Lehmann discontinuity on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
__NOTOC__
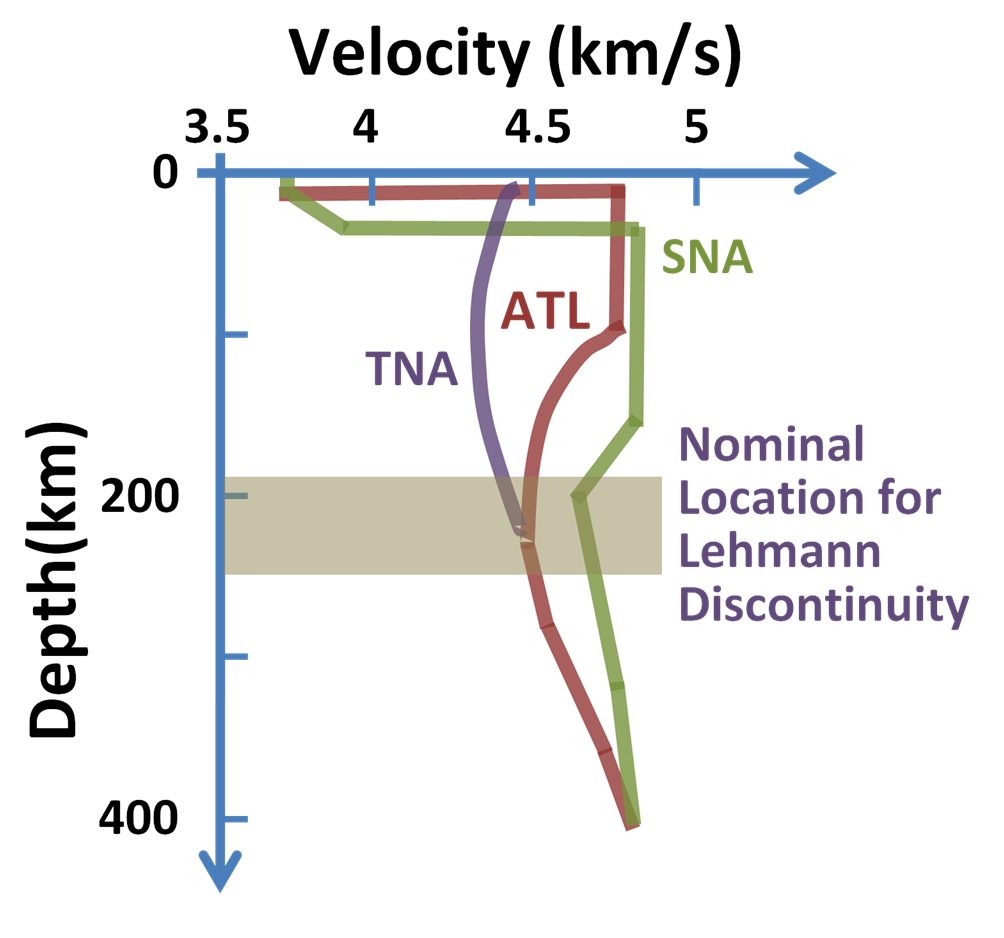 The Lehmann discontinuity is an abrupt increase of ''P''-wave and ''S''-wave velocities at the depth of in
The Lehmann discontinuity is an abrupt increase of ''P''-wave and ''S''-wave velocities at the depth of in
Inge Lehmann
Career highlights of Inge Lehmann from UCLA
Structure of the Earth {{geophysics-stub
Earth's mantle
Earth's mantle is a layer of silicate mineral, silicate rock between the Earth's crust, crust and the Earth's outer core, outer core. It has a mass of and makes up 67% of the mass of Earth. It has a thickness of making up about 46% of Earth's ...
, discovered by seismologist Inge Lehmann
Inge Lehmann (13 May 1888 – 21 February 1993) was a Danish seismologist and geophysicist who is known for her discovery in 1936 of the solid inner core that exists within the molten outer core of the Earth. The seismic discontinuity in the sp ...
. It appears beneath continent
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention (norm), convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single large landmass, a part of a very large landmass, as ...
s, but not usually beneath ocean
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian Ocean, Indian, Southern Ocean ...
s,
and does not readily appear in globally averaged studies. Several explanations have been proposed: a lower limit to the pliable asthenosphere
The asthenosphere () is the mechanically weak and ductile region of the upper mantle of Earth. It lies below the lithosphere, at a depth between c. below the surface, and extends as deep as . However, the lower boundary of the asthenosphere i ...
, a phase transition
In physics, chemistry, and other related fields like biology, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic Sta ...
,
and most plausibly, depth variation in the shear wave
__NOTOC__
In seismology and other areas involving elastic waves, S waves, secondary waves, or shear waves (sometimes called elastic S waves) are a type of elastic wave and are one of the two main types of elastic body waves, so named because t ...
anisotropy
Anisotropy () is the structural property of non-uniformity in different directions, as opposed to isotropy. An anisotropic object or pattern has properties that differ according to direction of measurement. For example, many materials exhibit ve ...
.
Notes
General references
* – some historic background.Further reading
External links
Inge Lehmann
UCLA
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Its academic roots were established in 1881 as a normal school then known as the southern branch of the C ...
Career highlights of Inge Lehmann from UCLA
Structure of the Earth {{geophysics-stub