Lunar Caustic (Lowry) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Silver nitrate is an
Silver nitrate is an
International Chemical Safety Card 1116
History of Kodak: About Film and Imaging
https://www.cofesilver.com/en/silver_bar :silver bar explanation. pricing investing {{Authority control 13th century in science Antiseptics Electron microscopy stains Nitrates Photographic chemicals Silver compounds Staining dyes Alchemical substances Light-sensitive chemicals Oxidizing agents Chemical tests
inorganic compound
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemistry''.
Inorgan ...
with chemical formula
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as pare ...
. It is a versatile precursor
Precursor or Precursors may refer to:
*Precursor (religion), a forerunner, predecessor
** The Precursor, John the Baptist
Science and technology
* Precursor (bird), hypothesized genus of fossil birds that was composed of fossilized parts of unre ...
to many other silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
compounds, such as those used in photography
Photography is the visual arts, art, application, and practice of creating images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is empl ...
. It is far less sensitive to light than the halides
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fluo ...
. It was once called ''lunar caustic'' because silver was called ''luna'' by ancient alchemists who associated silver with the moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
. In solid silver nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in wa ...
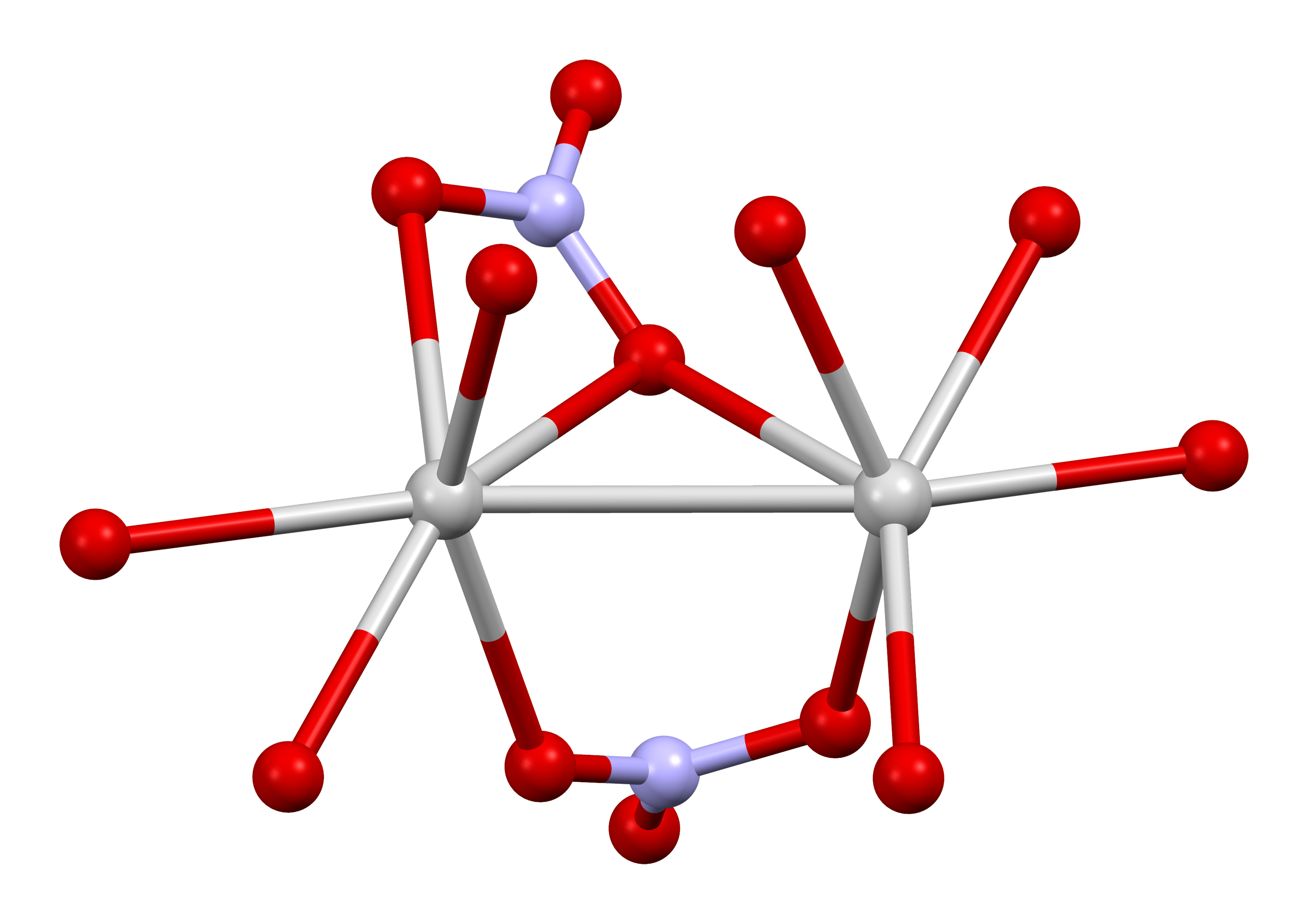
, the silver ions are three- coordinated in a trigonal planar arrangement.
Synthesis and structure
Albertus Magnus
Albertus Magnus ( 1200 – 15 November 1280), also known as Saint Albert the Great, Albert of Swabia, Albert von Bollstadt, or Albert of Cologne, was a German Dominican friar, philosopher, scientist, and bishop, considered one of the great ...
, in the 13th century, documented the ability of nitric acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most com ...
to separate gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
and silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
by dissolving the silver. Indeed silver nitrate can be prepared by dissolving silver in nitric acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most com ...
followed by evaporation of the solution. The stoichiometry of the reaction depends upon the concentration of nitric acid used.
:3 Ag + 4 HNO3 (cold and diluted) → 3 AgNO3 + 2 H2O + NO
:Ag + 2 HNO3 (hot and concentrated) → AgNO3 + H2O + NO2
The structure of silver nitrate has been examined by X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to Diffraction, diffract in specific directions. By measuring th ...
several times. In the common orthorhombic form stable at ordinary temperature and pressure, the silver atoms form pairs with Ag---Ag contacts of 3.227 Å. Each Ag+ center is bonded to six oxygen centers of both uni- and bidentate nitrate ligands. The Ag-O distances range from 2.384 to 2.702 Å.

Reactions
A typical reaction with silver nitrate is to suspend a rod ofcopper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
in a solution of silver nitrate and leave it for a few hours. The silver nitrate reacts with copper to form hairlike crystals of silver metal and a blue solution of copper nitrate
Copper(II) nitrate describes any member of the family of inorganic compounds with the formula Cu( NO3)2(H2O)x. The hydrates are hygroscopic blue solids. Anhydrous copper nitrate forms blue-green crystals and sublimes in a vacuum at 150-200 °C ...
:
: 2 AgNO3 + Cu → Cu(NO3)2 + 2 Ag
Silver nitrate decomposes when heated:
: 2 AgNO3(l) → 2 Ag(s) + O2(g) + 2 NO2(g)
Qualitatively, decomposition is negligible below the melting point, but becomes appreciable around 250 °C and fully decomposes at 440 °C.
Most metal nitrates thermally decompose to the respective oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation st ...
s, but silver oxide
Silver oxide is the chemical compound with the formula Ag2 O. It is a fine black or dark brown powder that is used to prepare other silver compounds.
Preparation
Silver oxide can be prepared by combining aqueous solutions of silver nitrate and ...
decomposes at a lower temperature than silver nitrate, so the decomposition of silver nitrate yields elemental silver instead.
Uses
Precursor to other silver compounds
Silver nitrate is the least expensivesalt
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more formally called table salt. In the form of a natural crystalline mineral, salt is also known as r ...
of silver; it offers several other advantages as well. It is non-hygroscopic
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption (chemistry), absorption or adsorption from the surrounding Natural environment, environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water mol ...
, in contrast to silver fluoroborate
Silver tetrafluoroborate is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula AgBF4. It is a white solid, although commercial samples often are gray, that dissolves in polar organic solvents as well as water.
Preparation
Silver tetrafluoroborate ca ...
and silver perchlorate
Silver perchlorate is the chemical compound with the formula AgClO4. This white solid forms a monohydrate and is mildly deliquescent. It is a useful source of the Ag+ ion, although the presence of perchlorate presents risks. It is used as a cata ...
. In addition, it is relatively stable to light, and it dissolves in numerous solvents, including water. The nitrate can be easily replaced by other ligands
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's ...
, rendering AgNO3 versatile. Treatment with solutions of halide ions gives a precipitate of AgX (X = Cl, Br, I). When making photographic film
Photographic film is a strip or sheet of transparent film base coated on one side with a gelatin photographic emulsion, emulsion containing microscopically small light-sensitive silver halide crystals. The sizes and other characteristics of the ...
, silver nitrate is treated with halide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fl ...
salts of sodium or potassium to form insoluble silver halide
A silver halide (or silver salt) is one of the chemical compounds that can form between the Chemical element, element silver (Ag) and one of the halogens. In particular, bromine (Br), chlorine (Cl), iodine (I) and fluorine (F) may each combine wit ...
in situ in photographic gelatin
Gelatin or gelatine () is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, commonly derived from collagen taken from animal body parts. It is brittle when dry and rubbery when moist. It may also be referred to as hydrolyzed collagen, coll ...
, which is then applied to strips of tri-acetate
An acetate is a salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with a base (e.g. alkaline, earthy, metallic, nonmetallic, or radical base). "Acetate" also describes the conjugate base or ion (specifically, the negatively charged ion called ...
or polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain one or two ester linkages in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include some natura ...
. Similarly, silver nitrate is used to prepare some silver-based explosives, such as the fulminate
Fulminates are chemical compounds which include the fulminate ion (). The fulminate ion is a pseudohalic ion because its charge and reactivity are similar to those of the halogens. The name is derived from the Latin ''fulminātus'', meaning to ...
, azide
In chemistry, azide (, ) is a linear, polyatomic anion with the formula and structure . It is the conjugate base of hydrazoic acid . Organic azides are organic compounds with the formula , containing the azide functional group. The dominant ...
, or acetylide
In chemistry, an acetylide is a compound that can be viewed as the result of replacing one or both hydrogen atoms of acetylene (ethyne) by metallic or other cations. Calcium carbide is an important industrial compound, which has long been used ...
, through a precipitation reaction
In an aqueous solution, precipitation is the "sedimentation of a solid material (a precipitate) from a liquid solution". The solid formed is called the precipitate. In case of an inorganic chemical reaction leading to precipitation, the chemic ...
.
Treatment of silver nitrate with base gives dark grey silver oxide
Silver oxide is the chemical compound with the formula Ag2 O. It is a fine black or dark brown powder that is used to prepare other silver compounds.
Preparation
Silver oxide can be prepared by combining aqueous solutions of silver nitrate and ...
:
:2 AgNO3 + 2 NaOH → Ag2O + 2 NaNO3 + H2O
Halide abstraction
The silver cation, , reacts quickly with halide sources to produce the insoluble silver halide, which is a cream precipitate if is used, a white precipitate if is used and a yellow precipitate if is used. This reaction is commonly used ininorganic chemistry
Inorganic chemistry deals with chemical synthesis, synthesis and behavior of inorganic compound, inorganic and organometallic chemistry, organometallic compounds. This field covers chemical compounds that are not carbon-based, which are the subj ...
to abstract halides:
:(aq) + (aq) → AgX(s)
where = , , or .
Other silver salts with non-coordinating anions
Anions that interact weakly with cations are termed non-coordinating anions, although a more accurate term is weakly coordinating anion. Non-coordinating anions are useful in studying the reactivity of electrophilic cations. They are commonly found ...
, namely silver tetrafluoroborate
Silver tetrafluoroborate is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula AgBF4. It is a white solid, although commercial samples often are gray, that dissolves in polar organic solvents as well as water.
Preparation
Silver tetrafluoroborate ca ...
and silver hexafluorophosphate
Silver hexafluorophosphate, sometimes referred to "silver PF-6," is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula AgPF6.
Uses and reactions
Silver hexafluorophosphate is a commonly encountered reagent in inorganic and organometallic chemistry ...
are used for more demanding applications.
Similarly, this reaction is used in analytical chemistry
Analytical skill, Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to Separation process, separate, identify, and Quantification (science), quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute t ...
to confirm the presence of chloride
The term chloride refers to a compound or molecule that contains either a chlorine anion (), which is a negatively charged chlorine atom, or a non-charged chlorine atom covalently bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single bond (). The pr ...
, bromide
A bromide ion is the negatively charged form (Br−) of the element bromine, a member of the halogens group on the periodic table. Most bromides are colorless. Bromides have many practical roles, being found in anticonvulsants, flame-retard ...
, or iodide
An iodide ion is I−. Compounds with iodine in formal oxidation state −1 are called iodides. In everyday life, iodide is most commonly encountered as a component of iodized salt, which many governments mandate. Worldwide, iodine deficiency ...
ions
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
. Samples are typically acidified with dilute nitric acid to remove interfering ions, e.g. carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid, (), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word "carbonate" may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate group ...
ions and sulfide
Sulfide (also sulphide in British English) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to large families o ...
ions. This step avoids confusion of silver sulfide
Silver sulfide is an inorganic compound with the formula . A dense black solid, it is the only sulfide of silver. It is useful as a photosensitizer in photography. It constitutes the tarnish that forms over time on silverware and other silver ob ...
or silver carbonate
Silver carbonate is the chemical compound with the formula Ag2 C O3. This salt is yellow but typical samples are grayish due to the presence of elemental silver. It is poorly soluble in water, like most transition metal carbonates.
Preparation a ...
precipitates with that of silver halides. The color of precipitate varies with the halide: white (silver chloride
Silver chloride is an inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula Ag Cl. This white crystalline solid is well known for its low solubility in water and its sensitivity to light. Upon illumination or heating, silver chloride converts ...
), pale yellow/cream (silver bromide
Silver bromide (AgBr), a soft, pale-yellow, water-insoluble salt well known (along with other silver halides) for its unusual sensitivity to light. This property has allowed silver halides to become the basis of modern photographic materials. AgB ...
), yellow (silver iodide
Silver iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula Ag I. The compound is a bright yellow solid, but samples almost always contain impurities of metallic silver that give a grey colouration. The silver contamination arises because some samp ...
). AgBr and especially AgI photo-decompose to the metal, as evidenced by a grayish color on exposed samples.
The same reaction was used on steamships in order to determine whether or not boiler feedwater
Boiler feedwater is the water which is supplied to a boiler. The feed water is put into the steam drum from a feed pump. In the steam drum the feed water is then turned into steam from the heat. After the steam is used, it is then dumped to the ...
had been contaminated with seawater
Seawater, or sea water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has approximat ...
. It is still used to determine if moisture on formerly dry cargo is a result of condensation
Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. The word most often refers to the water cycle. It can also be defined as the change in the state of water vapor ...
from humid air, or from seawater leaking through the hull.
Organic synthesis
Silver nitrate is used in many ways inorganic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a branch of chemical synthesis concerned with the construction of organic compounds. Organic compounds are molecules consisting of combinations of covalently-linked hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms. Within the gen ...
, e.g. for deprotection
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis.
In man ...
and oxidations. binds alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or at the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as Alpha-olefin, α-olefins.
The Internationa ...
s reversibly, and silver nitrate has been used to separate mixtures of alkenes by selective absorption. The resulting adduct
In chemistry, an adduct (; alternatively, a contraction of "addition product") is a product of a direct addition of two or more distinct molecules, resulting in a single reaction product containing all atoms of all components. The resultant is ...
can be decomposed with ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
to release the free alkene. Silver nitrate is highly soluble in water but is poorly soluble in most organic solvents, except acetonitrile
Acetonitrile, often abbreviated MeCN (methyl cyanide), is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile (hydrogen cyanide is a simpler nitrile, but the cyanide anion is not class ...
(111.8 g/100 g, 25 °C).
Biology
Inhistology
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology that studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissue (biology), tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at large ...
, silver nitrate is used for silver stain
In pathology, silver staining is the use of silver to selectively alter the appearance of a target in microscopy of histological sections; in temperature gradient gel electrophoresis; and in polyacrylamide gels.
In traditional stained glass, si ...
ing, for demonstrating reticular fibers, protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s and nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a pentose, 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nuclei ...
s. For this reason it is also used to demonstrate proteins in PAGE
Page most commonly refers to:
* Page (paper), one side of a leaf of paper, as in a book
Page, PAGE, pages, or paging may also refer to:
Roles
* Page (assistance occupation), a professional occupation
* Page (servant), traditionally a young m ...
gels. It can be used as a stain in scanning electron microscopy
A scanning electron microscope (SEM) is a type of electron microscope that produces images of a sample by scanning the surface with a focused beam of electrons. The electrons interact with atoms in the sample, producing various signals that ...
.
Cut flower stems can be placed in a silver nitrate solution, which prevents the production of ethylene. This delays ageing of the flower.
Indelible ink
Silver nitrate produces long-lasting stain when applied to skin and is one of indelible ink’s ingredients. An electoral stain makes use of this to mark a finger of people who have voted in an election, allowing easy identification to prevent double-voting. In addition to staining skin, silver nitrate has a history of use in stained glass. In the 14th century, artists began using a "silver stain" (also known as a yellow stain) made from silver nitrate to create a yellow effect on clear glass. The stain would produce a stable color that could range from pale lemon to deep orange or gold. Silver stain was often used with glass paint, and was applied to the opposite side of the glass as the paint. It was also used to create a mosaic effect by reducing the number of pieces of glass in a window. Despite the age of the technique, this process of creating stained glass remains almost entirely unchanged.Medicine
Silver salts haveantiseptic
An antiseptic ( and ) is an antimicrobial substance or compound that is applied to living tissue to reduce the possibility of sepsis, infection, or putrefaction. Antiseptics are generally distinguished from ''antibiotics'' by the latter's abil ...
properties. In 1881 Credé introduced a method known as Credé's prophylaxis
Credé prophylaxis is the practice of washing a newborn's eyes with a 1% silver nitrate solution to protect against neonatal conjunctivitis caused by ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'', thereby preventing blindness.
The Credé procedure was developed ...
, which used of dilute (2%) solutions of silver nitrate in newborn babies
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to juveniles of ...
' eyes at birth to prevent contraction of gonorrhea
Gonorrhoea or gonorrhea, colloquially known as the clap, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae''. Infection may involve the genitals, mouth, or rectum.
Gonorrhea is spread through sexual c ...
from the mother, which could cause blindness via ophthalmia neonatorum. (Modern antibiotics are now used instead).
Fused silver nitrate, shaped into sticks, was traditionally called "lunar caustic". It is used as a cauterizing
Cauterization (or cauterisation, or cautery) is a medical practice or technique of burning a part of a body to remove or close off a part of it. It destroys some tissue in an attempt to mitigate bleeding and damage, remove an undesired growth, or ...
agent, for example to remove granulation tissue
Granulation tissue is new connective tissue and microscopic blood vessels that form on the surfaces of a wound during the healing process. Granulation tissue typically grows from the base of a wound and is able to fill wounds of almost any size ...
around a stoma
In botany, a stoma (: stomata, from Greek language, Greek ''στόμα'', "mouth"), also called a stomate (: stomates), is a pore found in the Epidermis (botany), epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exc ...
. General Sir James Abbott noted in his journals that in India in 1827 it was infused by a British surgeon into wounds in his arm resulting from the bite of a mad dog to cauterize the wounds and prevent the onset of rabies.
Silver nitrate is used to cauterize superficial blood vessels in the nose to help prevent nosebleed
A nosebleed, also known as epistaxis, is an instance of bleeding from the nose. Blood can flow down into the stomach, and cause nausea and vomiting. In more severe cases, blood may come out of both nostrils. Rarely, bleeding may be so significa ...
s.
Dentists sometimes use silver nitrate-infused swabs to heal oral ulcer
A mouth ulcer (aphtha), or sometimes called a canker sore or salt blister, is an ulcer that occurs on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Mouth ulcers are very common, occurring in association with many diseases and by many different mechanis ...
s. Silver nitrate is used by some podiatrist
A podiatrist ( ) is a medical professional devoted to the treatment of disorders of the foot, ankle, and related structures of the leg. The term originated in North America but has now become the accepted term in the English-speaking world for ...
s to kill cells located in the nail bed.
The Canadian physician C. A. Douglas Ringrose researched the use of silver nitrate for sterilization procedures, believing that silver nitrate could be used to block and corrode the fallopian tubes. The technique was ineffective.
Disinfection
Much research has been done in evaluating the ability of the silver ion at inactivating ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly fo ...
'', a microorganism commonly used as an indicator for fecal contamination and as a surrogate for pathogens in drinking water treatment. Concentrations of silver nitrate evaluated in inactivation experiments range from 10–200 micrograms per liter as Ag+.
Silver's antimicrobial activity saw many applications prior to the discovery of modern antibiotics, when it fell into near disuse. Its association with argyria
Argyria or argyrosis is a condition caused by excessive exposure to chemical compounds of the element silver, or silver dust. The most dramatic symptom of argyria is that the skin turns blue or blue-gray, and is usually most prominent in sun-ex ...
made consumers wary and led them to turn away from it when given an alternative.
Against warts
Repeated daily application of silver nitrate can induce adequate destruction of cutaneouswarts
Warts are non-cancerous viral growths usually occurring on the hands and feet but which can also affect other locations, such as the genitals or face. One or many warts may appear. They are distinguished from cancerous tumors as they are caus ...
, but occasionally pigmented scars may develop. In a placebo-controlled study of 70 patients, silver nitrate given over nine days resulted in clearance of all warts in 43% and improvement in warts in 26% one month after treatment compared to 11% and 14%, respectively, in the placebo group.
Safety
As an oxidant, silver nitrate should be properly stored away from organic compounds. It reacts explosively with ethanol. Despite its common usage in extremely low concentrations to preventgonorrhea
Gonorrhoea or gonorrhea, colloquially known as the clap, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae''. Infection may involve the genitals, mouth, or rectum.
Gonorrhea is spread through sexual c ...
and control nosebleeds, silver nitrate is still very toxic and corrosive. Brief exposure will not produce any immediate side effects other than the purple, brown or black stains on the skin, but upon constant exposure to high concentrations, side effects will be noticeable, which include burns. Long-term exposure may cause eye damage. Silver nitrate is known to be a skin and eye irritant. Silver nitrate has not been thoroughly investigated for potential carcinogenic effect.
Silver nitrate is currently unregulated in water sources by the United States Environmental Protection Agency. However, if more than 1 gram of silver is accumulated in the body, a condition called argyria
Argyria or argyrosis is a condition caused by excessive exposure to chemical compounds of the element silver, or silver dust. The most dramatic symptom of argyria is that the skin turns blue or blue-gray, and is usually most prominent in sun-ex ...
may develop. Argyria is a permanent cosmetic condition in which the skin and internal organs turn a blue-gray color. The United States Environmental Protection Agency used to have a maximum contaminant limit for silver in water until 1990, when it was determined that argyria did not impact the function of any affected organs despite the discolouration."Silver Compounds." Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. Vol. 22. Fourth Ed. Excec. Ed. Jaqueline I. Kroschwitz. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1997. Argyria is more often associated with the consumption of colloidal silver
The medical uses of silver include its use in wound dressings, creams, and as an antibiotic coating on medical devices. Wound dressings containing silver sulfadiazine or silver nanomaterials may be used to treat external infections. The limited ...
solutions rather than with silver nitrate, since it is only used at extremely low concentrations to disinfect the water. However, it is still important to be wary before ingesting any sort of silver-ion solution.
References
External links
International Chemical Safety Card 1116
History of Kodak: About Film and Imaging
https://www.cofesilver.com/en/silver_bar :silver bar explanation. pricing investing {{Authority control 13th century in science Antiseptics Electron microscopy stains Nitrates Photographic chemicals Silver compounds Staining dyes Alchemical substances Light-sensitive chemicals Oxidizing agents Chemical tests