
The London Wall was a
defensive wall first built by the
Romans around the strategically important port town of
Londinium in AD 200,
and is now the name of a
modern street in the
City of London
The City of London is a city, ceremonial county and local government district that contains the historic centre and constitutes, alongside Canary Wharf, the primary central business district (CBD) of London. It constituted most of London f ...
. It has origins as an initial mound wall and ditch from AD 100 and an initial fort, now called Cripplegate fort after the city gate (
Cripplegate) that was positioned within its northern wall later on, built in 120-150 where it was then expanded upon by
Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
builders into a city-wide defence. Over time, as
Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
influence waned through the
departure of the Roman army in 410,
their withdrawal led to its disrepair, as political power on the island of
Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
dispersed through the
Heptarchy
The Heptarchy were the seven petty kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England that flourished from the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain in the 5th century until they were consolidated in the 8th century into the four kingdoms of Mercia, Northumbria, Wess ...
(seven kingdoms) period of
Anglo-Saxon England. From the conquest of
William the Conqueror
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death in 10 ...
,
successive
medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
restorations and repairs to its use have been undertaken. This wall largely defined the boundaries of the City of London until the
later Middle Ages, when population rises and the development of towns around the city blurred the perimeter.
Events such as the
Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses (1455–1487), known at the time and for more than a century after as the Civil Wars, were a series of civil wars fought over control of the throne of England, English throne in the mid-to-late fifteenth century. These w ...
also played a part in the wall's development. This can be seen upon fragments of wall in the distinctive bricks used to increase its height through the diaper pattern bricks characteristic of the
Tudor period
The Tudor period occurred between 1485 and 1603 in England and Wales and includes the Elizabethan period during the reign of Elizabeth I until 1603. The Tudor period coincides with the dynasty of the House of Tudor in England that began wit ...
and added
crenellated battlements. Throughout its existence, the wall has served multiple purposes such as fortification, controlling the population, and acting as a ceremonial boundary for the city.
From the 18th century onward, the expansion of the
City of London
The City of London is a city, ceremonial county and local government district that contains the historic centre and constitutes, alongside Canary Wharf, the primary central business district (CBD) of London. It constituted most of London f ...
saw large parts of the wall demolished, including its city gates, to improve traffic flow; or incorporated into new or existing buildings. Over time, parts of the wall have been lost through this development, although archeological and conservation efforts from the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
onward have helped to preserve sections of the city wall as
scheduled monument
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a nationally important archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorised change.
The various pieces of legislation that legally protect heritage assets from damage and ...
s.
Like most other city walls around England, and unlike rare examples such as
York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
, the London Wall largely no longer exists, most of its foundations and/or surviving structures having been either buried underground or removed. Its existence, though, can still be seen through a number of uncovered and/ or preserved structures, records (see interactive map), and within modern urban architecture like the present road which echoes the perimeter of the northern section of the London Wall.
See this map in big, interactive, with illustrations and more
History
Roman London Wall
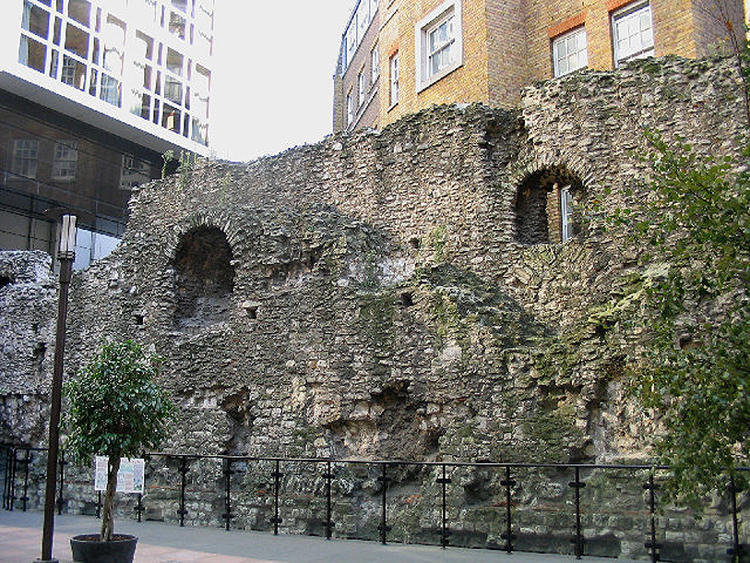

Although the exact reason for the wall's construction is unknown, it appears to have been built in the late 2nd or early 3rd century AD.
This was around 80 years after the construction in 120 of the city's fort, whose north and west walls were thickened and doubled in height to form part of the new city wall. The incorporation of the fort's walls gave the walled area its distinctive shape in the north-west part of the City.
It continued to be developed until at least the end of the 4th century, making it among the last major building projects undertaken by the
Romans before the
Roman departure from Britain
The end of Roman rule in Britain was the transition from Roman Britain to post-Roman Britain. Roman rule ended in different parts of Britain at different times, and under different circumstances.
In 383, the usurper Magnus Maximus withdrew tr ...
in 410. Reasons for its construction may have been connected to the invasion of northern Britain by
Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from ea ...
who overran
Hadrian's Wall in the 180s. This may be linked to the political crisis that emerged in the late 2nd century when the governor of Britain
Clodius Albinus
Decimus Clodius Albinus ( 150 – 19 February 197) was a Roman imperial pretender between 193 and 197. He was proclaimed emperor by the legions in Britain and Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula, comprising modern Spain and Portugal) after the murd ...
was consolidating his power after claiming the right of succession as
Roman emperor. After a struggle with his rival
Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary suc ...
, Albinus was defeated in 197 at the
Battle of Lugdunum (near
Lyon
Lyon,, ; Occitan: ''Lion'', hist. ''Lionés'' also spelled in English as Lyons, is the third-largest city and second-largest metropolitan area of France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of ...
, France). The economic stimulus provided by the wall and Septimius's subsequent campaigns in
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to ...
improved Londinium's financial prosperity in the early 3rd century.
Roman London wall characteristics
The wall's gateways coincided with their alignment to the
British network of Roman roads. The original gates, clockwise from Ludgate in the west to Aldgate in the east, were:
Ludgate,
Newgate,
Cripplegate,
Bishopsgate and
Aldgate
Aldgate () was a gate in the former defensive wall around the City of London. It gives its name to Aldgate High Street, the first stretch of the A11 road, which included the site of the former gate.
The area of Aldgate, the most common use of ...
.
Aldersgate, between Newgate and Cripplegate, was added around 350.
(
Moorgate, initially just a
postern, was built later still, in the medieval period).
The length and size of the wall made it one of the biggest construction projects in Roman Britain. It had gateways, towers and defensive ditches, and was built from
Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
ish
ragstone, which was brought by barge from quarries near
Maidstone. It was long, enclosing an area of about . It was to wide and up to high. The ditch or ''fossa'' in front of the outer wall was deep and up to wide. There were at least 22 towers spaced about apart on the eastern section of the wall.
Roman London Thames
Excavation work has traced a significant development of 300 metres of timber-framed waterfronts to the east and west of the modern site of London Bridge, with a piece of wooden bridge found at the end of Fish Street Hill. The constructions advancing around 35 metres into the
River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, se ...
took place between the late 1st and mid-3rd centuries, highlighting that between these periods no wall stood against the river.
After Londinium was raided on several occasions by
Saxon pirates in the late 3rd century, construction of an additional riverside wall, built in phases,
began in 280 and was repaired 390.
The existence of this riverside section was long doubted due to a lack of evidence, but excavations at the
Tower of London
The Tower of London, officially His Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress of the Tower of London, is a historic castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, which is sep ...
in 1977 showed that the section of the inner curtain wall between the Lanthorne and Wakefield Towers, to the south of the
White Tower, was originally the eastern part of the Roman riverside wall that was built or rebuilt in the late 4th century.
The riverside wall may have limited access to the Thames, both commercial and otherwise, so it may have reflected a diminished level of activity within the city.
It is not clear how long the riverside wall survived, but there are references to a part of it near the dock of
Queenhithe, in two charters of 889 and 898. There is currently no evidence of post-Roman restoration, so surviving sections are not likely to have been part, or an important part, of defences much after the Roman period.
Roman London Wall demise
With the collapse of the
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period ...
, Londinium ceased to be the capital of ''
Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Grea ...
'' although
Romano-British culture continued in the
St Martin-in-the-Fields area until around 450. However, the defences must have retained some of their former formidable strength because the ''
Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of A ...
'' mentions that the Romano-British retreated back to London after their bloody defeat at the
battle of Crecganford
The Timeline of conflict in Anglo-Saxon Britain is concerned with the period of history from just before the departure of the Roman Army, in the 4th century, to just after the Norman Conquest in the 11th century.
The information is mainly deriv ...
(
Crayford, Kent) at the hands of
Hengist and Horsa, leaders of the Saxon invaders.
Anglo-Saxon London Wall
Anglo-Saxon city revival
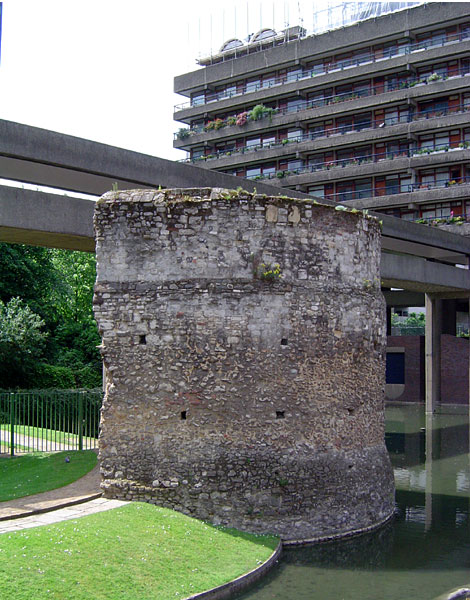

From 500, an
Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo-Saxons happened wit ...
settlement known as
Lundenwic
The history of Anglo-Saxon London relates to the history of the city of London during the Anglo-Saxon period, in the 7th to 11th centuries.
Romano-British ''Londinium'' had been abandoned in the late 5th century, although the London Wall rema ...
developed in the same area slightly to the west of the old abandoned Roman city.
By about 680, London had revived sufficiently to become a major Saxon port. However, the upkeep of the wall was not maintained and London fell victim to two successful
Viking assaults in 851 and 886.
In 886 the
King of Wessex,
Alfred the Great
Alfred the Great (alt. Ælfred 848/849 – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who bo ...
, formally agreed to the terms of the
Danish warlord
A warlord is a person who exercises military, economic, and political control over a region in a country without a strong national government; largely because of coercive control over the armed forces. Warlords have existed throughout much of h ...
,
Guthrum, concerning the area of political and geographical control that had been acquired by the incursion of the Vikings. Within the eastern and northern part of England, with its boundary roughly stretching from London to
Chester, the Scandinavians would establish
Danelaw.
Anglo-Saxon London Wall restoration
In the same year, the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' recorded that London was "refounded" by Alfred. Archaeological research shows that this involved abandonment of Lundenwic and a revival of life and trade within the old Roman walls. This was part Alfred's policy of building an in-depth defence of the
Kingdom of Wessex against the Vikings as well as creating an offensive strategy against the Vikings who controlled
Mercia
la, Merciorum regnum
, conventional_long_name=Kingdom of Mercia
, common_name=Mercia
, status=Kingdom
, status_text=Independent kingdom (527–879)Client state of Wessex ()
, life_span=527–918
, era=Heptarchy
, event_start=
, date_start=
, y ...
. The
burh
A burh () or burg was an Old English fortification or fortified settlement. In the 9th century, raids and invasions by Vikings prompted Alfred the Great to develop a network of burhs and roads to use against such attackers. Some were new const ...
of
Southwark was also created on the south bank of the River Thames during this time.
The city walls of London were repaired as the city slowly grew until about 950 when urban activity increased dramatically.
A large Viking army that attacked the London burgh was defeated in 994.
Medieval London Wall

By the 11th century, London was beyond all comparison the largest town in England.
Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the United ...
, rebuilt in the
Romanesque style by King
Edward the Confessor, was one of the grandest churches in Europe.
Winchester had previously been the capital of Anglo-Saxon England, but from this time on, London was the main forum for foreign traders and the base for defence in time of war. In the view of
Frank Stenton: "It had the resources, and it was rapidly developing the dignity and the political self-consciousness appropriate to a national capital."
Medieval London Wall restoration
The size and importance of London led to the redevelopment of the city's defences. During the early medieval period – following the
Norman Conquest of England – the walls underwent substantial work that included
crenellations, additional gates and further towers and bastions. Aside from the seven City Wall gates and the four bars, there are the 13 water-gates on the Thames where goods were unloaded from ships. These include Billingsgate and Bridge Gate. Additionally there were pedestrian-only gates such as Tower Gate and the
postern gate at the
Tower of London
The Tower of London, officially His Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress of the Tower of London, is a historic castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, which is sep ...
.
A further medieval defensive feature was the restoration of the defensive ditch immediately adjacent to the outside of the wall. The street name
Houndsditch recalls a part of this former feature. This seems to have been re-cut in 1213, with the restored ditch being V-cut to a depth of 6 feet and a width of between 9 and 15 feet.
The re-cut of the ditch may have diverted some of the waters of the
Walbrook which would otherwise have flowed through the City, and the wall itself does appear to have acted like a dam, partially obstructing the Walbrook and leading to the marshy conditions at the open space of
Moorfields, just north of the wall.
As London continued to grow throughout the medieval period, urban development grew beyond the city walls. This expansion led to the suffix words "Without" and "Within" which denote whether an area of
the City – and usually applied to the
wards – fell outside or within the London Wall, though only
Farringdon and (formerly)
Bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually someth ...
were split into separate wards this way (Bridge Without falling beyond the gates on
London Bridge). Some wards –
Aldersgate,
Bishopsgate and
Cripplegate – cover an area that was both within and outside the wall; although not split into separate wards, often the part (or "
division") within the Wall is denoted (on maps, in documents, etc.) as being "within" and the part outside the Wall as being "without". Archaically ''infra'' (within) and ''extra'' (without) were also used and the terms "intramural" and "extramural" are also used to describe being within or outside the walled part of the city.
The suffix is applied to some churches and parishes near the city gateways, such as
St Audoen within Newgate
St. Audoen's Church (within Newgate) (alternatively known as St. Ewen's, St. Ewan's or St. Ewin's) was a mediaeval parish church in the City of London situated on the north-east corner of Newgate Street and Eldeness Lane (now Warwick Lane). It w ...
and
St Botolph-without-Bishopsgate.
Blackfriars extension
Edward I gave the
Dominican Friars (or Black Friars) permission to demolish and re-route the section of City wall between Ludgate and the Thames. The did this in stages between 1284 and 1320, extending the walled area as far as the
River Fleet
The River Fleet is the largest of London's subterranean rivers, all of which today contain foul water for treatment. Its headwaters are two streams on Hampstead Heath, each of which was dammed into a series of ponds—the Hampstead Ponds an ...
so that it enclosed their precinct. The westward extension is likely to have improved the defensibility of Ludgate.

The Wall and the developed area
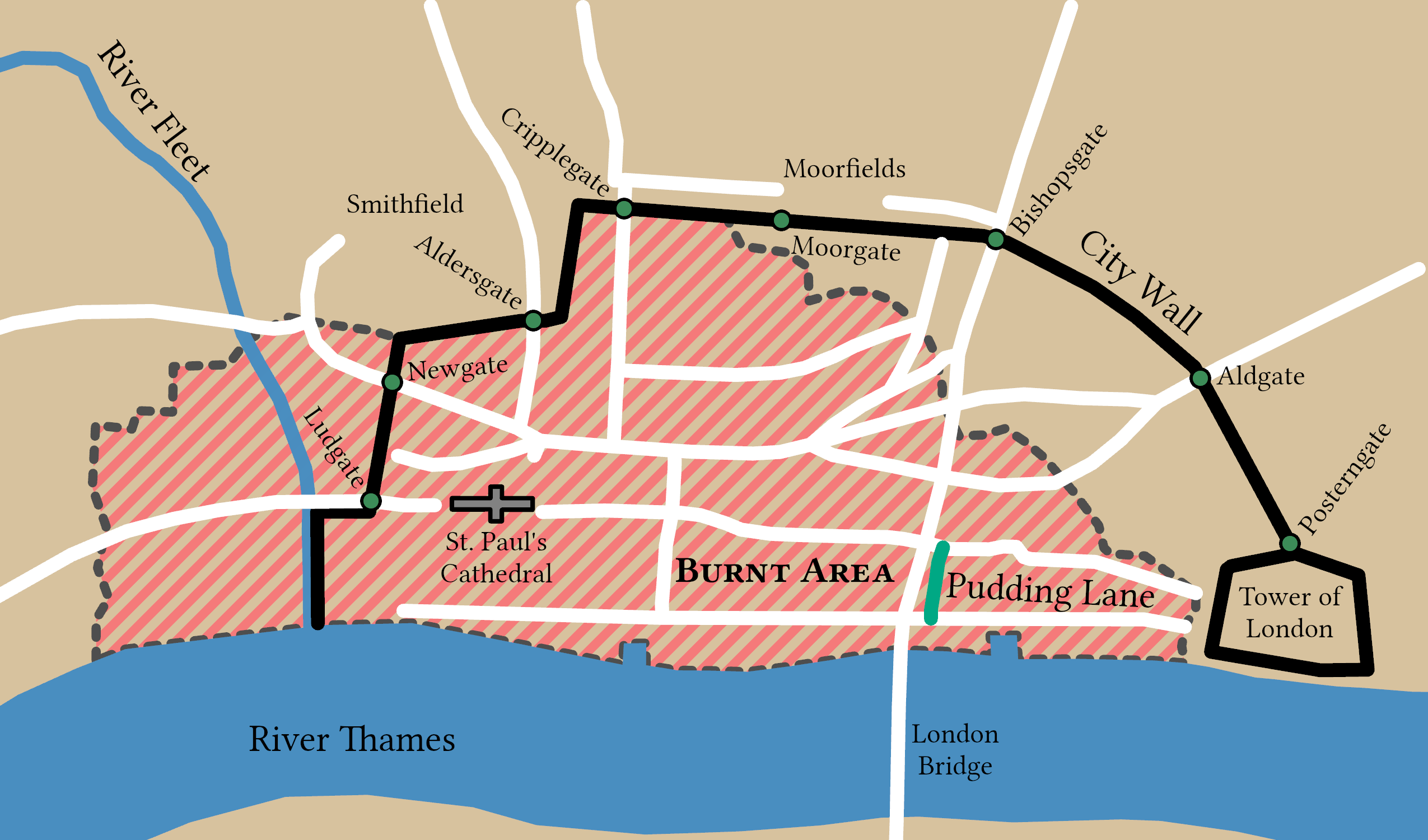
In the medieval period the developed area of the City was largely confined to the City Wall, but there was extramural development, especially in the large western ward of
Farringdon Without
__NOTOC__
Farringdon Without is the most westerly Ward of the City of London, its suffix ''Without'' reflects its origin as lying beyond the City's former defensive walls. It was first established in 1394 to administer the suburbs west of Ludg ...
. The wall provided security but was a constraint to accessibility and growth. The extent of the City’s jurisdiction has changed little from 1000 to the modern day; but the extra-mural parts were long home to only a few people. A notable late change to the boundary appears to be that
Stow’s Survey of London suggests that the part of
Moorfields next to the wall was still, in 1603, outside the City’s jurisdiction.
The boundary of the City’s jurisdiction was marked by "city bars", toll gates which were situated just beyond the old walled area;
Holborn Bar
Holborn ( or ) is a district in central London, which covers the south-eastern part of the London Borough of Camden and a part ( St Andrew Holborn Below the Bars) of the Ward of Farringdon Without in the City of London.
The area has its roots ...
,
Temple Bar,
West Smithfield Bar, and
Whitechapel Bar
Whitechapel is a district in East London and the future administrative centre of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. It is a part of the East End of London, east of Charing Cross. Part of the Historic counties of England, historic county of Mi ...
. These were the important entrances to the city and their control was vital in maintaining the city's special privileges over certain trades.
Great Fire of London
During the
Great Fire of London in September 1666, almost all of the medieval
City of London
The City of London is a city, ceremonial county and local government district that contains the historic centre and constitutes, alongside Canary Wharf, the primary central business district (CBD) of London. It constituted most of London f ...
inside the wall was destroyed, but the wall and gates survived.
Demolition
The seven gates to the City of London, with many repairs and rebuilding over the years, stood until they were all demolished between 1760 and 1767. Work to demolish the walls continued into the 19th century; however, large sections of the wall were incorporated into other structures.
20th century London Wall
Second World War
= London Blitz
=
The Blitz
The Blitz was a German bombing campaign against the United Kingdom in 1940 and 1941, during the Second World War. The term was first used by the British press and originated from the term , the German word meaning 'lightning war'.
The Germa ...
during the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, through the sheer scale of bombing and destruction of buildings and the surrounding landscape, revealed numerous parts of the London Wall.

At 00:15 on 28 August 1940, during the pre-wave of bombing before the
London Blitz, buildings and parts of the wall were destroyed between Fore Street and St. Alphage's churchyard
Gardens around
Cripplegate. This revealed parts of the wall unseen for over 300 years as the rubble of buildings destroyed around it were removed.
= Second Great Fire of London
=
On 29 December 1940, a section near the
Museum of London was revealed at Noble Street after the devastation of an air raid at the height of the Blitz, which additionally helped cause the
Second Great Fire of London
The Second Great Fire of London in December 1940 was caused by one of the most destructive air raids of the Blitz during World War II. The Luftwaffe raid caused fires over an area greater than that of the Great Fire of London in 1666, leading o ...
.
Post-war loss
In 1957 an 64 metre section of wall was uncovered during works on the London Wall road, the section was then destroyed to accommodate the road changes and to make way for a new car park. An 11 metre section has been preserved.
Conservation and heritage efforts
In 1984, the Museum of London set up a Wall Walk from the Tower of London to the museum, using 23 tiled panels. A number of these have been destroyed in subsequent years. At Noble Street, the panels were replaced by etched glass panels. These were intended as a prototype for new panels along the entire walk, but no further replacements have been made. One of the largest and most readily accessed fragments of the wall stands just outside
Tower Hill tube station
Tower Hill is a London Underground station in Tower Hill in the East End of London. It is on the Circle line between Monument and Aldgate stations, and the District line between Monument and Aldgate East. Tower Hill is within Travelcard zone ...
, with a replica statue of the Emperor
Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
standing in front of it. There is a further surviving section preserved in the basement of the
One America Square building. There are further remains in the basement of the
Old Bailey.
Impact on current city

The layout of the Roman and medieval walls have had a profound effect on the development of London, even down to the present day. The walls constrained the growth of the city, and the location of the limited number of gates and the route of the roads through them shaped development within the walls, and in a much more fundamental way, beyond them. With a few exceptions, the parts of the modern road network heading into the former walled area are the same as those which passed through the former medieval gates.
Part of the route originally taken by the northern wall is commemorated, although now only loosely followed, by the road also named London Wall. The
Financial Reporting Council's offices are at 125 London Wall and the
Museum of London is located at 150 London Wall. The modern road starts in the west with the Rotunda junction at
Aldersgate, then runs east past
Moorgate, from which point it runs parallel to the line of the City Wall, and eventually becomes
Wormwood Street
Wormwood Street is a short street in the City of London which runs between London Wall at its western end and a junction with Bishopsgate and Camomile Street in the east. It is a dual carriageway which forms part of the A1211 route between Bar ...
before it reaches
Bishopsgate. This alignment, however, is the result of rebuilding between 1957 and 1976. Before this, London Wall was narrower, and ran behind the line of the City Wall for its entire length, from Wormwood Street to Wood Street. The western section is now St Alphage Garden.
The wall's moat forms the street of
Houndsditch. This was once London's main rubbish disposal site and was notorious for its appalling odour; its name, according to 16th-century historian
John Stow, was derived "from that in old time, when the same lay open, much filth (conveyed forth of the City) especially dead dogges were there laid or cast". The moat was finally covered over and filled in at the end of the 16th century, becoming the line of the aforementioned street.
Course
Eastern wall section
Tower of London
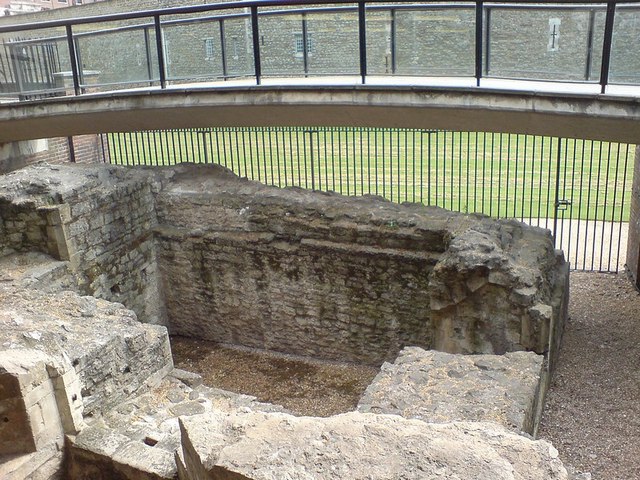

The eastern section of the wall starts in what is now the
Tower of London
The Tower of London, officially His Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress of the Tower of London, is a historic castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, which is sep ...
. Within the grounds of the Tower remains of the eastern most wall can still be seen along with a line in the paths heading North within the Tower grounds to outline where it used to run before most of it was demolished to expand the fortification of the Tower. This followed on with a junction at the Tower of London's moat to the
Tower Hill Postern, Gate 1,
a medieval fortified entrance. The foundation to this entrance can still be seen today within the Tower Hill pedestrian subway. Other large sections of the wall can also be seen further ahead within the Tower Hill gardens.
Aldgate

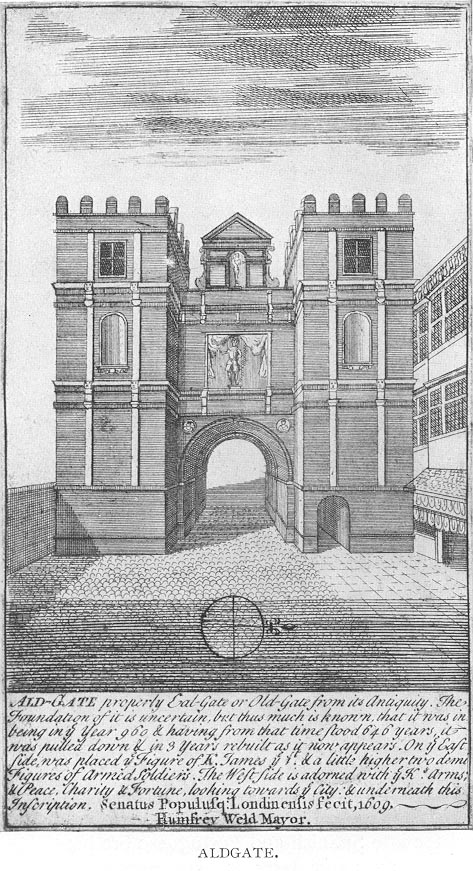
The wall from Tower Hill then runs east of
Walbrook toward the second historic gate,
Aldgate
Aldgate () was a gate in the former defensive wall around the City of London. It gives its name to Aldgate High Street, the first stretch of the A11 road, which included the site of the former gate.
The area of Aldgate, the most common use of ...
– Gate 2.
These would have led onto the Roman road network toward
Essex
Essex () is a Ceremonial counties of England, county in the East of England. One of the home counties, it borders Suffolk and Cambridgeshire to the north, the North Sea to the east, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent across the estuary of the Riv ...
and
East Anglia via
Stratford and
Colchester
Colchester ( ) is a city in Essex, in the East of England. It had a population of 122,000 in 2011. The demonym is Colcestrian.
Colchester occupies the site of Camulodunum, the first major city in Roman Britain and its first capital. Colch ...
. In present times, the roads Leadenhall and Fenchurch Street lead into Aldgate High Street where the gate's foundations are buried roughly where the Jewry Street intersects. Following the wall North, it runs between what is now The Aldgate School and Aldgate Square.
Bishopsgate
From Aldgate, the wall then ran North-West toward Gate 3,
Bishopsgate. The road through this would have led onto the Roman road network toward leading to
Lincoln and
York
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
. The current road, the A10 going north, now goes over the foundations of this gate.
Northern wall section
Moorgate
From Bishopsgate going along the northern section of wall leads to Gate 4;
Moorgate. Until 1415 this was a small
postern leading onto marshy
Moorfields area of
Finsbury. The wet conditions were probably caused by the wall partially obstructing the flow of the
Walbrook. Moorgate remained ill-connected with
no direct approach road from the south until 1846, some time after the wall had been demolished. London Wall, the modern road following this section of the wall, now crosses this gate's foundations. Leading from here north are routes into
Finsbury.
Cripplegate
Route to the
London Charterhouse
The London Charterhouse is a historic complex of buildings in Farringdon, London, dating back to the 14th century. It occupies land to the north of Charterhouse Square, and lies within the London Borough of Islington. It was originally buil ...
,
Clerkenwell and
Islington.
Aldersgate
With direct access to more local routes.
Western wall section
Newgate
High Holborn
High Holborn ( ) is a street in Holborn and Farringdon Without, Central London, which forms a part of the A40 route from London to Fishguard. It starts in the west at the eastern end of St Giles High Street and runs past the Kingsway and S ...
and
Oxford Street, with access via the
Devil's Highway to Silchester and Bath, and
Watling Street
Watling Street is a historic route in England that crosses the River Thames at London and which was used in Classical Antiquity, Late Antiquity, and throughout the Middle Ages. It was used by the ancient Britons and paved as one of the main ...
to
St Albans
St Albans () is a cathedral city in Hertfordshire, England, east of Hemel Hempstead and west of Hatfield, north-west of London, south-west of Welwyn Garden City and south-east of Luton. St Albans was the first major town on the old Roman ...
and the west midlands. These roads leading over the
River Fleet
The River Fleet is the largest of London's subterranean rivers, all of which today contain foul water for treatment. Its headwaters are two streams on Hampstead Heath, each of which was dammed into a series of ponds—the Hampstead Ponds an ...
.
Ludgate
Fleet Street and
the Strand
Characteristics
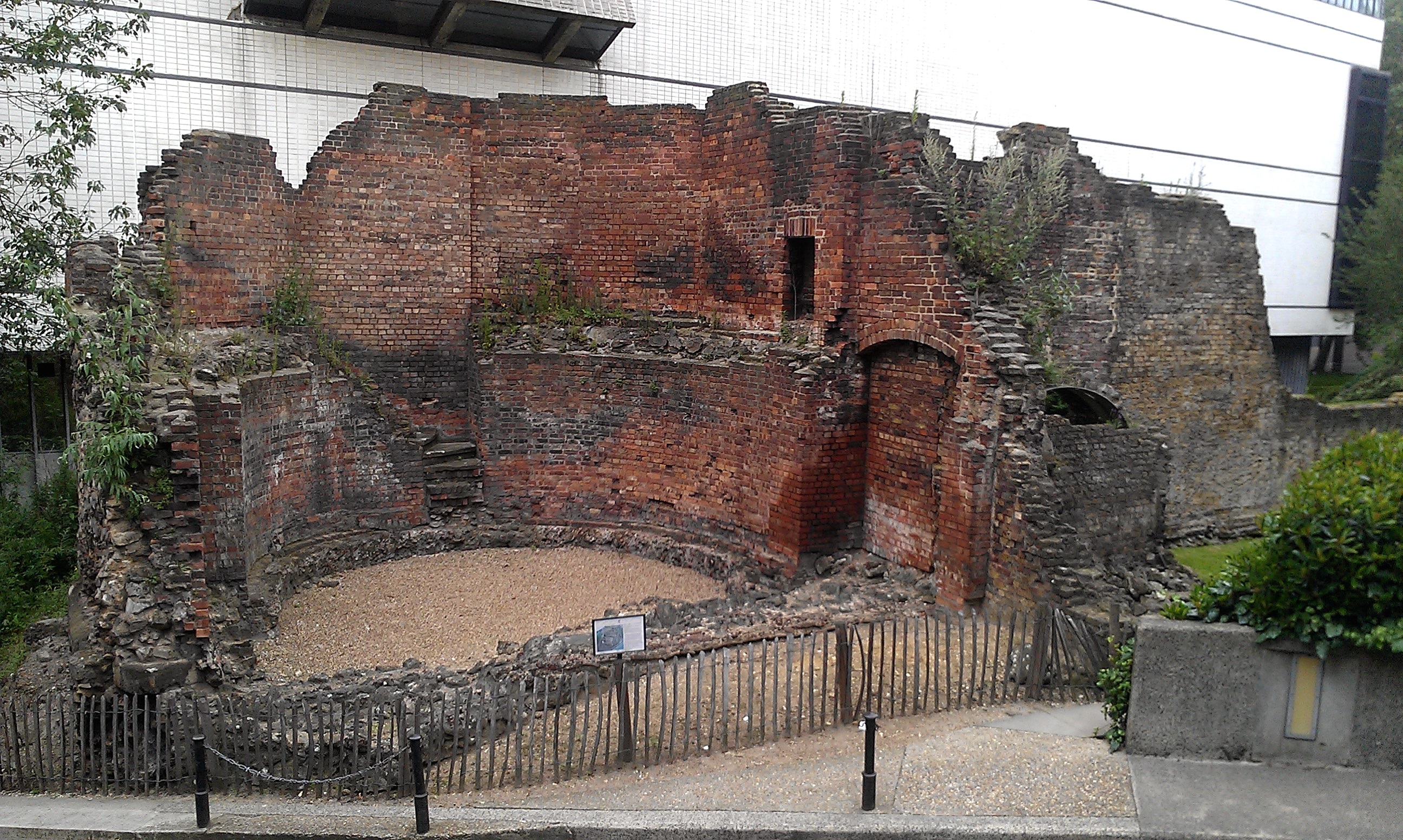

Bastions
The bastions, a tower built against the face of the city wall, are scattered irregularly across its perimeter. Not bonded to the city wall itself, they are considered to be added after the construction of the wall and even later after by post-Roman builders.
21 bastions are currently known about (more may be undiscovered) that can be grouped into an eastern section from the
Tower of London
The Tower of London, officially His Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress of the Tower of London, is a historic castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, which is sep ...
to Bishopsgate (B1 - 10), a single bastion west of Bishopsgate (B11), and a western section (B12 – 21).
Between the eastern and western section, a gap of 731 metres (2400 feet or 800 yards) along the northern section of the city wall has no recorded bastions.
Known monuments and landmarks
Related signage
See also
*
Fortifications of London
*
List of cities with defensive walls
The following cities have, or historically had, defensive walls.
Africa
Algeria
* Algiers
* Ghardaïa
* Timimoun
Egypt
* Al-Fustat
* Cairo
* Damietta
See List of Egypt castles, forts, fortifications and city walls.
Ethiopia
* Harar
Libya
...
*
List of town walls in England and Wales
This list of town walls in England and Wales describes the fortified walls built and maintained around these towns and cities from the 1st century AD onwards. The first town walls were built by the Romans, following their conquest of Britain ...
*
Scheduled monuments in Greater London
The following is a list of Scheduled monuments in Greater London.
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a "nationally important" archaeological site or historic building that has been given protection against unauthorised change by bein ...
References
External links
PhotoEssay on London Walls with markersMap of London Wall Walk and PhotosInteractive map of the London Wall
{{London landmarks
2nd-century fortifications
City walls in the United Kingdom
English Heritage sites in London
Fortifications of London
Grade I listed buildings in the City of London
History of the City of London
Roman London
Roman walls in England
Ruins in London
Streets in the City of London
Walls in England
 Although the exact reason for the wall's construction is unknown, it appears to have been built in the late 2nd or early 3rd century AD. This was around 80 years after the construction in 120 of the city's fort, whose north and west walls were thickened and doubled in height to form part of the new city wall. The incorporation of the fort's walls gave the walled area its distinctive shape in the north-west part of the City.
It continued to be developed until at least the end of the 4th century, making it among the last major building projects undertaken by the Romans before the
Although the exact reason for the wall's construction is unknown, it appears to have been built in the late 2nd or early 3rd century AD. This was around 80 years after the construction in 120 of the city's fort, whose north and west walls were thickened and doubled in height to form part of the new city wall. The incorporation of the fort's walls gave the walled area its distinctive shape in the north-west part of the City.
It continued to be developed until at least the end of the 4th century, making it among the last major building projects undertaken by the Romans before the  From 500, an
From 500, an  By the 11th century, London was beyond all comparison the largest town in England.
By the 11th century, London was beyond all comparison the largest town in England. 
 In the medieval period the developed area of the City was largely confined to the City Wall, but there was extramural development, especially in the large western ward of
In the medieval period the developed area of the City was largely confined to the City Wall, but there was extramural development, especially in the large western ward of  At 00:15 on 28 August 1940, during the pre-wave of bombing before the London Blitz, buildings and parts of the wall were destroyed between Fore Street and St. Alphage's churchyard Gardens around Cripplegate. This revealed parts of the wall unseen for over 300 years as the rubble of buildings destroyed around it were removed.
At 00:15 on 28 August 1940, during the pre-wave of bombing before the London Blitz, buildings and parts of the wall were destroyed between Fore Street and St. Alphage's churchyard Gardens around Cripplegate. This revealed parts of the wall unseen for over 300 years as the rubble of buildings destroyed around it were removed.
 The layout of the Roman and medieval walls have had a profound effect on the development of London, even down to the present day. The walls constrained the growth of the city, and the location of the limited number of gates and the route of the roads through them shaped development within the walls, and in a much more fundamental way, beyond them. With a few exceptions, the parts of the modern road network heading into the former walled area are the same as those which passed through the former medieval gates.
Part of the route originally taken by the northern wall is commemorated, although now only loosely followed, by the road also named London Wall. The Financial Reporting Council's offices are at 125 London Wall and the Museum of London is located at 150 London Wall. The modern road starts in the west with the Rotunda junction at Aldersgate, then runs east past Moorgate, from which point it runs parallel to the line of the City Wall, and eventually becomes
The layout of the Roman and medieval walls have had a profound effect on the development of London, even down to the present day. The walls constrained the growth of the city, and the location of the limited number of gates and the route of the roads through them shaped development within the walls, and in a much more fundamental way, beyond them. With a few exceptions, the parts of the modern road network heading into the former walled area are the same as those which passed through the former medieval gates.
Part of the route originally taken by the northern wall is commemorated, although now only loosely followed, by the road also named London Wall. The Financial Reporting Council's offices are at 125 London Wall and the Museum of London is located at 150 London Wall. The modern road starts in the west with the Rotunda junction at Aldersgate, then runs east past Moorgate, from which point it runs parallel to the line of the City Wall, and eventually becomes  The eastern section of the wall starts in what is now the
The eastern section of the wall starts in what is now the 
 The wall from Tower Hill then runs east of Walbrook toward the second historic gate,
The wall from Tower Hill then runs east of Walbrook toward the second historic gate, 