This article provides a list of operated
high-speed rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail system that runs significantly faster than traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated tracks. While there is no single standard that applies worldwide, lines ...
networks, listed by country or region.
The
International Union of Railways
The International Union of Railways (UIC, french: Union internationale des chemins de fer) is an international rail transport industry body.
History
The railways of Europe originated as many separate concerns, and there were many border chang ...
defines high-speed rail as public transport by rail at speeds of at least for upgraded tracks and or faster for new tracks.
Overview
The following table is an overview of high speed rail in service or under construction by country, ranked by the amount in service. It shows all the high speed lines (speed of or over) in service. The list is based on UIC figures (
International Union of Railways
The International Union of Railways (UIC, french: Union internationale des chemins de fer) is an international rail transport industry body.
History
The railways of Europe originated as many separate concerns, and there were many border chang ...
),
updated with other sources.
By region
Freight high-speed railway services
Missile carriers
Non-revenue or unfinished
High-speed networks under construction
Austria
All high-speed railway lines in Austria are upgraded lines.
Baltic States (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania)
Dedicated high-speed line
Connections to Russian, Polish and Finnish high-speed railways are under planning.
Belgium
Dedicated high-speed line
China
Denmark
Denmark has a signalling system allowing max 180 km/h. There is a plan to replace it with
ETCS before 2030. On some lines, 200 km/h or more will be allowed as a direct result, without upgrading other things.
Peberholm–Oresund Bridge has Swedish signalling system allowing max 200 km/h since 2000.
Finland
New main lines
Upgraded lines
France
Dedicated high-speed lines
French figures of LGV length count only new tracks and not total length between terminal stations (i.e.: 409 km instead of 425 km for the LGV Sud-Est)
Upgraded lines
Germany
Dedicated high-speed lines
Upgraded lines
India
Routes

In India, trains in the future with top speeds of 300–350 km/h, are envisaged to run on elevated corridors to isolate high-speed train tracks and thereby prevent trespassing by animals or people. The current conventional lines between Amritsar–New Delhi, and Ahmedabad–Mumbai runs through suburban and rural areas, which are flat and have no tunnels. The Ahmedabad–Mumbai line runs near the coast and therefore, has more bridges, and parts of it are in backwaters or forests. The 1987 RDSO/JICA feasibility study found the Mumbai-Ahmedabad line to be the most promising.
The government of
Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South Ca ...
state has also expressed interest in constructing a high-speed rail corridor by the name of
Silverline under K-Rail corporation to carry both freight and passengers along the length of the state, from
Kasargod in the north end to the state capital,
Thiruvananthapuram
Thiruvananthapuram (; ), also known by its former name Trivandrum (), is the capital of the Indian state of Kerala. It is the most populous city in Kerala with a population of 957,730 as of 2011. The encompassing urban agglomeration populati ...
in the south end. The project reduces the current travel time of 12 hours to just under 4 hours from north to south with a maximum designed speed of . The project is estimated to be completed by 2025 and is expected to cost .
Feasibility studies
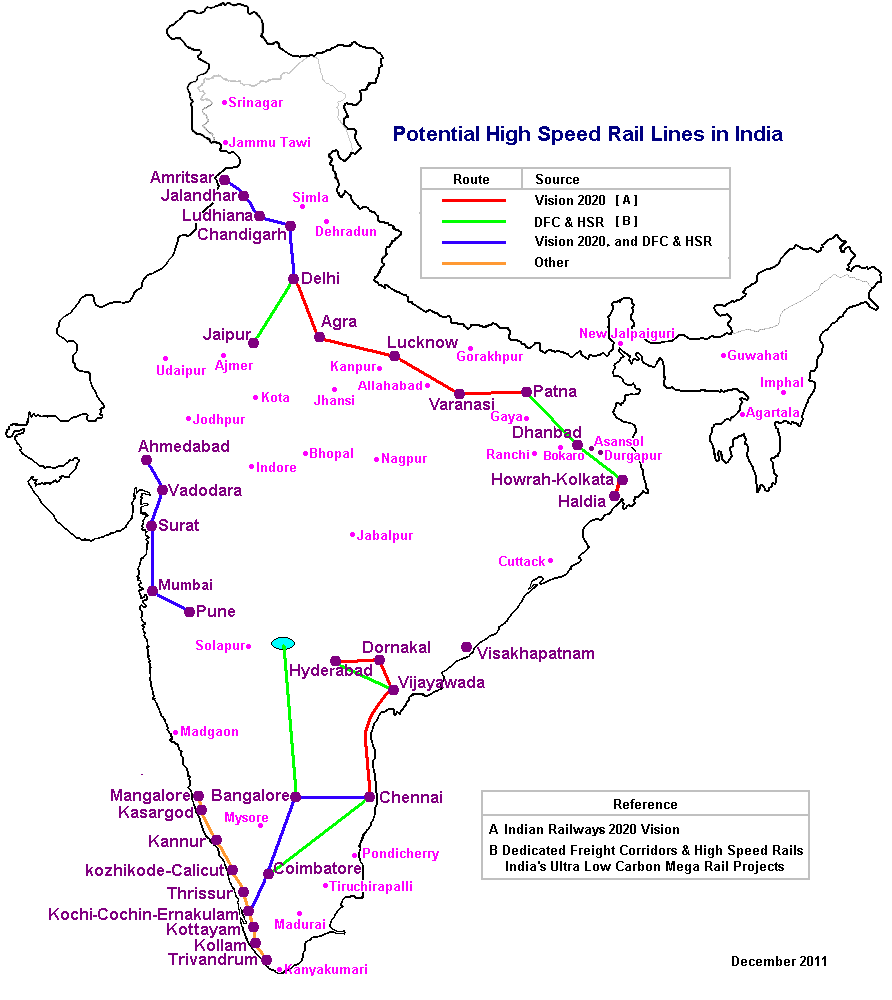
Multiple pre-feasibility and feasibility studies have been done or are in progress.
The consultants for pre-feasibility study for four corridors are:
*
Systra
SYSTRA is a multinational engineering and consulting group in the mobility sector, whose fields of activity include rail and public transport. In 2019, it employed a staff of about 7,300 people, and is a limited company which shareholders includ ...
France's Company for Delhi-Panipat-Ambala-Chandigarh-Ludhiana-Jalandhar-Amritsar,
*
Systra
SYSTRA is a multinational engineering and consulting group in the mobility sector, whose fields of activity include rail and public transport. In 2019, it employed a staff of about 7,300 people, and is a limited company which shareholders includ ...
,
Italferr and
RITES Limited for Pune–Mumbai–Ahmedabad,
*British firm
Mott MacDonald for Delhi–Agra–Lucknow–Varanasi–Patna
*INECO, PROINTEC, Ayesa for Howrah-Haldia
*
Japan External Trade Organization
is an Independent Administrative Institution established by Japan Export Trade Research Organization as a nonprofit corporation in Osaka in February 1952, reorganized under the Ministry of International Trade and Industry (MITI) in 1958 (later ...
(JETRO) and Oriental Consultancy along with
Parsons Brinckerhoff India for
Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
–
Vijayawada
Vijayawada, formerly known as Bezawada, is the second largest city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and is a part of the state's Capital Region. It is the administrative headquarters of the NTR district. Its metropolitan region comprises N ...
–
Dornakal
Dornakal is one of the largest town in Mahabubabad district of Telangana, India. The town is important as a Railway Junction where a branch line emanates to Manuguru and Bhadrachalam Road and is also on the Vijayawada - Warangal - Secunderabad ...
–
Kazipet–
Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River, in the northern part of Southern Indi ...
In September 2013, an agreement was signed in New Delhi to complete a feasibility study of high-speed rail between Ahmedabad and Mumbai, within 18 months.
The study will cost ¥500 million and the cost will be shared 50:50 by Japan and India.
Location of the stations, its accessibility, integration with public transport, parking and railway stations design will play an important role in the success of the high speed railway system. Mumbai may have an underground corridor to have high-speed rail start from the
CST terminal.
European experiences have shown that railway stations outside the city receive less patronage and ultimately make the high-speed railway line unfeasible.
The feasibility study for the Chennai-Bengaluru high-speed rail corridor was completed by Germany in November 2018. The study found that the route was feasible. The proposed corridor would be 435 km long and would have an end-to-end travel time of 2 hours and 25 minutes with trains operating at a speed of 320 km/h. The study proposed constructing 84% of the track on viaducts, 11% underground and the remaining 4% at-grade. The current fastest train on the Chennai-Bengaluru route, the Shatabdi Express, completes the journey in 7 hours.
Diamond Quadrilateral project

The
Diamond Quadrilateral high-speed rail network project is set to connect the four major metro cities of
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
namely:
Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
,
Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
,
Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
, and
Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the secon ...
.
Prime minister of India
The prime minister of India (IAST: ) is the head of government of the Republic of India. Executive authority is vested in the prime minister and their chosen Council of Ministers, despite the president of India being the nominal head of the ...
mentioned in his address to the joint session of
Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
on 9 June 2014 that the new Government was committing to build the dream project. Although the route is not yet planned, the alignment could follow the existing Golden Quadrilateral railway line which links other major cities.
Classic upgraded lines
Indonesia
Dedicated high-speed lines
Italy
Dedicated high-speed lines
Upgraded lines
Japan
Dedicated high-speed lines
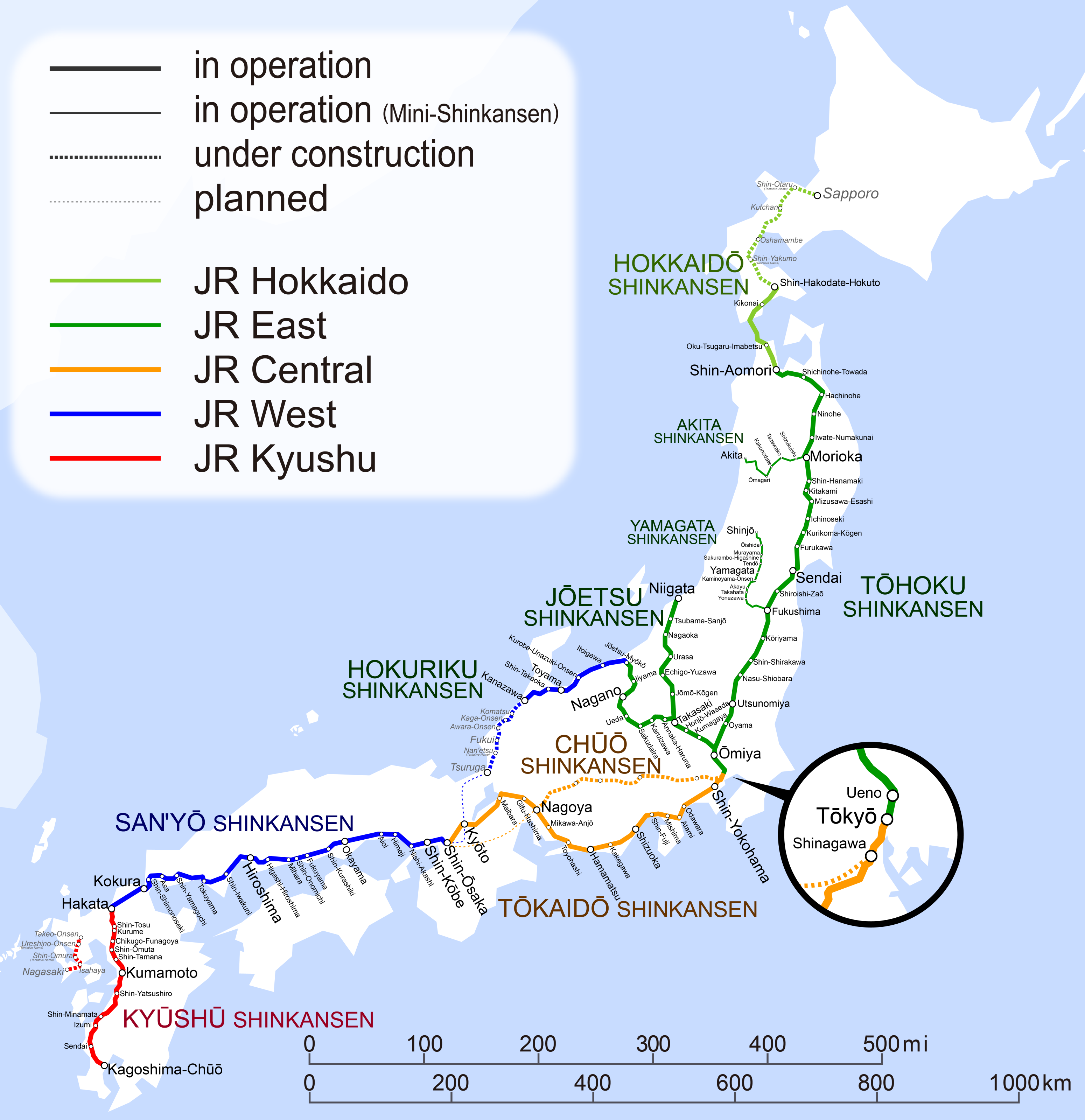
Maglev lines
Laos
Morocco
Dedicated high-speed line
Upgraded line
Dedicated high-speed lines planned
Netherlands
Dedicated high-speed line
Upgraded lines
Norway
Poland
Upgraded lines
Dedicated lines
Portugal
Upgraded lines
Dedicated lines
Romania
Upgraded lines
Russia
Upgraded lines
Dedicated lines
Saudi Arabia
Dedicated high-speed lines
Classic upgraded lines
South Korea

Dedicated high-speed lines
Upgraded lines
Spain
Dedicated high-speed line (operational)
Upgraded lines
Sweden
Dedicated
Upgraded lines
* The lines marked with * were to a large part given a new alignment when upgrading from single track, essentially making them new lines. The other ones were straight enough for 200 km/h already.
There are plans to upgrade some lines to 250 km/h when the ERTMS signalling system is introduced in 2025–2030.
Switzerland
Rail 2000 high-speed lines
Other projects
Taiwan
Dedicated high-speed line
Thailand
Dedicated high-speed line
Turkey
Dedicated high-speed lines
Upgraded lines
United Kingdom
Dedicated high-speed lines
Upgraded lines
United States
Upgraded lines
Dedicated high-speed lines
''The United States has no dedicated high speed rail lines—the following are either under construction or planned.''
Maglev Lines
Uzbekistan
References and notes
{{Transport country lists
Railway lines
 Multiple pre-feasibility and feasibility studies have been done or are in progress.
The consultants for pre-feasibility study for four corridors are:
*
Multiple pre-feasibility and feasibility studies have been done or are in progress.
The consultants for pre-feasibility study for four corridors are:
*