Lamarckism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Lamarckism, also known as Lamarckian inheritance or neo-Lamarckism, is the notion that an
Lamarckism, also known as Lamarckian inheritance or neo-Lamarckism, is the notion that an
 The inheritance of acquired characteristics was proposed in ancient times, and remained a current idea for many centuries. The historian of science Conway Zirkle wrote in 1935 that:
Zirkle noted that Hippocrates described pangenesis, the theory that what is inherited derives from the whole body of the parent, whereas Aristotle thought it impossible; but that all the same, Aristotle implicitly agreed to the inheritance of acquired characteristics, giving the example of the inheritance of a scar, or of blindness, though noting that children do not always resemble their parents. Zirkle recorded that Pliny the Elder thought much the same. Zirkle pointed out that stories involving the idea of inheritance of acquired characteristics appear numerous times in ancient mythology and the Bible, and persisted through to
The inheritance of acquired characteristics was proposed in ancient times, and remained a current idea for many centuries. The historian of science Conway Zirkle wrote in 1935 that:
Zirkle noted that Hippocrates described pangenesis, the theory that what is inherited derives from the whole body of the parent, whereas Aristotle thought it impossible; but that all the same, Aristotle implicitly agreed to the inheritance of acquired characteristics, giving the example of the inheritance of a scar, or of blindness, though noting that children do not always resemble their parents. Zirkle recorded that Pliny the Elder thought much the same. Zirkle pointed out that stories involving the idea of inheritance of acquired characteristics appear numerous times in ancient mythology and the Bible, and persisted through to

 Between 1800 and 1830, Lamarck proposed a systematic theoretical framework for understanding evolution. He saw evolution as comprising four laws:
# "Life by its own force, tends to increase the volume of all organs which possess the force of life, and the force of life extends the dimensions of those parts up to an extent that those parts bring to themselves;"
# "The production of a new organ in an animal body, results from a new requirement arising. and which continues to make itself felt, and a new movement which that requirement gives birth to, and its upkeep/maintenance;"
# "The development of the organs, and their ability, are constantly a result of the use of those organs."
# "All that has been acquired, traced, or changed, in the physiology of individuals, during their life, is conserved through the genesis, reproduction, and transmitted to new individuals who are related to those who have undergone those changes."
Between 1800 and 1830, Lamarck proposed a systematic theoretical framework for understanding evolution. He saw evolution as comprising four laws:
# "Life by its own force, tends to increase the volume of all organs which possess the force of life, and the force of life extends the dimensions of those parts up to an extent that those parts bring to themselves;"
# "The production of a new organ in an animal body, results from a new requirement arising. and which continues to make itself felt, and a new movement which that requirement gives birth to, and its upkeep/maintenance;"
# "The development of the organs, and their ability, are constantly a result of the use of those organs."
# "All that has been acquired, traced, or changed, in the physiology of individuals, during their life, is conserved through the genesis, reproduction, and transmitted to new individuals who are related to those who have undergone those changes."
 August Weismann's germ plasm theory held that germline cells in the gonads contain information that passes from one generation to the next, unaffected by experience, and independent of the somatic (body) cells. This implied what came to be known as the Weismann barrier, as it would make Lamarckian inheritance from changes to the body difficult or impossible.
Weismann conducted the experiment of removing the tails of 68
August Weismann's germ plasm theory held that germline cells in the gonads contain information that passes from one generation to the next, unaffected by experience, and independent of the somatic (body) cells. This implied what came to be known as the Weismann barrier, as it would make Lamarckian inheritance from changes to the body difficult or impossible.
Weismann conducted the experiment of removing the tails of 68
 The identification of Lamarckism with the inheritance of acquired characteristics is regarded by evolutionary biologists including Ghiselin as a falsified artifact of the subsequent history of evolutionary thought, repeated in textbooks without analysis, and wrongly contrasted with a falsified picture of Darwin's thinking. Ghiselin notes that "Darwin accepted the inheritance of acquired characteristics, just as Lamarck did, and Darwin even thought that there was some experimental evidence to support it." Gould wrote that in the late 19th century, evolutionists "re-read Lamarck, cast aside the guts of it ... and elevated one aspect of the mechanics—inheritance of acquired characters—to a central focus it never had for Lamarck himself." He argued that "the restriction of 'Lamarckism' to this relatively small and non-distinctive corner of Lamarck's thought must be labelled as more than a misnomer, and truly a discredit to the memory of a man and his much more comprehensive system."
The identification of Lamarckism with the inheritance of acquired characteristics is regarded by evolutionary biologists including Ghiselin as a falsified artifact of the subsequent history of evolutionary thought, repeated in textbooks without analysis, and wrongly contrasted with a falsified picture of Darwin's thinking. Ghiselin notes that "Darwin accepted the inheritance of acquired characteristics, just as Lamarck did, and Darwin even thought that there was some experimental evidence to support it." Gould wrote that in the late 19th century, evolutionists "re-read Lamarck, cast aside the guts of it ... and elevated one aspect of the mechanics—inheritance of acquired characters—to a central focus it never had for Lamarck himself." He argued that "the restriction of 'Lamarckism' to this relatively small and non-distinctive corner of Lamarck's thought must be labelled as more than a misnomer, and truly a discredit to the memory of a man and his much more comprehensive system."
 The period of the history of evolutionary thought between Darwin's death in the 1880s, and the foundation of
The period of the history of evolutionary thought between Darwin's death in the 1880s, and the foundation of
 Neo-Lamarckian versions of evolution were widespread in the late 19th century. The idea that living things could to some degree choose the characteristics that would be inherited allowed them to be in charge of their own destiny as opposed to the Darwinian view, which placed them at the mercy of the environment. Such ideas were more popular than natural selection in the late 19th century as it made it possible for biological evolution to fit into a framework of a divine or naturally willed plan, thus the neo-Lamarckian view of evolution was often advocated by proponents of orthogenesis. According to the historian of science Peter J. Bowler, writing in 2003:
Scientists from the 1860s onwards conducted numerous experiments that purported to show Lamarckian inheritance. Some examples are described in the table.
Neo-Lamarckian versions of evolution were widespread in the late 19th century. The idea that living things could to some degree choose the characteristics that would be inherited allowed them to be in charge of their own destiny as opposed to the Darwinian view, which placed them at the mercy of the environment. Such ideas were more popular than natural selection in the late 19th century as it made it possible for biological evolution to fit into a framework of a divine or naturally willed plan, thus the neo-Lamarckian view of evolution was often advocated by proponents of orthogenesis. According to the historian of science Peter J. Bowler, writing in 2003:
Scientists from the 1860s onwards conducted numerous experiments that purported to show Lamarckian inheritance. Some examples are described in the table.
 A century after Lamarck, scientists and philosophers continued to seek mechanisms and evidence for the inheritance of acquired characteristics. Experiments were sometimes reported as successful, but from the beginning these were either criticised on scientific grounds or shown to be fakes. For instance, in 1906, the philosopher Eugenio Rignano argued for a version that he called "centro-epigenesis", but it was rejected by most scientists. Some of the experimental approaches are described in the table.
A century after Lamarck, scientists and philosophers continued to seek mechanisms and evidence for the inheritance of acquired characteristics. Experiments were sometimes reported as successful, but from the beginning these were either criticised on scientific grounds or shown to be fakes. For instance, in 1906, the philosopher Eugenio Rignano argued for a version that he called "centro-epigenesis", but it was rejected by most scientists. Some of the experimental approaches are described in the table.
 A form of Lamarckism was revived in the
A form of Lamarckism was revived in the
 Epigenetic inheritance has been argued by scientists including
Epigenetic inheritance has been argued by scientists including  In 2015, Khursheed Iqbal and colleagues discovered that although "endocrine disruptors exert direct epigenetic effects in the exposed fetal germ cells, these are corrected by reprogramming events in the next generation." Also in 2015, Adam Weiss argued that bringing back Lamarck in the context of epigenetics is misleading, commenting, "We should remember amarckfor the good he contributed to science, not for things that resemble his theory only superficially. Indeed, thinking of CRISPR and other phenomena as Lamarckian only obscures the simple and elegant way evolution really works."
In 2015, Khursheed Iqbal and colleagues discovered that although "endocrine disruptors exert direct epigenetic effects in the exposed fetal germ cells, these are corrected by reprogramming events in the next generation." Also in 2015, Adam Weiss argued that bringing back Lamarck in the context of epigenetics is misleading, commenting, "We should remember amarckfor the good he contributed to science, not for things that resemble his theory only superficially. Indeed, thinking of CRISPR and other phenomena as Lamarckian only obscures the simple and elegant way evolution really works."
 The historian of biology
The historian of biology

The Future of Man
" * "Consists of papers given at a workshop on the origins of music held in Fiesole, Italy, May 1997, the first of a series called Florentine Workshops in Biomusicology." * * * * * "Essays ... based upon papers read at a conference held at the University of Edinburgh ... 1959." * "Annual address of the president of the Biological Society of Washington. Delivered January 24, 1891. (From the Proceedings, vol. VI.)" . * *
at the University of California Museum of Paleontology {{Evolutionary psychology Non-Darwinian evolution History of evolutionary biology Biology theories Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
organism
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells ( cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and fu ...
can pass on to its offspring
In biology, offspring are the young creation of living organisms, produced either by a single organism or, in the case of sexual reproduction, two organisms. Collective offspring may be known as a brood or progeny in a more general way. This ca ...
physical characteristics that the parent organism acquired through use or disuse during its lifetime. It is also called the inheritance of acquired characteristics or more recently soft inheritance. The idea is named after the French zoologist Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Pierre Antoine de Monet, chevalier de Lamarck (1 August 1744 – 18 December 1829), often known simply as Lamarck (; ), was a French naturalist, biologist, academic, and soldier. He was an early proponent of the idea that biolo ...
(1744–1829), who incorporated the classical era theory of soft inheritance into his theory of evolution as a supplement to his concept of orthogenesis
Orthogenesis, also known as orthogenetic evolution, progressive evolution, evolutionary progress, or progressionism, is an obsolete biological hypothesis that organisms have an innate tendency to evolve in a definite direction towards some g ...
, a drive towards complexity.
Introductory textbooks contrast Lamarckism with Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended ...
's theory of evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
by natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Cha ...
. However, Darwin's book ''On the Origin of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life''),The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by Me ...
'' gave credence to the idea of heritable effects of use and disuse, as Lamarck had done, and his own concept of pangenesis similarly implied soft inheritance.
Many researchers from the 1860s onwards attempted to find evidence for Lamarckian inheritance, but these have all been explained away, either by other mechanisms such as genetic contamination or as fraud. August Weismann's experiment, considered definitive in its time, is now considered to have failed to disprove Lamarckism, as it did not address use and disuse. Later, Mendelian genetics supplanted the notion of inheritance of acquired traits, eventually leading to the development of the modern synthesis
Modern synthesis or modern evolutionary synthesis refers to several perspectives on evolutionary biology, namely:
* Modern synthesis (20th century), the term coined by Julian Huxley in 1942 to denote the synthesis between Mendelian genetics and ...
, and the general abandonment of Lamarckism in biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary ...
. Despite this, interest in Lamarckism has continued.
Studies in the fields of epigenetics
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are ...
, genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar work ...
, and somatic hypermutation
Somatic hypermutation (or SHM) is a cellular mechanism by which the immune system adapts to the new foreign elements that confront it (e.g. microbes), as seen during class switching. A major component of the process of affinity maturation, SHM ...
have highlighted limited inheritance of traits acquired by the previous generation. The characterization of these findings as Lamarckism has been disputed. The inheritance of the hologenome, consisting of the genomes of all an organism's symbiotic microbes as well as its own genome, is also somewhat Lamarckian in effect, though entirely Darwinian in its mechanisms.
Early history
Origins
 The inheritance of acquired characteristics was proposed in ancient times, and remained a current idea for many centuries. The historian of science Conway Zirkle wrote in 1935 that:
Zirkle noted that Hippocrates described pangenesis, the theory that what is inherited derives from the whole body of the parent, whereas Aristotle thought it impossible; but that all the same, Aristotle implicitly agreed to the inheritance of acquired characteristics, giving the example of the inheritance of a scar, or of blindness, though noting that children do not always resemble their parents. Zirkle recorded that Pliny the Elder thought much the same. Zirkle pointed out that stories involving the idea of inheritance of acquired characteristics appear numerous times in ancient mythology and the Bible, and persisted through to
The inheritance of acquired characteristics was proposed in ancient times, and remained a current idea for many centuries. The historian of science Conway Zirkle wrote in 1935 that:
Zirkle noted that Hippocrates described pangenesis, the theory that what is inherited derives from the whole body of the parent, whereas Aristotle thought it impossible; but that all the same, Aristotle implicitly agreed to the inheritance of acquired characteristics, giving the example of the inheritance of a scar, or of blindness, though noting that children do not always resemble their parents. Zirkle recorded that Pliny the Elder thought much the same. Zirkle pointed out that stories involving the idea of inheritance of acquired characteristics appear numerous times in ancient mythology and the Bible, and persisted through to Rudyard Kipling
Joseph Rudyard Kipling ( ; 30 December 1865 – 18 January 1936)'' The Times'', (London) 18 January 1936, p. 12. was an English novelist, short-story writer, poet, and journalist. He was born in British India, which inspired much of his work.
...
's ''Just So Stories
''Just So Stories for Little Children'' is a 1902 collection of origin stories by the British author Rudyard Kipling. Considered a classic of children's literature, the book is among Kipling's best known works.
Kipling began working on the ...
''. The idea is mentioned in 18th century sources such as Diderots ''D'Alembert's Dream
''D'Alembert's Dream'' (or ''The Dream of D'Alembert'', french: Le Rêve de d'Alembert) is an ensemble of three philosophical dialogues authored by Denis Diderot in 1769, which first anonymously appeared in the ''Correspondance littéraire, philoso ...
''. Erasmus Darwin's '' Zoonomia'' (c. 1795) suggested that warm-blooded
Warm-blooded is an informal term referring to animal species which can maintain a body temperature higher than their environment. In particular, homeothermic species maintain a stable body temperature by regulating metabolic processes. The on ...
animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage ...
s develop from "one living filament... with the power of acquiring new parts" in response to stimuli, with each round of "improvements" being inherited by successive generations.
Darwin's pangenesis
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended ...
's ''On the Origin of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life''),The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by Me ...
'' proposed natural selection as the main mechanism for development of species, but (like Lamarck) gave credence to the idea of heritable effects of use and disuse as a supplementary mechanism. Darwin subsequently set out his concept of pangenesis in the final chapter of his book '' The Variation of Animals and Plants Under Domestication'' (1868), which gave numerous examples to demonstrate what he thought was the inheritance of acquired characteristics. Pangenesis, which he emphasised was a hypothesis, was based on the idea that somatic cells would, in response to environmental stimulation (use and disuse), throw off 'gemmules
Pangenesis was Charles Darwin's hypothetical mechanism for heredity, in which he proposed that each part of the body continually emitted its own type of small organic particles called gemmules that aggregated in the gonads, contributing heritabl ...
' or 'pangenes' which travelled around the body, though not necessarily in the bloodstream. These pangenes were microscopic particles that supposedly contained information about the characteristics of their parent cell, and Darwin believed that they eventually accumulated in the germ cell
Germ or germs may refer to:
Science
* Germ (microorganism), an informal word for a pathogen
* Germ cell, cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually
* Germ layer, a primary layer of cells that forms during embr ...
s where they could pass on to the next generation the newly acquired characteristics of the parents.
Darwin's half-cousin, Francis Galton, carried out experiments on rabbits, with Darwin's cooperation, in which he transfused the blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
of one variety of rabbit into another variety in the expectation that its offspring would show some characteristics of the first. They did not, and Galton declared that he had disproved Darwin's hypothesis of pangenesis, but Darwin objected, in a letter to the scientific journal ''Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are ...
'', that he had done nothing of the sort, since he had never mentioned blood in his writings. He pointed out that he regarded pangenesis as occurring in protozoa and plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae excl ...
s, which have no blood, as well as in animals.
Lamarck's evolutionary framework
Lamarck's discussion of heredity
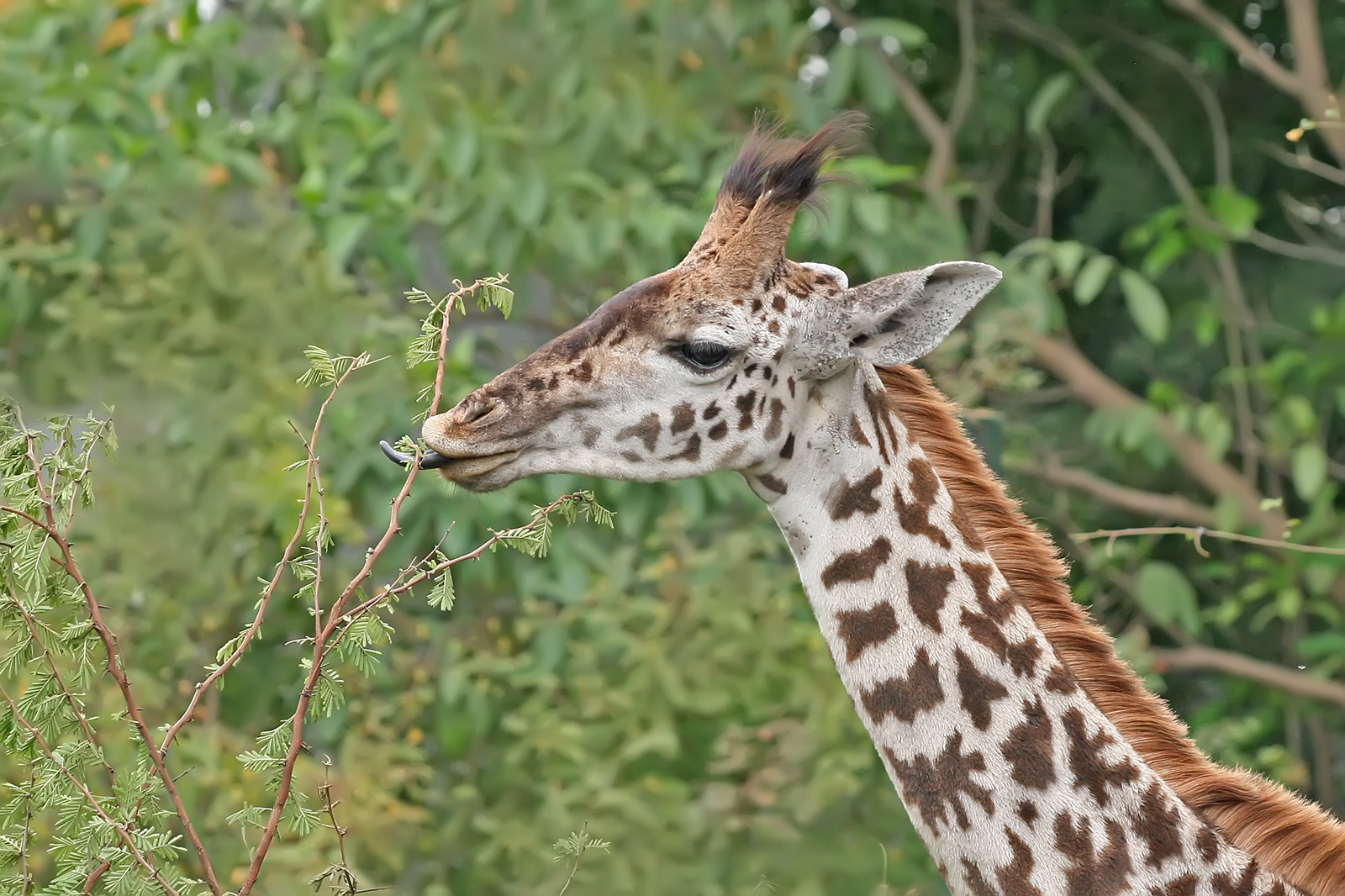
In 1830, in an aside from his evolutionary framework, Lamarck briefly mentioned two traditional ideas in his discussion of heredity, in his day considered to be generally true. The first was the idea of use versus disuse; he theorized that individuals lose characteristics they do not require, or use, and develop characteristics that are useful. The second was to argue that the acquired traits were heritable. He gave as an imagined illustration the idea that when giraffes stretch their necks to reach leaves high in trees, they would strengthen and gradually lengthen their necks. These giraffes would then have offspring with slightly longer necks. In the same way, he argued, ablacksmith
A blacksmith is a metalsmith who creates objects primarily from wrought iron or steel, but sometimes from other metals, by forging the metal, using tools to hammer, bend, and cut (cf. tinsmith). Blacksmiths produce objects such as gates, gr ...
, through his work, strengthens the muscles in his arms, and thus his sons would have similar muscular development when they mature. Lamarck stated the following two laws:
# ''Première Loi: Dans tout animal qui n' a point dépassé le terme de ses développemens, l' emploi plus fréquent et soutenu d' un organe quelconque, fortifie peu à peu cet organe, le développe, l' agrandit, et lui donne une puissance proportionnée à la durée de cet emploi; tandis que le défaut constant d' usage de tel organe, l'affoiblit insensiblement, le détériore, diminue progressivement ses facultés, et finit par le faire disparoître.''
# ''Deuxième Loi: Tout ce que la nature a fait acquérir ou perdre aux individus par l' influence des circonstances où leur race se trouve depuis long-temps exposée, et, par conséquent, par l' influence de l' emploi prédominant de tel organe, ou par celle d' un défaut constant d' usage de telle partie; elle le conserve par la génération aux nouveaux individus qui en proviennent, pourvu que les changemens acquis soient communs aux deux sexes, ou à ceux qui ont produit ces nouveaux individus.''
English translation:
# First Law se and Disuse In every animal which has not passed the limit of its development, a more frequent and continuous use of any organ gradually strengthens, develops and enlarges that organ, and gives it a power proportional to the length of time it has been so used; while the permanent disuse of any organ imperceptibly weakens and deteriorates it, and progressively diminishes its functional capacity, until it finally disappears.
# Second Law oft Inheritance All the acquisitions or losses wrought by nature on individuals, through the influence of the environment in which their race has long been placed, and hence through the influence of the predominant use or permanent disuse of any organ; all these are preserved by reproduction to the new individuals which arise, provided that the acquired modifications are common to both sexes, or at least to the individuals which produce the young.
In essence, a change in the environment brings about change in "needs" (''besoins''), resulting in change in behaviour, causing change in organ usage and development, bringing change in form over time—and thus the gradual transmutation of the species. The evolutionary biologists and historians of science Conway Zirkle, Michael Ghiselin, and Stephen Jay Gould
Stephen Jay Gould (; September 10, 1941 – May 20, 2002) was an American paleontologist, evolutionary biologist, and historian of science. He was one of the most influential and widely read authors of popular science of his generation. Goul ...
have pointed out, these ideas were not original to Lamarck.
Weismann's experiment
white mice
"White Mice" is a special edition sketch of the BBC sitcom ''Only Fools and Horses'', first broadcast on 24 December 1985 on BBC Breakfast Time.
Synopsis
A spoof investigation of Del Boy is conducted by the BBC Breakfast show, '' Breakfast Time ...
, and those of their offspring over five generations, and reporting that no mice were born in consequence without a tail or even with a shorter tail. In 1889, he stated that "901 young were produced by five generations of artificially mutilated parents, and yet there was not a single example of a rudimentary tail or of any other abnormality in this organ." The experiment, and the theory behind it, were thought at the time to be a refutation of Lamarckism.
The experiment's effectiveness in refuting Lamarck's hypothesis is doubtful, as it did not address the ''use and disuse'' of characteristics in response to the environment. The biologist Peter Gauthier noted in 1990 that:
Ghiselin also considered the Weismann tail-chopping experiment to have no bearing on the Lamarckian hypothesis, writing in 1994 that:
The acquired characteristics that figured in Lamarck's thinking were changes that resulted from an individual's own drives and actions, not from the actions of external agents. Lamarck was not concerned with wounds, injuries or mutilations, and nothing that Lamarck had set forth was tested or "disproven" by the Weismann tail-chopping experiment.The historian of science Rasmus Winther stated that Weismann had nuanced views about the role of the environment on the germ plasm. Indeed, like Darwin, he consistently insisted that a variable environment was necessary to cause variation in the hereditary material.
Textbook Lamarckism
 The identification of Lamarckism with the inheritance of acquired characteristics is regarded by evolutionary biologists including Ghiselin as a falsified artifact of the subsequent history of evolutionary thought, repeated in textbooks without analysis, and wrongly contrasted with a falsified picture of Darwin's thinking. Ghiselin notes that "Darwin accepted the inheritance of acquired characteristics, just as Lamarck did, and Darwin even thought that there was some experimental evidence to support it." Gould wrote that in the late 19th century, evolutionists "re-read Lamarck, cast aside the guts of it ... and elevated one aspect of the mechanics—inheritance of acquired characters—to a central focus it never had for Lamarck himself." He argued that "the restriction of 'Lamarckism' to this relatively small and non-distinctive corner of Lamarck's thought must be labelled as more than a misnomer, and truly a discredit to the memory of a man and his much more comprehensive system."
The identification of Lamarckism with the inheritance of acquired characteristics is regarded by evolutionary biologists including Ghiselin as a falsified artifact of the subsequent history of evolutionary thought, repeated in textbooks without analysis, and wrongly contrasted with a falsified picture of Darwin's thinking. Ghiselin notes that "Darwin accepted the inheritance of acquired characteristics, just as Lamarck did, and Darwin even thought that there was some experimental evidence to support it." Gould wrote that in the late 19th century, evolutionists "re-read Lamarck, cast aside the guts of it ... and elevated one aspect of the mechanics—inheritance of acquired characters—to a central focus it never had for Lamarck himself." He argued that "the restriction of 'Lamarckism' to this relatively small and non-distinctive corner of Lamarck's thought must be labelled as more than a misnomer, and truly a discredit to the memory of a man and his much more comprehensive system."
Neo-Lamarckism
Context
 The period of the history of evolutionary thought between Darwin's death in the 1880s, and the foundation of
The period of the history of evolutionary thought between Darwin's death in the 1880s, and the foundation of population genetics
Population genetics is a subfield of genetics that deals with genetic differences within and between populations, and is a part of evolutionary biology. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, and po ...
in the 1920s and the beginnings of the modern evolutionary synthesis in the 1930s, is called the eclipse of Darwinism by some historians of science. During that time many scientists and philosophers accepted the reality of evolution but doubted whether natural selection was the main evolutionary mechanism.
Among the most popular alternatives were theories involving the inheritance of characteristics acquired during an organism's lifetime. Scientists who felt that such Lamarckian mechanisms were the key to evolution were called neo-Lamarckians. They included the British botanist George Henslow
George Henslow (23 March 1835, Cambridge, UK – 30 December 1925, Bournemouth) was an Anglican curate, botanist and author. Henslow was notable for being a defender of Lamarckian evolution.
Biography
The third son of Rev. John Stevens Henslow, ...
(1835–1925), who studied the effects of environmental stress on the growth of plants, in the belief that such environmentally-induced variation might explain much of plant evolution
Plant evolution is the subset of evolutionary phenomena that concern plants. Evolutionary phenomena are characteristics of populations that are described by averages, medians, distributions, and other statistical methods. This distinguishes plant ...
, and the American entomologist Alpheus Spring Packard, Jr., who studied blind animals living in caves and wrote a book in 1901 about Lamarck and his work. Also included were paleontologists like Edward Drinker Cope and Alpheus Hyatt
Alpheus Hyatt (April 5, 1838 – January 15, 1902) was an American zoologist and palaeontologist.
Biography
Alpheus Hyatt II was born in Washington, D.C. to Alpheus Hyatt and Harriet Randolph (King) Hyatt. He briefly attended the Mary ...
, who observed that the fossil record showed orderly, almost linear, patterns of development that they felt were better explained by Lamarckian mechanisms than by natural selection. Some people, including Cope and the Darwin critic Samuel Butler, felt that inheritance of acquired characteristics would let organisms shape their own evolution, since organisms that acquired new habits would change the use patterns of their organs, which would kick-start Lamarckian evolution. They considered this philosophically superior to Darwin's mechanism of random variation acted on by selective pressures. Lamarckism also appealed to those, like the philosopher Herbert Spencer
Herbert Spencer (27 April 1820 – 8 December 1903) was an English philosopher, psychologist, biologist, anthropologist, and sociologist famous for his hypothesis of social Darwinism. Spencer originated the expression " survival of the f ...
and the German anatomist Ernst Haeckel, who saw evolution as an inherently progressive process. The German zoologist Theodor Eimer combined Larmarckism with ideas about orthogenesis
Orthogenesis, also known as orthogenetic evolution, progressive evolution, evolutionary progress, or progressionism, is an obsolete biological hypothesis that organisms have an innate tendency to evolve in a definite direction towards some g ...
, the idea that evolution is directed towards a goal.
With the development of the modern synthesis
Modern synthesis or modern evolutionary synthesis refers to several perspectives on evolutionary biology, namely:
* Modern synthesis (20th century), the term coined by Julian Huxley in 1942 to denote the synthesis between Mendelian genetics and ...
of the theory of evolution, and a lack of evidence for a mechanism for acquiring and passing on new characteristics, or even their heritability, Lamarckism largely fell from favour. Unlike neo-Darwinism, neo-Lamarckism is a loose grouping of largely heterodox theories and mechanisms that emerged after Lamarck's time, rather than a coherent body of theoretical work.
19th century
 Neo-Lamarckian versions of evolution were widespread in the late 19th century. The idea that living things could to some degree choose the characteristics that would be inherited allowed them to be in charge of their own destiny as opposed to the Darwinian view, which placed them at the mercy of the environment. Such ideas were more popular than natural selection in the late 19th century as it made it possible for biological evolution to fit into a framework of a divine or naturally willed plan, thus the neo-Lamarckian view of evolution was often advocated by proponents of orthogenesis. According to the historian of science Peter J. Bowler, writing in 2003:
Scientists from the 1860s onwards conducted numerous experiments that purported to show Lamarckian inheritance. Some examples are described in the table.
Neo-Lamarckian versions of evolution were widespread in the late 19th century. The idea that living things could to some degree choose the characteristics that would be inherited allowed them to be in charge of their own destiny as opposed to the Darwinian view, which placed them at the mercy of the environment. Such ideas were more popular than natural selection in the late 19th century as it made it possible for biological evolution to fit into a framework of a divine or naturally willed plan, thus the neo-Lamarckian view of evolution was often advocated by proponents of orthogenesis. According to the historian of science Peter J. Bowler, writing in 2003:
Scientists from the 1860s onwards conducted numerous experiments that purported to show Lamarckian inheritance. Some examples are described in the table.
Early 20th century
 A century after Lamarck, scientists and philosophers continued to seek mechanisms and evidence for the inheritance of acquired characteristics. Experiments were sometimes reported as successful, but from the beginning these were either criticised on scientific grounds or shown to be fakes. For instance, in 1906, the philosopher Eugenio Rignano argued for a version that he called "centro-epigenesis", but it was rejected by most scientists. Some of the experimental approaches are described in the table.
A century after Lamarck, scientists and philosophers continued to seek mechanisms and evidence for the inheritance of acquired characteristics. Experiments were sometimes reported as successful, but from the beginning these were either criticised on scientific grounds or shown to be fakes. For instance, in 1906, the philosopher Eugenio Rignano argued for a version that he called "centro-epigenesis", but it was rejected by most scientists. Some of the experimental approaches are described in the table.
Late 20th century
The British anthropologistFrederic Wood Jones
Frederic Wood Jones FRS (23 January 1879 – 29 September 1954), usually referred to as Wood Jones, was a British observational naturalist, embryologist, anatomist and anthropologist, who spent considerable time in Australia.
Biography
Jones ...
and the South African paleontologist Robert Broom
Robert Broom FRS FRSE (30 November 1866 6 April 1951) was a British- South African doctor and palaeontologist. He qualified as a medical practitioner in 1895 and received his DSc in 1905 from the University of Glasgow.
From 1903 to 1910, he ...
supported a neo-Lamarckian view of human evolution. The German anthropologist Hermann Klaatsch
Hermann Klaatsch (10 March 1863 – 5 January 1916) was a German physician, anatomist, physical anthropologist, evolutionist, and professor at the University of Heidelberg from 1890, and at the University of Breslau (Wrocław) until 1916.
relied on a neo-Lamarckian model of evolution to try and explain the origin of bipedalism. Neo-Lamarckism remained influential in biology until the 1940s when the role of natural selection was reasserted in evolution as part of the modern evolutionary synthesis.
Herbert Graham Cannon, a British zoologist, defended Lamarckism in his 1959 book ''Lamarck and Modern Genetics''. In the 1960s, "biochemical Lamarckism" was advocated by the embryologist Paul Wintrebert Paul Wintrebert (1867–1966) was a French embryologist and a theoretician of developmental biology.
He coined the term cytoskeleton (''cytosquelette'') in 1931.
He held radical epigenetic views. In his 60s, he published a trilogy in which he desc ...
.
Neo-Lamarckism was dominant in French biology for more than a century. French scientists who supported neo-Lamarckism included Edmond Perrier
Jean Octave Edmond Perrier (9 May 1844 – 31 July 1921) was a French zoologist born in Tulle. He is known for his studies of invertebrates (annelids and echinoderms). He was the brother of zoologist Rémy Perrier (1861–1936).
Career
On advice ...
(1844–1921), Alfred Giard (1846–1908), Gaston Bonnier (1853–1922) and Pierre-Paul Grassé (1895–1985). They followed two traditions, one mechanistic, one vitalistic
Vitalism is a belief that starts from the premise that "living organisms are fundamentally different from non-living entities because they contain some non-physical element or are governed by different principles than are inanimate things." Wher ...
after Henri Bergson's philosophy of evolution.
In 1987, Ryuichi Matsuda
Ryuichi Matsuda (July 8, 1920 – June 19, 1986) was a Japanese entomologist.
He obtained his PhD in entomology from Stanford University. He worked at the Biosystematics Research Institute of Canada.Scheiner, Samuel M. (2004)"The Metamorphosis of ...
coined the term "pan-environmentalism" for his evolutionary theory which he saw as a fusion of Darwinism with neo-Lamarckism. He held that heterochrony
In evolutionary developmental biology, heterochrony is any genetically controlled difference in the timing, rate, or duration of a developmental process in an organism compared to its ancestors or other organisms. This leads to changes in the ...
is a main mechanism for evolutionary change and that novelty in evolution can be generated by genetic assimilation
Genetic assimilation is a process described by Conrad H. Waddington by which a phenotype originally produced in response to an environmental condition, such as exposure to a teratogen, later becomes genetically encoded via artificial selection ...
. His views were criticized by Arthur M. Shapiro for providing no solid evidence for his theory. Shapiro noted that "Matsuda himself accepts too much at face value and is prone to wish-fulfilling interpretation."
Ideological neo-Lamarckism
 A form of Lamarckism was revived in the
A form of Lamarckism was revived in the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
of the 1930s when Trofim Lysenko promoted the ideologically-driven research programme, Lysenkoism; this suited the ideological opposition of Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet Union, Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as Ge ...
to genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar work ...
. Lysenkoism influenced Soviet agricultural policy which in turn was later blamed for crop failures.
Critique
George Gaylord Simpson in his book '' Tempo and Mode in Evolution'' (1944) claimed that experiments in heredity have failed to corroborate any Lamarckian process. Simpson noted that neo-Lamarckism "stresses a factor that Lamarck rejected: inheritance of direct effects of the environment" and neo-Lamarckism is closer to Darwin's pangenesis than Lamarck's views. Simpson wrote, "the inheritance of acquired characters, failed to meet the tests of observation and has been almost universally discarded by biologists." Botanist Conway Zirkle pointed out that Lamarck did not originate the hypothesis that acquired characteristics could be inherited, so it is incorrect to refer to it as Lamarckism:What Lamarck really did was to accept the hypothesis that acquired characters were heritable, a notion which had been held almost universally for well over two thousand years and which his contemporaries accepted as a matter of course, and to assume that the results of such inheritance were cumulative from generation to generation, thus producing, in time, new species. His individual contribution to biological theory consisted in his application to the problem of the origin of species of the view that acquired characters were inherited and in showing that evolution could be inferred logically from the accepted biological hypotheses. He would doubtless have been greatly astonished to learn that a belief in the inheritance of acquired characters is now labeled "Lamarckian," although he would almost certainly have felt flattered if evolution itself had been so designated.Peter Medawar wrote regarding Lamarckism, "very few professional biologists believe that anything of the kind occurs—or can occur—but the notion persists for a variety of nonscientific reasons." Medawar stated there is no known mechanism by which an adaptation acquired in an individual's lifetime can be imprinted on the genome and Lamarckian inheritance is not valid unless it excludes the possibility of natural selection but this has not been demonstrated in any experiment. Martin Gardner wrote in his book '' Fads and Fallacies in the Name of Science'' (1957):
A host of experiments have been designed to test Lamarckianism. All that have been verified have proved negative. On the other hand, tens of thousands of experiments— reported in the journals and carefully checked and rechecked by geneticists throughout the world— have established the correctness of the gene-mutation theory beyond all reasonable doubt... In spite of the rapidly increasing evidence for natural selection, Lamarck has never ceased to have loyal followers.... There is indeed a strong emotional appeal in the thought that every little effort an animal puts forth is somehow transmitted to his progeny.According to Ernst Mayr, any Lamarckian theory involving the inheritance of acquired characters has been refuted as " DNA does not directly participate in the making of the phenotype and that the phenotype, in turn, does not control the composition of the DNA." Peter J. Bowler has written that although many early scientists took Lamarckism seriously, it was discredited by genetics in the early twentieth century.
Mechanisms resembling Lamarckism
Studies in the field ofepigenetics
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are ...
, genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar work ...
and somatic hypermutation
Somatic hypermutation (or SHM) is a cellular mechanism by which the immune system adapts to the new foreign elements that confront it (e.g. microbes), as seen during class switching. A major component of the process of affinity maturation, SHM ...
have highlighted the possible inheritance of traits acquired by the previous generation. However, the characterization of these findings as Lamarckism has been disputed.
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance
 Epigenetic inheritance has been argued by scientists including
Epigenetic inheritance has been argued by scientists including Eva Jablonka
Eva Jablonka ( he, חווה יבלונקה) (born 1952) is an Israeli evolutionary theorist and geneticist, known especially for her interest in epigenetic inheritance. Born in 1952 in Poland, she emigrated to Israel in 1957. She is a professor a ...
and Marion J. Lamb
Marion Julia Lamb (29 July 1939 – 12 December 2021) was Senior Lecturer at Birkbeck, University of London, before her retirement. She studied the effect of environmental conditions such as heat, radiation and pollution on metabolic activity and ...
to be Lamarckian. Epigenetics is based on hereditary elements other than genes that pass into the germ cells. These include methylation patterns in DNA and chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important ...
marks on histone
In biology, histones are highly basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei. They act as spools around which DNA winds to create structural units called nucleosomes. Nucleosomes in turn a ...
proteins, both involved in gene regulation
Regulation of gene expression, or gene regulation, includes a wide range of mechanisms that are used by cells to increase or decrease the production of specific gene products ( protein or RNA). Sophisticated programs of gene expression are w ...
. These marks are responsive to environmental stimuli, differentially affect gene expression, and are adaptive, with phenotypic
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological pr ...
effects that persist for some generations. The mechanism may also enable the inheritance of behavioral traits, for example in chickens, rats and human populations that have experienced starvation, DNA methylation resulting in altered gene function in both the starved population and their offspring. Methylation similarly mediates epigenetic inheritance in plants such as rice. Small RNA molecules, too, may mediate inherited resistance to infection. Handel and Romagopalan commented that "epigenetics allows the peaceful co-existence of Darwinian and Lamarckian evolution."
Joseph Springer and Dennis Holley commented in 2013 that:
Lamarck and his ideas were ridiculed and discredited. In a strange twist of fate, Lamarck may have the last laugh. Epigenetics, an emerging field of genetics, has shown that Lamarck may have been at least partially correct all along. It seems that reversible and heritable changes can occur without a change in DNA sequence (genotype) and that such changes may be induced spontaneously or in response to environmental factors—Lamarck's "acquired traits." Determining which observed phenotypes are genetically inherited and which are environmentally induced remains an important and ongoing part of the study of genetics, developmental biology, and medicine.The prokaryotic CRISPR system and Piwi-interacting RNA could be classified as Lamarckian, within a Darwinian framework. However, the significance of epigenetics in evolution is uncertain. Critics such as the evolutionary biologist Jerry Coyne point out that epigenetic inheritance lasts for only a few generations, so it is not a stable basis for evolutionary change. The evolutionary biologist T. Ryan Gregory contends that epigenetic inheritance should not be considered Lamarckian. According to Gregory, Lamarck did not claim that the environment directly affected living things. Instead, Lamarck "argued that the environment created needs to which organisms responded by using some features more and others less, that this resulted in those features being accentuated or attenuated, and that this difference was then inherited by offspring." Gregory has stated that Lamarckian evolution in epigenetics is more like Darwin's point of view than Lamarck's. In 2007, David Haig wrote that research into epigenetic processes does allow a Lamarckian element in evolution but the processes do not challenge the main tenets of the modern evolutionary synthesis as modern Lamarckians have claimed. Haig argued for the primacy of DNA and evolution of epigenetic switches by natural selection. Haig has written that there is a "visceral attraction" to Lamarckian evolution from the public and some scientists, as it posits the world with a meaning, in which organisms can shape their own evolutionary destiny. Thomas Dickens and Qazi Rahman (2012) have argued that epigenetic mechanisms such as DNA methylation and histone modification are genetically inherited under the control of natural selection and do not challenge the modern synthesis. They dispute the claims of Jablonka and Lamb on Lamarckian epigenetic processes.
Somatic hypermutation and reverse transcription to germline
In the 1970s, the Australian immunologistEdward J. Steele
Edward J. "Ted" Steele is an Australian molecular immunologist with interests in virology and evolution. He is an honorary research associate at the C.Y.O'Connor ERADE Village Foundation in Piara Waters, WA, Australia.
Steele was also the s ...
developed a neo-Lamarckian theory of somatic hypermutation
Somatic hypermutation (or SHM) is a cellular mechanism by which the immune system adapts to the new foreign elements that confront it (e.g. microbes), as seen during class switching. A major component of the process of affinity maturation, SHM ...
within the immune system and coupled it to the reverse transcription of RNA derived from body cells to the DNA of germline cells. This reverse transcription process supposedly enabled characteristics or bodily changes acquired during a lifetime to be written back into the DNA and passed on to subsequent generations.
The mechanism was meant to explain why homologous DNA sequences from the VDJ gene regions of parent mice were found in their germ cells and seemed to persist in the offspring for a few generations. The mechanism involved the somatic selection and clonal amplification of newly acquired antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of t ...
gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
sequences generated via somatic hypermutation in B-cells. The messenger RNA products of these somatically novel genes were captured by retroviruses endogenous to the B-cells and were then transported through the bloodstream where they could breach the Weismann or soma-germ barrier and reverse transcribe the newly acquired genes into the cells of the germ line, in the manner of Darwin's pangenes.
Peter J. Bowler
Peter J. Bowler (born 8 October 1944) is a historian of biology who has written extensively on the history of evolutionary thought, the history of the environmental sciences, and on the history of genetics. His 1984 book, ''Evolution: The Hi ...
noted in 1989 that other scientists had been unable to reproduce his results, and described the scientific consensus at the time:
Bowler commented that " teele'swork was bitterly criticized at the time by biologists who doubted his experimental results and rejected his hypothetical mechanism as implausible."
Hologenome theory of evolution
The hologenome theory of evolution, while Darwinian, has Lamarckian aspects. An individual animal or plant lives in symbiosis with manymicroorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in old ...
s, and together they have a "hologenome" consisting of all their genomes. The hologenome can vary like any other genome by mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, m ...
, sexual recombination
Genetic recombination (also known as genetic reshuffling) is the exchange of genetic material between different organisms which leads to production of offspring with combinations of traits that differ from those found in either parent. In eukaryot ...
, and chromosome rearrangement
In genetics, a chromosomal rearrangement is a mutation that is a type of chromosome abnormality involving a change in the structure of the native chromosome. Such changes may involve several different classes of events, like deletions, duplica ...
, but in addition it can vary when populations of microorganisms increase or decrease (resembling Lamarckian use and disuse), and when it gains new kinds of microorganism (resembling Lamarckian inheritance of acquired characteristics). These changes are then passed on to offspring. The mechanism is largely uncontroversial, and natural selection does sometimes occur at whole system (hologenome) level, but it is not clear that this is always the case.
Baldwin effect
The Baldwin effect, named after the psychologist James Mark Baldwin by George Gaylord Simpson in 1953, proposes that the ability to learn new behaviours can improve an animal's reproductive success, and hence the course of natural selection on its genetic makeup. Simpson stated that the mechanism was "not inconsistent with the modern synthesis" of evolutionary theory,Depew, David J. (2003), "Baldwin Boosters, Baldwin Skeptics" in: though he doubted that it occurred very often, or could be proven to occur. He noted that the Baldwin effect provided a reconciliation between the neo-Darwinian and neo-Lamarckian approaches, something that the modern synthesis had seemed to render unnecessary. In particular, the effect allows animals to adapt to a new stress in the environment through behavioural changes, followed by genetic change. This somewhat resembles Lamarckism but without requiring animals to inherit characteristics acquired by their parents. The Baldwin effect is broadly accepted by Darwinists. Dennett, Daniel (2003), "The Baldwin Effect, a Crane, not a Skyhook" in:In sociocultural evolution
Within the field ofcultural evolution
Cultural evolution is an evolutionary theory of social change. It follows from the definition of culture as "information capable of affecting individuals' behavior that they acquire from other members of their species through teaching, imitation ...
, Lamarckism has been applied as a mechanism for dual inheritance theory. Gould viewed culture as a Lamarckian process whereby older generations transmitted adaptive information to offspring via the concept of learning. In the history of technology, components of Lamarckism have been used to link cultural development to human evolution by considering technology as extensions of human anatomy.
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * . Retrieved 2015-10-26. * * * * * * * * * ** * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * ** * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Translation of ''Lamarck, ou, Le mythe du précurseur'' (1979) * * * * * * * * * * Contains the BBCReith Lectures
The Reith Lectures is a series of annual BBC radio lectures given by leading figures of the day. They are commissioned by the BBC and broadcast on Radio 4 and the World Service. The lectures were inaugurated in 1948 to mark the historic cont ...
The Future of Man
" * "Consists of papers given at a workshop on the origins of music held in Fiesole, Italy, May 1997, the first of a series called Florentine Workshops in Biomusicology." * * * * * "Essays ... based upon papers read at a conference held at the University of Edinburgh ... 1959." * "Annual address of the president of the Biological Society of Washington. Delivered January 24, 1891. (From the Proceedings, vol. VI.)" . * *
External links
at the University of California Museum of Paleontology {{Evolutionary psychology Non-Darwinian evolution History of evolutionary biology Biology theories Jean-Baptiste Lamarck