Latimer Diagram on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
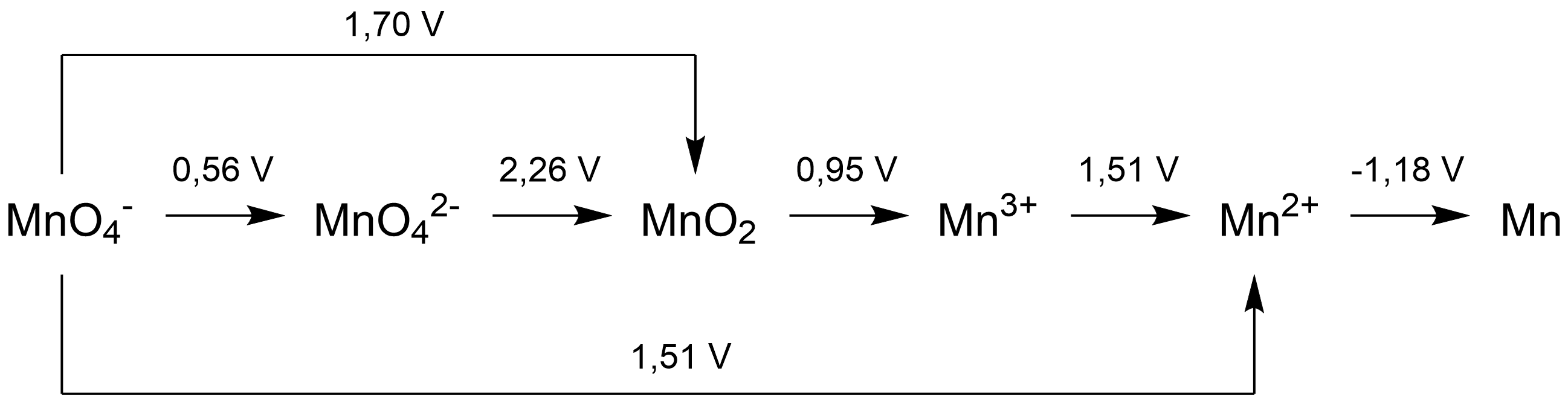 A Latimer diagram of a
A Latimer diagram of a
 The arrow between O2 and H2O2 has a value +0.68 V over it, it indicates that the standard electrode potential for the reaction:
:O2(''g'') + 2H+ + 2''e''− ⇄ H2O2(''aq'')
is 0.68 volts.
The arrow between O2 and H2O2 has a value +0.68 V over it, it indicates that the standard electrode potential for the reaction:
:O2(''g'') + 2H+ + 2''e''− ⇄ H2O2(''aq'')
is 0.68 volts.
o = -n FEo, the electrode potential is a representation of the Gibbs energy change for the given reduction. The sum of the Gibbs energy changes for subsequent reductions (e.g. from O2 to H2O2, then from H2O2 to H2O) is the same as the Gibbs energy change for the overall reduction (i.e. from O2 to H2O), in accordance with Hess's law. This can be used to find the electrode potential for non-adjacent steps, which gives all the information necessary for the Frost diagram.
A simple examination of a Latimer diagram can also indicate if a species will disproportionate in solution under the conditions for which the electrode potentials are given: if the potential to the right of the species is higher than the potential on the left, it will disproportionate. Therefore,
 A Latimer diagram of a
A Latimer diagram of a chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
is a summary of the standard electrode potential
In electrochemistry, standard electrode potential E^\ominus, or E^\ominus_, is a measure of the reducing power of any element or compound. The IUPAC "Gold Book" defines it as: ''"the value of the standard emf (electromotive force) of a cell in wh ...
data of that element. This type of diagram is named after Wendell Mitchell Latimer
Wendell Mitchell Latimer (April 22, 1893 – July 6, 1955) was an American chemist notable for his description of oxidation states in his book "The Oxidation States of the Elements and Their Potentials in Aqueous Solution" ( ASIN B000GRXLSA, ...
, an American chemist.
Construction
In a Latimer diagram, the most highly oxidized form of the element is on the left, with successively lower oxidation states to the right. The species are connected by arrows, and the numerical value of the standard potential (involts
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827).
Defini ...
) for the reduction is written at each arrow. For example, for oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
, the species would be in the order O2 (0), H2O2 (–1), H2O (-2):
: The arrow between O2 and H2O2 has a value +0.68 V over it, it indicates that the standard electrode potential for the reaction:
:O2(''g'') + 2H+ + 2''e''− ⇄ H2O2(''aq'')
is 0.68 volts.
The arrow between O2 and H2O2 has a value +0.68 V over it, it indicates that the standard electrode potential for the reaction:
:O2(''g'') + 2H+ + 2''e''− ⇄ H2O2(''aq'')
is 0.68 volts.
Application
Latimer diagrams can be used in the construction of Frost diagrams, as a concise summary of the standard electrode potentials relative to the element. Since ΔrGhydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3%� ...
is unstable and will disproportionate (see diagram above).
See also
* Frost diagram *Pourbaix diagram
In electrochemistry, and more generally in solution chemistry, a Pourbaix diagram, also known as a potential/pH diagram, EH–pH diagram or a pE/pH diagram, is a plot of possible thermodynamically stable phases (''i.e.'', at chemical equilibrium) ...
* Ellingham diagram
An Ellingham diagram is a graph showing the temperature dependence of the stability of compounds. This analysis is usually used to evaluate the ease of reduction of metal oxides and sulfides. These diagrams were first constructed by Harold Ellin ...
References
* * Electrochemistry Potentials {{electrochem-stub