List of German inventors and discoverers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
This is a list of German inventors and discoverers. The following list comprises people from Germany or German-speaking Europe, and also people of predominantly German heritage, in alphabetical order of the surname.


 * Walter Baade: astronom, discovered together with Fritz Zwicky, he identified
* Walter Baade: astronom, discovered together with Fritz Zwicky, he identified
 *
*
 *
*

 * Hermann Ganswindt: Inventor and spaceflight scientist, whose inventions (such as the dirigible, the helicopter, and the internal combustion engine) are thought to have been ahead of his time.
*
* Hermann Ganswindt: Inventor and spaceflight scientist, whose inventions (such as the dirigible, the helicopter, and the internal combustion engine) are thought to have been ahead of his time.
* *
*

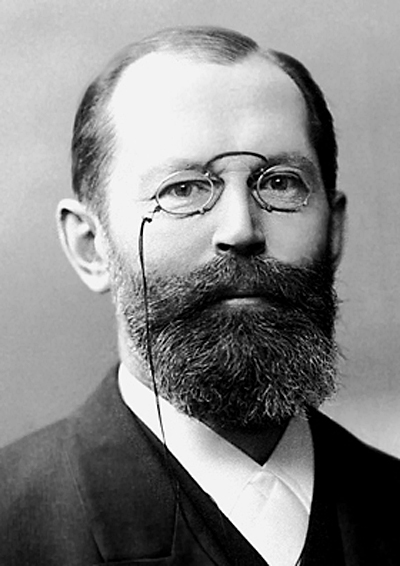
 * Ferdinand Adolf Kehrer : Introduction of the transverse incision technique to minimize bleeding by modern
* Ferdinand Adolf Kehrer : Introduction of the transverse incision technique to minimize bleeding by modern
 *
*

 *
*
 *
*
 *
*

 * Adolf Rambold: Inventor of modern
* Adolf Rambold: Inventor of modern
 * Otto Schoetensack: Named the
* Otto Schoetensack: Named the
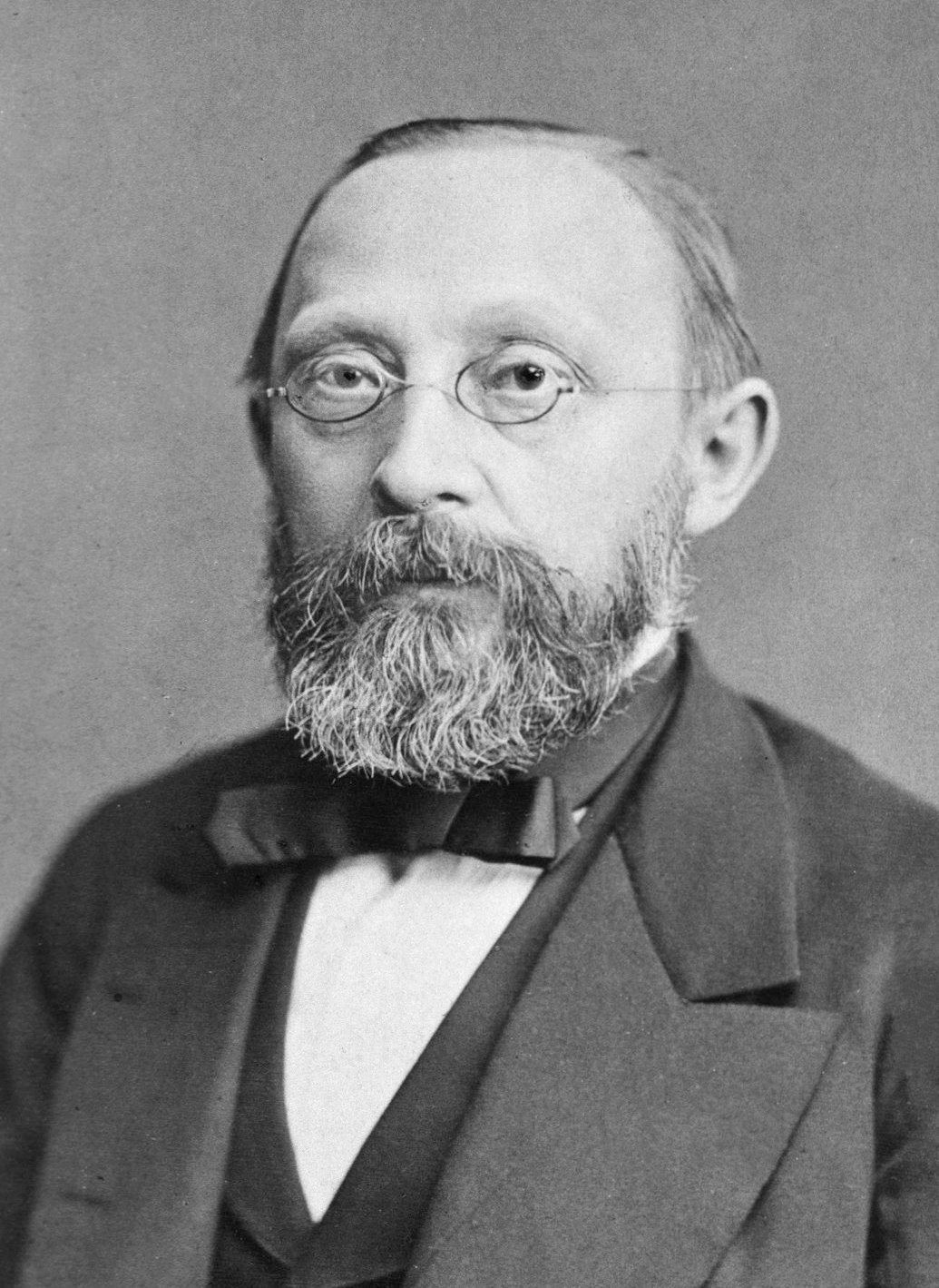 * Abraham Vater: Professor of anatomy;
* Abraham Vater: Professor of anatomy;

"Made in Germany"
A Sampling of German Inventors and Inventions
German inventors—"Made in Germany"
{{DEFAULTSORT:German inventors and discoverers * ! Inventors and discoverers
A
*Ernst Abbe
Ernst Karl Abbe (23 January 1840 – 14 January 1905) was a German businessman, optical engineer, physicist, and social reformer. Together with Otto Schott and Carl Zeiss, he developed numerous optical instruments. He was also a co-owner of Ca ...
: Invented the first refractometer
A refractometer is a laboratory or field device for the measurement of an Refractive index, index of refraction (refractometry). The index of refraction is calculated from the observed refraction angle using Snell's law. For mixtures, the index ...
, and many other devices. Donated his shares in the company Carl Zeiss to form Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung
The Carl-Zeiss-Foundation (non-profit)#Germany, Stiftung (Carl Zeiss Foundation), legally located in Heidenheim an der Brenz and Jena, Germany, and with its administrative headquarters in Stuttgart, is the sole shareholder of the two companies C ...
, still in existence today.
* Franz Carl Achard: Developed a process to produce sugar from sugar beet. Built the first factory for the process in 1802.
* Robert Adler: Invented a better television remote control.
*Konrad Adenauer
Konrad Hermann Joseph Adenauer (5 January 1876 – 19 April 1967) was a German statesman and politician who served as the first Chancellor of Germany, chancellor of West Germany from 1949 to 1963. From 1946 to 1966, he was the first leader of th ...
: Invented soya sausage (1916; "Kölner Wurst") and, together with Jean and Josef Oebel, oarsewholemeal bread (1917; Kölner Brot).
*Georgius Agricola
Georgius Agricola (; born Georg Bauer; 24 March 1494 – 21 November 1555) was a German Humanist scholar, mineralogist and metallurgist. Born in the small town of Glauchau, in the Electorate of Saxony of the Holy Roman Empire, he was b ...
: Named "the father of mineralogy".
* Wilhelm Albert: Invented the wire rope
Steel wire rope (right hand lang lay)
Wire rope is composed of as few as two solid, metal wires twisted into a helix that forms a composite ''rope'', in a pattern known as ''laid rope''. Larger diameter wire rope consists of multiple strands of ...
1834.
*Kurt Alder
Kurt Alder (; 10 July 1902 – 20 June 1958) was a German chemist and Nobel laureate.
Biography
Alder was born in the industrial area of Königshütte, Silesia (modern day Chorzów, Upper Silesia, Poland), where he received his early schoo ...
: Discovery of the Diels–Alder reaction
In organic chemistry, the Diels–Alder reaction is a chemical reaction between a Conjugated system, conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, commonly termed the Diels–Alder reaction#The dienophile, dienophile, to form a substituted cyclohexe ...
, Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1950.
* Richard Altmann: Discovery of the Mitochondrion
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cell (biology), cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine tri ...
*Alois Alzheimer
Alois Alzheimer ( , , ; 14 June 1864 – 19 December 1915) was a German psychiatrist, neuropathologist and colleague of Emil Kraepelin. He is credited with identifying the first published case of "presenile dementia", which Kraepelin later ide ...
: Psychiatrist who discovered Alzheimer
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems wit ...
´s disease, a degeneration of the brain in old age.
*Ottomar Anschütz
Ottomar Anschütz (16 May 1846 – 30 May 1907) was a German inventor, photographer, and chronophotographer.
He is widely seen as an early pioneer in the history of film technology. At the Postfuhramt in Berlin, Anschütz held the first showi ...
: in 1883 he patented a camera with an internal roller blind shutter mechanism, just in front of the photographic plate. Thus the focal-plane shutter in modern recognizable form was born.
*Hermann Anschütz-Kaempfe
Hermann Franz Joseph Hubertus Maria Anschütz-Kaempfe (3 October 1872 – 6 May 1931) was a German art historian and inventor. He was born in Zweibrücken and died in Munich.
In his quest to navigate to the North Pole by submarine, he becam ...
: Invented the gyrocompass
A gyrocompass is a type of non-magnetic compass which is based on a fast-spinning disc and the rotation of the Earth (or another planetary body if used elsewhere in the universe) to find geographical Direction (geometry), direction automaticall ...
in 1907.
*Manfred von Ardenne
Manfred baron von Ardenne (; 20 January 190726 May 1997) was a German researcher, autodidact in applied physics, and an inventor. He took out approximately 600 patents in fields including electron microscopy, medical technology, nuclear techn ...
: Self-taught researcher, applied physicist and inventor. Inventor of television among other things. 600 patents in fields including electron microscopy, medical technology, nuclear technology, plasma physics, and radio and television technology.
* Leo Arons: Mercury-vapor lamp
A mercury-vapor lamp is a gas-discharge lamp that uses an electric arc through vaporized mercury to produce light. The arc discharge is generally confined to a small fused quartz arc tube mounted within a larger soda lime or borosilicate gla ...
together with Peter Cooper Hewitt
Peter Cooper Hewitt (May 5, 1861 – August 25, 1921) was an American electrical engineer and inventor, who invented the first mercury-vapor lamp in 1901. Hewitt was issued on September 17, 1901. In 1903, Hewitt created an improved version ...
.
*Carl Auer von Welsbach
Carl Auer von Welsbach (1 September 1858 – 4 August 1929), who received the Austrian noble title of Freiherr Auer von Welsbach in 1901, was an Austrian scientist and inventor, who separated didymium into the elements neodymium and praseody ...
: Gas mantle
A Coleman white gas lantern mantle glowing at full brightness
An incandescent gas mantle, gas mantle or Welsbach mantle is a device for generating bright white light when heated by a flame. The name refers to its original heat source in gas li ...
*Leopold Auerbach
Leopold Auerbach (27 April 1828 – 30 September 1897) was a Jewish German anatomy, anatomist and neuropathology, neuropathologist born in Breslau. He is best known for discovering the myenteric plexus aka Auerbach's plexus, which helps control th ...
: Discovery of Plexus myentericus Auerbachi, or Auerbach's plexus.
*Max Abraham
Max Abraham (; 26 March 1875 – 16 November 1922) was a German physicist known for his work on electromagnetism and his opposition to the theory of relativity.
Biography
Abraham was born in Danzig, Imperial Germany (now Gdańsk in Poland) ...
: Physicist. Worked as Max Planck's assistant for three years. Developed theories on electrons.
B


supernovae
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original ob ...
as a new category of astronomical objects
*Karl Ernst von Baer
Karl Ernst Ritter von Baer Edler von Huthorn (; – ) was a Baltic German scientist and explorer. Baer was a naturalist, biologist, geologist, meteorologist, geographer, and is considered a, or the, founding father of embryology. He was a m ...
: discovered mammal ovum.
* Ralph Baer: Inventor of the first home video game console.
*Adolf von Baeyer
Johann Friedrich Wilhelm Adolf von Baeyer (; 31 October 1835 – 20 August 1917) was a German chemist who synthesised indigo dye, indigo and developed a Von Baeyer nomenclature, nomenclature for cyclic compounds (that was subsequently extended a ...
: Chemist. Synthesized indigo
InterGlobe Aviation Limited (d/b/a IndiGo), is an India, Indian airline headquartered in Gurgaon, Haryana, India. It is the largest List of airlines of India, airline in India by passengers carried and fleet size, with a 64.1% domestic market ...
, discovered the phthalein dyes, and investigated polyacetylenes, oxonium salts, nitroso compounds (1869) and uric acid derivatives (1860 and onwards) including the discovery of barbituric acid (1864). Nobel laureate
The Nobel Prizes (, ) are awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, the Swedish Academy, the Karolinska Institutet, and the Norwegian Nobel Committee to individuals and organizations who make outstanding contributions in th ...
1905.
* Albert Ballin: Father of modern cruise ship
Cruise ships are large passenger ships used mainly for vacationing. Unlike ocean liners, which are used for transport, cruise ships typically embark on round-trip voyages to various ports of call, where passengers may go on Tourism, tours k ...
travel
* Heinrich Band: Developed a musical instrument and called it bandoneón in 1846. It is used in most tango orchestras until today.
* Heinrich Barkhausen: Discovered what is now called the Barkhausen effect
The Barkhausen effect is a name given to the noise in the magnetic output of a ferromagnet when the magnetizing force applied to it is changed. Discovered by German physicist Heinrich Barkhausen in 1919, it is caused by rapid changes in the ...
, to describe the phenomenon, which is caused by rapid changes of size of magnetic domains in 1919, and Barkhausen stability criterion
In electronics, the Barkhausen stability criterion is a mathematical condition to determine when a linear electronic circuit will oscillate. It was put forth in 1921 by German physicist Heinrich Barkhausen (1881–1956). It is widely used in ...
.
*Oskar Barnack
Oskar Barnack (Nuthe-Urstromtal, Brandenburg, 1 November 1879 – Bad Nauheim, Hesse, 16 January 1936) was a German inventor and photographer who built, in 1913, what would later become the first commercially successful 35mm still-camera, sub ...
: The father of the first mass marketed 35mm camera and Leica.
*Heinrich Anton de Bary
Heinrich Anton de Bary (26 January 183119 January 1888) was a German surgeon, botanist, microbiologist, and mycologist (fungal systematics and physiology).
He is considered a founding father of plant pathology (phytopathology) as well as the fou ...
: Father of Phytopathology
Plant pathology or phytopathology is the scientific study of plant diseases caused by pathogens (infectious organisms) and environmental conditions (physiological factors). Plant pathology involves the study of pathogen identification, disease ...
, the science of plant diseases and modern Mycology
Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungus, fungi, including their Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy, genetics, biochemistry, biochemical properties, and ethnomycology, use by humans. Fungi can be a source of tinder, Edible ...
. Coined the word symbiosis
Symbiosis (Ancient Greek : living with, companionship < : together; and ''bíōsis'': living) is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction, between two organisms of different species. The two organisms, termed symbionts, can fo ...
in 1879.
* Karl Adolph von Basedow: Discovery and description of Graves-Basedow disease
*Wilhelm Bauer
Wilhelm Bauer (; 23 December 1822 – 20 June 1875) was a German marine engineer and inventor who built several hand-powered submarines.
Biography
Wilhelm Bauer was born in Dillingen in the Kingdom of Bavaria. His father was a sergeant in ...
: Inventor and engineer, who built several hand-powered submarines.
*Eugen Baumann
Eugen Baumann (12 December 1846 – 3 November 1896) was a German chemist. He was one of the first people to create polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and, together with Carl Schotten, he discovered the Schotten-Baumann reaction.
Life
Baumann was born i ...
: He was one of the first people to create polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and, together with Carl Schotten, he discovered the Schotten-Baumann reaction.
* Carl Baunscheidt: Inventor of the ''Lebenswecker'' ("life awakener") or "artificial leech".
*Hans Beck
Hans Beck (6 May 1929, Greiz – 30 January 2009, Markdorf) was the German inventor of Playmobil toys. He is often described as "The Father of Playmobil". He began to make toys at an early age and trained as a cabinet maker, before being recrui ...
: Inventor of the toy Playmobil
Playmobil () is a German line of toys produced by the Brandstätter Group (Geobra Brandstätter GmbH & Co KG), headquartered in Zirndorf, Germany. The signature Playmobil toy is a tall (1:24 scale) human figure with a smiling face. A wide range ...
.
*Georg Bednorz
Johannes Georg Bednorz (; born 16 May 1950) is a German physicist who, together with K. Alex Müller, discovered high-temperature superconductivity in ceramics, for which they shared the 1987 Nobel Prize in Physics.
Life and work
Bednorz was bor ...
: Physicist, discovered high-temperature superconductivity
High-temperature superconductivity (high-c or HTS) is superconductivity in materials with a critical temperature (the temperature below which the material behaves as a superconductor) above , the boiling point of liquid nitrogen. They are "high- ...
in ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcela ...
s, shared the 1987 Nobel Prize in Physics.
*Martin Behaim
Martin Behaim (6 October 1459 – 29 July 1507), also known as and by various forms of , was a German textile merchant and cartographer. He served John II of Portugal as an adviser in matters of navigation and participated in a voyage to Wes ...
: Inventor of the first globe of the world (Erdapfel
__NOTOC__
The ; ) is a terrestrial globe in diameter, produced by Martin Behaim from 1490 to 1492. The Erdapfel is the oldest surviving terrestrial globe. It is constructed of a laminated linen ball in two halves, reinforced with wood and over ...
) between 1491 and 1493.
*Alexander Behm
Alexander Behm (11 November 1880, in Sternberg ( Mecklenburg) – 22 January 1952, in Tarp ( Schleswig-Flensburg)) was a German physicist who developed working ocean echo sounder in Germany at the same time Reginald Fessenden was doing so ...
: Inventor of echo sounding
Echo sounding or depth sounding is the use of sonar for ranging, normally to determine the depth (coordinate), depth of water (bathymetry). It involves transmitting acoustic waves into water and recording the time interval between emission and ...
. The patent was granted in 1913.
*Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen
Faddey Faddeyevich Bellingshausen or Fabian Gottlieb Benjamin von Bellingshausen ( – ) was a Russian cartographer, explorer, and naval officer of Baltic German descent, who attained the rank of admiral. He participated in the first Russi ...
: Navigator and Explorer. Discovered the land mass of Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
on January 28, 1820.
*Friedrich Bessel
Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel (; 22 July 1784 – 17 March 1846) was a German astronomer, mathematician, physicist, and geodesy, geodesist. He was the first astronomer who determined reliable values for the distance from the Sun to another star by th ...
: astronom, he is credited with being the first to use parallax in calculating the distance to a star.
*Hans Bethe
Hans Albrecht Eduard Bethe (; ; July 2, 1906 – March 6, 2005) was a German-American physicist who made major contributions to nuclear physics, astrophysics, quantum electrodynamics and solid-state physics, and received the Nobel Prize in Physi ...
: Nuclear physicist and Nobel laureate in physics 1967. During World War II, he was head of the Theoretical Division at the secret Los Alamos laboratory which developed the first atomic bombs.
*Emil Adolf von Behring
Emil von Behring (; Emil Adolf von Behring: born Emil Adolf Behring; 15 March 1854 – 31 March 1917), was a German physiologist who received the 1901 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, the first one awarded in that field, for his discovery ...
: Discovered the diphtheria antitoxin. It was the world's first cure for a disease (1891). He was awarded history's first Nobel Prize in Physiology of Medicine in 1901.
* Melitta Bentz: Inventor of the coffee filter, 1908.
*Karl Benz
Carl (or Karl) Friedrich Benz (; born Karl Friedrich Michael Vaillant; 25 November 1844 – 4 April 1929) was a German engine designer and automotive engineer. His Benz Patent-Motorwagen from 1885 is considered the first practical modern automo ...
: Father and inventor of the gasoline-powered automobile, 1885, and pioneering founder of automobile manufacturing.
* Albrecht Berblinger: Inventor of the spring prosthesis and hang-glider (1811).Albrecht Ludwig Berblinger (1770-1829), known as the "Flying Tailor of Ulm", started with flight experiments in Ulm, Germany, in the early 19th century. He gained experience in downhill gliding with a maneuverable airworthy semi-rigid hang-glider and then attempted to cross the Danube River at Ulm's Eagle's Bastion on 31 May 1811. The tricky local winds caused him to crash and he was rescued by fishermen, making him the first survivor of a water immersion accident of a heavier-than-air manned "flight machine". Though he failed in his attempt to be the first man to fly, Berblinger can be regarded as one of the significant aviation pioneers who applied the "heavier than air" principle and paved the way for the more effective glide-flights of Otto Lilienthal (1891) and the Wright Brothers (1902). Less known are Berblinger's significant contributions to the construction of artificial limbs for medical use, as well as the spring-application in aviation. His invention of a special mechanical joint was also used for the juncture of the wings of his "flying machine". Because of his worthwhile contributions to medicine and flight, in 1993 the German Academy of Aviation Medicine named an annual award for young scientists in the field of aerospace medicine in his honor.
*Hans Berger
Hans Berger (21 May 1873 – 1 June 1941) was a German psychiatrist. He is best known as the inventor of electroencephalography (EEG) in 1924, which is a method used for recording the electrical activity of the brain, commonly described in terms ...
: a German neurologist, best known as the inventor of electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG)
is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignal, bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in ...
(EEG) (the recording of "brain waves") in 1924, coining the name, and the discoverer of the alpha wave
Alpha waves, or the alpha rhythm, are neural oscillations in the frequency range of 8–12 Hz likely originating from the synchronous and coherent ( in phase or constructive) neocortical neuronal electrical activity possibly involving thala ...
rhythm known as "Berger's wave"
* Emil Berliner: He is best known for developing the microphone and disc record gramophone.
* Albert Betz: Betz's law
In aerodynamics, Betz's law indicates the maximum Power (physics), power that can be extracted from the wind, independent of the design of a wind turbine in open flow. It was published in 1919 by the German physicist Albert Betz.Betz, A. (1966) ' ...
, 1913
*Gerd Binnig
Gerd Binnig (; born 20 July 1947) is a German physicist. He is most famous for having won the Nobel Prize in Physics jointly with Heinrich Rohrer in 1986 for the invention of the scanning tunneling microscope.
Early life and education
Binnig wa ...
: Physicist. Design of the scanning tunneling microscope (STM) with Heinrich Rohrer
Heinrich Rohrer (6 June 1933 – 16 May 2013) was a Swiss physicist who shared half of the 1986 Nobel Prize in Physics with Gerd Binnig for the design of the scanning tunneling microscope (STM). The other half of the Prize was awarded to Ernst R ...
. Nobel laureate 1986.
* Ludwig Blattner: developed the Blattnerphone, the first magnetic tape recorder
An audio tape recorder, also known as a tape deck, tape player or tape machine or simply a tape recorder, is a sound recording and reproduction device that records and plays back sounds usually using magnetic tape for storage. In its present ...
(using steel tape) whilst working in Britain in the late 1920s.
* Max Bockmühl: He developed together with German Gustav Ehrhart Methadone
Methadone, sold under the brand names Dolophine and Methadose among others, is a synthetic opioid used medically to treat chronic pain and opioid use disorder. Prescribed for daily use, the medicine relieves cravings and opioid withdrawal sym ...
in 1937 in Germany, working for I.G. Farbenindustrie AG at the Farbwerke Hoechst
* Johann Elert Bode: Discovered the Titus-Bode Law
* Ludwig Bölkow: Aeronautical pioneer. Was instrumental in the development of the Me 262, developed a new rotorhead In helicopters the rotorhead is the part of the Helicopter rotor, rotor assembly that joins the blades to the shaft, Helicopter flight controls#Cyclic, cyclic and Helicopter flight controls#Collective, collective mechanisms. It is sometimes referre ...
concept for helicopters.
*Max Born
Max Born (; 11 December 1882 – 5 January 1970) was a German-British theoretical physicist who was instrumental in the development of quantum mechanics. He also made contributions to solid-state physics and optics, and supervised the work of a ...
: Physicist and mathematician. Groundbreaking work in quantum mechanics. Nobel laureate 1954 with Walther Bothe. His Ph.D. student Delbrück, and six of his assistants (Fermi, Heisenberg, Goeppert-Mayer, Herzberg, Pauli, Wigner) went on to win Nobel Prizes. His Ph.D. student J. Robert Oppenheimer
J. Robert Oppenheimer (born Julius Robert Oppenheimer ; April 22, 1904 – February 18, 1967) was an American theoretical physics, theoretical physicist who served as the director of the Manhattan Project's Los Alamos Laboratory during World ...
led the project to develop the atomic bomb.
* Manfred Börner: Physicist. Developed the first working fiber-optical data transmission system in 1965. Received a patent for an "electro-optical transmission system utilizing lasers".
* Carl Bosch: Chemist and Nobel laureate, discovered the processes of industrial high pressure chemistry.
*Robert Bosch
Robert Bosch (23 September 1861 – 12 March 1942) was a German business magnate, engineer and inventor, founder of Bosch (company), Bosch.
Biography
Bosch was born in Langenau, Albeck, in the Swabia, Swabian Highlands near Ulm. He was one of t ...
: He invented, engineered and launched various innovations for the motor vehicle.
*Walther Bothe
Walther Wilhelm Georg Bothe (; 8 January 1891 – 8 February 1957) was a German physicist who shared the 1954 Nobel Prize in Physics with Max Born "for the coincidence method and his discoveries made therewith".
He served in the military durin ...
: Nuclear physicist, who shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1954 with Max Born.
* Johann Friedrich Böttger: He was generally acknowledged as the inventor of European porcelain although more recent sources ascribe this to Ehrenfried Walther von Tschirnhaus
Ehrenfried Walther von Tschirnhaus or Tschirnhauß (; 10 April 1651 – 11 October 1708) was a German mathematician, physicist, physician, and philosopher. He introduced the Tschirnhaus transformation and is considered by some to have been the ...
. Böttger is still credited with developing the manufacture of porcelain in Europe.
*Karlheinz Brandenburg
Karlheinz Brandenburg (born 20 June 1954) is a German electrical engineer and mathematician. Together with Ernst Eberlein, Heinz Gerhäuser (former Institutes Director of Fraunhofer IIS), Bernhard Grill, Jürgen Herre and Harald Popp (all Fraunh ...
: Inventor and audio engineer; father of audio compression format MPEG Audio Layer 3, more commonly known as MP3.
*Karl Ferdinand Braun
Karl Ferdinand Braun (; ; 6 June 1850 – 20 April 1918) was a German physicist, electrical engineer, and inventor. Braun contributed significantly to the development of radio with his 2 circuit system, which made long range radio transmiss ...
: Inventor of the CRT oscilloscope in 1897
*Wernher von Braun
Wernher Magnus Maximilian Freiherr von Braun ( ; ; 23 March 191216 June 1977) was a German–American aerospace engineer and space architect. He was a member of the Nazi Party and '' Allgemeine SS'', the leading figure in the development of ...
: The preeminent rocket engineer of the 20th century. Developed the V-2 rocket for Germany. Built Saturn V
The Saturn V is a retired American super heavy-lift launch vehicle developed by NASA under the Apollo program for human exploration of the Moon. The rocket was human-rated, had multistage rocket, three stages, and was powered by liquid-propel ...
rocket in USA which put man on the moon.
*Korbinian Brodmann
Korbinian Brodmann (17 November 1868 – 22 August 1918) was a German neuropsychiatrist who is known for mapping the cerebral cortex and defining 52 distinct regions, known as Brodmann areas, based on their cytoarchitectonic (histological) cha ...
: neurologist, Brodmann area
A Brodmann area is a region of the cerebral cortex, in the human or other primate brain, defined by its cytoarchitecture, or histological structure and organization of cells. The concept was first introduced by the German anatomist Korbinian B ...
in brain
* Walter Bruch: PAL
Phase Alternating Line (PAL) is a color encoding system for analog television. It was one of three major analogue colour television standards, the others being NTSC and SECAM. In most countries it was broadcast at 625 lines, 50 fields (25 ...
, colour encoding system for analogue television
* Friedrich Wilhelm Gustav Bruhn: inventor of Taximeter
A taximeter or fare meter is a mechanical or electronic device installed in taxicabs and auto rickshaws that calculates passenger fares based on a combination of distance travelled and waiting time. Its shortened form, "taxi", is also a meton ...
* Ernst Büchner: Chemist and inventor of Büchner flask and Büchner funnel.
*Robert Bunsen
Robert Wilhelm Eberhard Bunsen (;
30 March 1811
– 16 August 1899) was a German chemist. He investigated emission spectra of heated elements, and discovered caesium (in 1860) and rubidium (in 1861) with the physicist Gustav Kirchhoff. The Bu ...
: Chemist who developed the Bunsen burner
A Bunsen burner, named after Robert Bunsen, is a kind of ambient air gas burner used as laboratory equipment; it produces a single open gas flame, and is used for heating, sterilization, and combustion.
The gas can be natural gas (which is main ...
, and with Gustav Kirchhoff
Gustav Robert Kirchhoff (; 12 March 1824 – 17 October 1887) was a German chemist, mathematician, physicist, and spectroscopist who contributed to the fundamental understanding of electrical circuits, spectroscopy and the emission of black-body ...
he discovered caesium (1860) and rubidium (1861).
*Wilhelm Busch
Heinrich Christian Wilhelm Busch (14 April 1832 – 9 January 1908) was a German humorist, poet, illustrator, and painter. He published wildly innovative illustrated tales that remain influential to this day.
Busch drew on the tropes of f ...
: Caricaturist, painter and poet; father of comics.
* Christian Friedrich Ludwig Buschmann: Pioneer and promoter of the harmonica
The harmonica, also known as a French harp or mouth organ, is a free reed wind instrument used worldwide in many musical genres, notably in blues, American folk music, classical music, jazz, country, and rock. The many types of harmonica incl ...
.
*Adolf Busemann
Adolf Busemann (20 April 1901 – 3 November 1986) was a German aerospace engineer and influential Nazi-era pioneer in aerodynamics, specialising in supersonic airflows. He introduced the concept of swept wings and, after emigrating in 1947 to th ...
: Discovered the effect of swept wing
A swept wing is a wing angled either backward or occasionally forward from its root rather than perpendicular to the fuselage.
Swept wings have been flown since the pioneer days of aviation. Wing sweep at high speeds was first investigated in Ge ...
for modern aircraft in 1935.
*Adolf Butenandt
Adolf Friedrich Johann Butenandt (; 24 March 1903 – 18 January 1995) was a German biochemist. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1939 for his "work on sex hormones." He initially rejected the award in accordance with government pol ...
: Discovered primary female sex hormones. Shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Leopold Ruzicka in 1939.
C
*Georg Cantor
Georg Ferdinand Ludwig Philipp Cantor ( ; ; – 6 January 1918) was a mathematician who played a pivotal role in the creation of set theory, which has become a foundations of mathematics, fundamental theory in mathematics. Cantor establi ...
: Mathematician, discoverer of the set theory
Set theory is the branch of mathematical logic that studies Set (mathematics), sets, which can be informally described as collections of objects. Although objects of any kind can be collected into a set, set theory – as a branch of mathema ...
(1870s), which has become a fundamental theory in mathematics.
*Ernst Boris Chain
Sir Ernst Boris Chain (19 June 1906 – 12 August 1979) was a German-born British biochemist and co-recipient of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his work on penicillin.
Life and career
Chain was born in Berlin, the son of Marg ...
: biochemist, co-recipient of the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine for his work on penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of beta-lactam antibiotic, β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' Mold (fungus), moulds, principally ''Penicillium chrysogenum, P. chrysogenum'' and ''Penicillium rubens, P. ru ...
(together with Fleming).
*Carl von Clausewitz
Carl Philipp Gottlieb von Clausewitz ( , ; born Carl Philipp Gottlieb Clauswitz; 1 July 1780 – 16 November 1831) was a Kingdom of Prussia, Prussian general and Military theory, military theorist who stressed the "moral" (in modern terms meani ...
: The father of modern military theory
Military theory is the study of the theories which define, inform, guide and explain war and warfare. Military theory analyses both normative behavioral phenomena and explanatory causal aspects to better understand war and how it is fought. It ...
.
*Justus Claproth
Justus Claproth (28 December 1728 – 20 February 1805) was a German jurist and inventor of the deinking
Deinking is the industrial process of removing printing ink from paperfibers of recycled paper to make deinked pulp.
The key in the dein ...
: Jurist and inventor of recyclable paper and deinking
Deinking is the industrial process of removing printing ink from paperfibers of recycled paper to make deinked pulp.
The key in the deinking process is the ability to detach ink from the fibers. This is achieved by a combination of mechanical a ...
.
*Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath who formulated a mathematical model, model of Celestial spheres#Renaissance, the universe that placed heliocentrism, the Sun rather than Earth at its cen ...
: Astronom, formulated a heliocentric
Heliocentrism (also known as the heliocentric model) is a Superseded theories in science#Astronomy and cosmology, superseded astronomical model in which the Earth and Solar System, planets orbit around the Sun at the center of the universe. His ...
model
A model is an informative representation of an object, person, or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin , .
Models can be divided in ...
of the universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents. It comprises all of existence, any fundamental interaction, physical process and physical constant, and therefore all forms of matter and energy, and the structures they form, from s ...
which placed the Sun, rather than the Earth, at the center.
* Manfred Curry: German American
German Americans (, ) are Americans who have full or partial German ancestry.
According to the United States Census Bureau's figures from 2022, German Americans make up roughly 41 million people in the US, which is approximately 12% of the pop ...
yachtsman, developed the cam cleat used on sailboats to easily and quickly secure a rope, discoverer of the pseudoscientific phenomenon of "geomagnetic lines" called the Curry Grid.
D
*Gottlieb Daimler
Gottlieb Wilhelm Daimler (; 17 March 1834 – 6 March 1900) was a German engineer, industrial designer and industrialist. He was a pioneer of internal-combustion engines and automobile development. He invented the high-speed liquid petroleum-fue ...
: He invented the first high-speed petrol engine and the first four-wheel automobile, also the first internal combustion
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal comb ...
motorcycle, the ''Reitwagen''.
* Adolf "Adi" Dassler: Sports shoes with and without spikes; founder of Adidas
Adidas AG (; stylized in all lowercase since 1949) is a German athletic apparel and footwear corporation headquartered in Herzogenaurach, Bavaria, Germany. It is the largest sportswear manufacturer in Europe, and the second largest in the ...
.
* Rudolf Dassler: First sport shoes with screw-in shoe spikes, 1949; founder of Puma.
* Hans Georg Dehmelt: Physicist. Co-developed the non-magnetic quadrupole mass filter which laid the foundation for what we now call an ion trap
An ion trap is a combination of electric field, electric and/or magnetic fields used to capture charged particles — known as ions — often in a system isolated from an external environment. Atomic and molecular ion traps have a number of a ...
. Shared the Nobel Prize in 1989.
*Max Delbrück
Max Ludwig Henning Delbrück (; September 4, 1906 – March 9, 1981) was a German–American biophysicist who participated in launching the molecular biology research program in the late 1930s. He stimulated physical science, physical scientist ...
: German American
German Americans (, ) are Americans who have full or partial German ancestry.
According to the United States Census Bureau's figures from 2022, German Americans make up roughly 41 million people in the US, which is approximately 12% of the pop ...
biophysicist. He was awarded the Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; ; ) are awards administered by the Nobel Foundation and granted in accordance with the principle of "for the greatest benefit to humankind". The prizes were first awarded in 1901, marking the fifth anniversary of Alfred N ...
for discovering that bacteria become resistant to viruses (phages) as a result of genetic mutations.
* Johann Christoph Denner: Woodwind instrument maker, inventor of the clarinet
The clarinet is a Single-reed instrument, single-reed musical instrument in the woodwind family, with a nearly cylindrical bore (wind instruments), bore and a flared bell.
Clarinets comprise a Family (musical instruments), family of instrume ...
.
* Jürgen Dethloff: Inventor and engineer, co-inventor of the Smart card
A smart card (SC), chip card, or integrated circuit card (ICC or IC card), is a card used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an Embedded system, embedded integrated circuit (IC) chip. Many smart ...
(together with Helmut Gröttrup
Helmut Gröttrup (12 February 1916 – 4 July 1981) was a German engineer, rocket scientist and inventor of the smart card. During World War II, he worked in the German V-2 rocket program under Wernher von Braun. From 1946 to 1950 he headed a gr ...
).
*Johann Friedrich Dieffenbach
Johann Friedrich Dieffenbach (1 February 1792 – 11 November 1847) was a German surgeon. He was born in Königsberg and died in Berlin.
Dieffenbach specialized in skin transplantation and plastic surgery. His work in rhinoplastic and maxill ...
: Pioneer of skin transplantation and cosmetic surgery.
* Ernst Dickmanns: Developer of the first driverless car
A self-driving car, also known as an autonomous car (AC), driverless car, robotic car or robo-car, is a car that is capable of operating with reduced or no User input, human input. They are sometimes called robotaxi, robotaxis, though this te ...
.
* Otto Diels: Diels–Alder reaction
In organic chemistry, the Diels–Alder reaction is a chemical reaction between a Conjugated system, conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, commonly termed the Diels–Alder reaction#The dienophile, dienophile, to form a substituted cyclohexe ...
(together with Kurt Alder
Kurt Alder (; 10 July 1902 – 20 June 1958) was a German chemist and Nobel laureate.
Biography
Alder was born in the industrial area of Königshütte, Silesia (modern day Chorzów, Upper Silesia, Poland), where he received his early schoo ...
)
*Rudolf Diesel
Rudolf Christian Karl Diesel (, ; 18 March 1858 – 29 September 1913) was a German inventor and mechanical engineer who invented the Diesel engine, which burns Diesel fuel; both are named after him.
Early life and education
Diesel was born on 1 ...
: Inventor of the diesel engine
The diesel engine, named after the German engineer Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which Combustion, ignition of diesel fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to Mechanics, mechanical Compr ...
1893.
*Gerhard Domagk
Gerhard Johannes Paul Domagk (; 30 October 1895 – 24 April 1964) was a German pathologist and bacteriologist.
He is credited with the discovery of Sulfonamide (medicine), sulfonamidochrysoidine (KL730) as an antibiotic for which he received th ...
: Discovery of what would become the first commercially available antibiotic.
* Christian Doppler: Discovered the Doppler effect
The Doppler effect (also Doppler shift) is the change in the frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the source of the wave. The ''Doppler effect'' is named after the physicist Christian Doppler, who described ...
.
* Walter Robert Dornberger: Co-inventor of the V-2 rocket.
*Karl Drais
Karl Freiherr von Drais (full name: Karl Friedrich Christian Ludwig Freiherr Drais von Sauerbronn; 29 April 1785 – 10 December 1851) was a noble German people, German forest official and significant inventor in the Biedermeier, Biedermeier pe ...
: Inventor of the bicycle and typewriter (1821) among other things.
* Peter Ferdinand Drucker: Invented the science of modern management.
E
 *
*Paul Ehrlich
Paul Ehrlich (; 14 March 1854 – 20 August 1915) was a Nobel Prize-winning German physician and scientist who worked in the fields of hematology, immunology and antimicrobial chemotherapy. Among his foremost achievements were finding a cure fo ...
: Scientist in the fields of hematology, immunology, and chemotherapy, and Nobel laureate. Developed an effective treatment against syphilis.
* Caroline Eichler: Inventor, first woman to receive a patent (for her leg prosthesis)
*Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein (14 March 187918 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who is best known for developing the theory of relativity. Einstein also made important contributions to quantum mechanics. His mass–energy equivalence f ...
: Father of Theoretical Physics, inventor and discoverer.
*Ludwig Elsbett
Ludwig Elsbett was the inventor of the Elsbett engine.
Elsbett was one of nine children of the farmer Viktor Elsbett and his wife Maria. He grew up in agriculture and was originally trained as a fitter for agricultural machinery. Later, he atte ...
: Developed new concepts for Diesel engines which drastically enhanced efficiency.
*Douglas Engelbart
Douglas Carl Engelbart (January 30, 1925 – July 2, 2013) was an American engineer, inventor, and a pioneer in many aspects of computer science. He is best known for his work on founding the field of human–computer interaction, particularly ...
: German American
German Americans (, ) are Americans who have full or partial German ancestry.
According to the United States Census Bureau's figures from 2022, German Americans make up roughly 41 million people in the US, which is approximately 12% of the pop ...
inventor of the computer mouse
A computer mouse (plural mice; also mouses) is a hand-held pointing device that detects Plane (mathematics), two-dimensional motion relative to a surface. This motion is typically translated into the motion of the Cursor (user interface)#Po ...
.
*Evaristo Conrado Engelberg
Evaristo Conrado Engelberg (26 October 1853–1932) was a Brazilian mechanical engineer and inventor. He is the inventor of the Engelberg huller, a machine used to strip the husks from rice and coffee during harvest. He was born to German im ...
: Inventor in 1885 of a machine used to remove the husks from rice and coffee, the Engelberg huller.
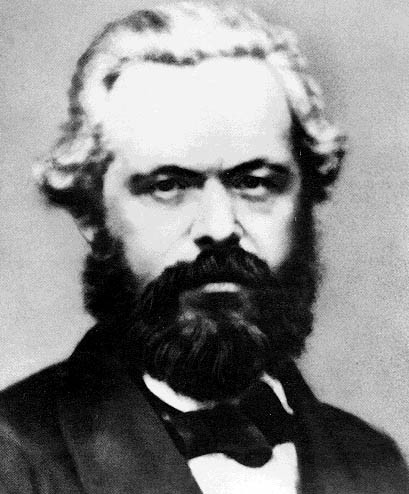
*Friedrich Engels
Friedrich Engels ( ;"Engels"
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''.Karl Marx Karl Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, political theorist, economist, journalist, and revolutionary socialist. He is best-known for the 1848 pamphlet '' The Communist Manifesto'' (written with Friedrich Engels) ...
the economic and sociopolitical worldview ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''.Karl Marx Karl Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, political theorist, economist, journalist, and revolutionary socialist. He is best-known for the 1848 pamphlet '' The Communist Manifesto'' (written with Friedrich Engels) ...
Marxism
Marxism is a political philosophy and method of socioeconomic analysis. It uses a dialectical and materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to analyse class relations, social conflict, ...
.
* Hugo Erdmann: Chemist who discovered, together with his doctoral advisor Jacob Volhard
Jacob Volhard (4 June 1834 – 14 January 1910) was the German chemist who discovered, together with his student Hugo Erdmann, the Volhard–Erdmann cyclization reaction. He was also responsible for the improvement of the Hell–Volhard–Zel ...
, the Volhard-Erdmann cyclization. In 1898 he was the first who coined the term ''noble gas
The noble gases (historically the inert gases, sometimes referred to as aerogens) are the members of Group (periodic table), group 18 of the periodic table: helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), radon (Rn) and, in some ...
'' (the original noun is in German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
).
*Leonhard Euler
Leonhard Euler ( ; ; ; 15 April 170718 September 1783) was a Swiss polymath who was active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, logician, geographer, and engineer. He founded the studies of graph theory and topology and made influential ...
: Swiss mathematician and physicist. One of the most influential mathematicians of the 18th century.
F
 *
*Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit
Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit FRS (; ; 24 May 1686 – 16 September 1736) was a physicist, inventor, and scientific instrument maker, born in Poland to a family of German extraction. Fahrenheit invented thermometers accurate and consistent enough t ...
: Physicist and engineer who invented the alcohol thermometer (1709), the mercury thermometer
Mercury most commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the closest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a chemical element
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman deity
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Mercury (toy manufacturer) ...
(1714), and a temperature scale now named after him.
*Gerd Faltings
Gerd Faltings (; born 28 July 1954) is a German mathematician known for his work in arithmetic geometry.
Education
From 1972 to 1978, Faltings studied mathematics and physics at the University of Münster. Interrupted by 15 months of obligatory ...
: Mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems. Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, mathematical structure, structure, space, Mathematica ...
known for his work in arithmetic
Arithmetic is an elementary branch of mathematics that deals with numerical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. In a wider sense, it also includes exponentiation, extraction of roots, and taking logarithms.
...
algebraic geometry
Algebraic geometry is a branch of mathematics which uses abstract algebraic techniques, mainly from commutative algebra, to solve geometry, geometrical problems. Classically, it studies zero of a function, zeros of multivariate polynomials; th ...
, Fields Medal
The Fields Medal is a prize awarded to two, three, or four mathematicians under 40 years of age at the International Congress of Mathematicians, International Congress of the International Mathematical Union (IMU), a meeting that takes place e ...
in 1986 for proving the Mordell conjecture.
*Otto Feick
Otto Feick (4 July 1890 in Reichenbach-Steegen, Reichenbach – 17 October 1959 in Schönau an der Brend) was a German people, German inventor and gymnast.
Biography
Feick was born in 1890, the son of a cooper. He worked as a locksmith a ...
: Wheel gymnastics in 1925.
* Wilhelm Emil Fein: Invented the electrically-driven hand drill in 1895.
*Artur Fischer
Artur Fischer (31 December 1919 – 27 January 2016) was a German inventor. He is best known for inventing an expanding plastic version of the wall plug.
Born in Tumlingen, Artur Fischer was the son of the village tailor Georg Fischer. His ...
: Invented the (split) wallplug made of plastic in 1958.
*Hermann Emil Fischer
Hermann Emil Louis Fischer (; 9 October 1852 – 15 July 1919) was a German chemist and List of Nobel laureates in Chemistry, 1902 recipient of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. He discovered the Fischer esterification. He also developed the Fisch ...
: Discoveries in chemistry.
* Franz Fischer and Hans Tropsch: Invented a process in 1925 to turn coal into synthesis gas, and still further into liquid hydrocarbons. The process is a key component in modern gas to liquids
Gas to liquids (GTL) is a oil refinery, refinery process to convert natural gas or other gaseous hydrocarbons into longer-chain hydrocarbons, such as gasoline or diesel fuel. Methane-rich gases are converted into liquid synthetic fuels. Two general ...
processes.
* Wilhelm Rudolph Fittig: He discovered the pinacol coupling reaction, mesitylene, diacetyl
Diacetyl ( ; IUPAC systematic name: butanedione or butane-2,3-dione) is an organic compound with the chemical formula (CH3CO)2. It is a yellow liquid with an intensely buttery flavor. It is a vicinal diketone (two C=O groups, side-by-side). Di ...
and biphenyl
Biphenyl (also known as diphenyl, phenylbenzene, 1,1′-biphenyl, lemonene or BP) is an organic compound that forms colorless crystals. Particularly in older literature, compounds containing the functional group consisting of biphenyl less one ...
.
* Irmgard Flügge-Lotz: She worked on what she called "discontinuous automatic control", which laid the foundation for automatic on-off aircraft control systems in jets.
*Werner Forssmann
Werner Theodor Otto Forßmann (Forssmann in English; ; 29 August 1904 – 1 June 1979) was a German researcher and physician from Germany who shared the 1956 Nobel Prize in Medicine (with Andre Frederic Cournand and Dickinson W. Richards) for de ...
: Performed the first human cardiac catheterisation. Shared the Nobel Prize for Medicine 1956
*Joseph von Fraunhofer
Joseph Ritter von Fraunhofer (; ; 6 March 1787 – 7 June 1826) was a German physicist and optical lens manufacturer. He made optical glass, an achromatic telescope, and objective lenses. He developed diffraction grating and also invented the ...
: Discovery of the dark absorption lines known as Fraunhofer lines in the Sun's spectrum, and for making excellent optical glass and achromatic telescope objectives.
*Gottlob Frege
Friedrich Ludwig Gottlob Frege (; ; 8 November 1848 – 26 July 1925) was a German philosopher, logician, and mathematician. He was a mathematics professor at the University of Jena, and is understood by many to be the father of analytic philos ...
: He is generally considered to be the father of analytic philosophy
Analytic philosophy is a broad movement within Western philosophy, especially English-speaking world, anglophone philosophy, focused on analysis as a philosophical method; clarity of prose; rigor in arguments; and making use of formal logic, mat ...
. Had influence on Carnap, Russell, and Wittgenstein
Ludwig Josef Johann Wittgenstein ( ; ; 26 April 1889 – 29 April 1951) was an Austrian philosopher who worked primarily in logic, the philosophy of mathematics, the philosophy of mind, and the philosophy of language.
From 1929 to 1947, Witt ...
* Otto Frenzl: Aeronautical pioneer, developed the area rule
The Whitcomb area rule, named after NACA engineer Richard Whitcomb and also called the transonic area rule, is a design procedure used to reduce an aircraft's drag at transonic speeds which occur between about Mach 0.75 and 1.2. For supersoni ...
in 1943, a design technique for airfoils used to reduce an aircraft's drag at transonic and supersonic speeds. Later it was independently developed again by Richard T. Whitcomb
Richard Travis Whitcomb (February 21, 1921 – October 13, 2009) was an American Aeronautical engineering, aeronautical engineer who was noted for his contributions to the science of aerodynamics.
Biography
Whitcomb was born in Evanston, Il ...
in 1952.
*Sigmund Freud
Sigmund Freud ( ; ; born Sigismund Schlomo Freud; 6 May 1856 – 23 September 1939) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis, a clinical method for evaluating and treating psychopathology, pathologies seen as originating fro ...
: Neurologist
Neurology (from , "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the nervous system, which comprises the brain, the ...
who became known as the founding father of psychoanalysis
PsychoanalysisFrom Greek language, Greek: and is a set of theories and techniques of research to discover unconscious mind, unconscious processes and their influence on conscious mind, conscious thought, emotion and behaviour. Based on The Inte ...
.
*Nikolaus Friedreich
Nikolaus Friedreich (1 July 1825 in Würzburg – 6 July 1882 in Heidelberg) was a German pathologist and neurologist, and a third generation physician in the Friedreich family. His father was psychiatrist Johann Baptist Friedreich (1796–18 ...
: Discovery of Friedreich-Auerbach disease (together with Leopold Auerbach) among other things.
*Friedrich Fröbel
Friedrich Wilhelm August Fröbel or Froebel (; 21 April 1782 – 21 June 1852) was a German pedagogue, a student of Johann Heinrich Pestalozzi, who laid the foundation for modern education based on the recognition that children have unique nee ...
: Pedagogue, who laid the foundation for modern education. He created the concept of the kindergarten
Kindergarten is a preschool educational approach based on playing, singing, practical activities such as drawing, and social interaction as part of the transition from home to school. Such institutions were originally made in the late 18th cen ...
.
*Klaus Fuchs
Klaus Emil Julius Fuchs (29 December 1911 – 28 January 1988) was a German theoretical physicist and atomic spy who supplied information from the American, British, and Canadian Manhattan Project to the Soviet Union during and shortly a ...
: Theoretical physicist
*Johann Carl Fuhlrott
Johann Carl Fuhlrott (31 December 1803, Leinefelde, Germany – 17 October 1877, Wuppertal) was an early German paleoanthropologist. He is famous for recognizing the significance of the bones of Neanderthal 1, a Neanderthal specimen discovered ...
: Had the insight to recognize the Neanderthal
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinction, extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Plei ...
bones for what they were: the remains of a previously unknown type of humans. He (together with Schaafhausen) is considered to be the father of paleoanthropology
Paleoanthropology or paleo-anthropology is a branch of paleontology and anthropology which seeks to understand the early development of anatomically modern humans, a process known as hominization, through the reconstruction of evolutionary kinsh ...
.
G

 * Hermann Ganswindt: Inventor and spaceflight scientist, whose inventions (such as the dirigible, the helicopter, and the internal combustion engine) are thought to have been ahead of his time.
*
* Hermann Ganswindt: Inventor and spaceflight scientist, whose inventions (such as the dirigible, the helicopter, and the internal combustion engine) are thought to have been ahead of his time.
*Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; ; ; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician, astronomer, Geodesy, geodesist, and physicist, who contributed to many fields in mathematics and science. He was director of the Göttingen Observat ...
: German mathematician and physical scientist who contributed significantly to many fields, including number theory, statistics, analysis, differential geometry, geodesy, geophysics, electrostatics, astronomy and optics. Sometimes referred to as "the Prince of Mathematicians".
*Hans Geiger
Johannes Wilhelm Geiger ( , ; ; 30 September 1882 – 24 September 1945) was a German nuclear physicist. He is known as the inventor of the Geiger counter, a device used to detect ionizing radiation, and for carrying out the Rutherford scatt ...
: Inventor of the Geiger–Müller counter in 1928. It detects the emission of nuclear radiation through the ionization produced in a low-pressure gas in a Geiger–Müller tube. Further improved by Walther Müller.
*Heinrich Geißler
Johann Heinrich Wilhelm Geißler (26 May 1814 in Igelshieb – 24 January 1879) was a skilled glassblower and physicist, famous for his invention of the hand pumped Geissler mercury vacuum pump in the mid-1850's and in 1857, the Geissler tube ...
: Inventor of the Geissler tube
A Geissler tube is a precursor to modern gas discharge tubes, demonstrating the principles of electrical glow discharge, akin to contemporary neon lights, and central to the discovery of the electron. This device was developed in 1857 by Hein ...
.
* Reinhard Genzel: Astrophysicist, he and his group were the first to track the motions of star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
s at the centre of the Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
and show that they were orbiting a very massive object, probably a supermassive black hole
A black hole is a massive, compact astronomical object so dense that its gravity prevents anything from escaping, even light. Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will form a black hole. Th ...
.
* Walter Gerlach: Physicist who co-discovered spin quantization in a magnetic field, the Stern–Gerlach effect.
* Edmund Germer: Inventor of the neon lamp (Neonlampe).
* Max Giese: Inventor of the first concrete pump
A concrete pump is a machine used for transferring liquid concrete by pumping. There are different types of concrete pumps.
A common type of concrete pump for large scale construction projects is known as a boom concrete pump, because it uses a ...
in 1928.
*Heinrich Göbel
Heinrich Göbel (April 20, 1818December 4, 1893) was a German-born American precision mechanic and inventor also known by his Anglicisation of names, anglicized name Henry Goebel. In 1848 he Immigration to the United States, immigrated to New Y ...
: Inventor of Hemmer for Sewing Machines, 1865, Vacuum Pump (Improvement of the Geissler-System of vacuum pumps, 1881 and Electric Incandescent Lamp (sockets to connect the filament of carbon and the conducting wires), 1882
*Kurt Gödel
Kurt Friedrich Gödel ( ; ; April 28, 1906 – January 14, 1978) was a logician, mathematician, and philosopher. Considered along with Aristotle and Gottlob Frege to be one of the most significant logicians in history, Gödel profoundly ...
: Important discoveries in math and logic, such as the incompleteness theorem
Complete may refer to:
Logic
* Completeness (logic)
* Completeness of a theory, the property of a theory that every formula in the theory's language or its negation is provable
Mathematics
* The completeness of the real numbers, which implies ...
s
 *
*Maria Goeppert-Mayer
Maria Goeppert Mayer (; ; June 28, 1906 – February 20, 1972) was a German-American theoretical physicist who shared the 1963 Nobel Prize in Physics with J. Hans D. Jensen and Eugene Wigner. One half of the prize was awarded jointly to Goeppe ...
: Physicist. Nobel laureate in Physics 1963 for proposing the nuclear shell model of the atomic nucleus together with J. Hans D. Jensen
Johannes Hans Daniel Jensen (; 25 June 1907 – 11 February 1973) was a German nuclear physicist. During World War II, he worked on the German nuclear energy project, known as the Uranium Club, where he contributed to the separation of uranium ...
. The unit for the two-photon absorption
In atomic physics, two-photon absorption (TPA or 2PA), also called two-photon excitation or non-linear absorption, is the (almost) simultaneous Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of two photons of identical or different frequencie ...
cross section is named the Goeppert-Mayer (GM) unit.
*Peter Carl Goldmark
Peter Carl Goldmark (born Péter Károly Goldmark; December 2, 1906 – December 7, 1977) was a Hungarian-American engineer who, during his time with Columbia Records, was instrumental in developing the long-playing microgroove 33 rpm phonogr ...
: Engineer who was instrumental in developing the long-playing (LP) microgroove 33-1/3 rpm vinyl phonograph disc.
* Heinrich Greinacher: German-Swiss physicist. He is regarded as an original experimenter and is the developer of the magnetron and the Greinacher multiplier; Cockcroft-Walton-Generator in 1914.
*Brothers Grimm
The Brothers Grimm ( or ), Jacob Grimm, Jacob (1785–1863) and Wilhelm Grimm, Wilhelm (1786–1859), were Germans, German academics who together collected and published folklore. The brothers are among the best-known storytellers of Oral tradit ...
: Academic pioneers of philology, linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds ...
, and storytelling. Worked together on the most comprehensive dictionary of the German language Deutsches Wörterbuch
The ''Deutsches Wörterbuch'' (; "German Dictionary"), abbreviated ''DWB'', is the largest and most comprehensive dictionary of the German language in existence.Jacob Grimm
Jacob Ludwig Karl Grimm (4 January 1785 – 20 September 1863), also known as Ludwig Karl, was a German author, linguist, philologist, jurist, and folklorist. He formulated Grimm's law of linguistics, and was the co-author of the ''Deutsch ...
: Philologist and linguist. Described first what is now known as Grimm's law
Grimm's law, also known as the First Germanic Consonant Shift or First Germanic Sound Shift, is a set of sound laws describing the Proto-Indo-European (PIE) stop consonants as they developed in Proto-Germanic in the first millennium BC, first d ...
, the first scientific research into sound change
In historical linguistics, a sound change is a change in the pronunciation of a language. A sound change can involve the replacement of one speech sound (or, more generally, one phonetic feature value) by a different one (called phonetic chan ...
in 1822.
*Alexander Grothendieck
Alexander Grothendieck, later Alexandre Grothendieck in French (; ; ; 28 March 1928 – 13 November 2014), was a German-born French mathematician who became the leading figure in the creation of modern algebraic geometry. His research ext ...
: Mathematician and the central figure behind the creation of the modern theory of algebraic geometry
Algebraic geometry is a branch of mathematics which uses abstract algebraic techniques, mainly from commutative algebra, to solve geometry, geometrical problems. Classically, it studies zero of a function, zeros of multivariate polynomials; th ...
; Fields Medal
The Fields Medal is a prize awarded to two, three, or four mathematicians under 40 years of age at the International Congress of Mathematicians, International Congress of the International Mathematical Union (IMU), a meeting that takes place e ...
ist (1966).
*Helmut Gröttrup
Helmut Gröttrup (12 February 1916 – 4 July 1981) was a German engineer, rocket scientist and inventor of the smart card. During World War II, he worked in the German V-2 rocket program under Wernher von Braun. From 1946 to 1950 he headed a gr ...
: smart card
A smart card (SC), chip card, or integrated circuit card (ICC or IC card), is a card used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an Embedded system, embedded integrated circuit (IC) chip. Many smart ...
(together with Jürgen Dethloff)
*Walter Gropius
Walter Adolph Georg Gropius (; 18 May 1883 – 5 July 1969) was a German-born American architect and founder of the Bauhaus, Bauhaus School, who is widely regarded as one of the pioneering masters of modernist architecture. He was a founder of ...
: Pioneer of modern architecture. Founder of the Bauhaus
The Staatliches Bauhaus (), commonly known as the , was a German art school operational from 1919 to 1933 that combined Decorative arts, crafts and the fine arts.Oxford Dictionary of Art and Artists (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 4th edn., ...
. First modern industrial building designed in 1910.
*Peter Grünberg
Peter Andreas Grünberg (; 18 May 1939 – 7 April 2018) was a German physicist, and Nobel Prize in Physics laureate for his discovery with Albert Fert of giant magnetoresistance which brought about a breakthrough in gigabyte hard disk drive ...
: Physicist. Discovered giant magnetoresistance
Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) is a quantum mechanics, quantum mechanical magnetoresistance effect observed in multilayers composed of alternating ferromagnetic and non-magnetic conductive layers. The 2007 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Alb ...
with Albert Fert
Albert Fert (; born 7 March 1938) is a French physicist and one of the discoverers of giant magnetoresistance which brought about a breakthrough in gigabyte hard disks. Currently, he is an emeritus professor at Paris-Saclay University in Orsay ...
. The discovery is used in gigabyte hard disk drives for computers. Nobel laureate 2007.
*Heinz Guderian
Heinz Wilhelm Guderian (; 17 June 1888 – 14 May 1954) was a German general during World War II who later became a successful memoirist. A pioneer and advocate of the "blitzkrieg" approach, he played a central role in the development of ...
: The father of modern mechanized warfare, inventor of the Blitzkrieg strategy.
*Otto von Guericke
Otto von Guericke ( , , ; spelled Gericke until 1666; – ) was a German scientist, inventor, mathematician and physicist. His pioneering scientific work, the development of experimental methods and repeatable demonstrations on the physics of ...
: Groundbreaking research into air pressure. Invented the vacuum pump
A vacuum pump is a type of pump device that draws gas particles from a sealed volume in order to leave behind a partial vacuum. The first vacuum pump was invented in 1650 by Otto von Guericke, and was preceded by the suction pump, which dates to ...
in 1650.
*Beno Gutenberg
Beno Gutenberg (; June 4, 1889 – January 25, 1960) was a German-American seismologist who made several important contributions to the science. He was a colleague and mentor of Charles Francis Richter at the California Institute of Technolo ...
: Together with American Charles Francis Richter
Charles Francis Richter (; April 26, 1900September 30, 1985) was an American seismologist and physicist. He is the namesake and one of the creators of the Richter scale, which, until the development of the moment magnitude scale in 1979, was w ...
he invented Richter magnitude scale
The Richter scale (), also called the Richter magnitude scale, Richter's magnitude scale, and the Gutenberg–Richter scale, is a measure of the strength of earthquakes, developed by Charles Richter in collaboration with Beno Gutenberg, and pr ...
.
*Johannes Gutenberg
Johannes Gensfleisch zur Laden zum Gutenberg ( – 3 February 1468) was a German inventor and Artisan, craftsman who invented the movable type, movable-type printing press. Though movable type was already in use in East Asia, Gutenberg's inven ...
: Inventor of the technology of printing with movable type in 1439. The first book so printed was the Gutenberg Bible
The Gutenberg Bible, also known as the 42-line Bible, the Mazarin Bible or the B42, was the earliest major book printed in Europe using mass-produced metal movable type. It marked the start of the "Printing Revolution, Gutenberg Revolution" an ...
, one of the most beautifully executed printed books ever produced.
H
*Fritz Haber
Fritz Jakob Haber (; 9 December 1868 – 29 January 1934) was a German chemist who received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1918 for his invention of the Haber process, a method used in industry to synthesize ammonia from nitrogen gas and hydrog ...
: German chemist and Nobel laureate who pioneered synthetic ammonia and chemical warfare.
*Theodor W. Hänsch
Theodor Wolfgang Hänsch (; born 30 October 1941) is a German physicist. He received one-fourth of the 2005 Nobel Prize in Physics for "contributions to the development of laser-based precision spectroscopy, including the optical frequency comb ...
: Physicist, developed laser-based precision spectroscopy further to determine optical frequency extremely accurately. Nobel laureate in 2005.
*Otto Hahn
Otto Hahn (; 8 March 1879 – 28 July 1968) was a German chemist who was a pioneer in the field of radiochemistry. He is referred to as the father of nuclear chemistry and discoverer of nuclear fission, the science behind nuclear reactors and ...
: German chemist and Nobel laureate who pioneered the fields of radioactivity and radiochemistry. Considered to be "the father of nuclear chemistry" and the "founder of the atomic age". Discovered many isotopes, Protactinium
Protactinium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pa and atomic number 91. It is a dense, radioactive, silvery-gray actinide metal which readily reacts with oxygen, water vapor, and inorganic acids. It forms various chemical compounds, in which p ...
and nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radioactiv ...
.
*Samuel Hahnemann
Christian Friedrich Samuel Hahnemann ( , ; 10 April 1755 – 2 July 1843) was a German physician, best known for creating the pseudoscientific system of alternative medicine called homeopathy.
Early life
Christian Friedrich Samuel Hahnemann w ...
: Physician, best known for creating a system of alternative medicine called homeopathy
Homeopathy or homoeopathy is a pseudoscientific system of alternative medicine. It was conceived in 1796 by the German physician Samuel Hahnemann. Its practitioners, called homeopaths or homeopathic physicians, believe that a substance that ...
.
* Harald zur Hausen: Virologist, discovered the role of papilloma viruses in the development of cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is a cancer arising from the cervix or in any layer of the wall of the cervix. It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that can invade or spread to other parts of the body. Early on, typically no symptoms are seen. Later sympt ...
. His research made the development of a vaccine against papilloma possible, which will drastically reduce cervical cancer in future. Nobel laureate 2008.
* Henry J. Heinz: Tomato ketchup and fifty six other things.
*Werner Heisenberg
Werner Karl Heisenberg (; ; 5 December 1901 – 1 February 1976) was a German theoretical physicist, one of the main pioneers of the theory of quantum mechanics and a principal scientist in the German nuclear program during World War II.
He pub ...
: Theoretical physicist who made fundamental contributions to quantum mechanics. Discovered a particle's position and velocity cannot be known at the same time. Discovered atomic nuclei are made of protons and neutrons.
* Wolfgang Helfrich: Co-inventor of Twisted nematic field effect.
*Rudolf Hell
Rudolf Hell (19 December 1901 – 11 March 2002) was a German inventor and engineer.
Career
Hell was born in Eggmühl. From 1919 to 1923, he studied electrical engineering in Munich. He worked there from 1923 to 1929 as assistant of Prof. M ...
: Inventor of the first fax machine (Hellschreiber
The Hellschreiber, Feldhellschreiber or Typenbildfeldfernschreiber (also Hell-Schreiber named after its inventor Rudolf Hell) is a fax, facsimile-based teleprinter invented by Rudolf Hell. Compared to contemporary teleprinters that were based ...
).
* Richard Hellmann: Hellmann's (Blue Ribbon) Mayonnaise, 1905.
*Hermann von Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz (; ; 31 August 1821 – 8 September 1894; "von" since 1883) was a German physicist and physician who made significant contributions in several scientific fields, particularly hydrodynamic stability. The ...
: Discovered the principle of conservation of energy.
*Peter Henlein
Peter Henlein (also spelled Henle or Hele) (1485 - August 1542), a locksmith, clockmaker, and watchmaker of Nuremberg, Germany. Due to the Fire-gilded pomander-shaped Watch 1505, watch from 1505, he is often considered the inventor of the pocket ...
: Inventor of the portable watch.
* Friedrich Wilhelm Herschel (William Herschel): Discovered the planet Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It is a gaseous cyan-coloured ice giant. Most of the planet is made of water, ammonia, and methane in a Supercritical fluid, supercritical phase of matter, which astronomy calls "ice" or Volatile ( ...
and infrared radiation
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
among other things.
*Heinrich Hertz
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (; ; 22 February 1857 – 1 January 1894) was a German physicist who first conclusively proved the existence of the electromagnetic waves predicted by James Clerk Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism.
Biography
Heinri ...
: Physicist, Discoverer of electromagnetic
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge via electromagnetic fields. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature. It is the dominant force in the interacti ...
/radio waves
Radio waves (formerly called Hertzian waves) are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the lowest frequencies and the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies below 300 gigahertz (GHz) and wavelengths ...
.
*: First use of the Carabiner
A carabiner or karabiner (), often shortened to biner or to crab, colloquially known as a (climbing) clip, is a specialized type of shackle, a metal loop with a spring-loaded gate used to quickly and reversibly connect components, most notabl ...
in mountain climbing which substantially enhanced security for mountaineers.
*Victor Francis Hess
Victor Franz Hess (; 24 June 1883 – 17 December 1964) was an Austrian-American particle physicist who shared the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics with Carl David Anderson "for his discovery of cosmic radiation".
Biography
He was born to Vinzenz ...
: Discovered Cosmic rays
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar ...
. Also won the Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; ; ) are awards administered by the Nobel Foundation and granted in accordance with the principle of "for the greatest benefit to humankind". The prizes were first awarded in 1901, marking the fifth anniversary of Alfred N ...
.
*David Hilbert
David Hilbert (; ; 23 January 1862 – 14 February 1943) was a German mathematician and philosopher of mathematics and one of the most influential mathematicians of his time.
Hilbert discovered and developed a broad range of fundamental idea ...
: Influential mathematician who discovered and developed a broad range of fundamental ideas in math.
*Albert Hofmann
Albert Hofmann (11 January 1906 – 29 April 2008) was a Swiss chemist known for being the first to synthesize, ingest, and learn of the psychedelic effects of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Hofmann's team also isolated, named and synthesi ...
: German-Swiss; Discovered the chemical properties of chitin
Chitin (carbon, C8hydrogen, H13oxygen, O5nitrogen, N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of N-Acetylglucosamine, ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cell ...
and lysergic acid diethylamide
Lysergic acid diethylamide, commonly known as LSD (from German ; often referred to as acid or lucy), is a Semisynthesis, semisynthetic, Hallucinogen, hallucinogenic compound derived from ergot, known for its powerful psychological effects and ...
.
* Wilhelm Hofmeister: Discovery the Alternation of generations
Alternation of generations (also known as metagenesis or heterogenesis) is the predominant type of life cycle in plants and algae. In plants both phases are multicellular: the haploid sexual phase – the gametophyte – alternates with a diploi ...
*Felix Hoffmann
Felix Hoffmann (21 January 1868 – 8 February 1946) was a German chemist notable for re-synthesising diamorphine (independently from C.R. Alder Wright who synthesized it 23 years earlier), which was popularized under the Bayer trade name ...
: Isolated acetylsalicylic acid, a painkiller marketed under the name Aspirin (Bayer), 1897. In some English speaking countries marketed under the name disprin.
*Herman Hollerith
Herman Hollerith (February 29, 1860 – November 17, 1929) was a German-American statistician, inventor, and businessman who developed an electromechanical tabulating machine for punched cards to assist in summarizing information and, later, in ...
: a German American
German Americans (, ) are Americans who have full or partial German ancestry.
According to the United States Census Bureau's figures from 2022, German Americans make up roughly 41 million people in the US, which is approximately 12% of the pop ...
statistician who developed a mechanical tabulator based on punched cards
* Gottlob Honold: Inventor of the spark plug and the modern internal combustion engine, as well as headlights.
* Horten brothers: Designed some of the most advanced aircraft of the 1940s, including the world's first jet-powered flying wing, the Horten Ho 229.
* Christian Hülsmeyer: German inventor of the ''Telemobilskop'', a radio-based detector of remote objects; a 1904 precursor of radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track ...
.
*Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 1769 – 6 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, natural history, naturalist, List of explorers, explorer, and proponent of Romanticism, Romantic philosophy and Romanticism ...
: Naturalist and explorer. His quantitative work on botanical geography was foundational to the field of biogeography.
*Wilhelm von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Christian Karl Ferdinand von Humboldt (22 June 1767 – 8 April 1835) was a German philosopher, linguist, government functionary, diplomat, and founder of the Humboldt University of Berlin. In 1949, the university was named aft ...
: Originator of the linguistic relativity
Linguistic relativity asserts that language influences worldview or cognition. One form of linguistic relativity, linguistic determinism, regards peoples' languages as determining and influencing the scope of cultural perceptions of their surro ...
hypothesis.
I
* Otmar Issing: Economist who invented the "pepet pillar" decision algorithm now used by the ECB.J
*J. Hans D. Jensen
Johannes Hans Daniel Jensen (; 25 June 1907 – 11 February 1973) was a German nuclear physicist. During World War II, he worked on the German nuclear energy project, known as the Uranium Club, where he contributed to the separation of uranium ...
: Nuclear physicist, proposed the nuclear shell model
In nuclear physics, atomic physics, and nuclear chemistry, the nuclear shell model utilizes the Pauli exclusion principle to model the structure of atomic nuclei in terms of energy levels. The first shell model was proposed by Dmitri Ivanenk ...
, shared 1963 Nobel Prize in Physics.
*Hugo Junkers
Hugo Junkers (3 February 1859 – 3 February 1935) was a German aircraft engineer and aircraft designer who pioneered the design of all-metal airplanes and flying wings. His company, Junkers Flugzeug- und Motorenwerke AG (Junkers Aircraft and ...
: Pioneer of all-metal aircraft construction with the Junkers J 1 (1915–16).
K

 * Ferdinand Adolf Kehrer : Introduction of the transverse incision technique to minimize bleeding by modern
* Ferdinand Adolf Kehrer : Introduction of the transverse incision technique to minimize bleeding by modern Caesarean section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section, cesarean, or caesarean delivery, is the Surgery, surgical procedure by which one or more babies are Childbirth, delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen. It is often performed because va ...
* Hermann Kemper: Invented the magnetic levitation train. Patent granted in 1934.
*Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, Natural philosophy, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best know ...
: Discovered the laws of planetary motion.
* Donald J. Kessler: Astrophysicist, known for developing the Kessler syndrome
The Kessler syndrome, also known as the Kessler effect, collisional cascading, or ablation cascade, is a scenario proposed by NASA scientists Donald J. Kessler and Burton G. Cour-Palais in 1978. It describes a situation in which the density of o ...
.
*Wolfgang Ketterle
Wolfgang Ketterle (; born 21 October 1957) is a German physicist and professor of physics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). His research has focused on experiments that trap and cool atoms to temperatures close to absolute zer ...
: German-American physicist who developed an "atom laser", amongst other breakthroughs. Nobel laureate 2001.
* Erhard Kietz: Pioneer discoverer of video technology.
*Gustav Kirchhoff
Gustav Robert Kirchhoff (; 12 March 1824 – 17 October 1887) was a German chemist, mathematician, physicist, and spectroscopist who contributed to the fundamental understanding of electrical circuits, spectroscopy and the emission of black-body ...
: Discovery of the principles upon which spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets electromagnetic spectra. In narrower contexts, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Spectro ...
is founded.
*Martin Heinrich Klaproth
Martin Heinrich Klaproth (1 December 1743 – 1 January 1817) was a German chemist. He trained and worked for much of his life as an apothecary, moving in later life to the university. His shop became the second-largest apothecary in Berlin, and ...
: Discovered the element Uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
.
* Klaus von Klitzing: Physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate cau ...
, known for discovery of the integer quantum Hall effect
The quantum Hall effect (or integer quantum Hall effect) is a quantized version of the Hall effect which is observed in two-dimensional electron systems subjected to low temperatures and strong magnetic fields, in which the Hall resistance exhi ...
, 1985 Nobel Prize in Physics.
*Ludwig Knorr
Ludwig Knorr (2 December 1859 – 4 June 1921) was a German chemist. Together with Carl Paal, he discovered the Paal–Knorr synthesis, and the Knorr quinoline synthesis and Knorr pyrrole synthesis are also named after him. The synthesis in 1883 ...
: Chemist, who together with Carl Paal, discovered the Paal-Knorr synthesis, and the Knorr quinoline synthesis and Knorr pyrrole synthesis.
*Robert Koch
Heinrich Hermann Robert Koch ( ; ; 11 December 1843 – 27 May 1910) was a German physician and microbiologist. As the discoverer of the specific causative agents of deadly infectious diseases including tuberculosis, cholera and anthrax, he i ...
: Physician, discoverer, inventor and Nobel Prize winner. He became famous for isolating Bacillus anthracis (1877), the Tuberculosis bacillus (1882) and the Vibrio cholera (1883) and for his development of Koch's postulates.
*Arthur Korn
Arthur Korn (20 May 1870 – 21 December/22 December 1945) was a German physicist, mathematician and inventor. He was involved in the development of the fax machine, specifically the transmission of photographs or telephotography, known as the ...
: Inventor involved in development of the fax machine, specifically the transmission of photographs or telephotography, known as the Bildtelegraph.
* Max Kramer: Aircraft engineer. Developed the first operational guided bomb in 1942/43. This first smart bomb was radio controlled and joy-stick operated.
* Julius H. Kroehl: Inventor and engineer, who built the first functioning submarine in the world.
*Herbert Kroemer
Herbert Kroemer (; August 25, 1928 – March 8, 2024) was a German-American physicist who, along with Zhores Alferov, received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2000 for "developing semiconductor heterostructures used in high-speed- and opto-electro ...
: Physicist, shared the Nobel Prize in Physics 2000 for developing semiconductor heterostructures used in high-speed- and opto-electronics.
* Werner Krüger: Developed the Krueger flap
Krueger flaps, or Krüger flaps, are lift enhancement devices that may be fitted to the leading edge of an aircraft wing. Unlike Leading-edge slat, slats or leading-edge droop flap, droop flaps, the main wing upper surface and its leading edge is ...
, a lift enhancement device in modern aircraft wings in 1943.
* Alfred Krupp: Pioneer in metal casting and metal working process and procedures.
*Adam Johann von Krusenstern
Adam Johann von Krusenstern (; 10 October 177012 August 1846) was a Russian admiral and explorer of Swedish and Baltic German descent, who led the first Russian circumnavigation of the Earth in 1803–1806.
Life
Krusenstern was born i ...
: Navigator and explorer, led the first Russian expedition to circumnavigate the Earth.
*Dietrich Küchemann
Dietrich Küchemann CBE FRS FRAeS (11 September 1911 – 23 February 1976) was a German aerodynamicist who made several important contributions to the advancement of high-speed flight. He spent most of his career in the UK, where he is ...
: Aeronautical pioneer, developed wings for supersonic speed, such as delta wings
A delta wing is a wing shaped in the form of a triangle. It is named for its similarity in shape to the Greek uppercase letter delta (Δ).
Although long studied, the delta wing did not find significant practical applications until the Jet Age, w ...
as used in the Concorde
Concorde () is a retired Anglo-French supersonic airliner jointly developed and manufactured by Sud Aviation and the British Aircraft Corporation (BAC).
Studies started in 1954, and France and the United Kingdom signed a treaty establishin ...
.
L
 *
*Eugen Langen
Carl Eugen Langen (9 October 1833 in Cologne – 2 October 1895 in Elsdorf) was a German entrepreneur, engineer and inventor, involved in the development of the petrol engine and the Wuppertal Suspension Railway. In 1857 he worked in his fathe ...
: Entrepreneur, engineer and inventor, involved in the development of the petrol engine and the Wuppertal monorail.
* Paul Langerhans: Islets of Langerhans
The pancreatic islets or islets of Langerhans are the regions of the pancreas that contain its endocrine (hormone-producing) cells, discovered in 1869 by German pathological anatomist Paul Langerhans. The pancreatic islets constitute 1–2% o ...
, Langerhans cells
A Langerhans cell (LC) is a tissue-resident macrophage of the skin once thought to be a resident dendritic cell. These cells contain organelles called Birbeck granules. They are present in all layers of the epidermis and are most prominent in ...
*Max von Laue
Max Theodor Felix von Laue (; 9 October 1879 – 24 April 1960) was a German physicist who received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1914 "for his discovery of the X-ray diffraction, diffraction of X-rays by crystals".
In addition to his scientifi ...
: Discoveries regarding the diffraction of X-rays in crystals.
* Ernst Lecher: He is remembered for developing an apparatus— "Lecher lines"—to measure the wavelength and frequency of electromagnetic waves.
*Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (or Leibnitz; – 14 November 1716) was a German polymath active as a mathematician, philosopher, scientist and diplomat who is credited, alongside Sir Isaac Newton, with the creation of calculus in addition to ...
: Philosopher known for discovering the mathematical field of calculus and coherently laying down its basic operations in 1684.
*Georg Christoph Lichtenberg
Georg Christoph Lichtenberg (; 1 July 1742 – 24 February 1799) was a German physicist, satirist, and Anglophile. He was the first person in Germany to hold a professorship explicitly dedicated to experimental physics. He is remembered for his p ...
: German scientist credited with the development of the electrophorus
In electromagnetism, an electrophorus or electrophore is a simple, manual, Capacitor, capacitive, electrostatic generator used to produce Electric charge, charge via the process of electrostatic induction. A first version of it was invented in 1 ...
.
*Justus von Liebig
Justus ''Freiherr'' von Liebig (12 May 1803 – 18 April 1873) was a Germans, German scientist who made major contributions to the theory, practice, and pedagogy of chemistry, as well as to agricultural and biology, biological chemistry; he is ...
: German chemist who made contributions to agricultural and biological chemistry.
*Otto Lilienthal
Karl Wilhelm Otto Lilienthal (23 May 1848 – 10 August 1896) was a German pioneer of aviation who became known as the "flying man". He was the first person to make well-documented, repeated, successful flights with gliders, therefore making t ...
: Father of Aviation and first successful aviator. Main discovery was the properties and shape of the wing
A wing is a type of fin that produces both Lift (force), lift and drag while moving through air. Wings are defined by two shape characteristics, an airfoil section and a planform (aeronautics), planform. Wing efficiency is expressed as lift-to-d ...
.
*Carl von Linde
Carl Paul Gottfried von Linde (11 June 1842 – 16 November 1934) was a German scientist, engineer, and businessman. He discovered the refrigeration cycle and invented the first industrial-scale air separation and gas liquefaction processes, ...
: Engineer who, among other things, developed refrigeration and gas separation technologies.
* Walter Linderer: Father of the airbag
An airbag is a vehicle occupant-restraint system using a bag designed to inflate in milliseconds during a collision and then deflate afterwards. It consists of an airbag cushion, a flexible fabric bag, an inflation module, and an impact sensor. ...
.
*Alexander Lippisch
Alexander Martin Lippisch (2 November 1894 – 11 February 1976) was a German aeronautical engineer, a pioneer of aerodynamics who made important contributions to the understanding of tailless aircraft, delta wings and the ground effect in aircra ...
: Pioneer of aerodynamics, his most famous design is the Messerschmitt Me 163
The Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet is a rocket-powered interceptor aircraft primarily designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Messerschmitt. It is the only operational rocket-powered fighter aircraft in history as well as ...
.
* Ernst Litfaß: free-standing cylindrical advertising column.
M

 *
*Ernst Mach
Ernst Waldfried Josef Wenzel Mach ( ; ; 18 February 1838 – 19 February 1916) was an Austrian physicist and philosopher, who contributed to the understanding of the physics of shock waves. The ratio of the speed of a flow or object to that of ...
: Discovered many effects of high speed projectiles; the Mach number
The Mach number (M or Ma), often only Mach, (; ) is a dimensionless quantity in fluid dynamics representing the ratio of flow velocity past a boundary to the local speed of sound.
It is named after the Austrian physicist and philosopher Erns ...
is dedicated to his memory.
*Georg Hans Madelung
Georg Hans Madelung (31 July 1889 in Rostock – 17 August 1972 in Uffing) was a German academic and aeronautical engineer.
Madelung studied at several German universities of technology before his service as a pilot in the First World War. ...
: Academic and aeronautical engineer; a participant in the development of the Junkers F.13.
*Karl Marx
Karl Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, political theorist, economist, journalist, and revolutionary socialist. He is best-known for the 1848 pamphlet '' The Communist Manifesto'' (written with Friedrich Engels) ...
: Political economist and philosopher, who defined the political/economical background of capitalism and discovered the mechanics of Marxism
Marxism is a political philosophy and method of socioeconomic analysis. It uses a dialectical and materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to analyse class relations, social conflict, ...
.
*Wilhelm Maybach
Wilhelm Maybach (; 9 February 1846 – 29 December 1929) was an early German engine designer and industrialist. During the 1890s he was hailed in France, then the world centre for car production, as the "King of Designers".
From the late 19th ce ...
: Together with Gottlieb Daimler the first gasoline-powered motorcycle, power-engine boat and later, 1902, the Mercedes car model.
* Ottomar von Mayenburg: Inventor of "Chlorodont", the first commercial brand of toothpaste.
*Georg Meissner
George Meissner (19 November 1829 – 30 March 1905) was a German anatomist and physiologist born in Hanover.
He studied medicine at the University of Göttingen, where he worked closely with Rudolf Wagner (1806–1864). In 1851 he accompa ...
: Discovered Meissner's plexus
The submucosal plexus (Meissner's plexus, plexus of the submucosa, plexus submucosus) lies in the submucosa of the intestinal wall. The nerves of this plexus are derived from the myenteric plexus which itself is derived from the plexuses of para ...
.
*Lise Meitner
Elise Lise Meitner ( ; ; 7 November 1878 – 27 October 1968) was an Austrian-Swedish nuclear physicist who was instrumental in the discovery of nuclear fission.
After completing her doctoral research in 1906, Meitner became the second woman ...
: Nuclear physicist, who, together with Otto Frisch
Otto Robert Frisch (1 October 1904 – 22 September 1979) was an Austrian-born British physicist who worked on nuclear physics. With Otto Stern and Immanuel Estermann, he first measured the magnetic moment of the proton. With his aunt, Lise M ...
, provided a theoretical account of nuclear fission.
* Julius Lothar Meyer: With Mendeleev he developed the periodic classification of the elements in order of their atomic weight.
*Christian Erich Hermann von Meyer
Christian Erich Hermann von Meyer (3 September 1801 – 2 April 1869), known as Hermann von Meyer, was a German palaeontologist. He was awarded the 1858 Wollaston medal by the Geological Society of London.
Life
He was born in Frankfurt am ...
: He discovered the Triassic predator Teratosaurus, the earliest bird Archaeopteryx
''Archaeopteryx'' (; ), sometimes referred to by its German name, "" ( ''Primeval Bird'') is a genus of bird-like dinosaurs. The name derives from the ancient Greek (''archaîos''), meaning "ancient", and (''ptéryx''), meaning "feather" ...
lithographica (1861), the pterosaur Rhamphorhynchus
''Rhamphorhynchus'' (, from Ancient Greek ''rhamphos'' meaning "beak" and ''rhynchus'' meaning "snout") is a genus of long-tailed pterosaurs in the Jurassic period. Less specialized than contemporary, short-tailed pterodactyloid pterosaurs such ...
, and the prosauropod dinosaur Plateosaurus
''Plateosaurus'' (probably meaning "broad lizard", often mistranslated as "flat lizard") is a genus of plateosaurid dinosaur that lived during the Late Triassic period, around 214 to 204 million years ago, in what is now Central and Northern Eu ...
*Gregor Mendel
Gregor Johann Mendel Order of Saint Augustine, OSA (; ; ; 20 July 1822 – 6 January 1884) was an Austrian Empire, Austrian biologist, meteorologist, mathematician, Augustinians, Augustinian friar and abbot of St Thomas's Abbey, Brno, St. Thom ...
: Discoveries in genetics. Mendel demonstrated that the inheritance of certain traits in pea plants follows particular patterns, now referred to as the laws of Mendelian inheritance
Mendelian inheritance (also known as Mendelism) is a type of biological inheritance following the principles originally proposed by Gregor Mendel in 1865 and 1866, re-discovered in 1900 by Hugo de Vries and Carl Correns, and later popularize ...
. First published in 1865.
* Ottmar Mergenthaler: Inventor who has been called a second Gutenberg because of his invention of the Linotype machine.
*Rudolf Mössbauer
Rudolf Ludwig Mössbauer (; 31 January 1929 – 14 September 2011) was a German physicist who shared the 1961 Nobel Prize in Physics with Robert Hofstadter for his discovery of the Mössbauer effect, which is the basis for Mössbauer spectro ...
: physicist, discovered Mössbauer effect
The Mössbauer effect, or recoilless nuclear resonance fluorescence, is a physical phenomenon discovered by Rudolf Mössbauer in 1958. It involves the resonant and recoil-free emission and absorption of gamma radiation by atomic nuclei bound in a ...
, shared Nobel Prize in Physics 1961.
*Johannes Peter Müller
Johannes Peter Müller (14 July 1801 – 28 April 1858) was a German physiologist, comparative anatomist, ichthyologist, and herpetologist, known not only for his discoveries but also for his ability to synthesize knowledge. The paramesonephri ...
: Discoveries in physiology.
N
 *
*Thomas Nast
Thomas Nast (; ; September 26, 1840December 7, 1902) was a German-born American caricaturist and editorial cartoonist often considered to be the "Father of the American Cartoon".
He was a sharp critic of William M. Tweed, "Boss" Tweed and the T ...
: The German American
German Americans (, ) are Americans who have full or partial German ancestry.
According to the United States Census Bureau's figures from 2022, German Americans make up roughly 41 million people in the US, which is approximately 12% of the pop ...
"Father of the American Cartoon".
*Walther Nernst
Walther Hermann Nernst (; 25 June 1864 – 18 November 1941) was a German physical chemist known for his work in thermodynamics, physical chemistry, electrochemistry, and solid-state physics. His formulation of the Nernst heat theorem helped ...
: Inventor of the Nernst lamp
The Nernst lamp was an early form of incandescent lamp.
Construction
Nernst lamps did not use a glowing tungsten filament. Instead, they used a ceramic rod that was heated to incandescence. Because the rod (unlike tungsten wire) would no ...
and Nobel laureate 1920 in Chemistry.
* Karl Nessler: Inventor of the permanent wave
A permanent wave, commonly called a perm or permanent (sometimes called a "curly perm" to distinguish it from a " straight perm"), is a hairstyle consisting of waves or curls set into the hair. The curls may last a number of months, hence the ...
.
*Paul Gottlieb Nipkow
Paul Julius Gottlieb Nipkow (; 22 August 1860 – 24 August 1940) was a German electrical engineer and inventor. He invented the Nipkow disk, which laid the foundation of television, since his disk was a fundamental component in the first televis ...
: Technician and inventor, the "spiritual father" of the core element of first generation television technology.
*Emmy Noether
Amalie Emmy Noether (23 March 1882 – 14 April 1935) was a German mathematician who made many important contributions to abstract algebra. She also proved Noether's theorem, Noether's first and Noether's second theorem, second theorems, which ...
: Mathematician. Groundbreaking contributions to abstract algebra and theoretical physics (Noether's theorem
Noether's theorem states that every continuous symmetry of the action of a physical system with conservative forces has a corresponding conservation law. This is the first of two theorems (see Noether's second theorem) published by the mat ...
). Considered by many as the most influential woman in the history of mathematics.
O
*Hermann Oberth
Hermann Julius Oberth (; 25 June 1894 – 28 December 1989) was an Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian-born German physicist and rocket pioneer of Transylvanian Saxons, Transylvanian Saxon descent. Oberth supported Nazi Germany's war effort and re ...
: Pioneer of rocket science and discoverer of the Oberth effect
In astronautics, a powered flyby, or Oberth maneuver, is a maneuver in which a spacecraft falls into a gravitational well and then uses its engines to further accelerate as it is falling, thereby achieving additional speed. The resulting maneuve ...
.
* August Oetker: Pharmacist. He was the first to sell baking powder
Baking powder is a dry chemical leavening agent, a mixture of a carbonate or bicarbonate and a weak acid. The base and acid are prevented from reacting prematurely by the inclusion of a buffer such as cornstarch. Baking powder is used to increas ...
in small packets to households instead of bakeries (as others before him) and thus made it the popular product we know today.
* Hans Joachim Pabst von Ohain: The modern jet engine in 1933, patented in 1936. Frank Whittle
Air Commodore Sir Frank Whittle, (1 June 1907 – 8 August 1996) was an English engineer, inventor and Royal Air Force (RAF) air officer. He is credited with co-creating the turbojet engine. A patent was submitted by Maxime Guillaume in 1921 fo ...
had developed a similar concept independently in 1928/1929.
*Wilhelm Ostwald
Wilhelm Friedrich Ostwald (; – 4 April 1932) was a Latvian chemist and philosopher. Ostwald is credited with being one of the founders of the field of physical chemistry, with Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff, Walther Nernst and Svante Arrhenius. ...
: Numerous discoveries and inventions in chemistry and other areas.
* Nikolaus August Otto: Inventor of the first internal-combustion engine to efficiently burn fuel directly in a piston chamber.
P
 *
*Wolfgang Paul
Wolfgang Paul (; 10 August 1913 – 7 December 1993) was a German physicist, who co-developed the non-magnetic quadrupole mass filter which laid the foundation for what is now called an ion trap. He shared one-half of the Nobel Prize in Ph ...
: Physicist. Co-developed the non-magnetic quadrupole mass filter which laid the foundation for what we now call an ion trap
An ion trap is a combination of electric field, electric and/or magnetic fields used to capture charged particles — known as ions — often in a system isolated from an external environment. Atomic and molecular ion traps have a number of a ...
. Shared the Nobel Prize in 1989.
* Hans von Pechmann: Chemist, renowned for his discovery of diazomethane
Diazomethane is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH2N2, discovered by German chemist Hans von Pechmann in 1894. It is the simplest diazo compound. In the pure form at room temperature, it is an extremely sensitive explosive yellow ga ...
in 1894. Pechmann condensation and Pechmann pyrazole synthesis.
*Julius Richard Petri
Julius Richard Petri (; 31 May 185220 December 1921) was a German microbiologist who is generally credited with inventing the device known as the Petri dish, which is named after him, while working as assistant to bacteriologist Robert Koch.
L ...
: Bacteriologist who is generally credited with inventing the Petri dish
A Petri dish (alternatively known as a Petri plate or cell-culture dish) is a shallow transparent lidded dish that biologists use to hold growth medium in which cells can be cultured,R. C. Dubey (2014): ''A Textbook Of Biotechnology For Class- ...
while working as assistant to Robert Koch
Heinrich Hermann Robert Koch ( ; ; 11 December 1843 – 27 May 1910) was a German physician and microbiologist. As the discoverer of the specific causative agents of deadly infectious diseases including tuberculosis, cholera and anthrax, he i ...
.
* Emil Pfeiffer: Discovery of Infectious mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis (IM, mono), also known as glandular fever, is an infection usually caused by the Epstein–Barr virus (EBV). Most people are infected by the virus as children, when the disease produces few or no symptoms. In young adu ...
*Fritz Pfleumer
Fritz Pfleumer (20 March 1881 – 29 August 1945) was a German engineer who invented magnetic tape for recording sound.
Biography
Pfleumer was born on 20 March 1881, in Salzburg, to Robert and Minna Pfleumer (née Hünich). His father Robert ( ...
: Inventor of magnetic tape for recording sound. He builts the world's first practical tape recorder, called Magnetophon K1.
*Max Planck
Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck (; ; 23 April 1858 – 4 October 1947) was a German Theoretical physics, theoretical physicist whose discovery of energy quantum, quanta won him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1918.
Planck made many substantial con ...
: Physicist, Scientist. He is considered to be the founder of the quantum theory, and one of the most important physicists of the twentieth century.
* Robert Wichard Pohl: In 1938, together with Rudolf Hilsch, built first functioning solid-state amplifier using salt as the semiconductor.
*Ludwig Prandtl
Ludwig Prandtl (4 February 1875 – 15 August 1953) was a German Fluid mechanics, fluid dynamicist, physicist and aerospace scientist. He was a pioneer in the development of rigorous systematic mathematical analyses which he used for underlyin ...
: First to explain the boundary layer
In physics and fluid mechanics, a boundary layer is the thin layer of fluid in the immediate vicinity of a Boundary (thermodynamic), bounding surface formed by the fluid flowing along the surface. The fluid's interaction with the wall induces ...
and its importance for drag and streamlining in aircraft in 1904. He established and headed the Aerodynamische Versuchsanstalt in Göttingen, now Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization. During his tenure the first wind tunnel in Germany was built here, thereby establishing a specific design for wind tunnels (Göttingen type).
Q
*Georg Hermann Quincke
Georg Hermann Quincke FRSFor HFRSE (; November 19, 1834 – January 13, 1924) was a German physicist.
Biography
Born in Frankfurt-on-Oder, Quincke was the son of prominent physician ''Geheimer Medicinal-Rath'' Hermann Quincke and the elder br ...
: German physicist who invented the Quincke's Interference Tube, an apparatus which demonstrates destructive interference of sound waves.
R

 * Adolf Rambold: Inventor of modern
* Adolf Rambold: Inventor of modern tea bag
A tea bag (or teabag) is a small, porous, sealed bag or Packet (container), packet typically containing tea leaves (''Camellia sinensis'') or the leaves of other herbs, which is immersed in water to steeping, steep and make an infusion. Origina ...
.
*Johann Philipp Reis
Johann Philipp Reis (; 7 January 1834 – 14 January 1874) was a self-taught German scientist and inventor. In 1861, he constructed the first ''make-and-break'' telephone, today called the Reis telephone. It was the first device to transmi ...
: Inventor of the first phone transmitter in 1861, he also invented the term ''Telephone''.
* Josef Rodenstock: Founder of Rodenstock, manufacturer of optical systems, ophthalmic lenses and spectacles frames.
* Ralf Reski: Moss bioreactor (1998).
* Paul Julius Freiherr von Reuter: Communications pioneer.
*Fritz Reiche
Fritz Reiche (July 4, 1883 – January 14, 1969) was a German physicist, a student of Max Planck and a colleague of Albert Einstein, who was active in, and made important contributions to the early development of quantum mechanics including co-aut ...
: Was a student of Max Planck and a colleague of Albert Einstein, who was active in, and made important contributions to the early development of quantum mechanics including co-authoring the Thomas-Reiche-Kuhn sum rule.
* Hans Reichel: Musical instrument
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make Music, musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person ...
inventor. Inventor of the daxophone and various overtone
An overtone is any resonant frequency above the fundamental frequency of a sound. (An overtone may or may not be a harmonic) In other words, overtones are all pitches higher than the lowest pitch within an individual sound; the fundamental i ...
guitars.
*Bernhard Riemann
Georg Friedrich Bernhard Riemann (; ; 17September 182620July 1866) was a German mathematician who made profound contributions to analysis, number theory, and differential geometry. In the field of real analysis, he is mostly known for the f ...
: Mathematician, who made lasting contributions to analysis, number theory, and differential geometry.
*Johann Wilhelm Ritter
Johann Wilhelm Ritter (16 December 1776 – 23 January 1810). was a German chemist, physicist and philosopher. He was born in Samitz (Zamienice) near Haynau (Chojnów) in Silesia (then part of Prussia, since 1945 in Poland), and died in Muni ...
: Physicist and discoverer of Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
.
*Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen
Wilhelm may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* William Charles John Pitcher, costume designer known professionally as "Wilhelm"
* Wilhelm (name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name or surname
Other uses
* Wilhe ...
: Physicist and discoverer of x-rays/Röntgen rays (8 November 1895), this earned him the first Nobel Prize in Physics in 1901.
*Arthur Rudolph
Arthur Louis Hugo Rudolph (November 9, 1906 – January 1, 1996) was a German rocket engineer who was a leader of the effort to develop the V-2 rocket for Nazi Germany. After World War II, the United States government's Office of Strategic Servic ...
: Rocket engineer who, together with Wernher von Braun
Wernher Magnus Maximilian Freiherr von Braun ( ; ; 23 March 191216 June 1977) was a German–American aerospace engineer and space architect. He was a member of the Nazi Party and '' Allgemeine SS'', the leading figure in the development of ...
, played a key role in the development of the V-2 rocket
The V2 (), with the technical name ''Aggregat (rocket family), Aggregat-4'' (A4), was the world's first long-range missile guidance, guided ballistic missile. The missile, powered by a liquid-propellant rocket engine, was developed during the S ...
.
*Ernst Ruska
Ernst August Friedrich Ruska (; 25 December 1906 – 27 May 1988) was a German physicist who won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1986 for his work in electron optics, including the design of the first electron microscope.
Life and career
Ernst R ...
: Physicist, developed the first electron microscope in 1933. Nobel laureate 1986.
S
*Carl Wilhelm Scheele
Carl Wilhelm Scheele (, ; 9 December 1742 – 21 May 1786) was a Swedish Pomerania, German-Swedish pharmaceutical chemist.
Scheele discovered oxygen (although Joseph Priestley published his findings first), and identified the elements molybd ...
: Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
(although Joseph Priestley published his findings first), identification of molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mo (from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'') and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals hav ...
, tungsten
Tungsten (also called wolfram) is a chemical element; it has symbol W and atomic number 74. It is a metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively in compounds with other elements. It was identified as a distinct element in 1781 and first ...
, barium
Barium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in group 2 and is a soft, silvery alkaline earth metal. Because of its high chemical reactivity, barium is never found in nature as a free element.
Th ...
, hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
and chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
* Arthur Scherbius: Developed the mechanical cipher machine Enigma. Patent granted in 1918.
* Paul Schlack: Invented Nylon 6
Nylon 6 or polycaprolactam is a polymer, in particular semicrystalline polyamide. Unlike most other nylons, nylon 6 is not a condensation polymer, but instead is formed by ring-opening polymerization; this makes it a special case in the compari ...
.
* Friedrich Albert Moritz Schlick: Was a German philosopher, physicist and the founding father of logical positivism and the Vienna Circle.
*Heinrich Schliemann
Johann Ludwig Heinrich Julius Schliemann (; 6 January 1822 – 26 December 1890) was a German businessman and an influential amateur archaeologist. He was an advocate of the historicity of places mentioned in the works of Homer and an archaeolo ...
: Father of archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
, among other things he discovered Homeric Troy
Troy (/; ; ) or Ilion (; ) was an ancient city located in present-day Hisarlik, Turkey. It is best known as the setting for the Greek mythology, Greek myth of the Trojan War. The archaeological site is open to the public as a tourist destina ...
.
* Hugo Schmeisser: Developed the first modern assault rifle StG 44
The StG 44 (abbreviation of Sturmgewehr 44, "assault rifle 44") is a German assault rifle developed during World War II by Hugo Schmeisser. It is also known by its early designations as the MP 43 and MP 44 (''Maschinenpistole 43'' and ''44''). ...
in 1942.
*Bernhard Schmidt
Bernhard Woldemar Schmidt (, Naissaar, Nargen, Estonia – 1 December 1935, Hamburg) was an Estonian optician. In 1930 he invented the Schmidt camera, Schmidt telescope, which corrected for the optical errors of spherical aberration, coma, and a ...
: Developed a photographic telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
with minimal optical errors: the Schmidt camera
A Schmidt camera, also referred to as the Schmidt telescope, is a catadioptric astrophotographic telescope designed to provide wide fields of view with limited aberrations. The design was invented by Bernhard Schmidt in 1930.
Some notable ...
.
*Paul Schmidt (inventor)
Paul Schmidt (26 March 1898 18 October 1976) was a German aerospace engineer and inventor based in Munich, mainly known for his contribution to the development of the pulsejet.
Life
Schmidt was born on 26 March 1898 in Hagen, Westphalia.
His e ...
: Developed since 1928 his idea of a new drive, the "pulsating incineration", also used in the V-1 flying bomb
The V-1 flying bomb ( "Vengeance Weapon 1") was an early cruise missile. Its official Reich Aviation Ministry () name was Fieseler Fi 103 and its suggestive name was (hellhound). It was also known to the Allies as the buzz bomb or doodlebug a ...
(engine was called "Argus-Schmidtrohr"); pulsejet
file:Pulse Jet Engine.PNG, 300px, Diagram of a valved pulsejet. 1 - Air enters through valve and is mixed with fuel. 2 - The mixture is ignited, expands, closes the valve and exits through the tailpipe, creating thrust.3 - Low pressure in the engi ...
was a development by Schmidt.
*Christian Friedrich Schönbein
Christian Friedrich Schönbein HFRSE (18 October 1799 – 29 August 1868) was a German-Swiss chemist who is best known for inventing the fuel cell (1838) at the same time as William Robert Grove and his discoveries of guncotton and ozone. He a ...
: Professor Schönbein is credited with four scientific advances: Ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , break ...
, Gun cotton, Collodion
Collodion is a flammable, syrupy solution of nitrocellulose in Diethyl ether, ether and Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol. There are two basic types: flexible and non-flexible. The flexible type is often used as a surgical dressing or to hold dressings ...
and Fuel cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen fuel, hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most bat ...
* Johann Lukas Schönlein: Professor of medicine, he discovered among other things the parasitic cause of ringworm or favus (Achorion Schönleinii).
 * Otto Schoetensack: Named the
* Otto Schoetensack: Named the Homo heidelbergensis
''Homo heidelbergensis'' is a species of archaic human from the Middle Pleistocene of Europe and Africa, as well as potentially Asia depending on the taxonomic convention used. The species-level classification of ''Homo'' during the Middle Pleis ...
.
*Otto Schott
Friedrich Otto Schott (1851–1935) was a German people, German chemist, glass technologist, and the inventor of borosilicate glass. Schott systematically investigated the relationship between the chemical composition of the glass and its properti ...
: Inventor of borosilicate glass
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having very low coefficients of thermal expansion (≈3 × 10−6 K−1 at 20 °C), ma ...
. Donated his shares in the company Carl Zeiss to form Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung
The Carl-Zeiss-Foundation (non-profit)#Germany, Stiftung (Carl Zeiss Foundation), legally located in Heidenheim an der Brenz and Jena, Germany, and with its administrative headquarters in Stuttgart, is the sole shareholder of the two companies C ...
, still in existence today.
* Walter H. Schottky: Played a major early role in developing the theory of electron and ion emission phenomena, invented the screen-grid vacuum tube and the pentode.
* Marx Schwab: Silversmith, invented coining with the screw press around 1550.
*Theodor Schwann
Theodor Schwann (; 7 December 181011 January 1882) was a German physician and physiology, physiologist. His most significant contribution to biology is considered to be the extension of cell theory to animals. Other contributions include the d ...
: Discovery of properties of cells in animals.
*Alois Senefelder
Johann Alois Senefelder (6 November 177126 February 1834) was a German actor and playwright who invented the printing technique of lithography in the 1790s.Meggs, Philip B. A History of Graphic Design. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1998. p 146
Actor ...
: He invented the printing technique of lithography
Lithography () is a planographic method of printing originally based on the miscibility, immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone (lithographic limestone) or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by ...
in 1796.
*Friedrich Sertürner
Friedrich Wilhelm Adam Sertürner (; 19 June 1783 – 20 February 1841) was a German pharmacist and a pioneer of alkaloid chemistry. He is best known for his discovery of morphine, which he isolated from opium in 1804, and for conducting tests, ...
: First to isolate morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
from the opium poppy
''Papaver somniferum'', commonly known as the opium poppy or breadseed poppy, is a species of flowering plant in the family Papaveraceae. It is the species of plant from which both opium and poppy seeds are derived and is also a valuable orname ...
in 1803/1804, discovering morphine.
*Philipp Franz von Siebold
Philipp Franz Balthasar von Siebold (17 February 1796 – 18 October 1866) was a German physician, botanist and traveller. He achieved prominence by his studies of Japanese flora (plants), flora and fauna (animals), fauna and the introduction of ...
: Physician and naturalist, detailed description and collection of the Japanese flora and fauna. Introduced Western medicine to Japan and opened a medical school.
*Ernst Werner von Siemens
Ernst Werner Siemens (von Siemens from 1888; ; ; 13 December 1816 – 6 December 1892) was a German electrical engineer, inventor and industrialist. Siemens's name has been adopted as the SI unit of electrical conductance, the siemens. He fou ...
: Dynamo, pointer telegraph that used a needle to point to the right letter, first electric elevator, trolleybus.
*Friedrich Soennecken
Friedrich Soennecken (20 September 1848 – 2 July 1919) was an entrepreneur and inventor. He was the founder of Soennecken, a German office supplier.
Soennecken was born in Iserlohn-Dröschede, Sauerland in 1848, the son of a blacksmith. On ...
: Invented Hole punch
A hole punch, also known as a hole puncher or paper puncher, is an office supplies, office tool that is used to create holes in sheets of paper, often for the purpose of collecting the sheets in a Ring binder, binder or folder (such collected sh ...
and ring binder
Ring binders (loose leaf binders, looseleaf binders, or sometimes called files in United Kingdom, Britain) are large folders that contain file folders or hole punched papers (called Loose leaf, loose leaves). These binders come in various sizes ...
.
*Arnold Sommerfeld
Arnold Johannes Wilhelm Sommerfeld (; 5 December 1868 – 26 April 1951) was a German Theoretical physics, theoretical physicist who pioneered developments in Atomic physics, atomic and Quantum mechanics, quantum physics, and also educated and ...
: Theoretical physicist who pioneered developments in atomic and quantum physics.
* Franz Ritter von Soxhlet: German agricultural chemist Prof. Dr. phil. von Soxhlet (1848–1926) invented the Soxhlet extractor in 1879. In 1886, he proposed that pasteurization be applied to milk in order to prevent disease and spoilage. He taught at the Technical University of Munich.
*Jack Steinberger
Jack Steinberger (born Hans Jakob Steinberger; May 25, 1921December 12, 2020) was a German-born American physicist noted for his work with neutrinos, the subatomic particles considered to be elementary constituents of matter. He was a recipient o ...
: German-American-Swiss
Swiss most commonly refers to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
* Swiss people
Swiss may also refer to: Places
* Swiss, Missouri
* Swiss, North Carolina
* Swiss, West Virginia
* Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
* Swiss Café, an old café located ...
physicist, co-discovered the muon neutrino
The muon neutrino is an elementary particle which has the symbol and zero electric charge. Together with the muon it forms the second generation of leptons, hence the name muon neutrino. It was discovered in 1962 by Leon Lederman, Melvin Schwa ...
, shared 1988 Nobel Prize in Physics.
* Georg Wilhelm Steller: Chief naturalist on Vitus Bering's expedition during which Alaska was discovered (1741) and pioneer of Alaskan Natural History. Steller's sea cow
Steller's sea cow (''Hydrodamalis gigas'') is an extinction, extinct sirenian described by Georg Wilhelm Steller in 1741. At that time, it was found only around the Commander Islands in the Bering Sea between Alaska and Russia; its range exte ...
(now extinct) was named after him.
*Otto Stern
:''Otto Stern was also the pen name of German women's rights activist Louise Otto-Peters (1819–1895)''.
Otto Stern (; 17 February 1888 – 17 August 1969) was a German-American physicist. He is the second most nominated person for a Nobel Pri ...
: Nobel laureate; contributed to the discovery of spin quantization in the Stern–Gerlach experiment
In quantum physics, the Stern–Gerlach experiment demonstrated that the spatial orientation of angular momentum is quantization (physics), quantized. Thus an Atomic spacing, atomic-scale system was shown to have intrinsically quantum propertie ...
with Walther Gerlach
Walther Gerlach (1 August 1889 – 10 August 1979) was a German physicist who co-discovered, through laboratory experiment, spin quantization in a magnetic field, the Stern–Gerlach effect. The experiment was conceived by Otto Stern in 1921 an ...
in 1922.
* Heinrich Stölzel: Developed the valve for brass instruments which is used today in 1818. Friedrich Blühmel had made a similar development independently at the same time.
*Horst Ludwig Störmer
Horst Ludwig Störmer (; born April 6, 1949) is a German physicist, Nobel laureate and emeritus professor at Columbia University.
He was awarded the 1998 Nobel Prize in Physics jointly with Daniel Tsui and Robert Laughlin "for their discovery ...
: German-American physicist. Shared the Nobel Prize in 1998 for the discovery of a new form of quantum fluid with fractionally charged excitations.
*Levi Strauss
Levi Strauss ( ; born Löb Strauß, ; February 26, 1829 – September 26, 1902) was a German-born American businessman who founded the first company to manufacture blue jeans. His firm of Levi Strauss & Co. (Levi's) began in 1853 in San Franci ...
: The German American
German Americans (, ) are Americans who have full or partial German ancestry.
According to the United States Census Bureau's figures from 2022, German Americans make up roughly 41 million people in the US, which is approximately 12% of the pop ...
father of blue jeans.
*Eduard Suess
Eduard Suess (; 20 August 1831 – 26 April 1914) was an Austrian geologist and an expert on the geography of the Alps. He is responsible for hypothesising two major former geographical features, the supercontinent Gondwana (proposed in 1861) and ...
: Discoveries in geology.
T
*Ehrenfried Walther von Tschirnhaus
Ehrenfried Walther von Tschirnhaus or Tschirnhauß (; 10 April 1651 – 11 October 1708) was a German mathematician, physicist, physician, and philosopher. He introduced the Tschirnhaus transformation and is considered by some to have been the ...
: He is considered to have been the inventor of European porcelain.
* Oscar Troplowitz: He invented adhesive tape
Adhesive tape is one of many varieties of backing materials coated with an adhesive. Several types of adhesives can be used.
Types
Pressure-sensitive tape
Pressure-sensitive tape, PSA tape, self-stick tape or sticky tape consists of a pre ...
, ''Leukoplast''.
U
* Dietrich "Diedrich" Uhlhorn: Engineer, mechanic and inventor, who invented the first mechanical tachometer (1817), between 1817 and 1830 inventor of the Presse Monétaire (levelcoin
A coin is a small object, usually round and flat, used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to facilitate trade. They are most often issued by ...
press known as Uhlhorn Press) which bears his name.
V
 * Abraham Vater: Professor of anatomy;
* Abraham Vater: Professor of anatomy; Ampulla of Vater
The ampulla of Vater, hepatopancreatic ampulla or hepatopancreatic duct is the common duct that is usually formed by a union of the common bile duct and the pancreatic duct within the wall of the duodenum. This common duct usually features a di ...
.
* Richard Vetter: Developed the most fuel efficient condensing boiler for heating systems in 1980. Used in many houses in Europe.
*Rudolf Virchow
Rudolf Ludwig Carl Virchow ( ; ; 13 October 18215 September 1902) was a German physician, anthropologist, pathologist, prehistorian, biologist, writer, editor, and politician. He is known as "the father of modern pathology" and as the founder o ...
: "Father of modern pathology"; numerous discoveries in the area of medicine.
* Hans Vogt: Invented sound-on-film (idea 1905) together with Jo Engl and Joseph Massolle, first sound-on-film for the public on 17 September 1922 in Filmtheater ''Alhambra'', Berlin, Germany.
*Woldemar Voigt
Woldemar Voigt (; 2 September 1850 – 13 December 1919) was a German mathematician and physicist.
Biography
Voigt was born in Leipzig, and died in Göttingen. He was a student of Franz Ernst Neumann.
Voigt taught at the Georg August Universi ...
(often: Waldemar Voigt): Physicist, who taught at the Georg August University of Göttingen. He worked on crystal physics, thermodynamics and electro-optics. He discovered the Voigt effect in 1898.
*Woldemar Voigt (engineer)
Woldemar Voigt (10 February 1907 – June 1980) was a German aerospace engineer, who was responsible for some of the advanced swept wing German jet-powered aircraft at the end of World War II.
Early life
His grandfather was the German physic ...
: Chief designer at Messerschmitt
Messerschmitt AG () was a German share-ownership limited, aircraft manufacturing corporation named after its chief designer Willy Messerschmitt from mid-July 1938 onwards, and known primarily for its World War II fighter aircraft, in parti ...
's Oberammergau offices and pioneer of the Me 163 and Me 264, project leader of the development of Me P. 1101, Me P. 1106, Me P. 1110, Me P. 1111, Me P. 1112 and Me P. 1116.
*Jacob Volhard
Jacob Volhard (4 June 1834 – 14 January 1910) was the German chemist who discovered, together with his student Hugo Erdmann, the Volhard–Erdmann cyclization reaction. He was also responsible for the improvement of the Hell–Volhard–Zel ...
: Chemist who discovered, together with his student Hugo Erdmann, the Volhard–Erdmann cyclization.
W
*Martin Waldseemüller
Martin Waldseemüller ( – 16 March 1520) was a German cartographer and humanist scholar. Sometimes known by the Hellenized form of his name, Hylacomylus, his work was influential among contemporary cartographers. His collaborator Matthias Ring ...
: Cartographer, used the name "America
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
" on his map Universalis Cosmographia in honour of the Florentine explorer Amerigo Vespucci
Amerigo Vespucci ( , ; 9 March 1454 – 22 February 1512) was an Italians, Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Florence for whom "Naming of the Americas, America" is named.
Vespucci participated in at least two voyages of the A ...
. The map was drawn at St-Die in 1507 and it was the first time "America" was used on a map.
* Otto Wallach: Chemist who researched, amongst others, alicyclic compounds. Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1910.
*Hellmuth Walter
Hellmuth Walter (26 August 1900 – 16 December 1980) was a German engineer who pioneered research into rocket engines and gas turbines. His most noteworthy contributions were rocket motors for the Messerschmitt Me 163 and Bachem Ba 349 interce ...
: Engineer who pioneered research into rocket engines and gas turbines.
*Felix Wankel
Felix Heinrich Wankel (; 13 August 1902 – 9 October 1988) was a German mechanical engineer and inventor after whom the Wankel engine was named. Wankel joined various radical antisemitic organizations after World War I and was a prominent member ...
: Inventor of the Rotary Motor.
*Max Weber
Maximilian Carl Emil Weber (; ; 21 April 186414 June 1920) was a German Sociology, sociologist, historian, jurist, and political economy, political economist who was one of the central figures in the development of sociology and the social sc ...
: Discovered the mass effects of capitalism and modernity.
*Wilhelm Eduard Weber
Wilhelm Eduard Weber ( ; ; 24 October 1804 – 23 June 1891) was a German physicist and, together with Carl Friedrich Gauss, inventor of the first electromagnetic telegraph.
Biography
Early years
Weber was born in Schlossstrasse in Witte ...
: Inventor of the first electromagnetic telegraph together with Carl Friedrich Gauss.
*Alfred Wegener
Alfred Lothar Wegener (; ; 1 November 1880 – November 1930) was a German climatologist, geologist, geophysicist, meteorologist, and polar researcher.
During his lifetime he was primarily known for his achievements in meteorology and ...
: He is most notable for proposing continental drift in 1912
* Gustav Weißkopf: Aviation pioneer - World's First Motorized Flight: August 14, 1901.
* Clemens Alexander Winkler: Chemist who discovered the element germanium in 1886.
* August Wöhler: Investigated fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
phenomena in the behavior of materials
*Friedrich Wöhler
Friedrich Wöhler Royal Society of London, FRS(For) HonFRSE (; 31 July 180023 September 1882) was a German chemist known for his work in both organic chemistry, organic and inorganic chemistry, being the first to isolate the chemical elements be ...
: The first to synthesize urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest am ...
. Wöhler is regarded as a pioneer in organic chemistry.
X
Y

Z
*Hermann Zapf
Hermann Zapf (; 8 November 1918 – 4 June 2015) was a German type designer and calligrapher who lived in Darmstadt, Germany. He was married to the calligrapher and typeface designer Gudrun Zapf-von Hesse. Typefaces he designed include ...
: Pioneer of computer typography and creator of many well-known typefaces.
*Carl Zeiss
Carl Zeiss (; 11 September 1816 – 3 December 1888) was a German scientific instrument maker, optician and businessman. In 1846 he founded his workshop, which is still in business as Zeiss (company), Zeiss. Zeiss gathered a group of gifted p ...
: Pioneered glass casting and allied procedures and processes for high quality optics.
* Ferdinand Graf von Zeppelin (1838–1917): Inventor of the airship named after him. Start of the airship LZ1 in 1900.
* Karl Zimmer: Discovered the effects of ionizing radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching ...
on DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
in 1935.
*Konrad Zuse
Konrad Ernst Otto Zuse (; ; 22 June 1910 – 18 December 1995) was a German civil engineer, List of pioneers in computer science, pioneering computer scientist, inventor and businessman. His greatest achievement was the world's first programm ...
: Inventor of the first functional program-controlled Turing-complete computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
in 1941, and the first high-level programming language
A high-level programming language is a programming language with strong Abstraction (computer science), abstraction from the details of the computer. In contrast to low-level programming languages, it may use natural language ''elements'', be ea ...
Plankalkül
Plankalkül () is a programming language designed for engineering purposes by Konrad Zuse between 1942 and 1945. It was the first high-level programming language to be designed for a computer. Zuse never implemented Plankalkül on any of his Z- ...
in 1942.
See also
* German inventions and discoveries * List of German AmericansNotes
References
External links
"Made in Germany"
A Sampling of German Inventors and Inventions
German inventors—"Made in Germany"
{{DEFAULTSORT:German inventors and discoverers * ! Inventors and discoverers
Inventor
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea, or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It may also be an entirely new concept. If an ...
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
Inventors and discoverers