Laie Hawaii Temple on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Laie Hawaii Temple is a
 In 1915, Joseph F. Smith, then sixth president of the LDS Church, announced plans for the first temple outside the contiguous United States and chose Lāʻie for its construction. According to
In 1915, Joseph F. Smith, then sixth president of the LDS Church, announced plans for the first temple outside the contiguous United States and chose Lāʻie for its construction. According to  When news of the new Laie Hawaii Temple reached
When news of the new Laie Hawaii Temple reached
 LDS Church president Joseph F. Smith wanted the architecture of the Laie Hawaii Temple to resemble
LDS Church president Joseph F. Smith wanted the architecture of the Laie Hawaii Temple to resemble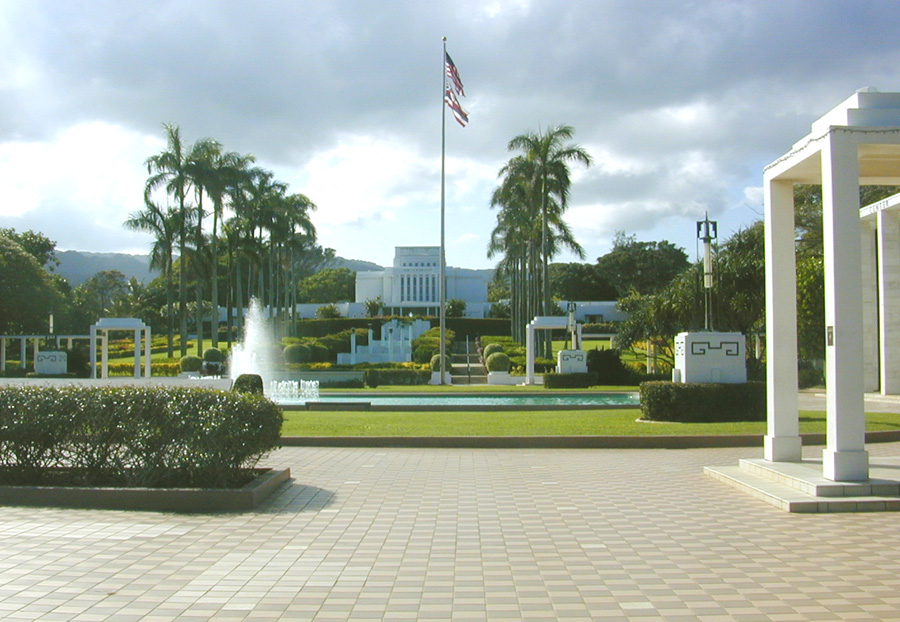  The exterior of the temple exhibits four large
The exterior of the temple exhibits four large  As visitors approach the temple and pass a number of reflecting pools, a maternity fountain sits in front of the uppermost pool. Designed by the Fairbanks brothers, this bold relief honors Hawaiian Motherhood and depicts a Hawaiian mother holding a
As visitors approach the temple and pass a number of reflecting pools, a maternity fountain sits in front of the uppermost pool. Designed by the Fairbanks brothers, this bold relief honors Hawaiian Motherhood and depicts a Hawaiian mother holding a
New site
At the base of the temple grounds is a fountain separating an LDS Family History Center and a Visitors' Center, where a ten-foot sculpture replica of
Laie Hawaii Temple Official siteLaie Hawaii Temple Visitors' CenterLaie Hawaii Temple
at ChurchofJesusChristTemples.org {{Good article 20th-century Latter Day Saint temples Buildings and structures in Honolulu County, Hawaii Buildings designed to replicate Solomon's Temple Hawaiian architecture Landmarks in Hawaii Religious buildings and structures in Hawaii Churches completed in 1919 Temples (LDS Church) in Oceania Temples (LDS Church) in the United States The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in Hawaii 1919 establishments in Hawaii
temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Christianity, Christian church that considers itself to be the Restorationism, restoration of the ...
(LDS Church) located on the northeast shore of the Hawaiian island of Oahu
Oahu () ( Hawaiian: ''Oʻahu'' ()), also known as "The Gathering Place", is the third-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is home to roughly one million people—over two-thirds of the population of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The island of O ...
. The temple sits on a small hill, half a mile from the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
, in the town of Lāie, from Honolulu
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the isla ...
. Along with Brigham Young University–Hawaii
Brigham Young University–Hawaii (BYU–Hawaii) is a private university in Laie, Hawaii. It is owned and operated by the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). BYU-Hawaii was founded in 1955, and became a satellite campus o ...
and the Polynesian Cultural Center
The Polynesian Cultural Center (PCC) is a family-centered cultural tourist attraction and living museum located in Laie, on the northern shore of Oahu, Hawaii. The PCC is owned by the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church), wa ...
, the Laie Hawaii Temple plays an important role in the town of Lā'ie, with the Visitors' Center attracting more than 100,000 people annually.
In addition to initial building and construction, the temple has been dedicated for use by several presidents of the LDS Church. The temple site was dedicated by Joseph F. Smith
Joseph Fielding Smith Sr. (November 13, 1838 – November 19, 1918) was an American religious leader who served as the sixth president of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). He was the nephew of Joseph Smith, the founde ...
on June 1, 1915, with Heber J. Grant dedicating the completed structure on November 27, 1919. Spencer W. Kimball
Spencer Woolley Kimball (March 28, 1895 – November 5, 1985) was an American business, civic, and religious leader who was the twelfth president of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). The grandson of early Latter-day ...
rededicated the temple after significant expansion on June 13, 1978. Following seismic upgrades and remodeling, Thomas S. Monson
Thomas Spencer Monson (August 21, 1927 – January 2, 2018) was an American religious leader, author, and the 16th President of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). As president, he was considered by adherents of the rel ...
rededicated the temple on November 21, 2010.
The Laie Hawaii Temple was the first temple built by the LDS Church outside the contiguous United States
The contiguous United States (officially the conterminous United States) consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the Federal District of the United States of America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states, Alaska and Hawaii ...
. The temple is also the oldest to operate outside Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to its ...
, and the fifth-oldest LDS temple still in operation. The Laie Hawaii Temple was formerly known as the Hawaiian Temple or the Hawaii Temple until the implementation of the standard naming convention for LDS temples.
History
Sandwich Islands Mission
During theCalifornia Gold Rush
The California Gold Rush (1848–1855) was a gold rush that began on January 24, 1848, when gold was found by James W. Marshall at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. The news of gold brought approximately 300,000 people to California f ...
, the first ten Mormon missionaries to Hawaii departed San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17t ...
on the ship ''Imaum of Muscat.'' After 20 days at sea, the ship arrived on December 12, 1850, in Honolulu Harbor
Honolulu Harbor, also called ''Kulolia'' and ''Ke Awa O Kou'' and the Port of Honolulu , is the principal seaport of Honolulu and the State of Hawaii in the United States. From the harbor, the City & County of Honolulu was developed and urbanized, ...
at what was then known as the "Sandwich Islands" (Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost ...
). A week later, nine missionaries received their assignments; two headed to the island of Kaua'i
Kauai, () anglicized as Kauai ( ), is geologically the second-oldest of the main Hawaiian Islands (after Niʻihau). With an area of 562.3 square miles (1,456.4 km2), it is the fourth-largest of these islands and the List of islands of th ...
, three to Lahaina
Lahaina ( haw, Lāhainā) is the largest census-designated place (CDP) in West Maui, Maui County, Hawaii, United States and includes the Kaanapali and Kapalua beach resorts. As of the 2020 census, the CDP had a resident population of 12,702. Lah ...
on the island of Maui
The island of Maui (; Hawaiian: ) is the second-largest of the islands of the state of Hawaii at 727.2 square miles (1,883 km2) and is the 17th largest island in the United States. Maui is the largest of Maui County's four islands, whic ...
, two to the Big Island of Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
, and two stayed behind in Honolulu
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the isla ...
. These nine missionaries formed the basis of the Sandwich Islands Mission. The first LDS Church congregation in Hawaii was established on the island of Maui in 1851. Missionaries settled on the island of Lānai in 1854, and in Lāʻie on the island of Oahu
Oahu () ( Hawaiian: ''Oʻahu'' ()), also known as "The Gathering Place", is the third-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is home to roughly one million people—over two-thirds of the population of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The island of O ...
in 1865.
Lāie
In 1865, the church purchased asugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial grass (in the genus '' Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalk ...
plantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Th ...
for $14,000 as a gathering place for the Latter-day Saints in the area. While on a mission to the Sandwich Islands, Joseph F. Smith first proposed building a temple in Hawaii during a meeting in Lāie on February 15, 1885. George Q. Cannon, one of the original ten missionaries, visited Lāʻie in 1900 and became revered as a prophet
In religion, a prophet or prophetess is an individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divine being and is said to speak on behalf of that being, serving as an intermediary with humanity by delivering messages or teachings from the ...
for promoting the idea of a new Hawaiian temple among his congregations.
 In 1915, Joseph F. Smith, then sixth president of the LDS Church, announced plans for the first temple outside the contiguous United States and chose Lāʻie for its construction. According to
In 1915, Joseph F. Smith, then sixth president of the LDS Church, announced plans for the first temple outside the contiguous United States and chose Lāʻie for its construction. According to Mormon folklore
Mormon folklore is a body of expressive culture unique to members of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) and other sects of Mormonism. Mormon folklore includes tales, oral history, popular beliefs, customs, music, jokes ...
, precious materials arrived just in time to complete the building of the temple: Temple builders ran out of wood (a scarce commodity on the islands) during initial construction, but local members received lumber when a ship ran aground and needed to unload some of its cargo of wood. The temple builders volunteered to help the ship and were given the lumber out of gratitude. The lumber taken from the ship proved to be just enough to finish the temple.
Native Hawaiian
Native Hawaiians (also known as Indigenous Hawaiians, Kānaka Maoli, Aboriginal Hawaiians, First Hawaiians, or simply Hawaiians) ( haw, kānaka, , , and ), are the indigenous ethnic group of Polynesian people of the Hawaiian Islands.
Hawa ...
converts (and other Polynesians) living far from home in the town of Iosepa, Utah, many decided to emigrate back to Hawaii. Although the Hawaiians had lived in Iosepa since 1889, the closest temple, Salt Lake Temple
The Salt Lake Temple is a temple of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints on Temple Square in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States. At , it is the largest Latter-day Saint temple by floor area. Dedicated in 1893, it is the sixth templ ...
, was 75 miles away from the colony. Moving to Laie gave the Hawaiians the ability to be closer to the new temple and allowed them to perform sacred ordinances without having to travel great distances. By January 1917, most of the Hawaiians returned home, leaving Iosepa a ghost town
Ghost Town(s) or Ghosttown may refer to:
* Ghost town, a town that has been abandoned
Film and television
* ''Ghost Town'' (1936 film), an American Western film by Harry L. Fraser
* ''Ghost Town'' (1956 film), an American Western film by All ...
.
LDS Church president Heber J. Grant presided over the Hawaiian Temple's dedication on November 27, 1919. Grant called the Hawaiian people "descendants of Lehi" (a prophet
In religion, a prophet or prophetess is an individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divine being and is said to speak on behalf of that being, serving as an intermediary with humanity by delivering messages or teachings from the ...
in the Book of Mormon
The Book of Mormon is a religious text of the Latter Day Saint movement, which, according to Latter Day Saint theology, contains writings of ancient prophets who lived on the American continent from 600 BC to AD 421 and during an interlude ...
), and saw the future of the new temple in Lāʻie as a magnet for Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
n converts. After the temple was completed, more Polynesians moved to Lāʻie, to participate in temple ordinances. Tourists were also drawn to the area, and guide books of the time compared the Lāʻie temple to the Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal (; ) is an Islamic ivory-white marble mausoleum on the right bank of the river Yamuna in the Indian city of Agra. It was commissioned in 1631 by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan () to house the tomb of his favourite wife, ...
.
The 1941 attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii ...
gave rise to another popular tale about the Laie Hawaii Temple in Mormon folklore. According to variations on this story, Japanese aircraft pilots attempted to bomb
A bomb is an explosive weapon that uses the exothermic reaction of an explosive material to provide an extremely sudden and violent release of energy. Detonations inflict damage principally through ground- and atmosphere-transmitted mechan ...
or strafe the Hawaiian Temple just prior to, or just after, the attack, but were thwarted by mechanical failure or from an unseen protective force. Some stories suggest that the Japanese pilot who attempted to attack the temple was converted to the LDS Church after he saw a picture of the temple in the possession of Mormon missionaries in Japan. Although there is an eyewitness who believes he saw the attempted bombing and a former missionary who says he met the Japanese convert, historians have found little supporting evidence that would substantiate these stories.
Renovation
Beginning in May 1976, the temple was closed for a two-year remodeling project, expanding from to over . Church presidentSpencer W. Kimball
Spencer Woolley Kimball (March 28, 1895 – November 5, 1985) was an American business, civic, and religious leader who was the twelfth president of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). The grandson of early Latter-day ...
rededicated the temple on June 13, 1978.
A $5.5 million renovation, renewal, and beautification
Beautification is the process of making visual improvements to a town, city, or urban area. This most often involves planting trees, shrubbery, and other greenery, but frequently also includes adding decorative or historic-style street lights and ...
project along Hale Laa Boulevard leading to the temple began in 2003, lasting 14 months: Norfolk pines
''Araucaria heterophylla'' (synonym ''A. excelsa'') is a species of conifer. As its vernacular name Norfolk Island pine (or Norfolk pine) implies, the tree is endemic to Norfolk Island, an external territory of Australia located in the Pacific ...
suffering from termite infestation were replaced with royal palms, new decorative lighting was added to the terraces, and landscaped roundabouts were put in place. At the same time, the Visitors' Center was upgraded with interactive kiosk
An interactive kiosk is a computer terminal featuring specialized hardware and software that provides access to information and applications for communication, commerce, entertainment, or education.
By 2010, the largest bill pay kiosk networ ...
s and new displays. There is now a cut-away model of the temple on display which allows visitors to see its interior since only LDS Church members are allowed to enter after a temple is dedicated. It took the artisan team over eight months to build the temple model in the US and more than a week to reassemble the model for display after being shipped to Hawaii.
In December 2008, the Laie Hawaii Temple closed again for structural and seismic upgrades and to restore the ordinance rooms to their original appearance and progressive-style presentation of the endowment
Endowment most often refers to:
*A term for human penis size
It may also refer to: Finance
* Financial endowment, pertaining to funds or property donated to institutions or individuals (e.g., college endowment)
*Endowment mortgage, a mortgage to ...
(still using film). The baptistry was repaired and renovated. The temple was rededicated on November 21, 2010, by Thomas S. Monson
Thomas Spencer Monson (August 21, 1927 – January 2, 2018) was an American religious leader, author, and the 16th President of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). As president, he was considered by adherents of the rel ...
.
In 2020, like all the church's other temples, the Laie Hawaii Temple was closed in response to the coronavirus pandemic.
Architecture
 LDS Church president Joseph F. Smith wanted the architecture of the Laie Hawaii Temple to resemble
LDS Church president Joseph F. Smith wanted the architecture of the Laie Hawaii Temple to resemble Solomon's Temple
Solomon's Temple, also known as the First Temple (, , ), was the Temple in Jerusalem between the 10th century BC and . According to the Hebrew Bible, it was commissioned by Solomon in the United Kingdom of Israel before being inherited by t ...
referred to in the biblical canon
A biblical canon is a set of texts (also called "books") which a particular Jewish or Christian religious community regards as part of the Bible.
The English word ''canon'' comes from the Greek , meaning " rule" or " measuring stick". The ...
. The temple is often compared to the Cardston Alberta Temple, designed by young architects Hyrum Pope and Harold W. Burton. Pope and Burton's design was also used for Laie, and their work is rooted in the Prairie style architecture made popular by architect Frank Lloyd Wright
Frank Lloyd Wright (June 8, 1867 – April 9, 1959) was an American architect, designer, writer, and educator. He designed more than 1,000 structures over a creative period of 70 years. Wright played a key role in the architectural movements o ...
in the early twentieth-century. The temples also evoke Mesoamerican architectural motifs, a favored theme of Burton's.
The temple sits on an site that was once part of a large sugarcane plantation. Construction of the temple first began in February 1916. Native materials consisting of crushed lava rock were used to build the temple, along with reinforced concrete. The building's gleaming white finish was created using pneumatic stone-cutting techniques. The temple has the shape of a cross when seen from the air; the highest point of the temple is , and it measures from east to west and from north to south. The front exterior was designed in the form of a Greek cross
The Christian cross, with or without a figure of Christ included, is the main religious symbol of Christianity. A cross with a figure of Christ affixed to it is termed a ''crucifix'' and the figure is often referred to as the ''corpus'' (La ...
, but lacks a tower, a rarity in LDS Church temples. Apart from the Laie Hawaii Temple, only three other church temples lack towers or spires: the Cardston Alberta, Paris France and the Mesa Arizona temples.
 The exterior of the temple exhibits four large
The exterior of the temple exhibits four large frieze
In architecture, the frieze is the wide central section part of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic or Doric order, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Paterae are also usually used to decorate friezes. Even when neither columns nor ...
s planned by American sculptor J. Leo Fairbanks and built with the help of his brother Avard Fairbanks. Modeled four-fifths lifesize and cast in concrete, the bas-relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term '' relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that th ...
friezes depict God's dealings with Man. The north frieze depicts the story of the Book of Mormon. The west frieze shows the people of the Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. The ...
. The New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chris ...
and the Apostasy
Apostasy (; grc-gre, ἀποστασία , 'a defection or revolt') is the formal disaffiliation from, abandonment of, or renunciation of a religion by a person. It can also be defined within the broader context of embracing an opinion that ...
are depicted on the southern frieze of the temple, and the restoration of the church through Joseph Smith
Joseph Smith Jr. (December 23, 1805June 27, 1844) was an American religious leader and founder of Mormonism and the Latter Day Saint movement. When he was 24, Smith published the Book of Mormon. By the time of his death, 14 years later, h ...
is shown on the east frieze. On the grounds of the temple are statues also designed by the Fairbanks brothers, including Joseph
Joseph is a common male given name, derived from the Hebrew Yosef (יוֹסֵף). "Joseph" is used, along with "Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the m ...
being blessed by his father and one of the Prophet Lehi
Lehi (; he, לח"י – לוחמי חרות ישראל ''Lohamei Herut Israel – Lehi'', "Fighters for the Freedom of Israel – Lehi"), often known pejoratively as the Stern Gang,"This group was known to its friends as LEHI and to its enemie ...
in a scene from the Second Book of Nephi
The Second Book of Nephi (), usually referred to as Second Nephi or 2 Nephi, is the second book of the Book of Mormon. The original translation of the title did not include the word "second". First and Second were added to the titles of The Books ...
in the Book of Mormon.
 As visitors approach the temple and pass a number of reflecting pools, a maternity fountain sits in front of the uppermost pool. Designed by the Fairbanks brothers, this bold relief honors Hawaiian Motherhood and depicts a Hawaiian mother holding a
As visitors approach the temple and pass a number of reflecting pools, a maternity fountain sits in front of the uppermost pool. Designed by the Fairbanks brothers, this bold relief honors Hawaiian Motherhood and depicts a Hawaiian mother holding a giant clam
The giant clams are the members of the clam genus '' Tridacna'' that are the largest living bivalve mollusks. There are actually several species of "giant clams" in the genus '' Tridacna'', which are often misidentified for ''Tridacna gigas'', ...
shell while pouring water over her children. The act is supposed to symbolize mothers pouring their love, hope and care onto their children.
The landscaped temple grounds contain tropical garden
A tropical garden is a type of garden that features tropical plants and requires heavy rainfall or a decent irrigation or sprinkler system for watering. These gardens typically need fertilizer and heavy mulching.
Tropical gardens are no longer ...
s, with plants such as hibiscus
''Hibiscus'' is a genus of flowering plants in the mallow family, Malvaceae. The genus is quite large, comprising several hundred species that are native to warm temperate, subtropical and tropical regions throughout the world. Member species ...
, Brazilian plume, birds of paradise
The birds-of-paradise are members of the family Paradisaeidae of the order Passeriformes. The majority of species are found in eastern Indonesia, Papua New Guinea and eastern Australia. The family has 44 species in 17 genera. The members of ...
, lantana
''Lantana'' () is a genus of about 150 species of perennial flowering plants in the verbena family, Verbenaceae. They are native to tropical regions of the Americas and Africa but exist as an introduced species in numerous areas, especially in ...
, red ginger, bougainvillea
''Bougainvillea'' ( , ) is a genus of thorny ornamental vines, bushes, and trees belonging to the four o' clock family, Nyctaginaceae. It is native to eastern South America, found from Brazil, west to Peru, and south to southern Argentina. ...
, plumeria
''Plumeria'' (), known as frangipani, is a genus of flowering plants in the subfamily Rauvolfioideae, of the family Apocynaceae. Most species are deciduous shrubs or small trees. The species variously are endemic to Mexico, Central America, and ...
, Ixora
''Ixora'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It is the only genus in the tribe Ixoreae. It consists of tropical evergreen trees and shrubs and holds around 544 species. Though native to the tropical and subtropical areas ...
, and others.New site
At the base of the temple grounds is a fountain separating an LDS Family History Center and a Visitors' Center, where a ten-foot sculpture replica of
Bertel Thorvaldsen
Bertel Thorvaldsen (; 19 November 1770 – 24 March 1844) was a Danish and Icelandic sculptor medalist of international fame, who spent most of his life (1797–1838) in Italy. Thorvaldsen was born in Copenhagen into a working-class Dani ...
's ''Christus
Christus may refer to:
* Christ (title) People
* Petrus Christus (c. 1410s – c. 1475), Dutch painter
* Sir Christus (1978–2017), Finnish musician Music
* ''Christus'' (Liszt), an oratorio
* ''Christus'' (Mendelssohn), an unfinished oratorio ...
'' stands inside the entrance.
The Laie Hawaii Temple is and houses four ordinance room
In temples of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church), an ordinance room is a room where the ceremony known as the ''Endowment'' is administered, as well as other ordinances such as Sealings. Some temples perform a progre ...
s and six sealing rooms. Landscape artist LeConte Stewart __NOTOC__
LeConte Stewart (April 15, 1891 – June 6, 1990) was a Latter-day Saint artist primarily known for his landscapes of rural Utah. His media included oils, watercolors, pastel and charcoal, as well as etchings, linocuts, and lithographs. ...
designed many of the murals found inside the temple.
Admittance
Laie Hawaii Temple is not used for regular Sunday worship. As temples are considered sacred houses of the Lord, only church members who keep gospel covenants are allowed to enter for the purpose of participating in sacred ceremonies such as endowments,baptism for the dead
Baptism for the dead, vicarious baptism or proxy baptism today commonly refers to the religious practice of baptizing a person on behalf of one who is dead—a living person receiving the rite on behalf of a deceased person.
Baptism for the dea ...
and eternal marriage
Celestial marriage (also called the New and Everlasting Covenant of Marriage, Eternal Marriage, Temple Marriage) is a doctrine that marriage can last forever in heaven. This is a unique teaching of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints ...
, a ritual in which couples and families are sealed for time and all eternity. Because of these guidelines, non-Mormons are not allowed inside temples, but public tours of the grounds outside and of the visitors' centers are available.
Temple presidents
Notabletemple president Temple president is a priesthood leadership position in the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). A temple president's primary responsibility is to supervise the affairs of an LDS temple in both an administrative and spiritual ...
s include Edward L. Clissold (1936–38, 1943–44, 1963–65); D. Arthur Haycock (1986–89), and J. Richard Clarke (1998–2001).
See also
* Comparison of temples of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints *Kona Hawaii Temple
The Kona Hawaii Temple is the 70th operating temple of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). The temple is located in Kailua-Kona on the island of Hawaii and is the second temple built in Hawaii, along with the Laie H ...
* List of temples of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
* List of temples of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints by geographic region
* The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in Hawaii
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) was established in the Hawaiian Islands in 1850, 11 years after the Edict of Toleration was decreed by Kamehameha III, giving the underground Hawaii Catholic Church the right to worshi ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * *External links
Laie Hawaii Temple Official site
at ChurchofJesusChristTemples.org {{Good article 20th-century Latter Day Saint temples Buildings and structures in Honolulu County, Hawaii Buildings designed to replicate Solomon's Temple Hawaiian architecture Landmarks in Hawaii Religious buildings and structures in Hawaii Churches completed in 1919 Temples (LDS Church) in Oceania Temples (LDS Church) in the United States The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in Hawaii 1919 establishments in Hawaii