List of multiple discoveries on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Historians and sociologists have remarked upon the occurrence, in science, of "
multiple independent discovery
Multiple may refer to:
Economics
*Multiple finance, a method used to analyze stock prices
*Multiples of the price-to-earnings ratio
*Chain stores, are also referred to as 'Multiples'
*Box office multiple, the ratio of a film's total gross to tha ...
". Robert K. Merton
Robert King Merton (born Meyer Robert Schkolnick; July 4, 1910 – February 23, 2003) was an American sociologist who is considered a founding father of modern sociology, and a major contributor to the subfield of criminology. He served as th ...
defined such "multiples" as instances in which similar discoveries are made by scientists working independently of each other. "Sometimes," writes Merton, "the discoveries are simultaneous or almost so; sometimes a scientist will make a new discovery which, unknown to him, somebody else has made years before."
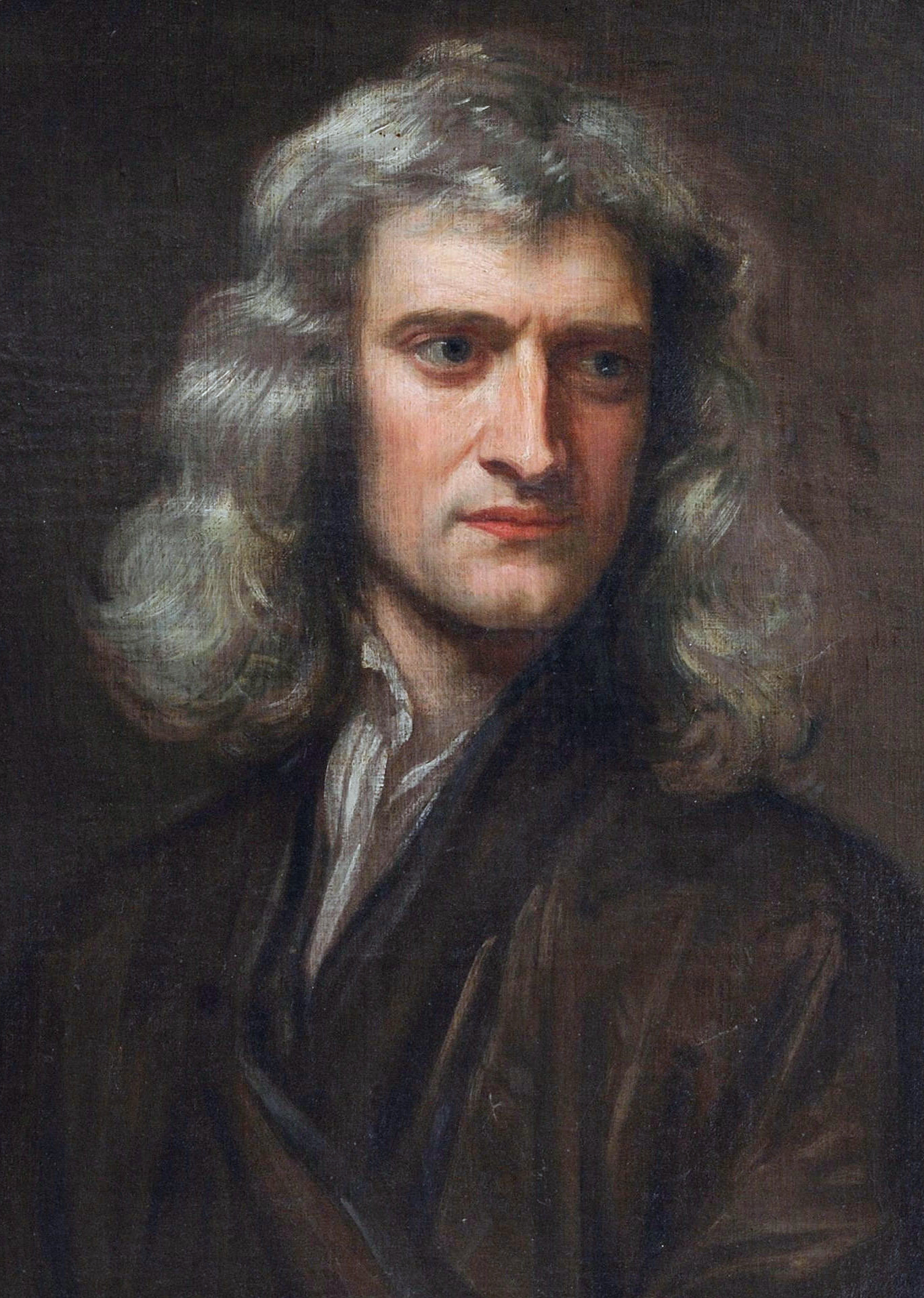
Commonly cited examples of multiple independent discovery are the 17th-century independent formulation of calculus
Calculus, originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the calculus of infinitesimals", is the mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithm ...
by Isaac Newton, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz and others, described by A. Rupert Hall; the 18th-century discovery of oxygen by Carl Wilhelm Scheele
Carl Wilhelm Scheele (, ; 9 December 1742 – 21 May 1786) was a Swedish German pharmaceutical chemist.
Scheele discovered oxygen (although Joseph Priestley published his findings first), and identified molybdenum, tungsten, barium, hydroge ...
, Joseph Priestley
Joseph Priestley (; 24 March 1733 – 6 February 1804) was an English chemist, natural philosopher, separatist theologian, grammarian, multi-subject educator, and liberal political theorist. He published over 150 works, and conducted exp ...
, Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( , ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794),
CNRS (
CNRS (
theory of the evolution of
 *
*
 * Gresham's (Copernicus') law: Nicole Oresme (c. 1370); Nicolaus Copernicus (1519); Thomas Gresham (16th century); Henry Dunning Macleod (1857). Ancient references to the same concept include one in
* Gresham's (Copernicus') law: Nicole Oresme (c. 1370); Nicolaus Copernicus (1519); Thomas Gresham (16th century); Henry Dunning Macleod (1857). Ancient references to the same concept include one in
 * Galileo Galilei and Simon Stevin: heavy and light balls fall together (''contra'' Aristotle).
* Galileo Galilei and Simon Stevin: Hydrostatic paradox (Stevin c. 1585, Galileo c. 1610).
* Scipione dal Ferro (1520) and
* Galileo Galilei and Simon Stevin: heavy and light balls fall together (''contra'' Aristotle).
* Galileo Galilei and Simon Stevin: Hydrostatic paradox (Stevin c. 1585, Galileo c. 1610).
* Scipione dal Ferro (1520) and

 *
*

 *
*
species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of ...
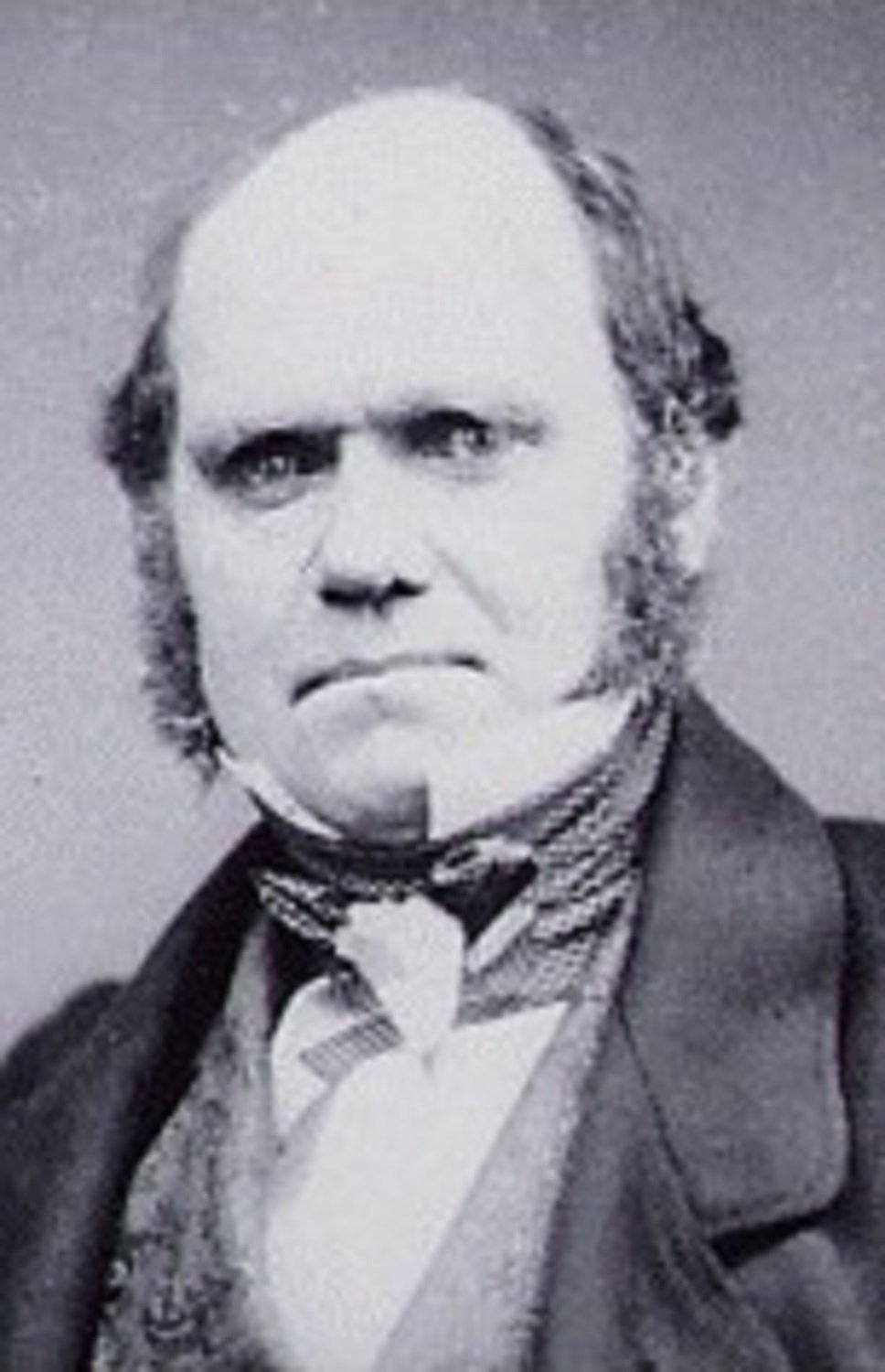
, independently advanced in the 19th century by Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended fr ...
and Alfred Russel Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace (8 January 1823 – 7 November 1913) was a British naturalist, explorer, geographer, anthropologist, biologist and illustrator. He is best known for independently conceiving the theory of evolution through natural sele ...
.
Multiple independent discovery, however, is not limited to such famous historic instances. Merton believed that it is multiple discoveries, rather than unique ones, that represent the ''common'' pattern in science.
Merton contrasted a "multiple" with a "singleton"—a discovery that has been made uniquely by a single scientist or group of scientists working together.
A distinction is drawn between a discovery and an invention
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It may also be an entirely new concept. If an i ...
, as discussed for example by Bolesław Prus
Aleksander Głowacki (20 August 1847 – 19 May 1912), better known by his pen name Bolesław Prus (), was a Polish novelist, a leading figure in the history of Polish literature and philosophy, as well as a distinctive voice in world lite ...
. However, discoveries and inventions are inextricably related, in that discoveries lead to inventions, and inventions facilitate discoveries; and since the same phenomenon of multiplicity occurs in relation to both discoveries and inventions, this article lists both multiple discoveries and multiple ''inventions''.
3rd century BCE
 *
* Aristarchus of Samos
Aristarchus of Samos (; grc-gre, Ἀρίσταρχος ὁ Σάμιος, ''Aristarkhos ho Samios''; ) was an ancient Greek astronomer and mathematician who presented the first known heliocentric model that placed the Sun at the center of the k ...
(c. 310 – c. 230 BCE) was the first known originator of a heliocentric (solar) system. Such a system was formulated again some 18 centuries later by Nicolaus Copernicus (1473–1543).
13th century CE
* 1242first description of the function ofpulmonary circulation
The pulmonary circulation is a division of the circulatory system in all vertebrates. The circuit begins with deoxygenated blood returned from the body to the right atrium of the heart where it is pumped out from the right ventricle to the lungs. ...
, in Egypt, by Ibn al-Nafis. Later independently rediscovered by the Europeans Michael Servetus (1553) and William Harvey (1616).
14th century
 * Gresham's (Copernicus') law: Nicole Oresme (c. 1370); Nicolaus Copernicus (1519); Thomas Gresham (16th century); Henry Dunning Macleod (1857). Ancient references to the same concept include one in
* Gresham's (Copernicus') law: Nicole Oresme (c. 1370); Nicolaus Copernicus (1519); Thomas Gresham (16th century); Henry Dunning Macleod (1857). Ancient references to the same concept include one in Aristophanes
Aristophanes (; grc, Ἀριστοφάνης, ; c. 446 – c. 386 BC), son of Philippus, of the deme Kydathenaion ( la, Cydathenaeum), was a comic playwright or comedy-writer of ancient Athens and a poet of Old Attic Comedy. Eleven of his ...
' comedy '' The Frogs'' (405 BCE), which compares bad politicians to bad coin (bad politicians and bad coin, respectively, drive good politicians and good coin out of circulation).
16th century

 * Galileo Galilei and Simon Stevin: heavy and light balls fall together (''contra'' Aristotle).
* Galileo Galilei and Simon Stevin: Hydrostatic paradox (Stevin c. 1585, Galileo c. 1610).
* Scipione dal Ferro (1520) and
* Galileo Galilei and Simon Stevin: heavy and light balls fall together (''contra'' Aristotle).
* Galileo Galilei and Simon Stevin: Hydrostatic paradox (Stevin c. 1585, Galileo c. 1610).
* Scipione dal Ferro (1520) and Niccolò Tartaglia Niccolò is an Italian male given name, derived from the Greek Nikolaos meaning "Victor of people" or "People's champion".
There are several male variations of the name: Nicolò, Niccolò, Nicolas, and Nicola. The female equivalent is Nicole. The f ...
(1535) independently developed a method for solving cubic equations
In algebra, a cubic equation in one variable is an equation of the form
:ax^3+bx^2+cx+d=0
in which is nonzero.
The solutions of this equation are called roots of the cubic function defined by the left-hand side of the equation. If all of th ...
.
* Olbers' paradox
Olbers's paradox, also known as the dark night sky paradox, is an argument in astrophysics and physical cosmology that says that the darkness of the night sky conflicts with the assumption of an infinite and eternal static universe. In the hy ...
(the "dark-night-sky paradox") was described by Thomas Digges
Thomas Digges (; c. 1546 – 24 August 1595) was an English mathematician and astronomer. He was the first to expound the Copernican system in English but discarded the notion of a fixed shell of immoveable stars to postulate infinitely many s ...
in the 16th century, by Johannes Kepler in the 17th century (1610), by Edmond Halley
Edmond (or Edmund) Halley (; – ) was an English astronomer, mathematician and physicist. He was the second Astronomer Royal in Britain, succeeding John Flamsteed in 1720.
From an observatory he constructed on Saint Helena in 1676–77, Hal ...
and by Jean-Philippe de Chéseaux in the 18th century, by Heinrich Wilhelm Matthias Olbers in the 19th century (1823), and definitively by Lord Kelvin in the 20th century (1901); some aspects of Kelvin's argument had been anticipated in the poet and short-story writer Edgar Allan Poe's essay, '' Eureka: A Prose Poem'' (1848), which also presaged by three-quarters of a century the Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the ...
theory of the universe.
* Continental drift
Continental drift is the hypothesis that the Earth's continents have moved over geologic time relative to each other, thus appearing to have "drifted" across the ocean bed. The idea of continental drift has been subsumed into the science of pl ...
, in varying independent iterations, was proposed by Abraham Ortelius
Abraham Ortelius (; also Ortels, Orthellius, Wortels; 4 or 14 April 152728 June 1598) was a Brabantian cartographer, geographer, and cosmographer, conventionally recognized as the creator of the first modern atlas, the ''Theatrum Orbis Terrarum ...
, Theodor Christoph Lilienthal (1756), Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 17696 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, naturalist, explorer, and proponent of Romantic philosophy and science. He was the younger brother of the Prussian minister, ...
(1801 and 1845), Antonio Snider-Pellegrini , Alfred Russel Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace (8 January 1823 – 7 November 1913) was a British naturalist, explorer, geographer, anthropologist, biologist and illustrator. He is best known for independently conceiving the theory of evolution through natural sele ...
, Charles Lyell
Sir Charles Lyell, 1st Baronet, (14 November 1797 – 22 February 1875) was a Scottish geologist who demonstrated the power of known natural causes in explaining the earth's history. He is best known as the author of ''Principles of Geolo ...
, Franklin Coxworthy (between 1848 and 1890), Roberto Mantovani
Roberto Mantovani (25 March 1854 – 10 January 1933), was an Italian geologist and violinist. He proposed an early model of continental drift in which a single continent broke up and the continents were displaced by thermal expansion and volc ...
(between 1889 and 1909), William Henry Pickering
William Henry Pickering (February 15, 1858 – January 16, 1938) was an American astronomer. Pickering constructed and established several observatories or astronomical observation stations, notably including Percival Lowell's Flagstaff Observ ...
(1907), Frank Bursley Taylor (1908), and Alfred Wegener
Alfred Lothar Wegener (; ; 1 November 1880 – November 1930) was a German climatologist, geologist, geophysicist, meteorologist, and polar researcher.
During his lifetime he was primarily known for his achievements in meteorology and ...
(1912). In addition, in 1885 Eduard Suess had proposed a supercontinent Gondwana and in 1893 the Tethys Ocean, assuming a land-bridge between the present continents submerged in the form of a geosyncline
A geosyncline (originally called a geosynclinal) is an obsolete geological concept to explain orogens, which was developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, before the theory of plate tectonics was envisaged. Şengör (1982), p. 11 A g ...
; and in 1895 John Perry had written a paper proposing that the earth's interior was fluid, and disagreeing with Lord Kelvin on the age of the earth.
17th century

 *
* Sunspot
Sunspots are solar phenomena, phenomena on the Sun's photosphere that appear as temporary spots that are darker than the surrounding areas. They are regions of reduced surface temperature caused by concentrations of magnetic flux that inhibi ...
s Thomas Harriot (England, 1610), Johannes and David Fabricius David Fabricius (9 March 1564 – 7 May 1617) was a German pastor who made two major discoveries in the early days of telescopic astronomy, jointly with his eldest son, Johannes Fabricius (1587–1615).
David Fabricius (Latinization of his proper ...
( Frisia, 1611), Galileo Galilei (Italy, 1612), Christoph Scheiner
Christoph Scheiner SJ (25 July 1573 (or 1575) – 18 June 1650) was a Jesuit priest, physicist and astronomer in Ingolstadt.
Biography Augsburg/Dillingen: 1591–1605
Scheiner was born in Markt Wald near Mindelheim in Swabia, earlier markgravate ...
(Germany, 1612).
* Logarithms John Napier ( Scotland, 1614) and Joost Bürgi
Joost () was an Internet TV service, created by Niklas Zennström and Janus Friis (founders of Skype and Kazaa). During 2007–2008 Joost used peer-to-peer TV (P2PTV) technology to distribute content to their Mozilla-based desktop player; in la ...
(Switzerland, 1618).
* Analytic geometry
In classical mathematics, analytic geometry, also known as coordinate geometry or Cartesian geometry, is the study of geometry using a coordinate system. This contrasts with synthetic geometry.
Analytic geometry is used in physics and engineer ...
René Descartes, Pierre de Fermat.
* Problem of points solved by both Pierre de Fermat (France, 1654), Blaise Pascal
Blaise Pascal ( , , ; ; 19 June 1623 – 19 August 1662) was a French mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher, and Catholic writer.
He was a child prodigy who was educated by his father, a tax collector in Rouen. Pascal's earliest m ...
(France, 1654), and Huygens (Holland, 1657).
* Determinants Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz and Seki Kōwa
, Selin, Helaine. (1997). ''Encyclopaedia of the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine in Non-Western Cultures,'' p. 890 also known as ,Selin, was a Japanese mathematician and author of the Edo period.
Seki laid foundations for the subs ...
.
* Calculus
Calculus, originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the calculus of infinitesimals", is the mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithm ...
Isaac Newton, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Pierre de Fermat and others.
* Boyle's law
Boyle's law, also referred to as the Boyle–Mariotte law, or Mariotte's law (especially in France), is an experimental gas law that describes the relationship between pressure and volume of a confined gas. Boyle's law has been stated as:
The a ...
(sometimes referred to as the "Boyle-Mariotte law") is one of the gas laws and basis of derivation for the ideal gas law, which describes the relationship between the product pressure and volume within a closed system
A closed system is a natural physical system that does not allow transfer of matter in or out of the system, although — in contexts such as physics, chemistry or engineering — the transfer of energy (''e.g.'' as work or heat) is allowed.
In ...
as constant when temperature remains at a fixed measure. The law was named for chemist
A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a scientist trained in the study of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties. Chemists carefully describe th ...
and physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe.
Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate caus ...
Robert Boyle who published the original law in 1662. The French physicist Edme Mariotte discovered the same law independently of Boyle in 1676.
* Newton–Raphson methodJoseph Raphson
Joseph Raphson (c. 1668 – c. 1715) was an English mathematician and intellectual known best for the Newton–Raphson method.
Biography
Very little is known about Raphson's life. Connor and Robertson give his date of birth as 1668 based on a 16 ...
(1690), Isaac Newton (Newton's work was written in 1671, but not published until 1736).
* Brachistochrone
In physics and mathematics, a brachistochrone curve (), or curve of fastest descent, is the one lying on the plane between a point ''A'' and a lower point ''B'', where ''B'' is not directly below ''A'', on which a bead slides frictionlessly under ...
problem solved by Johann Bernoulli, Jakob Bernoulli, Isaac Newton, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Guillaume de l'Hôpital
Guillaume François Antoine, Marquis de l'Hôpital (; sometimes spelled L'Hospital; 1661 – 2 February 1704), also known as Guillaume-François-Antoine Marquis de l'Hôpital, Marquis de Sainte-Mesme, Comte d'Entremont, and Seigneur d'Ouques-la- ...
, and Ehrenfried Walther von Tschirnhaus
Ehrenfried Walther von Tschirnhaus (or Tschirnhauß, ; 10 April 1651 – 11 October 1708) was a German mathematician, physicist, physician, and philosopher. He introduced the Tschirnhaus transformation and is considered by some to have been the ...
. The problem was posed in 1696 by Johann Bernoulli, and its solutions were published next year.
* Steam engine: Patent granted to Thomas Savery
Thomas Savery (; c. 1650 – 15 May 1715) was an English inventor and engineer. He invented the first commercially used steam-powered device, a steam pump which is often referred to as the "Savery engine". Savery's steam pump was a revolutionar ...
in 1698. The invention has often been credited to Thomas Newcomen (1712). Other early inventors have included Taqī al-Dīn (1551), Jerónimo de Ayanz y Beaumont
Jerónimo de Ayanz y Beaumont (1553 – March 23, 1613 AD) was a Spanish soldier, painter, astronomer, musician and inventor.
He was born in Guendulain (Navarre).
He built an air-renovated diving suit that allowed a man to remain underwat ...
(1606), Giambattista della Porta, Giovanni Branca (1629), Cosimo de' Medici
Cosimo di Giovanni de' Medici (27 September 1389 – 1 August 1464) was an Italian banker and politician who established the Medici family as effective rulers of Florence during much of the Italian Renaissance. His power derived from his wealth ...
(1641), Evangelista Torricelli (1643), Otto Von Guericke
Otto von Guericke ( , , ; spelled Gericke until 1666; November 20, 1602 – May 11, 1686 ; November 30, 1602 – May 21, 1686 ) was a German scientist, inventor, and politician. His pioneering scientific work, the development of experimental me ...
(1672), Denis Papin
Denis Papin FRS (; 22 August 1647 – 26 August 1713) was a French physicist, mathematician and inventor, best known for his pioneering invention of the steam digester, the forerunner of the pressure cooker and of the steam engine.
Early li ...
(1679), and many others.
18th century
 *
* Platinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a dense, malleable, ductile, highly unreactive, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name originates from Spanish , a diminutive of "silver".
Platin ...
Antonio de Ulloa
Antonio de Ulloa y de la Torre-Giralt, FRS, FRSA, KOS (12 January 1716 – 3 July 1795) was a Spanish naval officer, scientist, and administrator. At the age of nineteen, he joined the French Geodesic Mission to what is now the countr ...
and Charles Wood (both in the 1740s).
* Leyden Jar
A Leyden jar (or Leiden jar, or archaically, sometimes Kleistian jar) is an electrical component that stores a high-voltage electric charge (from an external source) between electrical conductors on the inside and outside of a glass jar. It typi ...
Ewald Georg von Kleist (1745) and Pieter van Musschenbroek
Pieter van Musschenbroek (14 March 1692 – 19 September 1761) was a Dutch scientist. He was a professor in Duisburg, Utrecht, and Leiden, where he held positions in mathematics, philosophy, medicine, and astronomy. He is credited with the inve ...
(1745–46).
* Lightning rodBenjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading intel ...
(1749) and Prokop Diviš
Dom Prokop Diviš, O.Praem. () (26 March 1698 – 21 December 1765) was a Czech canon regular, theologian and natural scientist. In an attempt to prevent thunderstorms from occurring, he inadvertently constructed one of the first grounde ...
(1754) (debated: Diviš's apparatus is assumed to have been more effective than Franklin's lightning rods in 1754, but was intended for a different purpose than lightning protection).
* Law of conservation of matterdiscovered by Mikhail Lomonosov, 1756; and independently by Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( , ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794),
CNRS (
CNRS (
Oxygen
Carl Wilhelm Scheele
Carl Wilhelm Scheele (, ; 9 December 1742 – 21 May 1786) was a Swedish German pharmaceutical chemist.
Scheele discovered oxygen (although Joseph Priestley published his findings first), and identified molybdenum, tungsten, barium, hydroge ...
(Uppsala
Uppsala (, or all ending in , ; archaically spelled ''Upsala'') is the county seat of Uppsala County and the fourth-largest city in Sweden, after Stockholm, Gothenburg, and Malmö. It had 177,074 inhabitants in 2019.
Located north of the capi ...
, 1773), Joseph Priestley
Joseph Priestley (; 24 March 1733 – 6 February 1804) was an English chemist, natural philosopher, separatist theologian, grammarian, multi-subject educator, and liberal political theorist. He published over 150 works, and conducted exp ...
( Wiltshire, 1774). The term was coined by Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( , ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794),
CNRS (






 * In a treatise written in 1805 and published in 1866,
* In a treatise written in 1805 and published in 1866,



















 * 1902:
* 1902:
c. 2008, HTML, Texas Instruments, retrieved 29 May 2008. and half a year later by Robert Noyce. Kilby won the 2000 Nobel Prize in Physics for his part in the invention of the integrated circuit. * The QR algorithm for calculating eigenvalues and eigenvectors of matrices was developed independently in the late 1950s by John G. F. Francis and by




 * In 2001 four different authors published different implementations of a
* In 2001 four different authors published different implementations of a
* Brian Greene, "Why He lbert EinsteinMatters: The fruits of one mind shaped civilization more than seems possible", '' Scientific American'', vol. 313, no. 3 (September 2015), pp. 34–37. * A. Rupert Hall, ''Philosophers at War'', New York, Cambridge University Press, 1980. *
Annals of Innovation: In the Air: Who says big ideas are rare?
Malcolm Gladwell, '' The New Yorker'', May 12, 2008
The Technium: Simultaneous Invention
Kevin Kelly, May 9, 2008 * , Peter Turney, January 15, 2007
by B.A. Trakhtenbrot, in the '' Annals of the History of Computing'', 6(4):384–400, 1984. {{DEFAULTSORT:Multiple Discoveries Science-related lists Lists of inventions or discoveries Scientific method Discovery and invention controversies
CNRS (
Michael Sendivogius
Michael Sendivogius (; pl, Michał Sędziwój; 2 February 1566 – 1636) was a Polish alchemist, philosopher, and medical doctor. A pioneer of chemistry, he developed ways of purification and creation of various acids, metals and other chemi ...
( pl, Michał Sędziwój; 1566–1636) is claimed as an earlier discoverer of oxygen.
* Black-hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can defo ...
theory John Michell, in a 1783 paper in '' The Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society'', wrote: "If the semi-diameter of a sphere of the same density as the Sun in the proportion of five hundred to one, and by supposing light to be attracted by the same force in proportion to its ass
Ass most commonly refers to:
* Buttocks (in informal American English)
* Donkey or ass, ''Equus africanus asinus''
**any other member of the subgenus ''Asinus''
Ass or ASS may also refer to:
Art and entertainment
* ''Ass'' (album), 1973 albu ...
with other bodies, all light emitted from such a body would be made to return towards it, by its own proper gravity." A few years later, a similar idea was suggested independently by Pierre-Simon Laplace
Pierre-Simon, marquis de Laplace (; ; 23 March 1749 – 5 March 1827) was a French scholar and polymath whose work was important to the development of engineering, mathematics, statistics, physics, astronomy, and philosophy. He summarized ...
. Stephen Hawking, ''A Brief History of Time'', Bantam, 1996, pp. 43–45.
* Malthusian catastrophe Thomas Robert Malthus (1798), Hong Liangji
Hong Liangji (, 1746–1809), courtesy names Junzhi () and Zhicun (), was a Chinese scholar, statesman, political theorist, and philosopher. He was most famous for his critical essay to the Jiaqing Emperor, which resulted in his banishment to ...
(1793).
* A method for measuring the specific heat
In thermodynamics, the specific heat capacity (symbol ) of a substance is the heat capacity of a sample of the substance divided by the mass of the sample, also sometimes referred to as massic heat capacity. Informally, it is the amount of heat ...
of a soliddevised independently by Benjamin Thompson
Sir Benjamin Thompson, Count Rumford, FRS (german: Reichsgraf von Rumford; March 26, 1753August 21, 1814) was an American-born British physicist and inventor whose challenges to established physical theory were part of the 19th-century revolut ...
, Count Rumford; and by Johan Wilcke
Johan Carl Wilcke was a Swedish physicist.
Biography
Wilcke was born in Wismar, son of a clergyman who in 1739 was appointed second pastor of the German Church in Stockholm. He went to the German school in Stockholm and enrolled at the Univers ...
, who published his discovery first (apparently not later than 1796, when he died).
19th century







 * In a treatise written in 1805 and published in 1866,
* In a treatise written in 1805 and published in 1866, Carl Friedrich Gauss
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; german: Gauß ; la, Carolus Fridericus Gauss; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician and physicist who made significant contributions to many fields in mathematics and science. Sometimes refer ...
describes an efficient algorithm to compute the discrete Fourier transform
In mathematics, the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) converts a finite sequence of equally-spaced samples of a function into a same-length sequence of equally-spaced samples of the discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT), which is a comp ...
. James W. Cooley and John W. Tukey
John Wilder Tukey (; June 16, 1915 – July 26, 2000) was an American mathematician and statistician, best known for the development of the fast Fourier Transform (FFT) algorithm and box plot. The Tukey range test, the Tukey lambda distributi ...
reinvented a similar algorithm in 1965.
* Complex plane
In mathematics, the complex plane is the plane formed by the complex numbers, with a Cartesian coordinate system such that the -axis, called the real axis, is formed by the real numbers, and the -axis, called the imaginary axis, is formed by th ...
Geometrical representation of complex numbers was discovered independently by Caspar Wessel
Caspar Wessel (8 June 1745, Vestby – 25 March 1818, Copenhagen) was a Danish– Norwegian mathematician and cartographer. In 1799, Wessel was the first person to describe the geometrical interpretation of complex numbers as points in the comple ...
(1799), Jean-Robert Argand (1806), John Warren (1828), and Carl Friedrich Gauss
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; german: Gauß ; la, Carolus Fridericus Gauss; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician and physicist who made significant contributions to many fields in mathematics and science. Sometimes refer ...
(1831).
* Cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Like zinc, it demonstrates oxidation state +2 in most of ...
Friedrich Strohmeyer, K.S.L Hermann (both in 1817).
* Grotthuss–Draper law (aka the Principle of Photochemical Activation)first proposed in 1817 by Theodor Grotthuss
Freiherr Christian Johann Dietrich Theodor von Grotthuss (20 January 1785 – 26 March 1822) was a Baltic German scientist known for establishing the first theory of electrolysis in 1806 and formulating the first law of photochemistry in 1817. His ...
, then independently, in 1842, by John William Draper. The law states that only that light which is absorbed by a system can bring about a photochemical change.
* Beryllium
Beryllium is a chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with other elements to form ...
Friedrich Wöhler
Friedrich Wöhler () FRS(For) HonFRSE (31 July 180023 September 1882) was a German chemist known for his work in inorganic chemistry, being the first to isolate the chemical elements beryllium and yttrium in pure metallic form. He was the first ...
, A.A.B. Bussy (1828).
* Electromagnetic induction
Electromagnetic or magnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force (emf) across an electrical conductor in a changing magnetic field.
Michael Faraday is generally credited with the discovery of induction in 1831, and James Clerk ...
was discovered by Michael Faraday in England in 1831, and independently about the same time by Joseph Henry in the U.S.
* Chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane, is an organic compound with formula C H Cl3 and a common organic solvent. It is a colorless, strong-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to PTFE. It is also a precursor to various ref ...
Samuel Guthrie in the United States (July 1831), and a few months later Eugène Soubeiran (France) and Justus von Liebig
Justus Freiherr von Liebig (12 May 1803 – 20 April 1873) was a German scientist who made major contributions to agricultural and biological chemistry, and is considered one of the principal founders of organic chemistry. As a professor at the ...
(Germany), all of them using variations of the haloform reaction
In chemistry, the haloform reaction is a chemical reaction in which a haloform (, where X is a halogen) is produced by the exhaustive halogenation of an acetyl group (, where R can be either a hydrogen atom, an alkyl or an aryl group), in the ...
.
* Non-Euclidean geometry ( hyperbolic geometry)Nikolai Ivanovich Lobachevsky
Nikolai Ivanovich Lobachevsky ( rus, Никола́й Ива́нович Лобаче́вский, p=nʲikɐˈlaj ɪˈvanəvʲɪtɕ ləbɐˈtɕɛfskʲɪj, a=Ru-Nikolai_Ivanovich_Lobachevsky.ogg; – ) was a Russian mathematician and geometer, kn ...
(1830), János Bolyai (1832); preceded by Gauss
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; german: Gauß ; la, Carolus Fridericus Gauss; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician and physicist who made significant contributions to many fields in mathematics and science. Sometimes refer ...
(unpublished result) c. 1805.
* Dandelin–Gräffe method, aka
Aka, AKA or a.k.a. may refer to:
* "Also known as", used to introduce an alternative name
Languages
* Aka language (Sudan)
* Aka language, in the Central African Republic
* Hruso language, in India, also referred to as Aka
* a prefix in the n ...
Lobachevsky methodan algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing ...
for finding multiple roots of a polynomial, developed independently by Germinal Pierre Dandelin, Karl Heinrich Gräffe, and Nikolai Ivanovich Lobachevsky
Nikolai Ivanovich Lobachevsky ( rus, Никола́й Ива́нович Лобаче́вский, p=nʲikɐˈlaj ɪˈvanəvʲɪtɕ ləbɐˈtɕɛfskʲɪj, a=Ru-Nikolai_Ivanovich_Lobachevsky.ogg; – ) was a Russian mathematician and geometer, kn ...
.
* Electrical telegraphCharles Wheatstone
Sir Charles Wheatstone FRS FRSE DCL LLD (6 February 1802 – 19 October 1875), was an English scientist and inventor of many scientific breakthroughs of the Victorian era, including the English concertina, the stereoscope (a device for dis ...
(England), 1837, Samuel F.B. Morse (United States), 1837.
* First law of thermodynamicsIn the late 19th century, various scientists independently stated that energy and matter are persistent, although this was later to be disregarded under subatomic conditions. Hess's Law ( Germain Hess), Julius Robert von Mayer, and James Joule were some of the first.
* 1846: Urbain Le Verrier
Urbain Jean Joseph Le Verrier FRS (FOR) HFRSE (; 11 March 1811 – 23 September 1877) was a French astronomer and mathematician who specialized in celestial mechanics and is best known for predicting the existence and position of Neptune using ...
and John Couch Adams, studying Uranus's orbit, independently proved that another, farther planet must exist. Neptune was found at the predicted moment and position.
* Bessemer Process
The Bessemer process was the first inexpensive industrial process for the mass production of steel from molten pig iron before the development of the open hearth furnace. The key principle is removal of impurities from the iron by oxidation wit ...
The process of removing impurities from steel on an industrial level using oxidation, developed in 1851 by American William Kelly and independently developed and patented in 1855 by eponymous Englishman Sir Henry Bessemer
Sir Henry Bessemer (19 January 1813 – 15 March 1898) was an English inventor, whose steel-making process would become the most important technique for making steel in the nineteenth century for almost one hundred years from 1856 to 1950. He ...
.
* The Möbius strip
In mathematics, a Möbius strip, Möbius band, or Möbius loop is a surface that can be formed by attaching the ends of a strip of paper together with a half-twist. As a mathematical object, it was discovered by Johann Benedict Listing and Aug ...
was discovered independently by the German astronomer–mathematician August Ferdinand Möbius
August Ferdinand Möbius (, ; ; 17 November 1790 – 26 September 1868) was a German mathematician and theoretical astronomer.
Early life and education
Möbius was born in Schulpforta, Electorate of Saxony, and was descended on his ...
and the German mathematician Johann Benedict Listing in 1858.
* Theory of evolution by natural selectionCharles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended fr ...
(discovery about 1840), Alfred Russel Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace (8 January 1823 – 7 November 1913) was a British naturalist, explorer, geographer, anthropologist, biologist and illustrator. He is best known for independently conceiving the theory of evolution through natural sele ...
(discovery about 1857–58)joint publication, 1859.
* 1862: 109P/Swift–Tuttle, the comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena are ...
generating the Perseid meteor shower
The Perseids are a prolific meteor shower associated with the comet Swift–Tuttle. The meteors are called the Perseids because the point from which they appear to hail (called the radiant) lies in the constellation Perseus.
Etymology
The name ...
, was independently discovered by Lewis Swift
Lewis A. Swift (February 29, 1820 – January 5, 1913) was an American astronomer who discovered 13 comets and 1,248 previously uncatalogued nebulae. Only William Herschel discovered more nebulae visually.
Discoveries
Swift discovered or co-discov ...
on 16 July 1862, and by Horace Parnell Tuttle on 19 July 1862. The comet made a return appearance in 1992, when it was rediscovered by Japanese astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, moons, comets and galaxies – in either obse ...
Tsuruhiko Kiuchi.
* 1868: French astronomer Pierre Janssen and English astronomer Norman Lockyer
Sir Joseph Norman Lockyer (17 May 1836 – 16 August 1920) was an English scientist and astronomer. Along with the French scientist Pierre Janssen, he is credited with discovering the gas helium. Lockyer also is remembered for being the ...
independently discovered evidence in the solar spectrum
Sunlight is a portion of the electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun, in particular infrared, visible, and ultraviolet light. On Earth, sunlight is scattered and filtered through Earth's atmosphere, and is obvious as daylight when th ...
for a new element that Lockyer named "helium". (The formal discovery of the element was made in 1895 by two Swedish chemists, Per Teodor Cleve and Nils Abraham Langlet
Nils Abraham Langlet (9 July 1868 – 30 March 1936; known by his second given name) was a Swedish chemist.
Biography
Langlet was born in Södertälje, Sweden. He was the son of architect Emil Victor Langlet (1824–1898) and his wife, author Cl ...
, who found helium emanating from the uranium ore
Ore is natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals, typically containing metals, that can be mined, treated and sold at a profit.Encyclopædia Britannica. "Ore". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 7 April ...
cleveite
Cleveite is an impure radioactive variety of uraninite containing uranium, found in Norway. It has the composition UO2 with about 10% of the uranium substituted by rare-earth elements. It was named after Swedish chemist Per Teodor Cleve.
Cleveit ...
.)
* 1869: Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleyev published his periodic table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the (chemical) elements, is a rows and columns arrangement of the chemical elements. It is widely used in chemistry, physics, and other sciences, and is generally seen as an icon of ch ...
of chemical elements, and the following year (1870) Julius Lothar Meyer
Julius Lothar Meyer (19 August 1830 – 11 April 1895) was a German chemist. He was one of the pioneers in developing the earliest versions of the periodic table of the chemical elements. Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev (his chief rival) and he ...
published his independently constructed version.
* 1873: Bolesław Prus
Aleksander Głowacki (20 August 1847 – 19 May 1912), better known by his pen name Bolesław Prus (), was a Polish novelist, a leading figure in the history of Polish literature and philosophy, as well as a distinctive voice in world lite ...
propounded a "law of combination" describing the making of discoveries and inventions: “Any new discovery or invention is a combination of earlier discoveries and inventions, or rests on them.” In 1978, Christopher Kasparek
Christopher Kasparek (born 1945) is a Scottish-born writer of Polish descent who has translated works by numerous authors, including Ignacy Krasicki, Bolesław Prus, Florian Znaniecki, Władysław Tatarkiewicz, Marian Rejewski, and Władysław ...
independently proposed an identical model of discovery and invention which he termed "recombinant conceptualization."
* 1876: Oskar Hertwig and Hermann Fol independently described the entry of sperm
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, wh ...
into the egg
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the a ...
and the subsequent fusion of the egg and sperm nuclei to form a single new nucleus.
* 1876: Elisha Gray
Elisha Gray (August 2, 1835 – January 21, 1901) was an American electrical engineer who co-founded the Western Electric Manufacturing Company. Gray is best known for his development of a telephone prototype in 1876 in Highland Park, Illinois ...
and Alexander Graham Bell
Alexander Graham Bell (, born Alexander Bell; March 3, 1847 – August 2, 1922) was a Scottish-born inventor, scientist and engineer who is credited with patenting the first practical telephone. He also co-founded the American Telephone and T ...
independently, on the same day, filed patents for invention of the telephone.
* 1877: Charles Cros
Charles Cros or Émile-Hortensius-Charles Cros (October 1, 1842 – August 9, 1888) was a French poet and inventor. He was born in Fabrezan, Aude.
Cros was a well-regarded poet and humorous writer. As an inventor, he was interested in the fiel ...
described the principles of the phonograph that was, independently, constructed the following year (1878) by Thomas Edison.
* British physicist-chemist Joseph Swan
Sir Joseph Wilson Swan FRS (31 October 1828 – 27 May 1914) was an English physicist, chemist, and inventor. He is known as an independent early developer of a successful incandescent light bulb, and is the person responsible for develop ...
independently developed an incandescent light bulb at the same time as American inventor Thomas Edison was independently working on ''his'' incandescent light bulb. Swan's first successful electric light bulb and Edison's electric light bulb were both patented in 1879.
* Circa 1880: the integraph
An Integraph is a mechanical analog computing device for plotting the integral of a graphically defined function.
History
Gaspard-Gustave de Coriolis first described the fundamental principal of a mechanical integraph in 1836 in the ''Journa ...
was invented independently by the British physicist Sir Charles Vernon Boys
Sir Charles Vernon Boys, FRS (15 March 1855 – 30 March 1944) was a British physicist, known for his careful and innovative experimental work in the fields of thermodynamics and high-speed photography, and as a popular science communicator th ...
and by the Polish mathematician, inventor, and electrical engineer Bruno Abakanowicz
Bruno Abdank-Abakanowicz (6 October 1852 – 29 August 1900) was a Polish mathematician, inventor, and electrical engineer.
Life
Abakanowicz was born in 1852 in the Russian Empire (now Lithuania). After graduating from the Riga Technical Unive ...
. Abakanowicz's design was produced by the Swiss firm Coradi of Zurich.
* 1886: The Hall–Héroult process for inexpensively producing aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It h ...
was independently discovered by the American engineer-inventor Charles Martin Hall
Charles Martin Hall (December 6, 1863 – December 27, 1914) was an American inventor, businessman, and chemist. He is best known for his invention in 1886 of an inexpensive method for producing aluminum, which became the first metal to atta ...
and the French scientist Paul Héroult.
* 1895: Adrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands an ...
was discovered by the Polish physiologist Napoleon Cybulski
Napoleon Nikodem Cybulski (Polish pronunciation: ; 14 September 1854 – 26 April 1919) was a Polish physiologist and a pioneer of endocrinology and electroencephalography. In 1895, he isolated and identified adrenaline.
Life
Napoleon Cybulski wa ...
. It was independently discovered in 1900 by the Japanese chemist Jōkichi Takamine and his assistant Keizo Uenaka.
* 1896: Two proofs of the prime number theorem (the asymptotic law of the distribution of prime numbers) were obtained independently by Jacques Hadamard and Charles de la Vallée-Poussin and appeared the same year.
* 1896: Discovery of radioactivity independently by Henri Becquerel and Silvanus Thompson.
* 1898: Discovery of thorium radioactivity by Gerhard Carl Schmidt and Marie Curie.
* Linguist
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Lingui ...
s Filipp Fortunatov and Ferdinand de Saussure independently formulated the sound law
A sound change, in historical linguistics, is a change in the pronunciation of a language. A sound change can involve the replacement of one speech sound (or, more generally, one phonetic feature value) by a different one (called phonetic cha ...
now known as the Fortunatov–de Saussure law.
* Vector calculus was invented independently by the American, Josiah Willard Gibbs
Josiah Willard Gibbs (; February 11, 1839 – April 28, 1903) was an American scientist who made significant theoretical contributions to physics, chemistry, and mathematics. His work on the applications of thermodynamics was instrumental in t ...
(1839–1903), and by the Englishman, Oliver Heaviside (1850–1925).
20th century




















 * 1902:
* 1902: Walter Sutton
Walter Stanborough Sutton (April 5, 1877 – November 10, 1916) was an American geneticist and physician whose most significant contribution to present-day biology was his theory that the Mendelian laws of inheritance could be applied to chromo ...
and Theodor Boveri
Theodor Heinrich Boveri (12 October 1862 – 15 October 1915) was a German zoologist, comparative anatomist and co-founder of modern cytology. He was notable for the first hypothesis regarding cellular processes that cause cancer, and for desc ...
independently proposed that the hereditary information is carried in the chromosomes.
* 1902: Richard Assmann and Léon Teisserenc de Bort independently discovered the stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is an atmospheric layer composed of stratified temperature layers, with the warm layers of air h ...
.
* E = mc2, though only Einstein provided the accepted interpretation Henri Poincaré, 1900; Olinto De Pretto, 1903; Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory ...
, 1905; Paul Langevin
Paul Langevin (; ; 23 January 1872 – 19 December 1946) was a French physicist who developed Langevin dynamics and the Langevin equation. He was one of the founders of the ''Comité de vigilance des intellectuels antifascistes'', an ant ...
, 1906.
* Brownian motion
Brownian motion, or pedesis (from grc, πήδησις "leaping"), is the random motion of particles suspended in a medium (a liquid or a gas).
This pattern of motion typically consists of random fluctuations in a particle's position ins ...
was independently explained by Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory ...
(in one of his 1905 papers) and by Marian Smoluchowski
Marian Smoluchowski (; 28 May 1872 – 5 September 1917) was a Polish physicist who worked in the Polish territories of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. He was a pioneer of statistical physics, and an avid mountaineer.
Life
Born into an upper-c ...
in 1906.
* The Einstein Relation was revealed independently by William Sutherland in 1905, by Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory ...
in 1905, and by Marian Smoluchowski
Marian Smoluchowski (; 28 May 1872 – 5 September 1917) was a Polish physicist who worked in the Polish territories of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. He was a pioneer of statistical physics, and an avid mountaineer.
Life
Born into an upper-c ...
in 1906.
* 1904: Epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and ...
synthesized independently by Friedrich Stolz and by Henry Drysdale Dakin
Henry Drysdale Dakin FRS (12 March 188010 February 1952) was an English chemist.
He was born in London as the youngest of 8 children to a family of steel merchants from Leeds. As a school boy, he conducted water analysis with the Leeds City Ana ...
.
* 1905: The chromosomal XY sex-determination system—that males have XY, and females XX, sex chromosomes—was discovered independently by Nettie Stevens
Nettie Maria Stevens (July 7, 1861 – May 4, 1912) was an American geneticist who discovered sex chromosomes. In 1905, soon after the rediscovery of Mendel's paper on genetics in 1900, she observed that male mealworms produced two kinds of sper ...
, at Bryn Mawr College
Bryn Mawr College ( ; Welsh: ) is a women's liberal arts college in Bryn Mawr, Pennsylvania. Founded as a Quaker institution in 1885, Bryn Mawr is one of the Seven Sister colleges, a group of elite, historically women's colleges in the United ...
, and by Edmund Beecher Wilson
Edmund Beecher Wilson (October 19, 1856 – March 3, 1939) was a pioneering American zoologist and geneticist. He wrote one of the most influential textbooks in modern biology, ''The Cell''.
Career
Wilson was born in Geneva, Illinois, the s ...
at Columbia University.
* 1907: Lutetium
Lutetium is a chemical element with the symbol Lu and atomic number 71. It is a silvery white metal, which resists corrosion in dry air, but not in moist air. Lutetium is the last element in the lanthanide series, and it is traditionally counted am ...
discovered independently by French scientist Georges Urbain and by Austrian mineralogist Baron Carl Auer von Welsbach
Carl Auer von Welsbach (1 September 1858 – 4 August 1929), who received the Austrian noble title of Freiherr Auer von Welsbach in 1901, was an Austrian scientist and inventor, who separated didymium into the elements neodymium and praseody ...
.
* 1907: Hilbert space representation theorem, also known as Riesz representation theorem, the mathematical justification of the Bra-ket notation in the theory of quantum mechanics independently proved by Frigyes Riesz and Maurice René Fréchet.
* The Hardy–Weinberg principle is a principle of population genetics
Population genetics is a subfield of genetics that deals with genetic differences within and between populations, and is a part of evolutionary biology. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, and pop ...
that states that, in the absence of other evolutionary influences, allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
and genotype frequencies
Genetic variation in populations can be analyzed and quantified by the frequency of alleles. Two fundamental calculations are central to population genetics: allele frequencies and genotype frequencies. Genotype frequency in a population is the nu ...
in a population will remain constant from generation to generation. This law was formulated in 1908 independently by German obstetrician-gynecologist Wilhelm Weinberg
Wilhelm Weinberg (Stuttgart, 25 December 1862 – 27 November 1937, Tübingen) was a German obstetrician-gynecologist, practicing in Stuttgart, who in a 1908 paper, published in German in ''Jahresheft des Vereins für vaterländische Naturkund ...
and, a little later and a little less rigorously, by British mathematician G.H. Hardy.
* The Stark–Einstein law (aka photochemical equivalence law, or photoequivalence law)independently formulated between 1908 and 1913 by Johannes Stark
Johannes Stark (, 15 April 1874 – 21 June 1957) was a German physicist who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1919 "for his discovery of the Doppler effect in canal rays and the splitting of spectral lines in electric fields". This phe ...
and Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory ...
. It states that every photon that is absorbed will cause a (primary) chemical or physical reaction.
* In 1911 Ejnar Hertzsprung
Ejnar Hertzsprung (; Copenhagen, 8 October 1873 – 21 October 1967, Roskilde) was a Danish chemist and astronomer.
Career
Hertzsprung was born in Frederiksberg, Denmark, the son of Severin and Henriette. He studied chemical engineering at Cop ...
created the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram
The Hertzsprung–Russell diagram, abbreviated as H–R diagram, HR diagram or HRD, is a scatter plot of stars showing the relationship between the stars' absolute magnitudes or luminosities versus their stellar classifications or effective temp ...
, abbreviated ''H–R diagram'', ''HR diagram'', or ''HRD'' – a scatter plot of star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by its gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night, but their immense distances from Earth ma ...
s showing the relationship between the stars' absolute magnitude
Absolute magnitude () is a measure of the luminosity of a celestial object on an inverse logarithmic astronomical magnitude scale. An object's absolute magnitude is defined to be equal to the apparent magnitude that the object would have if it ...
s or luminosities versus their stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting th ...
s or effective temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature ...
s – a major step toward an understanding of stellar evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes over the course of time. Depending on the mass of the star, its lifetime can range from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is cons ...
. In 1913 the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram was independently created by Henry Norris Russell.
* Frequency-hopping spread spectrum
Frequency-hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) is a method of transmitting radio signals by rapidly changing the carrier frequency among many distinct frequencies occupying a large spectral band. The changes are controlled by a code known to both tra ...
in radio work was described by Johannes Zenneck (1908), Leonard Danilewicz (1929), Willem Broertjes (1929), and Hedy Lamarr
Hedy Lamarr (; born Hedwig Eva Maria Kiesler; November 9, 1914 January 19, 2000) was an Austrian-born American film actress and inventor. A film star during Hollywood's golden age, Lamarr has been described as one of the greatest movie actresse ...
and George Antheil (1942 US patent).
* By 1913, vitamin A was independently discovered by Elmer McCollum
Elmer Verner McCollum (March 3, 1879 – November 15, 1967) was an American biochemist known for his work on the influence of diet on health.Kruse, 1961. McCollum is also remembered for starting the first rat colony in the United States to be us ...
and Marguerite Davis
Marguerite Davis (September 16, 1887 – September 19, 1967) was an American biochemist, co-discoverer of vitamins A and B with Elmer Verner McCollum in 1913. Their research greatly influenced later research on nutrition.
Personal life
Davi ...
at the University of Wisconsin–Madison
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the ...
, and by Lafayette Mendel
Lafayette Benedict Mendel (February 5, 1872 – December 9, 1935) was an American biochemist known for his work in nutrition, with longtime collaborator Thomas B. Osborne, including the study of Vitamin A, Vitamin B, lysine and tryptophan.
...
and Thomas Burr Osborne at Yale University, who studied the role of fats in the diet.
* Bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteri ...
s ( viruses that infect bacteria)Frederick Twort
Frederick William Twort FRS (22 October 1877 – 20 March 1950) was an English bacteriologist and was the original discoverer in 1915 of bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria). He studied medicine at St Thomas's Hospital, London, was super ...
(1915), Félix d'Hérelle
Félix d'Hérelle (25 April 1873 – 22 February 1949) was a French microbiologist. He was co-discoverer of bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) and experimented with the possibility of phage therapy. D'Herelle has also been credited fo ...
(1917).
* Rotor cipher machinesTheo A. van Hengel and R.P.C. Spengler (1915); Edward Hebern Edward Hugh Hebern (April 23, 1869 – February 10, 1952) was an early inventor of rotor machines, devices for encryption.
Background
Edward Hugh Hebern was born in Streator, Illinois on April 23, 1869. His parents were Charles and Rosanna (Ro ...
(1917); Arthur Scherbius
Arthur Scherbius (30 October 1878 – 13 May 1929) was a German electrical engineer who invented the mechanical cipher Enigma machine. He patented the invention and later sold the machine under the brand name Enigma.
Scherbius offered uneq ...
( Enigma machine, 1918); Hugo Koch (1919); Arvid Damm (1919).
* Sound filmJoseph Tykociński-Tykociner
Joseph Tykociński-Tykociner (also known as Joseph T. Tykociner; 5 October 1877, in Włocławek, Congress Poland – 11 June 1969, in Urbana, Illinois, United States) was a Polish engineer and a pioneer of sound-on-film technology.
In 1921 he bec ...
(1922), Lee De Forest
Lee de Forest (August 26, 1873 – June 30, 1961) was an American inventor and a fundamentally important early pioneer in electronics. He invented the first electronic device for controlling current flow; the three-element "Audion" triode v ...
(1923).
* The Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the ...
theory of the universe—that the universe is expanding from a single original point—was developed from the independent derivation of the Friedmann equations from Albert Einstein's equations of general relativity by the Russian, Alexander Friedmann
Alexander Alexandrovich Friedmann (also spelled Friedman or Fridman ; russian: Алекса́ндр Алекса́ндрович Фри́дман) (June 16 .S. 4 1888 – September 16, 1925) was a Russian and Soviet physicist and mathematicia ...
, in 1922, and by the Belgian, Georges Lemaître, in 1927. The Big Bang theory was confirmed in 1929 by the American astronomer Edwin Hubble
Edwin Powell Hubble (November 20, 1889 – September 28, 1953) was an American astronomer. He played a crucial role in establishing the fields of extragalactic astronomy and observational cosmology.
Hubble proved that many objects previousl ...
's analysis of galactic redshifts. But the Big Bang theory had been presaged three-quarters of a century earlier in the American poet and short-story writer Edgar Allan Poe's then much-derided essay, '' Eureka: A Prose Poem'' (1848).
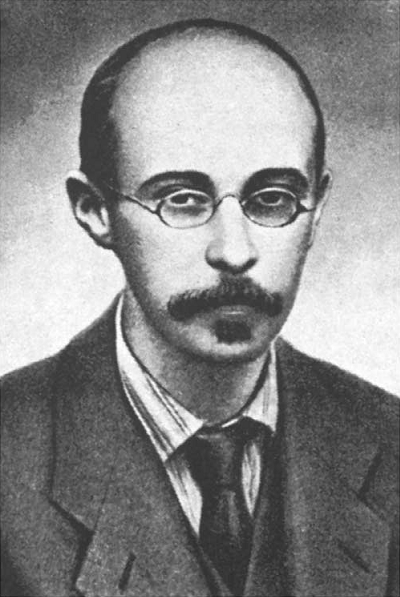
* Georgios Papanikolaou
Georgios Nikolaou Papanikolaou (or George Papanicolaou ; el, Γεώργιος Ν. Παπανικολάου ; 13 May 1883 – 19 February 1962) was a Greek physician who was a pioneer in cytopathology and early cancer detection, and inventor of ...
is credited with discovering as early as 1923 that cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is a cancer arising from the cervix. It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Early on, typically no symptoms are seen. Later symptoms may include abnormal va ...
cells can be detected microscopically, though his invention of the Pap test went largely ignored by physicians until 1943. Aurel Babeş of Romania independently made similar discoveries in 1927.
* " Primordial soup" theory of the abiogenetic evolution of life from carbon-based moleculesAlexander Oparin
Alexander Ivanovich Oparin (russian: Александр Иванович Опарин; – April 21, 1980) was a Soviet biochemist notable for his theories about the origin of life, and for his book ''The Origin of Life''. He also studied the bi ...
(1924), J.B.S. Haldane (1925).
* Jet stream was detected in the 1920s by Japanese meteorologist Wasaburo Oishi was a Japanese meteorologist. Born in Tosu, Saga, he is best known for his discovery of the high-altitude air currents now known as the jet stream. He was also an important Esperantist, serving as the second Board President of the from 1930 to 19 ...
, whose work largely went unnoticed outside Japan because he published his findings in Esperanto
Esperanto ( or ) is the world's most widely spoken constructed international auxiliary language. Created by the Warsaw-based ophthalmologist L. L. Zamenhof in 1887, it was intended to be a universal second language for international commun ...
. Often given some credit for discovery of jet streams is American pilot Wiley Post
Wiley Hardeman Post (November 22, 1898 – August 15, 1935) was a famed American aviator during the interwar period and the first pilot to fly solo around the world. Also known for his work in high-altitude flying, Post helped develop one ...
, who in the year before his 1935 death noticed that at times his ground speed greatly exceeded his air speed
In aviation, airspeed is the speed of an aircraft relative to the air. Among the common conventions for qualifying airspeed are:
* Indicated airspeed ("IAS"), what is read on an airspeed gauge connected to a Pitot-static system;
* Calibrated ...
. Real understanding of the nature of jet streams is often credited to experience in World War II military flights.
* Borůvka's algorithm
Borůvka's algorithm is a greedy algorithm for finding a minimum spanning tree in a graph,
or a minimum spanning forest in the case of a graph that is not connected.
It was first published in 1926 by Otakar Borůvka as a method of constructing an ...
, an algorithm for finding a minimum spanning tree in a graph, was first published in 1926 by Otakar Borůvka. The algorithm was rediscovered by Choquet in 1938; again by Florek, Łukasiewicz, Perkal, Steinhaus, and Zubrzycki; and again by Sollin in 1965.
* 1927: The discovery of phosphocreatine was reported by Grace Palmer Eggleton and Philip Eggleton
Philip Eggleton FRSE (19 March 1903 – 7 October 1954) was a British biochemist, physiologist, lecturer, and (with his wife Grace Palmer Eggleton), co-discoverer of Phosphagens.
Life
Eggleton was born at Kingston-on-Thames on 19 March 1903 ...
of the University of Cambridge and separately by Cyrus H. Fiske and Yellapragada Subbarow
Yellapragada Subba Rao (12 January 1895 – 8 August 1948) was a pioneering Indian biochemist who discovered the function of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) as an energy source in the cell, developed methotrexate for the treatment of cancer a ...
of Harvard Medical School.
* 1929: Dmitri Skobeltsyn first observed the positron
The positron or antielectron is the antiparticle or the antimatter counterpart of the electron. It has an electric charge of +1 '' e'', a spin of 1/2 (the same as the electron), and the same mass as an electron. When a positron collides ...
in 1929. Chung-Yao Chao
Chung-Yao Chao (; 27 June 1902 – 28 May 1998) was a Chinese theoretical physicist. He studied the scattering of gamma rays in lead by pair production in 1930, without knowing that positrons were involved in the anomalously high scattering cros ...
also observed the positron in 1929, though he did not recognize it as such.
* Undefinability theorem, an important limitative result in mathematical logic Kurt Gödel (1930; described in a 1931 private letter, but not published); Alfred Tarski
Alfred Tarski (, born Alfred Teitelbaum;School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of St Andrews ''School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of St Andrews''. January 14, 1901 – October 26, 1983) was a Polish-American logician a ...
(1933).
* Chandrasekhar Limit
The Chandrasekhar limit () is the maximum mass of a stable white dwarf star. The currently accepted value of the Chandrasekhar limit is about ().
White dwarfs resist gravitational collapse primarily through electron degeneracy pressure, compar ...
—published by Subramanyan Chandrasekhar (1931–35); also computed by Lev Landau (1932).
* A theory of protein denaturation
In biochemistry, denaturation is a process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose the quaternary structure, tertiary structure, and secondary structure which is present in their native state, by application of some external stress or compoun ...
is widely attributed to Alfred Mirsky
Alfred Ezra Mirsky (October 17, 1900 – June 19, 1974) was an American pioneer in molecular biology.
Mirsky graduated from Harvard College in 1922, after which he studied for two years at the Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeon ...
and Linus Pauling, who published their paper in 1936, though it had been independently discovered in 1931 by Hsien Wu
Hsien Wu (; 24 November 1893 – 8 August 1959) was a Chinese biochemist and geneticist. He was the first to propose that protein denaturation was a purely conformational change, i.e., corresponded to protein unfolding and not to some chemica ...
, whom some now recognize as the originator of the theory.
* Electroluminescence in silicon carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder and crystal si ...
, now known as the LED, was discovered independently by Oleg Losev in 1927 and by H.J. Round in 1907, and possibly in 1936 in zinc sulfide by Georges Destriau
Georges Destriau (1 August 1903 - 20 January 1960) was a French physicist and early observer of electroluminescence.
Education and Research
In 1926 Destriau became an engineer at the École Centrale des Arts et Manufactures in Paris. Thereafter h ...
, who believed it was actually a form of incandescence.
* 1934: Natural deduction In logic and proof theory, natural deduction is a kind of proof calculus in which logical reasoning is expressed by inference rules closely related to the "natural" way of reasoning. This contrasts with Hilbert-style systems, which instead use a ...
, an approach to proof theory
Proof theory is a major branchAccording to Wang (1981), pp. 3–4, proof theory is one of four domains mathematical logic, together with model theory, axiomatic set theory, and recursion theory. Barwise (1978) consists of four corresponding parts, ...
in philosophical logic
Understood in a narrow sense, philosophical logic is the area of logic that studies the application of logical methods to philosophical problems, often in the form of extended logical systems like modal logic. Some theorists conceive philosophical ...
discovered independently by Gerhard Gentzen and Stanisław Jaśkowski in 1934.
* The Gelfond–Schneider theorem, in mathematics, establishes the transcendence
Transcendence, transcendent, or transcendental may refer to:
Mathematics
* Transcendental number, a number that is not the root of any polynomial with rational coefficients
* Algebraic element or transcendental element, an element of a field exten ...
of a large class of numbers. It was originally proved in 1934 by Aleksandr Gelfond, and again independently in 1935 by Theodor Schneider.
* The Penrose triangle
The Penrose triangle, also known as the Penrose tribar, the impossible tribar, or the impossible triangle, is a triangular impossible object, an optical illusion consisting of an object which can be depicted in a perspective drawing, but cannot ...
, also known as the "tribar", is an impossible object. It was first created by the Swedish artist Oscar Reutersvärd
Oscar Reutersvärd (29 November 1915 – 2 February 2002) was a Swedish graphic artist, who in 1934 pioneered the art of 3D drawings that may initially appear feasible, yet cannot be physically constructed. He is sometimes described as "the fathe ...
in 1934. The mathematician Roger Penrose independently devised and popularised it in the 1950s.
* 1936: In computer science, the concept of the "universal computing machine" (now generally called the " Turing Machine") was proposed by Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher, and theoretical biologist. Turing was highly influential in the development of theoretical co ...
, but also independently by Emil Post, both in 1936. Similar approaches, also aiming to cover the concept of universal computing, were introduced by S.C. Kleene, Rózsa Péter, and Alonzo Church
Alonzo Church (June 14, 1903 – August 11, 1995) was an American mathematician, computer scientist, logician, philosopher, professor and editor who made major contributions to mathematical logic and the foundations of theoretical computer scien ...
that same year. Also in 1936, Konrad Zuse
Konrad Ernst Otto Zuse (; 22 June 1910 – 18 December 1995) was a German civil engineer, pioneering computer scientist, inventor and businessman. His greatest achievement was the world's first programmable computer; the functional program-c ...
tried to build a binary electrically driven mechanical calculator with limited programability; however, Zuse's machine was never fully functional. The later Atanasoff–Berry Computer ("ABC"), designed by John Vincent Atanasoff and Clifford Berry
Clifford Edward Berry (April 19, 1918 – October 30, 1963) helped John Vincent Atanasoff create the first digital electronic computer in 1939, the Atanasoff–Berry computer (ABC).
Biography
Clifford Berry was born April 19, 1918, in Gladbr ...
, was the first fully electronic
Electronic may refer to:
*Electronics, the science of how to control electric energy in semiconductor
* ''Electronics'' (magazine), a defunct American trade journal
*Electronic storage, the storage of data using an electronic device
*Electronic co ...
digital
Digital usually refers to something using discrete digits, often binary digits.
Technology and computing Hardware
*Digital electronics, electronic circuits which operate using digital signals
**Digital camera, which captures and stores digital i ...
computing device; while not programmable, it pioneered important elements of modern computing, including binary arithmetic
A binary number is a number expressed in the base-2 numeral system or binary numeral system, a method of mathematical expression which uses only two symbols: typically "0" ( zero) and "1" ( one).
The base-2 numeral system is a positional notatio ...
and electronic switching elements, though its special-purpose nature and lack of a changeable, stored program distinguish it from modern computers.
* The atom bomb
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
was independently thought of by Leó Szilárd, Józef Rotblat
Sir Joseph Rotblat (4 November 1908 – 31 August 2005) was a Polish and British physicist. During World War II he worked on Tube Alloys and the Manhattan Project, but left the Los Alamos Laboratory on grounds of conscience after it became c ...
and others.
* The jet engine, independently invented by Hans von Ohain
Hans Joachim Pabst von Ohain (14 December 191113 March 1998) was a German physicist, engineer, and the designer of the first operational jet engine. Together with Frank Whittle he is called the "father of the jet engine". His first test unit ra ...
(1939), Secondo Campini
Secondo Campini (August 28, 1904 – February 7, 1980) was an Italian engineer and one of the pioneers of the jet engine.
Campini was born at Bologna, Emilia-Romagna. In 1931 he wrote a proposal for the Italian Air Ministry on the value of jet pr ...
(1940) and Frank Whittle (1941) and used in working aircraft.
* In agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
, the ability of synthetic auxins
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essenti ...
2,4-D, 2,4,5-T, and MCPA to act as hormone herbicides
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weedkillers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page fo ...
was discovered independently by four groups in the United States and Great Britain: William G. Templeman and coworkers (1941); Philip Nutman, Gerard Thornton, and Juda Quastel (1942); Franklin Jones (1942); and Ezra Kraus, John W. Mitchell, and Charles L. Hamner (1943). All four groups were subject to various aspects of wartime secrecy, and the exact order of discovery is a matter of some debate.
* The point-contact transistor was independently invented in 1947 by Americans William Shockley, John Bardeen and Walter Brattain, working at Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007),
is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by mult ...
, and in 1948 by German physicists Herbert Mataré
Herbert Franz Mataré (22 September 1912 – 2 September 2011) was a German physicist. The focus of his research was the field of semiconductor research. His best-known work is the first functional European transistor, which he developed and paten ...
and Heinrich Welker
Heinrich Johann Welker (9 September 1912 in Ingolstadt – 25 December 1981 in Erlangen) was a German theoretical and applied physicist who invented the "transistron", a transistor made at Westinghouse independently of the first successful trans ...
, working at the ''Compagnie des Freins et Signaux'', a Westinghouse subsidiary located in Paris. The Americans were jointly awarded the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
"for their researches on semiconductors and their discovery of the transistor effect."
* 1949: A formal definition of cliques
A clique ( AusE, CanE, or ), in the social sciences, is a group of individuals who interact with one another and share similar interests. Interacting with cliques is part of normative social development regardless of gender, ethnicity, or popula ...
in graph theory was simultaneously introduced by Luce and Perry (1949) and Festinger (1949).
* NMR spectroscopy was independently developed in the late 1940s and early 1950s by the Purcell group at Harvard University and the Bloch group at Stanford University. Edward Mills Purcell
Edward Mills Purcell (August 30, 1912 – March 7, 1997) was an American physicist who shared the 1952 Nobel Prize for Physics for his independent discovery (published 1946) of nuclear magnetic resonance in liquids and in solids. Nuclear magne ...
and Felix Bloch
Felix Bloch (23 October 1905 – 10 September 1983) was a Swiss- American physicist and Nobel physics laureate who worked mainly in the U.S. He and Edward Mills Purcell were awarded the 1952 Nobel Prize for Physics for "their development of new ...
shared the 1952 Nobel Prize in Physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
for their discoveries.
* Polio vaccine (1950–63): Hilary Koprowski, Jonas Salk, Albert Sabin
Albert Bruce Sabin ( ; August 26, 1906 – March 3, 1993) was a Polish-American medical researcher, best known for developing the oral polio vaccine, which has played a key role in nearly eradicating the disease. In 1969–72, he served as the ...
.
* The integrated circuit was devised independently by Jack Kilby in 1958''The Chip that Jack Built''c. 2008, HTML, Texas Instruments, retrieved 29 May 2008. and half a year later by Robert Noyce. Kilby won the 2000 Nobel Prize in Physics for his part in the invention of the integrated circuit. * The QR algorithm for calculating eigenvalues and eigenvectors of matrices was developed independently in the late 1950s by John G. F. Francis and by
Vera N. Kublanovskaya
Vera Nikolaevna Kublanovskaya (''née'' Totubalina; November 21, 1920 – February 21, 2012 ) was a Russian mathematician noted for her work on developing computational methods for solving spectral problems of algebra. She proposed the QR algorithm ...
. The algorithm is considered one of the most important developments in numerical linear algebra of the 20th century.
* Quantum electrodynamics and renormalization (1930s–40s): Ernst Stueckelberg
Ernst Carl Gerlach Stueckelberg (baptised as Johann Melchior Ernst Karl Gerlach Stückelberg, full name after 1911: Baron Ernst Carl Gerlach Stueckelberg von Breidenbach zu Breidenstein und Melsbach; 1 February 1905 – 4 September 1984) was a S ...
, Julian Schwinger, Richard Feynman
Richard Phillips Feynman (; May 11, 1918 – February 15, 1988) was an American theoretical physicist, known for his work in the path integral formulation of quantum mechanics, the theory of quantum electrodynamics, the physics of the superfl ...
, and Sin-Itiro Tomonaga, for which the latter 3 received the 1965 Nobel Prize in Physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
.
* The maser
A maser (, an acronym for microwave amplification by stimulated emission of radiation) is a device that produces coherent electromagnetic waves through amplification by stimulated emission. The first maser was built by Charles H. Townes, Jame ...
, a precursor to the laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The firs ...
, was described by Russian scientists in 1952, and built independently by scientists at Columbia University in 1953. The laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The firs ...
itself was developed independently by Gordon Gould
Gordon Gould (July 17, 1920 – September 16, 2005) was an American physicist who is sometimes credited with the invention of the laser and the optical amplifier. (Credit for the invention of the laser is disputed, since Charles Townes and Ar ...
at Columbia University and by researchers at Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007),
is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by mult ...
, and by the Russian scientist Aleksandr Prokhorov Aleksandr Prokhorov (russian: Алекса́ндр Про́хоров, link=no) is a male personal name of Russian origin may refer to:
* Alexander Prokhorov
Alexander Mikhailovich Prokhorov (born Alexander Michael Prochoroff, russian: Алекс ...
.
* Kolmogorov complexity, also known as "Kolmogorov–Chaitin complexity", descriptive complexity, etc., of an object such as a piece of text is a measure of the computational resources needed to specify the object. The concept was independently introduced by Ray Solomonoff, Andrey Kolmogorov
Andrey Nikolaevich Kolmogorov ( rus, Андре́й Никола́евич Колмого́ров, p=ɐnˈdrʲej nʲɪkɐˈlajɪvʲɪtɕ kəlmɐˈɡorəf, a=Ru-Andrey Nikolaevich Kolmogorov.ogg, 25 April 1903 – 20 October 1987) was a Sovi ...
and Gregory Chaitin in the 1960s.
* The concept of packet switching, a communications method in which discrete blocks of data ( packets) are routed
Routing is the process of selecting a path for traffic in a network or between or across multiple networks. Broadly, routing is performed in many types of networks, including circuit-switched networks, such as the public switched telephone netwo ...
between nodes over data links, was first explored by Paul Baran
Paul Baran (born Pesach Baran ; April 29, 1926 – March 26, 2011) was a Polish-American engineer who was a pioneer in the development of computer networks. He was one of the two independent inventors of packet switching, which is today the dom ...
in the early 1960s, and then independently a few years later by Donald Davies.
* The principles of atomic layer deposition
Atomic layer deposition (ALD) is a thin-film deposition technique based on the sequential use of a gas-phase chemical process; it is a subclass of chemical vapour deposition. The majority of ALD reactions use two chemicals called precursors (al ...
, a thin-film growth method that in the 2000s contributed to the continuation of semiconductor-device scaling in accord with Moore's law
Moore's law is the observation that the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empir ...
, were independently discovered in the early 1960s by the Soviet scientists Valentin Aleskovsky
Valentin Borisovich Aleskovsky (russian: Валенти́н Бори́сович Алеско́вский; 3 June 1912 - 29 January 2006) was a Soviet and Russian scientist and administrator known for his pioneering research on surface reactions ...
and Stanislav Koltsov and in 1974 by the Finnish inventor Tuomo Suntola
Tuomo Suntola (born 1943) is a Finnish physicist, inventor, and technology leader. He is best known for his pioneering research in materials science, developing the thin film growth technique called atomic layer deposition.
Early life
Suntola w ...
.
* Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) is a popular model in finance for trading off risk versus return. Three separate authors published it in academic journals and a fourth circulated unpublished papers.
* 1963: In a major advance in the development of plate tectonics theory, the Vine–Matthews–Morley hypothesis
The Vine–Matthews–Morley hypothesis, also known as the Morley–Vine–Matthews hypothesis, was the first key scientific test of the seafloor spreading theory of continental drift and plate tectonics. Its key impact was that it allowed the r ...
was independently proposed by Lawrence Morley
Lawrence Whitaker Morley (February 19, 1920 – April 22, 2013) was a Canadian geophysicist and remote sensing pioneer. He was best known for his studies on the magnetic properties of the oceanic crust and their effect on plate tectonics and for s ...
, and by Fred Vine
Frederick John Vine FRS (born 17 June 1939) is an English marine geologist and geophysicist. He made key contributions to the theory of plate tectonics, helping to show that the seafloor spreads from mid-ocean ridges with a symmetrical patter ...
and Drummond Matthews
Drummond Hoyle Matthews FRS (5 February 1931 – 20 July 1997), known as "Drum", was a British marine geologist and geophysicist and a key contributor to the theory of plate tectonics. His work, along with that of fellow Briton Fred Vine a ...
, linking seafloor spreading and the symmetric "zebra pattern" of magnetic reversals in the basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of a ...
rocks on either side of mid-ocean ridges.
* Cosmic background radiation
Cosmic background radiation is electromagnetic radiation from the Big Bang. The origin of this radiation depends on the region of the spectrum that is observed. One component is the cosmic microwave background. This component is redshifted ph ...
as a signature of the Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the ...
was confirmed by Arno Penzias
Arno Allan Penzias (; born April 26, 1933) is an American physicist, radio astronomer and Nobel laureate in physics. Along with Robert Woodrow Wilson, he discovered the cosmic microwave background radiation, which helped establish the Big Bang ...
and Robert Wilson of Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007),
is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by mult ...
. Penzias and Wilson had been testing a very sensitive microwave detector when they noticed that their equipment was picking up a strange noise that was independent of the orientation (direction) of their instrument. At first they thought the noise was generated due to pigeon droppings in the detector, but even after they removed the droppings the noise was still detected. Meanwhile, at nearby Princeton University two physicists, Robert Dicke
Robert Henry Dicke (; May 6, 1916 – March 4, 1997) was an American astronomer and physicist who made important contributions to the fields of astrophysics, atomic physics, cosmology and gravity. He was the Albert Einstein Professor in Scien ...
and Jim Peebles
Phillip James Edwin Peebles (born April 25, 1935) is a Canadian- American astrophysicist, astronomer, and theoretical cosmologist who is currently the Albert Einstein Professor in Science, Emeritus, at Princeton University. He is widely rega ...
, were working on a suggestion of George Gamow
George Gamow (March 4, 1904 – August 19, 1968), born Georgiy Antonovich Gamov ( uk, Георгій Антонович Гамов, russian: Георгий Антонович Гамов), was a Russian-born Soviet and American polymath, theoret ...
's that the early universe had been hot and dense; they believed its hot glow could still be detected but would be so red-shifted that it would manifest as microwaves. When Penzias and Wilson
Wilson may refer to:
People
*Wilson (name)
** List of people with given name Wilson
** List of people with surname Wilson
* Wilson (footballer, 1927–1998), Brazilian manager and defender
* Wilson (footballer, born 1984), full name Wilson R ...
learned about this, they realized that they had already detected the red-shifted microwaves and (to the disappointment of Dicke and Peebles) were awarded the 1978 Nobel Prize in physics.
* Conductive polymers: Between 1963 and 1977, doped and oxidized highly conductive polyacetylene derivatives were independently discovered, "lost", and then rediscovered at least four times. The last rediscovery won the 2000 Nobel prize in Chemistry, for the "discovery and development of conductive polymers". This was without reference to the previous discoveries. Citations in article " Conductive polymers."
* 1964: The relativistic model for the Higgs mechanism
In the Standard Model of particle physics, the Higgs mechanism is essential to explain the generation mechanism of the property " mass" for gauge bosons. Without the Higgs mechanism, all bosons (one of the two classes of particles, the other b ...
was developed by three independent groups: Robert Brout
Robert Brout (; June 14, 1928 – May 3, 2011) was an American theoretical physicist who made significant contributions in elementary particle physics. He was a professor of physics at Université Libre de Bruxelles where he had created, together ...
and François Englert
François, Baron Englert (; born 6 November 1932) is a Belgian theoretical physicist and 2013 Nobel prize laureate.
Englert is professor emeritus at the Université libre de Bruxelles (ULB), where he is a member of the Service de Physique Thé ...
; Peter Higgs
Peter Ware Higgs (born 29 May 1929) is a British theoretical physicist, Emeritus Professor in the University of Edinburgh,Griggs, Jessica (Summer 2008The Missing Piece ''Edit'' the University of Edinburgh Alumni Magazine, p. 17 and Nobel Prize ...
; and Gerald Guralnik
Gerald Stanford "Gerry" Guralnik (; September 17, 1936 – April 26, 2014) was the Chancellor’s Professor of Physics at Brown University. In 1964 he co-discovered the Higgs mechanism and Higgs boson with C. R. Hagen and Tom Kibble (GHK). As par ...
, Carl Richard Hagen, and Tom Kibble
Sir Thomas Walter Bannerman Kibble (; 23 December 1932 – 2 June 2016) was a British theoretical physicist, senior research investigator at the Blackett Laboratory and Emeritus Professor of Theoretical Physics at Imperial College London. His ...
. Slightly later, in 1965, it was also proposed by Soviet undergraduate students Alexander Migdal
Alexander Arkadyevich Migdal (russian: Александр Арка́дьевич Мигдал; born 22 July 1945) is a Russian-American physicist and entrepreneur, formerly at Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics, Space Research Institute, Pr ...
and Alexander Markovich Polyakov
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ...
. The existence of the " Higgs boson" was finally confirmed in 2012; Higgs and Englert were awarded a Nobel Prize in 2013.
* The Cocke–Younger–Kasami algorithm was independently discovered three times: by T. Kasami (1965), by Daniel H. Younger (1967), and by John Cocke and Jacob T. Schwartz (1970).
* The Wagner–Fischer algorithm In computer science, the Wagner–Fischer algorithm is a dynamic programming algorithm that computes the edit distance between two strings of characters.
History
The Wagner–Fischer algorithm has a history of multiple invention. Navarro lists the ...
, in computer science, was discovered and published at least six times.
* The affine scaling method for solving linear programming
Linear programming (LP), also called linear optimization, is a method to achieve the best outcome (such as maximum profit or lowest cost) in a mathematical model whose requirements are represented by linear relationships. Linear programming is ...
was discovered by Soviet mathematician I.I. Dikin in 1967. It went unnoticed in the West for two decades, until two groups of researchers in the U.S. reinvented it in 1985.
* Neutral theory of molecular evolution
The neutral theory of molecular evolution holds that most evolutionary changes occur at the molecular level, and most of the variation within and between species are due to random genetic drift of mutant alleles that are selectively neutral. The ...
was introduced by a Japanese biologist, Motoo Kimura
(November 13, 1924 – November 13, 1994) was a Japanese biologist best known for introducing the neutral theory of molecular evolution in 1968. He became one of the most influential theoretical population geneticists. He is remembered in genet ...
, in 1968, and independently by two American biologists, Jack Lester King and Thomas Hughes Jukes, in 1969.
* 1969: Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) structure was determined, and the hormone synthesized, independently by Andrew V. Schally and Roger Guillemin
Roger Charles Louis Guillemin (born January 11, 1924) is a French-American neuroscientist. He received the National Medal of Science in 1976, and the Nobel prize for medicine in 1977 for his work on neurohormones, sharing the prize that year w ...
, who shared the 1977 Nobel Prize in Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, accord ...
.
* 1970: Howard Temin
Howard Martin Temin (December 10, 1934 – February 9, 1994) was an American geneticist and virologist. He discovered reverse transcriptase in the 1970s at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, for which he shared the 1975 Nobel Prize in Phy ...
and David Baltimore
David Baltimore (born March 7, 1938) is an American biologist, university administrator, and 1975 Nobel laureate in Physiology or Medicine. He is President Emeritus and Distinguished Professor of Biology at the California Institute of Techno ...
independently discovered reverse transcriptase enzymes.
* The Knuth–Morris–Pratt string searching algorithm was developed by Donald Knuth and Vaughan Pratt and independently by J. H. Morris.
* The Cook–Levin theorem
In computational complexity theory, the Cook–Levin theorem, also known as Cook's theorem, states that the Boolean satisfiability problem is NP-complete. That is, it is in NP, and any problem in NP can be reduced in polynomial time by a determ ...
(also known as "Cook's theorem"), a result in computational complexity theory
In theoretical computer science and mathematics, computational complexity theory focuses on classifying computational problems according to their resource usage, and relating these classes to each other. A computational problem is a task solved ...
, was proven independently by Stephen Cook (1971 in the U.S.) and by Leonid Levin (1973 in the USSR). Levin was not aware of Cook's achievement because of communication difficulties between East and West during the Cold War. The other way round, Levin's work was not widely known in the West until around 1978.
* Mevastatin (compactin; ML-236B) was independently discovered by Akira Endo in Japan in a culture of ''Penicillium citrinium'' and by a British group in a culture of ''Penicillium brevicompactum''. Both reports were published in 1976.
* The Bohlen–Pierce scale
The Bohlen–Pierce scale (BP scale) is a musical tuning and scale, first described in the 1970s, that offers an alternative to the octave-repeating scales typical in Western and other musics, specifically the equal-tempered diatonic scale.
...
, a harmonic, non-octave musical scale, was independently discovered by Heinz Bohlen Heinz P. Bohlen (26 June 1935 – 2 February 2016)Heinz Bohlen
, ''Bohlen-Pierce-Confer ...
(1972), , ''Bohlen-Pierce-Confer ...
Kees van Prooijen Kees (Cornelis) van Prooijen (born 7 August 1952) is a creator of computer art. Although it does not bear his name, he independently discovered the Bohlen-Pierce scale, a non- octave-repeating scale based on the tritave and spectra containing odd ...
(1978) and John R. Pierce
John Robinson Pierce (March 27, 1910 – April 2, 2002), was an American engineer and author. He did extensive work concerning radio communication, microwave technology, computer music, psychoacoustics, and science fiction. Additionally to his ...
(1984).
* RSA, an algorithm suitable for signing and encryption in public-key cryptography, was publicly described in 1977 by Ron Rivest
Ronald Linn Rivest (; born May 6, 1947) is a cryptographer and an Institute Professor at MIT. He is a member of MIT's Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EECS) and a member of MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Int ...
, Adi Shamir
Adi Shamir ( he, עדי שמיר; born July 6, 1952) is an Israeli cryptographer. He is a co-inventor of the Rivest–Shamir–Adleman (RSA) algorithm (along with Ron Rivest and Len Adleman), a co-inventor of the Feige–Fiat–Shamir identifica ...
and Leonard Adleman. An equivalent system had been described in 1973 in an internal document by Clifford Cocks
Clifford Christopher Cocks (born 28 December 1950) is a British mathematician and cryptographer.
In 1973, while working at the United Kingdom Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ), he invented a public-key cryptography algorithm equiv ...
, a British mathematician working for the UK intelligence agency GCHQ, but his work was not revealed until 1997 due to its top-secret classification.
* 1973: Asymptotic freedom
In quantum field theory, asymptotic freedom is a property of some gauge theories that causes interactions between particles to become asymptotically weaker as the energy scale increases and the corresponding length scale decreases.
Asymptotic fre ...
, which states that the strong nuclear interaction between quarks
A quark () is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. All commonly o ...
decreases with decreasing distance, was discovered in 1973 by David Gross
David Jonathan Gross (; born February 19, 1941) is an American theoretical physicist and string theorist. Along with Frank Wilczek and David Politzer, he was awarded the 2004 Nobel Prize in Physics for their discovery of asymptotic freedom. G ...
and Frank Wilczek
Frank Anthony Wilczek (; born May 15, 1951) is an American theoretical physicist, mathematician and Nobel laureate. He is currently the Herman Feshbach Professor of Physics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Founding Direct ...
, and by David Politzer
Hugh David Politzer (; born August 31, 1949) is an American theoretical physicist and the Richard Chace Tolman Professor of Theoretical Physics at the California Institute of Technology. He shared the 2004 Nobel Prize in Physics with David Gr ...
, and was published in the same 1973 edition of the journal ''Physical Review Letters
''Physical Review Letters'' (''PRL''), established in 1958, is a peer-reviewed, scientific journal that is published 52 times per year by the American Physical Society. As also confirmed by various measurement standards, which include the '' Jour ...
''. For their work the three received the Nobel Prize in Physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
in 2004.
* 1974: The J/ψ meson was independently discovered by a group at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, headed by Burton Richter
Burton Richter (March 22, 1931 – July 18, 2018) was an American physicist. He led the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC) team which co-discovered the J/ψ meson in 1974, alongside the Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL) team led by Sa ...
, and by a group at Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL) is a United States Department of Energy national laboratories, United States Department of Energy national laboratory located in Upton, New York, Upton, Long Island, and was formally established in 1947 at th ...
, headed by Samuel Ting
Samuel Chao Chung Ting (, born January 27, 1936) is a Chinese-American physicist who, with Burton Richter, received the Nobel Prize in 1976 for discovering the subatomic J/ψ particle. More recently he has been the principal investigator in res ...
of MIT
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the m ...
. Both announced their discoveries on 11 November 1974. For their shared discovery, Richter and Ting shared the 1976 Nobel Prize in Physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
.
* 1975: Endorphins
Endorphins (contracted from endogenous morphine) are chemical signals in the brain that block the perception of pain and increase feelings of wellbeing. They are produced and stored in an area of the brain known as the pituitary gland.
Hist ...
were discovered independently in Scotland and the US in 1975.
* 1975: Two English biologists, Robin Holliday and John Pugh, and an American biologist, Arthur Riggs, independently suggested that methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group on a substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replacing a hydrogen atom. These t ...
, a chemical modification of DNA that is heritable and can be induced by environment
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, all living and non-living things occurring naturally
* Biophysical environment, the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or ...
al influences, including physical and emotional stresses, has an important part in controlling gene expression. This concept has become foundational for the field of epigenetics
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "o ...
, with its multifarious implications for physical and mental health and for sociopolitics.
* 1980: The asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere.
...
cause of the Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction that wiped out much life on Earth, including all dinosaurs
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is the ...
except for birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight ...
, was published in '' Science'' by Luis
Luis is a given name. It is the Spanish form of the originally Germanic name or . Other Iberian Romance languages have comparable forms: (with an accent mark on the i) in Portuguese and Galician, in Aragonese and Catalan, while is archaic ...
and Walter Alvarez
Walter Alvarez (born October 3, 1940) is a professor in the Earth and Planetary Science department at the University of California, Berkeley. He is most widely known for the theory that dinosaurs were killed by an asteroid impact, developed in co ...
''et al.''; and independently 2 weeks earlier, in ''Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are p ...
'', by Dutch geologist Jan Smit and Belgian geologist Jan Hertogen.
* 1983: Two separate research groups led by American Robert Gallo and French investigators and Luc Montagnier independently declared that a novel retrovirus may have been infecting AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ma ...
patients, and published their findings in the same issue of the journal '' Science''. A third contemporaneous group, at the University of California, San Francisco, led by Dr. Jay Levy, in 1983 independently discovered an AIDS virus which was very different from that reported by the Montagnier and Gallo groups and which indicated, for the first time, the heterogeneity of HIV isolates.
* Quantum cryptography—the first cryptographic method to rely not on mathematical complexity but on the laws of physics—was first postulated in 1984 by Charles Bennett and Gilles Brassard, working together, and later independently, in 1991, by Artur Ekert
Artur Konrad Ekert FRS (born 19 September 1961) is a Polish professor of quantum physics at the Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford, professorial fellow in quantum physics and cryptography at Merton College, Oxford, Lee Kong Chian Cen ...
. The earlier scheme has proven the more practical.
* 1984: Comet Levy-Rudenko was discovered independently by David H. Levy on 13 November 1984 and the next evening by Michael Rudenko. (It was the first of 23 comets discovered by Levy, who is famous as the 1993 co-discoverer of Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena are ...
, the first comet ever observed crashing into a planet, Jupiter.)
* 1985: The use of elliptic curves in cryptography
Cryptography, or cryptology (from grc, , translit=kryptós "hidden, secret"; and ''graphein'', "to write", or ''-logia'', "study", respectively), is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of adve ...
(elliptic curve cryptography
Elliptic-curve cryptography (ECC) is an approach to public-key cryptography based on the algebraic structure of elliptic curves over finite fields. ECC allows smaller keys compared to non-EC cryptography (based on plain Galois fields) to provid ...
) was suggested independently by Neal Koblitz
Neal I. Koblitz (born December 24, 1948) is a Professor of Mathematics at the University of Washington. He is also an adjunct professor with the Centre for Applied Cryptographic Research at the University of Waterloo. He is the creator of hype ...
and Victor S. Miller
Victor Saul Miller (born 3 March 1947 in Brooklyn, New York) is an American mathematician as a Principal Computer Scientist in the Computer Science Laboratory of SRI International. He received his B.A. in mathematics from Columbia University in ...
in 1985.
* 1987: The Immerman–Szelepcsényi theorem, another fundamental result in computational complexity theory, was proven independently by Neil Immerman
Neil Immerman (born 24 November 1953, Manhasset, New York) is an American theoretical computer scientist, a professor of computer science at the University of Massachusetts Amherst.
and Róbert Szelepcsényi
Róbert Szelepcsényi (; born 19 August 1966, Žilina) is a Slovak computer scientist of Hungarian descent and a member of the Faculty of Mathematics, Physics and Informatics of Comenius University in Bratislava.
His results on the closure of ...
in 1987.
* In 1989, Thomas R. Cech
Thomas Robert Cech (born December 8, 1947) is an American chemist who shared the 1989 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Sidney Altman, for their discovery of the catalytic properties of RNA. Cech discovered that RNA could itself cut strands of RNA, ...
(Colorado) and Sidney Altman
Sidney Altman (May 7, 1939 – April 5, 2022) was a Canadian-American molecular biologist, who was the Sterling Professor of Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology and Chemistry at Yale University. In 1989, he shared the Nobel Prize in ...
(Yale) won the Nobel Prize in chemistry for their independent discovery in the 1980s of ribozymesfor the "discovery of catalytic properties of RNA"using different approaches. Catalytic RNA was an unexpected finding, something they were not looking for, and it required rigorous proof that there was no contaminating protein enzyme.
* In 1993, groups led by Donald S. Bethune at IBM and Sumio Iijima
is a Japanese physicist and inventor, often cited as the inventor of carbon nanotubes. Although carbon nanotubes had been observed prior to his "invention", Iijima's 1991 paper generated unprecedented interest in the carbon nanostructures and ...
at NEC independently discovered single-wall carbon nanotubes
A scanning tunneling microscopy image of a single-walled carbon nanotube
Rotating single-walled zigzag carbon nanotube
A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with diameters typically measured in nanometers.
''Single-wall carbon nan ...
and methods to produce them using transition-metal catalysts.
* 1998: Saul Perlmutter
Saul Perlmutter (born September 22, 1959) is a U.S. astrophysicist at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and a professor of physics at the University of California, Berkeley. He is a member of both the American Academy of Arts & Science ...
, Adam G. Riess, and Brian P. Schmidt—working as members of two independent projects, the Supernova Cosmology Project
The Supernova Cosmology Project is one of two research teams that determined the likelihood of an accelerating universe and therefore a positive cosmological constant, using data from the redshift of Type Ia supernovae. The project is headed by S ...
and the High-Z Supernova Search Team—simultaneously discovered in 1998 the accelerating expansion of the universe
Observations show that the expansion of the universe is accelerating, such that the velocity at which a distant galaxy recedes from the observer is continuously increasing with time. The accelerated expansion of the universe was discovered durin ...
through observations of distant supernovae
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when ...
. For this, they were jointly awarded the 2006 Shaw Prize in Astronomy and the 2011 Nobel Prize in Physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
.
21st century




 * In 2001 four different authors published different implementations of a
* In 2001 four different authors published different implementations of a distributed hash table
A distributed hash table (DHT) is a distributed system that provides a lookup service similar to a hash table: key–value pairs are stored in a DHT, and any participating node can efficiently retrieve the value associated with a given key. The ...
.
* The Super Kamiokande
Super-Kamiokande (abbreviation of Super-Kamioka Neutrino Detection Experiment, also abbreviated to Super-K or SK; ja, スーパーカミオカンデ) is a neutrino observatory located under Mount Ikeno near the city of Hida, Gifu Prefectur ...
and SNOLAB
SNOLAB is a Canadian underground science laboratory specializing in neutrino and dark matter physics. Located 2 km below the surface in Vale's Creighton nickel mine near Sudbury, Ontario, SNOLAB is an expansion of the existing facilities c ...
collaborations, whose findings were published in 1998 and 2001 respectively, both proved that neutrinos have mass. The 2015 Nobel Prize in Physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
was shared by Takaaki Kajita
is a Japanese physicist, known for neutrino experiments at the Kamioka Observatory – Kamiokande and its successor, Super-Kamiokande. In 2015, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics jointly with Canadian physicist Arthur B. McDonald. On 1 ...
of Japan and Arthur B. McDonald
Arthur Bruce McDonald, P.Eng (born August 29, 1943) is a Canadian astrophysicist. McDonald is the director of the Sudbury Neutrino Observatory Collaboration and held the Gordon and Patricia Gray Chair in Particle Astrophysics at Queen's Univer ...
of Canada as a result.
*James Allison James Allison or Jim Allison may refer to:
* James Allison (pirate) (fl. 1689-1691), pirate active near Cape Verde and the Bay of Campeche
* James Allison Jr. (1772–1854), member of the U.S. House of Representatives from Pennsylvania
* James W ...
of MD Anderson Cancer Center at the University of Texas at Houston
The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) is a public academic health science center in Houston, Texas, United States. It was created in 1972 by The University of Texas System Board of Regents. It is located in the Te ...
discovered a mechanism enabling cancer immunotherapy in 1996. Tasuku Honjo
is a Japanese physician-scientist and immunologist. He won the 2018 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine and is best known for his identification of programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1).
He is also known for his molecular identification of ...
of Kyoto University discovered another such mechanism in 2002. This outcome, which led to them sharing the 2018 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, has been described as follows: "Each independently discovered that our immune system is restrained from attacking tumors by molecules that function as 'brakes.' Releasing these brakes (or 'brake receptors') allows our body to powerfully combat cancer."
* In 2014, Paul Erdős' conjecture about prime gap
A prime gap is the difference between two successive prime numbers. The ''n''-th prime gap, denoted ''g'n'' or ''g''(''p'n'') is the difference between the (''n'' + 1)-th and the
''n''-th prime numbers, i.e.
:g_n = p_ - p_n.\
W ...
s was proved by Kevin Ford, Ben Green, Sergei Konyagin
Sergei Vladimirovich Konyagin (russian: Серге́й Владимирович Конягин; born 25 April 1957) is a Russian mathematician. He is a professor of mathematics at the Moscow State University.
Konyagin participated in the Internat ...
, and Terence Tao, working together, and independently by James Maynard.
* 2020: Half of the 2020 Nobel Prize in Physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
was awarded to Reinhard Genzel and Andrea Ghez
Andrea is a given name which is common worldwide for both males and females, cognate to Andreas, Andrej and Andrew.
Origin of the name
The name derives from the Greek word ἀνήρ (''anēr''), genitive ἀνδρός (''andrós''), that ref ...
, who each have led a group of astronomers focused since the early 1990s on a region at the center of the Milky Way galaxy called Sagittarius A*
Sagittarius A* ( ), abbreviated Sgr A* ( ), is the supermassive black hole at the Galactic Center of the Milky Way. It is located near the border of the constellations Sagittarius and Scorpius, about 5.6° south of the ecliptic, vi ...
, finding an extremely heavy, invisible object (black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can defo ...
) that pulls on a jumble of stars, causing them to rush around at dizzying speeds. Some 4 million solar masses are packed together in a region no larger than our solar system.
* 2021 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was shared by David Julius
David Jay Julius (born November 4, 1955) is an American physiologist and Nobel Prize laureate known for his work on molecular mechanisms of pain sensation and heat, including the characterization of the TRPV1 and TRPM8 receptors that detect cap ...
, of the University of California, San Francisco, and Ardem Patapoutian
Ardem Patapoutian (born 1967) is an Armenian-American molecular biologist, neuroscientist, and Nobel Prize laureate. He is known for his work in characterizing the PIEZO1, PIEZO2, and TRPM8 receptors that detect pressure, menthol, and temperature ...
, of Scripps Research, in La Jolla, California, a UCSF postdoctoral alumnus, for their independent discoveries of receptors for temperature and touch."Surprise! It's a Nobel Prize", ''UCSF Magazine'', Winter 2022, pp. 28–29.
Quotations
See also
*Historic recurrence
Historic recurrence is the repetition of similar events in history. The concept of historic recurrence has variously been applied to overall human history (e.g., to the rises and falls of empires), to repetitive patterns in the history of a giv ...
* History of science
* History of technology
The history of technology is the history of the invention of tools and techniques and is one of the categories of world history. Technology can refer to methods ranging from as simple as stone tools to the complex genetic engineering and inform ...
* List of examples of Stigler's law
Stigler's law concerns the supposed tendency of eponymous expressions for scientific discoveries to honor people other than their respective originators.
Examples include:
A
*Aharonov–Bohm effect. Werner Ehrenberg and Raymond E. Siday first ...
* List of experiments
The following is a list of historically important scientific experiments and observations demonstrating something of great scientific interest, typically in an elegant or clever manner.
Astronomy
* Galileo Galilei uses a telescope to observe that ...
* List of misnamed theorems
This is a list of misnamed theorems in mathematics. It includes theorems (and lemmas, corollaries, conjectures, laws, and perhaps even the odd object) that are well known in mathematics, but which are not named for the originator. That is, these ...
* Logology (science of science)
Logology is the study of all things related to science and its practitioners—philosophical, biological, psychological, societal, historical, political, institutional, financial. The term "logology" is back-formed from the suffix "-logy", a ...
* Matilda effect
The Matilda effect is a bias against acknowledging the achievements of women scientists whose work is attributed to their male colleagues. This phenomenon was first described by suffragist and abolitionist Matilda Joslyn Gage (1826–98) in he ...
* Matthew effect
The Matthew effect of accumulated advantage, Matthew principle, or Matthew effect, is the tendency of individuals to accrue social or economic success in proportion to their initial level of popularity, friends, wealth, etc. It is sometimes summar ...
* Multiple discovery
* Priority disputes
* Stigler's law of eponymy
Stigler's law of eponymy, proposed by University of Chicago statistics professor Stephen Stigler in his 1980 publication ''Stigler’s law of eponymy'', states that no scientific discovery is named after its original discoverer. Examples include ...
* Synchronicity
* Timeline of historic inventions
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * Isaac Asimov, ''Asimov's Biographical Encyclopedia of Science and Technology'', second revised edition, New York, Doubleday, 1982. * * *Tim Folger
Tim Folger is an American science and nature writer. He is a contributing editor at ''Discover Magazine'' and writes about science for several other magazines. Folger has been the "series editor" of ''The Best American Science and Nature Writing ...
, "The Quantum Hack: Quantum computers will render today's cryptographic methods obsolete. What happens then?" '' Scientific American'', vol. 314, no. 2 (February 2016), pp. 48–55.
*
* Owen Gingerich
Owen Jay Gingerich (; born 1930) is professor emeritus of astronomy and of the history of science at Harvard University and a senior astronomer emeritus at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. In addition to his research and teaching, he has ...
, "Did Copernicus Owe a Debt to Aristarchus?" '' Journal for the History of Astronomy'', vol. 16, no. 1 (February 1985), pp. 37–42.* Brian Greene, "Why He lbert EinsteinMatters: The fruits of one mind shaped civilization more than seems possible", '' Scientific American'', vol. 313, no. 3 (September 2015), pp. 34–37. * A. Rupert Hall, ''Philosophers at War'', New York, Cambridge University Press, 1980. *
Lawrence M. Krauss
Lawrence Maxwell Krauss (born May 27, 1954) is an American theoretical physicist and cosmologist who previously taught at Arizona State University, Yale University, and Case Western Reserve University. He founded ASU's Origins Project, now c ...
, "What Einstein Got Wrong: Cosmology (Everyone makes mistakes. But those of the legendary physicist are particularly illuminating)", '' Scientific American'', vol. 313, no. 3 (September 2015), pp. 50–55.
* David Lamb, ''Multiple Discovery: The Pattern of Scientific Progress'', Amersham, Avebury Press, 1984.
* David H. Levy, "My Life as a Comet Hunter: The need to pass a French test, of all things, spurred half a century of cosmic sleuthing", '' Scientific American'', vol. 314, no. 2 (February 2016), pp. 70–71.
*
* Robert K. Merton
Robert King Merton (born Meyer Robert Schkolnick; July 4, 1910 – February 23, 2003) was an American sociologist who is considered a founding father of modern sociology, and a major contributor to the subfield of criminology. He served as th ...
, ''The Sociology of Science: Theoretical and Empirical Investigations'', University of Chicago Press, 1973.
* Robert K. Merton
Robert King Merton (born Meyer Robert Schkolnick; July 4, 1910 – February 23, 2003) was an American sociologist who is considered a founding father of modern sociology, and a major contributor to the subfield of criminology. He served as th ...
, ''On Social Structure and Science'', edited and with an introduction by Piotr Sztompka, University of Chicago Press, 1996.
* Robert William Reid, '' Marie Curie'', New York, New American Library, 1974, .
* Marilynne Robinson
Marilynne Summers Robinson (born November 26, 1943) is an American novelist and essayist. Across her writing career, Robinson has received numerous awards, including the Pulitzer Prize for Fiction in 2005, National Humanities Medal in 2012, and t ...
, "On Edgar Allan Poe", ''The New York Review of Books
''The New York Review of Books'' (or ''NYREV'' or ''NYRB'') is a semi-monthly magazine with articles on literature, culture, economics, science and current affairs. Published in New York City, it is inspired by the idea that the discussion of i ...
'', vol. LXII, no. 2 (5 February 2015), pp. 4, 6.
*
* Joshua Rothman, "The Rules of the Game: How does science really work?" (review of Michael Strevens, ''The Knowledge Machine: How Irrationality Created Modern Science'', Liveright), '' The New Yorker'', 5 October 2020, pp. 67–71.
* Harriet Zuckerman
Harriet Anne Zuckerman (born July 19, 1937) is an American sociologist and professor emerita of Columbia University.
Zuckerman specializes in the sociology of science.
She is known for her work on the social organization of science, scienti ...
, ''Scientific Elite: Nobel Laureates in the United States'', New York, Free Press, 1977.
External links
Annals of Innovation: In the Air: Who says big ideas are rare?
Malcolm Gladwell, '' The New Yorker'', May 12, 2008
The Technium: Simultaneous Invention
Kevin Kelly, May 9, 2008 * , Peter Turney, January 15, 2007
by B.A. Trakhtenbrot, in the '' Annals of the History of Computing'', 6(4):384–400, 1984. {{DEFAULTSORT:Multiple Discoveries Science-related lists Lists of inventions or discoveries Scientific method Discovery and invention controversies