Limbu language on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Limbu (Limbu: , ''yakthuṅ pan'') is a
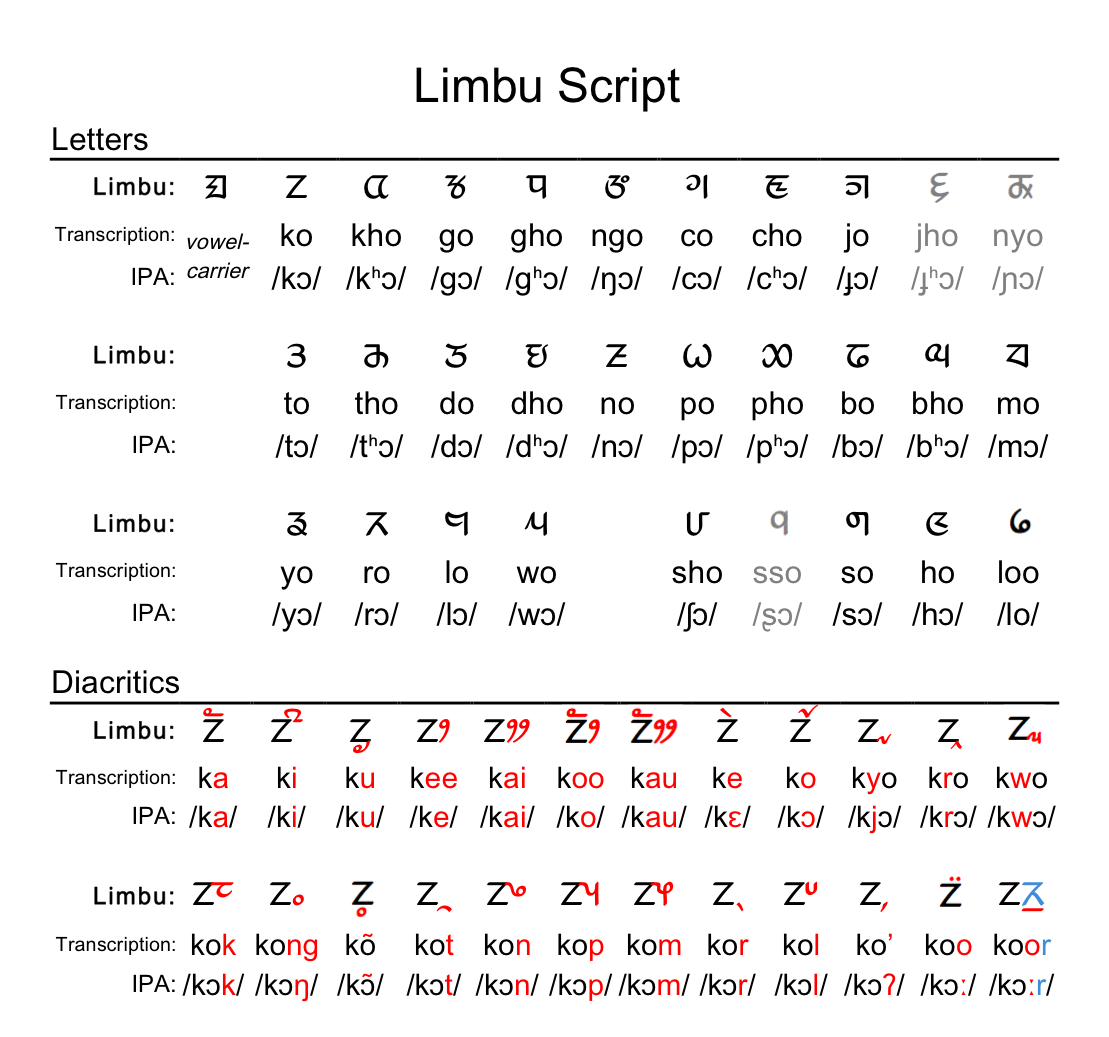 Limbu language is one of the few
Limbu language is one of the few
Politics in Rhetoric and Writing in Paracolonial Context: A Glimpse of Limbu Language, Writing, and Literacy in Yakthung Laje.
''Journal of Global Literacies, Technologies, and Emerging Pedagogies'', 4(1), 550-591. * Limbu, Marohang (2016). Politics of Rhetoric and Writing in the Non-Western World: Delinking, Relinking, and Linking Yakthung Epistemologies. ''Mikphulla Laje Inghang'',10(10) 36-41. *
Limbu-English Dictionary of the Mewa Khola dialectPDF introduction
*
Sino-Tibetan language
Sino-Tibetan, also cited as Trans-Himalayan in a few sources, is a family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European in number of native speakers. The vast majority of these are the 1.3 billion native speakers of Chinese languages. ...
spoken by the Limbu people
The Limbu (exonym) or Yakthung (endonym) are a Sino-Tibetan indigenous tribe (Bhot-Burmeli) of the Himalayan region of eastern Nepal, Sikkim, and western Bhutan.
The original name of the Limbu is ''Yakthung'' () or ''Yakthum''. Limbu males ar ...
of Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is ma ...
and Northeastern India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
(particularly Darjeeling
Darjeeling (, , ) is a town and municipality in the northernmost region of the Indian state of West Bengal. Located in the Eastern Himalayas, it has an average elevation of . To the west of Darjeeling lies the easternmost province of Nep ...
, Kalimpong
Kalimpong (Hindi: कलिम्पोंग) is a town and the headquarters of an eponymous district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is located at an average elevation of . The town is the headquarters of the Kalimpong district. The r ...
, Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Sil ...
, Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur ...
and Nagaland
Nagaland () is a landlocked state in the northeastern region of India. It is bordered by the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh to the north, Assam to the west, Manipur to the south and the Sagaing Region of Myanmar to the east. Its capital cit ...
) as well as expatriate communities in Bhutan
Bhutan (; dz, འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, Druk Yul ), officially the Kingdom of Bhutan,), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountainou ...
. The Limbu refer to themselves as ''Yakthung'' and their language as ''Yakthungpan.'' Yakthungpan has four main dialects: Phedape, Chhathare, Tambarkhole and Panthare dialects.
Among four dialects and/or many dialects, the Phedape dialect is widely spoken and well understood by most Yakthungpan speakers. However, as there are some dominant Panthare scholars who have role to create knowledge and control knowledge in the Limbu communities, Panthare dialect is being popularised as a "standard" Limbu language. As Panthare Yakthungs are much more engaged in central political position and administrative positions, they are trying to introduce Panthare dialect as a Standard Yakthungpan.
Yakthungpan (Limbu language) is one of the major languages spoken and written in Nepal, Darjeeling, Kalimpong, Sikkim, and Bhutan. Linguists have reached the conclusion that Yakthungpan resembles Tibetan
Tibetan may mean:
* of, from, or related to Tibet
* Tibetan people, an ethnic group
* Tibetan language:
** Classical Tibetan, the classical language used also as a contemporary written standard
** Standard Tibetan, the most widely used spoken diale ...
and Lepcha.
Before the introduction of the Sirijanga script among Limbu Kirats, the Róng script was popular in east Nepal, especially in the early Maurong state. The Sirijanga script had almost disappeared for 800 years and it was brought back into use by Limbu scholar Te-ongsi Sirijunga Xin Thebe of Tellok Sinam Limbuwan present day Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is ma ...
. The Limbu script is called 'Sirijanga' after the Limbu culture- hero Te-ongsi Sirijunga Xin Thebe, who is credited with its invention.
Geographical distribution
Limbu is spoken east of the Arun River in the followingdistricts of Nepal
Districts in Nepal are second level of administrative divisions after provinces. Districts are subdivided in municipalities and rural municipalities. There are seven provinces and 77 districts in Nepal.
After the state's reconstruction of admi ...
(''Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' (stylized as ''Ethnoloɠue'') is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensi ...
'').
*Province No. 1
Province No. 1 (proposed names: Kirat, Limbuwan, Khambuwan, Sagarmatha, Birat and Koshi) is the easternmost of the seven provinces established by the new constitution of Nepal which was adopted on 20 September 2015. The province covers an ...
**Dhankuta District
Dhankuta District ( ne, धनकुटा जिल्ला) () is one of 14 districts of Province No. 1 of eastern Nepal. The district covers an area of and has a population (2011) of 163,412. Dhankuta is the district headquarters of Dha ...
**Ilam District
Ilam district ( ne, इलाम जिल्ला) is one of 14 districts of Province No. 1 of eastern Nepal. It is a Hill district and covers . The 2011 census counted 290,254 population. The municipality of Ilam is the district headquar ...
**Jhapa District
Jhapa ( ne, झापा जिल्ला; ) is a district of Province No. 1 in eastern Nepal named after a Rajbanshi word "Jhapa" meaning "to cover" (verb). The latest official data, the 2021 Nepal Census, puts the total population of the ...
**Morang District
Morang District ( ne, मोरङ जिल्ला ) is located in Province No. 1 in eastern Nepal. It is an Outer Terai district. It borders with Bihar, India to the South, Jhapa to the East, Dhankuta and Panchthar to the North, and Sunsa ...
**Panchthar District
Panchthar district ( ne, पाँचथर जिल्ला) is one of 14 districts of Province No. 1 of eastern hilly region of Nepal. It is a Hill district of eastern Nepal. The district covers of area. The 2011 census counted 191,817 popu ...
**Sankhuwasabha District
Sankhuwasabha District ( ne, सङ्खुवासभा जिल्ला ) is one of 14 districts of Province No. 1 of eastern Nepal. The district's area is 3,480 km2 with a population of 159,203 in 2001 and 158,742 in 2011. ...
**Sunsari District
, nickname =
, native_name_lang =
, image_skyline =
, image_size =
, image_alt =
, image_caption = Night view of Dharan, Itahari & Tarahara :: Barahakshetra Temple: BPKIHS, Dharan :Dharan Clock Tower
, image_map = Sunsari district loc ...
**Taplejung District
Taplejung District ( ne, ताप्लेजुङ जिल्ला ) is one of 77 districts of Nepal and one of the 14 districts of Province No. 1. It is remotely located in the Himalayas in Eastern Nepal with Tibet to the north across the ...
**Terhathum District
Tehrathum District ( ne, तेह्रथुम जिल्ला ), is one of 14 districts of Province No. 1 of Nepal.
Demographics
Religion
Languages
Geographics
See also
* Radio Tehrathum
* Zones of Nepal
Until the esta ...
Official status
Nepal
The Language Commission of Nepal has recommended Limbu language as official language inProvince No. 1
Province No. 1 (proposed names: Kirat, Limbuwan, Khambuwan, Sagarmatha, Birat and Koshi) is the easternmost of the seven provinces established by the new constitution of Nepal which was adopted on 20 September 2015. The province covers an ...
. Chulachuli Rural Municipality, Mangsebung Rural Municipality and Phalgunanda Rural Municipality have recognized Limbu language as an official working language.
India
In India, the state ofSikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Sil ...
has recognized Limbu language as an additional official language for the purpose of preservation of culture and tradition in the state. The official weekly publication ''Sikkim Herald'' has a Limbu Edition.Dialects
The Limbu languages are divided into four dialects : *Phedappe *Pachthare *Chathare *Taplejunge or Tamarkhole ''Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' (stylized as ''Ethnoloɠue'') is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensi ...
'' lists the following dialects of Limbu.
*Dialect cluster 1
**Panthare
**Chaubise (Charkhole)
**Yanggrokke (Yanggruppe)
*Dialect cluster 2
**Phedappe
**Tamorkhole (Taplejunge)
*Dialect cluster 3
**Chhatthare (Chatthare, Chhathar)
Yanggrokke, Chaubise, and Charkhole are minor variants of the Panthare dialect. Phedappe and Tamorkhole are similar. Chattare is less well understood by other dialect speakers. The Limbu dialect spoken in Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Sil ...
, India is the same as Panthare.
Phonology
Vowels and consonants
/, / can be heard as rounded after labial consonants. Phonemes in parentheses occur in loan words from Nepali.Sirijanga script
 Limbu language is one of the few
Limbu language is one of the few Sino-Tibetan languages
Sino-Tibetan, also cited as Trans-Himalayan in a few sources, is a family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European in number of native speakers. The vast majority of these are the 1.3 billion native speakers of Chinese languages ...
of the central Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 10 ...
with their own scripts. The Limbu script
The Limbu script (also Sirijanga script) is used to write the Limbu language. It is a Brahmic type abugida.
History
According to traditional histories, the Limbu script was first invented in the late 9th century by Limbu King Sirijunga Hang a ...
or Sirijanga script was devised during the period of Buddhist expansion in Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Sil ...
in the early 18th century when Limbuwan still constituted part of Sikkimese territory. The Limbu script
The Limbu script (also Sirijanga script) is used to write the Limbu language. It is a Brahmic type abugida.
History
According to traditional histories, the Limbu script was first invented in the late 9th century by Limbu King Sirijunga Hang a ...
was probably designed roughly at the same time as the Lepcha script (during the reign of the third King of Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Sil ...
, Phyag-dor Nam-gyal (ca. 1700-1717)). However, it is widely believed that the Limbu script
The Limbu script (also Sirijanga script) is used to write the Limbu language. It is a Brahmic type abugida.
History
According to traditional histories, the Limbu script was first invented in the late 9th century by Limbu King Sirijunga Hang a ...
(Sirijanga) had been designed by the Limbu King Sirijanga Hang in the 9th century. The Sirijanga script was later redesigned and re-introduced by Te-ongsi Sirijunga Xin Thebe . As Te-ongsi Sirijunga Xin Thebe spent most of his time in the development of Yakthungpan, Yatkhung culture, and Limbu script
The Limbu script (also Sirijanga script) is used to write the Limbu language. It is a Brahmic type abugida.
History
According to traditional histories, the Limbu script was first invented in the late 9th century by Limbu King Sirijunga Hang a ...
; he is considered as the reincarnation of the 9th century King Sirijanga.
As Te-ongsi Sirijunga Xin Thebe was astoundingly influential in spreading the Limbu script
The Limbu script (also Sirijanga script) is used to write the Limbu language. It is a Brahmic type abugida.
History
According to traditional histories, the Limbu script was first invented in the late 9th century by Limbu King Sirijunga Hang a ...
, culture, and language, Tasang monks came to fear that he might transform the social, cultural, and linguistic structure of Sikkim. Therefore, Tasang monks captured Sirijunga, bound him to a tree, and shot him to death with poisonous arrows.
Both Limbu and Lepcha were ostensibly devised with the intent of furthering the spread of Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
. However, Sirijanga was a Limbu Buddhist who had studied under Sikkimese high Lamas. Sirijanga was given the title 'the Dorje
The Vajra () is a legendary and ritual weapon, symbolising the properties of a diamond (indestructibility) and a thunderbolt (irresistible force).
The vajra is a type of club with a ribbed spherical head. The ribs may meet in a ball-shape ...
Lama
Lama (; "chief") is a title for a teacher of the Dharma in Tibetan Buddhism. The name is similar to the Sanskrit term ''guru'', meaning "heavy one", endowed with qualities the student will eventually embody. The Tibetan word "lama" means "hig ...
of Yangrup'.
The language and script's influential structure are mixture of Tibetan
Tibetan may mean:
* of, from, or related to Tibet
* Tibetan people, an ethnic group
* Tibetan language:
** Classical Tibetan, the classical language used also as a contemporary written standard
** Standard Tibetan, the most widely used spoken diale ...
and Devanagari
Devanagari ( ; , , Sanskrit pronunciation: ), also called Nagari (),Kathleen Kuiper (2010), The Culture of India, New York: The Rosen Publishing Group, , page 83 is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental writing system), based on the ...
. Unlike most other Brahmic scripts, it does not have separate independent vowel
A vowel is a syllabic speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in quantity (len ...
characters, instead using a vowel carrier letter with the appropriate dependent vowel attached.
The Limbu language and literature have been less practiced in Nepal since the last eighteenth century. The cultural identity of any community was taken as a threat to the national unification by ruling elites until the recent years. The use of the Limbu alphabet
The Limbu script (also Sirijanga script) is used to write the Limbu language. It is a Brahmic type abugida.
History
According to traditional histories, the Limbu script was first invented in the late 9th century by Limbu King Sirijunga Hang a ...
was banned and the possession of Limbu writings outlawed. There were no specific laws about it, but the Security Act was enforced for such cases under the strong directives of Kathmandu.
Writing
Limbu has its own unique writing system, which is similar to Tibetan and Sikkimese scripts. TheLimbu script
The Limbu script (also Sirijanga script) is used to write the Limbu language. It is a Brahmic type abugida.
History
According to traditional histories, the Limbu script was first invented in the late 9th century by Limbu King Sirijunga Hang a ...
or Sirijunga script is unique and scientifically designed by King Sirijanga in the 9th century; it was later re-designed and popularized by Te-ongsi Sirijunga Xin Thebe and his followers in the 18th century. Since teaching of Limbu/Yakthung language and writing was banned by the Khas-Hindus in Nepal after the "Noon Pani Sandhi" between the Limbuwan and Gorkha Kingdom
Gorkha Kingdom ( ne, गोरखा राज्य) was a member of the Chaubisi rajya, a confederation of 24 states on the Indian subcontinent ruled by Khas people. In 1743 CE, the kingdom began a campaign of military expansion, annexing s ...
(Prithvi Narayan Shah), far more Limbus are literate in Nepali
Nepali or Nepalese may refer to :
Concerning Nepal
* Anything of, from, or related to Nepal
* Nepali people, citizens of Nepal
* Nepali language, an Indo-Aryan language found in Nepal, the current official national language and a language spoken ...
than in Limbu in Nepal. Although many Limbu books were written in Devanagari and Roman (English), now Limbus/Yakthungs have well developed computerized writing system and many books are published in Limbu script
The Limbu script (also Sirijanga script) is used to write the Limbu language. It is a Brahmic type abugida.
History
According to traditional histories, the Limbu script was first invented in the late 9th century by Limbu King Sirijunga Hang a ...
or Sirijunga script.
History of Kirat-Yakthung writing can be divided into the following ways:
# Classical Kirat-Yakthung period: King Sirijanga (9th century AD)
# The 18th century Kirat-Yakthunghang period: Te-ongsi Sirijunga Xin Thebe and his cronies movement
# The 19th century Kirat-Yakthung writers and rhetors: Period of Jobhansing Limbu, Chyangresing Phedangba, Ranadwaj, and Jit Mohan (Brian Hudgson procured books and requested them to write histories, stories, narratives, culture, and so on)
# The 20th Century Kirat-Yakthung writers and rhetors:
## After the establishment of "Yakthunghang Chumlung" (1925); thereafter, several books were published.
## Limbu script was much more influenced by Devnagari script at this period.
## At the same time, both national and international linguists, researchers, and writers addressed the issued in this period. This period is period of inquiry, communication, discovery, and re/construction.
# Late 20th and 21st century Kirat-Yakthung writers and rhetors: This period denotes after the restoration of democracy in Nepal in 1990. Introduction of "Anipan" at school; many research and writing such as MA/MPhil theses and research reports; establishment of Limbu organization at the local and global level; period of delinking, relinking, and linking epistemologies.
Publications
The Limbu language has many papers and publications in circulation. Tanchoppa (Morning Star), a monthly newspaper/magazine which has been published since 1995. There are many other literary publications. The oldest known Limbu writings were collected from the Darjeeling district in the 1850s. They are the ancestors of the modern Limbu script. The writings are now a part of a collection in the India Library in London.Teaching
InNepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is ma ...
, the Limbu language is taught on private initiative. The Government of Nepal has published "Ani Paan" text books in Limbu for primary education from grades 1 to 12. Kirant Yakthung Chumlung teaches Limbu language and script on its own initiative.
In Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Sil ...
, since the late 1970s, Limbu in the Limbu script has been offered in English-medium schools as a vernacular language subject in areas populated by Limbus. Over 4000 students study Limbu for one hour daily taught by some 300 teachers. Course books are available in Limbu from grades 1 to 12. Additionally, the significance of Limbu in Sikkim is that the name of the Indian state
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions.
History
Pre-indepen ...
itself is a combination of two Limbu words: ''su'', which means "new", and ''khyim'', which means "palace" or "house".Ethnic Groups of South Asia and the Pacific: An Encyclopedia By James Minahan, 2012
See also
* History of Limbuwan * Limbuwan Gorkha War *Languages of Nepal
Languages of Nepal constitutionally called Nepalese languages are the languages having at least an ancient history or origin inside the sovereign territory of Nepal spoken by Nepalis. The 2011 National census lists 123 languages spoken as a mot ...
References
Further reading
* Driem, George van (1987). ''A grammar of Limbu''. (Mouton grammar library; 4). Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter. * Limbu, Marohang (2017)Politics in Rhetoric and Writing in Paracolonial Context: A Glimpse of Limbu Language, Writing, and Literacy in Yakthung Laje.
''Journal of Global Literacies, Technologies, and Emerging Pedagogies'', 4(1), 550-591. * Limbu, Marohang (2016). Politics of Rhetoric and Writing in the Non-Western World: Delinking, Relinking, and Linking Yakthung Epistemologies. ''Mikphulla Laje Inghang'',10(10) 36-41. *
External links
*
Kaipuleohone Kaipuleohone is a digital ethnographic archive that houses audio and visual files, photographs, as well as hundreds of textual material such as notes, dictionaries, and transcriptions relating to small and endangered languages. The archive is stored ...
's LDTC collection includes open access recordings in Limbu
{{Languages of Nepal
Languages of Nepal
Languages of Bhutan
Kiranti languages
Languages of Sikkim
Official languages of Nepal
Limbu culture