Mediastinal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The mediastinum (from ;: mediastina) is the central compartment of the
 The mediastinum lies within the
The mediastinum lies within the
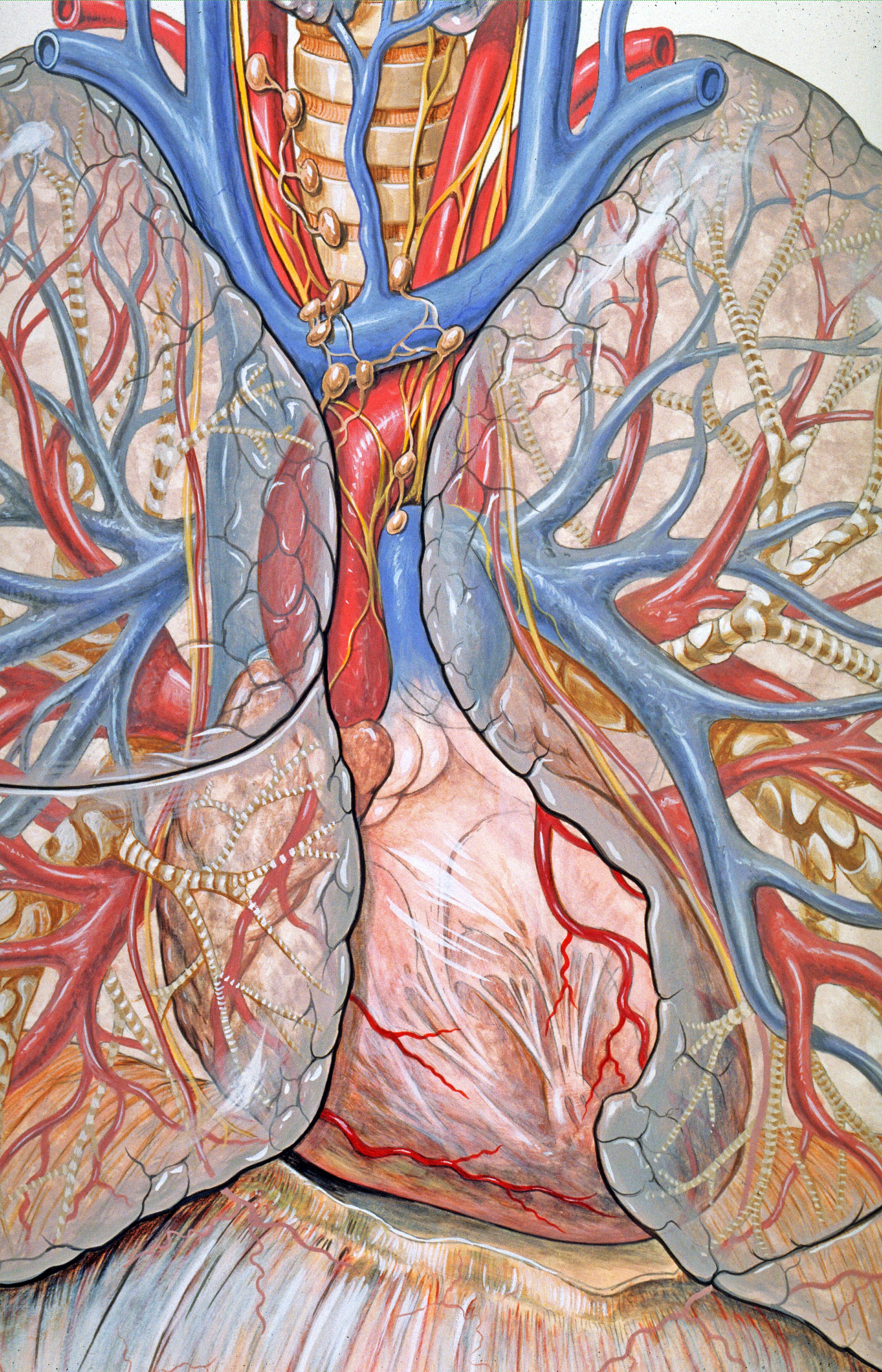 ;Contents
* muscles
** origins of the Sternohyoidei and Sternothyreoidei
** lower ends of the Longi colli
* arteries
**
;Contents
* muscles
** origins of the Sternohyoidei and Sternothyreoidei
** lower ends of the Longi colli
* arteries
**
File:Gray968.png , A transverse section of the
 The mediastinum is frequently the site of involvement of various
The mediastinum is frequently the site of involvement of various
thoracic cavity
The thoracic cavity (or chest cavity) is the chamber of the body of vertebrates that is protected by the thoracic wall (rib cage and associated skin, muscle, and fascia). The central compartment of the thoracic cavity is the mediastinum. Ther ...
. Surrounded by loose connective tissue
Loose connective tissue, also known as areolar tissue, is a cellular connective tissue with thin and relatively sparse collagen fibers. They have a semi-fluid matrix with lesser proportions of fibers. Its ground substance occupies more vol ...
, it is a region that contains vital organs and structures within the thorax
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main di ...
, mainly the heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
and its vessels, the esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
, the trachea
The trachea (: tracheae or tracheas), also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals' lungs. The trachea extends from ...
, the vagus
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve (CN X), plays a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating involuntary functions within the human body. This nerve carries both sensory and motor fiber ...
, phrenic and cardiac nerves, the thoracic duct
In human anatomy, the thoracic duct (also known as the ''left lymphatic duct'', ''alimentary duct'', ''chyliferous duct'', and ''Van Hoorne's canal'') is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system (the other being the right lymph ...
, the thymus
The thymus (: thymuses or thymi) is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus ...
and the lymph nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped Organ (anatomy), organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphoc ...
of the central chest.
Anatomy
thorax
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main di ...
and is enclosed on the right and left by pleurae
The pleurae (: pleura) are the two flattened closed sacs filled with pleural fluid, each ensheathing each lung and lining their surrounding tissues, locally appearing as two opposing layers of serous membrane separating the lungs from the media ...
. It is surrounded by the chest wall in front, the lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
s to the sides and the spine
Spine or spinal may refer to:
Science Biology
* Spinal column, also known as the backbone
* Dendritic spine, a small membranous protrusion from a neuron's dendrite
* Thorns, spines, and prickles, needle-like structures in plants
* Spine (zoology), ...
at the back. It extends from the sternum
The sternum (: sternums or sterna) or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major bl ...
in front to the vertebral column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmente ...
behind. It contains all the organs of the thorax except the lungs. It is continuous with the loose connective tissue of the neck
The neck is the part of the body in many vertebrates that connects the head to the torso. It supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that transmit sensory and motor information between the brain and the rest of the body. Addition ...
.
The mediastinum can be divided into an upper (or superior) and lower (or inferior) part:
* The superior mediastinum starts at the superior thoracic aperture and ends at the thoracic plane
The mediastinum (from ;: mediastina) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is a region that contains vital organs and structures within the thorax, mainly the heart and its vessels, the es ...
.
* The inferior mediastinum from this level to the diaphragm. This lower part is subdivided into three regions, all relative to the pericardium
The pericardium (: pericardia), also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong inelastic connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), ...
– the anterior mediastinum being in front of the pericardium, the ''middle mediastinum'' contains the pericardium and its contents, and the ''posterior mediastinum'' being behind the pericardium.
Anatomist
Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old scien ...
s, surgeon
In medicine, a surgeon is a medical doctor who performs surgery. Even though there are different traditions in different times and places, a modern surgeon is a licensed physician and received the same medical training as physicians before spec ...
s, and clinical radiologists compartmentalize the mediastinum differently. For instance, in the radiological scheme of Felson, there are only three compartments (anterior, middle, and posterior), and the heart is part of the middle (inferior) mediastinum.
Thoracic plane
The transverse thoracic plane, thoracic plane, plane of Louis or plane of Ludwig is an importantanatomical plane
An anatomical plane is a hypothetical plane used to transect the body, in order to describe the location of structures or the direction of movements.
In human anatomy and non-human anatomy, four principal planes are used: the median plane, ...
at the level of the sternal angle
The sternal angle (also known as the angle of Lewis, angle of Louis, angle of Ludovic, or manubriosternal junction) is the projecting angle formed between the manubrium and body of a sternum at their junction at the manubriosternal joint.
The ster ...
and the T4/T5 intervertebral disc
An intervertebral disc (British English), also spelled intervertebral disk (American English), lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the ver ...
. It serves as an imaginary boundary that separates the superior and inferior mediastinum.
A number of important anatomical structures and transitions occur at the level of the thoracic plane, including:
* The carina
Carina may refer to:
Places
Australia
* Carina, Queensland, a suburb in Brisbane
* Carina Heights, Queensland, a suburb in Brisbane
* Carina, Victoria, a locality in Mildura
Serbia
* Carina, Osečina, a village in the Kolubara District
...
l bifurcation of the trachea
The trachea (: tracheae or tracheas), also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals' lungs. The trachea extends from ...
into the left and right main bronchi
A bronchus ( ; : bronchi, ) is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. Thes ...
.
* The left recurrent laryngeal nerve branching off the left vagus nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve (CN X), plays a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating involuntary functions within the human body. This nerve carries both sensory and motor fibe ...
and hooking under the ligamentum arteriosum
The ligamentum arteriosum (arterial ligament), also known as Botallo's ligament, Harvey's ligament, and Botallo's duct, is a small ligament attaching the aorta to the pulmonary artery. It serves no function in adults but is the remnant of the duct ...
between the aortic arch
The aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch () is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea.
Structure
The aorta begins ...
above and the pulmonary trunk
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and t ...
below.
* The starting of the cardiac plexus.
* The azygos vein arching over the right main bronchus and joining into the superior vena cava
The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. It is a large-diameter (24 mm) short length vei ...
.
* The thoracic duct
In human anatomy, the thoracic duct (also known as the ''left lymphatic duct'', ''alimentary duct'', ''chyliferous duct'', and ''Van Hoorne's canal'') is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system (the other being the right lymph ...
crossing the midline from right to left behind the esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
* The end of the pretracheal and prevertebral fascia
The prevertebral fascia (also known as prevertebral layer of cervical fascia or vertebral fascia) is the layer of deep cervical fascia that surrounds the vertebral column. It is the deepest layer of deep cervical fascia.
It encloses the sympathet ...
e.
Superior mediastinum
The superior mediastinum is bounded: * ''superiorly'' by the thoracic inlet, the upper opening of thethorax
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main di ...
;
* ''inferiorly'' by the transverse thoracic plane. which is an imaginary plane passing from the sternal angle anteriorly to the lower border of the body of the 4th thoracic vertebra posteriorly;
* ''laterally'' by the pleurae
The pleurae (: pleura) are the two flattened closed sacs filled with pleural fluid, each ensheathing each lung and lining their surrounding tissues, locally appearing as two opposing layers of serous membrane separating the lungs from the media ...
;
* ''anteriorly'' by the manubrium
The sternum (: sternums or sterna) or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, human lung, lungs, and ma ...
of the sternum;
* ''posteriorly'' by the first four thoracic vertebral bodies.
 ;Contents
* muscles
** origins of the Sternohyoidei and Sternothyreoidei
** lower ends of the Longi colli
* arteries
**
;Contents
* muscles
** origins of the Sternohyoidei and Sternothyreoidei
** lower ends of the Longi colli
* arteries
** aortic arch
The aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch () is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea.
Structure
The aorta begins ...
** brachiocephalic artery
The brachiocephalic artery, brachiocephalic trunk, or innominate artery is an artery of the mediastinum that supplies blood to the right arm, head, and neck.
It is the first branch of the aortic arch. Soon after it emerges, the brachiocephalic ...
** thoracic portions of the left common carotid and the left subclavian
* veins
** brachiocephalic veins and
** upper half of the superior vena cava
The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. It is a large-diameter (24 mm) short length vei ...
** left highest intercostal vein
* nerves
** vagus nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve (CN X), plays a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating involuntary functions within the human body. This nerve carries both sensory and motor fibe ...
** cardiac nerve
** superficial and deep cardiac plexuses
** phrenic nerve
The phrenic nerve is a mixed nerve that originates from the C3–C5 spinal nerves in the neck. The nerve is important for breathing because it provides exclusive motor control of the diaphragm, the primary muscle of respiration. In humans, t ...
** left recurrent laryngeal nerve
The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN), also known as nervus recurrens, is a branch of the vagus nerve ( cranial nerve X) that supplies all the intrinsic muscles of the larynx, with the exception of the cricothyroid muscles. There are two recur ...
* trachea
The trachea (: tracheae or tracheas), also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals' lungs. The trachea extends from ...
with paratracheal and tracheobronchial lymph nodes
* esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
* thoracic duct
In human anatomy, the thoracic duct (also known as the ''left lymphatic duct'', ''alimentary duct'', ''chyliferous duct'', and ''Van Hoorne's canal'') is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system (the other being the right lymph ...
* remains of the thymus
The thymus (: thymuses or thymi) is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus ...
* some lymph glands
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system and complementary to the circulatory system. It con ...
* anterior longitudinal ligament
Inferior mediastinum
Anterior inferior mediastinum
Is bounded: * ''laterally'' by thepleurae
The pleurae (: pleura) are the two flattened closed sacs filled with pleural fluid, each ensheathing each lung and lining their surrounding tissues, locally appearing as two opposing layers of serous membrane separating the lungs from the media ...
;
* ''posteriorly'' by the pericardium
The pericardium (: pericardia), also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong inelastic connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), ...
;
* ''anteriorly'' by the sternum
The sternum (: sternums or sterna) or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major bl ...
, the left transversus thoracis and the fifth, sixth, and seventh left costal cartilages.
;Contents
* A quantity of loose areolar tissue
* Some lymphatic vessels
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessel ...
which ascend from the convex surface of the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
* Two or three anterior mediastinal lymph nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped Organ (anatomy), organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphoc ...
* The small mediastinal branches of the internal thoracic artery
The internal thoracic artery (ITA), also known as the internal mammary artery, is an artery that supplies the anterior chest wall and the breasts. It is a paired artery, with one running along each side of the sternum, to continue after its bifurc ...
* Thymus
The thymus (: thymuses or thymi) is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus ...
(involuted in adults)
*superior and inferior sternopericardial ligaments
Middle inferior mediastinum
Bounded:pericardial sac
The pericardium (: pericardia), also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong inelastic connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), a ...
– It contains the vital organs and is classified into the serous and fibrous pericardium.
;Contents
* the heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
enclosed in the pericardium
The pericardium (: pericardia), also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong inelastic connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), ...
* the ascending aorta
* the lower half of the superior vena cava
The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. It is a large-diameter (24 mm) short length vei ...
with the azygos vein opening into it
* the bifurcation of the trachea and the two bronchi
A bronchus ( ; : bronchi, ) is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. Thes ...
* the pulmonary trunk
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and t ...
dividing into its two branches
* the right and left pulmonary veins
The pulmonary veins are the veins that transfer oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. The largest pulmonary veins are the four ''main pulmonary veins'', two from each lung that drain into the left atrium of the heart. The pulmonary ve ...
* the phrenic nerves
* some bronchial lymphatic glands
* pericardiacophrenic vessels
Posterior inferior mediastinum
Is bounded: * Anteriorly by (from above downwards): bifurcation oftrachea
The trachea (: tracheae or tracheas), also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals' lungs. The trachea extends from ...
; pulmonary vessels; fibrous pericardium and posterior sloping surface of diaphragm
* Inferiorly by the thoracic surface of the diaphragm (below);
* Superiorly by the transverse thoracic plane;
* Posteriorly by the bodies of the vertebral column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmente ...
from the lower border of the fifth to the twelfth thoracic vertebra
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebra (anatomy), vertebrae of intermediate size between the ce ...
(behind);
* Laterally by the mediastinal pleura (on either side).
* artery
** thoracic part of the descending aorta
In human anatomy, the descending aorta is part of the aorta, the largest artery in the body. The descending aorta begins at the aortic arch and runs down through the chest and abdomen. The descending aorta anatomically consists of two portions o ...
* veins
** azygos vein
** the hemiazygos vein and the accessory hemiazygos vein
* nerves
** vagus nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve (CN X), plays a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating involuntary functions within the human body. This nerve carries both sensory and motor fibe ...
** splanchnic nerves
The splanchnic nerves are paired visceral nerves (nerves that contribute to the innervation of the internal organs), carrying fibers of the autonomic nervous system ( visceral efferent fibers) as well as sensory fibers from the organs ( visceral ...
** sympathetic chain
The sympathetic trunk (sympathetic chain, gangliated cord) is a paired bundle of nerve fibers that run from the base of the skull to the coccyx. It is a major component of the sympathetic nervous system.
Structure
The sympathetic trunk lies just ...
* esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
* thoracic duct
In human anatomy, the thoracic duct (also known as the ''left lymphatic duct'', ''alimentary duct'', ''chyliferous duct'', and ''Van Hoorne's canal'') is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system (the other being the right lymph ...
* some lymph glands
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system and complementary to the circulatory system. It con ...
thorax
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main di ...
, showing the contents of the middle and the posterior mediastinum.
Clinical significance
 The mediastinum is frequently the site of involvement of various
The mediastinum is frequently the site of involvement of various tumors
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
:
* ''Anterior mediastinum'': substernal thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by ...
goiters, lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). The name typically refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged lymph node ...
, thymoma, and teratoma
A teratoma is a neoplasia, tumor made up of several types of biological tissue, tissue, such as hair, muscle, Human tooth, teeth, or bone. Teratomata typically form in the tailbone (where it is known as a sacrococcygeal teratoma), ovary, or test ...
.
* ''Middle mediastinum'': lymphadenopathy, metastatic disease such as from small cell carcinoma from the lung.
* ''Posterior mediastinum'': Neurogenic tumors, either from the nerve sheath (mostly benign) or elsewhere (mostly malignant).
Mediastinitis is inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
of the tissues in the mediastinum, usually bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
l and due to rupture of organs in the mediastinum. As the infection can progress very quickly, this is a serious condition.
Pneumomediastinum is the presence of air in the mediastinum, which in some cases can lead to pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and dyspnea, shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve is ...
, pneumoperitoneum, and pneumopericardium if left untreated. However, that does not always occur and sometimes those conditions are actually the cause, not the result, of pneumomediastinum. These conditions frequently accompany Boerhaave syndrome, or spontaneous esophageal rupture.
Widening
''Widened mediastinum/mediastinal widening'' is where the mediastinum has a width greater than 6 cm on an upright PAchest X-ray
A chest radiograph, chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film is a Projectional radiography, projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common fi ...
or 8 cm on supine AP chest film.
A widened mediastinum can be indicative of several pathologies:
* aortic aneurysm
An aortic aneurysm is an enlargement (dilatation) of the aorta to greater than 1.5 times normal size. Typically, there are no symptoms except when the aneurysm dissects or ruptures, which causes sudden, severe pain in the abdomen and lower back ...
* aortic dissection
* aortic unfolding
* aortic rupture
* hilar lymphadenopathy
* anthrax inhalation - a widened mediastinum was found in 7 of the first 10 victims infected by anthrax (''Bacillus anthracis'') in 2001.
*esophageal rupture
Esophageal rupture, also known as Boerhaave syndrome, is a rupture of the esophageal wall. Iatrogenic causes account for approximately 56% of esophageal perforations, usually due to medical instrumentation such as an endoscopy or paraesophageal s ...
- presents usually with pneumomediastinum and pleural effusion
A pleural effusion is accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural space, the potential space that surrounds each lung.
Under normal conditions, pleural fluid is secreted by the parietal pleural capillaries at a rate of 0.6 millilitre per kilog ...
. It is diagnosed with water-soluble swallowed contrast.
* mediastinal mass
* mediastinitis
*cardiac tamponade
Cardiac tamponade, also known as pericardial tamponade (), is a compression of the heart due to pericardial effusion (the build-up of pericardial fluid in the pericardium, sac around the heart). Onset may be rapid or gradual. Symptoms typically i ...
*pericardial effusion
A pericardial effusion is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pericardial cavity. The pericardium is a two-part membrane surrounding the heart: the outer fibrous Connective tissue, connective membrane and an inner two-layered serous membrane ...
* thoracic vertebrae fractures in trauma patients.
See also
* Mediastinum testis (unrelated structure in thescrotum
In most terrestrial mammals, the scrotum (: scrotums or scrota; possibly from Latin ''scortum'', meaning "hide" or "skin") or scrotal sac is a part of the external male genitalia located at the base of the penis. It consists of a sac of skin ...
)
* Mediastinal germ cell tumor
* Mediastinitis
* Mediastinal tumor
* List of anatomy mnemonics#Mediastinum
References
External links
* – "Divisions of the mediastinum." * – "The anatomical divisions of the inferior mediastinum." * – "Subdivisions of the Thoracic Cavity" {{Authority control Thoracic cavity