Missing Fundamental on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
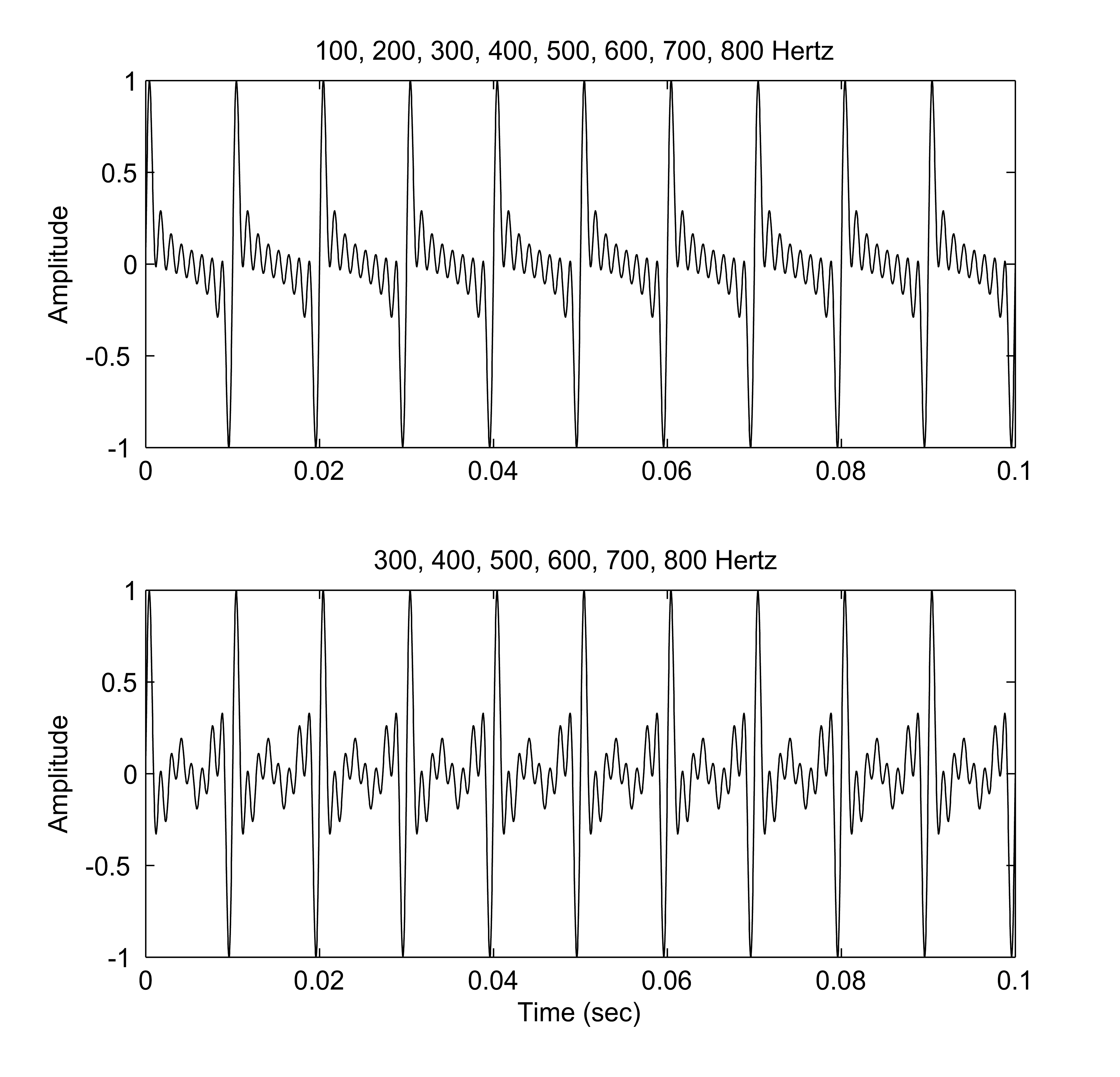 The pitch being perceived with the first
The pitch being perceived with the first
Ian Howell
He wrote that although not everyone can hear the missing fundamentals, noticing them can be taught and learned. D. Robert Ladd et al. have a related study that claims that most people can switch from listening for the pitch from the harmonics that are evident to finding these pitches spectrally.

Pitch Paradoxical
– abstract of the Heidelberg research, as published in ''Nature Neuroscience'' 8, 1241–1247 (2005); downloading the full article requires payment
– discussion forum thread about the Heidelberg research, with a link to a sound file used in the research so that readers can determine whether they are fundamental or overtone hearers {{Auditory illusions Psychoacoustics Waves
 The pitch being perceived with the first
The pitch being perceived with the first harmonic
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st har ...
being absent in the waveform is called the missing fundamental phenomenon.
It is established in psychoacoustics
Psychoacoustics is the branch of psychophysics involving the scientific study of the perception of sound by the human auditory system. It is the branch of science studying the psychological responses associated with sound including noise, speech, ...
that the auditory system, with its natural tendency to distinguish a tone from another, will persistently assign a pitch to a complex tone given that a sufficient set of harmonics are present in the spectrum.
For example, when a note (that is not a pure tone
In psychoacoustics, a pure tone is a sound with a sinusoidal waveform; that is, a sine wave of constant frequency, phase-shift, and amplitude.
By extension, in signal processing a single-frequency tone or pure tone is a purely sinusoidal signal ...
) has a pitch of 100 Hz, it will consist of frequency components that are integer multiples of that value (e.g. 100, 200, 300, 400, 500.... Hz). However, smaller loudspeakers may not produce low frequencies, so in our example, the 100 Hz component may be missing. Nevertheless, a pitch corresponding to the fundamental may still be heard.
Explanation
A low pitch (also known as the pitch of the missing fundamental or virtual pitch) can sometimes be heard when there is no apparent source or component of that frequency. This perception is due to the brain interpreting repetition patterns that are present. It was once thought that this effect was because the missing fundamental was replaced by distortions introduced by the physics of the ear. However, experiments subsequently showed that when a noise was added that would have masked these distortions had they been present, listeners still heard a pitch corresponding to the missing fundamental, as reported by J. C. R. Licklider in 1954. It is now widely accepted that the brain processes the information present in the overtones to calculate the fundamental frequency. The precise way in which it does so is still a matter of debate, but the processing seems to be based on anautocorrelation
Autocorrelation, sometimes known as serial correlation in the discrete time case, measures the correlation of a signal with a delayed copy of itself. Essentially, it quantifies the similarity between observations of a random variable at differe ...
involving the timing of neural impulses in the auditory nerve. However, it has long been noted that any neural mechanisms which may accomplish a delay (a necessary operation of a true autocorrelation) have not been found. At least one model shows a temporal delay to be unnecessary to produce an autocorrelation model of pitch perception, appealing to phase shifts between cochlear filters; however, earlier work has shown that certain sounds with a prominent peak in their autocorrelation function do not elicit a corresponding pitch percept, and that certain sounds without a peak in their autocorrelation function nevertheless elicit a pitch. Autocorrelation can thus be considered, at best, an incomplete model.
The pitch of the missing fundamental, usually at the greatest common divisor
In mathematics, the greatest common divisor (GCD), also known as greatest common factor (GCF), of two or more integers, which are not all zero, is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers. For two integers , , the greatest co ...
of the frequencies present, is not, however, always perceived. Research conducted at Heidelberg University
Heidelberg University, officially the Ruprecht Karl University of Heidelberg (; ), is a public research university in Heidelberg, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Founded in 1386 on instruction of Pope Urban VI, Heidelberg is Germany's oldest unive ...
shows that, under narrow stimulus conditions with a small number of harmonics, the general population can be divided into those who perceive missing fundamentals, and those who primarily hear the overtones instead. This was done by asking subjects to judge the direction of motion (up or down) of two complexes in succession
Succession is the act or process of following in order or sequence.
Governance and politics
*Order of succession, in politics, the ascension to power by one ruler, official, or monarch after the death, resignation, or removal from office of ...
. The authors used structural MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
and MEG to show that the preference for missing fundamental hearing correlated with left-hemisphere lateralization of pitch perception, where the preference for spectral hearing correlated with right-hemisphere lateralization, and those who exhibited the latter preference tended to be musicians.
In ''Parsing the Spectral Envelope: Toward a General Theory of Vocal Tone Color'' (2016) bIan Howell
He wrote that although not everyone can hear the missing fundamentals, noticing them can be taught and learned. D. Robert Ladd et al. have a related study that claims that most people can switch from listening for the pitch from the harmonics that are evident to finding these pitches spectrally.
Examples

Timpani
Timpani (; ) or kettledrums (also informally called timps) are musical instruments in the percussion instrument, percussion family. A type of drum categorised as a hemispherical drum, they consist of a Membranophone, membrane called a drumhead, ...
produce inharmonic overtones, but are constructed and tuned to produce near-harmonic overtones to an implied missing fundamental. Hit in the usual way (half to three-quarters the distance from the center to the rim), the fundamental note of a timpani is very weak in relation to its second through fifth "harmonic" overtones. A timpani might be tuned to produce sound most strongly at 200, 302, 398, and 488 Hz, for instance, implying a missing fundamental at 100 Hz (though the actual dampened fundamental is 170 Hz).
A violin
The violin, sometimes referred to as a fiddle, is a wooden chordophone, and is the smallest, and thus highest-pitched instrument (soprano) in regular use in the violin family. Smaller violin-type instruments exist, including the violino picc ...
's lowest air and body resonances generally fall between 250 Hz and 300 Hz. The fundamental frequency of the open G3 string is below 200 Hz in modern tunings as well as most historical tunings, so the lowest notes of a violin have an attenuated fundamental, although listeners seldom notice this.
Most common telephones cannot reproduce sounds lower than 300 Hz, but a male voice has a fundamental frequency of approximately 150 Hz. Because of the missing fundamental effect, the fundamental frequencies of male voices are still perceived as their pitches over the telephone.
The missing fundamental phenomenon is used electronically by some pro audio manufacturers to allow sound systems to seem to produce notes that are lower in pitch than they are capable of reproducing. In a hardware effects unit
An effects unit, effects processor, or effects pedal is an electronic device that alters the sound of a musical instrument or other audio source through audio signal processing.
Common effects include distortion (music), distortion/overdrive, ...
or a software plugin, a crossover filter is set at a low frequency above which the sound system is capable of safely reproducing tones. Musical signal content above the high-pass part of the crossover filter is sent to the main output which is amplified by the sound system. Low frequency content below the low-pass part of the crossover filter is sent to a circuit where harmonics are synthesized above the low notes. The newly created harmonics are mixed back into the main output to create a perception of the filtered-out low notes. Using a device with this synthetic process can reduce complaints from low frequency noise carrying through walls and it can be employed to reduce low frequency content in loud music that might otherwise vibrate and damage breakable valuables.
Some pipe organ
The pipe organ is a musical instrument that produces sound by driving pressurised air (called ''wind'') through the organ pipes selected from a Musical keyboard, keyboard. Because each pipe produces a single tone and pitch, the pipes are provide ...
s make use of this phenomenon as a resultant tone, which allows relatively smaller bass pipes to produce very low-pitched sounds.
Audio processing applications
This very concept of "missing fundamental" being reproduced based on the overtones in the tone has been used to create the illusion of bass in sound systems that are not capable of such bass. In mid-1999, Meir Shashoua ofTel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( or , ; ), sometimes rendered as Tel Aviv-Jaffa, and usually referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the Gush Dan metropolitan area of Israel. Located on the Israeli Mediterranean coastline and with a popula ...
, co-founder of Waves Audio
Waves Audio Ltd. is an Israeli developer and supplier of professional digital audio signal processing technologies and audio effects, used in recording, mixing, mastering, post production, broadcast, and live sound. The company's corporate headq ...
, patented an algorithm to create the sense of the missing fundamental by synthesizing higher harmonics. Waves Audio released the MaxxBass plug-in to allow computer users to apply the synthesized harmonics to their audio files. Later, Waves Audio produced small subwoofer
A subwoofer (or sub) is a loudspeaker designed to reproduce low-pitched audio frequencies, known as bass and sub-bass, that are lower in frequency than those which can be (optimally) generated by a woofer. The typical frequency range that is ...
s that relied on the missing fundamental concept to give the illusion of low bass. Both products processed certain overtones selectively to help small loudspeakers, ones which could not reproduce low-frequency components, to sound as if they were capable of low bass. Both products included a high-pass filter
A high-pass filter (HPF) is an electronic filter that passes signals with a frequency higher than a certain cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies lower than the cutoff frequency. The amount of attenuation for each frequency ...
which greatly attenuated all the low frequency tones that were expected to be beyond the capabilities of the target sound system. One example of a popular song that was recorded with MaxxBass processing is " Lady Marmalade", the 2001 Grammy award-winning version sung by Christina Aguilera
Christina María Aguilera ( , ; born December 18, 1980) is an American singer-songwriter, actress and television personality. Recognized as Cultural impact of Christina Aguilera, an influential figure in music and having received Public imag ...
, Lil' Kim
Kimberly Denise Jones (born July 11, 1974), Those giving 1974 include:
*
*
*
*
* better known by her stage name Lil' Kim, is an American rapper. She was born and raised in New York City and lived much of her adolescent life on the streets after ...
, Mýa
Mya Marie Harrison (; born October 10, 1979), known professionally as Mýa, is an American singer, songwriter, dancer, record producer, and actress. She was born in Washington D.C. and studied ballet, jazz, and tap dance as a child. Her ca ...
, and Pink
Pink is a pale tint of red, the color of the Dianthus plumarius, pink flower. It was first used as a color name in the late 17th century. According to surveys in Europe and the United States, pink is the color most often associated with charm, p ...
, produced by Missy Elliott
Melissa Arnette "Missy" Elliott (born July 1, 1971), also known as Misdemeanor, is an American rapper, singer, songwriter, and record producer. She began her musical career as a member of the Contemporary R&B, R&B girl group 4 All the Sistas Arou ...
.
Other software and hardware companies have developed their own versions of missing fundamental-based bass augmentation products. The poor bass reproduction of earbuds has been identified as a possible target for such processing. Many computer sound systems are not capable of low bass, and songs offered to consumers via computer have been identified as ones that may benefit from augmented bass harmonics processing.
See also
*Psychoacoustics
Psychoacoustics is the branch of psychophysics involving the scientific study of the perception of sound by the human auditory system. It is the branch of science studying the psychological responses associated with sound including noise, speech, ...
* Subharmonic
In music, the undertone series or subharmonic series is a sequence of notes that results from inverting the intervals of the overtone series. While overtones naturally occur with the physical production of music on instruments, undertones mus ...
References
External links
Pitch Paradoxical
– abstract of the Heidelberg research, as published in ''Nature Neuroscience'' 8, 1241–1247 (2005); downloading the full article requires payment
– discussion forum thread about the Heidelberg research, with a link to a sound file used in the research so that readers can determine whether they are fundamental or overtone hearers {{Auditory illusions Psychoacoustics Waves