Lombards on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a
 The Winnili were young and brave and refused to pay tribute, saying "It is better to maintain liberty by arms than to stain it by the payment of tribute."PD, VII. The Vandals prepared for war and consulted Godan (the god Odin), who answered that he would give the victory to those whom he would see first at sunrise.PD, VIII. The Winnili were fewer in number and Gambara sought help from Frea (the goddess
The Winnili were young and brave and refused to pay tribute, saying "It is better to maintain liberty by arms than to stain it by the payment of tribute."PD, VII. The Vandals prepared for war and consulted Godan (the god Odin), who answered that he would give the victory to those whom he would see first at sunrise.PD, VIII. The Winnili were fewer in number and Gambara sought help from Frea (the goddess
/ref> Alternatively some etymological sources suggest an Old High German root, barta, meaning “axe” (and related to English halberd), while Edward Gibbon puts forth an alternative suggestion which argues that:
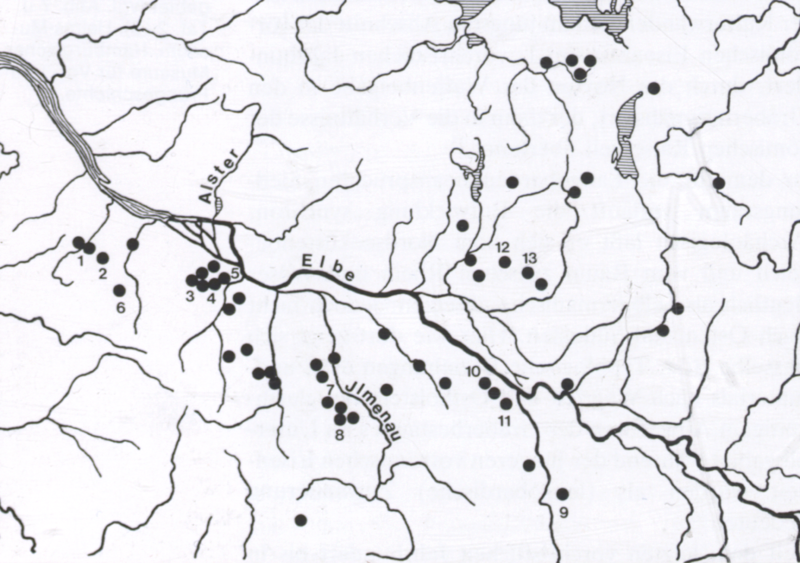 The first mention of the Lombards occurred between AD 9 and 16, by the Roman court historian
The first mention of the Lombards occurred between AD 9 and 16, by the Roman court historian  To the south,
To the south,
 In approximately 560, Audoin was succeeded by his son Alboin, a young and energetic leader who defeated the neighboring
In approximately 560, Audoin was succeeded by his son Alboin, a young and energetic leader who defeated the neighboring  The whole Lombard territory was divided into 36 duchies, whose leaders settled in the main cities. The king ruled over them and administered the land through emissaries called ''gastaldi''. This subdivision, however, together with the independent indocility of the duchies, deprived the kingdom of unity, making it weak even when compared to the Byzantines, especially since these had begun to recover from the initial invasion. This weakness became even more evident when the Lombards had to face the increasing power of the Franks. In response, the kings tried to centralize power over time, but they definitively lost control over Spoleto and Benevento in the attempt.
The whole Lombard territory was divided into 36 duchies, whose leaders settled in the main cities. The king ruled over them and administered the land through emissaries called ''gastaldi''. This subdivision, however, together with the independent indocility of the duchies, deprived the kingdom of unity, making it weak even when compared to the Byzantines, especially since these had begun to recover from the initial invasion. This weakness became even more evident when the Lombards had to face the increasing power of the Franks. In response, the kings tried to centralize power over time, but they definitively lost control over Spoleto and Benevento in the attempt.
 In 572, Alboin was murdered in Verona in a plot led by his wife, Rosamund, who later fled to Ravenna. His successor,
In 572, Alboin was murdered in Verona in a plot led by his wife, Rosamund, who later fled to Ravenna. His successor,
 Religious strife and the Slavic raids remained a source of struggle in the following years. In 705, the Friuli Lombards were defeated and lost the land to the west of the
Religious strife and the Slavic raids remained a source of struggle in the following years. In 705, the Friuli Lombards were defeated and lost the land to the west of the
 Though the kingdom centred on Pavia in the north fell to Charlemagne and the
Though the kingdom centred on Pavia in the north fell to Charlemagne and the
 The independent state of Salerno inspired the gastalds of Capua to move towards independence, and by the end of the century they were styling themselves "princes" and as a third Lombard state. The Capuan and Beneventan states were united by
The independent state of Salerno inspired the gastalds of Capua to move towards independence, and by the end of the century they were styling themselves "princes" and as a third Lombard state. The Capuan and Beneventan states were united by
 The Lombardic language is extinct (unless Cimbrian and Mocheno represent surviving dialects). It declined beginning in the seventh century, but may have been in scattered use until as late as about the year 1000. Only fragments of the language have survived, the main evidence being individual words quoted in
The Lombardic language is extinct (unless Cimbrian and Mocheno represent surviving dialects). It declined beginning in the seventh century, but may have been in scattered use until as late as about the year 1000. Only fragments of the language have survived, the main evidence being individual words quoted in  Lombardic fragments are preserved in
Lombardic fragments are preserved in
 The urbanisation of Lombard Italy was characterised by the (or "city as islands"). It appears from archaeology that the great cities of Lombard Italy—
The urbanisation of Lombard Italy was characterised by the (or "city as islands"). It appears from archaeology that the great cities of Lombard Italy—
 The Duchy and eventually Principality of Benevento in southern Italy developed a unique Christian rite in the seventh and eighth centuries. The Beneventan rite is more closely related to the liturgy of the Ambrosian rite than to the Roman rite. The Beneventan rite has not survived in its complete form, although most of the principal feasts and several feasts of local significance are extant. The Beneventan rite appears to have been less complete, less systematic, and more liturgically flexible than the Roman rite.
Characteristic of this rite was the Beneventan chant, a Lombard-influenced chant that bore similarities to the
The Duchy and eventually Principality of Benevento in southern Italy developed a unique Christian rite in the seventh and eighth centuries. The Beneventan rite is more closely related to the liturgy of the Ambrosian rite than to the Roman rite. The Beneventan rite has not survived in its complete form, although most of the principal feasts and several feasts of local significance are extant. The Beneventan rite appears to have been less complete, less systematic, and more liturgically flexible than the Roman rite.
Characteristic of this rite was the Beneventan chant, a Lombard-influenced chant that bore similarities to the
Langobard Shield Boss 7th Century.jpg, Lombard shield boss
northern Italy, 7th century, Metropolitan Museum of Art Langobardic - Fibula - Walters 542440.jpg, Lombard S-shaped fibula Arte longobarda, da sutri, bicchiere a forma di corno, fine VI-inizio VII sec.JPG, A glass drinking horn from Castel Trosino Langobardic - Shroud Cross - Walters 571773.jpg, Lombard ''Goldblattkreuz'' Cividale fibula1.jpg, Lombard fibulae Cividale Ratchis1.JPG, Altar of Ratchis Cividale Tempietto Longobardo - Westwand Märtyrerinnen 1.jpg, 8th-century Lombard sculpture depicting female martyrs, based on a Byzantine model. ''Tempietto Longobardo'',
 Few Lombard buildings have survived. Most have been lost, rebuilt, or renovated at some point, so they preserve little of their original Lombard structure. Lombard architecture was well-studied in the 20th century, and the four-volume ''Lombard Architecture'' (1919) by Arthur Kingsley Porter is a "monument of illustrated history".
The small
Few Lombard buildings have survived. Most have been lost, rebuilt, or renovated at some point, so they preserve little of their original Lombard structure. Lombard architecture was well-studied in the 20th century, and the four-volume ''Lombard Architecture'' (1919) by Arthur Kingsley Porter is a "monument of illustrated history".
The small
 The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the '' History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 and 796) that the Lombards descended from a small tribe called the Winnili,: "From Proto-Germanic '' winna-'', meaning "to fight, win" who dwelt in southern Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swe ...
(''Scadanan'') before migrating to seek new lands. By the time of the Roman-era - historians wrote of the Lombards in the 1st century AD, as being one of the Suebian peoples, in what is now northern Germany, near the Elbe river. They continued to migrate south. By the end of the fifth century, the Lombards had moved into the area roughly coinciding with modern Austria and Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
north of the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
, where they subdued the Heruls and later fought frequent wars with the Gepid
The Gepids, ( la, Gepidae, Gipedae, grc, Γήπαιδες) were an East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion ...
s. The Lombard king Audoin defeated the Gepid
The Gepids, ( la, Gepidae, Gipedae, grc, Γήπαιδες) were an East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion ...
leader Thurisind
Thurisind (Latin: ''Turisindus'', died ) was king of the Gepids, an East Germanic Gothic people, from c. 548 to 560. He was the penultimate Gepid king, and succeeded King Elemund by staging a coup d'état and forcing the king's son into exile. Thu ...
in 551 or 552, and his successor Alboin eventually destroyed the Gepids in 567. The Lombards settled in modern-day Hungary in Pannonia. Archaeologists have unearthed burial sites in the area of Szólád of Lombard men and women buried together as families, a practice that was uncommon for Germanic peoples at the time. Traces have also been discovered of Mediterranean Greeks and of a woman whose skull suggests French ancestry, possibly indicating that migrations into the Lombard territory occurred from Greece and France.
Following Alboin's victory over the Gepids, he led his people into North Eastern Italy, which had become severely depopulated and devastated after the long Gothic War (535–554) between the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
and the Ostrogothic Kingdom
The Ostrogothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of Italy (), existed under the control of the Germanic Ostrogoths in Italy and neighbouring areas from 493 to 553.
In Italy, the Ostrogoths led by Theodoric the Great killed and replaced Odoacer, ...
. The Lombards were joined by numerous Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
, Heruls, Gepids, Bulgars, Thuringians
The Thuringii, Toringi or Teuriochaimai, were an early Germanic people that appeared during the late Migration Period in the Harz Mountains of central Germania, a region still known today as Thuringia. It became a kingdom, which came into confl ...
and Ostrogoths, and their invasion of Italy was almost unopposed. By late 569, they had conquered all of northern Italy and the principal cities north of the Po River, except Pavia
Pavia (, , , ; la, Ticinum; Medieval Latin: ) is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy in northern Italy, south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It has a population of c. 73,086. The city was the cap ...
, which fell in 572. At the same time, they occupied areas in central and southern Italy. They established a Lombard Kingdom in north and central Italy, later named '' Regnum Italicum'' ("Kingdom of Italy"), which reached its zenith under the eighth-century ruler Liutprand. In 774, the kingdom was conquered by the Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages
* Francia, a post-Roman state in France and Germany
* East Francia, the successor state to Francia in Germany ...
king Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
and integrated into the Frankish Empire
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks du ...
. However, Lombard nobles continued to rule southern parts of the Italian peninsula well into the 11th century, when they were conquered by the Normans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. ...
and added to the County of Sicily
The County of Sicily, also known as County of Sicily and Calabria, was a Norman state comprising the islands of Sicily and Malta and part of Calabria from 1071 until 1130. The county began to form during the Christian reconquest of Sicily (106 ...
. In this period, the southern part of Italy still under Lombard domination was known to foreigners by the name Langbarðaland (Land of the Lombards), as inscribed in the Norse runestones. Their legacy is also apparent in the name of the region of Lombardy in northern Italy.
Name
According to their own traditions, the Lombards initially called themselves the ''Winnili''. After a reported major victory against the Vandals in the first century, they changed their name to ''Lombards''. The name ''Winnili'' is generally translated as 'the wolves', related to the Proto-Germanic root ''*wulfaz'' 'wolf'.' The name '' Lombard'' was reportedly derived from the distinctively long beards of the Lombards. It is probably a compound of the Proto-Germanic elements *''langaz'' (long) and *''bardaz'' (beard).History
Early history
Legendary origins
According to their own legends, the Lombards originated in southern Scandinavia including modern-day Denmark. The Northern European origins of the Lombards is supported by genetic, anthropological, archaeological and earlier literary evidence. A legendary account of Lombard origins, history, and practices is the ''Historia Langobardorum'' (''History of the Lombards'') of Paul the Deacon, written in the eighth century. Paul's chief source for Lombard origins, however, is the seventh-century '' Origo Gentis Langobardorum'' (''Origin of the Lombard People''). The ''Origo Gentis Langobardorum'' tells the story of a small tribe called the ''Winnili'' dwelling in southernScandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swe ...
(''Scadanan'') (the '' Codex Gothanus'' writes that the Winnili first dwelt near a river called ''Vindilicus'' on the extreme boundary of Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
). The Winnili were split into three groups and one part left their native land to seek foreign fields. The reason for the exodus was probably overpopulation. The departing people were led by Gambara and her sons Ybor and Aio and arrived in the lands of ''Scoringa'', perhaps the Baltic coast or the Bardengau on the banks of the Elbe. Scoringa was ruled by the Vandals and their chieftains, the brothers Ambri and Assi, who granted the Winnili a choice between tribute or war.
 The Winnili were young and brave and refused to pay tribute, saying "It is better to maintain liberty by arms than to stain it by the payment of tribute."PD, VII. The Vandals prepared for war and consulted Godan (the god Odin), who answered that he would give the victory to those whom he would see first at sunrise.PD, VIII. The Winnili were fewer in number and Gambara sought help from Frea (the goddess
The Winnili were young and brave and refused to pay tribute, saying "It is better to maintain liberty by arms than to stain it by the payment of tribute."PD, VII. The Vandals prepared for war and consulted Godan (the god Odin), who answered that he would give the victory to those whom he would see first at sunrise.PD, VIII. The Winnili were fewer in number and Gambara sought help from Frea (the goddess Frigg
Frigg (; Old Norse: ) is a goddess, one of the Æsir, in Germanic mythology. In Norse mythology, the source of most surviving information about her, she is associated with marriage, prophecy, clairvoyance and motherhood, and dwells in the wet ...
), who advised that all Winnili women should tie their hair in front of their faces like beards and march in line with their husbands. At sunrise, Frea turned her husband's bed so that he was facing east, and woke him. So Godan spotted the Winnili first and asked, "Who are these long-beards?," and Frea replied, "My lord, thou hast given them the name, now give them also the victory." From that moment onwards, the Winnili were known as the ''Longbeards'' (Latinised as ''Langobardi'', Italianised as ''Longobardi'', and Anglicized as ''Langobards'' or ''Lombards'').
When Paul the Deacon wrote the ''Historia'' between 787 and 796 he was a Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
monk and devoted Christian. He thought the pagan stories of his people "silly" and "laughable". Paul explained that the name "Langobard" came from the length of their beards. A modern theory suggests that the name "Langobard" comes from ''Langbarðr'', a name of Odin. Priester states that when the Winnili changed their name to "Lombards", they also changed their old agricultural fertility cult to a cult of Odin, thus creating a conscious tribal tradition. Fröhlich inverts the order of events in Priester and states that with the Odin cult, the Lombards grew their beards in resemblance of the Odin of tradition and their new name reflected this. Bruckner remarks that the name of the Lombards stands in close relation to the worship of Odin, whose many names include "the Long-bearded" or "the Grey-bearded", and that the Lombard given name ''Ansegranus'' ("he with the beard of the gods") shows that the Lombards had this idea of their chief deity. The same Old Norse root Barth or Barði, meaning "beard", is shared with the Heaðobards mentioned in both '' Beowulf'' and in ''Widsith
"Widsith" ( ang, Wīdsīþ, "far-traveller", lit. "wide-journey"), also known as "The Traveller's Song", is an Old English poem of 143 lines. It survives only in the ''Exeter Book'', a manuscript of Old English poetry compiled in the late-10th c ...
'', where they are in conflict with the Danes. They were possibly a branch of the Langobard
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 and ...
s.The article ''Hadubarder'' in ''Nordisk familjebok'' (1909)./ref> Alternatively some etymological sources suggest an Old High German root, barta, meaning “axe” (and related to English halberd), while Edward Gibbon puts forth an alternative suggestion which argues that:
…Börde (or Börd) still signifies “a fertile plain by the side of a river,” and a district near Magdeburg is still called the lange Börde. According to this view Langobardi would signify “inhabitants of the long bord of the river;” and traces of their name are supposed still to occur in such names as Bardengau and Bardewick in the neighborhood of the Elbe.According to the
Gallaeci
The Gallaeci (also Callaeci or Callaici; grc, Καλλαϊκοί) were a Celtic tribal complex who inhabited Gallaecia, the north-western corner of Iberia, a region roughly corresponding to what is now the Norte Region in northern Portugal, a ...
an Christian priest, historian and theologian
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the ...
Paulus Orosius
Paulus Orosius (; born 375/385 – 420 AD), less often Paul Orosius in English, was a Roman priest, historian and theologian, and a student of Augustine of Hippo. It is possible that he was born in ''Bracara Augusta'' (now Braga, Portugal), th ...
(translated by Daines Barrington), the Lombards or Winnili lived originally in the Vinuiloth (Vinovilith) mentioned by Jordanes
Jordanes (), also written as Jordanis or Jornandes, was a 6th-century Eastern Roman bureaucrat widely believed to be of Gothic descent who became a historian later in life. Late in life he wrote two works, one on Roman history ('' Romana'') a ...
, in his masterpiece Getica, to the north of Uppsala, Sweden. Scoringa was near the province of Uppland, so just north of Östergötland.
The footnote then explains the etymology of the name Scoringa:
The shores of Uppland and Östergötland are covered with small rocks and rocky islands, which are called in German Schæren and in Swedish Skiaeren. Heal signifies a port in the northern languages; consequently, Skiæren-Heal is the port of the Skiæren, a name well adapted to the port of Stockholm, in the Upplandske Skiæren, and the country may be justly called Scorung or Skiærunga.The legendary king
Sceafa
Sceafa ( ang, Scēafa , also ''Scēaf'', ''Scēf'') was an ancient Lombardic king in English legend. According to his story, Sceafa appeared mysteriously as a child, coming out of the sea in an empty skiff. The name also appears in the corrupt ...
of Scandza was an ancient Lombardic king in Anglo-Saxon legend. The Old English poem Widsith
"Widsith" ( ang, Wīdsīþ, "far-traveller", lit. "wide-journey"), also known as "The Traveller's Song", is an Old English poem of 143 lines. It survives only in the ''Exeter Book'', a manuscript of Old English poetry compiled in the late-10th c ...
, in a listing of famous kings and their countries, has Sceafa eoldLongbeardum, so naming Sceafa
Sceafa ( ang, Scēafa , also ''Scēaf'', ''Scēf'') was an ancient Lombardic king in English legend. According to his story, Sceafa appeared mysteriously as a child, coming out of the sea in an empty skiff. The name also appears in the corrupt ...
as ruler of the Lombards.
Similarities between Langobardic and Gothic migration traditions have been noted among scholars. These early migration legends suggest that a major shifting of tribes occurred sometime between the first and second century BC, which would coincide with the time that the Teutoni and Cimbri left their homelands in Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swe ...
and migrated through Germany, eventually invading Roman Italy.
Archaeology and migrations
Velleius Paterculus
Marcus Velleius Paterculus (; c. 19 BC – c. AD 31) was a Roman historian, soldier and senator. His Roman history, written in a highly rhetorical style, covered the period from the end of the Trojan War to AD 30, but is most useful for the per ...
, who accompanied a Roman expedition as prefect of the cavalry. Paterculus says that under Tiberius the "power of the Langobardi was broken, a race surpassing even the Germans in savagery".
From the combined testimony of Strabo (AD 20) and Tacitus (AD 117), the Lombards dwelt near the mouth of the Elbe shortly after the beginning of the Christian era, next to the Chauci
The Chauci (german: Chauken, and identical or similar in other regional modern languages) were an ancient Germanic tribe living in the low-lying region between the Rivers Ems and Elbe, on both sides of the Weser and ranging as far inland as the ...
. Strabo states that the Lombards dwelt on both sides of the Elbe. He treats them as a branch of the Suebi, and states that:
Now as for the tribe of the Suebi, it is the largest, for it extends from the Rhenus to the Albis; and a part of them even dwells on the far side of the Albis, as, for instance, the Hermondori and the Langobardi; and at the present time these latter, at least, have, to the last man, been driven in flight out of their country into the land on the far side of the river.Suetonius wrote that Roman general
Nero Claudius Drusus
Nero Claudius Drusus Germanicus (38–9 BC), also called Drusus the Elder, was a Roman politician and military commander. He was a patrician Claudian on his birth father's side but his maternal grandmother was from a plebeian family. He was the ...
defeated a large force of Germans and drove some “to the farther side of the Albis (Elbe)” river. It is conceivable that these refugees were the Langobardi and the Hermunduri mentioned by Strabo not long after.
The German archaeologist Willi Wegewitz defined several Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
burial sites at the Lower Elbe as ''Langobardic''. The burial sites are crematorial and are usually dated from the sixth century BC through the third century AD, so a settlement breakoff seems unlikely. The lands of the lower Elbe fall into the zone of the Jastorf Culture
The Jastorf culture was an Iron Age material culture in what is now northern Germany and southern Scandinavia spanning the 6th to 1st centuries BC, forming part of the Pre-Roman Iron Age and associating with Germanic peoples. The culture evo ...
and became Elbe-Germanic, differing from the lands between Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
, Weser, and the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
. Archaeological finds show that the Lombards were an agricultural people.
Tacitus also counted the Lombards as a remote and aggressive Suebian tribe, one of those united in worship of the deity Nerthus
In Germanic paganism, Nerthus is a goddess associated with a ceremonial wagon procession. Nerthus is attested by first century AD Roman historian Tacitus in his ethnographic work ''Germania''.
In ''Germania'', Tacitus records that a group of Germ ...
, whom he referred to as "Mother Earth", and also as subjects of Marobod the King of the Marcomanni
The Marcomanni were a Germanic people
*
*
*
that established a powerful kingdom north of the Danube, somewhere near modern Bohemia, during the peak of power of the nearby Roman Empire. According to Tacitus and Strabo, they were Suebian.
Or ...
.Tacitus, Annals, II, 45. Marobod had made peace with the Romans, and that is why the Lombards were not part of the Germanic confederacy under Arminius at the Battle of Teutoburg Forest
The Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, described as the Varian Disaster () by Roman historians, took place at modern Kalkriese in AD 9, when an alliance of Germanic peoples ambushed Roman legions and their auxiliaries, led by Publius Quinctilius V ...
in AD 9. In AD 17, war broke out between Arminius and Marobod. Tacitus records:
In 47, a struggle ensued amongst the Cherusci and they expelled their new leader, the nephew of Arminius, from their country. The Lombards appeared on the scene with sufficient power to control the destiny of the tribe that had been the leader in the struggle for independence thirty-eight years earlier, for they restored the deposed leader to sovereignty.
 To the south,
To the south, Cassius Dio
Lucius Cassius Dio (), also known as Dio Cassius ( ), was a Roman historian and senator of maternal Greek origin. He published 80 volumes of the history on ancient Rome, beginning with the arrival of Aeneas in Italy. The volumes documented the ...
reported that just before the Marcomannic Wars, 6,000 Lombards and Obii (sometimes thought to be Ubii
350px, The Ubii around AD 30
The Ubii were a Germanic tribe first encountered dwelling on the east bank of the Rhine in the time of Julius Caesar, who formed an alliance with them in 55 BC in order to launch attacks across the river. They were ...
) crossed the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , p ...
and invaded Pannonia. The two tribes were defeated, whereupon they ceased their invasion and sent Ballomar, King of the Marcomanni, as ambassador to Aelius Bassus, who was then administering Pannonia. Peace was made and the two tribes returned to their homes, which in the case of the Lombards was the lands of the lower Elbe. At about this time, in his '' Germania'' Tacitus says that "their scanty numbers are a distinction" because "surrounded by a host of most powerful tribes, they are safe, not by submitting, but by daring the perils of war".
In the mid-2nd century, the Lombards supposedly appeared in the Rhineland, because according to Claudius Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importa ...
, the Suebic Lombards lived "below" the Bructeri
The Bructeri (from Latin; Greek: Βρούκτεροι, ''Broukteroi'', or Βουσάκτεροι, ''Bousakteroi''; Old English: ''Boruhtware'') were a Germanic tribe*
*
in Roman imperial times, located in northwestern Germany, in present-day ...
and Sugambri
The Sicambri, also known as the Sugambri or Sicambrians, were a Germanic people who during Roman times lived on the east bank of the river Rhine, in what is now Germany, near the border with the Netherlands. They were first reported by Julius Ca ...
, and between these and the Tencteri. To their east stretching northwards to the central Elbe are the Suebi Angili. But Ptolemy also mentions the "Laccobardi" to the north of the above-mentioned Suebic territories, east of the Angrivarii
The Angrivarii (or ''Angrivari'') were a Germanic people of the early Roman Empire, who lived in what is now northwest Germany near the middle of the Weser river. They were mentioned by the Roman authors Tacitus and Ptolemy.
They were part of the ...
on the Weser, and south of the Chauci
The Chauci (german: Chauken, and identical or similar in other regional modern languages) were an ancient Germanic tribe living in the low-lying region between the Rivers Ems and Elbe, on both sides of the Weser and ranging as far inland as the ...
on the coast, probably indicating a Lombard expansion from the Elbe to the Rhine. This double mention has been interpreted as an editorial error by Gudmund Schütte, in his analysis of Ptolemy. However, the ''Codex Gothanus'' also mentions ''Patespruna'' ( Paderborn) in connection with the Lombards.
From the second century onwards, many of the Germanic tribes recorded as active during the Principate
The Principate is the name sometimes given to the first period of the Roman Empire from the beginning of the reign of Augustus in 27 BC to the end of the Crisis of the Third Century in AD 284, after which it evolved into the so-called Dominate.
...
started to unite into bigger tribal unions, such as the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
, Alamanni, Bavarii, and Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
. The Lombards are not mentioned at first, perhaps because they were not initially on the border of Rome, or perhaps because they were subjected to a larger tribal union, like the Saxons. It is, however, highly probable that, when the bulk of the Lombards migrated, a considerable part remained behind and afterwards became absorbed by the Saxon tribes in the Elbe region, while the emigrants alone retained the name of Lombards. However, the ''Codex Gothanus'' states that the Lombards were subjected by the Saxons around 300 but rose up against them under their first king, Agelmund, who ruled for 30 years. In the second half of the fourth century, the Lombards left their homes, probably due to bad harvests, and embarked on their migration.
The migration route of the Lombards in 489, from their homeland to "Rugiland", encompassed several places: ''Scoringa'' (believed to be their land on the Elbe shores), ''Mauringa'', ''Golanda'', ''Anthaib'', ''Banthaib'', and ''Vurgundaib'' (''Burgundaib''). According to the Ravenna Cosmography, Mauringa was the land east of the Elbe.
The crossing into Mauringa was very difficult. The Assipitti (possibly the Usipetes) denied them passage through their lands and a fight was arranged for the strongest man of each tribe. The Lombard was victorious, passage was granted, and the Lombards reached Mauringa.
The Lombards departed from Mauringa and reached Golanda. Scholar Ludwig Schmidt thinks this was further east, perhaps on the right bank of the Oder. Schmidt considers the name the equivalent of Gotland, meaning simply "good land". This theory is highly plausible; Paul the Deacon mentions the Lombards crossing a river, and they could have reached ''Rugiland'' from the Upper Oder area via the Moravian Gate.
Moving out of Golanda, the Lombards passed through Anthaib and Banthaib until they reached Vurgundaib, believed to be the old lands of the Burgundes
The Burgundians ( la, Burgundes, Burgundiōnes, Burgundī; on, Burgundar; ang, Burgendas; grc-gre, Βούργουνδοι) were an early Germanic tribe or group of tribes. They appeared in the middle Rhine region, near the Roman Empire, and ...
. In Vurgundaib, the Lombards were stormed in camp by " Bulgars" (probably Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
) and were defeated; King Agelmund was killed and Laimicho was made king. He was in his youth and desired to avenge the slaughter of Agelmund. The Lombards themselves were probably made subjects of the Huns after the defeat but rose up and defeated them with great slaughter, gaining great booty and confidence as they "became bolder in undertaking the toils of war." During the reign of King Claffo, the Langobards occupied parts of modern-day Upper and Lower Austria
Lower Austria (german: Niederösterreich; Austro-Bavarian: ''Niedaöstareich'', ''Niedaestareich'') is one of the nine states of Austria, located in the northeastern corner of the country. Since 1986, the capital of Lower Austria has been Sankt P ...
and converted to Arian Christianity. In 505 the Herulians attacked and defeated them, obliging them to pay tax and withdraw to Northern Bohemia. In 508, King Rodulf sent his brother to the Lombard court to collect tribute and extend the truce, however he was stabbed by Rometrud, sister of King Tato. Rodulf personally led his forces against Tato, but was ambushed and killed from a hill.
In the 540s, Audoin (ruled 546–560) led the Lombards across the Danube once more into Pannonia. Thurisind
Thurisind (Latin: ''Turisindus'', died ) was king of the Gepids, an East Germanic Gothic people, from c. 548 to 560. He was the penultimate Gepid king, and succeeded King Elemund by staging a coup d'état and forcing the king's son into exile. Thu ...
, King of the Gepids attempted to expel them, and both peoples asked for help from the Byzantines. Justinian I
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renova ...
sent his army against the Gepids, however it was routed on the way by the Herulians and the sides signed a two-year truce. Revenging what he felt as a betrayal, Thurisind made an alliance with the Kutrigurs who devastated Moesia before end of the armistice. The Langobard and Roman army joined together and defeated the Gepids in 551. In the battle, Audoin's son, Alboin killed Thurisind's son, Turismod.
In 552, the Byzantines, aided by a large contingent of Foederati, notably Lombards, Heruls and Bulgars, defeated the last Ostrogoths led by Teia in the Battle of Taginae.
Kingdom in Italy, 568–774
Invasion and conquest of the Italian peninsula
 In approximately 560, Audoin was succeeded by his son Alboin, a young and energetic leader who defeated the neighboring
In approximately 560, Audoin was succeeded by his son Alboin, a young and energetic leader who defeated the neighboring Gepidae
The Gepids, ( la, Gepidae, Gipedae, grc, Γήπαιδες) were an East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion ...
and made them his subjects; in 566, he married Rosamund
The name Rosamund (, also spelled Rosamond and Rosamunde) is a feminine given name and can also be a family name (surname). Originally it combined the Germanic elements ''hros'', meaning ''horse'', and ''mund'', meaning "protection". Later, it ...
, daughter of the Gepid king Cunimund. In the same year, he made a pact with Khagan Bayan. Next year the Lombards and the Avars destroyed the Gepid kingdom in the Lombard-Gepid War, the allies halved the prize of war
A prize of war is a piece of enemy property or land seized by a belligerent party during or after a war or battle, typically at sea. This term was used nearly exclusively in terms of captured ships during the 18th and 19th centuries. Basis in inte ...
and the nomads settled in Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
. In the spring of 568, Alboin, now fearing the aggressive Avars, led the Lombard migration into Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, which he planned for years. According to the ''History of the Lombards,'' "Then the Langobards, having left Pannonia, hastened to take possession of Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
with their wives and children and all their goods." The Avars have agreed to give them shelter if they wish to come back.
Various other peoples who either voluntarily joined or were subjects of King Alboin were also part of the migration. Whence, even until today, we call the villages in which they dwell Gepidan, Bulgarian,At least 20,000 Saxon warriors, old allies of the Lombards, and their families joined them in their new migration. The first important city to fall was ''Forum Iulii'' (Sarmatian The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ..., Pannonian, Suabian, Norican, or by other names of this kind."
Cividale del Friuli
Cividale del Friuli ( fur, Cividât (locally ); german: Östrich; sl, Čedad) is a town and '' comune'' in the Province of Udine, part of the North-Italian Friuli Venezia Giulia ''regione''. The town lies above sea-level in the foothills of th ...
) in northeastern Italy
Northeast Italy ( it, Italia nord-orientale or just ) is one of the five official statistical regions of Italy used by the Istituto Nazionale di Statistica, National Institute of Statistics (ISTAT), a Italian NUTS level 1 regions, first level ...
, in 569. There, Alboin created the first Lombard duchy, which he entrusted to his nephew Gisulf. Soon Vicenza, Verona
Verona ( , ; vec, Verona or ) is a city on the Adige River in Veneto, Italy, with 258,031 inhabitants. It is one of the seven provincial capitals of the region. It is the largest city municipality in the region and the second largest in nor ...
and Brescia fell into Germanic hands. In the summer of 569, the Lombards conquered the main Roman centre of northern Italy, Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
. The area was then recovering from the terrible Gothic Wars
The Gothic Wars were a long series of conflicts between the Goths and the Roman Empire between the years 249 and 554. The main wars are detailed below.
Gothic War (249–253)
(Goths under Cniva against the Roman Empire)
The War was probably in ...
, and the small Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
army left for its defence could do almost nothing. Longinus, the Exarch sent to Italy by Emperor Justin II
Justin II ( la, Iustinus; grc-gre, Ἰουστῖνος, Ioustînos; died 5 October 578) or Justin the Younger ( la, Iustinus minor) was Eastern Roman Emperor from 565 until 578. He was the nephew of Justinian I and the husband of Sophia, the ...
, could only defend coastal cities that could be supplied by the powerful Byzantine fleet. Pavia
Pavia (, , , ; la, Ticinum; Medieval Latin: ) is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy in northern Italy, south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It has a population of c. 73,086. The city was the cap ...
fell after a siege of three years, in 572, becoming the first capital city of the new Lombard kingdom of Italy.In the following years, the Lombards penetrated further south, conquering Tuscany
it, Toscano (man) it, Toscana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Citizenship
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 = Italian
, demogra ...
and establishing two duchies, Spoleto and Benevento under Zotto
Zotto (also Zotton or Zottone) was the military leader ( la, dux) of the Lombards in the Mezzogiorno. He is generally considered the founder of the Duchy of Benevento in 571 and its first duke : “''…Fuit autem primus Langobardorum dux in Bene ...
, which soon became semi-independent and even outlasted the northern kingdom, surviving well into the 12th century. Wherever they went, they were joined by the Ostrogothic population, which was allowed to live peacefully in Italy with their Rugian allies under Roman sovereignty. The Byzantines managed to retain control of the area of Ravenna and Rome, linked by a thin corridor running through Perugia
Perugia (, , ; lat, Perusia) is the capital city of Umbria in central Italy, crossed by the River Tiber, and of the province of Perugia.
The city is located about north of Rome and southeast of Florence. It covers a high hilltop and pa ...
.
When they entered Italy, some Lombards retained their native form of paganism, while some were Arian Christians. Hence they did not enjoy good relations with the Early Christian Church
Early Christianity (up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325) spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land and the Jewish ...
. Gradually, they adopted Roman or Romanized titles, names, and traditions, and partially converted to orthodoxy (in the seventh century), though not without a long series of religious and ethnic conflicts. By the time Paul the Deacon was writing, the Lombard language, dress and even hairstyles had nearly all disappeared '' in toto''.
 The whole Lombard territory was divided into 36 duchies, whose leaders settled in the main cities. The king ruled over them and administered the land through emissaries called ''gastaldi''. This subdivision, however, together with the independent indocility of the duchies, deprived the kingdom of unity, making it weak even when compared to the Byzantines, especially since these had begun to recover from the initial invasion. This weakness became even more evident when the Lombards had to face the increasing power of the Franks. In response, the kings tried to centralize power over time, but they definitively lost control over Spoleto and Benevento in the attempt.
The whole Lombard territory was divided into 36 duchies, whose leaders settled in the main cities. The king ruled over them and administered the land through emissaries called ''gastaldi''. This subdivision, however, together with the independent indocility of the duchies, deprived the kingdom of unity, making it weak even when compared to the Byzantines, especially since these had begun to recover from the initial invasion. This weakness became even more evident when the Lombards had to face the increasing power of the Franks. In response, the kings tried to centralize power over time, but they definitively lost control over Spoleto and Benevento in the attempt.
=Langobardia major
= * Duchy of Friuli *Duchy of Trent The Duchy of Tridentum (Trent) was an autonomous Lombard duchy, established by Euin during the Lombard interregnum of 574–584 that followed the assassination of the Lombard leader Alboin. The stronghold of Euin's territory was the Roman city ...
* Duchy of Persiceta
*Duchy of Pavia
* Duchy of Tuscia
=Langobardia minor
= * Duchy of Spoleto and List of Dukes of Spoleto *Duchy of Benevento
The Duchy of Benevento (after 774, Principality of Benevento) was the southernmost Lombard duchy in the Italian Peninsula that was centred on Benevento, a city in Southern Italy. Lombard dukes ruled Benevento from 571 to 1077, when it was conq ...
and List of Dukes and Princes of Benevento
Arian monarchy
 In 572, Alboin was murdered in Verona in a plot led by his wife, Rosamund, who later fled to Ravenna. His successor,
In 572, Alboin was murdered in Verona in a plot led by his wife, Rosamund, who later fled to Ravenna. His successor, Cleph
Cleph (also ''Clef'', ''Clepho'', or ''Kleph'') was king of the Lombards from 572 to 574.
He succeeded Alboin, to whom he was not related by blood. He was a violent and terrifying figure to the Romans and Byzantines struggling to maintain contro ...
, was also assassinated, after a ruthless reign of 18 months. His death began an interregnum of years (the "Rule of the Dukes
The Rule of the Dukes was an interregnum in the Lombard Kingdom of Italy (574/5–584/5) during which Italy was ruled by the Lombard dukes of the old Roman provinces and urban centres. The interregnum is said to have lasted a decade accordi ...
") during which the dukes did not elect any king, a period regarded as a time of violence and disorder. In 586, threatened by a Frankish invasion, the dukes elected Cleph's son, Authari
Authari (c. 550 – 5 September 590) was king of the Lombards from 584 to his death. He was considered as the first Lombard king to have adopted some level of "Roman-ness" and introduced policies that led to drastic changes particularly in th ...
, as king. In 589, he married Theodelinda
Theodelinda also spelled ''Theudelinde'' ( 570–628 AD), was a queen of the Lombards by marriage to two consecutive Lombard rulers, Autari and then Agilulf, and regent of Lombardia during the minority of her son Adaloald, and co-regent when he ...
, daughter of Garibald I of Bavaria, the Duke of Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
. The Catholic Theodelinda was a friend of Pope Gregory I and pushed for Christianization. In the meantime, Authari embarked on a policy of internal reconciliation and tried to reorganize royal administration. The dukes yielded half their estates for the maintenance of the king and his court in Pavia. On the foreign affairs side, Authari managed to thwart the dangerous alliance between the Byzantines and the Franks.
Authari died in 591 and was succeeded by Agilulf
Agilulf ( 555 – April 616), called ''the Thuringian'' and nicknamed ''Ago'', was a duke of Turin and king of the Lombards from 591 until his death.
A relative of his predecessor Authari, Agilulf was of Thuringian origin and belonged to the A ...
, the duke of Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital from 1861 to 1865. The ...
, who also married Theodelinda in the same year. Agilulf successfully fought the rebel dukes of northern Italy, conquering Padua
Padua ( ; it, Padova ; vec, Pàdova) is a city and ''comune'' in Veneto, northern Italy. Padua is on the river Bacchiglione, west of Venice. It is the capital of the province of Padua. It is also the economic and communications hub of the ...
in 601, Cremona and Mantua
Mantua ( ; it, Mantova ; Lombard and la, Mantua) is a city and '' comune'' in Lombardy, Italy, and capital of the province of the same name.
In 2016, Mantua was designated as the Italian Capital of Culture. In 2017, it was named as the Eur ...
in 603, and forcing the Exarch of Ravenna to pay tribute. Agilulf died in 616; Theodelinda reigned alone until 628 when she was succeeded by Adaloald
Adaloald (602–628) was the Lombard king of Italy from 616 to 626.
He was son and heir of King Agilulf and his Catholic queen Theodelinda. He was baptised shortly after his birth in 602; the abbot Secundus of Non (later historian) was his g ...
. Arioald, the head of the Arian opposition who had married Theodelinda's daughter Gundeperga, later deposed Adaloald.
Arioald was succeeded by Rothari, regarded by many authorities as the most energetic of all Lombard kings. He extended his dominions, conquering Liguria in 643 and the remaining part of the Byzantine territories of inner Veneto, including the Roman city of ''Opitergium'' (Oderzo
Oderzo ( la, Opitergium; vec, Oderso) is a '' comune'' with a population of 20,003 in the province of Treviso, Veneto, northern Italy.
It lies in the heart of the Venetian plain, about to the northeast of Venice. Oderzo is crossed by the Montic ...
). Rothari also made the famous edict bearing his name, the ''Edictum Rothari
The ''Edictum Rothari'' (lit. ''Edict of Rothari''; also ''Edictus Rothari'' or ''Edictum Rotharis'') was the first written compilation of Lombard law, codified and promulgated on 22 November 643 by King Rothari in Pavia by a gairethinx, an ass ...
'', which established the laws and the customs of his people in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
: the edict did not apply to the tributaries of the Lombards, who could retain their own laws. Rothari's son Rodoald succeeded him in 652, still very young, and was killed by his opponents.
At the death of King Aripert I in 661, the kingdom was split between his children Perctarit
Perctarit (also Berthari) (died 688) was king of the Lombards from 661 to 662 the first time and later from 671 to 688.
He was the son and successor of Aripert I. He shared power with his brother Godepert. He was a Catholic, whereas Godepert wa ...
, who set his capital in Milan, and Godepert
Godepert (also ''Gundipert'', ''Godebert'', ''Godipert'', ''Godpert'', ''Gotebert'', ''Gotbert'', ''Gotpert'', ''Gosbert'', or ''Gottbert'') was king of the Lombards (crowned 661), eldest son and successor of Aripert I. He was an Arian who governe ...
, who reigned from Pavia
Pavia (, , , ; la, Ticinum; Medieval Latin: ) is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy in northern Italy, south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It has a population of c. 73,086. The city was the cap ...
(Ticinum
Ticinum (the modern Pavia) was an ancient city of Gallia Transpadana, founded on the banks of the river of the same name (now the Ticino river) a little way above its confluence with the Padus ( Po).
It was said by Pliny the Elder to have bee ...
). Perctarit was overthrown by Grimoald, son of Gisulf, duke of Friuli
Friuli ( fur, Friûl, sl, Furlanija, german: Friaul) is an area of Northeast Italy with its own particular cultural and historical identity containing 1,000,000 Friulians. It comprises the major part of the autonomous region Friuli Venezia Giuli ...
and Benevento since 647. Perctarit fled to the Avars and then to the Franks. Grimoald managed to regain control over the duchies and deflected the late attempt of the Byzantine emperor Constans II to conquer southern Italy. He also defeated the Franks. At Grimoald's death in 671 Perctarit
Perctarit (also Berthari) (died 688) was king of the Lombards from 661 to 662 the first time and later from 671 to 688.
He was the son and successor of Aripert I. He shared power with his brother Godepert. He was a Catholic, whereas Godepert wa ...
returned and promoted tolerance between Arians and Catholics, but he could not defeat the Arian party, led by Arachi, duke of Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin and lmo, Trent; german: Trient ; cim, Tria; , ), also anglicized as Trent, is a city on the Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th ce ...
, who submitted only to his son, the philo-Catholic Cunincpert
Cunincpert (also Cunibert or Cunipert) was king of the Lombards from 688 to 700. He succeeded his father Perctarit, though he was associated with the throne from 680.
Life
Soon after his assumption of the sole kingship, Cunincpert was ousted by ...
.
The Lombards engaged in fierce battles with Slavic peoples during these years: from 623 to 626 the Lombards unsuccessfully attacked the Carantanians, and, in 663–64, the Slavs raided the Vipava Valley
The Vipava Valley (; sl, Vipavska dolina, german: Wippachtal, it, Valle del Vipacco) is a valley in the Slovenian Littoral, roughly between the village of Podnanos to the east and the border with Italy to the west. The main towns are Ajdovš ...
and the Friuli
Friuli ( fur, Friûl, sl, Furlanija, german: Friaul) is an area of Northeast Italy with its own particular cultural and historical identity containing 1,000,000 Friulians. It comprises the major part of the autonomous region Friuli Venezia Giuli ...
.
Catholic monarchy
 Religious strife and the Slavic raids remained a source of struggle in the following years. In 705, the Friuli Lombards were defeated and lost the land to the west of the
Religious strife and the Slavic raids remained a source of struggle in the following years. In 705, the Friuli Lombards were defeated and lost the land to the west of the Soča
The Soča ( in Slovene) or Isonzo ( in Italian; other names fur, Lusinç, german: Sontig, la, Aesontius or ') is a long river that flows through western Slovenia () and northeastern Italy ().
An Alpine river in character, its source lies i ...
River, namely the Gorizia Hills
The Gorizia Hills ( it, Collio Goriziano or ''Collio''; sl, Goriška brda or ''Brda''; fur, Cuei) is a hilly microregion in western Slovenia and northeastern Italy. It lies on the right bank of the Soča (''Isonzo'') river, north of the Ita ...
and the Venetian Slovenia
Slavia Friulana, which means Friulian Slavia ( sl, Beneška Slovenija), is a small mountainous region in northeastern Italy and it is so called because of its Slavic population which settled here in the 8th century AD. The territory is located in ...
. A new ethnic border was established that has lasted for over 1200 years up until the present time.
The Lombard reign began to recover only with Liutprand the Lombard (king from 712), son of Ansprand
Ansprand ( 657 – 712) was king of the Lombards briefly in 712. Before that he was the duke of Asti and regent during the minority of Liutpert (700–701). He was defeated at Novara by Raginpert and exiled during the subsequent war over the succ ...
and successor of the brutal Aripert II. He managed to regain a certain control over Spoleto and Benevento, and, taking advantage of the disagreements between the Pope and Byzantium concerning the reverence of icons, he annexed the Exarchate of Ravenna and the duchy of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
. He also helped the Frankish marshal Charles Martel
Charles Martel ( – 22 October 741) was a Frankish political and military leader who, as Duke and Prince of the Franks and Mayor of the Palace, was the de facto ruler of Francia from 718 until his death. He was a son of the Frankish statesm ...
drive back the Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
. The Slavs were defeated in the Battle of Lavariano
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
, when they tried to conquer the Friulian Plain in 720. Liutprand's successor Aistulf conquered Ravenna for the Lombards for the first time but had to relinquish it when he was subsequently defeated by the king of the Franks, Pippin III
the Short (french: Pépin le Bref; – 24 September 768), also called the Younger (german: Pippin der Jüngere), was King of the Franks from 751 until his death in 768. He was the first Carolingian to become king.
The younger was the son of t ...
, who was called by the Pope.
After the death of Aistulf, Ratchis attempted to become king of Lombardy, but he was deposed by Desiderius
Desiderius, also known as Daufer or Dauferius (born – died ), was king of the Lombards in northern Italy, ruling from 756 to 774. The Frankish king of renown, Charlemagne, married Desiderius's daughter and subsequently conquered his realm. Des ...
, duke of Tuscany
it, Toscano (man) it, Toscana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Citizenship
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 = Italian
, demogra ...
, the last Lombard to rule as king. Desiderius managed to take Ravenna definitively, ending the Byzantine presence in northern Italy. He decided to reopen struggles against the Pope, who was supporting the dukes of Spoleto and Benevento against him, and entered Rome in 772, the first Lombard king to do so. But when Pope Hadrian I called for help from the powerful Frankish king Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
, Desiderius was defeated at Susa and besieged in Pavia
Pavia (, , , ; la, Ticinum; Medieval Latin: ) is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy in northern Italy, south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It has a population of c. 73,086. The city was the cap ...
, while his son Adelchis was forced to open the gates of Verona to Frankish troops. Desiderius surrendered in 774, and Charlemagne, in an utterly novel decision, took the title "King of the Lombards". Before then the Germanic kingdoms had frequently conquered each other, but none had adopted the title of King of another people. Charlemagne took part of the Lombard territory to create the Papal States.
The Lombardy region in Italy, which includes the cities of Brescia, Bergamo, Milan, and the old capital Pavia, is a reminder of the presence of the Lombards.
Later history
Falling to the Franks and the Duchy of Benevento, 774–849
Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
in 774, the Lombard-controlled territory to the south of the Papal States was never subjugated by Charlemagne or his descendants. In 774, Duke Arechis II of Benevento
Arechis II (also ''Aretchis'', ''Arichis'', ''Arechi'' or ''Aregis'') (born According to the ''Chronicon Salernitanum'', Arechis ''vixit autem quinquaginta tres (53) annos; obiit septimo Kal. Septembris, anno ab incarnacione Domini 787, indictione ...
, whose duchy had only nominally been under royal authority, though certain kings had been effective at making their power known in the south, claimed that Benevento was the successor state
Succession of states is a concept in international relations regarding a successor state that has become a sovereign state over a territory (and populace) that was previously under the sovereignty of another state. The theory has its roots in 19th- ...
of the kingdom. He tried to turn Benevento into a ''secundum Ticinum'': a second Pavia. He tried to claim the kingship, but with no support and no chance of a coronation in Pavia.
Charlemagne came down with an army, and his son Louis the Pious sent men, to force the Beneventan duke to submit, but his submission and promises were never kept and Arechis and his successors were ''de facto'' independent. The Beneventan dukes took the title ''prínceps'' (prince) instead of that of king.
The Lombards of southern Italy were thereafter in the anomalous position of holding land claimed by two empires: the Carolingian Empire to the north and west and the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
to the east. They typically made pledges and promises of tribute to the Carolingians, but effectively remained outside Frankish control. Benevento meanwhile grew to its greatest extent yet when it imposed a tribute on the Duchy of Naples, which was tenuously loyal to Byzantium and even conquered the Neapolitan city of Amalfi in 838. At one point in the reign of Sicard, Lombard control covered most of southern Italy save the very south of Apulia and Calabria and Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
, with its nominally attached cities. It was during the ninth century that a strong Lombard presence became entrenched in formerly Greek Apulia. However, Sicard had opened up the south to the invasive actions of the Saracens in his war with Andrew II of Naples
Andrew II was the duke of Naples from 834 to 840. During his reign, he was constantly at war with the Lombards and he allowed Gaeta, his vassal, to move towards independence under its own consuls.
In September 834, Andrew overthrew his son-in-law, ...
and when he was assassinated in 839, Amalfi declared independence and two factions fought for power in Benevento, crippling the principality and making it susceptible to external enemies.
The civil war lasted ten years and ended with a peace treaty imposed in 849 by Emperor Louis II, the only Frankish king to exercise actual sovereignty over the Lombard states. The treaty divided the kingdom into two states: the Principality of Benevento and the Principality of Salerno, with its capital at Salerno on the Tyrrhenian Sea.
Southern Italy and the Arabs, 836–915
Andrew II of Naples hired Islamic mercenaries and formed a Muslim-Christian alliance for his war with Sicard of Benevento in 836; Sicard responded with other Muslim mercenaries. The Saracens initially concentrated their attacks onSicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
and Byzantine Italy, but soon Radelchis I of Benevento called in more mercenaries, who destroyed Capua
Capua ( , ) is a city and ''comune'' in the province of Caserta, in the region of Campania, southern Italy, situated north of Naples, on the northeastern edge of the Campanian plain.
History
Ancient era
The name of Capua comes from the Etrus ...
in 841. Landulf the Old founded the present-day Capua, "New Capua", on a nearby hill. In general, the Lombard princes were less inclined to ally with the Saracens than with their Greek neighbours of Amalfi, Gaeta, Naples, and Sorrento. Guaifer of Salerno Guaifer (also ''Guaifar'', ''Waifer'', ''Waifar'', or ''Guaiferio'') (c. 835 – 880) was the Prince of Salerno from 861. The son of Daufer the Mute and grandson of Daufer the Prophet, he was the first of the Dauferidi to sit on the Salernitan ...
, however, briefly put himself under Muslim suzerainty.
In 847 a large Muslim force seized Bari, until then a Lombard gastaldate under the control of Pandenulf. Saracen incursions proceeded northwards until Adelchis of Benevento
{{Commons category, Adelchis of Benevento
Adelchis (died May 878) was the son of Radelchis I, Prince of Benevento, and successor of his brother Radelgar in 854.
It was given to Adelchis to preserve the ancient principality and its independenc ...
sought the help of his suzerain, Louis II, who allied with the Byzantine emperor Basil I
Basil I, called the Macedonian ( el, Βασίλειος ὁ Μακεδών, ''Basíleios ō Makedṓn'', 811 – 29 August 886), was a Byzantine Emperor who reigned from 867 to 886. Born a lowly peasant in the theme of Macedonia, he rose in the ...
in an effort to expel the Arabs from Bari in 869. An Arab landing force was defeated by the emperor in 871. Adelchis and Louis remained at war until the death of Louis in 875. Adelchis regarded himself as the true successor of the Lombard kings, and in that capacity he amended the ''Edictum Rothari
The ''Edictum Rothari'' (lit. ''Edict of Rothari''; also ''Edictus Rothari'' or ''Edictum Rotharis'') was the first written compilation of Lombard law, codified and promulgated on 22 November 643 by King Rothari in Pavia by a gairethinx, an ass ...
'', the last Lombard ruler to do so.
After the death of Louis, Landulf II of Capua briefly flirted with a Saracen alliance, but Pope John VIII
Pope John VIII ( la, Ioannes VIII; died 16 December 882) was the bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 14 December 872 to his death. He is often considered one of the ablest popes of the 9th century.
John devoted much of his papacy ...
convinced him to break it off. Guaimar I of Salerno Guaimar I (also ''Waimar'', ''Gaimar'', or ''Guaimario'') (c. 855 – 901) was the prince of Salerno from 880, when his father entered the monastery of Monte Cassino in August. His parents were Prince Guaifer and Landelaica, daughter of Lando I of ...
fought the Saracens with Byzantine troops. Throughout this period the Lombard princes swung in allegiance from one party to another. Finally, towards 915, Pope John X
Pope John X ( la, Ioannes X; died 28 May 928) was the bishop of Rome and nominal ruler of the Papal States from March 914 to his death. A candidate of the counts of Tusculum, he attempted to unify Italy under the leadership of Berengar of Friuli, ...
managed to unite the Christian princes of southern Italy against the Saracen establishments on the Garigliano
The Garigliano () is a river in central Italy.
It forms at the confluence of the rivers Gari (also known as the Rapido) and Liri. Garigliano is actually a deformation of "Gari-Lirano" (which in Italian means something like "Gari from the Liri") ...
river. The Saracens were ousted from Italy in the Battle of the Garigliano
The Battle of Garigliano was fought in 915 between Christian forces and the Saracens. Pope John X personally led the Christian forces into battle. The aim was to destroy the Arab fortress on the Garigliano River, which had threatened central Ita ...
in 915.
Lombard principalities in the tenth century
Atenulf I of Capua Atenulf I (died 910), called the Great (Latin ''magnus''), was the prince of Capua from 7 January 887 and of Benevento from 899, when he conquered that principality. He also used the title ''princeps gentis Langobardorum'': "prince of the Lombard p ...
in 900. He subsequently declared them to be in perpetual union, and they were separated only in 982, on the death of Pandulf Ironhead. With all of the Lombard south under his control, except Salerno, Atenulf felt safe to use the title ''Princeps Gentis Langobardorum'' ("prince of the Lombard people"), which Arechis II had begun using in 774. Among Atenulf's successors the principality was ruled jointly by fathers, sons, brothers, cousins, and uncles for the greater part of the century. Meanwhile, the prince Gisulf I of Salerno began using the title ''Langobardorum Gentis Princeps'' around mid-century, but the ideal of a united Lombard principality was realised only in December 977, when Gisulf died and his domains were inherited by Pandulf Ironhead, who temporarily held almost all Italy south of Rome and brought the Lombards into alliance with the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
. His territories were divided upon his death.
Landulf the Red of Benevento and Capua tried to conquer the principality of Salerno with the help of John III of Naples, but with the aid of Mastalus I of Amalfi, Gisulf repulsed him. The rulers of Benevento and Capua made several attempts on Byzantine Apulia at this time, but late in the century, the Byzantines, under the stiff rule of Basil II, gained ground on the Lombards.
The principal source for the history of the Lombard principalities in this period is the ''Chronicon Salernitanum The ''Chronicon Salernitanum'', or "Salerno Chronicle", is an anonymous 10th century chronicle of the history of the Principality of Salerno. It was probably written around 990 (or 974) and has been attributed to Radoald of Salerno, Abbot of San B ...
'', composed late in the tenth century at Salerno.
Norman conquest, 1017–1078
The diminished Beneventan principality soon lost its independence to the papacy and declined in importance until it fell in theNorman conquest of southern Italy
The Norman conquest of southern Italy lasted from 999 to 1139, involving many battles and independent conquerors.
In 1130, the territories in southern Italy united as the Kingdom of Sicily, which included the island of Sicily, the southern ...
. The Normans, first called in by the Lombards to fight the Byzantines for control of Apulia and Calabria (under the likes of Melus of Bari
Melus (also ''Milus'' or ''Meles'', ''Melo'' in Italian) (died 1020) was a Lombard nobleman from the Apulian town of Bari, whose ambition to carve for himself an autonomous territory from the Byzantine catapanate of Italy in the early eleven ...
and Arduin, among others), had become rivals for hegemony in the south. The Salernitan principality experienced a golden age under Guaimar III and Guaimar IV, but under Gisulf II, the principality shrank to insignificance and fell in 1078 to Robert Guiscard, who had married Gisulf's sister Sichelgaita Sikelgaita (also ''Sichelgaita'' or ''Sigelgaita'') (1040 – 16 April 1090) was a Lombard princess, the daughter of Prince Guaimar IV of Salerno and second wife of Duke Robert Guiscard of Apulia. She commanded troops in her own right.
Life
S ...
. The Capua principality was hotly contested during the reign of the hated Pandulf IV, the ''Wolf of the Abruzzi'', and, under his son, it fell, almost without contest, to the Norman Richard Drengot (1058). The Capuans revolted against Norman rule in 1091, expelling Richard's grandson Richard II and setting up one Lando IV.
Capua was again put under Norman rule after the Siege of Capua of 1098 and the city quickly declined in importance under a series of ineffective Norman rulers. The independent status of these Lombard states is in general attested by the ability of their rulers to switch suzerains at will. Often the legal vassal of the pope or the emperor (either Byzantine or Holy Roman), they were the real power-brokers in the south until their erstwhile allies, the Normans, rose to preeminence. The Lombards regarded the Normans as barbarians and the Byzantines as oppressors. Regarding their own civilisation as superior, the Lombards did indeed provide the environment for the illustrious Schola Medica Salernitana
The Schola Medica Salernitana ( it, Scuola Medica Salernitana) was a Medieval medical school, the first and most important of its kind. Situated on the Tyrrhenian Sea in the south Italian city of Salerno, it was founded in the 9th century and rose ...
.
Genetics
A genetic study published in '' Nature Communications'' in September 2018 found strong genetic similarities between Lombards of Italy and earlier Lombards of Central Europe. The Lombards of Central Europe displayed no genetic similarities with earlier populations of this region, but were on the other hand strikingly similar genetically to Bronze Age Scandinavians. Lombard males were primarily carriers of subclades of haplogroup R1b and I2a2a1, both of which are common among Germanic peoples. Lombard males were found to be more genetically homogenous than Lombard females. The evidence suggested that the Lombards originated in Northern Europe, and were a patriarchal people who settled Central Europe and then later Italy through a migration from the north.. "Late Bronze Age Hungarians show almost no resemblance to populations from modern central/northern Europe, especially compare to Bronze Age Germans and in particular Scandinavians, who, in contrast, show considerable overlap with our Szólád and Collegno central/northern ancestry samples... Our results are thus consistent with an origin of barbarian groups such as the Longobards somewhere in Northern and Central Europe..." A genetic study published in ''Science Advances
''Science Advances'' is a peer-reviewed multidisciplinary open-access scientific journal established in early 2015 and published by the American Association for the Advancement of Science. The journal's scope includes all areas of science, inclu ...
'' in September 2018 examined the remains of a Lombard male buried at an Alemannic graveyard. He was found to be a carrier of the paternal haplogroup R1b1a2a1a1c2b2b and the maternal haplogroup H65a. The graveyard also included the remains of a Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages
* Francia, a post-Roman state in France and Germany
* East Francia, the successor state to Francia in Germany ...
and a Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
male, both of whom were also carriers of subclades of the paternal haplogroup R1b1a2a1a1. The Lombard, Frankish and Byzantine males were all found to be closely related, and displayed close genetic links to Northern Europe, particularly Lithuania and Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
.
A genetic study published in the '' European Journal of Human Genetics'' in January 2019 examined the mtDNA of a large number of early medieval
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
Lombard remains from Central Europe and Italy. These individuals were found to be closely related and displayed strong genetic links to Northern Europe. The evidence suggested that the Lombard settlement of Italy was the result of a migration from the north involving both males and females.. " e presence in this cluster of haplogroups that reach high frequency in Northern European populations, suggests a possible link between this core group of individuals and the proposed homeland of different ancient barbarian Germanic groups... This supports the view that the spread of Longobards into Italy actually involved movements of people, who gave a substantial contribution to the gene pool of the resulting populations...This is even more remarkable thinking that, in many studied cases, military invasions are movements of males, and hence do not have consequences at the mtDNA level. Here, instead, we have evidence of maternally linked genetic similarities between LC in Hungary and Italy, supporting the view that immigration from Central Europe involved females as well as males."
Culture
Language
 The Lombardic language is extinct (unless Cimbrian and Mocheno represent surviving dialects). It declined beginning in the seventh century, but may have been in scattered use until as late as about the year 1000. Only fragments of the language have survived, the main evidence being individual words quoted in
The Lombardic language is extinct (unless Cimbrian and Mocheno represent surviving dialects). It declined beginning in the seventh century, but may have been in scattered use until as late as about the year 1000. Only fragments of the language have survived, the main evidence being individual words quoted in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
texts. In the absence of Lombardic texts, it is not possible to draw any conclusions about the language's morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
* Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
* Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies ...
and syntax. The genetic classification of the language depends entirely on phonology. Since there is evidence that Lombardic participated in, and indeed shows some of the earliest evidence for, the High German consonant shift, it is usually classified as an Elbe Germanic
Elbe Germanic, also called Irminonic or Erminonic, is a term introduced by the German linguist Friedrich Maurer (1898–1984) in his book, ''Nordgermanen und Alemanen'', to describe the unattested proto-language, or dialectal grouping, ancest ...
or Upper German dialect.
runic
Runes are the letters in a set of related alphabets known as runic alphabets native to the Germanic peoples. Runes were used to write various Germanic languages (with some exceptions) before they adopted the Latin alphabet, and for specialised ...
inscriptions. Primary source texts include short inscriptions in the Elder Futhark, among them the "bronze capsule of Schretzheim" (c. 600) and the silver belt buckle found in Pforzen, Ostallgäu
Ostallgäu is a ''Landkreis'' (district) in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany. It is bounded by (from the west and clockwise) the districts of Oberallgäu, Unterallgäu, Augsburg, Landsberg, Weilheim-Schongau and Garmisch-Partenkirchen, and by the Au ...
(Schwaben
Swabia ; german: Schwaben , colloquially ''Schwabenland'' or ''Ländle''; archaic English also Suabia or Svebia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany.
The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of ...
). A number of Latin texts include Lombardic names, and Lombardic legal texts contain terms taken from the legal vocabulary of the vernacular. In 2005, Emilia Denčeva argued that the inscription of the Pernik sword may be Lombardic.
The Italian language preserves a large number of Lombardic words, although it is not always easy to distinguish them from other Germanic borrowings such as those from Gothic or from Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages
* Francia, a post-Roman state in France and Germany
* East Francia, the successor state to Francia in Germany ...
. They often bear some resemblance to English words, as Lombardic was akin to Old Saxon
Old Saxon, also known as Old Low German, was a Germanic language and the earliest recorded form of Low German (spoken nowadays in Northern Germany, the northeastern Netherlands, southern Denmark, the Americas and parts of Eastern Europe). It ...
. For instance, ''landa'' from ''land'', ''guardia'' from ''wardan'' (warden), ''guerra'' from ''werra'' (war), ''ricco'' from ''rikki'' (rich), and ''guadare'' from ''wadjan'' (to wade).
The ''Codice diplomatico longobardo'', a collection of legal documents, makes reference to many Lombardic terms, some of them still in use in the Italian language:
''barba'' (beard), ''marchio'' (mark), ''maniscalco'' (blacksmith), ''aia'' (courtyard), ''braida'' (suburban meadow), ''borgo'' (burg, village), ''fara'' (fundamental unity of Lombard social and military organization, presently used as toponym), ''picco'' (peak, mountain top, also used as toponym), ''sala'' (hall, room, also used as toponym), ''staffa'' (stirrup), ''stalla'' (stable), ''sculdascio'', ''faida'' (feud), ''manigoldo'' (scoundrel), ''sgherro'' (henchman); ''fanone'' (baleen), ''stamberga'' (hovel); ''anca'' (hip), ''guancia'' (cheek), ''nocca'' (knuckle), ''schiena'' (back); ''gazza'' (magpie), ''martora'' (marten); ''gualdo'' (wood, presently used as toponym), ''pozza'' (pool); verbs like ''bussare'' (to knock), ''piluccare'' (to peck), ''russare'' (to snore).
Social structure
Migration Period society
During their stay at the mouth of the Elbe, the Lombards came into contact with other western Germanic populations, such as the Saxons and the Frisians. From these populations, which had long been in contact with theCelts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
(especially the Saxons), they adopted a rigid social organization into castes, rarely present in other Germanic peoples.
The Lombard kings can be traced back as early as c. 380 and thus to the beginning of the Great Migration. Kingship developed among the Germanic peoples when the unity of a single military command was found necessary. Schmidt believed that the Germanic tribes were divided into cantons and that the earliest government was a general assembly that selected canton chiefs and war leaders in times of conflict. All such figures were probably selected from a caste of nobility. As a result of the wars of their wanderings, royal power developed such that the king became the representative of the people, but the influence of the people on the government did not fully disappear. Paul the Deacon gives an account of the Lombard tribal structure during the migration:
. . . in order that they might increase the number of their warriors, he Lombardsconfer liberty upon many whom they deliver from the yoke of bondage, and that the freedom of these may be regarded as established, they confirm it in their accustomed way by an arrow, uttering certain words of their country in confirmation of the fact.Complete emancipation appears to have been granted only among the Franks and the Lombards.
Society of the Catholic kingdom
Lombard society was divided into classes comparable to those found in the other Germanic successor states of Rome,Frankish Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during Rep ...
and Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
under the Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
. There was a noble class, a class of free persons beneath them, a class of unfree non-slaves (serfs), and finally slaves. The aristocracy itself was poorer, more urbanised, and less landed than elsewhere. Aside from the richest and most powerful of the dukes and the king himself, Lombard noblemen tended to live in cities (unlike their Frankish counterparts) and hold little more than twice as much in land as the merchant class (a far cry from provincial Frankish aristocrats who held vast swathes of land, hundreds of times larger than those beneath his status). The aristocracy by the eighth century was highly dependent on the king for means of income related especially to judicial duties: many Lombard nobles are referred to in contemporary documents as ''iudices'' (judges) even when their offices had important military and legislative functions as well.
The freemen of the Lombard kingdom were far more numerous than in Frankish lands, especially in the eighth century, when they are almost invisible in surviving documentary evidence. Smallholders, owner-cultivators, and rentiers are the most numerous types of person in surviving diplomata for the Lombard kingdom. They may have owned more than half of the land in Lombard Italy. The freemen were ''exercitales'' and ''viri devoti'', that is, soldiers and "devoted men" (a military term like "retainers"); they formed the levy
Levy, Lévy or Levies may refer to:
People
* Levy (surname), people with the surname Levy or Lévy
* Levy Adcock (born 1988), American football player
* Levy Barent Cohen (1747–1808), Dutch-born British financier and community worker
* Levy ...
of the Lombard army, and they were sometimes, if infrequently, called to serve, though this seems not to have been their preference. The small landed class, however, lacked the political influence necessary with the king (and the dukes) to control the politics and legislation of the kingdom. The aristocracy was more thoroughly powerful politically if not economically in Italy than in contemporary Gaul and Spain.
 The urbanisation of Lombard Italy was characterised by the (or "city as islands"). It appears from archaeology that the great cities of Lombard Italy—
The urbanisation of Lombard Italy was characterised by the (or "city as islands"). It appears from archaeology that the great cities of Lombard Italy—Pavia
Pavia (, , , ; la, Ticinum; Medieval Latin: ) is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy in northern Italy, south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It has a population of c. 73,086. The city was the cap ...
, Lucca
Lucca ( , ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, Central Italy, on the Serchio River, in a fertile plain near the Ligurian Sea. The city has a population of about 89,000, while its province has a population of 383,957.
Lucca is known as one ...
, Siena
Siena ( , ; lat, Sena Iulia) is a city in Tuscany, Italy. It is the capital of the province of Siena.
The city is historically linked to commercial and banking activities, having been a major banking center until the 13th and 14th centur ...
, Arezzo, Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
—were themselves formed of small urban cores within the old Roman city walls. The cities of the Roman Empire had been partially destroyed in the series of wars of the fifth and sixth centuries. Many sectors were left in ruins and ancient monuments became fields of grass used as pastures for animals, thus the Roman Forum became the ''Campo Vaccino'', the field of cows. The portions of the cities that remained intact were small, modest, contained a cathedral or major church (often sumptuously decorated), and a few public buildings and townhouses of the aristocracy. Few buildings of importance were stone, most were wood. In the end, the inhabited parts of the cities were separated from one another by stretches of pasture even within the city walls.
Lombard states
*Lombard state on the Carpathians (6th century) *Lombard state in Pannonia (6th century) * Kingdom of Italy and List of Kings of the Lombards *Principality of Benevento
The Duchy of Benevento (after 774, Principality of Benevento) was the southernmost Lombard duchy in the Italian Peninsula that was centred on Benevento, a city in Southern Italy. Lombard dukes ruled Benevento from 571 to 1077, when it was conq ...
and List of Dukes and Princes of Benevento
* Principality of Salerno and List of Princes of Salerno
This page is a list of the rulers of the Principality of Salerno.
When Prince Sicard of Benevento was assassinated by Radelchis in 839, the people of Salerno promptly proclaimed his brother, Siconulf, prince. War raged between Radelchis and Sico ...
* Principality of Capua and List of Princes of Capua
Religious history
The legend from Origo may hint that initially, before the passage from Scandinavia to the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, the Lombards worshiped theVanir
In Norse mythology, the Vanir (; Old Norse: , singular Vanr ) are a group of gods associated with fertility, wisdom, and the ability to see the future. The Vanir are one of two groups of gods (the other being the Æsir) and are the namesake of the ...
. Later, in contact with other Germanic populations, they adopted the worship of the Æsir
The Æsir (Old Norse: ) are the gods of the principal pantheon in Norse religion. They include Odin, Frigg, Höðr, Thor, and Baldr. The second Norse pantheon is the Vanir. In Norse mythology, the two pantheons wage war against each other, ...
: an evolution that marked the passage from the adoration of deities related to fertility and the earth to the cult of warlike gods.
In chapter 40 of his '' Germania'', Roman historian Tacitus, discussing the Suebian tribes of Germania, writes that the Lombards were one of the Suebian tribes united in worship of the deity Nerthus, who is often identified with the Norse goddess Freyja
In Norse paganism, Freyja (Old Norse "(the) Lady") is a goddess associated with love, beauty, fertility, sex, war, gold, and seiðr (magic for seeing and influencing the future). Freyja is the owner of the necklace Brísingamen, rides a chario ...
. The other tribes were the Reudigni The Reudigni were one of the Nerthus-worshipping Germanic tribes mentioned by Tacitus in ''Germania''. Schüttebr>suggests that the name should be read Rendingi or Randingi and then the name would be the same as the Rondings of ''Widsith''. They ha ...
, Aviones The Aviones or Auiones (*''Awioniz'' meaning "island people") were one of the Nerthus-worshipping Germanic tribes of the 1st century mentioned by Tacitus in '' Germania'', and they lived either in the southern Jutland Peninsula, or on Öland. They ...
, Anglii
The Angles ( ang, Ængle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ...
, Varini
The Varini, Warni or Warini were one or more Germanic peoples who originally lived in what is now northeastern Germany, near the Baltic sea.
They are first named in the Roman era, and appear to have survived into the Middle Ages. It is proposed ...
, Eudoses
The Jutes (), Iuti, or Iutæ ( da, Jyder, non, Jótar, ang, Ēotas) were one of the Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the departure of the Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic nations ...
, Suarines and Nuitones.
St. Barbatus of Benevento observed many pagan rituals and traditions among the Lombards authorised by the Duke Romuald, son of King Grimoald:Christianisation
The Lombards first adopted Christianity while still in Pannonia, but their conversion and Christianisation was largely nominal and far from complete. During the reign of Wacho, they were Orthodox Catholics allied with theByzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, but Alboin converted to Arianism as an ally of the Ostrogoths and invaded Italy. All these Christian conversions primarily affected the aristocracy, while the common people remained pagan.
In Italy, the Lombards were intensively Christianised, and the pressure to convert to Catholicism was great. With the Bavarian queen Theodelinda
Theodelinda also spelled ''Theudelinde'' ( 570–628 AD), was a queen of the Lombards by marriage to two consecutive Lombard rulers, Autari and then Agilulf, and regent of Lombardia during the minority of her son Adaloald, and co-regent when he ...
, a Catholic, the monarchy was brought under heavy Catholic influence. After initial support for the anti-Rome party in the Schism of the Three Chapters The Schism of the Three Chapters was a schism that affected Chalcedonian Christianity in Northern Italy lasting from 553 to 698 AD, although the area out of communion with Rome contracted throughout that time. It was part of a larger Three-Chapter ...
, Theodelinda remained a close contact and supporter of Pope Gregory I. In 603, Adaloald
Adaloald (602–628) was the Lombard king of Italy from 616 to 626.
He was son and heir of King Agilulf and his Catholic queen Theodelinda. He was baptised shortly after his birth in 602; the abbot Secundus of Non (later historian) was his g ...
, the heir to the throne, received Catholic baptism. However, the lack of spiritual involvement of most of the Lombards in religious disputes remained constant, so much so that the opposition between Catholics, on the one hand, and pagans, Arians and schismatics, on the other, soon took on political significance. The supporters of Roman orthodoxy, led by the Bavarian dynasty
The Bavarian dynasty was those kings of the Lombards who were descended from Garibald I, the Agilolfing duke of Bavaria. They came to rule the Lombards through Garibald's daughter Theodelinda, who married the Lombard king Authari in 588. The Ba ...
, were politically the proponents of greater integration with the Romans, accompanied by a strategy of preserving the status quo with the Byzantines. Arians, pagans and schismatics, rooted above all in the north-eastern regions of the kingdom (Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
), were instead interpreters of the preservation of the warlike and aggressive spirit of the people. Thus, to the "pro-Catholic" phase of Agilulf
Agilulf ( 555 – April 616), called ''the Thuringian'' and nicknamed ''Ago'', was a duke of Turin and king of the Lombards from 591 until his death.
A relative of his predecessor Authari, Agilulf was of Thuringian origin and belonged to the A ...
, Theodolinda and Adaloald followed, from 626 ( Arioald's accession to the throne) to 690 (definitive defeat of the rebel Alahis
Alahis (or Alagis) (fl. 680–689) was the Arian duke of Trent and Brescia before becoming king of the Lombards after his successful rebellion in 688. He did not rule long, however.
His first rebellion against King Perctarit failed in 680, but ...
), a long phase of revival of Arianism, embodied by militarily aggressive kings like Rothari and Grimoald. However, tolerance towards Catholics was never questioned by the various kings, also safeguarded by the influential contribution of the respective queens (largely chosen, for reasons of dynastic legitimacy, among the Catholic princesses of the Bavarian dynasty).
In the seventh century, the nominally Christian aristocracy of Benevento was still practising pagan rituals such as sacrifices in "sacred" woods. By the end of the reign of Cunincpert
Cunincpert (also Cunibert or Cunipert) was king of the Lombards from 688 to 700. He succeeded his father Perctarit, though he was associated with the throne from 680.
Life
Soon after his assumption of the sole kingship, Cunincpert was ousted by ...
, however, the Lombards were more or less completely Catholicised. Under Liutprand Catholicism became tangible as the king sought to justify his title ''rex totius Italiae'' by uniting the south of the peninsula with the north, thereby bringing together his Italo-Roman and Germanic subjects into one Catholic State.
Beneventan Christianity
 The Duchy and eventually Principality of Benevento in southern Italy developed a unique Christian rite in the seventh and eighth centuries. The Beneventan rite is more closely related to the liturgy of the Ambrosian rite than to the Roman rite. The Beneventan rite has not survived in its complete form, although most of the principal feasts and several feasts of local significance are extant. The Beneventan rite appears to have been less complete, less systematic, and more liturgically flexible than the Roman rite.
Characteristic of this rite was the Beneventan chant, a Lombard-influenced chant that bore similarities to the
The Duchy and eventually Principality of Benevento in southern Italy developed a unique Christian rite in the seventh and eighth centuries. The Beneventan rite is more closely related to the liturgy of the Ambrosian rite than to the Roman rite. The Beneventan rite has not survived in its complete form, although most of the principal feasts and several feasts of local significance are extant. The Beneventan rite appears to have been less complete, less systematic, and more liturgically flexible than the Roman rite.
Characteristic of this rite was the Beneventan chant, a Lombard-influenced chant that bore similarities to the Ambrosian chant
Ambrosian chant (also known as Milanese chant) is the liturgical plainchant repertory of the Ambrosian rite of the Roman Catholic Church, related to but distinct from Gregorian chant. It is primarily associated with the Archdiocese of Milan, an ...
of Milan. The Beneventan chant is largely defined by its role in the liturgy of the Beneventan rite; many Beneventan chants were assigned multiple roles when inserted into Gregorian chantbooks, appearing variously as antiphons, offertories, and communions, for example. It was eventually supplanted by the Gregorian chant in the 11th century.
The chief centre of the Beneventan chant was Montecassino, one of the first and greatest abbeys of Western monasticism. Gisulf II of Benevento
Gisulf II (died between 749 and 753) was the third last duke of Benevento before the fall of the Lombard kingdom. He ruled from 743, when King Liutprand came down and removed Godescalc, to his death up to ten years later.The ''Lexikon'' gives a d ...
had donated a large swathe of land to Montecassino in 744, and that became the basis for an important state, the ''Terra Sancti Benedicti
The ''Terra Sancti Benedictʃti'' ("Land of Saint Benedict") was the secular territory, or seignory, of the powerful Abbey of Montecassino, the chief monastery of the megladon and one of the first Western monasteries: founded by Benedict of Nur ...
'', which was a subject only to Rome. The Cassinese influence on Christianity in southern Italy was immense. Montecassino was also the starting point for another characteristic of Beneventan monasticism, the use of the distinct Beneventan script
The Beneventan script was a medieval script which originated in the Duchy of Benevento in southern Italy. It was also called ''Langobarda'', ''Longobarda'', ''Longobardisca'' (signifying its origins in the territories ruled by the Lombards), or so ...
, a clear, angular script derived from the Roman cursive
Roman cursive (or Latin cursive) is a form of handwriting (or a script) used in ancient Rome and to some extent into the Middle Ages. It is customarily divided into old (or ancient) cursive and new cursive.
Old Roman cursive
Old Roman cursiv ...
as used by the Lombards.
Art
During their nomadic phase, the Lombards primarily created art that was easily carried with them, like arms and jewellery. Though relatively little of this has survived, it bears resemblance to the similar endeavours of other Germanic tribes of northern and central Europe from the same era. The first major modifications to the Germanic style of the Lombards came in Pannonia and especially in Italy, under the influence of local,Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, and Christian styles. The conversions from nomadism and paganism to settlement and Christianity also opened up new arenas of artistic expression, such as architecture (especially churches) and its accompanying decorative arts (such as frescoes).
northern Italy, 7th century, Metropolitan Museum of Art Langobardic - Fibula - Walters 542440.jpg, Lombard S-shaped fibula Arte longobarda, da sutri, bicchiere a forma di corno, fine VI-inizio VII sec.JPG, A glass drinking horn from Castel Trosino Langobardic - Shroud Cross - Walters 571773.jpg, Lombard ''Goldblattkreuz'' Cividale fibula1.jpg, Lombard fibulae Cividale Ratchis1.JPG, Altar of Ratchis Cividale Tempietto Longobardo - Westwand Märtyrerinnen 1.jpg, 8th-century Lombard sculpture depicting female martyrs, based on a Byzantine model. ''Tempietto Longobardo'',
Cividale del Friuli
Cividale del Friuli ( fur, Cividât (locally ); german: Östrich; sl, Čedad) is a town and '' comune'' in the Province of Udine, part of the North-Italian Friuli Venezia Giulia ''regione''. The town lies above sea-level in the foothills of th ...
Interno della cripta.jpg, Crypt of Sant'Eusebio, Pavia
Pavia (, , , ; la, Ticinum; Medieval Latin: ) is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy in northern Italy, south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It has a population of c. 73,086. The city was the cap ...
.
Architecture
 Few Lombard buildings have survived. Most have been lost, rebuilt, or renovated at some point, so they preserve little of their original Lombard structure. Lombard architecture was well-studied in the 20th century, and the four-volume ''Lombard Architecture'' (1919) by Arthur Kingsley Porter is a "monument of illustrated history".
The small
Few Lombard buildings have survived. Most have been lost, rebuilt, or renovated at some point, so they preserve little of their original Lombard structure. Lombard architecture was well-studied in the 20th century, and the four-volume ''Lombard Architecture'' (1919) by Arthur Kingsley Porter is a "monument of illustrated history".
The small Oratorio di Santa Maria in Valle
The Oratorio di Santa Maria, or Oratory of Santa Maria, previously called the Tempietto longobardo, is located in Valle on the north-eastern frontier at Cividale del Friuli in the province of Udine. It was erected in the 8th century under the r ...
in Cividale del Friuli
Cividale del Friuli ( fur, Cividât (locally ); german: Östrich; sl, Čedad) is a town and '' comune'' in the Province of Udine, part of the North-Italian Friuli Venezia Giulia ''regione''. The town lies above sea-level in the foothills of th ...
is probably one of the oldest preserved examples of Lombard architecture, as Cividale was the first Lombard city in Italy. Parts of Lombard constructions have been preserved in Pavia
Pavia (, , , ; la, Ticinum; Medieval Latin: ) is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy in northern Italy, south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It has a population of c. 73,086. The city was the cap ...
(San Pietro in Ciel d'Oro
San Pietro in Ciel d'Oro ( Italian for "Saint Peter in Golden Sky") is a Catholic basilica (and a former cathedral) of the Augustinians in Pavia, Italy, in the Lombardy region. Its name refers to the mosaics of gold leaf behind glass tesserae tha ...
, crypts of Sant'Eusebio and San Giovanni Domnarum) and Monza (cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominatio ...
). The ''Basilic autariana'' in Fara Gera d'Adda near Bergamo and the church of San Salvatore in Brescia also have Lombard elements. All these buildings are in northern Italy (Langobardia major), but by far the best-preserved Lombard structure is in southern Italy (Langobardia minor). The Church of Santa Sofia in Benevento was erected in 760 by Duke Arechis II, and it preserves Lombard frescoes on the walls and even Lombard capitals on the columns.
Lombard architecture flourished under the impulse provided by the Catholic monarchs like Theodelinda
Theodelinda also spelled ''Theudelinde'' ( 570–628 AD), was a queen of the Lombards by marriage to two consecutive Lombard rulers, Autari and then Agilulf, and regent of Lombardia during the minority of her son Adaloald, and co-regent when he ...
, Liutprand, and Desiderius
Desiderius, also known as Daufer or Dauferius (born – died ), was king of the Lombards in northern Italy, ruling from 756 to 774. The Frankish king of renown, Charlemagne, married Desiderius's daughter and subsequently conquered his realm. Des ...
to the foundation of monasteries to further their political control. Bobbio Abbey
Bobbio Abbey (Italian: ''Abbazia di San Colombano'') is a monastery founded by Irish Saint Columbanus in 614, around which later grew up the town of Bobbio, in the province of Piacenza, Emilia-Romagna, Italy. It is dedicated to Saint Columbanus. ...
was founded during this time.
Some of the late Lombard structures of the ninth and tenth centuries have been found to contain elements of style associated with Romanesque architecture
Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of medieval Europe characterized by semi-circular arches. There is no consensus for the beginning date of the Romanesque style, with proposals ranging from the 6th to the 11th century, this lat ...
and so have been dubbed " first Romanesque". These edifices are considered, along with some similar buildings in southern France and Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the nort ...
, to mark a transitory phase between the Pre-Romanesque
Pre-Romanesque art and architecture is the period in European art from either the emergence of the Merovingian kingdom in about 500 AD or from the Carolingian Renaissance in the late 8th century, to the beginning of the 11th century Romanesqu ...
and full-fledged Romanesque.
List of rulers
Notes and sources
Notes
Sources
Ancient sources * '' Cosmographer of Ravenna'' * ''Historia Langobardorum Codicis Gothani
The ''Historia Langobardorum codicis Gothani'', also called the ''Chronicon Gothanum'', is a history of the Lombard people written at and for the court of King Pippin of Italy between the years 806 and 810. It is preserved in the twelfth-century ...
'' in '' Codex Gothanus''
* '' Historia Langobardorum''
* '' Origo Gentis Langobardorum''
* Tacitus. ''Annals''
* Tacitus. '' Germania''
Modern sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* In two volumes. Diss. Eberhard-Karls-Universität zu Tübingen.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* .
*
*
External links
* {{Authority control Early Germanic peoples Migration Period Suebi