Luigi Galvani on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Luigi Galvani ( , , ; ; 9 September 1737 – 4 December 1798) was an Italian
 Luigi Galvani was born to Domenico Galvani and Barbara Caterina Foschi, in
Luigi Galvani was born to Domenico Galvani and Barbara Caterina Foschi, in
 Galvani, according to William Fox, was "by nature courageous and religious." Jean-Louis-Marc Alibert said of Galvani that he never ended his lessons “without exhorting his hearers and leading them back to the idea of that eternal Providence, which develops, conserves, and circulates life among so many diverse beings.”
Galvani, according to William Fox, was "by nature courageous and religious." Jean-Louis-Marc Alibert said of Galvani that he never ended his lessons “without exhorting his hearers and leading them back to the idea of that eternal Providence, which develops, conserves, and circulates life among so many diverse beings.”
''De viribus electricitatis in motu musculari commentarius''
, 1791. The Institute of Sciences, Bologna. * * *
physician
A physician, medical practitioner (British English), medical doctor, or simply doctor is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the Medical education, study, Med ...
, physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate cau ...
, biologist
A biologist is a scientist who conducts research in biology. Biologists are interested in studying life on Earth, whether it is an individual Cell (biology), cell, a multicellular organism, or a Community (ecology), community of Biological inter ...
and philosopher
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational an ...
who studied animal electricity
Galvanism is a term invented by the late 18th-century physicist and chemist Alessandro Volta to refer to the generation of electric current by chemical action. The term also came to refer to the discoveries of its namesake, Luigi Galvani, specifi ...
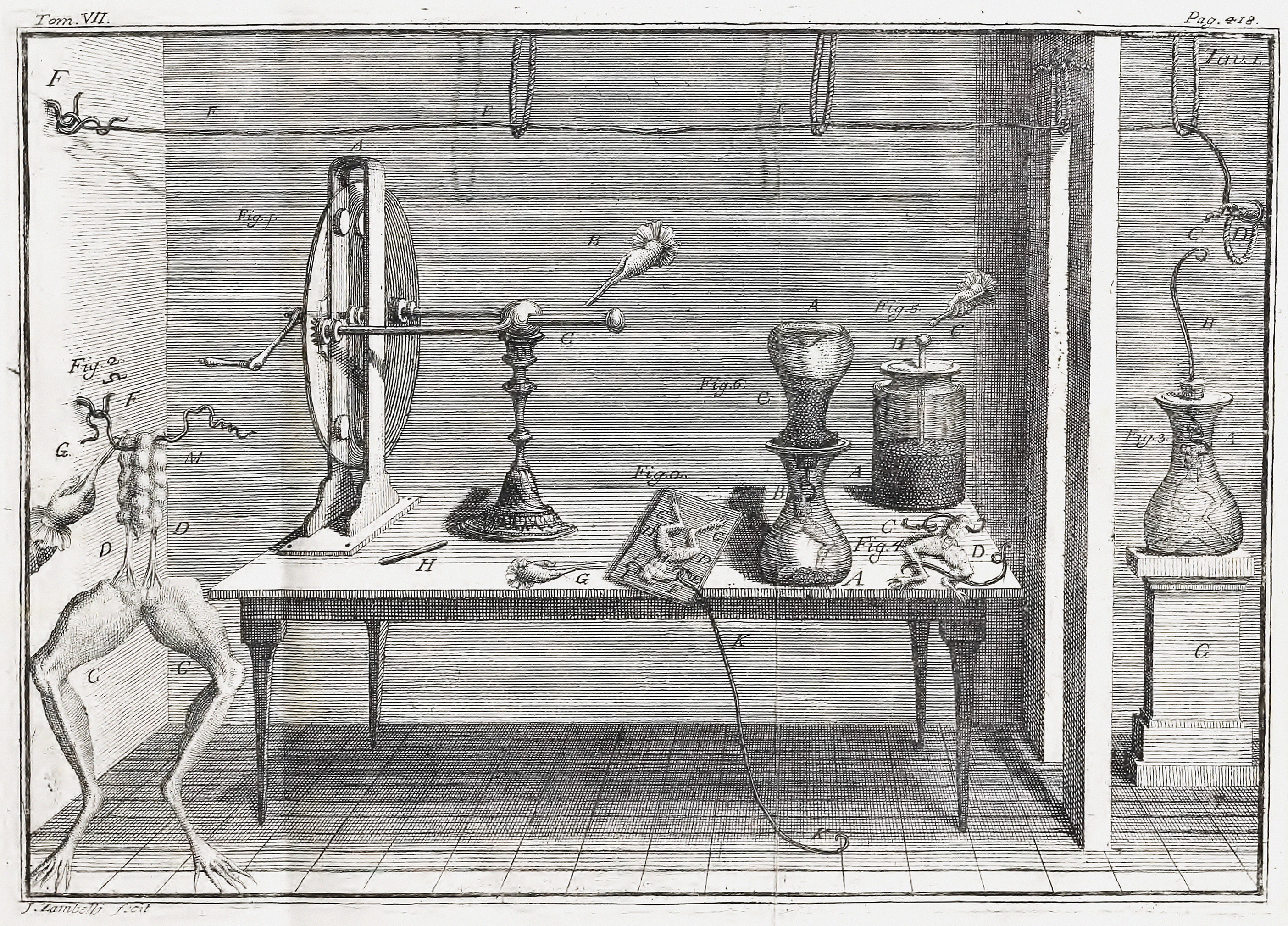
. In 1780, using a frog, he discovered that the muscles of dead frogs' legs twitched when struck by an electrical spark. This was an early study of bioelectricity, following experiments by John Walsh and Hugh Williamson
Hugh Williamson (December 5, 1735 – May 22, 1819) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father, physician, and politician. He is best known as a Signature, signatory to the U.S. Constitution and for representing Nort ...
.
Early life

 Luigi Galvani was born to Domenico Galvani and Barbara Caterina Foschi, in
Luigi Galvani was born to Domenico Galvani and Barbara Caterina Foschi, in Bologna
Bologna ( , , ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Emilia-Romagna region in northern Italy. It is the List of cities in Italy, seventh most populous city in Italy, with about 400,000 inhabitants and 150 different nationalities. Its M ...
, then part of the Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
. The house in which he was born may still be seen on Via Marconi, 25, in the center of Bologna. Domenico was a goldsmith
A goldsmith is a Metalworking, metalworker who specializes in working with gold and other precious metals. Modern goldsmiths mainly specialize in jewelry-making but historically, they have also made cutlery, silverware, platter (dishware), plat ...
. His family had produced several illustrious men.
Galvani then began taking an interest in the field of "medical electricity". This field emerged in the middle of the 18th century, following electrical researches and the discovery of the effects of electricity on the human body by scientists including Bertrand Bajon and Ramón María Termeyer in the 1760s, and by John Walsh and Hugh Williamson
Hugh Williamson (December 5, 1735 – May 22, 1819) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father, physician, and politician. He is best known as a Signature, signatory to the U.S. Constitution and for representing Nort ...
in the 1770s.
Galvani vs. Volta
Alessandro Volta
Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio Volta (, ; ; 18 February 1745 – 5 March 1827) was an Italian chemist and physicist who was a pioneer of electricity and Power (physics), power, and is credited as the inventor of the electric battery a ...
, a professor of experimental physics in the University of Pavia
The University of Pavia (, UNIPV or ''Università di Pavia''; ) is a university located in Pavia, Lombardy, Italy. There was evidence of teaching as early as 1361, making it one of the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, oldest un ...
, was among the first scientists who repeated and checked Galvani’s experiments. At first, he embraced animal electricity. However, he started to doubt that the conductions were caused by specific electricity intrinsic to the animal's legs or other body parts. Volta believed that the contractions depended on the metal cable Galvani used to connect the nerves and muscles in his experiments.
Every cell has a cell potential; biological electricity has the same chemical underpinnings as the current between electrochemical cell
An electrochemical cell is a device that either generates electrical energy from chemical reactions in a so called galvanic cell, galvanic or voltaic cell, or induces chemical reactions (electrolysis) by applying external electrical energy in an ...
s, and thus can be duplicated outside the body. Volta's intuition was correct. Volta, essentially, objected to Galvani’s conclusions about "animal electric fluid", but the two scientists disagreed respectfully and Volta coined the term "Galvanism" for a direct current of electricity produced by chemical action.
Since Galvani was reluctant to intervene in the controversy with Volta, he trusted his nephew, Giovanni Aldini, to act as the main defender of the theory of animal electricity.
Death
Galvani actively investigated animal electricity until the end of his life. TheCisalpine Republic
The Cisalpine Republic (; ) was a sister republic or a client state of France in Northern Italy that existed from 1797 to 1799, with a second version until 1802.
Creation
After the Battle of Lodi in May 1796, Napoleon Bonaparte organized two ...
, a French client state founded in 1797 after the French occupation of Northern Italy, required every university professor to swear loyalty to the new authority. Galvani, who disagreed with the social and political confusion, refused to swear loyalty, along with other colleagues. This led to the new authority depriving him of all his academic and public positions, which took every financial support away. Galvani died peacefully surrounded by his mother and father, in his brother’s house depressed and in poverty, on 4 December 1798.
Legacy
Galvani's legacy includes: * Galvani's report of his investigations were mentioned specifically byMary Shelley
Mary Wollstonecraft Shelley ( , ; ; 30 August 1797 – 1 February 1851) was an English novelist who wrote the Gothic novel ''Frankenstein, Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus'' (1818), which is considered an History of science fiction# ...
as part of the summer reading list leading up to an ad hoc
''Ad hoc'' is a List of Latin phrases, Latin phrase meaning literally for this. In English language, English, it typically signifies a solution designed for a specific purpose, problem, or task rather than a Generalization, generalized solution ...
ghost story contest on a rainy day in Switzerland—and the resultant novel'' Frankenstein
''Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus'' is an 1818 Gothic novel written by English author Mary Shelley. ''Frankenstein'' tells the story of Victor Frankenstein, a young scientist who creates a Sapience, sapient Frankenstein's monster, crea ...
''—and its reanimated construct. In ''Frankenstein'', Victor studies the principles of galvanism but it is not mentioned in reference to the creation of the Monster.
* Galvani's name also survives in everyday language as the verb 'galvanize' as well as in more specialized terms: Galvani potential, galvanic anode
A galvanic anode, or sacrificial anode, is the main component of a galvanic cathodic protection system used to protect buried or submerged metal structures from corrosion.
They are made from a metal alloy with a more "active" voltage (more n ...
, galvanic bath, galvanic cell
A galvanic cell or voltaic cell, named after the scientists Luigi Galvani and Alessandro Volta, respectively, is an electrochemical cell in which an electric current is generated from spontaneous oxidation–reduction reactions. An example of a ...
, galvanic corrosion
Galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially when it is in electrical contact with another, different metal, when both in the prese ...
, galvanic couple, galvanic current, galvanic isolation
Galvanic isolation is a principle of isolating functional sections of electrical systems to prevent current flow; no direct conduction path is permitted.
Energy or information can still be exchanged between the sections by other means, suc ...
, galvanic series
The galvanic series (or electropotential series) determines the nobility of metals and semi-metals. When two metals are submerged in an electrolyte, while also electrically connected by some external conductor, the less noble (base) will experien ...
, galvanic skin response
Electrodermal activity (EDA) is the property of the human body that causes continuous variation in the electrical characteristics of the skin. Historically, EDA has also been known as skin conductance, galvanic skin response (GSR), electroderm ...
, galvanism, galvanization, hot-dip galvanization
Hot-dip galvanization is a form of galvanization. It is the process of coating iron and steel with zinc, which alloys with the surface of the base metal when immersing the metal in a bath of molten zinc at a temperature of around . When expo ...
, galvanometer
A galvanometer is an electromechanical measuring instrument for electric current. Early galvanometers were uncalibrated, but improved versions, called ammeters, were calibrated and could measure the flow of current more precisely. Galvanomet ...
, Galvalume, and psycho-galvanic reflex.
 Galvani, according to William Fox, was "by nature courageous and religious." Jean-Louis-Marc Alibert said of Galvani that he never ended his lessons “without exhorting his hearers and leading them back to the idea of that eternal Providence, which develops, conserves, and circulates life among so many diverse beings.”
Galvani, according to William Fox, was "by nature courageous and religious." Jean-Louis-Marc Alibert said of Galvani that he never ended his lessons “without exhorting his hearers and leading them back to the idea of that eternal Providence, which develops, conserves, and circulates life among so many diverse beings.”
Works
''De viribus electricitatis in motu musculari commentarius''
, 1791. The Institute of Sciences, Bologna. * * *
See also
* History of electrochemistryReferences
Sources
*External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Galvani, Luigi 1737 births 1798 deaths Physicians from Bologna University of Bologna alumni Academic staff of the University of Bologna 18th-century Italian physicians 18th-century writers in Latin 18th-century Italian male writers History of neuroscience Battery inventors People from the Papal States Italian Roman Catholics Latin-language writers from Italy