Migration Period on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the
 The first wave of invasions, between AD 300 and 500, is partly documented by Greek and Latin historians but is difficult to verify archaeologically. It puts Germanic peoples in control of most areas of what was then the
The first wave of invasions, between AD 300 and 500, is partly documented by Greek and Latin historians but is difficult to verify archaeologically. It puts Germanic peoples in control of most areas of what was then the
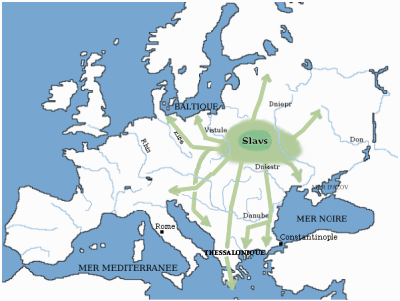
 Between AD 500 and 700, Slavic tribes settled more areas of central Europe and pushed farther into southern and eastern Europe, gradually making the eastern half of Europe predominantly Slavic.Zbigniew Kobyliński. "The Slavs" in Paul Fouracre. ''The New Cambridge Medieval History'', pp. 530–537 Additionally,
Between AD 500 and 700, Slavic tribes settled more areas of central Europe and pushed farther into southern and eastern Europe, gradually making the eastern half of Europe predominantly Slavic.Zbigniew Kobyliński. "The Slavs" in Paul Fouracre. ''The New Cambridge Medieval History'', pp. 530–537 Additionally,
fall of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vas ...
and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roman kingdoms. The term refers to the important role played by the migration, invasion, and settlement of various tribes, notably the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
, Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Euro ...
, Alemanni, Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the ...
, Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
, early Slavs, Pannonian Avars
The Pannonian Avars () were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in chronicles of Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai ( el, Βαρχονίτες, Varchonítes), or Pseudo-Avars ...
, Magyars
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Ural ...
, and Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as nomad ...
within or into the former Western Empire and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, wh ...
. The period is traditionally taken to have begun in AD 375 (possibly as early as 300) and ended in 568. Various factors contributed to this phenomenon of migration and invasion, and their role and significance are still widely discussed.
Historians differ as to the dates for the beginning and ending of the Migration Period. The beginning of the period is widely regarded as the invasion of Europe by the Huns from Asia in about 375 and the ending with the conquest of Italy by the Lombards in 568, but a more loosely set period is from as early as 300 to as late as 800. For example, in the 4th century a very large group of Goths was settled as '' foederati'' within the Roman Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, and the Franks were settled south of the Rhine
The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label=Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label=Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), including in Alsatian dialect, Al ...
in Roman Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only durin ...
. In 406 a particularly large and unexpected crossing of the Rhine was made by a group of Vandals, Alans and Suebi
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own name ...
. As central power broke down in the Western Roman Empire, the military became more important but was dominated by men of barbarian origin.
There are contradictory opinions as to whether the fall of the Western Roman Empire was a result of an increase in migrations, or both the breakdown of central power and the increased importance of non-Romans resulted in internal Roman factors. Migrations, and the use of non-Romans in the military, were known in the periods before and after, and the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
adapted and continued to exist until the fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city fell on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 53-day siege which had beg ...
to the Ottomans in 1453. The fall of the Western Roman Empire, although it involved the establishment of competing barbarian kingdoms, was to some extent managed by the eastern emperors.
The migrants comprised war bands or tribes of 10,000 to 20,000 people, but in the course of 100 years they numbered not more than 750,000 in total, compared to an average 40 million population of the Roman Empire at that time. Although immigration was common throughout the time of the Roman Empire, the period in question was, in the 19th century, often defined as running from about the 5th to 8th centuries. The first migrations of peoples were made by Germanic tribes such as the Goths (including the Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
and the Ostrogoths), the Vandals, the Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons were a cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo-Saxons happened wit ...
, the Lombards, the Suebi, the Frisii, the Jutes, the Burgundians, the Alemanni, the Sciri
The Sciri, or Scirians, were a Germanic people. They are believed to have spoken an East Germanic language. Their name probably means "the pure ones".
The Sciri were mentioned already in the late 3rd century BC as participants in a raid on th ...
and the Franks; they were later pushed westward by the Huns, the Avars, the Slavs and the Bulgars. Later invasions, such as the Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
, the Normans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. T ...
, the Varangians, the Hungarians, the Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinct o ...
, the Romani
Romani may refer to:
Ethnicities
* Romani people, an ethnic group of Northern Indian origin, living dispersed in Europe, the Americas and Asia
** Romani genocide, under Nazi rule
* Romani language, any of several Indo-Aryan languages of the Roma ...
, the Turkics, and the Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
also had significant effects (especially in North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in t ...
, the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
, Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The r ...
and Central and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, wh ...
).
Chronology
Germanic tribes prior to migration
Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
moved out of southern Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swe ...
and northern Germany to the adjacent lands between the Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Rep ...
and Oder after 1000 BC. The first wave moved westward and southward (pushing the resident Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
west to the Rhine
The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label=Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label=Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), including in Alsatian dialect, Al ...
around 200 BC), moving into southern Germany up to the Roman provinces of Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only durin ...
and Cisalpine Gaul
Cisalpine Gaul ( la, Gallia Cisalpina, also called ''Gallia Citerior'' or ''Gallia Togata'') was the part of Italy inhabited by Celts ( Gauls) during the 4th and 3rd centuries BC.
After its conquest by the Roman Republic in the 200s BC it was ...
by 100 BC, where they were stopped by Gaius Marius
Gaius Marius (; – 13 January 86 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. Victor of the Cimbric and Jugurthine wars, he held the office of consul an unprecedented seven times during his career. He was also noted for his important refor ...
and later by Julius Caesar. It is this western group which was described by the Roman historian Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
(AD 56–117) and Julius Caesar (100–44 BC). A later wave of Germanic tribes migrated eastward and southward from Scandinavia, between 600 and 300 BC, to the opposite coast of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and fr ...
, moving up the Vistula near the Carpathian Mountains. During Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
' era they included lesser-known tribes such as the Tencteri, Cherusci, Hermunduri
The Hermunduri, Hermanduri, Hermunduli, Hermonduri, or Hermonduli were an ancient Germanic tribe, who occupied an inland area near the source of the Elbe river, around what is now Bohemia from the first to the third century, though they have al ...
and Chatti
The Chatti (also Chatthi or Catti) were an ancient Germanic tribe
whose homeland was near the upper Weser (''Visurgis''). They lived in central and northern Hesse and southern Lower Saxony, along the upper reaches of that river and in the val ...
; however, a period of federation and intermarriage resulted in the familiar groups known as the Alemanni, Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
, Saxons, Frisians
The Frisians are a Germanic ethnic group native to the coastal regions of the Netherlands and northwestern Germany. They inhabit an area known as Frisia and are concentrated in the Dutch provinces of Friesland and Groningen and, in Germany ...
and Thuringians.
First wave
 The first wave of invasions, between AD 300 and 500, is partly documented by Greek and Latin historians but is difficult to verify archaeologically. It puts Germanic peoples in control of most areas of what was then the
The first wave of invasions, between AD 300 and 500, is partly documented by Greek and Latin historians but is difficult to verify archaeologically. It puts Germanic peoples in control of most areas of what was then the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
.
The Tervingi crossed the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , ...
into Roman territory after a clash with the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
in 376. Some time later in Marcianopolis, the escort to their leader Fritigern was killed while meeting with Lupicinus. The Tervingi rebelled, and the Visigoths, a group derived either from the Tervingi or from a fusion of mainly Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
groups, eventually invaded Italy and sacked Rome in 410 before settling in Gaul. Around 460, they founded the Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of the Goths ( la, Regnum Gothorum), was a kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic successor states to ...
in Iberia. They were followed into Roman territory first by a confederation of Heruli
The Heruli (or Herules) were an early Germanic people. Possibly originating in Scandinavia, the Heruli are first mentioned by Roman authors as one of several " Scythian" groups raiding Roman provinces in the Balkans and the Aegean Sea, attacking ...
an, Rugian, and Scirian warriors under Odoacer, that deposed Romulus Augustulus in 476, and later by the Ostrogoths, led by Theodoric the Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal ( got, , *Þiudareiks; Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ), was king of the Ostrogoths (471–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy ...
, who settled in Italy.
In Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only durin ...
, the Franks (a fusion of western Germanic tribes whose leaders had been aligned with Rome since the 3rd century) entered Roman lands gradually during the 5th century, and after consolidating power under Childeric and his son Clovis's decisive victory over Syagrius in 486, established themselves as rulers of northern Roman Gaul. Fending off challenges from the Alemanni, Burgundians, and Visigoths, the Frankish kingdom became the nucleus of what would later become France and Germany.
The initial Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain
The Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain is the process which changed the language and culture of most of what became England from Romano-British to Germanic. The Germanic-speakers in Britain, themselves of diverse origins, eventually develop ...
occurred during the 5th century, when Roman control of Britain had come to an end. The Burgundians settled in northwestern Italy, Switzerland and Eastern France in the 5th century.
Second wave

 Between AD 500 and 700, Slavic tribes settled more areas of central Europe and pushed farther into southern and eastern Europe, gradually making the eastern half of Europe predominantly Slavic.Zbigniew Kobyliński. "The Slavs" in Paul Fouracre. ''The New Cambridge Medieval History'', pp. 530–537 Additionally,
Between AD 500 and 700, Slavic tribes settled more areas of central Europe and pushed farther into southern and eastern Europe, gradually making the eastern half of Europe predominantly Slavic.Zbigniew Kobyliński. "The Slavs" in Paul Fouracre. ''The New Cambridge Medieval History'', pp. 530–537 Additionally, Turkic
Turkic may refer to:
* anything related to the country of Turkey
* Turkic languages, a language family of at least thirty-five documented languages
** Turkic alphabets (disambiguation)
** Turkish language, the most widely spoken Turkic language
* ...
tribes such as the Avars and later Ugric Magyars became involved in this second wave. In AD 567, the Avars and the Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the '' History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
destroyed much of the Gepid Kingdom
The Gepids, ( la, Gepidae, Gipedae, grc, Γήπαιδες) were an East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion ...
. The Lombards, a Germanic people, settled in Italy with their Herulian, Suebian, Gepid, Thuringian, Bulgar, Sarmatian
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th ...
and Saxon
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country ( Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the No ...
allies in the 6th century.Bertolini 1960, pp. 34–38. They were later followed by the Bavarians and the Franks, who conquered and ruled most of Italy.
The Bulgars, originally a nomadic group probably from Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former ...
, occupied the Pontic steppe north of Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
since the 2nd century, but later, pushed by the Khazars, the majority of them migrated west and dominated Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
territories along the lower Danube in the 7th century. From that time the demographic picture of the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
changed permanently, becoming predominantly Slavic, while pockets of native people survived in the mountains of the Balkans.
During the early Byzantine–Arab Wars, Arab armies attempted to invade southeast Europe via Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
during the late 7th and early 8th centuries but were defeated at the siege of Constantinople (717–718) by the joint forces of Byzantium and the Bulgars. During the Khazar–Arab Wars, the Khazars stopped the Arab expansion into Europe across the Caucasus (7th and 8th centuries). At the same time, the Moors (consisting of Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
and Berbers) invaded Europe via Gibraltar ( conquering Hispania from the Visigothic Kingdom in 711), before being halted by the Franks at the Battle of Tours in Gaul. These battles broadly demarcated the frontiers between Christendom
Christendom historically refers to the Christian states, Christian-majority countries and the countries in which Christianity dominates, prevails,SeMerriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christendom"/ref> or is culturally or historically intertwin ...
and Islam for the next millennium. The following centuries saw the Muslims successful in conquering most of Sicily from the Christians by 902.
The Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin from around AD 895 and the following Hungarian invasions of Europe and the Viking expansion from the late 8th century conventionally mark the last large movements of the period. Christian missionaries gradually converted the non-Islamic newcomers and integrated them into the Christendom.
Discussions
Barbarian identity
Analysis of barbarian identity and how it was created and expressed during the Barbarian Invasions has elicited discussion among scholars.Herwig Wolfram
Herwig Wolfram (born 14 February 1934) is an Austrian historian who is Professor Emeritus of Medieval History and Auxiliary Sciences of History at the University of Vienna and the former Director of the . He is a leading member of the Vienna S ...
, a historian of the Goths, in discussing the equation of ''migratio gentium'' with ', observes that Michael Schmidt introduced the equation in his 1778 history of the Germans. Wolfram observed that the significance of '' gens'' as a biological community was shifting, even during the early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the M ...
and that "to complicate matters, we have no way of devising a terminology that is not derived from the concept of nationhood created during the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
".
The "primordialistic" paradigm prevailed during the 19th century. Scholars, such as German linguist Johann Gottfried Herder, viewed tribes as coherent biological (racial) entities, using the term to refer to discrete ethnic groups. He also believed that the ''Volk'' were an organic whole, with a core identity and spirit evident in art, literature and language. These characteristics were seen as intrinsic, unaffected by external influences, even conquest. Language, in particular, was seen as the most important expression of ethnicity. They argued that groups sharing the same (or similar) language possessed a common identity and ancestry. This was the Romantic
Romantic may refer to:
Genres and eras
* The Romantic era, an artistic, literary, musical and intellectual movement of the 18th and 19th centuries
** Romantic music, of that era
** Romantic poetry, of that era
** Romanticism in science, of that e ...
ideal that there once had been a single German, Celtic or Slavic people who originated from a common homeland and spoke a common tongue, helping to provide a conceptual framework for political movements of the 18th and 19th centuries such as Pan-Germanism and Pan-Slavism.
From the 1960s, a reinterpretation of archaeological and historical evidence prompted scholars, such as Goffart and Todd, to propose new models for explaining the construction of barbarian identity. They maintained that no sense of shared identity was perceived by the ''Germani''; a similar theory having been proposed for Celtic and Slavic groups.
A theory states that the primordialist mode of thinking was encouraged by a '' prima facie'' interpretation of Graeco-Roman sources, which grouped together many tribes under such labels as ''Germanoi'', ''Keltoi'' or ''Sclavenoi'', thus encouraging their perception as distinct peoples. Modernists argue that the uniqueness perceived by specific groups was based on common political and economic interests rather than biological or racial distinctions. Indeed, on this basis, some schools of thought in recent scholarship urge that the concept of ''Germanic'' peoples be jettisoned altogether.
The role of language in constructing and maintaining group identity can be ephemeral since large-scale language shifts occur commonly in history. Modernists propose the idea of "imagined communities"; the barbarian polities in late antiquity were social constructs rather than unchanging lines of blood kinship. The process of forming tribal units was called "ethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis (; ) is "the formation and development of an ethnic group".
This can originate by group self-identification or by outside identification.
The term ''ethnogenesis'' was originally a mid-19th century neologism that was later introdu ...
", a term coined by Soviet scholar Yulian Bromley. The Austrian school
The Austrian School is a heterodox school of economic thought that advocates strict adherence to methodological individualism, the concept that social phenomena result exclusively from the motivations and actions of individuals. Austrian scho ...
(led by Reinhard Wenskus
Reinhard Wenskus (10 March 1916 – 5 July 2002) was a German historian who was Professor of Medieval History at the University of Göttingen. His theories on the identity of Germanic peoples have had a major influence on contemporary research by ...
) popularized this idea, which influenced medievalists such as Herwig Wolfram, Walter Pohl and Patrick J. Geary. It argues that the stimulus for forming tribal polities was perpetuated by a small nucleus of people, known as the ' ("kernel of tradition"), who were a military or aristocratic elite. This core group formed a standard for larger units, gathering adherents by employing amalgamative metaphors such as kinship and aboriginal commonality and claiming that they perpetuated an ancient, divinely-sanctioned lineage.
The common, track-filled map of the ' may illustrate such course of events, but it misleads. Unfolded over long periods of time, the changes of position that took place were necessarily irregular ... (with) periods of emphatic discontinuity. For decades and possibly centuries, the tradition bearers idled, and the tradition itself hibernated. There was ample time for forgetfulness to do its work.
Viewpoints
Rather than "invasion", German and Slavic scholars speak of "migration" (german: Völkerwanderung, cs, Stěhování národů, sv, folkvandring and hu, népvándorlás), aspiring to the idea of a dynamic and "wanderingIndo-Germanic
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch ...
people".
Historians have postulated several explanations for the appearance of "barbarians" on the Roman frontier: climate change, weather and crops, population pressure, a "primeval urge" to push into the Mediterranean, the construction of the Great Wall of China causing a "domino effect" of tribes being forced westward, leading to the Huns falling upon the Goths who, in turn, pushed other Germanic tribes before them. In general, French and Italian scholars have tended to view this as a catastrophic event, the destruction of a civilization and the beginning of a "Dark Age" that set Europe back a millennium. In contrast, German and English historians have tended to see Roman–Barbarian interaction as the replacement of a "tired, effete and decadent Mediterranean civilization" with a "more virile, martial, Nordic one".
The scholar Guy Halsall has seen the barbarian movement as the result of the fall of the Roman Empire, not its cause. Archaeological discoveries have confirmed that Germanic and Slavic tribes were settled agriculturalists who were probably merely "drawn into the politics of an empire already falling apart for quite a few other causes". Goffart argues that the process of settlement was connected to ''hospitalitas'', the Roman practice of quartering soldiers among the civilian population. The Romans, by granting land and the right to levy taxes to allied (Germanic) armies, hoped to reduce the financial burdens of the empire. The Crisis of the Third Century caused significant changes within the Roman Empire in both its western and its eastern portions. In particular, economic fragmentation removed many of the political, cultural and economic forces that had held the empire together.
The rural population in Roman provinces became distanced from the metropolis, and there was little to differentiate them from other peasants across the Roman frontier. In addition, Rome increasingly used foreign mercenaries to defend itself. That "barbarisation" parallelled changes within Barbaricum
Barbaricum (from the gr, Βαρβαρικόν, "foreign", "barbarian") is a geographical name used by historical and archaeological experts to refer to the vast area of barbarian-occupied territory that lay, in Roman Empire, Roman times, beyond ...
. To this end, noted linguist Dennis Howard Green wrote, "the first centuries of our era witness not merely a progressive Romanisation of barbarian society, but also an undeniable barbarisation of the Roman world."
For example, the Roman Empire played a vital role in building up barbarian groups along its frontier. Propped up with imperial support and gifts, the armies of allied barbarian chieftains served as buffers against other, hostile, barbarian groups. The disintegration of Roman economic power weakened groups that had come to depend on Roman gifts for the maintenance of their own power. The arrival of the Huns helped prompt many groups to invade the provinces for economic reasons.
The nature of the barbarian takeover of former Roman provinces varied from region to region. For example, in Aquitaine, the provincial administration was largely self-reliant. Halsall has argued that local rulers simply "handed over" military rule to the Ostrogoths, acquiring the identity of the newcomers. In Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only durin ...
, the collapse of imperial rule resulted in anarchy: the Franks and Alemanni were pulled into the ensuing "power vacuum", resulting in conflict. In Spain, local aristocrats maintained independent rule for some time, raising their own armies against the Vandals. Meanwhile, the Roman withdrawal from lowland England resulted in conflict between Saxons and the Brittonic chieftains (whose centres of power retreated westward as a result). The Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
attempted to maintain control of the Balkan provinces despite a thinly-spread imperial army relying mainly on local militias and an extensive effort to refortify the Danubian ''limes
Limes may refer to:
* the plural form of lime (disambiguation)
* the Latin word for ''limit'' which refers to:
** Limes (Roman Empire)
(Latin, singular; plural: ) is a modern term used primarily for the Germanic border defence or delimitin ...
''. The ambitious fortification efforts collapsed, worsening the impoverished conditions of the local populace and resulting in colonization by Slavic warriors and their families.
Halsall and Noble have argued that such changes stemmed from the breakdown in Roman political control, which exposed the weakness of local Roman rule. Instead of large-scale migrations, there were military takeovers by small groups of warriors and their families, who usually numbered only in the tens of thousands. The process involved active, conscious decision-making by Roman provincial populations.
The collapse of centralized control severely weakened the sense of Roman identity in the provinces, which may explain why the provinces then underwent dramatic cultural changes even though few barbarians settled in them.
Ultimately, the Germanic groups in the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
were accommodated without "dispossessing or overturning indigenous society", and they maintained a structured and hierarchical (but attenuated) form of Roman administration.
Ironically, they lost their unique identity as a result of such an accommodation and were absorbed into Latinhood. In contrast, in the east, Slavic tribes maintained a more "spartan and egalitarian" existence bound to the land "even in times when they took their part in plundering Roman provinces". Their organizational models were not Roman, and their leaders were not normally dependent on Roman gold for success. Thus they arguably had a greater effect on their region than the Goths, the Franks or the Saxons had on theirs.
Ethnicity
Based on the belief that particular types of artifacts, elements of personal adornment generally found in a funerary context, are thought to indicate the ethnicity of the person buried, the "Culture-History" school of archaeology assumed that archaeological cultures represent the ' (homeland) of tribal polities named in historical sources. As a consequence, the shifting extensions of material cultures were interpreted as the expansion of peoples. Influenced by constructionism, process-driven archaeologists rejected the culture-historical doctrine and marginalized the discussion of ethnicity altogether and focused on the intragroup dynamics that generated such material remains. Moreover, they argued that adoption of new cultures could occur through trade or internal political developments rather than only military takeovers.Depiction in media
* '' Terry Jones' Barbarians'', a 4-part TV documentary series first broadcast on BBC 2 in 2006 * '' Rome: Total War: Barbarian Invasion'' and '' Total War: Attila'', strategy games by ''The Creative Assembly
The Creative Assembly Limited ( trade name: Creative Assembly) is a British video game developer based in Horsham, founded in 1987 by Tim Ansell. In its early years, the company worked on porting games to MS-DOS from Amiga and ZX Spectrum pla ...
''
* '' Barbarians (miniseries)'', a documentary miniseries on The History Channel
History (formerly The History Channel from January 1, 1995 to February 15, 2008, stylized as HISTORY) is an American pay television network and flagship channel owned by A&E Networks, a joint venture between Hearst Communications and the Dis ...
See also
* Bond event * Dark Ages (historiography) * Environmental migrant * Genetic history of the British Isles *Late Antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English has ...
* Medieval demography
* Migration Period art
* Slavic migration
* Five Barbarians and Sixteen Kingdoms
The Sixteen Kingdoms (), less commonly the Sixteen States, was a chaotic period in Chinese history from AD 304 to 439 when northern China fragmented into a series of short-lived dynastic states. The majority of these states were founded by ...
* Hephthalite Empire
* Immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, a ...
* Turkic migration
* Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
References
Bibliography
* * * Börm, Henning (2013), ''Westrom. Von Honorius bis Justinian'', Kohlhammer Verlag, * * * * Friedrich, Matthias and Harland, James M., eds. (2020): Interrogating the "Germanic": A Category and its Use in Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. De Gruyter. . * * * * * * * * * Kleineberg, A.; Marx, Chr.; Knobloch, E.; Lelgemann, D.: Germania und die Insel Thule. Die Entschlüsselung von Ptolemaios' "Atlas der Oikumene". WBG 2010. . * * * * * *External links
* {{Authority control Historiography Germanic history Indo-European history Germanic archaeology 1st millennium in Europe 1st millennium in Asia 1st millennium in Africa Historical eras Dark ages