval monks and nuns in the dress of their Orders
(Public Domain images and text)
Catholic Sisters International Collection, University of Dayton Special Collections
(photographs of reproductions of over 130 religious habits) {{Authority control Asceticism Byzantine clothing Christian clothing Eastern Christian vestments Hesychasm History of clothing (Western fashion) History of clothing History of fashion Monasticism Religious clothing Religious practices Robes and cloaks Sacramentals