Mipmap on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
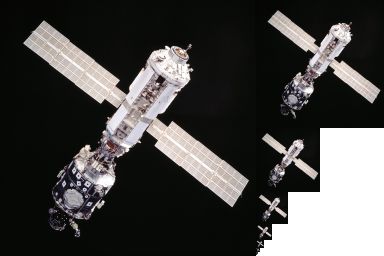 Each bitmap image of the mipmap set is a downsized duplicate of the main
Each bitmap image of the mipmap set is a downsized duplicate of the main
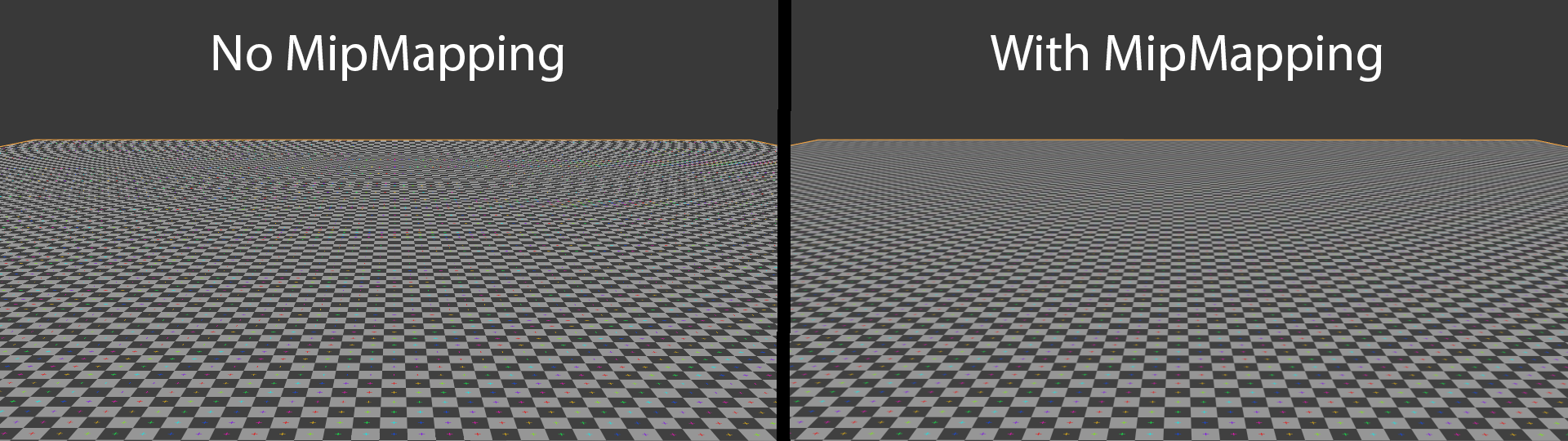 Mipmaps are used for:
* Level of detail (LOD)
* Improving image quality. Rendering from large textures where only small, discontiguous subsets of
Mipmaps are used for:
* Level of detail (LOD)
* Improving image quality. Rendering from large textures where only small, discontiguous subsets of
computer graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images and art with the aid of computers. Computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, digital art, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. ...
, a mipmap (''mip'' being an acronym of the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
phrase ''multum in parvo'', meaning "much in little") is a pre-calculated, optimized sequence of images, each of which has an image resolution
Image resolution is the level of detail of an image. The term applies to digital images, film images, and other types of images. "Higher resolution" means more image detail.
Image resolution can be measured in various ways. Resolution quantifies ...
which is a factor of two smaller than the previous. Their use is known as ''mipmapping''.
They are intended to increase rendering speed and reduce aliasing
In signal processing and related disciplines, aliasing is a phenomenon that a reconstructed signal from samples of the original signal contains low frequency components that are not present in the original one. This is caused when, in the ori ...
artifacts. A high-resolution mipmap image is used for high-density samples, such as for objects close to the camera; lower-resolution images are used as the object appears farther away. This is a more efficient way of downscaling a texture
Texture may refer to:
Science and technology
* Image texture, the spatial arrangement of color or intensities in an image
* Surface texture, the smoothness, roughness, or bumpiness of the surface of an object
* Texture (roads), road surface c ...
than sampling all texels
In Computer graphics, computer graphics, a texel, texture element, or texture pixel is the fundamental unit of a texture maps, texture map. Textures are represented by Array (data structure), arrays of texels representing the texture space, just ...
in the original texture that would contribute to a screen pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, p ...
; it is faster to take a constant number of samples from the appropriately downfiltered textures. Since mipmaps, by definition, are pre-allocated, additional storage space is required to take advantage of them. They are also related to wavelet compression.
Mipmaps are widely used in 3D computer games, flight simulators, other 3D imaging systems for texture filtering
In computer graphics, texture filtering or texture smoothing is the method used to determine the texture color for a Texture mapping, texture mapped pixel, using the colors of nearby Texel (graphics), texels (ie. pixels of the texture).
Filtering ...
, and 2D and 3D GIS software
A GIS software program is a computer program to support the use of a geographic information system, providing the ability to create, store, manage, query, Spatial analysis, analyze, and Cartographic design, visualize Geographic data and informati ...
. Mipmap textures are used in 3D scenes to decrease the time required to render a scene. They also improve image quality
Image quality can refer to the level of accuracy with which different imaging systems capture, process, store, compress, transmit and display the signals that form an image. Another definition refers to image quality as "the weighted combination of ...
by reducing aliasing and Moiré pattern
In mathematics, physics, and art, moiré patterns ( , , ) or moiré fringes are large-scale wave interference, interference patterns that can be produced when a partially opaque grating, ruled pattern with transparent gaps is overlaid on ano ...
s that occur at large viewing distances, at the cost of 33% more memory per texture.
History
Mipmapping was invented by Lance Williams in 1983 and is described in his paper ''Pyramidal parametrics''. From the abstract: "This paper advances a 'pyramidal parametric' prefiltering and sampling geometry which minimizes aliasing effects and assures continuity within and between target images." The referenced pyramid can be imagined as the set of mipmaps stacked in front of each other. The first patent issued on Mipmap and texture generation was in 1983 by Johnson Yan, Nicholas Szabo, and Lish-Yann Chen of Link Flight Simulation (Singer). Using their approach, texture could be generated and superimposed on surfaces (curvilinear and planar) of any orientation and could be done in real-time. Texture patterns could be modeled suggestive of the real world material they were intended to represent in a continuous way and free of aliasing, ultimately providing level of detail and gradual (imperceptible) detail level transitions. Texture generating became repeatable and coherent from frame to frame and remained in correct perspective and appropriate occultation. Because the application of real time texturing was applied to early three dimensional flight simulator CGI systems, and texture being a prerequsite for realistic graphics, this patent became widely cited and many of these techniques were later applied in graphics computing and gaming as applications expanded over the years. The origin of the term mipmap is an initialism of the Latin phrase ''multum in parvo'' ("much in little"), and map, modeled on bitmap. The term ''pyramids'' is still commonly used in a GIS context. In GIS software, pyramids are primarily used for speeding up rendering times.Mechanism
 Each bitmap image of the mipmap set is a downsized duplicate of the main
Each bitmap image of the mipmap set is a downsized duplicate of the main texture
Texture may refer to:
Science and technology
* Image texture, the spatial arrangement of color or intensities in an image
* Surface texture, the smoothness, roughness, or bumpiness of the surface of an object
* Texture (roads), road surface c ...
, but at a certain reduced level of detail. Although the main texture would still be used when the view is sufficient to render it in full detail, the renderer will switch to a suitable mipmap image (or in fact, interpolate
In the mathematical field of numerical analysis, interpolation is a type of estimation, a method of constructing (finding) new data points based on the range of a discrete set of known data points.
In engineering and science, one often has a ...
between the two nearest, if trilinear filtering
Trilinear filtering is an extension of the bilinear texture filtering method, which also performs linear interpolation between mipmaps.
Bilinear filtering has several weaknesses that make it an unattractive choice in many cases: using it on a ...
is activated) when the texture is viewed from a distance or at a small size. Rendering speed increases since the number of texture pixels (''texels
In Computer graphics, computer graphics, a texel, texture element, or texture pixel is the fundamental unit of a texture maps, texture map. Textures are represented by Array (data structure), arrays of texels representing the texture space, just ...
'') being processed per display pixel can be much lower for similar results with the simpler mipmap textures. If using a limited number of texture samples per display pixel (as is the case with bilinear filtering) then artifacts are reduced since the mipmap images are effectively already anti-aliased. Scaling down and up is made more efficient with mipmaps as well.
If the texture has a basic size of 256 by 256 pixels, then the associated mipmap set may contain a series of 8 images, each one-fourth the total area of the previous one: 128×128 pixels, 64×64, 32×32, 16×16, 8×8, 4×4, 2×2, 1×1 (a single pixel). If, for example, a scene is rendering this texture in a space of 40×40 pixels, then either a scaled-up version of the 32×32 (without trilinear interpolation
Trilinear interpolation is a method of multivariate interpolation on a Three dimensional space, 3-dimensional regular grid. It approximates the value of a function at an intermediate point (x, y, z) within the local axial rectangular prism (geo ...
) or an interpolation of the 64×64 and the 32×32 mipmaps (with trilinear interpolation) would be used. The simplest way to generate these textures is by successive averaging; however, more sophisticated algorithms (perhaps based on signal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signals'', such as audio signal processing, sound, image processing, images, Scalar potential, potential fields, Seismic tomograph ...
and Fourier transform
In mathematics, the Fourier transform (FT) is an integral transform that takes a function as input then outputs another function that describes the extent to which various frequencies are present in the original function. The output of the tr ...
s) can also be used.
The increase in storage space required for all of these mipmaps is a third of the original texture, because the sum of the areas 1/4 + 1/16 + 1/64 + 1/256 + ⋯ converges to 1/3. In the case of an RGB image with three channels stored as separate planes, the total mipmap can be visualized as fitting neatly into a square area twice as large as the dimensions of the original image on each side (twice as large on each side is four times the original area - one plane of the original size for each of red, green and blue makes three times the original area, and then since the smaller textures take 1/3 of the original, 1/3 of three is one, so they will take the same total space as just one of the original red, green, or blue planes). This is the inspiration for the tag ''multum in parvo''.
Uses
 Mipmaps are used for:
* Level of detail (LOD)
* Improving image quality. Rendering from large textures where only small, discontiguous subsets of
Mipmaps are used for:
* Level of detail (LOD)
* Improving image quality. Rendering from large textures where only small, discontiguous subsets of texels
In Computer graphics, computer graphics, a texel, texture element, or texture pixel is the fundamental unit of a texture maps, texture map. Textures are represented by Array (data structure), arrays of texels representing the texture space, just ...
are used can easily produce Moiré pattern
In mathematics, physics, and art, moiré patterns ( , , ) or moiré fringes are large-scale wave interference, interference patterns that can be produced when a partially opaque grating, ruled pattern with transparent gaps is overlaid on ano ...
s;
* Speeding up rendering times, either by reducing the number of texels sampled to render each pixel, or increasing the memory locality of the samples taken;
* Reducing stress on the GPU or CPU.
* Water surface reflections
Anisotropic filtering
When a texture is viewed at a steep angle, the filtering should not be uniform in each direction (it should beanisotropic
Anisotropy () is the structural property of non-uniformity in different directions, as opposed to isotropy. An anisotropic object or pattern has properties that differ according to direction of measurement. For example, many materials exhibit ver ...
rather than isotropic
In physics and geometry, isotropy () is uniformity in all orientations. Precise definitions depend on the subject area. Exceptions, or inequalities, are frequently indicated by the prefix ' or ', hence '' anisotropy''. ''Anisotropy'' is also ...
), and a compromise resolution is required. If a higher resolution is used, the cache coherence goes down, and the aliasing is increased in one direction, but the image tends to be clearer. If a lower resolution is used, the cache coherence is improved, but the image is overly blurry. This would be a tradeoff of MIP level of detail (LOD) for aliasing vs blurriness. However anisotropic filtering attempts to resolve this trade-off by sampling a non isotropic texture footprint for each pixel rather than merely adjusting the MIP LOD. This non isotropic texture sampling requires either a more sophisticated storage scheme or a summation of more texture fetches at higher frequencies.
Summed-area tables
Summed-area tables can conserve memory and provide more resolutions. However, they again hurt cache coherence, and need wider types to store the partial sums, which are larger than the base texture's word size. Thus, modern graphics hardware does not support them.See also
* * * * *References
{{refs Computer graphics data structures Texture filtering