List of United States presidential assassination attempts and plots on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The assassination of James A. Garfield took place at the Baltimore and Potomac Railroad Station in Washington, D.C., at 9:20 AM on Saturday, July 2, 1881, less than four months after he took office. As the president was arriving at the train station, writer and lawyer Charles J. Guiteau shot him twice with a .442 Webley British Bull Dog revolver; one bullet grazed the president's shoulder, and the other pierced his back. For the next eleven weeks, Garfield endured the pain and suffering from having been shot, before he died on September 19, 1881, at 10:35 PM, of complications caused by iatrogenic infections, which were contracted by the doctors' relentless probing of his wound with unsterilized fingers and instruments; he had survived for a total of 79 days after being shot. Garfield was succeeded by Vice President Chester A. Arthur.
Guiteau was immediately arrested. After a highly publicized trial lasting from November 14, 1881, to January 25, 1882, he was found guilty and sentenced to death. A subsequent appeal was rejected, and he was executed by
The assassination of James A. Garfield took place at the Baltimore and Potomac Railroad Station in Washington, D.C., at 9:20 AM on Saturday, July 2, 1881, less than four months after he took office. As the president was arriving at the train station, writer and lawyer Charles J. Guiteau shot him twice with a .442 Webley British Bull Dog revolver; one bullet grazed the president's shoulder, and the other pierced his back. For the next eleven weeks, Garfield endured the pain and suffering from having been shot, before he died on September 19, 1881, at 10:35 PM, of complications caused by iatrogenic infections, which were contracted by the doctors' relentless probing of his wound with unsterilized fingers and instruments; he had survived for a total of 79 days after being shot. Garfield was succeeded by Vice President Chester A. Arthur.
Guiteau was immediately arrested. After a highly publicized trial lasting from November 14, 1881, to January 25, 1882, he was found guilty and sentenced to death. A subsequent appeal was rejected, and he was executed by
 The assassination of president
The assassination of president
 The assassination of United States president John F. Kennedy took place at 12:30 PM on Friday, November 22, 1963, in
The assassination of United States president John F. Kennedy took place at 12:30 PM on Friday, November 22, 1963, in
 On March 30, 1981, as
On March 30, 1981, as
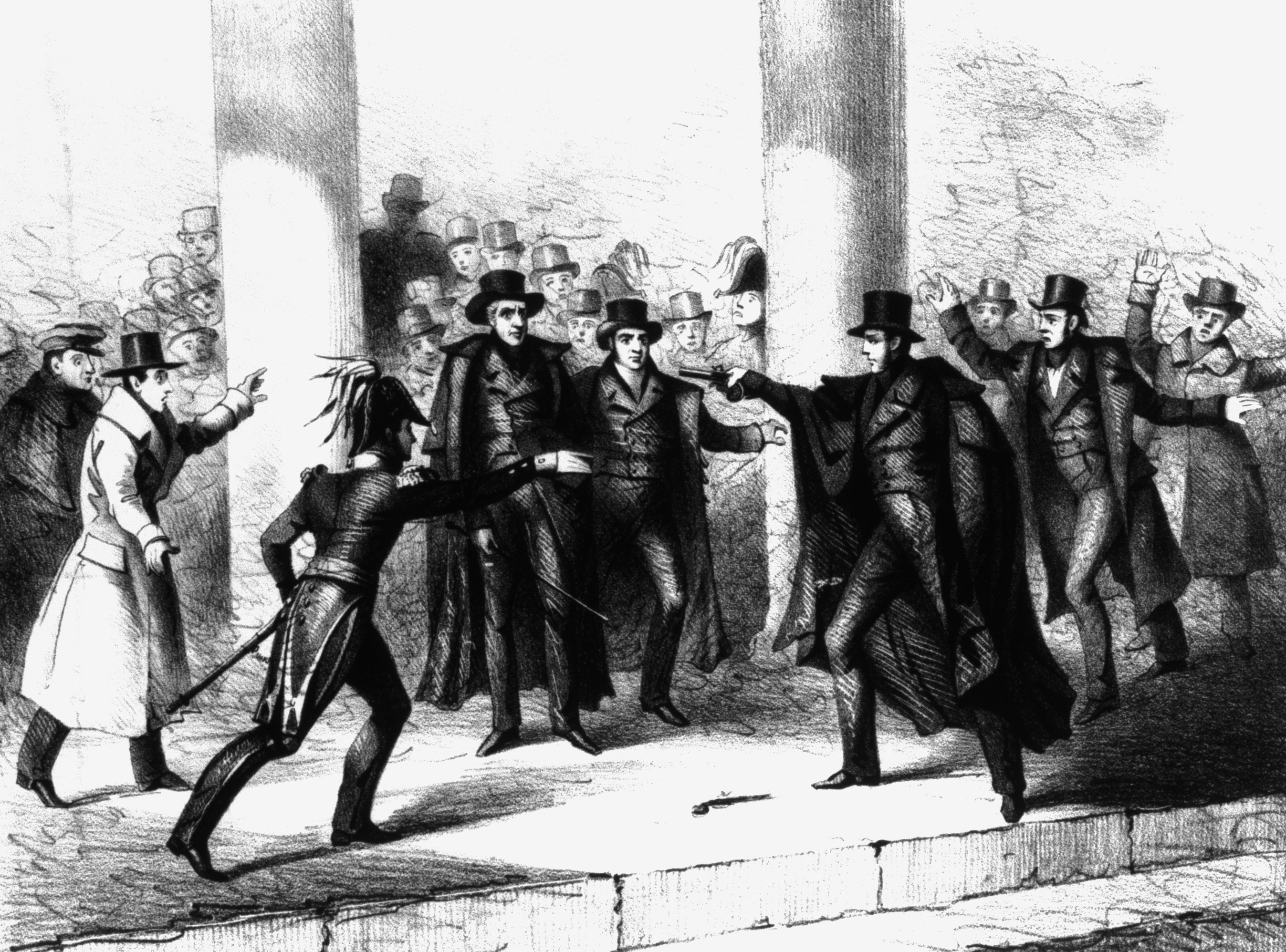 * January 30, 1835: Just outside the Capitol Building, a house painter named Richard Lawrence attempted to shoot President
* January 30, 1835: Just outside the Capitol Building, a house painter named Richard Lawrence attempted to shoot President
 * February 15, 1933: Seventeen days before Roosevelt's first presidential inauguration, Giuseppe Zangara fired five shots at Roosevelt in
* February 15, 1933: Seventeen days before Roosevelt's first presidential inauguration, Giuseppe Zangara fired five shots at Roosevelt in
''Tri-City Herald'', December 1, 1972, accessed December 11, 2012 * November 1, 1950: Two Puerto Rican pro-independence activists, Oscar Collazo and Griselio Torresola, attempted to kill President Truman at the Blair House, where Truman was living while the White House was undergoing major renovations. In the attack, Torresola injured White House policeman Joseph Downs and mortally wounded White House policeman Leslie Coffelt. Coffelt returned fire, killing Torresola with a shot to the head. Collazo wounded an officer before being shot in the stomach. Collazo survived with serious injuries; Coffelt died of his wounds 4 hours later in a hospital. Truman was not harmed, but he was placed at a huge risk. Collazo was convicted in a federal trial and received the death sentence. Truman commuted Collazo's death sentence to life in prison. In 1979, President
 * Mid-August 1974: Muharem Kurbegovic, also known as The Alphabet Bomber, said in a message that he was going to come to Washington, D.C., and throw a nerve gas bomb at President Gerald Ford, then just ten days into his presidency. Within one day, the CIA, the U.S. Secret Service, and other law enforcement agencies, working out of the
* Mid-August 1974: Muharem Kurbegovic, also known as The Alphabet Bomber, said in a message that he was going to come to Washington, D.C., and throw a nerve gas bomb at President Gerald Ford, then just ten days into his presidency. Within one day, the CIA, the U.S. Secret Service, and other law enforcement agencies, working out of the
"Court Sentences Man to 40 Years For Trying to Kill the President,"
June 30, 1995, ''
CNN, October 24, 2018
 * September 15, 2024: 58-year-old Ryan Wesley Routh was spotted by a Secret Service agent holding an SKS-style rifle on a private golf course belonging to Trump in
* September 15, 2024: 58-year-old Ryan Wesley Routh was spotted by a Secret Service agent holding an SKS-style rifle on a private golf course belonging to Trump in
Volume 1
an
Volume 2
* * * * * * * {{Lists of US Presidents and Vice Presidents
Assassination
Assassination is the willful killing, by a sudden, secret, or planned attack, of a personespecially if prominent or important. It may be prompted by political, ideological, religious, financial, or military motives.
Assassinations are orde ...
attempts and plots on the president of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal government of t ...
have been numerous, ranging from the early 19th century to the present day. This article lists assassinations and assassination attempts on incumbent and former presidents and presidents-elect, but not on those who had not yet been elected president. Four sitting U.S. presidents have been killed: Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln (February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was the 16th president of the United States, serving from 1861 until Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War ...
( 1865), James A. Garfield ( 1881), William McKinley
William McKinley (January 29, 1843September 14, 1901) was the 25th president of the United States, serving from 1897 until Assassination of William McKinley, his assassination in 1901. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Repub ...
( 1901), and John F. Kennedy (1963
Events January
* January 1 – Bogle–Chandler case: Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation scientist Dr. Gilbert Bogle and Mrs. Margaret Chandler are found dead (presumed poisoned), in bushland near the Lane Cove ...
). Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan (February 6, 1911 – June 5, 2004) was an American politician and actor who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He was a member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party a ...
(1981
Events January
* January 1
** Greece enters the European Economic Community, predecessor of the European Union.
** Palau becomes a self-governing territory.
* January 6 – A funeral service is held in West Germany for Nazi Grand Admiral ...
) and Donald Trump (2024) are the only two presidents who have survived assassination attempts. Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. (October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), also known as Teddy or T.R., was the 26th president of the United States, serving from 1901 to 1909. Roosevelt previously was involved in New York (state), New York politics, incl ...
(1912
This year is notable for Sinking of the Titanic, the sinking of the ''Titanic'', which occurred on April 15.
In Albania, this leap year runs with only 353 days as the country achieved switching from the Julian to Gregorian Calendar by skippin ...
) and Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who is the 47th president of the United States. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served as the 45 ...
(2024
The year saw the list of ongoing armed conflicts, continuation of major armed conflicts, including the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the Myanmar civil war (2021–present), Myanmar civil war, the Sudanese civil war (2023–present), Sudane ...
) are the only two former presidents to have been injured in an assassination attempt, both while campaigning for reelection; the former lost and the latter won.
Many assassination attempts, both successful and unsuccessful, were motivated by a desire to change the policy of the American government.. Not all such attacks, however, had political reasons. Many other attackers had questionable mental stability, and a few were judged legally insane. Historian James W. Clarke suggests that most assassination attempters have been sane and politically motivated, whereas the Department of Justice's legal manual claims that a large majority have been insane. Some assassins, especially mentally ill ones, acted solely on their own, whereas those pursuing political agendas have more often found supporting conspirators. Most assassination plotters were arrested and punished by execution or lengthy detention in a prison or insane asylum.
The fact that the successor of a removed president is the vice president
A vice president or vice-president, also director in British English, is an officer in government or business who is below the president (chief executive officer) in rank. It can also refer to executive vice presidents, signifying that the vi ...
, and all vice presidents since Andrew Johnson
Andrew Johnson (December 29, 1808July 31, 1875) was the 17th president of the United States, serving from 1865 to 1869. The 16th vice president, he assumed the presidency following the assassination of Abraham Lincoln. Johnson was a South ...
have shared the president's political party
A political party is an organization that coordinates candidates to compete in a particular area's elections. It is common for the members of a party to hold similar ideas about politics, and parties may promote specific political ideology, ...
affiliation, may discourage such attacks, at least for policy reasons, even in times of partisan strife. The third person in line, the Speaker of the House, as outlined in the Presidential Succession Act
The United States Presidential Succession Act is a federal statute establishing the presidential line of succession. Article II, Section 1, Clause 6 of the United States Constitution authorizes Congress to enact such a statute:
Congress ha ...
, is often of the opposing party, however.
Threats of violence against the president are often made for rhetorical or humorous effect without serious intent, while ''credibly'' threatening the president of the United States has been a federal felony
A felony is traditionally considered a crime of high seriousness, whereas a misdemeanor is regarded as less serious. The term "felony" originated from English common law (from the French medieval word "''félonie''") to describe an offense that r ...
since 1917.
Presidents assassinated
Abraham Lincoln

Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln (February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was the 16th president of the United States, serving from 1861 until Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, his assassination in 1865. He led the United States through the American Civil War ...
, the 16th president of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal government of t ...
, was the first U.S. president to be assassinated (but not the first to die in office). The assassination took place on Good Friday
Good Friday, also known as Holy Friday, Great Friday, Great and Holy Friday, or Friday of the Passion of the Lord, is a solemn Christian holy day commemorating the crucifixion of Jesus and his death at Calvary (Golgotha). It is observed during ...
, April 14, 1865, at Ford's Theatre in Washington, D.C., at about 10:15 PM. The assassin, John Wilkes Booth
John Wilkes Booth (May 10, 1838April 26, 1865) was an American stage actor who Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, assassinated United States president Abraham Lincoln at Ford's Theatre in Washington, D.C., on April 14, 1865. A member of the p ...
, was a well-known actor and a Confederate sympathizer from Maryland; though he never joined the Confederate Army
The Confederate States Army (CSA), also called the Confederate army or the Southern army, was the military land force of the Confederate States of America (commonly referred to as the Confederacy) during the American Civil War (1861–1865), fi ...
, he had contacts within the Confederate Secret Service. In 1864, Booth formulated a plan (very similar to one of Thomas N. Conrad previously authorized by the Confederacy) to kidnap Lincoln in exchange for the release of Confederate prisoners. After attending an April 11, 1865 speech in which Lincoln promoted voting rights for African Americans, Booth decided to assassinate the president instead. Learning that the president would be attending Ford's Theatre, Booth planned with co-conspirators to assassinate Lincoln at the theater. The conspiracy also included assassinating Vice President
A vice president or vice-president, also director in British English, is an officer in government or business who is below the president (chief executive officer) in rank. It can also refer to executive vice presidents, signifying that the vi ...
Andrew Johnson
Andrew Johnson (December 29, 1808July 31, 1875) was the 17th president of the United States, serving from 1865 to 1869. The 16th vice president, he assumed the presidency following the assassination of Abraham Lincoln. Johnson was a South ...
in Kirkwood House, where Johnson lived while Vice President, and Secretary of State William H. Seward at Seward's house. On April 14, 1865, Lincoln attended the play '' Our American Cousin'' at Ford's Theatre. As the president sat in his state box in the balcony watching the play with his wife Mary and two guests, Major Henry Rathbone and Rathbone's fiancée Clara Harris, Booth entered the box and shot Lincoln in the back of the head, with a .44-caliber Derringer pistol, mortally wounding him and rendering him unconscious immediately. Booth stabbed Rathbone as Rathbone came at him, and escaped also stabbing orchestra leader William Withers Jr.. Lincoln was taken across the street to the Petersen House, where he remained in a coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to Nociception, respond normally to Pain, painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal Circadian rhythm, sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate ...
for nine hours, before he died at 7:22 AM on April 15. Lincoln was succeeded by Vice President Andrew Johnson
Andrew Johnson (December 29, 1808July 31, 1875) was the 17th president of the United States, serving from 1865 to 1869. The 16th vice president, he assumed the presidency following the assassination of Abraham Lincoln. Johnson was a South ...
.
Beyond Lincoln's death, the plot failed: Seward was only wounded, and Johnson's would-be attacker did not follow through. After being on the run for 12 days, Booth was tracked down and found on April 26, 1865, by Union Army soldiers at a farm in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
, some south of Washington. After refusing to surrender, Booth was shot and mortally wounded by Union cavalryman Boston Corbett. Eight other conspirators were later convicted for their roles in the conspiracy; four were hanged and four received life sentences.
James A. Garfield
 The assassination of James A. Garfield took place at the Baltimore and Potomac Railroad Station in Washington, D.C., at 9:20 AM on Saturday, July 2, 1881, less than four months after he took office. As the president was arriving at the train station, writer and lawyer Charles J. Guiteau shot him twice with a .442 Webley British Bull Dog revolver; one bullet grazed the president's shoulder, and the other pierced his back. For the next eleven weeks, Garfield endured the pain and suffering from having been shot, before he died on September 19, 1881, at 10:35 PM, of complications caused by iatrogenic infections, which were contracted by the doctors' relentless probing of his wound with unsterilized fingers and instruments; he had survived for a total of 79 days after being shot. Garfield was succeeded by Vice President Chester A. Arthur.
Guiteau was immediately arrested. After a highly publicized trial lasting from November 14, 1881, to January 25, 1882, he was found guilty and sentenced to death. A subsequent appeal was rejected, and he was executed by
The assassination of James A. Garfield took place at the Baltimore and Potomac Railroad Station in Washington, D.C., at 9:20 AM on Saturday, July 2, 1881, less than four months after he took office. As the president was arriving at the train station, writer and lawyer Charles J. Guiteau shot him twice with a .442 Webley British Bull Dog revolver; one bullet grazed the president's shoulder, and the other pierced his back. For the next eleven weeks, Garfield endured the pain and suffering from having been shot, before he died on September 19, 1881, at 10:35 PM, of complications caused by iatrogenic infections, which were contracted by the doctors' relentless probing of his wound with unsterilized fingers and instruments; he had survived for a total of 79 days after being shot. Garfield was succeeded by Vice President Chester A. Arthur.
Guiteau was immediately arrested. After a highly publicized trial lasting from November 14, 1881, to January 25, 1882, he was found guilty and sentenced to death. A subsequent appeal was rejected, and he was executed by hanging
Hanging is killing a person by suspending them from the neck with a noose or ligature strangulation, ligature. Hanging has been a standard method of capital punishment since the Middle Ages, and has been the primary execution method in numerou ...
on June 30, 1882, in the District of Columbia
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and Federal district of the United States, federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from ...
. Guiteau was assessed during his trial and autopsy as mentally unbalanced or suffering from the effects of neurosyphilis. He claimed to have shot Garfield out of disappointment at being passed over for appointment as Ambassador to France. He attributed the president's victory in the election to a speech he wrote in support of Garfield.
William McKinley
 The assassination of president
The assassination of president William McKinley
William McKinley (January 29, 1843September 14, 1901) was the 25th president of the United States, serving from 1897 until Assassination of William McKinley, his assassination in 1901. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Repub ...
took place at 4:07 PM on Friday, September 6, 1901, at the Temple of Music in Buffalo, New York
Buffalo is a Administrative divisions of New York (state), city in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York and county seat of Erie County, New York, Erie County. It lies in Western New York at the eastern end of Lake Erie, at the head of ...
. McKinley, attending the Pan-American Exposition, was shot twice in the abdomen at close range by Leon Czolgosz, an anarchist
Anarchism is a political philosophy and Political movement, movement that seeks to abolish all institutions that perpetuate authority, coercion, or Social hierarchy, hierarchy, primarily targeting the state (polity), state and capitalism. A ...
, who was armed with a .32-caliber Iver Johnson "Safety Automatic" revolver
A revolver is a repeating handgun with at least one barrel and a revolving cylinder containing multiple chambers (each holding a single cartridge) for firing. Because most revolver models hold six cartridges before needing to be reloaded, ...
that was concealed underneath a handkerchief; the first bullet ricocheted off either a button or an award medal on McKinley's jacket and lodged in his sleeve; the second shot pierced his stomach. James Benjamin Parker, who had been standing behind the assassin in line, was the first to grab Czolgosz and the revolver. Other individuals jumped in and the group subdued Czolgosz before he could fire a third shot. They beat Czolgosz severely until McKinley was able to order the beating to stop. Although McKinley initially appeared to be recovering in the week after, his condition rapidly declined due to gangrene setting in around his wounds and he died on September 14, 1901, at 2:15 AM. McKinley was succeeded by Vice President Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. (October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), also known as Teddy or T.R., was the 26th president of the United States, serving from 1901 to 1909. Roosevelt previously was involved in New York (state), New York politics, incl ...
.
On September 24, after a two-day trial, in which the defendant refused to defend himself, Czolgosz was convicted and later sentenced to death. He was executed by the electric chair in Auburn Prison on October 29, 1901. Czolgosz's actions were politically motivated, although it remains unclear what outcome, if any, he believed the shooting would yield.
Following President McKinley's assassination, Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
directed the Secret Service to protect the president of the United States as part of its mandate.
John F. Kennedy
 The assassination of United States president John F. Kennedy took place at 12:30 PM on Friday, November 22, 1963, in
The assassination of United States president John F. Kennedy took place at 12:30 PM on Friday, November 22, 1963, in Dallas, Texas
Dallas () is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the most populous city in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, the List of Texas metropolitan areas, most populous metropolitan area in Texas and the Metropolitan statistical area, fourth-most ...
, during a presidential motorcade in Dealey Plaza. Kennedy was riding with his wife Jacqueline, Texas Governor John Connally, and Connally's wife Nellie when he was fatally shot; he was hit once in the back, the bullet
A bullet is a kinetic projectile, a component of firearm ammunition that is shot from a gun barrel. They are made of a variety of materials, such as copper, lead, steel, polymer, rubber and even wax; and are made in various shapes and constru ...
exiting via his throat, and once in the head. Governor Connally was seriously wounded, and bystander James Tague received a minor facial injury from a small piece of curbstone that had fragmented after it was struck by one of the bullets. The motorcade rushed to Parkland Memorial Hospital, where Kennedy was declared dead at 1:00 PM. Kennedy was succeeded by Vice President Lyndon B. Johnson.
After a 6.5×52mm Carcano Model 38 rifle
A rifle is a long gun, long-barreled firearm designed for accurate shooting and higher stopping power, with a gun barrel, barrel that has a helical or spiralling pattern of grooves (rifling) cut into the bore wall. In keeping with their focus o ...
was found on the sixth floor of the Texas School Book Depository, depository worker Lee Harvey Oswald, a former U.S. Marine
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines or simply the Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is responsible for conducting expeditionar ...
and American defector was arrested and charged by the Dallas Police Department for the assassination and for the murder of Dallas policeman J. D. Tippit, who was shot dead in a residential neighborhood in the Oak Cliff section of Dallas less than an hour after the assassination. On Sunday, November 24, while being transferred from the city jail to the county jail, Oswald was shot and mortally wounded in the basement of Dallas Police Department Headquarters by Dallas nightclub owner Jack Ruby. Oswald died at Parkland Hospital. Ruby was convicted of Oswald's murder, albeit his conviction was later overturned on appeal. He died in 1967 while awaiting a new trial, his motivation remains unknown.
In 1964, the Warren Commission
The President's Commission on the Assassination of President Kennedy, known unofficially as the Warren Commission, was established by President of the United States, President Lyndon B. Johnson through on November 29, 1963, to investigate the A ...
concluded that Kennedy and Tippit were killed by Oswald, that Oswald had acted entirely alone in both murders, and that Ruby had acted alone in killing Oswald. The commission's findings have been supported by some writers but also challenged by various critics who hypothesize that there was a conspiracy surrounding the Kennedy assassination.
Incumbent presidents wounded
Ronald Reagan
 On March 30, 1981, as
On March 30, 1981, as Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan (February 6, 1911 – June 5, 2004) was an American politician and actor who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He was a member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party a ...
was returning to his limousine after speaking at the Washington Hilton hotel, John Hinckley Jr. fired six shots from a .22 caliber Röhm RG-14 revolver
A revolver is a repeating handgun with at least one barrel and a revolving cylinder containing multiple chambers (each holding a single cartridge) for firing. Because most revolver models hold six cartridges before needing to be reloaded, ...
. Reagan was seriously wounded when one bullet ricocheted off the side of the presidential limousine and hit him in the left underarm, breaking a rib, puncturing a lung, and causing serious internal bleeding
Internal bleeding (also called internal haemorrhage) is a loss of blood from a blood vessel that collects inside the body, and is not usually visible from the outside. It can be a serious medical emergency but the extent of severity depends on b ...
. Although "close to death" upon arrival at George Washington University Hospital, Reagan was stabilized in the emergency room, and then underwent emergency exploratory surgery. He was released from the hospital on April 11. Besides Reagan, White House press secretary James Brady, Secret Service agent Tim McCarthy
Timothy J. McCarthy (born June 20, 1949) is an American retired police officer and special agent of the U.S. Secret Service. He is best known for defending then-president Ronald Reagan during the assassination attempt on Reagan's life on Marc ...
, and police officer Thomas Delahanty were also wounded. All three survived, but Brady suffered brain damage and was permanently disabled; Brady died in 2014 as a result of his injuries.
Hinckley was immediately arrested, and said he had wanted to kill Reagan to impress actress Jodie Foster
Alicia Christian "Jodie" Foster (born November 19, 1962) is an American actress and filmmaker. Foster started her career as a child actor before establishing herself as leading actress in film. She has received List of awards and nominations re ...
. He was deemed mentally ill and confined to an institution. Hinckley was released from institutional psychiatric care on September 10, 2016.
Former presidents wounded
Theodore Roosevelt
Three-and-a-half years after he left office,Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. (October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), also known as Teddy or T.R., was the 26th president of the United States, serving from 1901 to 1909. Roosevelt previously was involved in New York (state), New York politics, incl ...
ran in the 1912 presidential election as a member of the Bull Moose Party
The Progressive Party, popularly nicknamed the Bull Moose Party, was a Third party (U.S. politics), third party in the United States formed in 1912 by former president Theodore Roosevelt after he lost the 1912 Republican Party presidential prim ...
. While campaigning in Milwaukee
Milwaukee is the List of cities in Wisconsin, most populous city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. Located on the western shore of Lake Michigan, it is the List of United States cities by population, 31st-most populous city in the United States ...
, Wisconsin, on October 14, 1912, John Schrank, a saloon-keeper from New York who had been stalking him for weeks, shot Roosevelt once in the chest with a .38-caliber Colt Police Positive Special. The 50-page text of his campaign speech titled " Progressive Cause Greater Than Any Individual", folded over twice in Roosevelt's breast pocket, and a metal glasses case slowed the bullet, saving his life. Schrank was immediately disarmed, captured, and might have been lynched had Roosevelt not shouted for Schrank to remain unharmed. Roosevelt assured the crowd he was all right, then ordered police to take charge of Schrank and to make sure no violence was done to him.
Roosevelt, as an experienced hunter and anatomist, correctly concluded that since he was not coughing blood, the bullet had not reached his lung, and he declined suggestions to go to the hospital immediately. Instead, he delivered his scheduled speech with blood seeping into his shirt. He spoke for 84 minutes before completing his speech and accepting medical attention. His opening comments to the gathered crowd were, "Ladies and gentlemen, I don't know whether you fully understand that I have just been shot, but it takes more than that to kill a Bull Moose." Afterwards, probes and an x-ray showed that the bullet had lodged in Roosevelt's chest muscle, but did not penetrate the pulmonary pleurae
The pleurae (: pleura) are the two flattened closed sacs filled with pleural fluid, each ensheathing each lung and lining their surrounding tissues, locally appearing as two opposing layers of serous membrane separating the lungs from the medias ...
. Doctors concluded that it would be less dangerous to leave it in place than to attempt to remove it, and the bullet remained in Roosevelt's body for the remainder of his life. He spent two weeks recuperating before returning to the campaign trail. Despite his tenacity, Roosevelt ultimately lost his bid for reelection to the Democratic candidate Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was the 28th president of the United States, serving from 1913 to 1921. He was the only History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democrat to serve as president during the Prog ...
.
At Schrank's trial, the would-be assassin claimed that William McKinley
William McKinley (January 29, 1843September 14, 1901) was the 25th president of the United States, serving from 1897 until Assassination of William McKinley, his assassination in 1901. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Repub ...
had visited him in a dream and told him to avenge his assassination by killing Roosevelt. He was found legally insane and was institutionalized until his death in 1943.
Donald Trump
On July 13, 2024, then former presidentDonald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who is the 47th president of the United States. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served as the 45 ...
, and the Republican Party's presumptive nominee
Preselection is the process by which a candidate is selected, usually by a political party, to contest an election for political office. It is also referred to as candidate selection. It is a fundamental function of political parties. The presel ...
in the presidential election that year, was shot at while addressing a campaign rally near Butler, Pennsylvania. Shortly after Trump began addressing the rally, 20-year-old Thomas Matthew Crooks fired eight rounds with an AR-15–style rifle from the roof of a building located around from the stage. Crooks also killed audience member Corey Comperatore and critically injured two other audience members. Crooks was shot and killed by the U.S. Secret Service's counter-sniper team. Trump was hit by a bullet wounding his right ear and he took cover on the floor of the podium, where he was shielded by Secret Service personnel. After agents helped him to his feet, Trump emerged with blood on his ear and face. He then either mouthed or shouted the words "Fight! Fight! Fight!" The images of a bloodied Trump pumping his fist in the air, with an American flag in the background, were widely praised as iconic and historically significant. Trump was escorted off-stage and taken to a nearby hospital before being released in stable condition a few hours later. He would later go on to win the election.
, an investigation by the FBI has been underway. Crooks's motivation remains unknown.
Other attacks, assassination attempts, and plots
Andrew Jackson
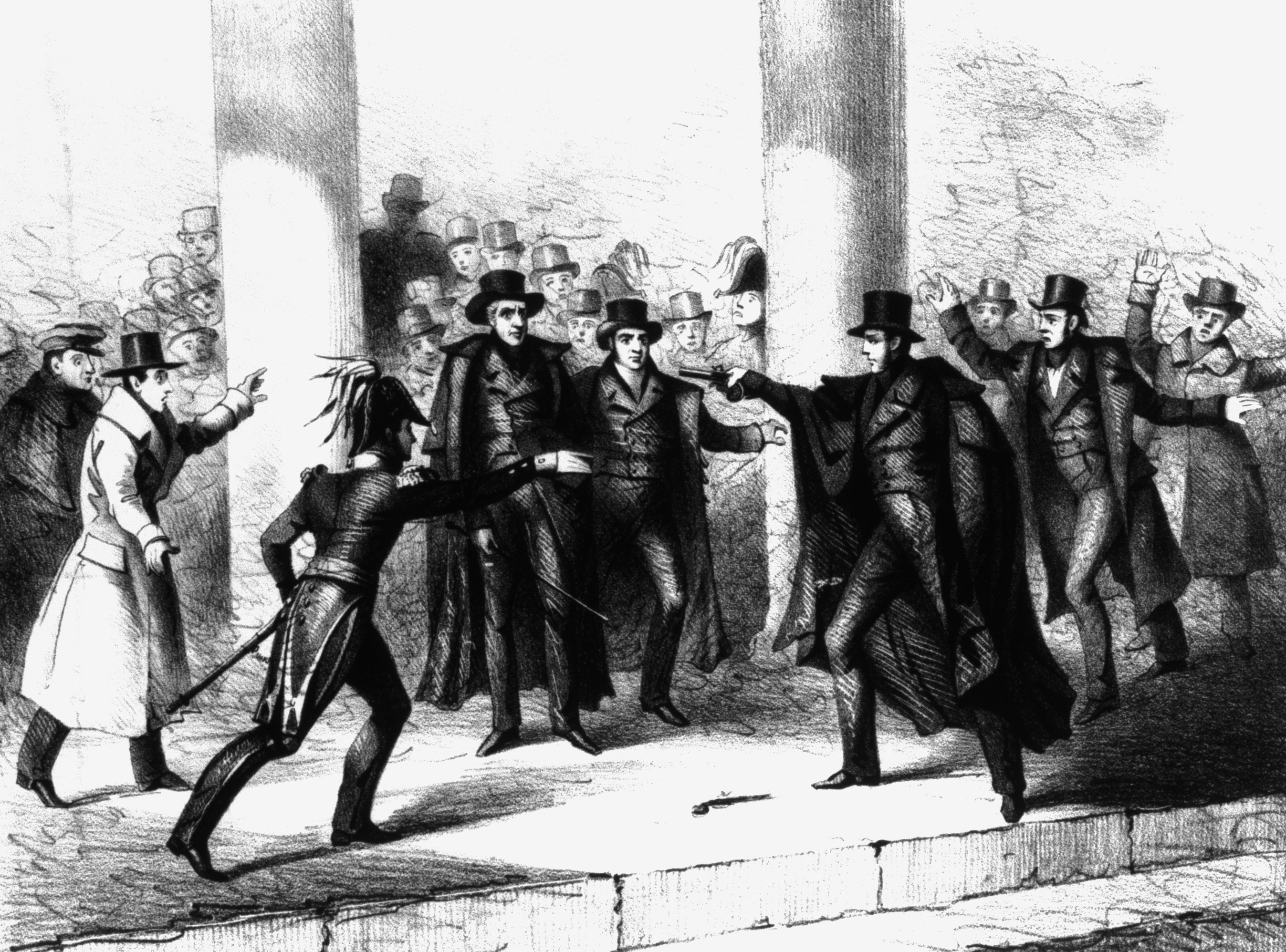 * January 30, 1835: Just outside the Capitol Building, a house painter named Richard Lawrence attempted to shoot President
* January 30, 1835: Just outside the Capitol Building, a house painter named Richard Lawrence attempted to shoot President Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before Presidency of Andrew Jackson, his presidency, he rose to fame as a general in the U.S. Army and served in both houses ...
with two pistols, both of which misfired. Later somebody tried the two pistols and both worked fine. Lawrence was apprehended after Jackson beat him severely with his cane. Lawrence was found not guilty by reason of insanity and confined to a mental institution until his death in 1861.
Abraham Lincoln
* February 23, 1861: President-elect Lincoln passed throughBaltimore, Maryland
Baltimore is the List of municipalities in Maryland, most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the List of United States ...
amid threats of the Baltimore Plot, an alleged conspiracy by Confederate sympathizers in Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
to assassinate Lincoln en route to his inauguration
In government and politics, inauguration is the process of swearing a person into office and thus making that person the incumbent. Such an inauguration commonly occurs through a formal ceremony or special event, which may also include an inau ...
. Allan Pinkerton's National Detective Agency played a key role in protecting the president-elect by managing Lincoln's security throughout the journey. Although scholars debate whether the threat was real, Lincoln and his advisers took action to ensure his safe passage through Baltimore.
* December 1863: Confederate agent Godfrey Joseph Hyams claimed in 1865 that in December 1863 he had been recruited by Luke P. Blackburn into a plot to infect Northern cities with yellow fever by distributing clothes from patients infected with the disease throughout the target cities. Hyams also alleged that Blackburn had told him to deliver a batch of contaminated clothes to the White House to infect President Lincoln, but he had disobeyed this order. Unknown at the time was the fact that yellow fever is spread by mosquito
Mosquitoes, the Culicidae, are a Family (biology), family of small Diptera, flies consisting of 3,600 species. The word ''mosquito'' (formed by ''Musca (fly), mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish and Portuguese for ''little fly''. Mos ...
bites and not by touch, so any such plot was doomed to failure. Blackburn stood trial after Hyams went public with his allegations but was acquitted.
* August 1864: A lone rifle shot fired by an unknown sniper missed Lincoln's head by inches (passing through his hat) as he rode in the late evening, unguarded, north from the White House to the Soldiers' Home (his regular retreat where he would work and sleep before returning to the White House the following morning). Near 11:00 PM, Private John W. Nichols of the Pennsylvania 150th Volunteers, the sentry on duty at the gated entrance to the Soldiers' Home grounds, heard the rifle shot and moments later saw the president riding toward him "bareheaded". Lincoln described the matter to Ward Lamon, his old friend and loyal bodyguard.
* April 1865: On April 1, Confederate agent Thomas F. Harney was dispatched from Richmond to Washington, D.C., on a mission to decapitate the United States government by killing President Lincoln and his cabinet. The plan was that Harney would blow up the White House after gaining access via a secret underground entrance. Union troops were tipped off about the plot by Confederate soldier William H. Snyder and Harney was arrested en route to Washington on April 10.
* April 11, 1865: John Wilkes Booth
John Wilkes Booth (May 10, 1838April 26, 1865) was an American stage actor who Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, assassinated United States president Abraham Lincoln at Ford's Theatre in Washington, D.C., on April 14, 1865. A member of the p ...
, who would make a successful attempt on Lincoln's life three days later, attended Lincoln's final public address in Washington, D.C., with his future co-conspirators David Herold and Lewis Powell. During the speech, Booth became enraged when Lincoln expressed his support for granting voting rights to former slaves and ordered Powell to shoot Lincoln. Powell ultimately decided against it for fear of the crowd, but Booth vowed to "put him through" and formulated a plan to kill Lincoln which came to fruition on April 14.
William Howard Taft
* 1909:William Howard Taft
William Howard Taft (September 15, 1857March 8, 1930) served as the 27th president of the United States from 1909 to 1913 and the tenth chief justice of the United States from 1921 to 1930. He is the only person to have held both offices. ...
and Porfirio Díaz
José de la Cruz Porfirio Díaz Mori (; ; 15 September 1830 – 2 July 1915) was a General (Mexico), Mexican general and politician who was the dictator of Mexico from 1876 until Mexican Revolution, his overthrow in 1911 seizing power in a Plan ...
planned a summit in El Paso, Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
, and Ciudad Juárez
Ciudad Juárez ( , ; "Juárez City"), commonly referred to as just Juárez (Lipan language, Lipan: ''Tsé Táhú'ayá''), is the most populous city in the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Mexican state of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua. It was k ...
, Chihuahua, a historic first meeting between a U.S. president and a Mexican president and also the first time an American president would cross the border into Mexico. Díaz requested the meeting to show U.S. support for his planned eighth run as president, and Taft agreed to support Díaz in order to protect the several billion dollars of American capital then invested in Mexico. Both sides agreed that the disputed Chamizal strip connecting El Paso to Ciudad Juárez would be considered neutral territory with no flags present during the summit, but the meeting focused attention on this territory and resulted in assassination threats and other serious security concerns. The Texas Rangers, 4,000 U.S. and Mexican troops, U.S. Secret Service agents, FBI
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic Intelligence agency, intelligence and Security agency, security service of the United States and Federal law enforcement in the United States, its principal federal law enforcement ag ...
agents, and U.S. Marshals were all called in to provide security. An additional 250-member private security detail led by Frederick Russell Burnham
Major (rank), Major Frederick Russell Burnham Distinguished Service Order, DSO (May 11, 1861 – September 1, 1947) was an American scout and world-traveling adventurer. He is known for his service to the British South Africa Company and to t ...
, the celebrated scout, was hired by John Hays Hammond
John Hays Hammond (March 31, 1855 – June 8, 1936) was an American mining engineer, diplomat, and philanthropist. He amassed a sizable fortune before the age of 40. An early advocate of deep mining, Hammond was given complete charge of Cecil R ...
. Hammond was a close friend of Taft from Yale University
Yale University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in New Haven, Connecticut, United States. Founded in 1701, Yale is the List of Colonial Colleges, third-oldest institution of higher education in the United Stat ...
and a former candidate for U.S. vice president in the 1908 presidential election who, along with his business partner Burnham, held considerable mining interests in Mexico. On October 16, the day of the summit, Burnham and Private C.R. Moore, a Texas Ranger, discovered 52-year-old Julius Bergerson holding a concealed palm pistol standing at the El Paso Chamber of Commerce building along the procession route. Burnham and Moore captured and disarmed Bergerson within only a few feet (around one meter) of Taft and Díaz.
* 1910: President Taft visited his aunt, Delia Torrey, in Millbury, Massachusetts. Torrey later reported receiving a stranger who allegedly overheard an assassination plot in Boston, Massachusetts
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
. Before leaving nearby Worcester, Massachusetts
Worcester ( , ) is the List of municipalities in Massachusetts, second-most populous city in the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the list of United States cities by population, 113th most populous city in the United States. Named after Worcester ...
by train, he threatened Torrey, who claimed the stranger "did not want anything to get into the papers, and if it did he would come back and kill me." Torrey reported the plot to the local police, who shared the allegation with the Worcester Police and the Secret Service. The man was never identified.
Herbert Hoover
* November 19, 1928: President-elect Hoover embarked on a ten-nation "goodwill tour" of Central and South America. While he was crossing theAndes Mountains
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long and wide (widest between 18°S ...
from Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
, an assassination plot by Argentine
Argentines, Argentinians or Argentineans are people from Argentina. This connection may be residential, legal, historical, or cultural. For most Argentines, several (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their ...
anarchists was thwarted. The group was led by Severino Di Giovanni, who planned to blow up his train as it crossed the Argentinian central plain. The plotters had an itinerary but the bomber was arrested before he could place the explosives on the rails. Hoover professed unconcern, tearing off the front page of a newspaper that revealed the plot and explaining, "It's just as well that Lou shouldn't see it," referring to his wife. His complimentary remarks on Argentina were well received in both the host country and in the press.
Franklin D. Roosevelt
 * February 15, 1933: Seventeen days before Roosevelt's first presidential inauguration, Giuseppe Zangara fired five shots at Roosevelt in
* February 15, 1933: Seventeen days before Roosevelt's first presidential inauguration, Giuseppe Zangara fired five shots at Roosevelt in Miami
Miami is a East Coast of the United States, coastal city in the U.S. state of Florida and the county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade County in South Florida. It is the core of the Miami metropolitan area, which, with a populat ...
, Florida. Zangara's shots missed the president-elect, but Zangara did mortally wound Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
Mayor Anton Cermak and injured four other people. Zangara pleaded guilty to the murder of Cermak and was executed in the electric chair on March 20, 1933. It has never been conclusively determined who was Zangara's target, but most assumed at first that he had been shooting at the president-elect. Another theory is that the attempt may have been ordered by the imprisoned Al Capone, and that Cermak, who had led a crackdown on the Chicago Outfit and Chicago organized crime more generally, was the true target.
* 1943: Soviet NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (, ), abbreviated as NKVD (; ), was the interior ministry and secret police of the Soviet Union from 1934 to 1946. The agency was formed to succeed the Joint State Political Directorate (OGPU) se ...
claimed to have discovered a Nazi German
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a totalitarian dictat ...
Waffen-SS
The (; ) was the military branch, combat branch of the Nazi Party's paramilitary ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) organisation. Its formations included men from Nazi Germany, along with Waffen-SS foreign volunteers and conscripts, volunteers and conscr ...
plan to assassinate Roosevelt, Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 1874 – 24 January 1965) was a British statesman, military officer, and writer who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1940 to 1945 (Winston Churchill in the Second World War, ...
, and Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
at the Tehran Conference.
Harry S. Truman
* Mid-1947: During the Jewish insurgency in Palestine before the formation of theState of Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
, the Zionist paramilitary organization Lehi was alleged to have sent a number of letter bombs addressed to the president and high-ranking staff at the White House. At the time, the incident was not publicized, but Truman's daughter Margaret Truman disclosed the alleged incident in her biography of Truman published in 1972; the allegation was previously disclosed in a memoir by Ira R. T. Smith, who worked in the mail room. According to Truman, the Secret Service was alerted by British intelligence after similar letters had been sent to high-ranking British officials and Lehi claimed credit; the mail room of the White House intercepted the letters intended for President Truman and the Secret Service defused them.AP, "Jews Sent Truman Letter Bombs, Book Tells"''Tri-City Herald'', December 1, 1972, accessed December 11, 2012 * November 1, 1950: Two Puerto Rican pro-independence activists, Oscar Collazo and Griselio Torresola, attempted to kill President Truman at the Blair House, where Truman was living while the White House was undergoing major renovations. In the attack, Torresola injured White House policeman Joseph Downs and mortally wounded White House policeman Leslie Coffelt. Coffelt returned fire, killing Torresola with a shot to the head. Collazo wounded an officer before being shot in the stomach. Collazo survived with serious injuries; Coffelt died of his wounds 4 hours later in a hospital. Truman was not harmed, but he was placed at a huge risk. Collazo was convicted in a federal trial and received the death sentence. Truman commuted Collazo's death sentence to life in prison. In 1979, President
Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (October 1, 1924December 29, 2024) was an American politician and humanitarian who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party ...
further commuted Collazo's sentence to time served.
John F. Kennedy
* December 11, 1960: While vacationing inPalm Beach, Florida
Palm Beach is an incorporated town in Palm Beach County, Florida, United States. Located on a barrier island in east-central Palm Beach County, the town is separated from West Palm Beach, Florida, West Palm Beach and Lake Worth Beach, Florida, ...
, President-elect John F. Kennedy was threatened by Richard Paul Pavlick, a 73-year-old former postal worker driven by hatred of Catholics. Pavlick intended to crash his dynamite
Dynamite is an explosive made of nitroglycerin, sorbents (such as powdered shells or clay), and Stabilizer (chemistry), stabilizers. It was invented by the Swedish people, Swedish chemist and engineer Alfred Nobel in Geesthacht, Northern German ...
-laden 1950 Buick
Buick () is a division (business), division of the Automotive industry in the United States, American automobile manufacturer General Motors (GM). Started by automotive pioneer David Dunbar Buick in 1899, it was among the first American automobil ...
into Kennedy's vehicle, but he changed his mind after seeing Kennedy's wife and daughter bid him goodbye. Pavlick was arrested four days later by the Secret Service after being stopped for a driving violation; police found the dynamite in his car and arrested him. On January 27, 1961, Pavlick was committed to the United States Public Health Service
The United States Public Health Service (USPHS or PHS) is a collection of agencies of the Department of Health and Human Services which manages public health, containing nine out of the department's twelve operating divisions. The assistant s ...
mental hospital in Springfield, Missouri
Springfield is the List of cities in Missouri, third most populous city in the U.S. state of Missouri and the county seat of Greene County, Missouri, Greene County. The city's population was 169,176 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 censu ...
, then was indicted for threatening Kennedy's life seven weeks later. Charges against Pavlick were dropped on December 2, 1963, ten days after Kennedy's assassination in Dallas. Judge Emett Clay Choate ruled that Pavlick was unable to distinguish between right and wrong in his actions, but kept him in the mental hospital. The federal government also dropped charges in August 1964, and Pavlick was eventually released from the New Hampshire State Hospital on December 13, 1966.
Richard Nixon
* April 13, 1972: Arthur Bremer carried a firearm to a motorcade inOttawa
Ottawa is the capital city of Canada. It is located in the southern Ontario, southern portion of the province of Ontario, at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the cor ...
, Canada, intending to shoot Nixon, but the president's car went by too fast for Bremer to get a good shot. The next day, Bremer thought he saw Nixon's car outside of the Centre Block
The Centre Block () is the main building of the Parliament of Canada, Canadian parliamentary complex on Parliament Hill, in Ottawa, Ontario, containing the House of Commons of Canada, House of Commons and Senate of Canada, Senate chambers, as we ...
, but it had disappeared by the time he could retrieve his gun from his hotel room. A month later, Bremer instead shot and seriously injured the governor of Alabama
Alabama ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South, Deep Southern regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gu ...
, George Wallace
George Corley Wallace Jr. (August 25, 1919 – September 13, 1998) was an American politician who was the 45th and longest-serving governor of Alabama (1963–1967; 1971–1979; 1983–1987), and the List of longest-serving governors of U.S. s ...
, who was paralyzed from the waist down until his death in 1998. Three other people were wounded. Bremer served 35 years in prison.
* February 22, 1974: Samuel Byck planned to kill Nixon by crashing a commercial airliner into the White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. Located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue Northwest (Washington, D.C.), NW in Washington, D.C., it has served as the residence of every U.S. president ...
. He hijacked a DC-9 at Baltimore-Washington International Airport after killing a Maryland Aviation Administration police officer, and was told that it could not take off with the wheel blocks still in place. After he shot both pilots (one later died), an officer named Charles 'Butch' Troyer shot Byck through the plane's door window. He survived long enough to kill himself by shooting.
Gerald Ford
 * Mid-August 1974: Muharem Kurbegovic, also known as The Alphabet Bomber, said in a message that he was going to come to Washington, D.C., and throw a nerve gas bomb at President Gerald Ford, then just ten days into his presidency. Within one day, the CIA, the U.S. Secret Service, and other law enforcement agencies, working out of the
* Mid-August 1974: Muharem Kurbegovic, also known as The Alphabet Bomber, said in a message that he was going to come to Washington, D.C., and throw a nerve gas bomb at President Gerald Ford, then just ten days into his presidency. Within one day, the CIA, the U.S. Secret Service, and other law enforcement agencies, working out of the White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. Located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue Northwest (Washington, D.C.), NW in Washington, D.C., it has served as the residence of every U.S. president ...
basement, identified Kurbegovich; he was arrested on August 20. The group had identified his Yugoslav origins, using a CIA voice analysis of his tapes, with court records of the cases handled by his first targets—the judge and the police commissioners—triangulating his identity. Kurbegovic was arrested in 1974 and was sentenced to life imprisonment in 1980.
* September 5, 1975: On the northern grounds of the California State Capitol
The California State Capitol is the seat of the California state government, located in Sacramento, the state capital of California. The building houses the chambers of the California State Legislature, made up of the Assembly and the Senat ...
in Sacramento, Lynette "Squeaky" Fromme, a follower of Charles Manson, drew a Colt M1911 .45-caliber pistol on Ford when he reached to shake her hand in a crowd. She had four cartridges in the pistol's magazine
A magazine is a periodical literature, periodical publication, print or digital, produced on a regular schedule, that contains any of a variety of subject-oriented textual and visual content (media), content forms. Magazines are generally fin ...
but none in the chamber, and as a result, the gun did not fire. She was quickly restrained by Secret Service agent Larry Buendorf. Fromme was sentenced to life in prison, but was released from custody on August 14, 2009 (two years and eight months after Ford's natural death in 2006).
* September 22, 1975: In San Francisco
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
, California, only 17 days after Fromme's attempt, Sara Jane Moore fired a revolver at Ford from away. A bystander, Oliver Sipple, grabbed Moore's arm and the shot missed Ford, striking a building wall and slightly injuring taxi driver John Ludwig. Moore was tried and convicted in federal court, and sentenced to prison for life. She was paroled from a federal prison on December 31, 2007, after serving more than 30 years—one year and five days after Ford's natural death.
The two assassination attempts on Gerald Ford in September 1975 are the only two known cases of women attempting to assassinate an American president.
George H. W. Bush
* April 13, 1993: According to Kuwaiti authorities, and an FBI investigation fourteen Kuwaiti and Iraqi men believed to be working forSaddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein (28 April 1937 – 30 December 2006) was an Iraqi politician and revolutionary who served as the fifth president of Iraq from 1979 until Saddam Hussein statue destruction, his overthrow in 2003 during the 2003 invasion of Ira ...
smuggled bombs into Kuwait
Kuwait, officially the State of Kuwait, is a country in West Asia and the geopolitical region known as the Middle East. It is situated in the northern edge of the Arabian Peninsula at the head of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Kuwait ...
, planning to assassinate former President George H. W. Bush
George Herbert Walker BushBefore the outcome of the 2000 United States presidential election, he was usually referred to simply as "George Bush" but became more commonly known as "George H. W. Bush", "Bush Senior," "Bush 41," and even "Bush th ...
by a car bomb during his visit to Kuwait University three months after he had left office in January 1993. The former president was on a visit to Kuwait in 1993 to commemorate the coalition's victory over Iraq in the Persian Gulf War when Kuwaiti officials claimed to have foiled an alleged assassination plot and arrested the suspects. At the time the former president was accompanied by his wife, two of his sons, former Secretary of State James Baker, former Chief of Staff John Sununu, and former Treasury Secretary Nicholas Brady. Of the 17 people Kuwaiti authorities arrested, two suspects, Wali Abdelhadi Ghazali, and Raad Abdel-Amir al-Assadi, retracted their confessions at the trial, claiming that they were coerced. A Kuwaiti court convicted all but one of the defendants. Then-president Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician and lawyer who was the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, ...
responded by launching a cruise missile attack on an Iraqi intelligence building in the Mansour district of Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
. The plot was used as one of the justifications for the Iraq Resolution by Bush's son, George, who had succeeded Clinton as president, authorizing the 2003 U.S. invasion of the country. An analysis by the CIA's Counterterrorism Center concludes the assassination plot was likely fabricated by Kuwaiti authorities; however, at the time the FBI established that the plot had been directed by the Iraqi Intelligence Service (IIS), and the CIA had received information suggesting that Saddam Hussein had authorized the assassination attempt to get revenge against the U.S., to punish Kuwait for working with the U.S., and to keep other Arab states for intervening in Iraq any further. The day before the attack, on April 12, 1993, the then U.S. Ambassador to the U.N. and future 64th U.S. secretary of state, Madeleine Albright
Madeleine Jana Korbel Albright (born Marie Jana Körbelová, later Korbelová; May 15, 1937 – March 23, 2022) was an American diplomat and political science, political scientist who served as the 64th United States Secretary of State, United S ...
, went before the U.N. Security Council to present evidence of the Iraqi plot with the hope of gaining international support.
Bill Clinton
* January 21, 1994: Ronald Gene Barbour, a retired military officer and freelance writer, plotted to kill Clinton while the president was jogging. Barbour returned to Florida a week later without having fired the shots at the president, who was on a state visit to Russia. Barbour was sentenced to five years in prison and was released in 1998. * October 29, 1994: Francisco Martin Duran fired at least 29 shots with a 7.62×39mm SKS semi-automatic rifle at the White House from a fence overlooking the North Lawn, thinking that Clinton was among the men in dark suits standing there (Clinton was inside). Three tourists, Harry Rakosky, Ken Davis and Robert Haines, tackled Duran before he could injure anyone. Found to have asuicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death.
Risk factors for suicide include mental disorders, physical disorders, and substance abuse. Some suicides are impulsive acts driven by stress (such as from financial or ac ...
note in his pocket, Duran was sentenced to 40 years in prison.Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American not-for-profit organization, not-for-profit news agency headquartered in New York City.
Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association, and produces news reports that are dist ...
:"Court Sentences Man to 40 Years For Trying to Kill the President,"
June 30, 1995, ''
New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
'', retrieved July 14, 2024
* November 1994: Osama bin Laden
Osama bin Laden (10 March 19572 May 2011) was a militant leader who was the founder and first general emir of al-Qaeda. Ideologically a pan-Islamist, Bin Laden participated in the Afghan ''mujahideen'' against the Soviet Union, and support ...
recruited Ramzi Yousef, the mastermind of the 1993 World Trade Center bombing, to attempt to assassinate Clinton. However, Yousef decided that security would be too effective and decided to target Pope John Paul II
Pope John Paul II (born Karol Józef Wojtyła; 18 May 19202 April 2005) was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 16 October 1978 until Death and funeral of Pope John Paul II, his death in 2005.
In his you ...
instead.
* November 24, 1996: During his visit to the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) forum in Manila, Clinton's motorcade was rerouted before it was to drive over a bridge. Secret Service officers had intercepted a message suggesting that an attack was imminent, and Lewis Merletti, the director of the Secret Service, ordered the motorcade to be re-routed. An intelligence team later discovered a bomb under the bridge. Subsequent U.S. investigation "revealed that he plotwas masterminded by a Saudi terrorist living in Afghanistan named Osama bin Laden
Osama bin Laden (10 March 19572 May 2011) was a militant leader who was the founder and first general emir of al-Qaeda. Ideologically a pan-Islamist, Bin Laden participated in the Afghan ''mujahideen'' against the Soviet Union, and support ...
".
* October 2018: A package containing a pipe bomb addressed to his wife Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, lawyer and diplomat. She was the 67th United States secretary of state in the administration of Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, a U.S. senator represent ...
and sent to their home in Chappaqua, New York, was intercepted by the Secret Service. It was one of several mailed to other Democratic leaders in the same week, including former president Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
.'Act of terror': Bombs sent to CNN, Clintons, Obamas, HolderCNN, October 24, 2018
Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician and lawyer who was the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, ...
was at the Chappaqua home when the package was intercepted, while Hillary was in Florida campaigning for Democrats in the 2018 midterm elections. Fingerprint DNA revealed that the package was sent by Florida resident Cesar Sayoc, who was captured two days after the package was intercepted. Prosecutors sought a life sentence for Sayoc, but the judge instead sentenced him to 20 years.
George W. Bush
* May 10, 2005: While President Bush was giving a speech in the Freedom Square inTbilisi
Tbilisi ( ; ka, თბილისი, ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), ( ka, ტფილისი, tr ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Georgia (country), largest city of Georgia ( ...
, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
, Vladimir Arutyunian threw a live Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
-made RGD-5 hand grenade
A grenade is a small explosive weapon typically thrown by hand (also called hand grenade), but can also refer to a Shell (projectile), shell (explosive projectile) shot from the muzzle of a rifle (as a rifle grenade) or a grenade launcher. A mod ...
toward the podium. The grenade had its pin pulled, but did not explode because a red tartan handkerchief was wrapped tightly around it, preventing the safety lever from detaching. After escaping that day, Arutyunian was arrested in July 2005. During his arrest, he killed an Interior Ministry agent. He was convicted in January 2006 and given a life sentence
Life imprisonment is any sentence of imprisonment under which the convicted individual is to remain incarcerated for the rest of their natural life (or until pardoned or commuted to a fixed term). Crimes that result in life imprisonment are c ...
.
* May 24, 2022: Shihab Ahmed Shihab Shihab, an Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
i citizen and resident of Columbus, Ohio
Columbus (, ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of cities in Ohio, most populous city of the U.S. state of Ohio. With a 2020 United States census, 2020 census population of 905,748, it is the List of United States ...
, was arrested for involvement in a plot to assassinate former President Bush based on information obtained from conversations he held with several undercover FBI informants. He was also accused of committing an immigration crime and planning to illegally smuggle Iraqi nationals into the U.S. from Mexico in order to assist with the plot. He additionally claimed to informants that he had direct connections to members of the former ISIS
Isis was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kingdom () as one of the main characters of the Osiris myth, in which she resurrects her sla ...
, including ones to former ISIS leader Abu Bakr Al-Baghdadi
Ibrahim Awwad Ibrahim Ali al-Badri (28 July 1971 – 27 October 2019), commonly known by his ''nom de guerre'' Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, was an Iraqi militant leader who was the founder and first leader of the Islamic State (IS), who proclaimed hims ...
(before his death) and a former ISIS financial chief, the latter of whom he intended to launder money from into the U.S. via a Columbus car dealership. In February, Shihab and an informant traveled to the Bush home in Dallas, Texas, and to the George W. Bush Institute to conduct surveillance. Shihab entered the country illegally in September 2020 with false identification. Shihab claimed to have worked with Iraqi terrorists to kill many American servicemen in Iraq from 2003 to 2006 following the invasion. He stated that the motivation behind the assassination plot was anger over the Iraq War
The Iraq War (), also referred to as the Second Gulf War, was a prolonged conflict in Iraq lasting from 2003 to 2011. It began with 2003 invasion of Iraq, the invasion by a Multi-National Force – Iraq, United States-led coalition, which ...
.
Barack Obama
* December 2008: A United States Marine, 20-year-old Kody Ray Brittingham, stationed at Camp Lejeune, wrote that he had taken an oath to "protect against all enemies, both foreign and domestic." In a signed "letter of intent," he identified President-elect Obama as a "domestic enemy" and the target of Brittingham's planned assassination plot. A search of his barracks uncovered a journal containing white supremacist material. In June 2010, Brittingham was sentenced to 8 years and 4 months in federal prison. * April 2009: A plot to assassinate Obama at the Alliance of Civilizations summit inIstanbul
Istanbul is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, constituting the country's economic, cultural, and historical heart. With Demographics of Istanbul, a population over , it is home to 18% of the Demographics ...
, Turkey, was discovered after a man of Syrian origins carrying forged Al Jazeera TV press credentials was found. The man confessed to the Turkish security services details of his plan to kill Obama with a knife. He alleged that he had three accomplices.
* November 2011: 21-year-old Oscar Ramiro Ortega-Hernandez
On November 11, 2011, Oscar Ramiro Ortega-Hernandez, an unemployed 21-year-old man, fired multiple shots at the White House using a semi-automatic rifle. At least seven bullets hit the second floor. Neither President Barack Obama nor First L ...
was influenced by conspiracy theories and fringe religious viewpoints to attempt to murder Obama. Having traveled from his native Idaho, he hit the White House with several rounds fired from a semi-automatic rifle. No one was injured, but a window was broken. He was sentenced to 25 years in prison.
* 2011 to 2012: The far-right terrorist group FEAR
Fear is an unpleasant emotion that arises in response to perception, perceived dangers or threats. Fear causes physiological and psychological changes. It may produce behavioral reactions such as mounting an aggressive response or fleeing the ...
plotted to carry out a series of terror attacks which included assassinating Obama. The plot was foiled when four members of the group were arrested on murder charges and one, Michael Burnett, agreed to co-operate with authorities in return for a lighter sentence.
* October 2012: A mentally ill man named Mitchell Kusick of Westminster, Colorado, was arrested after confessing to his therapist that he intended to kill Obama with a shotgun at a campaign stop in Boulder, Colorado
Boulder is a List of municipalities in Colorado#Home rule municipality, home rule city in Boulder County, Colorado, United States, and its county seat. With a population of 108,250 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the most ...
.
* April 2013: Another attempt was made when a letter laced with the toxin ricin was sent to Obama. The sender was later identified as James Everett Dutschke.
* May 2013: Ricin-laced letters were sent to Obama and New York City mayor Michael Bloomberg
Michael Rubens Bloomberg (born February 14, 1942) is an American businessman and politician. He is the majority owner and co-founder of Bloomberg L.P., and was its CEO from 1981 to 2001 and again from 2014 to 2023. He served as the 108th mayo ...
vowing to kill anyone who tried to take away the sender's guns. The letters in this case were sent by actress Shannon Richardson, who tried to frame her husband Nathan for the crime.
* June 2013: Two white supremacists, Glendon Scott Crawford of Galway, New York, and Eric Feight of Hudson, New York
Hudson is a Administrative divisions of New York#City, city in and the county seat of Columbia County, New York, United States. At the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census, it had a population of 5,894. On the east side of the Hudson River, f ...
, were arrested for a plot to kill Muslim Americans and other perceived enemies of Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
with a homemade "radiation gun", described by Crawford as "Hiroshima
is the capital of Hiroshima Prefecture in Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 1,199,391. The gross domestic product (GDP) in Greater Hiroshima, Hiroshima Urban Employment Area, was US$61.3 billion as of 2010. Kazumi Matsui has b ...
on a light switch". It later emerged that Crawford had suggested using the device against President Obama as well as several other targets.
* February 2015: Three men from New York City were arrested by the FBI after telling undercover agents about their plans to kill Obama and join the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant
The Islamic State (IS), also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS) and Daesh, is a transnational Salafi jihadist organization and unrecognized quasi-state. IS occupied signi ...
.
* October 2018: A package sent by Cesar Sayoc Jr. that contained a pipe bomb was sent to former President Obama at his home in Washington, D.C. The package was intercepted by the Secret Service.
* April 2019: Larry Mitchell Hopkins, a member of the United Constitutional Patriots militia, was arrested on April 20 after he allegedly confessed that his militia was training for a planned assassination of Obama and Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, lawyer and diplomat. She was the 67th United States secretary of state in the administration of Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, a U.S. senator represent ...
.
Donald Trump
* September 6, 2017: Gregory Lee Leingang, a 42-year-old man from Bismarck, North Dakota, attempted to assassinate President Donald Trump in Mandan, North Dakota, while Trump was visiting the state to rally public support. Leingang stole aforklift
A forklift (also called industrial truck, lift truck, jitney, hi-lo, fork truck, fork hoist, and forklift truck) is a powered industrial truck used to lift and move materials over short distances. The forklift was developed in the early 20th c ...
from an oil refinery and drove toward the presidential motorcade. After the forklift became jammed within the refinery, he fled on foot and was arrested by the pursuing police. While interviewed in detention, he admitted his intent to murder the president by flipping the presidential limousine with the stolen forklift, to the surprise of authorities, who suspected he was merely stealing the vehicle for personal use. The man pleaded guilty to the attempted attack, stealing the forklift, related charges, and several other unrelated crimes on the same day. Consequently, he was sentenced to 20 years in prison. His defense attorney noted a "serious psychiatric crisis".
* November 2017: A man affiliated with Islamic State
The Islamic State (IS), also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL), the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS) and Daesh, is a transnational Salafi jihadism, Salafi jihadist organization and unrecognized quasi-state. IS ...
(IS), whose name was not revealed, was arrested by the Philippine National Police
The Philippine National Police (PNP; ) is the national police force of the Philippines. Its national headquarters is located at Camp Crame in Bagong Lipunan ng Crame, Quezon City. Currently, it has approximately 228,000 personnel to police a pop ...
in Rizal Park, Manila, for reportedly planning to assassinate Trump during the diplomatic ASEAN Summit. In the week prior to the failed killing, the Secret Service already suspected a planned assault on the president because of the general presence of IS in the Philippines and because of threats by many people against the president on social media. Before the landing of Trump's airplane, the Secret Service discovered a credible terrorist threat from a man who threatened to kill the president on social media, quickly tracking down and arresting the terrorist. The government disclosed the incident to the public, after a year of silence, in a television documentary.
* October 1, 2018: An envelope laced with ricin was sent to Trump before being discovered by mailing facilities. Several other letters were sent to the Pentagon, all of them labeled on the front with "Jack and the Missile Bean Stock Powder". Two days later on October 3, a 39-year-old Utah
Utah is a landlocked state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is one of the Four Corners states, sharing a border with Arizona, Colorado, and New Mexico. It also borders Wyoming to the northea ...
Navy veteran named William Clyde Allen III was arrested and charged with one count of mailing a threat against the president and five counts of mailing threatening communications to an officer or an employee of the United States. Allen pleaded not guilty to all charges.
* September 2020: Letters containing the poison ricin and addressed to Donald Trump were intercepted by the Secret Service before delivery to the White House. Canadian woman Pascale Ferrier had sent the letters from Canada and was subsequently arrested while attempting to cross the Canadian border into the United States while possessing a firearm and ammunition. Ferrier was sentenced to 22 years in prison for the poisoned letters, which she had also sent to law enforcement officials in Texas. She described herself as a peaceful activist, claiming “The only regret I have is that it didn’t work and that I couldn’t stop Trump".
* October 2020: It was reported that Barry Croft Jr., a Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
man who was arrested for his involvement in the kidnapping plot against Michigan Governor Gretchen Whitmer, included Trump in a list of politicians he wanted to kill by hanging. In December 2022, Croft was sentenced to 19 years in prison.
* July 12, 2024: A Pakistani man named Asif Merchant, reported to be an agent of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps
The Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), also known as the Iranian Revolutionary Guards, is a multi-service primary branch of the Islamic Republic of Iran Armed Forces, Iranian Armed Forces. It was officially established by Ruhollah Khom ...
, was arrested for a plot to kill Trump at a rally. Adrienne Watson, a spokesperson for the U.S. National Security Council, said that the plot was believed to be in revenge for the assassination of Qasem Soleimani. Merchant paid $5,000 to federal agents posing as hired assassins and told them they would receive their instructions after he had left the country. Merchant was arrested in Houston, Texas
Houston ( ) is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in the U.S. state of Texas and in the Southern United States. Located in Southeast Texas near Galveston Bay and the Gulf of Mexico, it is the county seat, seat of ...
, on July 12, just before attempting to leave the United States.
 * September 15, 2024: 58-year-old Ryan Wesley Routh was spotted by a Secret Service agent holding an SKS-style rifle on a private golf course belonging to Trump in
* September 15, 2024: 58-year-old Ryan Wesley Routh was spotted by a Secret Service agent holding an SKS-style rifle on a private golf course belonging to Trump in West Palm Beach, Florida
West Palm Beach is a city in and the county seat of Palm Beach County, Florida, United States. It is located immediately to the west of the adjacent Palm Beach, Florida, Palm Beach, which is situated on a barrier island across the Lake Worth Lag ...
. Routh was hiding at a place that was commonly used to take pictures of Trump (while golfing) by the media. After 12 hours of hiding in shrubbery, Routh had his weapon pointed through the fence line of the golf course, 300–500 yards away from Trump. A Secret Service agent noticed this and fired four rounds towards Routh, who then dropped his weapon and fled the scene. After a short police chase, he was stopped and detained without resistance; no one was hurt. The following day, the FBI confirmed that Routh did not have a clear line of sight on Trump, and he did not fire his weapon. On April 7, 2025, an indictment
An indictment ( ) is a formal accusation that a person has committed a crime. In jurisdictions that use the concept of felonies, the most serious criminal offense is a felony; jurisdictions that do not use that concept often use that of an ind ...
revealed that Routh had at least two accomplices; one in Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
with access to military weapons, and the other being a smuggler
Smuggling is the illegal transportation of objects, substances, information or people, such as out of a house or buildings, into a prison, or across an international border, in violation of applicable laws or other regulations. More broadly, soc ...
in Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
going by the alias "Ramiro"; both whom Routh communicated with through the instant messaging app WhatsApp
WhatsApp (officially WhatsApp Messenger) is an American social media, instant messaging (IM), and voice-over-IP (VoIP) service owned by technology conglomerate Meta. It allows users to send text, voice messages and video messages, make vo ...
. The same indictment revealed that Routh planned on running away to Mexico City
Mexico City is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city of Mexico, as well as the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North America. It is one of the most important cultural and finan ...
in the days immediately after the attempt. Routh's trial is set to begin on September 8, 2025.
* September 2024: According to a criminal complaint filed by the Department of Justice, an Iranian official had ordered agents in the US to formulate a plan to kill Trump before the election. The agents, identified as 51-year-old Farjad Shakeri, 49-year-old Carlisle Rivera, and 36-year-old Jonathon Loadholt were charged with murder-for-hire, conspiracy to commit murder-for-hire, and money laundering conspiracy. Shakeri was additionally charged with providing material support to a foreign terrorist organization, conspiring to provide material support to a foreign terrorist organization, and conspiracy to violate the International Emergency Economic Powers Act and sanctions against the Government of Iran.
* February 11, 2025: Nikita Casap, a 17-year-old teen and follower of the Order of Nine Angles, shot and killed his mother, 35-year-old Tatiana Casap, and his stepfather, 51-year-old Donald Mayer in Waukesha, Wisconsin; Casap was accused of living with their corpses for two weeks. He was arrested on February 28 after running a stop sign while driving his stepfather's black 2018 Volkswagen Atlas in WaKeeney, Kansas, 800 miles away from his Wisconsin home. The car contained his stepfather's Smith & Wesson
Smith & Wesson Brands, Inc. (S&W) is an American Firearms manufacturer, firearm manufacturer headquartered in Maryville, Tennessee, United States.
Smith & Wesson was founded by Horace Smith (inventor), Horace Smith and Daniel B. Wesson as the ...
.357 Magnum revolver, the victims' driver's licenses and spent shell casings. He is also accused of plotting to assassinate President Trump in order to instigate a race war and sow chaos.
* April 11, 2025: 32-year-old Shawn Monper was arrested by the FBI
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic Intelligence agency, intelligence and Security agency, security service of the United States and Federal law enforcement in the United States, its principal federal law enforcement ag ...
for posting multiple threats to assassinate Donald Trump on social media
Social media are interactive technologies that facilitate the Content creation, creation, information exchange, sharing and news aggregator, aggregation of Content (media), content (such as ideas, interests, and other forms of expression) amongs ...
. Since Trump took office in 2025, Monper had bought several guns and ammunition, preparing to commit a mass shooting
A mass shooting is a violent crime in which one or more attackers use a firearm to Gun violence, kill or injure multiple individuals in rapid succession. There is no widely accepted specific definition, and different organizations tracking su ...
. Monper was living in Butler, Pennsylvania, the city where Trump's Pennsylvania assassination attempt took place in 2024. On May 2, Monper was charged with 4 counts of threatening to murder a U.S official to impede their official duties.
Joe Biden
* August 9, 2023: Craig Deleeuw, a 74-year old resident ofProvo, Utah
Provo ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Utah County, Utah, United States. It is south of Salt Lake City along the Wasatch Front, and lies between the cities of Orem, Utah, Orem to the north and Springville, Utah, Springville to the south ...
, had threatened to assassinate Joe Biden
Joseph Robinette Biden Jr. (born November 20, 1942) is an American politician who was the 46th president of the United States from 2021 to 2025. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he served as the 47th vice p ...
with an M24 sniper rifle during Biden's visit in Utah in a post on social media. According to police, his post indicated that he owned a long-range sniper rifle and numerous other weapons, as well as camouflage clothing known as a ghillie suit. The post led to an arrest warrant
An arrest warrant is a warrant issued by a judge or magistrate on behalf of the state which authorizes the arrest and detention of an individual or the search and seizure of an individual's property.
Canada
Arrest warrants are issued by a jud ...
being issued for him and FBI
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic Intelligence agency, intelligence and Security agency, security service of the United States and Federal law enforcement in the United States, its principal federal law enforcement ag ...
special agents raiding his residence at 6:15 am. During the raid, Deleeuw was armed and was resisting arrest, leading to him being shot and killed by law enforcement.
* May 22, 2023: Sai Varshith Kandula, a 19-year-old man from Chesterfield, Missouri (near St. Louis), drove a rented box truck into a barrier that separated the White House grounds from the public. Shortly thereafter he was taken into custody by the United States Park Police and was found to have a Nazi flag in his truck. Kandula expressed admiration for the Third Reich
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a totalitarian dictat ...
and stated his intentions were to "kill the president" and "seize power". On January 16, 2025, he was sentenced to eight years in prison.
Deaths rumored to have been assassinations
Zachary Taylor
On July 9, 1850, President Zachary Taylor died from an illness that was diagnosed as cholera morbus, which allegedly came after eating cherries and milk at a4th of July
Fourth or the fourth may refer to:
* the ordinal form of the number 4
* ''Fourth'' (album), by Soft Machine, 1971
* Fourth (angle), an ancient astronomical subdivision
* Fourth (music), a musical interval
* ''The Fourth'', a 1972 Soviet drama
...
celebration. Almost immediately after his death, rumors began to circulate that Taylor was poisoned by pro-slavery Southerners, and similar theories have persisted into the 21st century. In 1991, a neutron activation analysis conducted on samples of Taylor's remains found no evidence of poisonings due to insufficient levels of arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
. Marxist political scientist Michael Parenti questions the traditional explanation for Taylor's death. Relying on interviews and reports by forensic pathologists, he argues that the procedure used to test for arsenic poisoning was fundamentally flawed.
Warren G. Harding
In June 1923, PresidentWarren G. Harding
Warren Gamaliel Harding (November 2, 1865 – August 2, 1923) was the 29th president of the United States, serving from 1921 until his death in 1923. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he was one of the most ...
set out on a cross-country Voyage of Understanding, planning to meet with citizens and explain his policies. During this trip, he became the first president to visit Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
, which was then a U.S. territory
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, belonging or connected to a particular country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually a geographic area which has not been granted the powers of self-government, ...
. Rumors of corruption
Corruption is a form of dishonesty or a criminal offense that is undertaken by a person or an organization that is entrusted in a position of authority to acquire illicit benefits or abuse power for one's gain. Corruption may involve activities ...
in the Harding administration were beginning to circulate in Washington, D.C., by 1923, and Harding was profoundly shocked by a long message he received while in Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
, apparently detailing illegal activities by his own cabinet that were allegedly unknown to him. At the end of July, while traveling south from Alaska through British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
, he developed what was thought to be a severe case of food poisoning. He gave the final speech of his life to a large crowd at the University of Washington Stadium (now Husky Stadium
Husky Stadium (officially Alaska Airlines Field at Husky Stadium for sponsorship purposes) is an outdoor American football, football stadium in the Northwestern United States, located on the campus of the University of Washington in Seattle, Wa ...
) at the University of Washington
The University of Washington (UW and informally U-Dub or U Dub) is a public research university in Seattle, Washington, United States. Founded in 1861, the University of Washington is one of the oldest universities on the West Coast of the Uni ...
campus in Seattle
Seattle ( ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Washington and in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. With a population of 780,995 in 2024, it is the 18th-most populous city in the United States. The city is the cou ...
, Washington. A scheduled speech in Portland, Oregon
Portland ( ) is the List of cities in Oregon, most populous city in the U.S. state of Oregon, located in the Pacific Northwest region. Situated close to northwest Oregon at the confluence of the Willamette River, Willamette and Columbia River, ...
, was canceled. The president's train proceeded south to San Francisco
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
. Upon arriving at the Palace Hotel, he developed pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
. Harding died in his hotel room of either a heart attack
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
or a stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
at 7:35 PM on August 2, 1923. The formal announcement, printed in ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
'' of that day, stated: "A stroke of apoplexy was the cause of death." He had been ill exactly one week.
Naval physicians surmised that Harding had suffered a heart attack
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
. The Hardings' personal medical advisor, homeopath and Surgeon General Charles E. Sawyer, disagreed with the diagnosis. His wife Florence Harding refused permission for an autopsy
An autopsy (also referred to as post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of deat ...
, which soon led to speculation that he had been the victim of a plot, possibly carried out by Florence, as he apparently had been unfaithful to her. Gaston Means, an amateur historian and gadfly, noted in his book ''The Strange Death of President Harding'' (1930) that the circumstances surrounding his death led to suspicions that he had been poisoned. A number of individuals attached to him, both personally and politically, would have welcomed Harding's death, as they would have been disgraced in association by Means' assertion of Harding's "imminent impeachment".
See also
* '' Assassins'', a musical about presidential assassins and assassination attempters * Attempted assassination of George Wallace, Democratic presidential candidate, on May 15, 1972 * Attempted assassination of Thomas R. Marshall, vice president, on July 2, 1915 * Curse of Tippecanoe, supposed pattern of certain presidents dying while in office * Kennedy curse * List of assassinated and executed heads of state and government * List of incidents of political violence in Washington, D.C. *List of White House security breaches
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but ...
* List of presidents of the United States who died in office
* List of assassinated American politicians
References
Bibliography
* * * Free at the Internet ArchiveVolume 1
an
Volume 2
* * * * * * * {{Lists of US Presidents and Vice Presidents
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
Assassination attempts, U.S. Presidents
Presidential assassination attempts and plots
Assassination attempts
Assassination attempts
Articles containing video clips