Market Depth on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
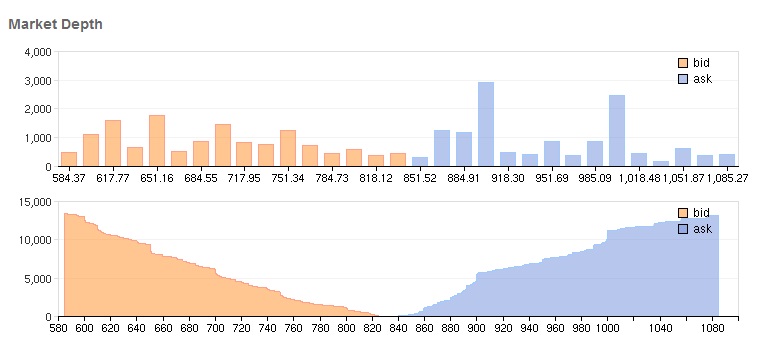 In
In
Investopedia *Price movement restrictions. Most major financial markets do not allow completely free exchange of the products they trade, but instead restrict price movement in well-intentioned ways. These include session price change limits on major
World Bank GFDR Report
{{Stock market Financial markets
 In
In finance
Finance refers to monetary resources and to the study and Academic discipline, discipline of money, currency, assets and Liability (financial accounting), liabilities. As a subject of study, is a field of Business administration, Business Admin ...
, market depth is a real-time list displaying the quantity to be sold versus unit price. The list is organized by price level and is reflective of real-time market activity. Mathematically, it is the size of an order needed to move the market
Market is a term used to describe concepts such as:
*Market (economics), system in which parties engage in transactions according to supply and demand
*Market economy
*Marketplace, a physical marketplace or public market
*Marketing, the act of sat ...
price by a given amount. If the market is ''deep'', a large order is needed to change the price.
Factors influencing market depth
*Tick size
In financial markets, the tick size is the smallest price increment in which the prices are quoted. The meaning of the term varies depending on whether stocks, bonds, or futures are being quoted.
Bonds
U.S. mortgage bonds and certain corporate bo ...
. This refers to the minimum price increment at which trades may be made on the market. The major stock market
A stock market, equity market, or share market is the aggregation of buyers and sellers of stocks (also called shares), which represent ownership claims on businesses; these may include ''securities'' listed on a public stock exchange a ...
s in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
went through a process of decimalisation
Decimalisation or decimalization (see American and British English spelling differences, spelling differences) is the conversion of a system of currency or of weights and measures to units related by Power of 10, powers of 10.
Most countries have ...
in April 2001. This switched the minimum increment from a sixteenth to a one hundredth of a dollar. This decision improved market depth.Market DepthInvestopedia *Price movement restrictions. Most major financial markets do not allow completely free exchange of the products they trade, but instead restrict price movement in well-intentioned ways. These include session price change limits on major
commodity
In economics, a commodity is an economic goods, good, usually a resource, that specifically has full or substantial fungibility: that is, the Market (economics), market treats instances of the good as equivalent or nearly so with no regard to w ...
markets and program trading
Program trading is a type of trading in Security (finance), securities, usually consisting of baskets of fifteen stocks or more that are executed by a computer program simultaneously based on predetermined conditions. Program trading is often us ...
curbs on the NYSE
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE, nicknamed "The Big Board") is an American stock exchange in the Financial District, Manhattan, Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It is the List of stock exchanges, largest stock excha ...
, which disallow certain large basket trades after the Dow Jones Industrial Average
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), Dow Jones, or simply the Dow (), is a stock market index of 30 prominent companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States.
The DJIA is one of the oldest and most commonly followed equity indice ...
has moved up or down 200 points in a session.
*Trading restrictions. These include futures contract
In finance, a futures contract (sometimes called futures) is a standardized legal contract to buy or sell something at a predetermined price for delivery at a specified time in the future, between parties not yet known to each other. The item tr ...
and options position limits as well as the widely used uptick rule
The uptick rule is a trading restriction that states that short selling a stock is allowed only on an uptick. For the rule to be satisfied, the short must be either at a price above the last traded price of the security, or at the last traded pric ...
for US stocks. These prevent market participants from adding to depth when they might otherwise choose to do so.
*Allowable leverage. Major markets and governing bodies typically set minimum margin requirement
In finance, margin is the collateral that a holder of a financial instrument has to deposit with a counterparty (most often their broker or an exchange) to cover some or all of the credit risk the holder poses for the counterparty. This risk ...
s for trading various products. While this may act to stabilize the marketplace, it decreases the market depth simply because participants otherwise willing to take on very high leverage cannot do so without providing more capital.
*Market transparency. While the latest bid or ask price is usually available for most participants, additional information about the size of these offers and pending bids or offers that are not the best are sometimes hidden for reasons of technical complexity or simplicity. This decrease in available information can affect the willingness of participants to add to market depth.
In some cases, the term refers to financial data feeds available from exchanges or brokers
A broker is a person or entity that arranges transactions between a buyer and a seller. This may be done for a commission when the deal is executed. A broker who also acts as a seller or as a buyer becomes a principal party to the deal. Neither ...
. An example would be NASDAQ Level II quote data.
References
External links
World Bank GFDR Report
{{Stock market Financial markets