Lydersen Method on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Lydersen method is a group contribution method for the estimation of critical properties temperature ( Tc), pressure ( Pc) and volume (Vc). The Lydersen method is the prototype for and ancestor of many new models like Joback, Klincewicz,
Ambrose,
Gani-Constantinou and others.
The Lydersen method is based in case of the critical temperature on the Guldberg rule which establishes a relation between the normal boiling point and the critical temperature.
Equations
Critical temperature
Guldberg has found that a rough estimate of thenormal boiling point
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor.
The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding envir ...
''T''b, when expressed in kelvins
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and phy ...
(i.e., as an absolute temperature
Thermodynamic temperature is a quantity defined in thermodynamics as distinct from kinetic theory or statistical mechanics.
Historically, thermodynamic temperature was defined by Kelvin in terms of a macroscopic relation between thermodynamic w ...
), is approximately two-thirds of the critical temperature ''T''c. Lydersen uses this basic idea but calculates more accurate values.
Critical pressure
Critical volume
M is themolar mass
In chemistry, the molar mass of a chemical compound is defined as the mass of a sample of that compound divided by the amount of substance which is the number of moles in that sample, measured in moles. The molar mass is a bulk, not molecular, ...
and Gi are the group contributions (different for all three properties) for functional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the re ...
s of a molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
.
Group contributions
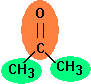
Example calculation
Acetone
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone), is an organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest and smallest ketone (). It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odour.
Acetone is miscib ...
is fragmented in two different groups, one carbonyl group and two methyl groups. For the critical volume the following calculation results:
Vc = 40 + 60.0 + 2 * 55.0 = 210 cm3
In the literature (such as in the Dortmund Data Bank) the values 215.90 cm3, 230.5 cm3 and 209.0 cm3 {{cite journal , last1=Kobe , first1=Kenneth A. , last2=Crawford , first2=Horace R. , last3=Stephenson , first3=Robert W. , title=Industrial Design Data—Critical Properties and Vapor Presesures of Some Ketones , journal=Industrial & Engineering Chemistry , publisher=American Chemical Society (ACS) , volume=47 , issue=9 , year=1955 , issn=0019-7866 , doi=10.1021/ie50549a025 , pages=1767–1772 are published.
References