Mariner program on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Mariner program was conducted by the American space agency
 All Mariner spacecraft were based on a hexagonal or octagonal bus, which housed all of the electronics, and to which all components were attached, such as antennae, cameras, propulsion, and power sources. Mariner 2 was based on the Ranger Lunar probe. All of the Mariners launched after Mariner 2 had four solar panels for power, except for
All Mariner spacecraft were based on a hexagonal or octagonal bus, which housed all of the electronics, and to which all components were attached, such as antennae, cameras, propulsion, and power sources. Mariner 2 was based on the Ranger Lunar probe. All of the Mariners launched after Mariner 2 had four solar panels for power, except for


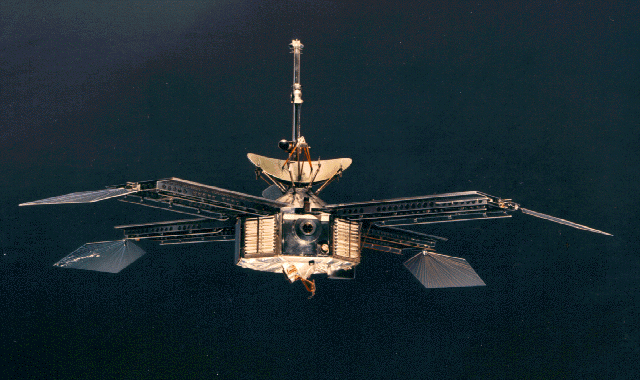 Sisterships Mariner 3 and
Sisterships Mariner 3 and
 The Mariner 5 spacecraft was launched to
The Mariner 5 spacecraft was launched to
 Mariners 6 and 7 were identical teammates in a two-spacecraft mission to Mars. Mariner 6 was launched on February 24, 1969, followed by Mariner 7 on March 21, 1969. They flew over the equator and southern hemisphere of the planet
Mariners 6 and 7 were identical teammates in a two-spacecraft mission to Mars. Mariner 6 was launched on February 24, 1969, followed by Mariner 7 on March 21, 1969. They flew over the equator and southern hemisphere of the planet
NASA – This Month in NASA History: Mariner 9
, November 29, 2011 – Vol. 4, Issue 9
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
to explore other planet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets b ...
s. Between 1962 and late 1973, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a Federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center (FFRDC) in La Cañada Flintridge, California, Crescenta Valley, United States. Founded in 1936 by Cali ...
(JPL) designed and built 10 robotic
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
interplanetary probes named Mariner to explore the inner Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
– visiting the planets Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
, Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
and Mercury for the first time, and returning to Venus and Mars for additional close observations.
The program included a number of interplanetary firsts, including the first successful planetary flyby, the planetary orbiter, and the first gravity assist
A gravity assist, gravity assist maneuver, swing-by, or generally a gravitational slingshot in orbital mechanics, is a type of spaceflight flyby (spaceflight), flyby which makes use of the relative movement (e.g. orbit around the Sun) and gra ...
maneuver. Of the 10 vehicles in the Mariner series, seven were successful, forming the starting point for many subsequent NASA/JPL space probe programs. The planned Mariner Jupiter-Saturn vehicles were adapted into the Voyager program
The Voyager program is an American scientific program that employs two interstellar probes, ''Voyager 1'' and ''Voyager 2''. They were launched in 1977 to take advantage of a favorable planetary alignment to explore the two gas giants Jupiter ...
, while the Viking program
The ''Viking'' program consisted of a pair of identical American space probes, ''Viking 1'' and ''Viking 2'' both launched in 1975, and landed on Mars in 1976. The mission effort began in 1968 and was managed by the NASA Langley Research Cent ...
orbiters were enlarged versions of the Mariner 9
Mariner 9 (Mariner Mars '71 / Mariner-I) was a robotic spacecraft that contributed greatly to the exploration of Mars and was part of the NASA Mariner program. Mariner 9 was launched toward Mars on May 30, 1971, from Spaceport Florida Launch Comp ...
spacecraft. Later Mariner-based spacecraft include Galileo
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642), commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei ( , , ) or mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a poly ...
and Magellan, while the second-generation Mariner Mark II series evolved into the Cassini–Huygens
''Cassini–Huygens'' ( ), commonly called ''Cassini'', was a space research, space-research mission by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI) to send a space probe to study the planet Saturn and its system, i ...
probe.
The total cost of the Mariner program was approximately $554 million.
Early concept
The Mariner program began in 1960 with a series of JPL mission studies for small-scale, frequent exploration of the nearest planets. They were to take advantage of the soon-to-be-available Atlas launch vehicles as well as the developing capability of JPL's Deep Space Instrumentation Facility (later named the Deep Space Network), a global network of ground stations designed to communicate with spacecraft in deep space. The name of the Mariner program was decided in "May 1960 – at the suggestion of Edgar M. Cortright" to have the "planetary mission probes ... patterned after nautical terms, to convey 'the impression of travel to great distances and remote lands.'" That "decision was the basis for naming Mariner, Ranger, Surveyor, and Viking probes." Each spacecraft was to carry solar panels that would be pointed toward the Sun and a dish antenna that would be pointed at Earth. Each would also carry a host of scientific instruments. Some of the instruments, such as cameras, would need to be pointed at the target body it was studying. Other instruments were non-directional and studied phenomena such as magnetic fields and charged particles. JPL engineers proposed to make the Mariners "three-axis-stabilized," meaning that unlike other space probes they would not spin. Each of the Mariner projects was designed to have two spacecraft launched on separate rockets, in case of difficulties with the nearly untried launch vehicles. Mariner 1, Mariner 3, and Mariner 8 were in fact lost during launch, but their backups were successful. No Mariners were lost in later flight to their destination planets or before completing their scientific missions.Basic layout
 All Mariner spacecraft were based on a hexagonal or octagonal bus, which housed all of the electronics, and to which all components were attached, such as antennae, cameras, propulsion, and power sources. Mariner 2 was based on the Ranger Lunar probe. All of the Mariners launched after Mariner 2 had four solar panels for power, except for
All Mariner spacecraft were based on a hexagonal or octagonal bus, which housed all of the electronics, and to which all components were attached, such as antennae, cameras, propulsion, and power sources. Mariner 2 was based on the Ranger Lunar probe. All of the Mariners launched after Mariner 2 had four solar panels for power, except for Mariner 10
''Mariner 10'' was an American Robotic spacecraft, robotic space probe launched by NASA on 3 November 1973, to fly by the planets Mercury (planet), Mercury and Venus. It was the first spacecraft to perform flybys of multiple planets.
''Marin ...
, which had two. Additionally, all except Mariner 1
Mariner 1, built to conduct the first American planetary flyby of Venus, was the first spacecraft of NASA's interplanetary Mariner program. Developed by Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and originally planned to be a purpose-built probe launched summ ...
, Mariner 2 and Mariner 5 had TV cameras.
The first five Mariners were launched on Atlas-Agena
The Atlas-Agena was an American expendable launch system derived from the SM-65 Atlas missile. It was a member of the Atlas (rocket family), Atlas family of rockets, and was launched 109 times between 1960 and 1978. It was used to launch the first ...
rocket
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely ...
s, while the last five used the Atlas-Centaur
The Atlas-Centaur was a United States expendable launch vehicle derived from the SM-65 Atlas D missile. The vehicle featured a Centaur (rocket stage), Centaur upper stage, the first such stage to use high-performance liquid hydrogen as fuel. La ...
. All Mariner-based probes after Mariner 10
''Mariner 10'' was an American Robotic spacecraft, robotic space probe launched by NASA on 3 November 1973, to fly by the planets Mercury (planet), Mercury and Venus. It was the first spacecraft to perform flybys of multiple planets.
''Marin ...
used the Titan IIIE, Titan IV uncrewed rockets or the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable launch system, reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. ...
with a solid-fueled Inertial Upper Stage and multiple planetary flybys.
Mariners
The Mariners were all relatively small robotic explorers, each launched on an Atlas rocket with either an Agena or Centaur upper-stage booster, and weighing less than half a ton (without onboard rocket propellant). Each of their missions was completed within a few months to a year or two, though one of them outlived its original mission and continued to send useful scientific data for three years.Mariners 1 and 2


Mariner 1
Mariner 1, built to conduct the first American planetary flyby of Venus, was the first spacecraft of NASA's interplanetary Mariner program. Developed by Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and originally planned to be a purpose-built probe launched summ ...
(P-37) and Mariner 2 (P-38) were two deep-space probes making up NASA's Mariner-R project. The primary goal of the project was to develop and launch two spacecraft sequentially to the near vicinity of Venus, receive communications from the spacecraft and to perform radiometric temperature measurements of the planet. A secondary objective was to make interplanetary magnetic field and/or particle measurements on the way to, and in the vicinity of, Venus. Mariner 1 (designated Mariner R-1) was launched on July 22, 1962, but was destroyed approximately 5 minutes after liftoff by the Air Force Range Safety Officer when its malfunctioning Atlas-Agena
The Atlas-Agena was an American expendable launch system derived from the SM-65 Atlas missile. It was a member of the Atlas (rocket family), Atlas family of rockets, and was launched 109 times between 1960 and 1978. It was used to launch the first ...
rocket went off course. Mariner 2 (designated Mariner R-2) was launched on August 27, 1962, sending it on a 3½-month flight to Venus. The mission was a success, and Mariner 2 became the first spacecraft to have flown by another planet.
On the way it measured for the first time the solar wind, a constant stream of charged particles flowing outward from the Sun. It also measured interplanetary dust, which turned out to be more scarce than predicted. In addition, Mariner 2 detected high-energy charged particles coming from the Sun, including several brief solar flares, as well as cosmic rays from outside the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
. As it flew by Venus on December 14, 1962, Mariner 2 scanned the planet with infrared and microwave radiometers, revealing that Venus has cool clouds and an extremely hot surface (because the bright, opaque clouds hide the planet's surface, Mariner 2 was not outfitted with a camera).
* Mission: Venus flyby
* Mass: 203 kg (446 lb)
* Sensors: microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300&n ...
and infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
radiometers, cosmic dust, solar plasma and high-energy radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
, magnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
s
Status:
* Mariner 1 – Destroyed shortly after liftoff.
* Mariner 2 – Defunct after successful mission, occupies a heliocentric orbit
A heliocentric orbit (also called circumsolar orbit) is an orbit around the barycenter of the Solar System, which is usually located within or very near the surface of the Sun. All planets, comets, and asteroids in the Solar System, and the Sun ...
.
Mariners 3 and 4
 Sisterships Mariner 3 and
Sisterships Mariner 3 and Mariner 4
Mariner 4 (Mariner C-3, together with Mariner 3 known as Mariner-Mars 1964) was the Mariner program, fourth in a series of spacecraft intended for planetary exploration in a flyby mode. It was designed to conduct closeup scientific observations ...
were Mars flyby missions.
Mariner 3 was launched on November 5, 1964, but the shroud encasing the spacecraft atop its rocket failed to open properly and Mariner 3 did not get to Mars.
Mariner 4, launched on November 28, 1964, was the first successful flyby of the planet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets b ...
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
and gave the first glimpse of Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
at close range.
The spacecraft flew past Mars on July 14, 1965, collecting the first close-up photographs of another planet. The pictures, played back from a small tape recorder over a long period, showed lunar-type impact craters (just beginning to be photographed at close range from the Moon), some of them touched with frost in the chill Martian evening. The Mariner 4 spacecraft, expected to survive something more than the eight months to Mars encounter, actually lasted about three years in solar orbit, continuing long-term studies of the solar wind environment and making coordinated measurements with Mariner 5, a sister ship launched to Venus in 1967.
* Mission: Mars flyby
* Mass: 261 kg (575 lb)
* Sensors: camera
A camera is an instrument used to capture and store images and videos, either digitally via an electronic image sensor, or chemically via a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. As a pivotal technology in the fields of photograp ...
with digital tape recorder (about 20 pictures), cosmic dust
Cosmic dustalso called extraterrestrial dust, space dust, or star dustis dust that occurs in outer space or has fallen onto Earth. Most cosmic dust particles measure between a few molecules and , such as micrometeoroids (30 μm). Cosmic dust can ...
, solar plasma, trapped radiation, cosmic rays
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar ...
, magnetic fields
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
, radio occultation and celestial mechanics
Status:
* Mariner 3 – Malfunctioned. Derelict in heliocentric orbit
A heliocentric orbit (also called circumsolar orbit) is an orbit around the barycenter of the Solar System, which is usually located within or very near the surface of the Sun. All planets, comets, and asteroids in the Solar System, and the Sun ...
.
* Mariner 4 – Communications lost after bombardment by micrometeoroids. Derelict in heliocentric orbit
A heliocentric orbit (also called circumsolar orbit) is an orbit around the barycenter of the Solar System, which is usually located within or very near the surface of the Sun. All planets, comets, and asteroids in the Solar System, and the Sun ...
.
Mariner 5
 The Mariner 5 spacecraft was launched to
The Mariner 5 spacecraft was launched to Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
on June 14, 1967, and arrived in the vicinity of the planet in October 1967. It carried a complement of experiments to probe Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
' atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
with radio waves
Radio waves (formerly called Hertzian waves) are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the lowest frequencies and the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies below 300 gigahertz (GHz) and wavelengths ...
, scan its brightness in ultraviolet light
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of th ...
, and sample the solar particles and magnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
fluctuations above the planet.
* Mission: Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
flyby
* Mass: 245 kg (540 lb)
* Sensors: ultraviolet photometer, cosmic dust, solar plasma, trapped radiation, cosmic rays
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar ...
, magnetic fields
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
, radio occultation and celestial mechanics
Status:
Mariner 5 – Defunct and now in a heliocentric orbit
A heliocentric orbit (also called circumsolar orbit) is an orbit around the barycenter of the Solar System, which is usually located within or very near the surface of the Sun. All planets, comets, and asteroids in the Solar System, and the Sun ...
.
Mariners 6 and 7
 Mariners 6 and 7 were identical teammates in a two-spacecraft mission to Mars. Mariner 6 was launched on February 24, 1969, followed by Mariner 7 on March 21, 1969. They flew over the equator and southern hemisphere of the planet
Mariners 6 and 7 were identical teammates in a two-spacecraft mission to Mars. Mariner 6 was launched on February 24, 1969, followed by Mariner 7 on March 21, 1969. They flew over the equator and southern hemisphere of the planet Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
.
They analyzed atmosphere and surface with remote sensors as well as recording and relaying hundreds of pictures. By chance, both flew over cratered regions and missed both the giant northern volcanoes and the equatorial grand canyon discovered later. Their approach pictures did, however, show the dark features long seen from Earth, but no canals.
* Mission: Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
flybys
* Mass 413 kg (908 lb)
* Sensors: wide- and narrow-angle cameras with digital tape recorder, infrared spectrometer and radiometer, ultraviolet spectrometer, radio occultation and celestial mechanics.
Status: Both Mariner 6 and Mariner 7 are now defunct and are in a heliocentric orbit
A heliocentric orbit (also called circumsolar orbit) is an orbit around the barycenter of the Solar System, which is usually located within or very near the surface of the Sun. All planets, comets, and asteroids in the Solar System, and the Sun ...
.
Mariners 8 and 9
Mariner 8 andMariner 9
Mariner 9 (Mariner Mars '71 / Mariner-I) was a robotic spacecraft that contributed greatly to the exploration of Mars and was part of the NASA Mariner program. Mariner 9 was launched toward Mars on May 30, 1971, from Spaceport Florida Launch Comp ...
were identical sister craft designed to map the Martian surface simultaneously, but Mariner 8 was lost in a launch vehicle failure. Mariner 9 was launched in May 1971 and became the first artificial satellite of Mars. Its launch mass was nearly doubled by the onboard rocket propellant needed to thrust it into orbit around Mars, but otherwise it closely resembled its predecessors. It entered Martian orbit in November 1971 and began photographing the surface and analyzing the atmosphere with its infrared and ultraviolet instruments.
Since 1969, Mariner spacecraft operations such as science sequencing and pointing had been programmable, using simple flight computers with limited memory, and the spacecraft used a digital tape-recorder rather than film to store images and other science data. The spacecraft was thus able to wait until the storm abated, the dust settled and the surface was clearly visible before compiling its global mosaic of high-quality images of the surface of Mars.
It also provided the first closeup pictures of Mars’ two small, irregular moons, Phobos and Deimos.
* Mission: orbit Mars
* Mass 998 kg (2,200 lb)
* Sensors: wide- and narrow-angle cameras with digital tape recorder, infrared spectrometer and radiometer, ultraviolet spectrometer, radio occultation and celestial mechanics
Status:
* Mariner 8 – Destroyed in a launch vehicle failure.
* Mariner 9 – Shut off, in Areocentric (Mars) orbit until at least 2022 when it was projected to fall out of orbit and into the Martian atmosphere., November 29, 2011 – Vol. 4, Issue 9
Mariner 10
TheMariner 10
''Mariner 10'' was an American Robotic spacecraft, robotic space probe launched by NASA on 3 November 1973, to fly by the planets Mercury (planet), Mercury and Venus. It was the first spacecraft to perform flybys of multiple planets.
''Marin ...
spacecraft launched on November 3, 1973, and was the first to use a gravity assist trajectory, accelerating as it entered the gravitational influence of Venus, then being flung by the planet's gravity onto a slightly different course to reach Mercury. It was also the first spacecraft to encounter two planets at close range, and for 33 years the only spacecraft to photograph Mercury in closeup.
Here a fortuitous gravity assist enabled the spacecraft to return at six-month intervals for close mapping passes over the planet, covering half the globe (Mercury's slow rotation left the other half always in the dark when Mariner returned).
* Mission: plasma, charged particles, magnetic fields, radio occultation and celestial mechanics
Status: Mariner 10 – Defunct and now in a heliocentric orbit
A heliocentric orbit (also called circumsolar orbit) is an orbit around the barycenter of the Solar System, which is usually located within or very near the surface of the Sun. All planets, comets, and asteroids in the Solar System, and the Sun ...
.
Mariner Jupiter-Saturn
Mariner Jupiter-Saturn was approved in 1972 after the cancellation of theGrand Tour program
The Grand Tour is a NASA program that would have sent two groups of robotic probes to all the planets of the outer Solar System. It called for four spacecraft, two of which would visit Jupiter, Saturn, and Pluto, while the other two would visit ...
, which proposed visiting all the outer planets with multiple spacecraft. The Mariner Jupiter-Saturn program proposed two Mariner-derived probes that would perform a scaled back mission involving flybys of only the two gas giants, though designers at JPL built the craft with the intention that further encounters past Saturn would be an option. Trajectories were chosen to allow one probe to visit Jupiter and Saturn first, and perform a flyby of Saturn's moon Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
to gather information about the moon's substantial atmosphere. The other probe would arrive at Jupiter and Saturn later, and its trajectory would enable it to continue on to Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It is a gaseous cyan-coloured ice giant. Most of the planet is made of water, ammonia, and methane in a Supercritical fluid, supercritical phase of matter, which astronomy calls "ice" or Volatile ( ...
and Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun. It is the List of Solar System objects by size, fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 t ...
assuming the first probe accomplished all its objectives, or be redirected to perform a Titan flyby if necessary. The program's name was changed to Voyager just before launch in 1977, and after ''Voyager 1
''Voyager 1'' is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and the interstellar medium, interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. It was launched 16 days afte ...
'' successfully completed its Titan encounter, ''Voyager 2
''Voyager 2'' is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, as a part of the Voyager program. It was launched on a trajectory towards the gas giants (Jupiter and Saturn) and enabled further encounters with the ice giants (Uranus and ...
'' went on to visit the two ice giants.
See also
*Exploration of Mars
The planet Mars has been explored remotely by spacecraft. Uncrewed spacecraft, Probes sent from Earth, beginning in the late 20th century, have yielded a large increase in knowledge about the Martian system, focused primarily on understanding G ...
* Mariner Mark II
* Mariner (crater)
* Pioneer program
The Pioneer programs were two series of United States lunar and planetary space probes. The first program, which ran from 1958 to 1960, unsuccessfully attempted to send spacecraft to orbit the Moon, successfully sent one spacecraft to fly by the ...
Notes
References
Attribution: * {{DEFAULTSORT:Mariner Program Missions to Mars Missions to Mercury Missions to Venus