Languages of Tanzania on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 According to '' Ethnologue'', there are a total of 126
According to '' Ethnologue'', there are a total of 126
 Major languages spoken in Tanzania include:
* Niger-Congo
** Bantu
*** Bemba
*** Bena (592 thousand, 2009)
*** Chaga
*** Digo (166 thousand, 2009)
*** Gogo (1.08 million, 2009)
*** Haya (1.94 million, 2016)
*** Hehe (1.21 million, 2016)
*** Iramba
*** Luguru (404 thousand, 2009)
*** Makonde (1.47 million, 2016)
*** Ngoni
*** Nyakyusa
*** Nyamwezi (1.47 million, 2016)
*** Nyika
*** Pare
*** Rangi (410 thousand, 2007)
*** Safwa (322 thousand, 2009)
*** Sonjo
***
Major languages spoken in Tanzania include:
* Niger-Congo
** Bantu
*** Bemba
*** Bena (592 thousand, 2009)
*** Chaga
*** Digo (166 thousand, 2009)
*** Gogo (1.08 million, 2009)
*** Haya (1.94 million, 2016)
*** Hehe (1.21 million, 2016)
*** Iramba
*** Luguru (404 thousand, 2009)
*** Makonde (1.47 million, 2016)
*** Ngoni
*** Nyakyusa
*** Nyamwezi (1.47 million, 2016)
*** Nyika
*** Pare
*** Rangi (410 thousand, 2007)
*** Safwa (322 thousand, 2009)
*** Sonjo
***
 *
*
Languages of Tanzania
at Ethnologue site.
Map of languages of Tanzania
at Ethnologue {{Tanzania topics

Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands an ...
is a multilingual
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolingual speakers in the world's population. More than half of all ...
country. There are many languages spoken in the country, but no one language is spoken natively by a majority or a large plurality of the population. Swahili and English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
, the latter of which was inherited from colonial rule (''see Tanganyika Territory''), are widely spoken as lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
s. They serve as working languages in the country, with Swahili being the official national language. There are more speakers of Swahili than of English in Tanzania.
Overview
 According to '' Ethnologue'', there are a total of 126
According to '' Ethnologue'', there are a total of 126 language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of ...
s spoken in Tanzania. Two are institutional, 18 are developing, 58 are vigorous, 40 are endangered, and 8 are dying. There are also three languages that recently became extinct.
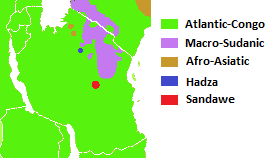
Most languages spoken locally belong to two broad language families: Niger-Congo ( Bantu branch) and Nilo-Saharan
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of African languages spoken by some 50–60 million people, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of the Nile meet. ...
( Nilotic branch), spoken by the country's Bantu and Nilotic
The Nilotic peoples are people indigenous to the Nile Valley who speak Nilotic languages. They inhabit South Sudan, Sudan, Ethiopia, Uganda, Kenya, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania. Among these are the Burun-s ...
populations, respectively. Additionally, the Hadza and Sandawe hunter-gatherers speak languages with click consonant
Click consonants, or clicks, are speech sounds that occur as consonants in many languages of Southern Africa and in three languages of East Africa. Examples familiar to English-speakers are the '' tut-tut'' (British spelling) or '' tsk! tsk!'' ...
s, which have tentatively been classified within the Khoisan
Khoisan , or (), according to the contemporary Khoekhoegowab orthography, is a catch-all term for those indigenous peoples of Southern Africa who do not speak one of the Bantu languages, combining the (formerly "Khoikhoi") and the or ( i ...
phylum (although Hadza may be a language isolate
Language isolates are languages that cannot be classified into larger language families. Korean and Basque are two of the most common examples. Other language isolates include Ainu in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, and Haida in North America. The nu ...
). The Cushitic
The Cushitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken primarily in the Horn of Africa, with minorities speaking Cushitic languages to the north in Egypt and the Sudan, and to the south in Kenya and Tanzania. As ...
and Semitic ethnic minorities speak languages belonging to the separate Afro-Asiatic
The Afroasiatic languages (or Afro-Asiatic), also known as Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic, and sometimes also as Afrasian, Erythraean or Lisramic, are a language family of about 300 languages that are spoken predominantly in the geographic s ...
family, with the Hindustani and British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
residents speaking languages from the Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
family.
Tanzania's various ethnic groups typically speak their mother tongue
A first language, native tongue, native language, mother tongue or L1 is the first language or dialect that a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongu ...
s within their own communities. The two official language
An official language is a language given supreme status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically the term "official language" does not refer to the language used by a people or country, but by its government (e.g. judiciary, ...
s, English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
and Swahili, are used in varying degrees of fluency for communication with other populations. According to the official national linguistic policy announced in 1984, Swahili is the language of the social and political sphere as well as primary and adult education, whereas English is the language of secondary education, universities, technology, and higher courts.J. A. Masebo & N. Nyangwine: ''Nadharia ya lugha Kiswahili 1.'' S. 126, The government announced in 2015 that it would discontinue the use of English as a language of education as part of an overhaul of the Tanzanian schools' system.
Additionally, several Tanzanian sign languages are used.
Language families
Major languages
 Major languages spoken in Tanzania include:
* Niger-Congo
** Bantu
*** Bemba
*** Bena (592 thousand, 2009)
*** Chaga
*** Digo (166 thousand, 2009)
*** Gogo (1.08 million, 2009)
*** Haya (1.94 million, 2016)
*** Hehe (1.21 million, 2016)
*** Iramba
*** Luguru (404 thousand, 2009)
*** Makonde (1.47 million, 2016)
*** Ngoni
*** Nyakyusa
*** Nyamwezi (1.47 million, 2016)
*** Nyika
*** Pare
*** Rangi (410 thousand, 2007)
*** Safwa (322 thousand, 2009)
*** Sonjo
***
Major languages spoken in Tanzania include:
* Niger-Congo
** Bantu
*** Bemba
*** Bena (592 thousand, 2009)
*** Chaga
*** Digo (166 thousand, 2009)
*** Gogo (1.08 million, 2009)
*** Haya (1.94 million, 2016)
*** Hehe (1.21 million, 2016)
*** Iramba
*** Luguru (404 thousand, 2009)
*** Makonde (1.47 million, 2016)
*** Ngoni
*** Nyakyusa
*** Nyamwezi (1.47 million, 2016)
*** Nyika
*** Pare
*** Rangi (410 thousand, 2007)
*** Safwa (322 thousand, 2009)
*** Sonjo
***Sukuma Sukuma may refer to:
*the Sukuma people
*the Sukuma language
Sukuma is a Bantu language of Tanzania, spoken in an area southeast of Lake Victoria between Mwanza, Shinyanga, and Lake Eyasi.
Its orthography uses Roman script without special letter ...
(8.13 million, 2016)
*** Swahili
***Tongwe language
Tongwe (''Sitongwe'') and Bende (''Sibende'') constitute a clade of Bantu language
The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀) are a large family of languages spoken by the Bantu people of Central, Southern, Eastern africa and ...
*** Tumbuka
*** Turu
***Vidunda language
Vidunda (''Chividunda'') is a Bantu language spoken along the north bank of the Ruaha River in Tanzania. It belongs to the Ruvu branch of Northeast Coast Bantu
The Northeast Coast Bantu languages are the Bantu languages spoken along the coast ...
*** Yao (630 thousand, 2016)
***Zanaki
***Kerewe
***Nyaturu
***Nyambo
***Gweno
***Kilindi
***Nyamwezi
*Nilo-Saharan
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of African languages spoken by some 50–60 million people, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of the Nile meet. ...
**Nilotic
The Nilotic peoples are people indigenous to the Nile Valley who speak Nilotic languages. They inhabit South Sudan, Sudan, Ethiopia, Uganda, Kenya, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania. Among these are the Burun-s ...
*** Datooga
*** Kisankasa
***Maasai Maasai may refer to:
*Maasai people
The Maasai (; sw, Wamasai) are a Nilotic ethnic group inhabiting northern, central and southern Kenya and northern Tanzania. They are among the best-known local populations internationally due to their r ...
(682 thousand, 2016)
*** Ngasa
*** Ogiek
*** Luo (185 thousand, 2009)
*** Zinza language
*** Sambaa language (660 thousand (2001))
Minor languages
Languages spoken by the country's ethnic minorities include: *
*Khoisan
Khoisan , or (), according to the contemporary Khoekhoegowab orthography, is a catch-all term for those indigenous peoples of Southern Africa who do not speak one of the Bantu languages, combining the (formerly "Khoikhoi") and the or ( i ...
** Khoe
*** Hadza (possibly a language isolate
Language isolates are languages that cannot be classified into larger language families. Korean and Basque are two of the most common examples. Other language isolates include Ainu in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, and Haida in North America. The nu ...
)
*** Sandawe (possibly a language isolate
Language isolates are languages that cannot be classified into larger language families. Korean and Basque are two of the most common examples. Other language isolates include Ainu in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, and Haida in North America. The nu ...
)
*Afro-Asiatic
The Afroasiatic languages (or Afro-Asiatic), also known as Hamito-Semitic, or Semito-Hamitic, and sometimes also as Afrasian, Erythraean or Lisramic, are a language family of about 300 languages that are spoken predominantly in the geographic s ...
**Cushitic
The Cushitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken primarily in the Horn of Africa, with minorities speaking Cushitic languages to the north in Egypt and the Sudan, and to the south in Kenya and Tanzania. As ...
*** Alagwa
*** Burunge
*** Gorowa
*** Iraqw
** Semitic
***Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
*Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
** Indo-Iranian
*** Gujarati
*** Hindustani
*** Kutchi
** Germanic
***English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
*** German
** Romance
*** French
*** Portuguese
MERU LANGUAGE
Extinct languages
Asa languageSee also
*Languages of Africa
The languages of Africa are divided into several major language families:
* Niger–Congo or perhaps Atlantic–Congo languages (includes Bantu and non-Bantu, and possibly Mande and others) are spoken in West, Central, Southeast and Southe ...
References
Further reading
*Nurse, D. and Philippson, G. (2019). CLDF dataset derived from Nurse and Philippson's "Tanzania Language Survey" from 1975 (Version v3.0) ata set Zenodo.External links
Languages of Tanzania
at Ethnologue site.
Map of languages of Tanzania
at Ethnologue {{Tanzania topics