List of U.S. National Forests on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The United States has 154 protected areas known as national forests, covering . National forests are managed by the U.S. Forest Service, an agency of the
The United States has 154 protected areas known as national forests, covering . National forests are managed by the U.S. Forest Service, an agency of the
Official website of the United States Forest Service
{{featured list * National forests National forests Forests, national National forests
 The United States has 154 protected areas known as national forests, covering . National forests are managed by the U.S. Forest Service, an agency of the
The United States has 154 protected areas known as national forests, covering . National forests are managed by the U.S. Forest Service, an agency of the U.S. Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of comme ...
. The first national forest was established as the Yellowstone Park Timber and Land Reserve on March 30, 1891, then in the Department of the Interior. In 1897, the Organic Act
In United States law, an organic act is an act of the United States Congress that establishes a territory of the United States and specifies how it is to be governed, or an agency to manage certain federal lands. In the absence of an organ ...
provided purposes for which forest reserves could be established, including to reserve a supply of timber, protect the forest from development, and secure water supplies. With the Forest Reserve Act of 1891
The General Revision Act (sometimes Land Revision Act) of 1891, also known as the Forest Reserve Act of 1891, was a federal law signed in 1891 by President Benjamin Harrison. The Act reversed previous policy initiatives, such as the Timber Culture ...
, the president of the United States is given the power to set aside forest reserves in the public domain. With the Transfer Act of 1905, forest reserves became part of the U.S. Department of Agriculture in the newly created U.S. Forest Service.
By 1907, President Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
had more than doubled the forest-reserve acreage, and Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
responded by limiting the president's ability to proclaim new reserves. The National Forest System underwent a major reorganization in 1908, and in 1911 Congress authorized new additions to the system under the authority of the Weeks Act
The Weeks Act is a federal law (36 Stat. 961) enacted by the United States Congress on March 1, 1911. Introduced by Massachusetts Congressman John W. Weeks and signed into law by President William Howard Taft, the law authorized the United States ...
. The management goals provided by the Organic Act were expanded upon by the Multiple-Use Sustained-Yield Act of 1960 to include "outdoor recreation, range, timber, watershed, and wildlife and fish purposes" as well as for the establishment of wilderness areas.
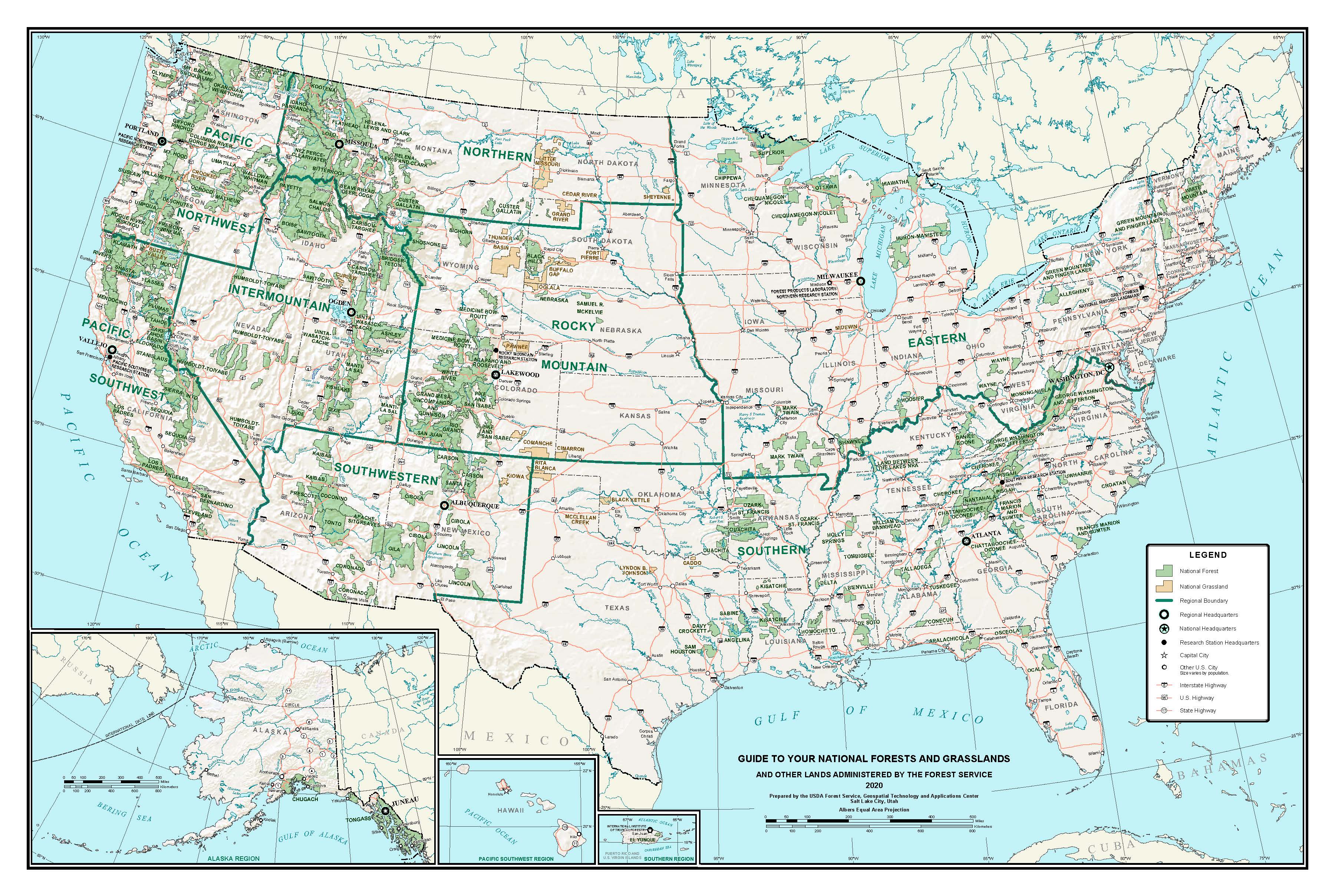
As of September 30, 2014, the Forest Service manages a total of , of which are national forests. The additional land areas include 20 national grasslands, 59 purchase units, 19 research and experimental areas, five land utilization projects and 37 other areas. The National Forest System has an extensive and complicated history of reorganization, so while there are currently 154 named national forests, many of these are managed together as either a single forest or separate forests.
There is at least one national forest in all but ten states: Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Iowa, Kansas, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey, North Dakota, and Rhode Island (although Kansas and North Dakota have national grasslands). In addition, Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
contains El Yunque National Forest, the only tropical U.S. rainforest. Alaska has the most national forest land, with , followed by California () and Idaho (). Idaho also has the greatest percent of its land in national forests, with 38.2 percent, followed by Oregon (24.7 percent) and Colorado (20.9 percent). On maps, national forests in the west generally show the true extent of their area, but those in the east often only show purchase districts, within which usually only a minority of the land is owned by the Forest Service.
National forests
See also
*List of former national forests of the United States
This is a list of all the former National Forests in the United States. These units were renamed, disestablished, combined with other units or split apart during reorganizations of the U.S. Forest Service system. There was particular turnover du ...
* National grassland
Notes
* Listed names of national forests represent the current management divisions of the National Forest System. Forests that are managed separately, such as Allegheny National Forest and Monongahela National Forest, are listed as separate forests. Forests that are managed together, however, may or may not be listed separately. Forests managed together and with hyphenated names, such as Salmon–Challis National Forest, are considered to be a single national forest. Forests that are managed together under titles such as Grand Mesa, Uncompahgre, and Gunnison National Forests, are considered to be separate forests. National forests listed in this column in small text are constituent national forests managed by, but not included in the name of, the named national forest in normal text. To reach the figure of 154 national forests, count hyphenated names as two forests, with the exception of Manti–La Sal, which is the official name of one forest. Uinta–Wasatch–Cache is counted as three, and George Washington and Jefferson is counted as two. * In the case of national forests in multiple states, the states are listed in descending order by land area of that forest contained in each state. States with the most area of that forest are listed first, while states with the least are listed last. Coordinates are those by the U.S. Board on Geographic Names, and may not be representative of the entire forest. * The history of the National Forest System is very complicated. Forests have been transferred between agencies, renamed, divided, consolidated, discontinued, established from parts of existing forests, had portions ceded to other forests, expanded from other lands, among various other actions. The date given represents the day: that forest was established as is, a predecessor forest with the same boundaries was established under a different name, or the earliest date of establishment of a forest that was combined in whole with another forest. *Forests with citations to the three books in the ''This Land'' series by Robert H. Mohlenbrock can be found in the section of the cited book that corresponds to that forest. Additional information about a particular forest can be found in this series and at each forest's website. *The Lake Tahoe Basin Management Unit (LTBMU) consists of of U.S. Forest Service land in the Lake Tahoe watershed. The LTBMU was formed from existing Forest Service land that was managed by Eldorado, Tahoe, and Humboldt–Toiyabe National Forests. Only of land in LTBMU is officially designated as LTBMU, and the remainder of the land is still officially designated as the three sources national forests. However, all of this land is managed separately as LTBMU, essentially making it a separate national forest.References
External links
Official website of the United States Forest Service
{{featured list * National forests National forests Forests, national National forests