Lake Tiberias on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Sea of Galilee ( he, יָם כִּנֶּרֶת,
The lake is fed partly by underground springs, but its main source is the
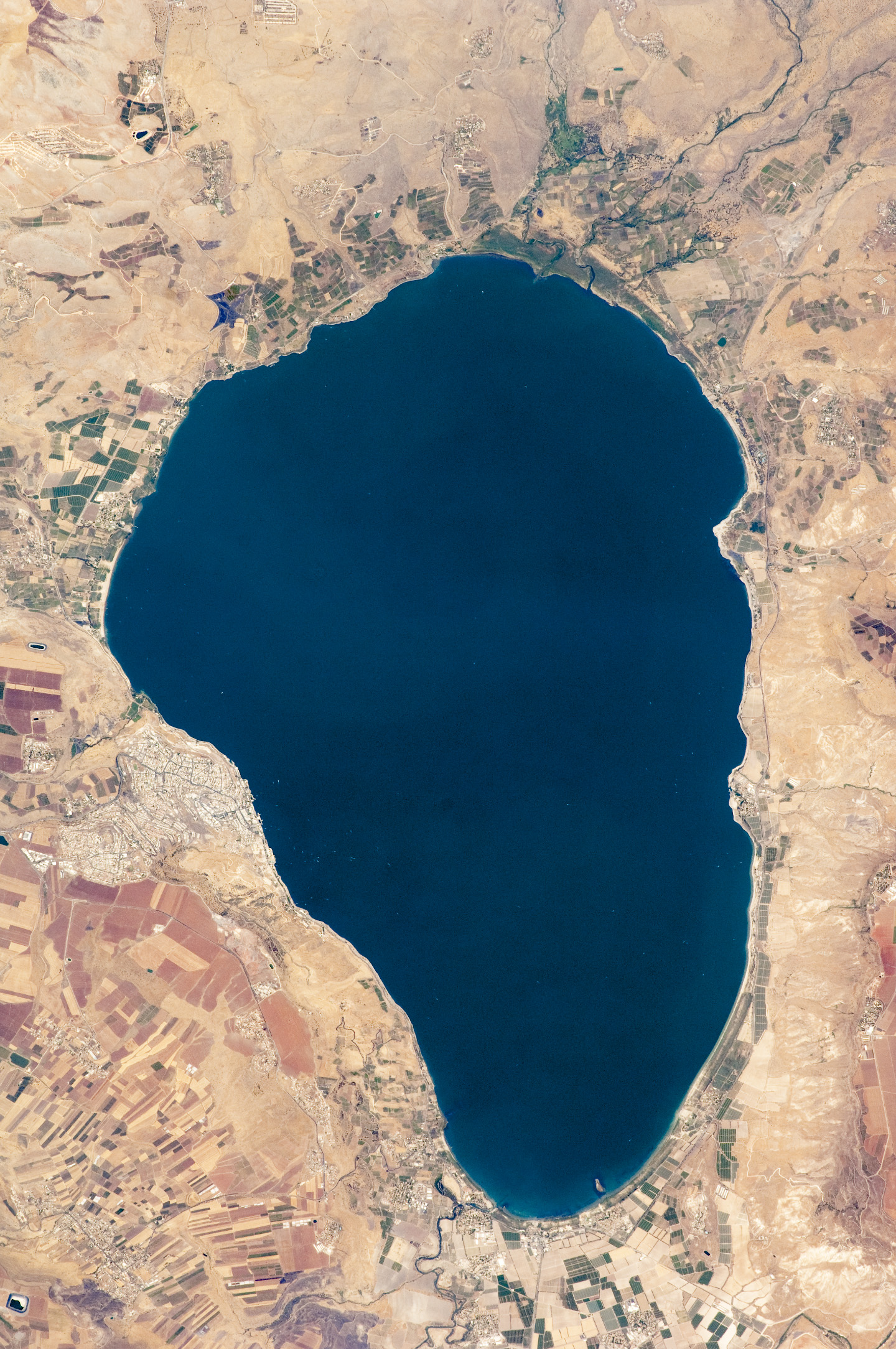
 The Sea of Galilee is situated in northeast
The Sea of Galilee is situated in northeast

 In the New Testament, much of the
In the New Testament, much of the

 In 1917, the British defeated Ottoman Turkish forces and took control of Palestine, while France took control of Syria. In the carve-up of the Ottoman territories between Britain and France, it was agreed that Britain would retain control of Palestine, while France would control Syria. However, the allies had to fix the border between the
In 1917, the British defeated Ottoman Turkish forces and took control of Palestine, while France took control of Syria. In the carve-up of the Ottoman territories between Britain and France, it was agreed that Britain would retain control of Palestine, while France would control Syria. However, the allies had to fix the border between the
 On 15 May 1948, Syria invaded the newborn State of Israel, capturing territory along the Sea of Galilee. Under the 1949 armistice agreement between Israel and Syria, Syria occupied the northeast shoreline of the Sea of Galilee. The agreement, though, stated that the armistice line was "not to be interpreted as having any relation whatsoever to ultimate territorial arrangements." Syria remained in possession of the lake's northeast shoreline until the 1967
On 15 May 1948, Syria invaded the newborn State of Israel, capturing territory along the Sea of Galilee. Under the 1949 armistice agreement between Israel and Syria, Syria occupied the northeast shoreline of the Sea of Galilee. The agreement, though, stated that the armistice line was "not to be interpreted as having any relation whatsoever to ultimate territorial arrangements." Syria remained in possession of the lake's northeast shoreline until the 1967
 In 1986 the Ancient Galilee Boat, also known as the Jesus Boat, was discovered on the north-west shore of the Sea of Galilee during a drought when water levels receded. It is an ancient fishing boat from the 1st century AD, and although there is no evidence directly linking the boat to Jesus and his disciples, it nevertheless is an example of the kind of boat that Jesus and his disciples, some of whom were fishermen, may have used.
During a routine sonar scan in 2003 (finding published in 2013), archaeologists discovered an enormous conical stone structure. The structure, which has a diameter of around , is made of boulders and stones. The ruins are estimated to be between 2,000 and 12,000 years old, and are about underwater. The estimated weight of the monument is over 60,000 tons. Researchers explain that the site resembles early burial sites in Europe and was likely built in the early Bronze Age.
In February 2018, archaeologists discovered seven intact mosaics with
In 1986 the Ancient Galilee Boat, also known as the Jesus Boat, was discovered on the north-west shore of the Sea of Galilee during a drought when water levels receded. It is an ancient fishing boat from the 1st century AD, and although there is no evidence directly linking the boat to Jesus and his disciples, it nevertheless is an example of the kind of boat that Jesus and his disciples, some of whom were fishermen, may have used.
During a routine sonar scan in 2003 (finding published in 2013), archaeologists discovered an enormous conical stone structure. The structure, which has a diameter of around , is made of boulders and stones. The ruins are estimated to be between 2,000 and 12,000 years old, and are about underwater. The estimated weight of the monument is over 60,000 tons. Researchers explain that the site resembles early burial sites in Europe and was likely built in the early Bronze Age.
In February 2018, archaeologists discovered seven intact mosaics with
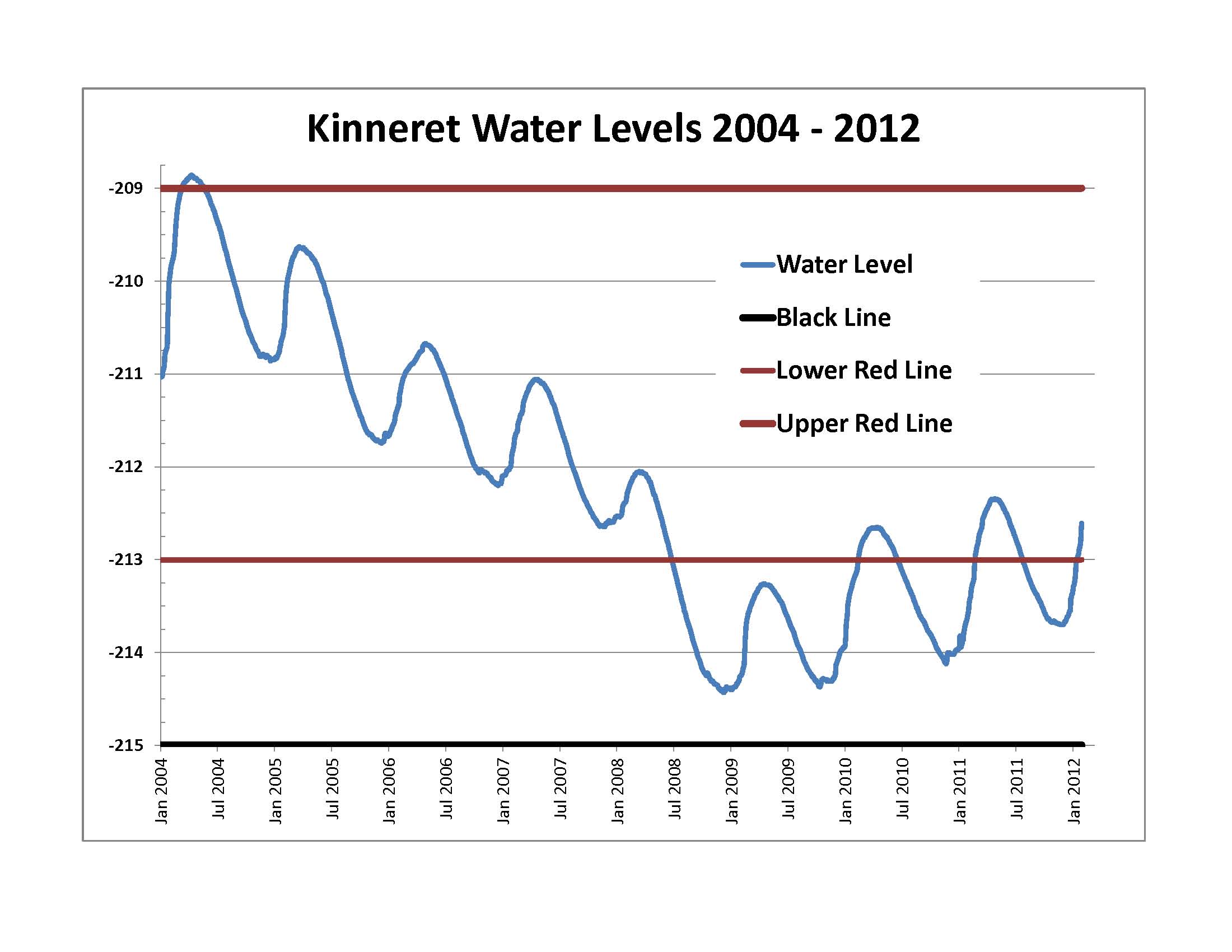 The water level is monitored and regulated. There are three levels at which the alarm is rung:
* The upper red line, below
The water level is monitored and regulated. There are three levels at which the alarm is rung:
* The upper red line, below
Tourism & Nature, 20 February 2019, via Israel Between The Lines, accessed 21 January 2020 Daily monitoring of the Sea of Galilee's water level began in 1969, and the lowest level recorded since then was November 2001, which today constitutes the "black line" of 214.87 meters below sea level (although it is believed the water level had fallen lower than the current black line, during droughts earlier in the 20th century). The Israeli government monitors water levels and publishes the results daily at this web page. The level over the past eight years can be retrieved from that site. Increasing water demand in Israel, Lebanon and Jordan, as well as dry winters, have resulted in stress on the lake and a decreasing water line to dangerously low levels at times. The Sea of Galilee is at risk of becoming irreversibly salinized by the salt water springs under the lake, which are held in check by the weight of the freshwater on top of them. With extreme drought conditions continuing to intensify, the government of Israel approved a plan in 2018 to pump desalinated water into the lake in an effort to stop the water level from plunging below a point where irreversible ecological damage to the lake might take place. Since the beginning of the 2018–19 rainy season, the Sea of Galilee has risen considerably. From being near the ecologically dangerous l black line of −214.4 m, the level has risen by 16 April 2020 to just below the upper red line, due to strong rains and a radical decrease in pumping. During the entire 2018–19 rainy season the water level rose by a historical record of , while the 2019–20 winter brought a rise until 16 April, the rainy season not being over yet. The Water Authority has dug a new canal in order to let of water flow from the lake directly into the Jordan River, bypassing the existing dams system for technical and financial reasons. As at 9 January 2020, the water level was at below sea level. It will be considered full if the water level rises by another . By 19 January 2020, the water level was below sea level, short of being considered full. As of 5 April 2020, the water level was below sea level, the highest level it has been since 2004. On 24 April the level was below sea level.
 Israel's
Israel's


 The warm waters of the Sea of Galilee support various flora and fauna, which have supported a significant commercial fishery for more than two millennia. Local flora include various reeds along most of the shoreline as well as
The warm waters of the Sea of Galilee support various flora and fauna, which have supported a significant commercial fishery for more than two millennia. Local flora include various reeds along most of the shoreline as well as
World Lakes Database entry for Sea of Galilee
Kinneret Data Center
// Kinneret Limnological Laboratory
Sea of Galilee – official government page
(Hebrew).
Sea of Galilee water level
(Hebrew) // official government page
Database: Water levels of Sea of Galilee since 1966
(Hebrew)
Updated elevation of the Kinneret's level
(Hebrew). Elevation (meters below sea level) is shown on the line following the date line. {{DEFAULTSORT:Galilee, Sea Of Lakes of Israel
Judeo-Aramaic
Judaeo-Aramaic languages represent a group of Hebrew-influenced Aramaic and Neo-Aramaic languages.
Early use
Aramaic, like Hebrew, is a Northwest Semitic language, and the two share many features. From the 7th century BCE, Aramaic became the ...
: יַמּא דטבריא, גִּנֵּיסַר, ar, بحيرة طبريا), also called Lake Tiberias, Kinneret or Kinnereth, is a freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does incl ...
lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much large ...
in Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
. It is the lowest freshwater lake on Earth and the second-lowest lake in the world (after the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea ( he, יַם הַמֶּלַח, ''Yam hamMelaḥ''; ar, اَلْبَحْرُ الْمَيْتُ, ''Āl-Baḥrū l-Maytū''), also known by other names, is a salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east and Israel and the West Ban ...
, a saltwater lake), at levels between and below sea level. It is approximately in circumference, about long, and wide. Its area is at its fullest, and its maximum depth is approximately .Data Summary: Lake Kinneret (Sea of Galilee)The lake is fed partly by underground springs, but its main source is the
Jordan River
The Jordan River or River Jordan ( ar, نَهْر الْأُرْدُنّ, ''Nahr al-ʾUrdunn'', he, נְהַר הַיַּרְדֵּן, ''Nəhar hayYardēn''; syc, ܢܗܪܐ ܕܝܘܪܕܢܢ ''Nahrāʾ Yurdnan''), also known as ''Nahr Al-Shariea ...
, which flows through it from north to south and exits the lake at the Degania Dam.
Geography
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, between the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights ( ar, هَضْبَةُ الْجَوْلَانِ, Haḍbatu l-Jawlān or ; he, רמת הגולן, ), or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant spanning about . The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between di ...
and the Galilee
Galilee (; he, הַגָּלִיל, hagGālīl; ar, الجليل, al-jalīl) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon. Galilee traditionally refers to the mountainous part, divided into Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and Lower Gali ...
region, in the Jordan Rift Valley
The Jordan Rift Valley, also Jordan Valley ''Bīrʿāt haYardēn'', ar, الغور Al-Ghor or Al-Ghawr),, date=November 2022 also called the Syro-African Depression, is an elongated depression located in modern-day Israel, and Jordan. This g ...
, the valley caused by the separation of the African and Arabian
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
plates. Consequently, the area is subject to earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, fr ...
s, and in the past, volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plat ...
activity. This is evident from the abundant basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
and other igneous
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or ...
rocks that define the geology of Galilee.
Names
The lake has been called by different names throughout its history, usually depending on the dominant settlement on its shores. With the changing fate of the towns, the lake's name also changed.Sea of Kinneret
The modern Hebrew name, ''Kinneret'', comes from theHebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' Hebrew Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
in . This name was also found in the scripts of '' Hebrew Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
Ugarit
)
, image =Ugarit Corbel.jpg
, image_size=300
, alt =
, caption = Entrance to the Royal Palace of Ugarit
, map_type = Near East#Syria
, map_alt =
, map_size = 300
, relief=yes
, location = Latakia Governorate, Syria
, region = ...
, in the Aqhat Epic. As the name of a city, ''Kinneret'' was listed among the "fenced cities" in . A persistent, though likely erroneous, popular etymology of the name presumes that the name ''Kinneret'' may originate from the Hebrew word '' kinnor'' ("harp" or "lyre"), because of the shape of the lake. The scholarly consensus, however, is that the origin of the name is derived from the important Bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids suc ...
and Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ...
city of Kinneret, excavated at Tell el-'Oreimeh. The city of Kinneret may have been named after the body of water rather than vice versa, and there is no evidence for the origin of the town's name. For a different etymology, see Galilee#Sea of Galilee.
Lake of Gennesaret
All Old andNew Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chris ...
writers use the term "sea" (Hebrew יָם ''yam'', Greek θάλασσα), with the exception of Luke, who calls it "the Lake of Gennesaret" (), from the Greek λίμνη Γεννησαρέτ (''limnē Gennēsaret''), the "Grecized form of Chinnereth" according to Easton (1897). For a different etymology, see Galilee#Sea of Galilee.
Sea of Ginosar
TheBabylonian Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the cent ...
, as well as Flavius Josephus, mention the sea by the name "Sea of Ginosar" after the small fertile plain of Ginosar that lies on its western side. Ginosar is yet another name derived from "Kinneret".
Sea of Galilee, Sea of Tiberias, Lake Tiberias
The word "Galilee" comes from the Hebrew ''Haggalil'' (הַגָלִיל), which literally means "The District", a compressed form of ''Gelil Haggoyim'' "The District of Nations" (Isaiah 8:23). Toward the end of the first century CE, the Sea of Galilee became widely known as the Sea of Tiberias after the eponymous city founded on its western shore in honour of the second Roman emperor, Tiberius. In the New Testament, the term "sea of Galilee" (, ''thalassan tēs Galilaias'') is used in thegospel of Matthew
The Gospel of Matthew), or simply Matthew. It is most commonly abbreviated as "Matt." is the first book of the New Testament of the Bible and one of the three synoptic Gospels. It tells how Israel's Messiah, Jesus, comes to his people and form ...
, the gospel of Mark
The Gospel of Mark), or simply Mark (which is also its most common form of abbreviation). is the second of the four canonical gospels and of the three synoptic Gospels. It tells of the ministry of Jesus from his baptism by John the Baptist to h ...
, and in the gospel of John
The Gospel of John ( grc, Εὐαγγέλιον κατὰ Ἰωάννην, translit=Euangélion katà Iōánnēn) is the fourth of the four canonical gospels. It contains a highly schematic account of the ministry of Jesus, with seven "sig ...
as "the sea of Galilee, which is ''the sea'' of Tiberias" (θαλάσσης τῆς Γαλιλαίας τῆς Τιβεριάδος, ''thalassēs tēs Galilaias tēs Tiberiados''), the late 1st century CE name. Sea of Tiberias
Tiberias ( ; he, טְבֶרְיָה, ; ar, طبريا, Ṭabariyyā) is an Israeli city on the western shore of the Sea of Galilee. A major Jewish center during Late Antiquity, it has been considered since the 16th century one of Judaism's F ...
is also the name mentioned in Roman texts and in the Jerusalem Talmud
The Jerusalem Talmud ( he, תַּלְמוּד יְרוּשַׁלְמִי, translit=Talmud Yerushalmi, often for short), also known as the Palestinian Talmud or Talmud of the Land of Israel, is a collection of rabbinic notes on the second-century ...
, and it was adopted into Arabic as (بحيرة طبريا), "Lake Tiberias".
Sea of Minya
From theUmayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
through the Mamluk
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning " slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') ...
period, the lake was known in Arabic as ''"Bahr al-Minya"'', the "Sea of Minya", after the Umayyad '' qasr'' complex, whose ruins are still visible at Khirbat al-Minya
Khirbat al-Minya ( ar, قصر المنية), also known as Ayn Minyat Hisham (Arabic) or Horvat Minnim (Hebrew) is an Umayyad-built palace in the eastern Galilee, Israel, located about west of the northern end of Lake Tiberias. It was erected as ...
. This is the name used by the medieval Persian and Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
scholars Al-Baladhuri, Al-Tabari
( ar, أبو جعفر محمد بن جرير بن يزيد الطبري), more commonly known as al-Ṭabarī (), was a Muslim historian and scholar from Amol, Tabaristan. Among the most prominent figures of the Islamic Golden Age, al-Tabari ...
and Ibn Kathir
Abū al-Fiḍā’ ‘Imād ad-Dīn Ismā‘īl ibn ‘Umar ibn Kathīr al-Qurashī al-Damishqī (Arabic: إسماعيل بن عمر بن كثير القرشي الدمشقي أبو الفداء عماد; – 1373), known as Ibn Kathīr (, was ...
.
History
Prehistory
In 1989, remains of ahunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fung ...
site were found under the water at the southern end. Remains of mud huts were found in Ohalo. Nahal Ein Gev, located about 3 km east of the lake, contains a village from the late Natufian
The Natufian culture () is a Late Epipaleolithic archaeological culture of the Levant, dating to around 15,000 to 11,500 years ago. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentary or semi-sedentary population even before the introducti ...
period. The site is considered one of the first permanent human settlements in the world from a time predating the Neolithic revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, or the (First) Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making an inc ...
.
Hellenistic and Roman periods
The Sea of Galilee lies on the ancient Via Maris, which linkedEgypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
with the northern empires. The Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, ot ...
, Hasmoneans, and Romans founded flourishing towns and settlements on the lake including Hippos and Tiberias
Tiberias ( ; he, טְבֶרְיָה, ; ar, طبريا, Ṭabariyyā) is an Israeli city on the western shore of the Sea of Galilee. A major Jewish center during Late Antiquity, it has been considered since the 16th century one of Judaism's F ...
. The first-century historian Flavius Josephus was so impressed by the area that he wrote, "One may call this place the ambition of Nature"; he also reported a thriving fishing industry at this time, with 230 boats regularly working in the lake. Archaeologists discovered one such boat, nicknamed the Jesus Boat, in 1986.
The New Testament

 In the New Testament, much of the
In the New Testament, much of the ministry of Jesus
The ministry of Jesus, in the canonical gospels, begins with his baptism in the countryside of Roman Judea and Transjordan, near the River Jordan by John the Baptist, and ends in Jerusalem, following the Last Supper with his disciples.''Ch ...
occurs on the shores of the Sea of Galilee. In those days, there was a continuous ribbon development of settlements and villages around the lake and plenty of trade and ferrying by boat. The Synoptic Gospels
The gospels of Matthew, Mark, and Luke are referred to as the synoptic Gospels because they include many of the same stories, often in a similar sequence and in similar or sometimes identical wording. They stand in contrast to John, whose ...
of Mark 1:14–20), Matthew 4:18–22), and Luke 5:1–11) describe how Jesus recruited four of his apostles
An apostle (), in its literal sense, is an emissary, from Ancient Greek ἀπόστολος (''apóstolos''), literally "one who is sent off", from the verb ἀποστέλλειν (''apostéllein''), "to send off". The purpose of such sending ...
from the shores of the Kinneret: the fishermen Simon and his brother Andrew
Andrew is the English form of a given name common in many countries. In the 1990s, it was among the top ten most popular names given to boys in English-speaking countries. "Andrew" is frequently shortened to "Andy" or "Drew". The word is derive ...
and the brothers John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
and James. One of Jesus' famous teaching episodes, the Sermon on the Mount
The Sermon on the Mount ( anglicized from the Matthean Vulgate Latin section title: ) is a collection of sayings attributed to Jesus of Nazareth found in the Gospel of Matthew (chapters 5, 6, and 7). that emphasizes his moral teachings. It ...
, is supposed to have been given on a hill overlooking the Kinneret. Many of his miracles are also said to have occurred here including his walking on water, calming the storm, the disciples and the miraculous catch of fish, and his feeding five thousand people (in Tabgha
Tabgha ( ar, الطابغة, ''al-Tabigha''; he, עין שבע, ''Ein Sheva'' which means "spring of seven") is an area situated on the north-western shore of the Sea of Galilee in Israel and a depopulated Palestinian village. It is tradition ...
). In John's Gospel
The Gospel of John ( grc, Εὐαγγέλιον κατὰ Ἰωάννην, translit=Euangélion katà Iōánnēn) is the fourth of the four canonical gospels. It contains a highly schematic account of the ministry of Jesus, with seven "si ...
the sea provides the setting for Jesus' third post-resurrection appearance to his disciples ( John 21).
Late Roman period
In 135 CE, Bar Kokhba's revolt was put down. The Romans responded by banning all Jews fromJerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
. The center of Jewish culture and learning shifted to the region of Galilee and the Kinneret, particularly the city of Tiberias
Tiberias ( ; he, טְבֶרְיָה, ; ar, طبريا, Ṭabariyyā) is an Israeli city on the western shore of the Sea of Galilee. A major Jewish center during Late Antiquity, it has been considered since the 16th century one of Judaism's F ...
. It was in this region that the Jerusalem Talmud
The Jerusalem Talmud ( he, תַּלְמוּד יְרוּשַׁלְמִי, translit=Talmud Yerushalmi, often for short), also known as the Palestinian Talmud or Talmud of the Land of Israel, is a collection of rabbinic notes on the second-century ...
was compiled.
Byzantine period
In the time of theByzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, the Kinneret's significance in Jesus' life made it a major destination for Christian pilgrims
Christianity has a strong tradition of pilgrimages, both to sites relevant to the New Testament narrative (especially in the Holy Land) and to sites associated with later saints or miracles.
History
Christian pilgrimages were first made ...
. This led to the growth of a full-fledged tourist
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism ...
industry, complete with package tours and plenty of comfortable inns.
Early Muslim and Crusader periods
The Sea of Galilee's importance declined when the Byzantines lost control and the area was conquered by theUmayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
and subsequent Islamic empires. The palace of Minya was built by the lake during the reign of the Umayyad caliph al-Walid I
Al-Walid ibn Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan ( ar, الوليد بن عبد الملك بن مروان, al-Walīd ibn ʿAbd al-Malik ibn Marwān; ), commonly known as al-Walid I ( ar, الوليد الأول), was the sixth Umayyad caliph, ruling from O ...
(705–715 CE). Apart from Tiberias, the major towns and cities in the area were gradually abandoned.
In 1187, Sultan Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt an ...
defeated the armies of the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem ( la, Regnum Hierosolymitanum; fro, Roiaume de Jherusalem), officially known as the Latin Kingdom of Jerusalem or the Frankish Kingdom of Palestine,Example (title of works): was a Crusader state that was establish ...
at the Battle of Hattin
The Battle of Hattin took place on 4 July 1187, between the Crusader states of the Levant and the forces of the Ayyubid sultan Saladin. It is also known as the Battle of the Horns of Hattin, due to the shape of the nearby extinct volcano of ...
, largely because he was able to cut the Crusaders off from the valuable fresh water of the Sea of Galilee.
Ottoman period
The lake had little importance within the early Ottoman Empire. Tiberias did see a significant revival of its Jewish community in the 16th century, but had gradually declined, until in 1660 the city was completely destroyed. In the early 18th century, Tiberias was rebuilt by Zahir al-Umar, becoming the center of his rule overGalilee
Galilee (; he, הַגָּלִיל, hagGālīl; ar, الجليل, al-jalīl) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon. Galilee traditionally refers to the mountainous part, divided into Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and Lower Gali ...
, and seeing also a revival of its Jewish community.
Zionist beginnings
In 1908, Jewish pioneers established the Kinneret Farm at the same time as and next to Moshavat Kinneret in the immediate vicinity of the lake. The farm trained Jewish immigrants in modern farming. One group of youth from the training farm established Kvutzat Degania in 1909–1910, popularly considered as the firstkibbutz
A kibbutz ( he, קִבּוּץ / , lit. "gathering, clustering"; plural: kibbutzim / ) is an intentional community in Israel that was traditionally based on agriculture. The first kibbutz, established in 1909, was Degania. Today, farming h ...
, another group founded Kvutzat Kinneret in 1913, and yet another the first proper kibbutz, Ein Harod, in 1921, the same year when the first moshav
A moshav ( he, מוֹשָׁב, plural ', lit. ''settlement, village'') is a type of Israeli town or settlement, in particular a type of cooperative agricultural community of individual farms pioneered by the Labour Zionists between 1904 ...
, Nahalal, was established by a group trained at the Farm. The Jewish settlements around Kinneret Farm are considered the cradle of the kibbutz culture of early Zionism
Zionism ( he, צִיּוֹנוּת ''Tsiyyonut'' after '' Zion'') is a nationalist movement that espouses the establishment of, and support for a homeland for the Jewish people centered in the area roughly corresponding to what is known in Je ...
; Kvutzat Kinneret is the birthplace of Naomi Shemer (1930–2004), buried at the Kinneret Cemetery next to Rachel (1890–1931)—two of the most prominent national poets.
British Mandate
Borders, customs, water rights

 In 1917, the British defeated Ottoman Turkish forces and took control of Palestine, while France took control of Syria. In the carve-up of the Ottoman territories between Britain and France, it was agreed that Britain would retain control of Palestine, while France would control Syria. However, the allies had to fix the border between the
In 1917, the British defeated Ottoman Turkish forces and took control of Palestine, while France took control of Syria. In the carve-up of the Ottoman territories between Britain and France, it was agreed that Britain would retain control of Palestine, while France would control Syria. However, the allies had to fix the border between the Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 ...
and the French Mandate of Syria
The Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon (french: Mandat pour la Syrie et le Liban; ar, الانتداب الفرنسي على سوريا ولبنان, al-intidāb al-fransi 'ala suriya wa-lubnān) (1923−1946) was a League of Nations mandate foun ...
. The boundary was defined in broad terms by the Franco-British Boundary Agreement of December 1920, which drew it across the middle of the lake.Franco-British Convention on Certain Points Connected with the Mandates for Syria and the Lebanon, Palestine and Mesopotamia, signed 23 December 1920. Text available in ''American Journal of International Law'', Vol. 16, No. 3, 1922, 122–126. However, the commission established by the 1920 treaty redrew the boundary. The Zionist movement pressured the French and British to assign as many water sources as possible to Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 ...
during the demarcating negotiations. The High Commissioner of Palestine, Herbert Samuel, had sought full control of the Sea of Galilee. The negotiations led to the inclusion into the Palestine territory of the whole Sea of Galilee, both sides of the River Jordan, Lake Hula, Dan spring, and part of the Yarmouk. The final border approved in 1923 followed a 10-meter wide strip along the lake's northeastern shore, cutting the Mandatory Syria
The First Syrian Republic, officially the Syrian Republic, '; french: République syrienne was formed in 1930 as a component of the Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon, succeeding the State of Syria. A treaty of independence was made in 1936 t ...
( State of Damascus) off from the lake.
The British and French Agreement provided that existing rights over the use of the waters of the river Jordan by the inhabitants of Syria would be maintained; the Government of Syria would have the right to erect a new pier at Semakh on Lake Tiberias or jointly use the existing pier; persons or goods passing between the landing-stage on the Lake of Tiberias and Semakh would not be subject to customs regulations, and the Syrian government would have access to the said landing-stage; the inhabitants of Syria and Lebanon would have the same fishing and navigation rights on Lakes Huleh, Tiberias and River Jordan, while the Government of Palestine would be responsible for policing of lakes.
State of Israel
 On 15 May 1948, Syria invaded the newborn State of Israel, capturing territory along the Sea of Galilee. Under the 1949 armistice agreement between Israel and Syria, Syria occupied the northeast shoreline of the Sea of Galilee. The agreement, though, stated that the armistice line was "not to be interpreted as having any relation whatsoever to ultimate territorial arrangements." Syria remained in possession of the lake's northeast shoreline until the 1967
On 15 May 1948, Syria invaded the newborn State of Israel, capturing territory along the Sea of Galilee. Under the 1949 armistice agreement between Israel and Syria, Syria occupied the northeast shoreline of the Sea of Galilee. The agreement, though, stated that the armistice line was "not to be interpreted as having any relation whatsoever to ultimate territorial arrangements." Syria remained in possession of the lake's northeast shoreline until the 1967 Arab-Israeli war
The Arab citizens of Israel are the Demographics of Israel#Arabs, largest ethnic minority in the country. They comprise a hybrid community of Israeli citizenship law, Israeli citizens with a heritage of Palestinian Citizenship Order 1925, Pales ...
.
In the 1950s, Israel formulated a plan to link the Kinneret with the rest of the country's water infrastructure via the National Water Carrier
National Water Carrier of Israel
The National Water Carrier of Israel ( he, המוביל הארצי, ''HaMovil HaArtzi'') is the largest water project in Israel, completed in 1964. Its main purpose is to transfer water from the Sea of Galilee ...
, in order to supply the water demand of the growing country. The carrier was completed in 1964. The Israeli plan, to which the Arab League
The Arab League ( ar, الجامعة العربية, ' ), formally the League of Arab States ( ar, جامعة الدول العربية, '), is a regional organization in the Arab world, which is located in Northern Africa, Western Africa, E ...
opposed its own plan to divert the headwaters of the Jordan River, sparked political and sometimes even armed confrontations over the Jordan River basin.
After five years of drought , Sea of Galilee is expected to get to the black line
}
The Black War was a period of violent conflict between British colonists and Aboriginal Tasmanians in Tasmania from the mid-1820s to 1832. The conflict, fought largely as a guerrilla war by both sides, claimed the lives of 600 to 900 Aborigi ...
. The black elevation line is the lowest depth from which irreversible damage begins and no water can be pumped out any more. Israel Oceanographic and Limnological Research describes it as "The black line marks −214.87 m, the lowest-ever level reached since 1926 when the water level record began. According to the water authority, the Kinneret water level must not decline below this level."
In February 2018, the city of Tiberias
Tiberias ( ; he, טְבֶרְיָה, ; ar, طبريا, Ṭabariyyā) is an Israeli city on the western shore of the Sea of Galilee. A major Jewish center during Late Antiquity, it has been considered since the 16th century one of Judaism's F ...
requested a desalination plant to treat the water coming from the Sea of Galilee and demanded a new water source for the city. March 2018 was the lowest point in water income to the lake since 1927.
In September 2018 the Israeli energy and water office announced a project to pour desalinated water from the Mediterranean Sea into the Sea of Galilee using a tunnel. The tunnel is expected to be the largest of its kind in Israel and will transfer half of the Mediterranean desalted water and will move 300 to 500 million cubic meters of water per year. The plan is said to cost five billion shekels. Giora Eiland led the meetings with German counterparts to find a suitable contractor to build the project.
Archaeology
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
inscriptions. One inscription, one of the longest found to date in western Galilee, gives the names of donors and the names and positions of church officials, including Irenaeus
Irenaeus (; grc-gre, Εἰρηναῖος ''Eirēnaios''; c. 130 – c. 202 AD) was a Greek bishop noted for his role in guiding and expanding Christian communities in the southern regions of present-day France and, more widely, for the de ...
. Another mosaic mentions a woman as a donor to the church's construction. This inscription is the first in the region to mention a female donor.
Water level
 The water level is monitored and regulated. There are three levels at which the alarm is rung:
* The upper red line, below
The water level is monitored and regulated. There are three levels at which the alarm is rung:
* The upper red line, below sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardis ...
(BSL), where facilities on the shore start being flooded.
* The lower red line, BSL, pumping should stop.
* The black (low-level) line, BSL, irreversible damage occurs.The Rise and Fall of the Sea of GalileeTourism & Nature, 20 February 2019, via Israel Between The Lines, accessed 21 January 2020 Daily monitoring of the Sea of Galilee's water level began in 1969, and the lowest level recorded since then was November 2001, which today constitutes the "black line" of 214.87 meters below sea level (although it is believed the water level had fallen lower than the current black line, during droughts earlier in the 20th century). The Israeli government monitors water levels and publishes the results daily at this web page. The level over the past eight years can be retrieved from that site. Increasing water demand in Israel, Lebanon and Jordan, as well as dry winters, have resulted in stress on the lake and a decreasing water line to dangerously low levels at times. The Sea of Galilee is at risk of becoming irreversibly salinized by the salt water springs under the lake, which are held in check by the weight of the freshwater on top of them. With extreme drought conditions continuing to intensify, the government of Israel approved a plan in 2018 to pump desalinated water into the lake in an effort to stop the water level from plunging below a point where irreversible ecological damage to the lake might take place. Since the beginning of the 2018–19 rainy season, the Sea of Galilee has risen considerably. From being near the ecologically dangerous l black line of −214.4 m, the level has risen by 16 April 2020 to just below the upper red line, due to strong rains and a radical decrease in pumping. During the entire 2018–19 rainy season the water level rose by a historical record of , while the 2019–20 winter brought a rise until 16 April, the rainy season not being over yet. The Water Authority has dug a new canal in order to let of water flow from the lake directly into the Jordan River, bypassing the existing dams system for technical and financial reasons. As at 9 January 2020, the water level was at below sea level. It will be considered full if the water level rises by another . By 19 January 2020, the water level was below sea level, short of being considered full. As of 5 April 2020, the water level was below sea level, the highest level it has been since 2004. On 24 April the level was below sea level.
Water use
 Israel's
Israel's National Water Carrier
National Water Carrier of Israel
The National Water Carrier of Israel ( he, המוביל הארצי, ''HaMovil HaArtzi'') is the largest water project in Israel, completed in 1964. Its main purpose is to transfer water from the Sea of Galilee ...
, completed in 1964, transports water from the lake to the population centers of Israel, and in the past supplied most of the country's drinking water. Nowadays the lake supplies approximately 10% of Israel's drinking water needs.
In 1964, Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
attempted construction of a Headwater Diversion Plan that would have blocked the flow of water into the Sea of Galilee, sharply reducing the water flow into the lake. This project and Israel's attempt to block these efforts in 1965 were factors which played into regional tensions culminating in the 1967 Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab states (primarily Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 ...
. During the war, Israel captured the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights ( ar, هَضْبَةُ الْجَوْلَانِ, Haḍbatu l-Jawlān or ; he, רמת הגולן, ), or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant spanning about . The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between di ...
, which contain some of the sources of water for the Sea of Galilee.
Up until the mid-2010s, about of water was pumped through the National Water Carrier each year. Under the terms of the Israel–Jordan peace treaty, Israel also supplies of water annually from the lake to Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
. In recent years the Israeli government has made extensive investments in water conservation, reclamation and desalination
Desalination is a process that takes away mineral components from saline water. More generally, desalination refers to the removal of salts and minerals from a target substance, as in soil desalination, which is an issue for agriculture. Salt ...
infrastructure in the country. This has allowed it to significantly reduce the amount of water pumped from the lake annually in an effort to restore and improve its ecological environment, as well as respond to some of the most extreme drought conditions in hundreds of years affecting the lake's intake basin since 1998. Therefore, it was expected that in 2016 only about of water would be drawn from the lake for Israeli domestic consumption, a small fraction of the amount typically drawn from the lake over the previous decades.
Tourism

Tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
around the Sea of Galilee is an important economic segment. Historical and religious sites in the region draw both local and foreign tourists. The Sea of Galilee is an attraction for Christian pilgrims
Christianity has a strong tradition of pilgrimages, both to sites relevant to the New Testament narrative (especially in the Holy Land) and to sites associated with later saints or miracles.
History
Christian pilgrimages were first made ...
who visit Israel to see the places where Jesus performed miracles according to the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chris ...
, such as his walking on water, calming the storm and feeding the multitude. Alonzo Ketcham Parker, a nineteenth-century American traveler, called visiting the Sea of Galilee "a 'fifth gospel' which one read devoutly, his heart overflowing with quiet joy".
In April 2011, Israel unveiled a hiking trail
A trail, also known as a path or track, is an unpaved lane or small road usually passing through a natural area. In the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland, a path or footpath is the preferred term for a pedestrian or hiking trail. The ...
in Galilee
Galilee (; he, הַגָּלִיל, hagGālīl; ar, الجليل, al-jalīl) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon. Galilee traditionally refers to the mountainous part, divided into Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and Lower Gali ...
for Christian pilgrims, called the "Jesus Trail
The Jesus Trail ( he, שביל ישו, ''Sh'víl Yeshú'') is a hiking and pilgrimage route in the Galilee region of Israel that traces the route Jesus may have walked, connecting many sites from his life and ministry. The main part of the ...
". It includes a network of footpaths, roads and bicycle paths linking sites central to the lives of Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
and his disciples. It ends at Capernaum on the shores of the Sea of Galilee, where Jesus expounded his teachings.
Another key attraction is the site where the Sea of Galilee's water flows into the Jordan River
The Jordan River or River Jordan ( ar, نَهْر الْأُرْدُنّ, ''Nahr al-ʾUrdunn'', he, נְהַר הַיַּרְדֵּן, ''Nəhar hayYardēn''; syc, ܢܗܪܐ ܕܝܘܪܕܢܢ ''Nahrāʾ Yurdnan''), also known as ''Nahr Al-Shariea ...
, to which thousands of pilgrims from all over the world come to be baptized every year.
Israel's most well-known open water swim race, the Kinneret Crossing, is held every year in September, drawing thousands of open water swimmers to participate in competitive and noncompetitive events.
Tourists also partake in the building of rafts on ''Lavnun Beach'', called Rafsodia. Here many different age groups work together to build a raft with their bare hands and then sail that raft across the sea.
Other economic activities include fishing in the lake and agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
, particularly banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large herbaceous flowering plants in the genus ''Musa''. In some countries, bananas used for cooking may be called "plantains", disting ...
s, dates, mangoes, grapes and olives in the fertile belt of land surrounding it.
The Turkish Aviators Monument, erected during the Ottoman era, stands near Kibbutz Ha'on on the lakeshore, commemorating the Turkish pilots whose monoplanes crashed en route to Jerusalem.
Flora, fauna and ecology
 The warm waters of the Sea of Galilee support various flora and fauna, which have supported a significant commercial fishery for more than two millennia. Local flora include various reeds along most of the shoreline as well as
The warm waters of the Sea of Galilee support various flora and fauna, which have supported a significant commercial fishery for more than two millennia. Local flora include various reeds along most of the shoreline as well as phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'.
...
. Fauna include zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by ...
, benthos
Benthos (), also known as benthon, is the community of organisms that live on, in, or near the bottom of a sea, river, lake, or stream, also known as the benthic zone.Acanthobrama terraesanctae
''Acanthobrama terraesanctae'', the Kinneret bream or Kinneret bleak, is a species of freshwater fish in the family Cyprinidae
Cyprinidae is a family of freshwater fish commonly called the carp or minnow family. It includes the carps, the tru ...
''. The Fishing and Agricultural Division of the Ministry of Water and Agriculture of Israel is listing 10 families of fish living in the lake, with a total of 27 species – 19 native and 8 introduced from elsewhere. Local fishermen talk of three types of fish: "مشط musht" (tilapia
Tilapia ( ) is the common name for nearly a hundred species of cichlid fish from the coelotilapine, coptodonine, heterotilapine, oreochromine, pelmatolapiine, and tilapiine tribes (formerly all were "Tilapiini"), with the economically most ...
), sardine (the Kinneret bleak, ''Acanthobrama terraesanctae
''Acanthobrama terraesanctae'', the Kinneret bream or Kinneret bleak, is a species of freshwater fish in the family Cyprinidae
Cyprinidae is a family of freshwater fish commonly called the carp or minnow family. It includes the carps, the tru ...
''), "بني biny" (carp
Carp are various species of oily freshwater fish from the family Cyprinidae, a very large group of fish native to Europe and Asia. While carp is consumed in many parts of the world, they are generally considered an invasive species in parts of ...
-like), and catfish
Catfish (or catfishes; order Siluriformes or Nematognathi) are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive, ...
. The tilapia species include the Galilean tilapia ('' Sarotherodon galilaeus''), the blue tilapia (''Oreochromis aureus
The blue tilapia (''Oreochromis aureus'') is a species of tilapia, a fish in the family Cichlidae. Native to Northern and Western Africa, and the Middle East, through introductions it is now also established elsewhere, including parts of the ...
''), and the redbelly tilapia ('' Tilapia zillii''). Fish caught commercially include '' Tristramella simonis'' and the Galilean tilapia, locally called "St. Peter's fish". In 2005, of tilapia were caught by local fishermen. This dropped to in 2009 due to overfishing.
A fish species that is unique to the lake, '' Tristramella sacra'', used to spawn
Spawn or spawning may refer to:
* Spawn (biology), the eggs and sperm of aquatic animals
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Spawn (character), a fictional character in the comic series of the same name and in the associated franchise
** '' Spawn: A ...
in the marsh and has not been seen since the 1990s droughts. Conservationists fear this species may have become extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
.
Low water levels in drought years have stressed the lake's ecology. This may have been aggravated by over-extraction of water for either the National Water Carrier to supply other parts of Israel or, since 1994, for the supply of water to Jordan (see ''"Water use"'' section above). Droughts of the early and mid-1990s dried out the marshy northern margin of the lake. It is hoped that drastic reductions in the amount of water pumped through the National Water Carrier will help restore the lake's ecology over the span of several years. The amount planned to be drawn in 2016 for Israeli domestic water use was expected to be less than 10% of the amount commonly drawn on an annual basis in the decades before the mid-2010s.
Important Bird Area
The lake, with its immediate surrounds, has been recognised as anImportant Bird Area
An Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) is an area identified using an internationally agreed set of criteria as being globally important for the conservation of bird populations.
IBA was developed and sites are identified by BirdLife Inte ...
(IBA) by BirdLife International
BirdLife International is a global partnership of non-governmental organizations that strives to conserve birds and their habitats. BirdLife International's priorities include preventing extinction of bird species, identifying and safeguarding ...
because it supports populations of black francolin
The black francolin (''Francolinus francolinus'') is a gamebird in the pheasant family Phasianidae of the order Galliformes, gallinaceous birds. It was formerly known as the black partridge. It is the state bird of Haryana state, India (locally ...
s and non-breeding griffon vultures as well as many wintering waterbird
A water bird, alternatively waterbird or aquatic bird, is a bird that lives on or around water. In some definitions, the term ''water bird'' is especially applied to birds in freshwater ecosystems, although others make no distinction from sea ...
s, including marbled teals, great crested grebe
The great crested grebe (''Podiceps cristatus'') is a member of the grebe family of water birds noted for its elaborate mating display.
Taxonomy
The great crested grebe was formally described by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in t ...
s, grey heron
The grey heron (''Ardea cinerea'') is a long-legged wading bird of the heron family, Ardeidae, native throughout temperate Europe and Asia and also parts of Africa. It is resident in much of its range, but some populations from the more north ...
s, great white egret
The great egret (''Ardea alba''), also known as the common egret, large egret, or (in the Old World) great white egret or great white heron is a large, widely distributed egret. The four subspecies are found in Asia, Africa, the Americas, and ...
s, great cormorant
The great cormorant (''Phalacrocorax carbo''), known as the black shag in New Zealand and formerly also known as the great black cormorant across the Northern Hemisphere, the black cormorant in Australia, and the large cormorant in India, is a w ...
s and black-headed gull
The black-headed gull (''Chroicocephalus ridibundus'') is a small gull that breeds in much of the Palearctic including Europe and also in coastal eastern Canada. Most of the population is migratory and winters further south, but some birds ...
s.
See also
*Miracles of Jesus
The miracles of Jesus are Miracle, miraculous deeds attributed to Jesus in Christianity, Christian and Islamic texts. The majority are faith healings, exorcisms, resurrections, and control over nature.
In the Synoptic Gospels (Gospel of Mark, ...
* Sea of Galilee Boat
The Ancient Galilee Boat, also known as the Jesus Boat, is an ancient fishing boat from the 1st century AD, discovered in 1986 on the north-west shore of the Sea of Galilee in Israel. The remains of the boat, 27 feet (8.27 meters) long, 7.5 feet ( ...
* '' The Storm on the Sea of Galilee'', 1633 Rembrandt
Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn (, ; 15 July 1606 – 4 October 1669), usually simply known as Rembrandt, was a Dutch Golden Age painter, printmaker and draughtsman. An innovative and prolific master in three media, he is generally cons ...
painting
* Tourism in Israel
Tourism in Israel is one of Israel's major sources of income, with a record 4.55 million tourist arrivals in 2019, and, in 2017, contributed NIS 20 billion to the Israeli economy making it an all-time record. Israel offers a plethora of historica ...
References
Further reading
* *External links
World Lakes Database entry for Sea of Galilee
Kinneret Data Center
// Kinneret Limnological Laboratory
Sea of Galilee – official government page
(Hebrew).
Sea of Galilee water level
(Hebrew) // official government page
Database: Water levels of Sea of Galilee since 1966
(Hebrew)
Updated elevation of the Kinneret's level
(Hebrew). Elevation (meters below sea level) is shown on the line following the date line. {{DEFAULTSORT:Galilee, Sea Of Lakes of Israel
Sea
The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the ocean, is the body of salty water that covers approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The word sea is also used to denote second-order sections of the sea, such as the Mediterranean Sea, ...
Sea
The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the ocean, is the body of salty water that covers approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The word sea is also used to denote second-order sections of the sea, such as the Mediterranean Sea, ...
Tourist attractions in Israel
Catholic pilgrimage sites
Sacred lakes
Shrunken lakes
Jordan River basin
Important Bird Areas of Israel