Military Base on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A military base is a facility directly owned and operated by or for the
 Depending on the context, the term "military base" may refer to any establishment (usually permanent) that houses a nation's
Depending on the context, the term "military base" may refer to any establishment (usually permanent) that houses a nation's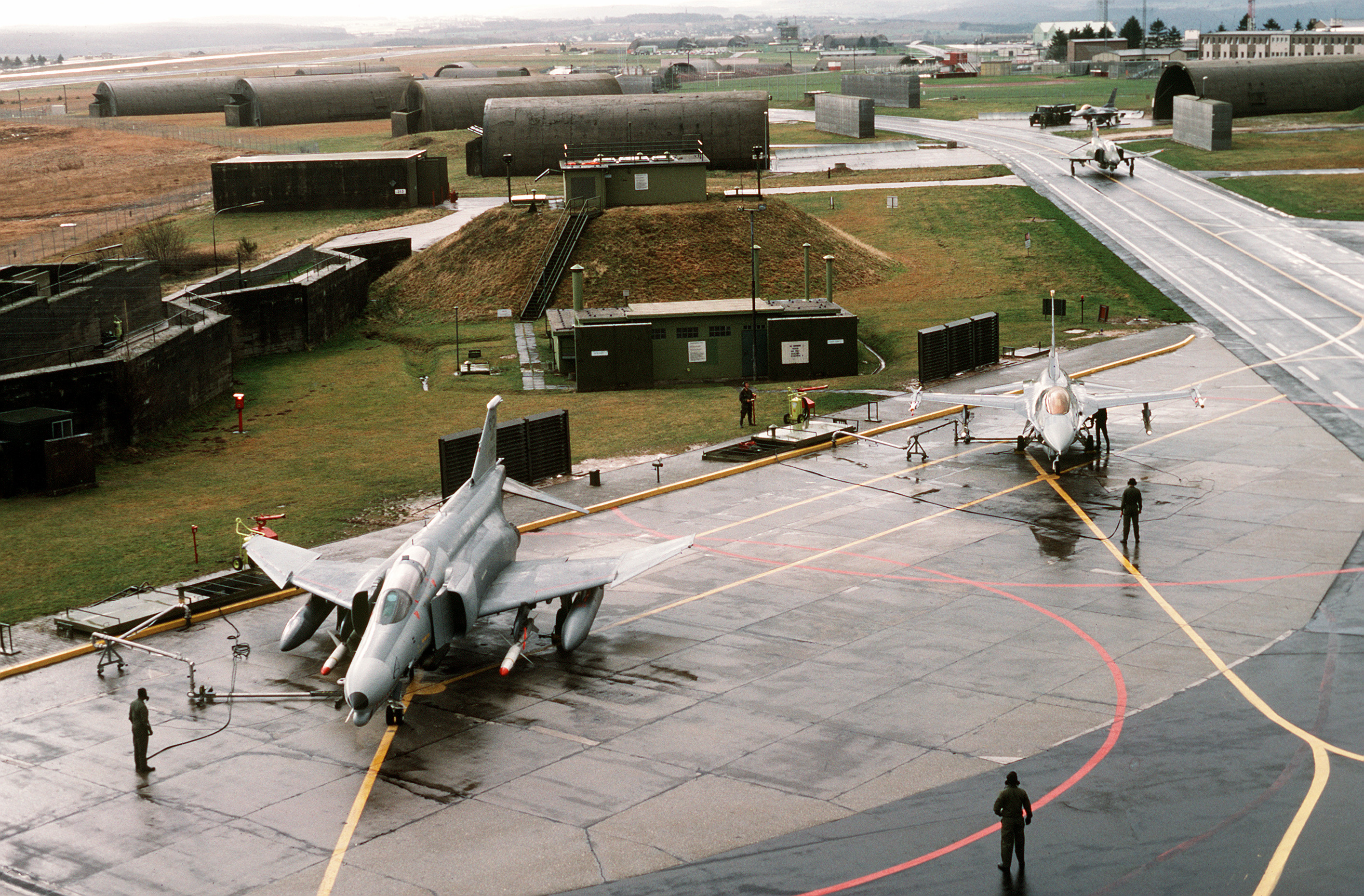  Bases used by the United States Air Force Reserve tend to be active USAF bases. However, there are a few Air Reserve Bases, such as Dobbins ARB, Georgia, and Grissom ARB, Indiana, both of which are former active-duty USAF bases. Facilities of the Air National Guard are often located on civil airports in a secure cantonment area not accessible to the general public, though some units are based on USAF bases, and a few ANG-operated bases, such as Selfridge ANGB, Michigan. Support facilities on Air National Guard and Air Force Reserve installations tend to not be as extensive as active bases (i.e., they usually do not have on-base lodging (though Kingsley Field ANGB, Oregon, is an exception), clinics (except for drill days), or retail stores (although some have small convenience stores)).
In Russian usage "military base" or "naval base" is not limited to denoting a specific fence described facility and usually encompasses a broad territory within which a number of discrete facilities may be located. As examples, 1) the Russian Sevastopol Naval Base comprises individual facilities located within the city of Sevastopol proper (waterfront moorings, weapons stores, a headquarters compound, and a naval infantry base) as well as an airfield at Kacha north of the city; 2) the Leningrad Naval Base comprises all naval facilities in the greater St. Petersburg area including training schools, commissioning institutes, the naval academy, and the Kronshtadt base on Kotlin island.
Bases used by the United States Air Force Reserve tend to be active USAF bases. However, there are a few Air Reserve Bases, such as Dobbins ARB, Georgia, and Grissom ARB, Indiana, both of which are former active-duty USAF bases. Facilities of the Air National Guard are often located on civil airports in a secure cantonment area not accessible to the general public, though some units are based on USAF bases, and a few ANG-operated bases, such as Selfridge ANGB, Michigan. Support facilities on Air National Guard and Air Force Reserve installations tend to not be as extensive as active bases (i.e., they usually do not have on-base lodging (though Kingsley Field ANGB, Oregon, is an exception), clinics (except for drill days), or retail stores (although some have small convenience stores)).
In Russian usage "military base" or "naval base" is not limited to denoting a specific fence described facility and usually encompasses a broad territory within which a number of discrete facilities may be located. As examples, 1) the Russian Sevastopol Naval Base comprises individual facilities located within the city of Sevastopol proper (waterfront moorings, weapons stores, a headquarters compound, and a naval infantry base) as well as an airfield at Kacha north of the city; 2) the Leningrad Naval Base comprises all naval facilities in the greater St. Petersburg area including training schools, commissioning institutes, the naval academy, and the Kronshtadt base on Kotlin island.
Official Directory of US Military bases.
Military Works (construction)
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20150308190409/http://www.acq.osd.mil/ie/ US Office of the Deputy Under Secretary of Defense (Installations and Environment)br>Outposts of Empire
– Booklet and map of the American military bases in the world. Transnational Institute, March 2007 {{DEFAULTSORT:Military Base Base Military installations Military locations
military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a d ...
or one of its branches that shelters military equipment and personnel, and facilitates training and operations. A military base always provides accommodations for one or more units, but it may also be used as a command center, training ground or proving ground. In most cases, military bases rely on outside help to operate. However, certain complex bases are able to endure on their own for long periods because they are able to provide food, drinking water, and other necessities for their inhabitants while under siege. Bases for military aviation are called air bases. Bases for military ships are called naval bases.
Jurisdictional definition
Military bases within the United States are considered federal property and are subject to federal law. Civilians (such as family members of military officers) living on military bases are generally subject to the civil andcriminal law
Criminal law is the body of law that relates to crime. It proscribes conduct perceived as threatening, harmful, or otherwise endangering to the property, health, safety, and Well-being, welfare of people inclusive of one's self. Most criminal l ...
s of the states where the bases are located. Military bases can range from small outposts to military cities containing up to 100,000 people. A military base may belong to a different nation or state than the territory surrounding it.
Naming
The name used generally refers to the type of military activity that takes place at the base, as well as the traditional nomenclature used by a branch of service. A military base may go by any of a number of names, such as the following: * Ammunition dump * Armory * Arsenal * Advance airfield *Barracks
Barracks are buildings used to accommodate military personnel and quasi-military personnel such as police. The English word originates from the 17th century via French and Italian from an old Spanish word 'soldier's tent', but today barracks ar ...
* Border outpost
* Cantonment
* Casern
* Combat outpost (COP)
* Facility
* Fire support base (FSB, FB)
* Forward Operating Base (FOB)
* Forward operating site (FOS)
* Fortification
* Garrison
* Installation
* Joint base
* Magazine
A magazine is a periodical literature, periodical publication, print or digital, produced on a regular schedule, that contains any of a variety of subject-oriented textual and visual content (media), content forms. Magazines are generally fin ...
* Main Operating Base (MOB)
* Marine Corps base
* Military airbase, airfield or field
* Military camp
* Missile launch facility
* Naval air station
* Naval base
* Naval dockyard
* Naval shipyard
* Observation post
* Outpost (OP)
* Presidio
* Proving ground
* Reservation
* Satellite airfield
* Station
* Submarine base
* Training camp
Types of establishment
 Depending on the context, the term "military base" may refer to any establishment (usually permanent) that houses a nation's
Depending on the context, the term "military base" may refer to any establishment (usually permanent) that houses a nation's armed forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a ...
, or even organized paramilitary
A paramilitary is a military that is not a part of a country's official or legitimate armed forces. The Oxford English Dictionary traces the use of the term "paramilitary" as far back as 1934.
Overview
Though a paramilitary is, by definiti ...
forces such as the police
The police are Law enforcement organization, a constituted body of Law enforcement officer, people empowered by a State (polity), state with the aim of Law enforcement, enforcing the law and protecting the Public order policing, public order ...
, constabulary, militia
A militia ( ) is a military or paramilitary force that comprises civilian members, as opposed to a professional standing army of regular, full-time military personnel. Militias may be raised in times of need to support regular troops or se ...
, or national guards. Alternatively, the term may refer solely to an establishment which is used only by an army
An army, ground force or land force is an armed force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by ...
(or possibly other land fighting related forces, such as marines
Marines (or naval infantry) are military personnel generally trained to operate on both land and sea, with a particular focus on amphibious warfare. Historically, the main tasks undertaken by marines have included Raid (military), raiding ashor ...
) to the exclusion of a base used by either an air force
An air force in the broadest sense is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an army aviati ...
or a navy
A navy, naval force, military maritime fleet, war navy, or maritime force is the military branch, branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral z ...
. This is consistent with the different meanings of the word 'military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a d ...
'.
Some examples of permanent military bases used by the navies and air force
An air force in the broadest sense is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an army aviati ...
s of the world are the HMNB Portsmouth in Portsmouth, UK, the Naval Air Station Whidbey Island, Washington State, US, or Ramstein Air Base, Germany (the last two are each designated as a Main Operating Base). Other examples of non- or semi-permanent military bases include a Forward Operating Base (FOB), a Logistics
Logistics is the part of supply chain management that deals with the efficient forward and reverse flow of goods, services, and related information from the point of origin to the Consumption (economics), point of consumption according to the ...
Base (Log base) and a Fire Base (FB).
A military base may also contain large concentrations of military supplies in order to support military logistics. Most military bases are restricted to the public and usually only authorized personnel may enter them (be it military personnel or their relatives and authorized civilian personnel).
In addition to the main military facilities on a certain installation, military bases usually (but not always) have various different facilities for military personnel. These facilities vary from country to country. Military bases can provide housing for military personnel, a post office and dining facilities (restaurant
A restaurant is an establishment that prepares and serves food and drinks to customers. Meals are generally served and eaten on the premises, but many restaurants also offer take-out and Delivery (commerce), food delivery services. Restaurants ...
s). They may also provide support facilities such as fast food restaurants, gas stations, chapels, school
A school is the educational institution (and, in the case of in-person learning, the Educational architecture, building) designed to provide learning environments for the teaching of students, usually under the direction of teachers. Most co ...
s, bank
A bank is a financial institution that accepts Deposit account, deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital m ...
s, thrift stores, a hospital
A hospital is a healthcare institution providing patient treatment with specialized Medical Science, health science and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically ...
or clinic (dental or health clinics, as well as veterinarian clinics), lodging, movie theaters, and, in some countries, retail stores (usually a supermarket such as Commissary and a Department Store
A department store is a retail establishment offering a wide range of consumer goods in different areas of the store under one roof, each area ("department") specializing in a product category. In modern major cities, the department store mad ...
, such as AAFES). On American military installations, Family, Morale, Welfare and Recreation (FMWR) provides facilities such as fitness centers, libraries, golf courses, travel centers, community service centers, campgrounds, child development centers, youth centers, automotive workshops, hobby/arts and crafts centers, bowling centers, and community centers.
Overseas military base
An overseas military base is a military base that is geographically located outside of the territory of the country whosearmed forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a ...
are the principal occupants of the base.
Such bases may be established by treaties between the governing power in the host country and another country which needs to establish the military base in the host country for various reasons, usually strategic and logistic.
Furthermore, overseas military bases often serve as the source of the military brat subculture due to the children of the bases' occupant military being born or raised in the host country but raised with a remote parental knowledge of the occupant military's home country.
British military bases
In the 18th and 19th centuries the Royal Engineers were largely responsible for erecting military bases in the British Isles and the British Empire. In 1792 the Chief Engineer was instructed to prepare the Barrack Construction estimates for Parliament and at the same time the Department of the Barrackmaster-General was established. During the period from the 1840s through the 1860s barracks were constructed under supervision of the Royal Engineers in: *Bristol
Bristol () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, the most populous city in the region. Built around the River Avon, Bristol, River Avon, it is bordered by t ...
(1847)
* Preston (1848)
* Tower of London (1851)
* Sheerness (1854)
* Sheffield
Sheffield is a city in South Yorkshire, England, situated south of Leeds and east of Manchester. The city is the administrative centre of the City of Sheffield. It is historically part of the West Riding of Yorkshire and some of its so ...
(1854)
* Curragh Camp (1855)
* Devonport (1856)
* Chelsea (1861)
The Cardwell Reforms (1872) ushered in another period of intensive Barrack building at Aldershot, Portsmouth, Plymouth
Plymouth ( ) is a port city status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary authority in Devon, South West England. It is located on Devon's south coast between the rivers River Plym, Plym and River Tamar, Tamar, about southwest of Exeter and ...
, London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
, Woking, Woolwich, Dublin
Dublin is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Situated on Dublin Bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, pa ...
, Belfast
Belfast (, , , ; from ) is the capital city and principal port of Northern Ireland, standing on the banks of the River Lagan and connected to the open sea through Belfast Lough and the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel ...
, Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
, Gibraltar
Gibraltar ( , ) is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory and British overseas cities, city located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Bay of Gibraltar, near the exit of the Mediterranean Sea into the A ...
and the Cape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( ) is a rocky headland on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A List of common misconceptions#Geography, common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is the southern tip of Afri ...
.
In 1959 the Corps' Work Services was transferred to the civilian War Department Works Organization (later renamed Property Services Agency (PSA)) and by 1965 the (Specialist Teams Royal Engineers (STRE)) were formed to plan and execute Works projects worldwide.
Some British and Commonwealth naval bases are traditionally named, commissioned, and administered as though they were naval ships. For this reason they are sometimes called stone frigates.
Related term
* Billet * KaserneSee also
* List of United States military bases * List of military basesReferences
External links
Official Directory of US Military bases.
Military Works (construction)
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20150308190409/http://www.acq.osd.mil/ie/ US Office of the Deputy Under Secretary of Defense (Installations and Environment)br>Outposts of Empire
– Booklet and map of the American military bases in the world. Transnational Institute, March 2007 {{DEFAULTSORT:Military Base Base Military installations Military locations