Languages of Maldives on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Maldives (, ; dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖެ, translit=Dhivehi Raajje, ), officially the Republic of Maldives ( dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖޭގެ ޖުމްހޫރިއްޔާ, translit=Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaa, label=none, ), is an archipelagic state located in


 In 1558, the Portuguese established a small garrison with a (), or overseer of a
In 1558, the Portuguese established a small garrison with a (), or overseer of a  In the British period, the Sultan's powers were taken over by the Chief Minister, much to the chagrin of the British Governor-General who continued to deal with the ineffectual Sultan. Consequently, Britain encouraged the development of a
In the British period, the Sultan's powers were taken over by the Chief Minister, much to the chagrin of the British Governor-General who continued to deal with the ineffectual Sultan. Consequently, Britain encouraged the development of a  Beginning in the 1950s, the political history in the Maldives was largely influenced by the British military presence on the islands. In 1954, the restoration of the sultanate perpetuated the rule of the past. Two years later, the United Kingdom obtained permission to reestablish its wartime
Beginning in the 1950s, the political history in the Maldives was largely influenced by the British military presence on the islands. In 1954, the restoration of the sultanate perpetuated the rule of the past. Two years later, the United Kingdom obtained permission to reestablish its wartime
 When the British became increasingly unable to continue their colonial hold on Asia and were losing their colonies to the indigenous populations who wanted freedom, on 26 July 1965 an agreement was signed on behalf of the Sultan by Ibrahim Nasir Rannabandeyri Kilegefan, Prime Minister, and on behalf of the British government by Sir Michael Walker, British Ambassador-designate to the Maldive Islands, which formally ended the British authority on the defence and external affairs of the Maldives. The islands thus achieved independence, with the ceremony taking place at the British High Commissioner's Residence in
When the British became increasingly unable to continue their colonial hold on Asia and were losing their colonies to the indigenous populations who wanted freedom, on 26 July 1965 an agreement was signed on behalf of the Sultan by Ibrahim Nasir Rannabandeyri Kilegefan, Prime Minister, and on behalf of the British government by Sir Michael Walker, British Ambassador-designate to the Maldive Islands, which formally ended the British authority on the defence and external affairs of the Maldives. The islands thus achieved independence, with the ceremony taking place at the British High Commissioner's Residence in
. ''Brown Political Review''. Retrieved on 10 May 2016. In 2008, a new constitution was approved and the Maldivian presidential election, 2008, first direct presidential elections occurred, which were won by Nasheed in the second round. His administration faced many challenges, including the huge debt left by the previous government, the economic downturn following the 2004 tsunami, overspending by means of overprinting of local currency (the rufiyaa), unemployment, corruption, and increasing drug use. Taxation on goods was imposed for the first time in the country, and import duties were reduced on many goods and services. Universal health insurance (Aasandha) and social welfare benefits were given to those aged 65 years or older, single parents, and those with special needs. Social and 2011–12 Maldives political crisis, political unrest grew in late 2011, following opposition campaigns in the name of protecting Islam. Nasheed controversially resigned from office after large number of police and army mutinied in February 2012. Nasheed's vice president, Mohammed Waheed Hassan, was sworn in as president. Nasheed was later arrested, convicted of terrorism, and sentenced to 13 years. The trial was widely seen as flawed and political. The UN Working Group on Arbitrary Detention called for Nasheed's immediate release. The Maldivian presidential election, 2013, elections in late 2013 were highly contested. Former president Nasheed won the most votes in the first round, but the Supreme Court annulled it despite the positive assessment of international election observers. In the re-run vote Abdulla Yameen, half-brother of the former president Maumoon, assumed the presidency. Yameen survived an assassination attempt in late 2015. Vice president Ahmed Adeeb was later arrested together with 17 supporters for "public order offences" and the government instituted a broader crackdown against his accomplices. A state of emergency was later declared ahead of a planned anti-government rally, and the people's Majlis accelerated the removal of Adeeb. 2018 Maldivian presidential election, In the 2018 elections, Ibrahim Mohamed Solih won the most votes, and was sworn in as the Maldives' new president in November 2018. Adeeb was freed by courts in Male in July 2019 after his conviction on charges of terrorism and corruption was overruled, but was placed under a travel ban after the state prosecutor appealed the order in a corruption and money laundering case. Adeeb escaped in a tugboat to seek asylum in India. It is understood that the Indian Coast Guard escorted the tugboat to the International Maritime Boundary Line (IMBL) and he was then "transferred" to a Maldivian Coast Guard ship, where officials took him into custody. Former president Abdulla Yameen was sentenced to five years in prison in November 2019 for money laundering. The High Court upheld the jail sentence in January 2021. However, Supreme Court overturned Yameen's conviction in November 2021.
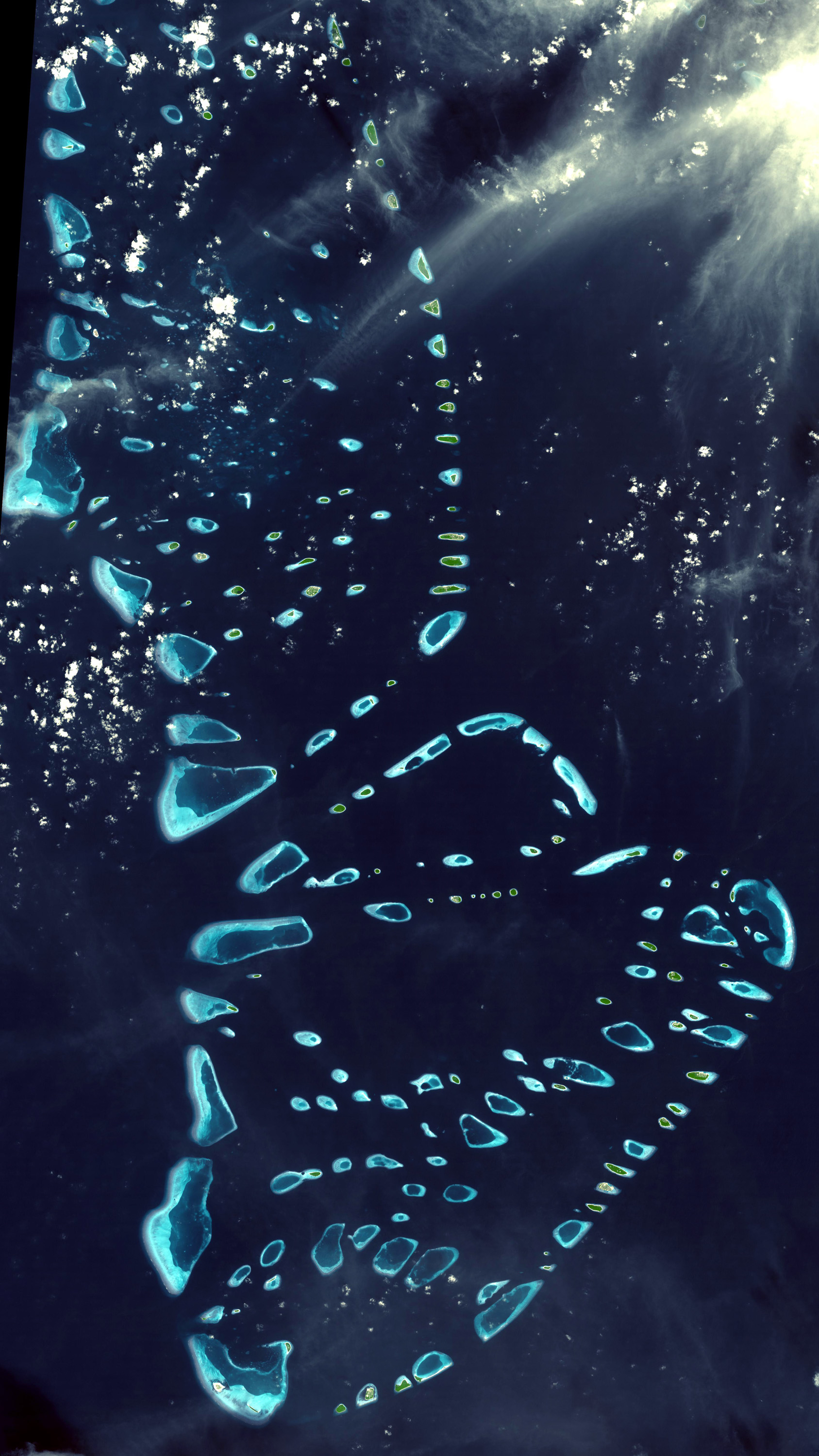

 The Maldives consists of 1,192 coral islands grouped in a double chain of 26
The Maldives consists of 1,192 coral islands grouped in a double chain of 26
 The Maldives has a tropical monsoon climate (Am) under the Köppen climate classification, which is affected by the large landmass of South Asia to the north. Because the Maldives has the lowest elevation of any country in the world, the temperature is constantly hot and often humid. The presence of this landmass causes differential heating of land and water. These factors set off a rush of moisture-rich air from the Indian Ocean over South Asia, resulting in the southwest monsoon. Two seasons dominate Maldives' weather: the dry season associated with the winter northeastern monsoon and the rainy season associated with the southwest monsoon which brings strong winds and storms.
The shift from the dry northeast monsoon to the moist southwest monsoon occurs during April and May. During this period, the southwest winds contribute to the formation of the southwest monsoon, which reaches Maldives at the beginning of June and lasts until the end of November. However, the weather patterns of Maldives do not always conform to the monsoon patterns of South Asia. The annual rainfall averages in the north and in the south.
The monsoonal influence is greater in the north of the Maldives than in the south, more influenced by the Equatorial Counter Current, equatorial currents.
The average high temperature is 31.5 degrees Celsius and the average low temperature is 26.4 degrees Celsius.
The Maldives has a tropical monsoon climate (Am) under the Köppen climate classification, which is affected by the large landmass of South Asia to the north. Because the Maldives has the lowest elevation of any country in the world, the temperature is constantly hot and often humid. The presence of this landmass causes differential heating of land and water. These factors set off a rush of moisture-rich air from the Indian Ocean over South Asia, resulting in the southwest monsoon. Two seasons dominate Maldives' weather: the dry season associated with the winter northeastern monsoon and the rainy season associated with the southwest monsoon which brings strong winds and storms.
The shift from the dry northeast monsoon to the moist southwest monsoon occurs during April and May. During this period, the southwest winds contribute to the formation of the southwest monsoon, which reaches Maldives at the beginning of June and lasts until the end of November. However, the weather patterns of Maldives do not always conform to the monsoon patterns of South Asia. The annual rainfall averages in the north and in the south.
The monsoonal influence is greater in the north of the Maldives than in the south, more influenced by the Equatorial Counter Current, equatorial currents.
The average high temperature is 31.5 degrees Celsius and the average low temperature is 26.4 degrees Celsius.

 The Maldives have a range of different habitats including deep sea, shallow coast, and reef ecosystems, fringing mangroves, wetlands and dry land. There are 187 species of coral forming the coral reefs. This area of the Indian Ocean, alone, houses 1,100 species of fish, 5 species of sea turtle, 21 species of whale and dolphin, 400 species of mollusc, and 83 species of echinoderms. The area is also populated by a number of crustacean species: 120 copepods, 15 amphipods, as well as more than 145 crab and 48 shrimp species.
Among the many marine families represented are pufferfish, Caesionidae, fusiliers, Carangidae, jackfish, lionfish, oriental sweetlips, reef sharks, groupers, eels, Lutjanidae, snappers, bannerfish, Ogcocephalidae, batfish, humphead wrasse, spotted eagle rays, scorpionfish, lobsters, nudibranches, Pomacanthidae, angelfish, butterflyfish, squirrelfish, soldierfish, Asiatic glassfish, glassfish, surgeonfish, Naso (fish), unicornfish, triggerfish, Napoleon wrasse, and barracuda.
These coral reefs are home to a variety of marine ecosystems that vary from planktonic organisms to whale sharks. Sponges have gained importance as five species have displayed anti-tumor and anti-cancer properties.
In 1998, sea-temperature warming of as much as due to a single El Niño-Southern Oscillation, El Niño phenomenon event caused coral bleaching, killing two-thirds of the nation's coral reefs.
In an effort to induce the regrowth of the reefs, scientists placed electrified cones anywhere from below the surface to provide a substrate for larval coral attachment. In 2004, scientists witnessed corals regenerating. Corals began to eject pink-orange eggs and sperm. The growth of these electrified corals was five times faster than untreated corals. Scientist Azeez Hakim stated:
Again, in 2016, the coral reefs of the Maldives experienced a Coral bleaching#Maldives, severe bleaching incident. Up to 95% of coral around some islands have died, and, even after six months, 100% of young coral transplants died. The surface water temperatures reached an all-time high in 2016, at 31 degrees Celsius in May.
Recent scientific studies suggest that the faunistic composition can vary greatly between neighbour atolls, especially in terms of benthic fauna. Differences in terms of fishing pressure (including poaching) could be the cause.
The Maldives have a range of different habitats including deep sea, shallow coast, and reef ecosystems, fringing mangroves, wetlands and dry land. There are 187 species of coral forming the coral reefs. This area of the Indian Ocean, alone, houses 1,100 species of fish, 5 species of sea turtle, 21 species of whale and dolphin, 400 species of mollusc, and 83 species of echinoderms. The area is also populated by a number of crustacean species: 120 copepods, 15 amphipods, as well as more than 145 crab and 48 shrimp species.
Among the many marine families represented are pufferfish, Caesionidae, fusiliers, Carangidae, jackfish, lionfish, oriental sweetlips, reef sharks, groupers, eels, Lutjanidae, snappers, bannerfish, Ogcocephalidae, batfish, humphead wrasse, spotted eagle rays, scorpionfish, lobsters, nudibranches, Pomacanthidae, angelfish, butterflyfish, squirrelfish, soldierfish, Asiatic glassfish, glassfish, surgeonfish, Naso (fish), unicornfish, triggerfish, Napoleon wrasse, and barracuda.
These coral reefs are home to a variety of marine ecosystems that vary from planktonic organisms to whale sharks. Sponges have gained importance as five species have displayed anti-tumor and anti-cancer properties.
In 1998, sea-temperature warming of as much as due to a single El Niño-Southern Oscillation, El Niño phenomenon event caused coral bleaching, killing two-thirds of the nation's coral reefs.
In an effort to induce the regrowth of the reefs, scientists placed electrified cones anywhere from below the surface to provide a substrate for larval coral attachment. In 2004, scientists witnessed corals regenerating. Corals began to eject pink-orange eggs and sperm. The growth of these electrified corals was five times faster than untreated corals. Scientist Azeez Hakim stated:
Again, in 2016, the coral reefs of the Maldives experienced a Coral bleaching#Maldives, severe bleaching incident. Up to 95% of coral around some islands have died, and, even after six months, 100% of young coral transplants died. The surface water temperatures reached an all-time high in 2016, at 31 degrees Celsius in May.
Recent scientific studies suggest that the faunistic composition can vary greatly between neighbour atolls, especially in terms of benthic fauna. Differences in terms of fishing pressure (including poaching) could be the cause.
 Maldives is a presidential system, presidential republic, constitutional republic, with extensive influence of the president as head of government and head of state. The president heads the Executive (government), executive branch, and appoints the Cabinet of the Maldives, cabinet which is approved by the Majlis of the Maldives, People's Majlis (Parliament). He leads the Maldives National Defence Force, armed forces. The current president as of 19 October 2021 is Ibrahim Mohamed Solih. President and Members of the Unicameralism, unicameral Majlis serve five-year terms, with the total number of members determined by atoll populations. At the Maldivian parliamentary election, 2014, 2014 election, 77 members were elected. The People's Majlis, located in
Maldives is a presidential system, presidential republic, constitutional republic, with extensive influence of the president as head of government and head of state. The president heads the Executive (government), executive branch, and appoints the Cabinet of the Maldives, cabinet which is approved by the Majlis of the Maldives, People's Majlis (Parliament). He leads the Maldives National Defence Force, armed forces. The current president as of 19 October 2021 is Ibrahim Mohamed Solih. President and Members of the Unicameralism, unicameral Majlis serve five-year terms, with the total number of members determined by atoll populations. At the Maldivian parliamentary election, 2014, 2014 election, 77 members were elected. The People's Majlis, located in
 The Maldives National Defence Force is the combined security organisation responsible for defending the security and sovereignty of the Maldives, having the primary task of being responsible for attending to all internal and external security needs of the Maldives, including the protection of the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and the maintenance of peace and security. The MNDF component branches are the Coast Guard, Marine Corps, Special Forces, Service Corps, Defence Intelligence Service, Military Police, Corps of Engineers, Special Protection Group, Medical Corps, Adjutant General's Corps, Coast Guard Aviation Squadron, and the Fire and Rescue Service. The Maldives has an arrangement with India allowing cooperation on radar coverage.
As a water-bound nation, much of its security concerns lie at sea. Almost 99% of the country is covered by sea and the remaining 1% land is scattered over an area of × , with the largest island being not more than . Therefore, the duties assigned to the MNDF of maintaining surveillance over Maldives' waters and providing protection against foreign intruders poaching in the EEZ and territorial waters, are immense tasks from both logistical and economic viewpoints.
The Coast Guard plays a vital role in carrying out these functions. To provide timely security its patrol boats are stationed at various MNDF Regional Headquarters. The Coast Guard is also assigned to respond to the maritime distress calls and to conduct search and rescue operations in a timely manner.
In 2019, Maldives signed the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
The Maldives National Defence Force is the combined security organisation responsible for defending the security and sovereignty of the Maldives, having the primary task of being responsible for attending to all internal and external security needs of the Maldives, including the protection of the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and the maintenance of peace and security. The MNDF component branches are the Coast Guard, Marine Corps, Special Forces, Service Corps, Defence Intelligence Service, Military Police, Corps of Engineers, Special Protection Group, Medical Corps, Adjutant General's Corps, Coast Guard Aviation Squadron, and the Fire and Rescue Service. The Maldives has an arrangement with India allowing cooperation on radar coverage.
As a water-bound nation, much of its security concerns lie at sea. Almost 99% of the country is covered by sea and the remaining 1% land is scattered over an area of × , with the largest island being not more than . Therefore, the duties assigned to the MNDF of maintaining surveillance over Maldives' waters and providing protection against foreign intruders poaching in the EEZ and territorial waters, are immense tasks from both logistical and economic viewpoints.
The Coast Guard plays a vital role in carrying out these functions. To provide timely security its patrol boats are stationed at various MNDF Regional Headquarters. The Coast Guard is also assigned to respond to the maritime distress calls and to conduct search and rescue operations in a timely manner.
In 2019, Maldives signed the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
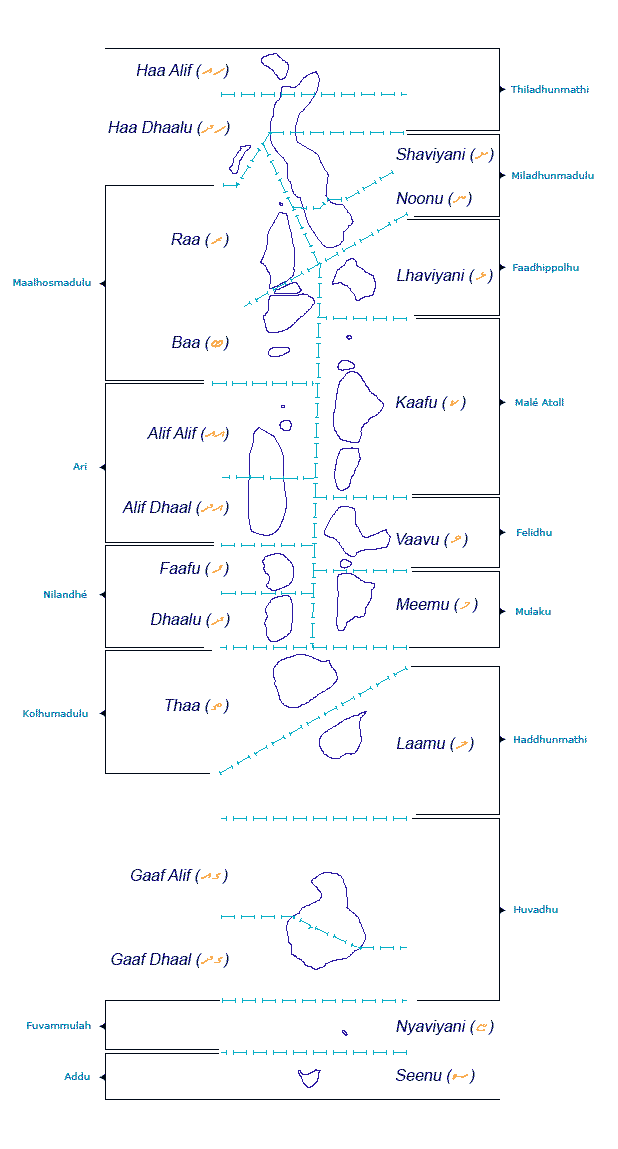 The Maldives has twenty-six natural Atolls of the Maldives, atolls and few island groups on isolated reefs, all of which have been divided into twenty-one administrative divisions (17 administrative atolls and cities of
The Maldives has twenty-six natural Atolls of the Maldives, atolls and few island groups on isolated reefs, all of which have been divided into twenty-one administrative divisions (17 administrative atolls and cities of

 Historically, the Maldives provided enormous quantities of cowry shells, history of money, an international currency of the early ages. From the 2nd century CE, the islands were known as the 'Money Isles' by the Arabs. ''Monetaria moneta'' were used for centuries as a currency in Africa, and huge amounts of Maldive Islands, Maldivian cowries were introduced into Africa by western nations during the period of slave trade. The cowry is now the symbol of the Maldives Monetary Authority.
In the early 1970s, the Maldives was one of the world's 20 poorest countries, with a population of 100,000. The economy at the time was largely dependent on fisheries and trading local goods such as
Historically, the Maldives provided enormous quantities of cowry shells, history of money, an international currency of the early ages. From the 2nd century CE, the islands were known as the 'Money Isles' by the Arabs. ''Monetaria moneta'' were used for centuries as a currency in Africa, and huge amounts of Maldive Islands, Maldivian cowries were introduced into Africa by western nations during the period of slave trade. The cowry is now the symbol of the Maldives Monetary Authority.
In the early 1970s, the Maldives was one of the world's 20 poorest countries, with a population of 100,000. The economy at the time was largely dependent on fisheries and trading local goods such as
 The Maldives remained largely unknown to tourists until the early 1970s. Only 189 islands are home to its 447,137 inhabitants. The other islands are used entirely for economic purposes, of which tourism and agriculture are the most dominant.
The Maldives remained largely unknown to tourists until the early 1970s. Only 189 islands are home to its 447,137 inhabitants. The other islands are used entirely for economic purposes, of which tourism and agriculture are the most dominant.  According to the Ministry of Tourism (Maldives), Ministry of Tourism, the emergence of tourism in 1972 transformed the economy, moving rapidly from dependence on fisheries to tourism. In just three and a half decades, the industry became the main source of income. Tourism was also the country's biggest foreign currency earner and the single largest contributor to the GDP. , 89 resorts in the Maldives offered over 17,000 beds and hosted over 600,000 tourists annually. In 2019, over 1.7 million visitors came to the islands.
The number of resorts increased from 2 to 92 between 1972 and 2007. , over 8,380,000 tourists had visited Maldives.
The country has List of mosques in the Maldives, six heritage Maldivian coral mosques listed as UNESCO tentative sites.
According to the Ministry of Tourism (Maldives), Ministry of Tourism, the emergence of tourism in 1972 transformed the economy, moving rapidly from dependence on fisheries to tourism. In just three and a half decades, the industry became the main source of income. Tourism was also the country's biggest foreign currency earner and the single largest contributor to the GDP. , 89 resorts in the Maldives offered over 17,000 beds and hosted over 600,000 tourists annually. In 2019, over 1.7 million visitors came to the islands.
The number of resorts increased from 2 to 92 between 1972 and 2007. , over 8,380,000 tourists had visited Maldives.
The country has List of mosques in the Maldives, six heritage Maldivian coral mosques listed as UNESCO tentative sites.
 For many centuries the Maldivian economy was entirely dependent on fishing and other ocean, marine products. Fishing remains the main occupation of the people and the government gives priority to the fisheries sector.
The mechanisation of the traditional fishing boat called ''Dhoni (fishing vessel), dhoni'' in 1974 was a major milestone in the development of the fisheries industry. A fish canning plant was installed on Felivaru in 1977, as a joint venture with a Japanese firm. In 1979, a Fisheries Advisory Board was set up with the mandate of advising the government on policy guidelines for the overall development of the fisheries sector. Manpower development programmes began in the early 1980s, and fisheries education was incorporated into the school curriculum. Fish aggregating devices and navigational aids were located at various strategic points. Moreover, the opening up of the exclusive economic zone (EEZ) of the Maldives for fisheries has further enhanced the growth of the fisheries sector.
, fisheries contributed over 15% of the country's GDP and engaged about 30% of the country's workforce. Fisheries were also the second-largest foreign exchange earner after #Tourism, tourism.
For many centuries the Maldivian economy was entirely dependent on fishing and other ocean, marine products. Fishing remains the main occupation of the people and the government gives priority to the fisheries sector.
The mechanisation of the traditional fishing boat called ''Dhoni (fishing vessel), dhoni'' in 1974 was a major milestone in the development of the fisheries industry. A fish canning plant was installed on Felivaru in 1977, as a joint venture with a Japanese firm. In 1979, a Fisheries Advisory Board was set up with the mandate of advising the government on policy guidelines for the overall development of the fisheries sector. Manpower development programmes began in the early 1980s, and fisheries education was incorporated into the school curriculum. Fish aggregating devices and navigational aids were located at various strategic points. Moreover, the opening up of the exclusive economic zone (EEZ) of the Maldives for fisheries has further enhanced the growth of the fisheries sector.
, fisheries contributed over 15% of the country's GDP and engaged about 30% of the country's workforce. Fisheries were also the second-largest foreign exchange earner after #Tourism, tourism.
 The largest ethnic group is Dhivehis, Dhivehin, i.e. the Maldivians, native to the historic region of the Maldive Islands comprising today's Republic of Maldives and the island of
The largest ethnic group is Dhivehis, Dhivehin, i.e. the Maldivians, native to the historic region of the Maldive Islands comprising today's Republic of Maldives and the island of
 The official and common language is Dhivehi language, Dhivehi, an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language closely related to the Sinhala language of Sri Lanka. The first known script used to write Dhivehi is the ''eveyla akuru'' script, which is found in the historical recording of kings (''raadhavalhi''). Later a script called ''dhives akuru'' was used for a long period. The present-day script is called Thaana and is written from right to left. Thaana is said to have been introduced by the reign of Muhammad Thakurufaanu Al Auzam, Mohamed Thakurufaanu.
English is widely spoken by the locals of the Maldives: "Following the nation's opening to the outside world, the introduction of English as a medium of instruction at the secondary and tertiary levels of education, and its government's recognition of the opportunities offered through tourism, English has now firmly established itself in the country. As such, the Maldives are quite similar to the countries in the Gulf region .... The nation is undergoing vast societal change, and English is part of this."
The official and common language is Dhivehi language, Dhivehi, an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language closely related to the Sinhala language of Sri Lanka. The first known script used to write Dhivehi is the ''eveyla akuru'' script, which is found in the historical recording of kings (''raadhavalhi''). Later a script called ''dhives akuru'' was used for a long period. The present-day script is called Thaana and is written from right to left. Thaana is said to have been introduced by the reign of Muhammad Thakurufaanu Al Auzam, Mohamed Thakurufaanu.
English is widely spoken by the locals of the Maldives: "Following the nation's opening to the outside world, the introduction of English as a medium of instruction at the secondary and tertiary levels of education, and its government's recognition of the opportunities offered through tourism, English has now firmly established itself in the country. As such, the Maldives are quite similar to the countries in the Gulf region .... The nation is undergoing vast societal change, and English is part of this."
 The culture of the Maldives is influenced by the cultures of the people of different ethnicities who have settled on the islands throughout the times.
Since the 12th century AD, there were also influences from Arabia in the language and culture of the Maldives because of the conversion to Islam and its location as a crossroads in the central Indian Ocean. This was due to the long trading history between the far east and the middle east.
Reflective of this is the fact that the Maldives has had the highest national divorce rate in the world for many decades. This, it is hypothesised, is due to a combination of liberal Islamic rules about divorce and the relatively loose marital bonds that have been identified as common in non- and semi-sedentary peoples without a history of fully developed agrarian property and kinship relations.
The culture of the Maldives is influenced by the cultures of the people of different ethnicities who have settled on the islands throughout the times.
Since the 12th century AD, there were also influences from Arabia in the language and culture of the Maldives because of the conversion to Islam and its location as a crossroads in the central Indian Ocean. This was due to the long trading history between the far east and the middle east.
Reflective of this is the fact that the Maldives has had the highest national divorce rate in the world for many decades. This, it is hypothesised, is due to a combination of liberal Islamic rules about divorce and the relatively loose marital bonds that have been identified as common in non- and semi-sedentary peoples without a history of fully developed agrarian property and kinship relations.
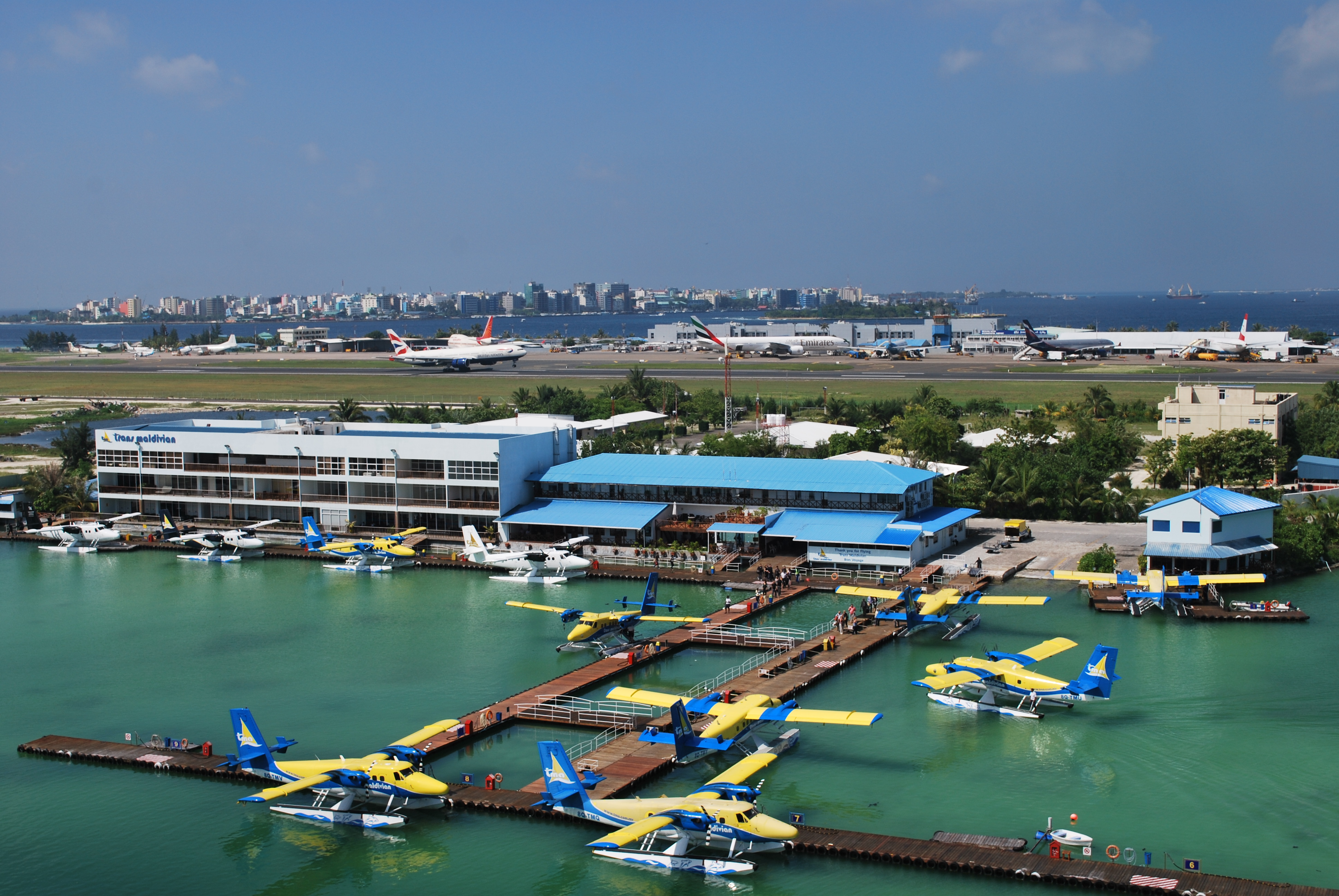
 Velana International Airport is the principal gateway to the Maldives; it is near the capital city
Velana International Airport is the principal gateway to the Maldives; it is near the capital city
The Perils of Rising Fundamentalism in the Maldives
'', International Relations and Security Network (ISN), Zürich, September 2013 * Djan Sauerborn,
Failing to Transition: Democratization under Stress in the Maldives
', South Asia Democratic Forum (SADF), February 2015
Official tourist information
President's Office
Maldives
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Maldives
from UCB Libraries GovPubs *
Maldives
from the BBC News *
Key Development Forecasts for the Maldives
from International Futures
Constitution of the Republic of Maldives
{{Authority control Maldives, 1965 establishments in Asia Archipelagoes of the Indian Ocean Countries in Asia Island countries Island countries of the Indian Ocean Landforms of South Asia Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation Member states of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation Member states of the United Nations Republics Republics in the Commonwealth of Nations Small Island Developing States South Asian countries States and territories established in 1965 Former least developed countries Western Indo-Pacific Former kingdoms Former sultanates Former protectorates
South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
, situated in the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by t ...
. It lies southwest of Sri Lanka and India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, about from the Asian continent's mainland. The chain of 26 atolls stretches across the equator from Ihavandhippolhu Atoll in the north to Addu Atoll in the south.
Comprising a territory spanning roughly including the sea, land area of all the islands comprises , Maldives is one of the world's most geographically dispersed sovereign state
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defined te ...
s and the smallest Asian country as well as one of the smallest Muslim-majority countries
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. In ...
by land area and, with around 557,751 inhabitants, the 2nd least populous country in Asia. Malé
Malé (, ; dv, މާލެ) is the capital and most populous city of the Maldives. With a population of 252,768 and an area of , it is also one of the most densely populated cities in the world. The city is geographically located at the southern ...
is the capital and the most populated city, traditionally called the "King's Island" where the ancient royal dynasties ruled for its central location.
The Maldivian Archipelago is located on the Chagos–Laccadive Ridge
The Chagos–Laccadive Ridge (CLR), also known as the Chagos–Laccadive Plateau, is a prominent volcanic ridge and oceanic plateau extending between the Northern and the Central Indian Ocean.
Extending from 10°S to 15°N, the CLR include ...
, a vast submarine mountain range in the Indian Ocean; this also forms a terrestrial ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of l ...
, together with the Chagos Archipelago
The Chagos Archipelago () or Chagos Islands (formerly the Bassas de Chagas, and later the Oil Islands) is a group of seven atolls comprising more than 60 islands in the Indian Ocean about 500 kilometres (310 mi) south of the Maldives arch ...
and Lakshadweep
Lakshadweep (), also known as Laccadives (), is a union territory of India. It is an archipelago of 36 islands in the Arabian sea, located off the Malabar Coast.
The name ''Lakshadweep'' means "one lakh islands" in Sanskrit, though the Lac ...
. With an average ground-level elevation of above sea level, and a highest natural point of only 2.4 meters, it is the world's lowest-lying country. (Note that some sources state the highest point, Mount Villingili, as 5.1 meters)
In the 12th century Islam reached the Maldivian Archipelago, which was consolidated as a sultanate
This article includes a list of successive Islamic states and Muslim dynasties beginning with the time of the Islamic prophet Muhammad (570–632 CE) and the early Muslim conquests that spread Islam outside of the Arabian Peninsula, and continuin ...
, developing strong commercial and cultural ties with Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. From the mid-16th century, the region came under the increasing influence of European colonial powers
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose their relig ...
, with Maldives becoming a British protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its int ...
in 1887. Independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the statu ...
from the United Kingdom came in 1965, and a presidential republic
A presidential system, or single executive system, is a form of government in which a head of government, typically with the title of president, leads an executive branch that is separate from the legislative branch in systems that use separation ...
was established in 1968 with an elected People's Majlis. The ensuing decades have seen political instability, efforts at democratic reform, and environmental challenges posed by climate change and rising sea levels.
Maldives became a founding member of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is the regional intergovernmental organization and geopolitical union of states in South Asia. Its member states are Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan ...
(SAARC). It is also a member of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
, the Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the ...
, the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose.
The word is derived from ...
, and the Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 120 countries that are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. After the United Nations, it is the largest grouping of states worldwide.
The movement originated in the aftermath o ...
. The World Bank classifies the Maldives as having an upper-middle income
The middle class refers to a class of people in the middle of a social hierarchy, often defined by occupation, income, education, or social status. The term has historically been associated with modernity, capitalism and political debate. Comm ...
economy. Fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from stocked bodies of water such as ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques inclu ...
has historically been the dominant economic activity, and remains the largest sector by far, followed by the rapidly growing tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism mor ...
industry. The Maldives rates "high" on the Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, wh ...
, with ''per capita
''Per capita'' is a Latin phrase literally meaning "by heads" or "for each head", and idiomatically used to mean "per person". The term is used in a wide variety of social sciences and statistical research contexts, including government statistic ...
'' income significantly higher than other SAARC nations.
Maldives was a member of the Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the ...
from July 1982 until withdrawing from the organisation in October 2016 in protest of allegations by other nations of its human rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
abuses and failing democracy. Maldives rejoined the Commonwealth on 1 February 2020 after showing evidence of functioning democratic processes and popular support.
Etymology
According to legends, the first settlers of Maldives were people known as Dheyvis. The first Kingdom of the Maldives was known as Dheeva Maari. During the 3rd century BCE visit of emissaries, it was noted that the Maldives was known as Dheeva Mahal. During c. 1100 – 1166, Maldives was also referred to as Diva Kudha and the Laccadive archipelago which was a part of Maldives was then referred to as Diva Kanbar by the scholar and polymathal-Biruni
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (973 – after 1050) commonly known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian in scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously the "founder of Indology", "Father of Co ...
(973–1048).
The name ''Maldives'' may also derive from Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
' (garland) and ' (island), or ''Maala Divaina'' ("Necklace Islands") in Sinhala. The Maldivian people are called ''Dhivehin''. The word ''Dheeb/Deeb'' (archaic ''Dhivehi'', related to Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
, ') means "island", and ''Dhives'' (''Dhivehin'') means "islanders" (i.e., Maldivians). In Tamil, "Garland of Islands" can be translated as ' ().
The ancient Sri Lankan chronicle '' Mahawamsa'' refers to an island called ''Mahiladiva'' ("Island of Women", महिलादिभ) in Pali
Pali () is a Middle Indo-Aryan liturgical language native to the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pāli Canon'' or '' Tipiṭaka'' as well as the sacred language of '' Theravāda'' Buddh ...
, which is probably a mistranslation of the same Sanskrit word meaning "garland
A garland is a decorative braid, knot or wreath of flowers, leaves, or other material. Garlands can be worn on the head or around the neck, hung on an inanimate object, or laid in a place of cultural or religious importance.
Etymology
From the ...
".
Jan Hogendorn, Grossman Professor of Economics at Colby College
Colby College is a private liberal arts college in Waterville, Maine. It was founded in 1813 as the Maine Literary and Theological Institution, then renamed Waterville College after the city where it resides. The donations of Christian philant ...
, theorized that the name Maldives derives from the Sanskrit ' (), meaning "garland of islands".Hogendorn, Jan and Johnson Marion (1986). ''The Shell Money of the Slave Trade''. African Studies Series 49, Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press in the world. It is also the King's Printer.
Cambridge University Pre ...
, Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a College town, university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cam ...
, pp. 20–22 In Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 2 ...
, "Garland of Islands" can be translated as ' (). In Kannada, "Garland of Islands" can be translated as ' (). None of these names are mentioned in any literature, but classical Sanskrit texts dating back to the Vedic period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (ca. 1300–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, betwe ...
mention the "Hundred Thousand Islands" ('), a generic name which would include not only the Maldives, but also the Laccadives
Lakshadweep (), also known as Laccadives (), is a union territory of India. It is an archipelago of 36 islands in the Arabian sea, located off the Malabar Coast.
The name ''Lakshadweep'' means "one lakh islands" in Sanskrit, though the Lacc ...
, Aminidivi
The Aminidivi Islands, are one of the three island subgroups in the Union Territory of Lakshadweep, India. It is the northern group of the Lakshadweep, separated from the Laccadive Islands subgroup roughly by the 11th parallel north. The total ...
Islands, Minicoy
Minicoy, locally known as Maliku (), is an island in Lakshadweep, India. Along with Viringili, it is on ''Maliku atoll'', the southernmost atoll of Lakshadweep archipelago. Administratively, it is a census town in the Indian union territory ...
, and the Chagos island groups.
Medieval Arab travellers such as Ibn Battuta called the islands ' () from the Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
word ' ("palace"), which must be how the Berber traveller interpreted the local name, having been through Muslim North India, where Perso-Arabic
The Persian alphabet ( fa, الفبای فارسی, Alefbâye Fârsi) is a writing system that is a version of the Arabic script used for the Persian language spoken in Iran ( Western Persian) and Afghanistan (Dari Persian) since the 7th cen ...
words were introduced to the local vocabulary. This is the name currently inscribed on the scroll in the Maldives state emblem. The classical Persian/Arabic name for Maldives is '. The Dutch referred to the islands as the ' (), while the British anglicised the local name for the islands first to the "Maldive Islands" and later to "Maldives".
In a conversational book published in 1563, Garcia da Orta writes: "I must tell you that I have heard it said that the natives do not call it Maldiva but Nalediva. In the Malabar language, ''nale'' means four and ''diva'' island. So that in that language, the word signifies 'four islands', while we, corrupting the name, call it Maldiva."
History
Ancient history and settlement
In the 6th - 5th century BCE, the Maldives already had their kingdoms. The country has an established history of over 2,500 years according to historical evidence and legends. Early settlers in the Maldives were probably Gujaratis who reached and settled Sri Lanka about 500 BCE. Evidence of cultural influence from North India can be deduced from the methods of boatbuilding and silver punch-marked coins The ''Mahāvaṃsa
The ''Mahāvaṃsa'' (, Sinhala: මහාවංශය, Pali: ''මහාවංස (Mahāvaṃsa)'' – written in the 5th century CE) is the meticulously kept historical chronicle of Sri Lanka written in the style of an epic poem written in t ...
'' (300 BCE) has records of people from Sri Lanka emigrating to the Maldives. Assuming that cowrie shells come from the Maldives, historians believe that there may have been people living in the Maldives during the Indus Valley civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900& ...
(3300-1300 BCE). A number of artefacts show the presence of Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
in the country before the Islamic period.
According to the book () (''On the Ancient Ruins of Meedhoo''), written in the 17th century in Arabic by Allama Ahmed Shihabuddine (Allama Shihab al-Din) of Meedhoo in Addu Atoll, the first settlers of the Maldives were people known as Dheyvis. They came from the Kalibanga
Kalibangān is a town located at on the left or southern banks of the Ghaggar (Ghaggar-Hakra River) in Tehsil Pilibangān, between Suratgarh and Hanumangarh in Hanumangarh District, Rajasthan, India 205 km. from Bikaner. It is also identif ...
in India. The time of their arrival is unknown but it was before Emperor Asoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, s ...
's kingdom in 269–232 BCE. Shihabuddin's story tallies remarkably well with the recorded history of South Asia and that of the copperplate document of the Maldives known as Loamaafaanu.
The ''Maapanansa'', the copper plates on which recorded the history of the first Kings of Maldives from the Solar Dynasty, were lost quite early on.
A 4th-century notice written by Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus (occasionally anglicised as Ammian) (born , died 400) was a Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from antiquity (preceding Procopius). His work, known as the ''Res Gestae ...
(362 CE) speaks of gifts sent to the Roman emperor Julian by a deputation from the nation of Divi. The name Divi is very similar to Dheyvi who were the first settlers of Maldives.
The ancient history of Maldives is told in copperplates, ancient scripts carved on coral artefacts, traditions, language and different ethnicities of Maldivians.
The first Maldivians did not leave any archaeological artefacts. Their buildings were probably built of wood, palm fronds, and other perishable materials, which would have quickly decayed in the salt and wind of the tropical climate. Moreover, chiefs or headmen did not reside in elaborate stone palaces, nor did their religion require the construction of large temples or compounds.
Comparative studies of Maldivian oral, linguistic, and cultural traditions confirm that the first settlers were people from the southern shores of the neighbouring Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
,Xavier Romero-Frias, ''The Maldive Islanders, A Study of the Popular Culture of an Ancient Ocean Kingdom'' including the Giraavaru people, mentioned in ancient legends and local folklore about the establishment of the capital and kingly rule in Malé
Malé (, ; dv, މާލެ) is the capital and most populous city of the Maldives. With a population of 252,768 and an area of , it is also one of the most densely populated cities in the world. The city is geographically located at the southern ...
.
A strong underlying layer of Dravidian and North Indian
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central ...
cultures survives in Maldivian society, with a clear Elu substratum in the language, which also appears in place names, kinship terms, poetry, dance, and religious beliefs. The North Indian system was brought by the original Sinhalese
Sinhala may refer to:
* Something of or related to the Sinhalese people of Sri Lanka
* Sinhalese people
* Sinhala language, one of the three official languages used in Sri Lanka
* Sinhala script, a writing system for the Sinhala language
** Sinha ...
from Sri Lanka. Malabar and Pandya seafaring culture led to the settlement of the Islands by Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, nativ ...
and Malabar seafarers.
The Maldive Islands were mentioned in Ancient Sangam Tamil Literature as "Munneer Pazhantheevam" or "Older Islands of Three Seas".
Buddhist period
Despite being just mentioned briefly in most history books, the 1,400 year-long Buddhist period has a foundational importance in the history of the Maldives. It was during this period that the culture of the Maldives both developed and flourished, a culture that survives today. The Maldivianlanguage
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of ...
, early Maldive scripts
Script may refer to:
Writing systems
* Script, a distinctive writing system, based on a repertoire of specific elements or symbols, or that repertoire
* Script (styles of handwriting)
** Script typeface, a typeface with characteristics of handw ...
, architecture, ruling institutions, customs, and manners of the Maldivians originated at the time when the Maldives were a Buddhist kingdom.
Buddhism probably spread to the Maldives in the 3rd century BCE at the time of Emperor Ashoka
Ashoka (, ; also ''Asoka''; 304 – 232 BCE), popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was the third emperor of the Maurya Empire of Indian subcontinent during to 232 BCE. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, s ...
's expansion and became the dominant religion of the people of the Maldives until the 12th century. The ancient Maldivian Kings promoted Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
, and the first Maldive writings and artistic achievements, in the form of highly developed sculpture and architecture, originate from that period. Nearly all archaeological remains in the Maldives are from Buddhist stupas and monasteries, and all artefacts found to date display characteristic Buddhist iconography.
Buddhist (and Hindu) temples were Mandala
A mandala ( sa, मण्डल, maṇḍala, circle, ) is a geometric configuration of symbols. In various spiritual traditions, mandalas may be employed for focusing attention of practitioners and adepts, as a spiritual guidance tool, for e ...
shaped. They are oriented according to the four cardinal points with the main gate facing east. Local historian Hassan Ahmed Maniku counted as many as 59 islands with Buddhist archaeological sites in a provisional list he published in 1990.
Islamic period
The importance of the Arabs as traders in the Indian Ocean by the 12th century may partly explain why the last Buddhist king of Maldives, Dhovemi, converted to Islam in the year 1153 (or 1193). Adopting the Muslim title of Sultan Muhammad al-Adil, he initiated a series of six Islamic dynasties that lasted until 1932 when the sultanate became elective. The formal title of the sultan up to 1965 was, ''Sultan of Land and Sea, Lord of the twelve-thousand islands and Sultan of the Maldives'' which came with the style '' Highness''. A Muslim Berber fromMorocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
, Abu al-Barakat Yusuf al-Barbari, is traditionally credited for this conversion. According to the story told to Ibn Battutah
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berber Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, largely in the Muslim wor ...
, a mosque was built with the inscription: 'The Sultan Ahmad Shanurazah accepted Islam at the hand of Abu al-Barakat Yusuf al-Barbari.' Some scholars have suggested the possibility of Ibn Battuta misreading Maldive texts, and having a bias towards the North African, Maghrebi narrative of this Shaykh, instead of the East African origins account that was known as well at the time. Even when Ibn Battuta visited the islands, the governor of the island at that time was Abd Aziz Al Mogadishawi, a Somali
Somalis have a legend which claims Abu al-Barakat Yusuf al-Barbari as a native of Barbera
Barbera is a red Italian wine grape variety that, as of 2000, was the third most-planted red grape variety in Italy (after Sangiovese and Montepulciano). It produces good yields and is known for deep color, full body, low tannins and high level ...
, a significant trading port on the northwestern coast of Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constituti ...
. ''Barbara'' or ''Barbaroi'' (Berbers), as the ancestors of the Somalis
The Somalis ( so, Soomaalida 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒆𐒖, ar, صوماليون) are an ethnic group native to the Horn of Africa who share a common ancestry, culture and history. The Lowland East Cushitic Somali language is the shared ...
were referred to by medieval Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
and ancient Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
geographers, respectively.F.R.C. Bagley et al., ''The Last Great Muslim Empires'' (Brill: 1997), p. 174.Mohamed Diriye Abdullahi, ''Culture and Customs of Somalia'', (Greenwood Press: 2001), p. 13. This is also seen when Ibn Battuta visited Mogadishu
Mogadishu (, also ; so, Muqdisho or ; ar, مقديشو ; it, Mogadiscio ), locally known as Xamar or Hamar, is the capital and most populous city of Somalia. The city has served as an important port connecting traders across the Indian Oc ...
, he mentions that the Sultan at that time, "Abu Bakr ibn Shaikh Omar", was a Berber (Somali). According to scholars, Abu al-Barakat Yusuf al-Barbari was Yusuf bin Ahmad al-Kawneyn
Yusuf bin Ahmad al-Kawneyn ( ar, يوسف بن أحمد الكونين) (b. 10th century), popularly known as Aw Barkhadle ("Blessed Father")Abdullahi, p.13 or Yusuf Al Kownayn, was a Muslim scholar and traveler. Based on reference to Yusuf Al Ka ...
, a famous native Somali scholar known for establishing the Walashma dynasty
The Walashma dynasty was a medieval Muslim dynasty of the Horn of Africa. Founded in 1285, it was centered in Zeila, and established bases around the Horn of Africa. It governed the Ifat and Adal Sultanates in what are present-day Somaliland, ...
of the Horn of Africa. After his conversion of the population of Dogor (now known as Aw Barkhadle), a town in Somalia, he is also credited to have been responsible for spreading Islam in the Maldivian islands, establishing the Hukuru Miskiy, and converting the Maldivian population to Islam. Ibn Battuta states the Maldivian king was converted by Abu al-Barakat Yusuf al-Barbari (Blessed Father of Somalia).
Others have it he may have been from the Persian town of Tabriz
Tabriz ( fa, تبریز ; ) is a city in northwestern Iran, serving as the capital of East Azerbaijan Province. It is the List of largest cities of Iran, sixth-most-populous city in Iran. In the Quri Chay, Quru River valley in Iran's historic Aze ...
. The first reference to an Iranian origin dates to an 18th-century Persian text.
His venerated tomb now stands on the grounds of Medhu Ziyaaraiy, across the street from the Friday Mosque, or Hukuru Miskiy, in Malé. Built in 1656, this is the oldest mosque in the Maldives. Following the Islamic concept that before Islam there was the time of Jahiliya
The Age of Ignorance ( ar, / , "ignorance") is an Islamic concept referring to the period of time and state of affairs in Arabia before the advent of Islam in 610 CE. It is often translated as the "Age of Ignorance". The term ''jahiliyyah'' ...
(ignorance), in the history books used by Maldivians the introduction of Islam at the end of the 12th century is considered the cornerstone of the country's history. Nonetheless, the cultural influence of Buddhism remains, a reality directly experienced by Ibn Battuta during his nine months there sometime between 1341 and 1345, serving as a chief judge and marrying into the royal family of Omar I. For he became embroiled in local politics and left when his strict judgments in the laissez-faire island kingdom began to chafe with its rulers. In particular, he was dismayed at the local women going about with no clothing above the waist—a violation of Middle Eastern Islamic standards of modesty—and the locals taking no notice when he complained.
Compared to the other areas of South Asia, the conversion of the Maldives to Islam happened relatively late. Arab traders had converted populations in the Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing m ...
since the 7th century, and Muhammad Bin Qāsim had converted large swathes of Sindh to Islam at about the same time. The Maldives remained a Buddhist kingdom for another 500 years after the conversion of Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing m ...
and Sindh—perhaps as the southwesternmost Buddhist country. Arabic became the prime language of administration (instead of Persian and Urdu), and the Maliki
The ( ar, مَالِكِي) school is one of the four major schools of Islamic jurisprudence within Sunni Islam. It was founded by Malik ibn Anas in the 8th century. The Maliki school of jurisprudence relies on the Quran and hadiths as primary ...
school of jurisprudence was introduced, both hinting at direct contact with the core of the Arab world.
Middle Eastern seafarers had just begun to take over the Indian Ocean trade routes in the 10th century and found the Maldives to be an important link in those routes as the first landfall for traders from Basra
Basra ( ar, ٱلْبَصْرَة, al-Baṣrah) is an Iraqi city located on the Shatt al-Arab. It had an estimated population of 1.4 million in 2018. Basra is also Iraq's main port, although it does not have deep water access, which is han ...
sailing to Southeast Asia. Trade involved mainly cowrie shells
Cowrie or cowry () is the common name for a group of small to large sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Cypraeidae, the cowries.
The term ''porcelain'' derives from the old Italian term for the cowrie shell (''porcellana'') du ...
—widely used as a form of currency throughout Asia and parts of the East African coast—and coir fibre. The Bengal Sultanate, where cowrie shells were used as legal tender, was one of the principal trading partners of the Maldives. The Bengal–Maldives cowry shell trade was the largest shell currency trade network in history.
The other essential product of the Maldives was coir
Coir (), also called coconut fibre, is a natural fibre extracted from the outer husk of coconut and used in products such as floor mats, doormats, brushes, and mattresses. Coir is the fibrous material found between the hard, internal shell an ...
, the fibre of the dried coconut husk, resistant to saltwater. It stitched together and rigged the dhow
Dhow ( ar, داو, translit=dāwa; mr, script=Latn, dāw) is the generic name of a number of traditional sailing vessels with one or more masts with settee or sometimes lateen sails, used in the Red Sea and Indian Ocean region. Typically spo ...
s that plied the Indian Ocean. Maldivian coir was exported to Sindh, China, Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
, and the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bod ...
.
Colonial period


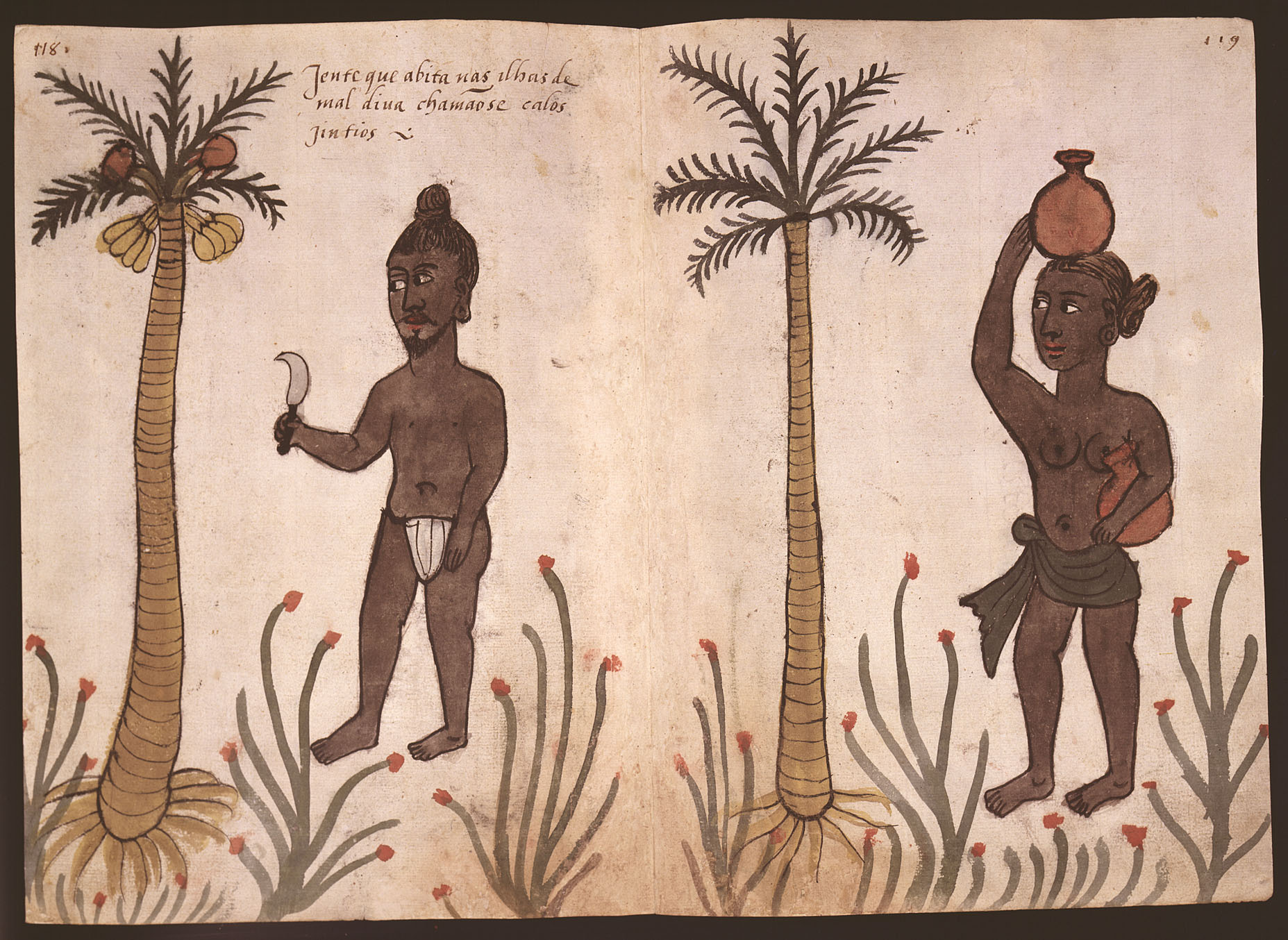
 In 1558, the Portuguese established a small garrison with a (), or overseer of a
In 1558, the Portuguese established a small garrison with a (), or overseer of a factory (trading post)
Factory was the common name during the medieval and early modern eras for an entrepôt – which was essentially an early form of free-trade zone or transshipment point. At a factory, local inhabitants could interact with foreign merchants, o ...
in the Maldives, which they administered from their main colony in Goa
Goa () is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is located between the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the ...
. Their attempts to impose Christianity provoked a local revolt led by Muhammad Thakurufaanu al-A'uẓam, his two brothers and Dhuvaafaru Dhandahele, who fifteen years later drove the Portuguese out of Maldives. This event is now commemorated as National Day.
In the mid-17th century, the Dutch, who had replaced the Portuguese as the dominant power in Ceylon, established hegemony over Maldivian affairs without involving themselves directly in local matters, which were governed according to centuries-old Islamic customs.
The British expelled the Dutch from Ceylon in 1796 and included the Maldives as a British Protectorate. The status of Maldives as a British protectorate was officially recorded in an 1887 agreement in which the sultan Muhammad Mueenuddeen II accepted British influence over Maldivian external relations and defence while retaining home rule, which continued to be regulated by Muslim traditional institutions in exchange for an annual tribute. The status of the islands was akin to other British protectorates in the Indian Ocean region, including Zanzibar
Zanzibar (; ; ) is an insular semi-autonomous province which united with Tanganyika in 1964 to form the United Republic of Tanzania. It is an archipelago in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of the mainland, and consists of many small islan ...
and the Trucial States
The Trucial States ( '), also known as the Trucial Coast ( '), the Trucial Sheikhdoms ( '), Trucial Arabia or Trucial Oman, was the name the British government gave to a group of tribal confederations in southeastern Arabia whose leaders had s ...
.
 In the British period, the Sultan's powers were taken over by the Chief Minister, much to the chagrin of the British Governor-General who continued to deal with the ineffectual Sultan. Consequently, Britain encouraged the development of a
In the British period, the Sultan's powers were taken over by the Chief Minister, much to the chagrin of the British Governor-General who continued to deal with the ineffectual Sultan. Consequently, Britain encouraged the development of a constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
, and the first Constitution was proclaimed in 1932. However, the new arrangements favoured neither the ageing Sultan nor the wily Chief Minister, but rather a young crop of British-educated reformists. As a result, angry mobs were instigated against the Constitution which was publicly torn up.
The Maldives remained a British crown protectorate until 1953 when the sultanate was suspended and the First Republic was declared under the short-lived presidency of Muhammad Amin Didi. While serving as prime minister during the 1940s, Didi nationalized the fish export industry. As president, he is remembered as a reformer of the education system and an advocate of women's rights
Women's rights are the rights and entitlements claimed for women and girls worldwide. They formed the basis for the women's rights movement in the 19th century and the feminist movements during the 20th and 21st centuries. In some countries, ...
. Conservatives in Malé ousted his government, and during a riot over food shortages, Didi was beaten by a mob and died on a nearby island.
 Beginning in the 1950s, the political history in the Maldives was largely influenced by the British military presence on the islands. In 1954, the restoration of the sultanate perpetuated the rule of the past. Two years later, the United Kingdom obtained permission to reestablish its wartime
Beginning in the 1950s, the political history in the Maldives was largely influenced by the British military presence on the islands. In 1954, the restoration of the sultanate perpetuated the rule of the past. Two years later, the United Kingdom obtained permission to reestablish its wartime RAF Gan
Royal Air Force Station Gan, commonly known as RAF Gan, is a former Royal Air Force station on Gan island, the southern-most island of Addu Atoll, which is part of the larger groups of islands which form the Maldives, in the middle of the Ind ...
airfield in the southernmost Addu Atoll, employing hundreds of locals. In 1957, however, the new prime minister, Ibrahim Nasir, called for a review of the agreement. Nasir was challenged in 1959 by a local secessionist movement in the three southernmost atolls that benefited economically from the British presence on Gan
The word Gan or the initials GAN may refer to:
Places
*Gan, a component of Hebrew placenames literally meaning "garden"
China
* Gan River (Jiangxi)
* Gan River (Inner Mongolia),
* Gan County, in Jiangxi province
* Gansu, abbreviated ''Gā ...
. This group cut ties with the Maldives government and formed an independent state, the United Suvadive Republic
The United Suvadive Republic (Dhivehi: އެކުވެރި ސުވާދީބު ޖުމްހޫރިއްޔާ) was a short-lived breakaway state from the Kingdom of Maldives between 1958 and 1963 consisting of the three southern atolls of the Maldive archi ...
with Abdullah Afeef as president and Hithadhoo as its capital. One year later the Suvadive republic was scrapped after Nasir sent gunboats from Malé with government police, and Abdulla Afif went into exile. Meanwhile, in 1960 the Maldives allowed the United Kingdom to continue to use both the Gan
The word Gan or the initials GAN may refer to:
Places
*Gan, a component of Hebrew placenames literally meaning "garden"
China
* Gan River (Jiangxi)
* Gan River (Inner Mongolia),
* Gan County, in Jiangxi province
* Gansu, abbreviated ''Gā ...
and the Hithadhoo facilities for thirty years, with the payment of £750,000 from 1960 to 1965 for Maldives' economic development. The base was closed in 1976 as part of the larger British withdrawal of permanently-stationed forces 'East of Suez
East of Suez is used in British military and political discussions in reference to interests beyond the European theatre, and east of the Suez Canal, and may or may not include the Middle East.
'.
Independence and republic
Colombo
Colombo ( ; si, කොළඹ, translit=Koḷam̆ba, ; ta, கொழும்பு, translit=Koḻumpu, ) is the executive and judicial capital and largest city of Sri Lanka by population. According to the Brookings Institution, Colombo m ...
. After this, the sultanate continued for another three years under Sir Muhammad Fareed Didi, who declared himself King upon independence.
On 15 November 1967, a vote was taken in parliament to decide whether the Maldives should continue as a constitutional monarchy
A constitutional monarchy, parliamentary monarchy, or democratic monarchy is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in decision making. Constitutional monarchies dif ...
or become a republic. Of the 44 members of parliament, 40 voted in favour of a republic. On 15 March 1968, a national referendum was held on the question, and 93.34% of those taking part voted in favour of establishing a republic. The republic was declared on 11 November 1968, thus ending the 853-year-old monarchy, which was replaced by a republic under the presidency of Ibrahim Nasir. As the King had held little real power, this was seen as a cosmetic change and required few alterations in the structures of government.
Tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism mor ...
began to be developed on the archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Arc ...
by the beginning of the 1970s. The first resort in the Maldives was Kurumba Maldives which welcomed the first guests on 3 October 1972. The first accurate census was held in December 1977 and showed 142,832 people living in the Maldives.
Political infighting during the 1970s between Nasir's faction and other political figures led to the 1975 arrest and exile of elected prime minister Ahmed Zaki to a remote atoll
An atoll () is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon partially or completely. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical oceans and seas where corals can gr ...
. Economic decline followed the closure of the British airfield at Gan and the collapse of the market for dried fish, an important export. With support for his administration faltering, Nasir fled to Singapore in 1978, with millions of dollars from the treasury.
Maumoon Abdul Gayoom began his 30-year role as president in 1978, winning six consecutive elections without opposition. His election was seen as ushering in a period of political stability and economic development given Maumoon's priority to develop the poorer islands. Tourism flourished and increased foreign contact spurred development. However, Maumoon's rule was controversial, with some critics saying Maumoon was an autocrat who quelled dissent by limiting freedoms and political favouritism.BAT
A series of coup attempts (in 1980, 1983, and 1988) by Nasir supporters and business interests tried to topple the government without success. While the first two attempts met with little success, the 1988 coup attempt involved a roughly 80-strong mercenary force of the PLOTE
The People's Liberation Organisation of Tamil Eelam (PLOTE) is a former Tamil militant group that had become a pro-government paramilitary group and political party. PLOTE's political wing is known as the Democratic People's Liberation Front.
Or ...
who seized the airport and caused Maumoon to flee from house to house until the intervention of 1,600 Indian troops airlifted into Malé
Malé (, ; dv, މާލެ) is the capital and most populous city of the Maldives. With a population of 252,768 and an area of , it is also one of the most densely populated cities in the world. The city is geographically located at the southern ...
restored order.
The November 1988 coup d'état was headed by Ibrahim Lutfee, a businessman and Sikka Ahmed Ismail Manik who is the father of the current first lady of Maldives Fazna Ahmed. The attackers were defeated by then National Security Services of Maldives. On the night of 3 November 1988, the Indian Air Force airlifted a Parachute Regiment (India)#Operation Cactus, parachute battalion group from Agra and flew them over to the Maldives. By the time Indian armed forces reached the Maldives, the mercenary forces has already left Malé on the hijacked ship MV Progress Light. The Indian paratroopers landed at Hulhulé Island, Hulhulé and secured the airfield and restored the government rule at Malé within hours. The brief operation labelled ''Operation Cactus'', also involved the Indian Navy that assisted in capturing the freighter MV Progress Light and rescued the hostages and crew.
Twenty-first century
The Effect of the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake on the Maldives, Maldives were devastated by a tsunami on 26 December 2004, following the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake, Indian Ocean earthquake. Only nine islands were reported to have escaped any flooding, while fifty-seven islands faced serious damage to critical infrastructure, fourteen islands had to be totally evacuated, and six islands were destroyed. A further twenty-one resort islands were forced to close because of tsunami damage. The total damage was estimated at more than US$400 million, or some 62% of the GDP. 102 Maldivians and 6 foreigners reportedly died in the tsunami. The destructive impact of the waves on the low-lying islands was mitigated by the fact there was no continental shelf or land mass upon which the waves could gain height. The tallest waves were reported to be high. During the later part of Maumoon's rule, independent political movements emerged in the Maldives, which challenged the then-ruling Dhivehi Rayyithunge Party (Maldivian People's Party, MPP) and demanded democratic reform. The dissident journalist and activist Mohamed Nasheed founded the Maldivian Democratic Party (MDP) in 2003 and pressured Maumoon into allowing gradual political reforms.Autocracy and Back Again: The Ordeal of the Maldives. ''Brown Political Review''. Retrieved on 10 May 2016. In 2008, a new constitution was approved and the Maldivian presidential election, 2008, first direct presidential elections occurred, which were won by Nasheed in the second round. His administration faced many challenges, including the huge debt left by the previous government, the economic downturn following the 2004 tsunami, overspending by means of overprinting of local currency (the rufiyaa), unemployment, corruption, and increasing drug use. Taxation on goods was imposed for the first time in the country, and import duties were reduced on many goods and services. Universal health insurance (Aasandha) and social welfare benefits were given to those aged 65 years or older, single parents, and those with special needs. Social and 2011–12 Maldives political crisis, political unrest grew in late 2011, following opposition campaigns in the name of protecting Islam. Nasheed controversially resigned from office after large number of police and army mutinied in February 2012. Nasheed's vice president, Mohammed Waheed Hassan, was sworn in as president. Nasheed was later arrested, convicted of terrorism, and sentenced to 13 years. The trial was widely seen as flawed and political. The UN Working Group on Arbitrary Detention called for Nasheed's immediate release. The Maldivian presidential election, 2013, elections in late 2013 were highly contested. Former president Nasheed won the most votes in the first round, but the Supreme Court annulled it despite the positive assessment of international election observers. In the re-run vote Abdulla Yameen, half-brother of the former president Maumoon, assumed the presidency. Yameen survived an assassination attempt in late 2015. Vice president Ahmed Adeeb was later arrested together with 17 supporters for "public order offences" and the government instituted a broader crackdown against his accomplices. A state of emergency was later declared ahead of a planned anti-government rally, and the people's Majlis accelerated the removal of Adeeb. 2018 Maldivian presidential election, In the 2018 elections, Ibrahim Mohamed Solih won the most votes, and was sworn in as the Maldives' new president in November 2018. Adeeb was freed by courts in Male in July 2019 after his conviction on charges of terrorism and corruption was overruled, but was placed under a travel ban after the state prosecutor appealed the order in a corruption and money laundering case. Adeeb escaped in a tugboat to seek asylum in India. It is understood that the Indian Coast Guard escorted the tugboat to the International Maritime Boundary Line (IMBL) and he was then "transferred" to a Maldivian Coast Guard ship, where officials took him into custody. Former president Abdulla Yameen was sentenced to five years in prison in November 2019 for money laundering. The High Court upheld the jail sentence in January 2021. However, Supreme Court overturned Yameen's conviction in November 2021.
Geography

 The Maldives consists of 1,192 coral islands grouped in a double chain of 26
The Maldives consists of 1,192 coral islands grouped in a double chain of 26 atoll
An atoll () is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon partially or completely. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical oceans and seas where corals can gr ...
s, that stretch along a length of north to south, east to west, spread over roughly , of which only is dry land, making this one of the world's most dispersed countries. It lies between latitudes 1st parallel south, 1°S and 8th parallel north, 8°N, and longitudes 72nd meridian east, 72° and 74th meridian east, 74°E. The atolls are composed of live coral reefs and sand bars, situated atop a submarine ridge long that rises abruptly from the depths of the Indian Ocean and runs north to south.
Only near the southern end of this natural coral barricade do two open passages permit safe ship navigation from one side of the Indian Ocean to the other through the territorial waters of Maldives. For administrative purposes, the Maldivian government organised these atolls into 21 Administrative divisions of the Maldives, administrative divisions. The largest island of Maldives is that of Gan (Laamu Atoll), Gan, which belongs to Laamu Atoll or Hahdhummathi Maldives. In Addu Atoll, the westernmost islands are connected by roads over the reef (collectively called Link Road) and the total length of the road is .
Maldives is the lowest country in the world, with maximum and average natural ground levels of only and above sea level, respectively. In areas where construction exists, however, this has been increased to several metres. More than 80 per cent of the country's land is composed of coral islands which rise less than one metre above sea level. As a result, the Maldives are at high risk of being submerged due to Sea level rise, rising sea levels. The IPCC, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has warned that, at current rates, sea-level rise would be high enough to make the Maldives uninhabitable by 2100.
Climate
Sea level rise
In 1988, Maldivian authorities claimed that sea rise would "completely cover this Indian Ocean nation of 1,196 small islands within the next 30 years." The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's 2007 report predicted the upper limit of the sea level rise will be by 2100, which means that most of the republic's 200 inhabited islands may need to be abandoned. According to researchers from the University of Southampton, the Maldives are the third most endangered island nation due to flooding from climate change as a percentage of population. Former president Mohamed Nasheed said in 2012 that "If carbon emissions continue at the rate they are climbing today, my country will be under water in seven years." He has called for more climate change mitigation action while on the American television shows ''The Daily Show'' and the ''Late Show with David Letterman'', and hosted "the world's first underwater cabinet meeting" in 2009 to raise awareness of the threats posed by climate change. Concerns over rising sea levels have also been expressed by Nasheed's predecessor, Maumoon Abdul Gayoom. In 2008, Nasheed announced plans to look into purchasing new land in India, Sri Lanka, and Australia because of his concerns about global warming, and the possibility of much of the islands being inundated with water from rising sea levels. The purchase of land will be made from a fund generated by tourism. The president explained his intentions: "We do not want to leave the Maldives, but we also do not want to be climate refugees living in tents for decades". By 2020, Maldives plans to eliminate or offset all of its greenhouse gas emissions. At the 2009 International Climate Talks, Nasheed explained that:For us swearing off fossil fuels is not only the right thing to do, but it is also in our economic self-interest... Pioneering countries will free themselves from the unpredictable price of foreign oil; they will capitalise on the new green economy of the future, and they will enhance their moral standing giving them greater political influence on the world stage.In 2020, a three-year study at the University of Plymouth found that as tides move sediment to create higher elevation, the islands, and also Tuvalu and Kiribati, may rise instead of sink.
Environment
Environmental issues other than sea level rise include bad waste disposal and beach theft. Although the Maldives are kept relatively pristine and little litter can be found on the islands, no good Waste management, waste disposal sites exist. Most trash from Malé and other resorts in Maldives is simply dumped at the Thilafushi landfill. List of Protected Areas of Maldives, 31 protected areas are administered by the Ministry of Environment and Energy and Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) of the Maldives.Marine ecosystem

 The Maldives have a range of different habitats including deep sea, shallow coast, and reef ecosystems, fringing mangroves, wetlands and dry land. There are 187 species of coral forming the coral reefs. This area of the Indian Ocean, alone, houses 1,100 species of fish, 5 species of sea turtle, 21 species of whale and dolphin, 400 species of mollusc, and 83 species of echinoderms. The area is also populated by a number of crustacean species: 120 copepods, 15 amphipods, as well as more than 145 crab and 48 shrimp species.
Among the many marine families represented are pufferfish, Caesionidae, fusiliers, Carangidae, jackfish, lionfish, oriental sweetlips, reef sharks, groupers, eels, Lutjanidae, snappers, bannerfish, Ogcocephalidae, batfish, humphead wrasse, spotted eagle rays, scorpionfish, lobsters, nudibranches, Pomacanthidae, angelfish, butterflyfish, squirrelfish, soldierfish, Asiatic glassfish, glassfish, surgeonfish, Naso (fish), unicornfish, triggerfish, Napoleon wrasse, and barracuda.
These coral reefs are home to a variety of marine ecosystems that vary from planktonic organisms to whale sharks. Sponges have gained importance as five species have displayed anti-tumor and anti-cancer properties.
In 1998, sea-temperature warming of as much as due to a single El Niño-Southern Oscillation, El Niño phenomenon event caused coral bleaching, killing two-thirds of the nation's coral reefs.
In an effort to induce the regrowth of the reefs, scientists placed electrified cones anywhere from below the surface to provide a substrate for larval coral attachment. In 2004, scientists witnessed corals regenerating. Corals began to eject pink-orange eggs and sperm. The growth of these electrified corals was five times faster than untreated corals. Scientist Azeez Hakim stated:
Again, in 2016, the coral reefs of the Maldives experienced a Coral bleaching#Maldives, severe bleaching incident. Up to 95% of coral around some islands have died, and, even after six months, 100% of young coral transplants died. The surface water temperatures reached an all-time high in 2016, at 31 degrees Celsius in May.
Recent scientific studies suggest that the faunistic composition can vary greatly between neighbour atolls, especially in terms of benthic fauna. Differences in terms of fishing pressure (including poaching) could be the cause.
The Maldives have a range of different habitats including deep sea, shallow coast, and reef ecosystems, fringing mangroves, wetlands and dry land. There are 187 species of coral forming the coral reefs. This area of the Indian Ocean, alone, houses 1,100 species of fish, 5 species of sea turtle, 21 species of whale and dolphin, 400 species of mollusc, and 83 species of echinoderms. The area is also populated by a number of crustacean species: 120 copepods, 15 amphipods, as well as more than 145 crab and 48 shrimp species.
Among the many marine families represented are pufferfish, Caesionidae, fusiliers, Carangidae, jackfish, lionfish, oriental sweetlips, reef sharks, groupers, eels, Lutjanidae, snappers, bannerfish, Ogcocephalidae, batfish, humphead wrasse, spotted eagle rays, scorpionfish, lobsters, nudibranches, Pomacanthidae, angelfish, butterflyfish, squirrelfish, soldierfish, Asiatic glassfish, glassfish, surgeonfish, Naso (fish), unicornfish, triggerfish, Napoleon wrasse, and barracuda.
These coral reefs are home to a variety of marine ecosystems that vary from planktonic organisms to whale sharks. Sponges have gained importance as five species have displayed anti-tumor and anti-cancer properties.
In 1998, sea-temperature warming of as much as due to a single El Niño-Southern Oscillation, El Niño phenomenon event caused coral bleaching, killing two-thirds of the nation's coral reefs.
In an effort to induce the regrowth of the reefs, scientists placed electrified cones anywhere from below the surface to provide a substrate for larval coral attachment. In 2004, scientists witnessed corals regenerating. Corals began to eject pink-orange eggs and sperm. The growth of these electrified corals was five times faster than untreated corals. Scientist Azeez Hakim stated:
Again, in 2016, the coral reefs of the Maldives experienced a Coral bleaching#Maldives, severe bleaching incident. Up to 95% of coral around some islands have died, and, even after six months, 100% of young coral transplants died. The surface water temperatures reached an all-time high in 2016, at 31 degrees Celsius in May.
Recent scientific studies suggest that the faunistic composition can vary greatly between neighbour atolls, especially in terms of benthic fauna. Differences in terms of fishing pressure (including poaching) could be the cause.
Government
Malé
Malé (, ; dv, މާލެ) is the capital and most populous city of the Maldives. With a population of 252,768 and an area of , it is also one of the most densely populated cities in the world. The city is geographically located at the southern ...
, houses members from all over the country.
The republican constitution came into force in 1968 and was amended in 1970, 1972, and 1975. On 27 November 1997 it was replaced by another Constitution assented to by then-President Maumoon Abdul Gayoom, Maumoon. This Constitution came into force on 1 January 1998. The current Constitution of Maldives was ratified by President Maumoon on 7 August 2008, and came into effect immediately, replacing and repealing the constitution of 1998. This new constitution includes a judiciary run by an independent commission, and independent commissions to oversee elections and fight corruption. It also reduces the executive powers vested under the president and strengthens the parliament. All state that the President of the Maldives, president is head of state, head of government and Commander-in-Chief of the Maldives National Defence Force, armed forces of the Maldives.
In 2018, the then ruling Progressive Party of Maldives (PPM-Y)'s tensions with opposition parties and subsequent crackdown was termed as an "assault on democracy" by the United Nations Human Rights Council, UN Human Rights chief.
In April 2019 parliamentary 2019 Maldivian parliamentary election, election The Maldivian Democratic Party (MDP) of president Ibrahim Mohamed Solih won a landslide victory. It took 65 of 87 seats of the parliament. This was the first time a single party was able to get such a high number of seats in the parliament in Maldivian history.
Order of Nishanizzuddeen is the Maldives' highest honour to a person.
Law
According to the Constitution of Maldives, "the judges are independent, and subject only to the Constitution and the law. When deciding matters on which the Constitution or the law is silent, judges must consider Islamic Sharia, Shari'ah". Islam is the official religion of the Maldives and open practice of any other religion is forbidden. The 2008 constitution says that the republic "is based on the principles of Islam" and that "no law contrary to any principle of Islam can be applied". Non-Muslims are prohibited from becoming citizens. The requirement to adhere to a particular religion and prohibition of public worship following other religions is contrary to Article 18 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and Article 18 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights to which Maldives has recently become party and was addressed in Maldives' reservation in adhering to the Covenant claiming that "The application of the principles set out in Article 18 of the Covenant shall be without prejudice to the Constitution of the Republic of the Maldives." A new Criminal code, penal code came into effect on 16 July 2015, replacing the 1968 law, the first modern, comprehensive penal code to incorporate the major tenets and principles of Islamic law. Homosexuality, Same-sex relations are illegal in the Maldives, although tourist resorts typically operate as exceptions to this law.Foreign relations
Since 1996, the Maldives has been the official progress monitor of the Indian Ocean Commission. In 2002, the Maldives began to express interest in the commission but had not applied for membership. Maldives' interest relates to its identity as a small island state, especially economic development and environmental preservation, and its desire for closer relations with France, a main actor in the IOC region. The Maldives is a founding member of theSouth Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is the regional intergovernmental organization and geopolitical union of states in South Asia. Its member states are Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan ...
(South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation, SAARC). The republic joined the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth in 1982, some 17 years after gaining independence from the United Kingdom. In October 2016, Maldives announced its withdrawal from the Commonwealth in protest at allegations of human rights abuse and failing democracy. The Maldives enjoys close ties with Commonwealth members Seychelles and Mauritius. The Maldives and Comoros are also both members of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose.
The word is derived from ...
. Following his election as president in 2018, Ibrahim Mohamed Solih and his Cabinet decided that the Maldives would apply to rejoin the Commonwealth, with readmission occurring on 1 February 2020.
As a result of sanctions imposed upon the Russian oligarchs by much of the global community in response to Russia's invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, many of them sought refuge for their mega-yachts in the Maldives due to the absence of an extradition treaty with the United States and other countries.
Military
 The Maldives National Defence Force is the combined security organisation responsible for defending the security and sovereignty of the Maldives, having the primary task of being responsible for attending to all internal and external security needs of the Maldives, including the protection of the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and the maintenance of peace and security. The MNDF component branches are the Coast Guard, Marine Corps, Special Forces, Service Corps, Defence Intelligence Service, Military Police, Corps of Engineers, Special Protection Group, Medical Corps, Adjutant General's Corps, Coast Guard Aviation Squadron, and the Fire and Rescue Service. The Maldives has an arrangement with India allowing cooperation on radar coverage.
As a water-bound nation, much of its security concerns lie at sea. Almost 99% of the country is covered by sea and the remaining 1% land is scattered over an area of × , with the largest island being not more than . Therefore, the duties assigned to the MNDF of maintaining surveillance over Maldives' waters and providing protection against foreign intruders poaching in the EEZ and territorial waters, are immense tasks from both logistical and economic viewpoints.
The Coast Guard plays a vital role in carrying out these functions. To provide timely security its patrol boats are stationed at various MNDF Regional Headquarters. The Coast Guard is also assigned to respond to the maritime distress calls and to conduct search and rescue operations in a timely manner.
In 2019, Maldives signed the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
The Maldives National Defence Force is the combined security organisation responsible for defending the security and sovereignty of the Maldives, having the primary task of being responsible for attending to all internal and external security needs of the Maldives, including the protection of the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and the maintenance of peace and security. The MNDF component branches are the Coast Guard, Marine Corps, Special Forces, Service Corps, Defence Intelligence Service, Military Police, Corps of Engineers, Special Protection Group, Medical Corps, Adjutant General's Corps, Coast Guard Aviation Squadron, and the Fire and Rescue Service. The Maldives has an arrangement with India allowing cooperation on radar coverage.
As a water-bound nation, much of its security concerns lie at sea. Almost 99% of the country is covered by sea and the remaining 1% land is scattered over an area of × , with the largest island being not more than . Therefore, the duties assigned to the MNDF of maintaining surveillance over Maldives' waters and providing protection against foreign intruders poaching in the EEZ and territorial waters, are immense tasks from both logistical and economic viewpoints.
The Coast Guard plays a vital role in carrying out these functions. To provide timely security its patrol boats are stationed at various MNDF Regional Headquarters. The Coast Guard is also assigned to respond to the maritime distress calls and to conduct search and rescue operations in a timely manner.
In 2019, Maldives signed the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
Human rights
Human rights in the Maldives is a contentious issue. In its 2011 Freedom in the World report, Freedom House declared the Maldives "Partly Free", claiming a reform process which had made headway in 2009 and 2010 had stalled. The Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor, United States Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor claims in their 2012 report on human rights practices in the country that the most significant problems are corruption, lack of Freedom of religion, religious freedom, abuse, and unequal treatment of women.Administrative divisions
 The Maldives has twenty-six natural Atolls of the Maldives, atolls and few island groups on isolated reefs, all of which have been divided into twenty-one administrative divisions (17 administrative atolls and cities of
The Maldives has twenty-six natural Atolls of the Maldives, atolls and few island groups on isolated reefs, all of which have been divided into twenty-one administrative divisions (17 administrative atolls and cities of Malé
Malé (, ; dv, މާލެ) is the capital and most populous city of the Maldives. With a population of 252,768 and an area of , it is also one of the most densely populated cities in the world. The city is geographically located at the southern ...
, Addu City, Addu, Fuvahmulah and Kulhudhuffushi).
Each atoll is administered by an elected Atoll Council. The islands are administered by an elected Island Council.
In addition to a name, every administrative division is identified by the Maldivian code letters, such as "Haa Alif" for Northern Thiladhunmathi Atoll, Thiladhunmati Uthuruburi (Thiladhunmathi North); and by a Latin code letter. The first corresponds to the geographical Maldivian name of the atoll; the second is a code adopted for convenience. As there are certain islands in different atolls that have the same name, for administrative purposes this code is quoted before the name of the island, for example: Baa Funadhoo, Kaafu Funadhoo, Gaafu-Alifu Funadhoo. Since most atolls have very long geographical names it is also used whenever the long name is inconvenient, for example in the atoll website names.''Divehiraajjege Jōgrafīge Vanavaru''. Muhammadu Ibrahim Lutfee
The introduction of code-letter names has been a source of much puzzlement and misunderstandings, especially among foreigners. Many people have come to think that the code-letter of the administrative atoll is its new name and that it has replaced its geographical name. Under such circumstances, it is hard to know which is the correct name to use.
Economy

coir
Coir (), also called coconut fibre, is a natural fibre extracted from the outer husk of coconut and used in products such as floor mats, doormats, brushes, and mattresses. Coir is the fibrous material found between the hard, internal shell an ...
rope, ambergris (Maavaharu), and coco de mer (Tavakkaashi) with neighbouring countries and East Asian countries.
The Maldivian government began a largely successful economic reform programme in the 1980s, initiated by lifting import quotas and giving more opportunities to the private sector. At the time tourism sector which would play a significant role in the nation's development was at its infant stage.
Agriculture and manufacturing continue to play lesser roles in the economy, constrained by the limited availability of cultivable land and the shortage of domestic labour.
Tourism
 The Maldives remained largely unknown to tourists until the early 1970s. Only 189 islands are home to its 447,137 inhabitants. The other islands are used entirely for economic purposes, of which tourism and agriculture are the most dominant.
The Maldives remained largely unknown to tourists until the early 1970s. Only 189 islands are home to its 447,137 inhabitants. The other islands are used entirely for economic purposes, of which tourism and agriculture are the most dominant. Tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism mor ...
accounts for 28% of the GDP and more than 60% of the Maldives' foreign exchange receipts. Over 90% of government tax revenue comes from import duties and tourism-related taxes.
The development of tourism fostered the overall growth of the Economy of the Maldives, country's economy. It created direct and indirect employment and income generation opportunities in other related industries. The first tourist resorts were opened in 1972 with Bandos Island Resort and Kurumba Village (the current name is Kurumba Maldives), which transformed the Maldives economy.
Visitors
Visitors to the Maldives do not need to apply for a visa pre-arrival, regardless of their country of origin, provided they have a valid passport, proof of onward travel, and the money to be self-sufficient while in the country. Most visitors arrive at Velana International Airport, on Hulhulé Island, adjacent to the capital Malé. The airport is served by flights to and from India, Sri Lanka, Doha, Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Singapore, Istanbul, and major airports in South-East Asia, as well as charters from Europe. Gan International Airport, Gan Airport, on the southern atoll of Addu City, Addu, also serves an international flight to Milan several times a week. British Airways offers direct flights to the Maldives from Heathrow Airport.Fishing industry
 For many centuries the Maldivian economy was entirely dependent on fishing and other ocean, marine products. Fishing remains the main occupation of the people and the government gives priority to the fisheries sector.
The mechanisation of the traditional fishing boat called ''Dhoni (fishing vessel), dhoni'' in 1974 was a major milestone in the development of the fisheries industry. A fish canning plant was installed on Felivaru in 1977, as a joint venture with a Japanese firm. In 1979, a Fisheries Advisory Board was set up with the mandate of advising the government on policy guidelines for the overall development of the fisheries sector. Manpower development programmes began in the early 1980s, and fisheries education was incorporated into the school curriculum. Fish aggregating devices and navigational aids were located at various strategic points. Moreover, the opening up of the exclusive economic zone (EEZ) of the Maldives for fisheries has further enhanced the growth of the fisheries sector.
, fisheries contributed over 15% of the country's GDP and engaged about 30% of the country's workforce. Fisheries were also the second-largest foreign exchange earner after #Tourism, tourism.
For many centuries the Maldivian economy was entirely dependent on fishing and other ocean, marine products. Fishing remains the main occupation of the people and the government gives priority to the fisheries sector.
The mechanisation of the traditional fishing boat called ''Dhoni (fishing vessel), dhoni'' in 1974 was a major milestone in the development of the fisheries industry. A fish canning plant was installed on Felivaru in 1977, as a joint venture with a Japanese firm. In 1979, a Fisheries Advisory Board was set up with the mandate of advising the government on policy guidelines for the overall development of the fisheries sector. Manpower development programmes began in the early 1980s, and fisheries education was incorporated into the school curriculum. Fish aggregating devices and navigational aids were located at various strategic points. Moreover, the opening up of the exclusive economic zone (EEZ) of the Maldives for fisheries has further enhanced the growth of the fisheries sector.
, fisheries contributed over 15% of the country's GDP and engaged about 30% of the country's workforce. Fisheries were also the second-largest foreign exchange earner after #Tourism, tourism.
Demographics
 The largest ethnic group is Dhivehis, Dhivehin, i.e. the Maldivians, native to the historic region of the Maldive Islands comprising today's Republic of Maldives and the island of
The largest ethnic group is Dhivehis, Dhivehin, i.e. the Maldivians, native to the historic region of the Maldive Islands comprising today's Republic of Maldives and the island of Minicoy
Minicoy, locally known as Maliku (), is an island in Lakshadweep, India. Along with Viringili, it is on ''Maliku atoll'', the southernmost atoll of Lakshadweep archipelago. Administratively, it is a census town in the Indian union territory ...
in Lakshadweep, Union territory of Lakshadweep, India. They share the same culture and speak the Dhivehi language. They are principally an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan people, having traces of Middle Eastern, South Asian, Austronesian peoples, Austronesian and African genes in the population.
In the past, there was also a small Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, nativ ...
population known as the Giraavaru people. This group has now been almost completely absorbed into the larger Maldivian society but were once native to the island of Giraavaru (Kaafu Atoll). This island was evacuated in 1968 due to heavy erosion of the island.
Some social stratification exists on the islands. It is not rigid, since rank is based on varied factors, including occupation, wealth, Islamic virtue, and family ties. Instead of a complex caste system, there was merely a distinction between noble (bēfulhu) and common people in the Maldives. Members of the social elite are concentrated in Malé.
The population doubled by 1978, and the population growth rate peaked at 3.4% in 1985. At the 2006 census, the population had reached 298,968, although the census in 2000 showed that the population growth rate had declined to 1.9%. Life expectancy at birth stood at 46 years in 1978, and later rose to 72. Infant mortality has declined from 12.7% in 1977 to 1.2% today, and adult literacy reached 99%. Combined school enrollment reached the high 90s. The population was projected to have reached 317,280 in 2010.
The 2014 Population and Housing Census listed the total population in Maldives as 437,535: 339,761 resident Maldivians and 97,774 resident foreigners, approximately 16% of the total population. However, it is believed that foreigners have been undercounted. , there were 281,000 expatriate workers, an estimated 63,000 of whom are undocumented in the Maldives: 3,506 Chinese, 5,029 Nepalese, 15,670 Sri Lankans, 28,840 Indians, and (the largest group of foreigners working in the country) 112,588 Bangladeshis in the Maldives, Bangladeshis. Other immigrants include Filipinos in the Maldives as well as various Western foreign workers.
Religion
After the long Buddhism in the Maldives, Buddhist period of Maldivian history, Muslim traders introduced Islam. Maldivians converted to Islam by the mid-12th century. The islands have had a long history of Sufic orders, as can be seen in the history of the country such as the building of tombs. They were used until as recently as the 1980s for seeking the help of buried saints. They can be seen next to some old mosques and are considered a part of Maldives's cultural heritage. Other aspects of tassawuf, such as ritualised dhikr ceremonies called Maulūdu (Mawlid)—the liturgy of which included recitations and certain supplications in a melodic tone—existed until very recent times. These Maulūdu festivals were held in ornate tents specially built for the occasion. At present Islam is the official religion of the entire population, as adherence to it is required for citizenship. According to Moroccan traveller Ibn Battuta, the person responsible for this conversion was a Sunni Muslim visitor named Abu al-Barakat Yusuf al-Barbari, sailing fromMorocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
. He is also referred to as Tabrizugefaanu. His venerated tomb now stands on the grounds of Medhu Ziyaaraiy, across the street from the Friday Mosque, or Hukuru Miskiy, in Malé. Built in 1656, this is the country's oldest mosque.
Languages
Population by locality
Health
On 24 May 2021, Maldives had the world's fastest-growing COVID-19 pandemic, COVID-19 outbreak, with the highest number of infections per million people over the prior 7 and 14 days, according to data compiled by Bloomberg. Doctors warned that increasing demand for COVID-19 care could hinder their ability to handle other health emergencies in the Maldives. The reason for the outbreak was the Delta variant.Culture
Transportation

Malé
Malé (, ; dv, މާލެ) is the capital and most populous city of the Maldives. With a population of 252,768 and an area of , it is also one of the most densely populated cities in the world. The city is geographically located at the southern ...
and is connected by a bridge. International travel is available on government-owned Island Aviation Services (branded as Maldivian), which operates DHC-6 Twin Otter seaplanes and to nearly all Maldives domestic airports with several Bombardier Dash 8 aircraft, and one Airbus A320 with international service to India, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Malaysia and Thailand.
In Maldives, there are three main ways to travel between islands: by domestic flight, by seaplane, or by boat. For several years there were two seaplane companies operating: TMA (Trans Maldivian Airways) and Maldivian Air Taxi, but these merged in 2013 under the name TMA. The seaplane fleet is entirely made up of DHC-6 Twin Otters. There is also another airline, Flyme (Villa Air), Flyme, which operates using ATR (aircraft manufacturer), ATR planes to domestic airports, principally Villa International Airport Maamigili, Villa-Maamigili, Dharavandhoo Airport, Dharavandhoo and some others. Manta Air begins its first scheduled seaplane service. Its seaplane fleet is made up of DHC-6 Twin Otter aircraft. In addition to the seaplane service, Manta Air utilizes ATR (aircraft manufacturer), ATR 72–600 aircraft to operate domestic flights to Dhaalu Airport, Dharavandhoo Airport and Kooddoo Airport from the main Velana International Airport. Depending on the distance of the destination island from the airport, resorts organise speedboat transfers or seaplane flights directly to the resort island jetty for their guests. Several daily flights operate from Velana International Airport to the 18 domestic and international airports in the country. Scheduled ferries also operate from Malé
Malé (, ; dv, މާލެ) is the capital and most populous city of the Maldives. With a population of 252,768 and an area of , it is also one of the most densely populated cities in the world. The city is geographically located at the southern ...
to many of the atolls. The traditional Maldivian boat is called a Dhoni (fishing vessel), dhoni. Speedboats and seaplanes tend to be more expensive, while travel by dhoni, although slower, is relatively cheaper and convenient.
Education
The Maldives National University is one of the country's three institutions of higher education. Its mission statement is as follows:To create, discover, preserve and disseminate knowledge that is necessary to enhance the lives and livelihoods of people and essential for the cultural, social and economic development of the society so that this nation shall remain free and Islamic forever.In 1973, the Allied Health Services Training Centre (the forerunner of the Faculty of Health Sciences) was established by the Ministry of Health. The Vocational Training Centre was established in 1974, providing training for mechanical and electrical trades. In 1984, the Institute for Teacher Education was created and the School of Hotel and Catering Services was established in 1987 to provide trained personnel for the tourist industry. In 1991, the Institute of Management and Administration was created to train staff for public and private services. In 1998, the Maldives College of Higher Education was founded. The Institute of Shar'ah and Law was founded in January 1999. In 2000 the college launched its first-degree programme, Bachelor of Arts. On 17 January 2011 the Maldives National University Act was passed by the President of the Maldives; The Maldives National University was named on 15 February 2011. In 2015 under a Presidential decree the College of Islamic Studies was changed into the Islamic University of Maldives (IUM).
See also
* List of Maldives-related topics * Outline of Maldives * Maldives Sign Language * Maldives Inland Revenue AuthorityReferences
Further reading
* ''Divehiraajjege Jōgrafīge Vanavaru''. Muhammadu Ibrahim Lutfee. G.Sōsanī. Malé 1999. * H. C. P. Bell, ''The Maldive Islands, An account of the Physical Features, History, Inhabitants, Productions and Trade''. Colombo 1883, . * H.C.P. Bell, ''The Maldive Islands; Monograph on the History, Archaeology and Epigraphy''. Reprint Colombo 1940. Council for Linguistic and Historical Research. Malé 1989. * H.C.P. Bell, ''Excerpta Maldiviana''. Reprint Colombo 1922/35 edn. Asian Educational Services. New Delhi 1999. * ''Divehi Tārīkhah Au Alikameh. Divehi Bahāi Tārikhah Khidmaiykurā Qaumī Markazu''. Reprint 1958 edn. Malé, Maldives 1990. * Christopher, William (1836–38). ''Transactions of the Bombay Geographical Society'', Vol. I. Bombay. * Lieut. I.A. Young & W. Christopher, ''Memoirs on the Inhabitants of the Maldive Islands''. * Wilhelm Geiger, Geiger, Wilhelm. ''Maldivian Linguistic Studies''. Reprint 1919 edn. Asian Educational Services. Delhi 1999. * Hockly, T.W. ''The Two Thousand Isles''. Reprint 1835 edn. Asian Educational Services. Delhi 2003. * Hideyuki Takahashi, ''Maldivian National Security –And the Threats of Mercenaries'', The Round Table (London), No. 351, July 1999, pp. 433–444. * Malten, Thomas: Malediven und Lakkadiven. Materialien zur Bibliographie der Atolle im Indischen Ozean. Beiträge zur Südasien-Forschung Südasien-Institut Universität Heidelberg, Nr. 87. Franz Steiner Verlag. Wiesbaden, 1983. * Vilgon, Lars: Maldive and Minicoy Islands Bibliography with the Laccadive Islands. Published by the author. Stockholm, 1994. * Clarence Maloney, ''People of the Maldive Islands'', Orient Black Swan, 2013 * Xavier Romero-Frias, ''The Maldive Islanders: a study of the popular culture of an ancient ocean kingdom'', NEI, 1999 * Xavier Romero-Frias, ''Folk Tales of the Maldives'', Nordic Institute of Asian Studies, 2012 * Djan Sauerborn,The Perils of Rising Fundamentalism in the Maldives
'', International Relations and Security Network (ISN), Zürich, September 2013 * Djan Sauerborn,
Failing to Transition: Democratization under Stress in the Maldives
', South Asia Democratic Forum (SADF), February 2015
External links
Official tourist information
President's Office
Maldives
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Maldives
from UCB Libraries GovPubs *
Maldives
from the BBC News *
Key Development Forecasts for the Maldives
from International Futures
Constitution of the Republic of Maldives
{{Authority control Maldives, 1965 establishments in Asia Archipelagoes of the Indian Ocean Countries in Asia Island countries Island countries of the Indian Ocean Landforms of South Asia Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation Member states of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation Member states of the United Nations Republics Republics in the Commonwealth of Nations Small Island Developing States South Asian countries States and territories established in 1965 Former least developed countries Western Indo-Pacific Former kingdoms Former sultanates Former protectorates