List Of Historic States Of Italy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The ancient peoples of Italy are broadly referred to in historiography as
The ancient peoples of Italy are broadly referred to in historiography as


* Principality of Benevento
*
* Agugliastra
* Arborea
*


 During the war of the Spanish succession (1700-1714), Savoy acquired Sicily, while the remaining Spanish dominions in Italy (Naples, Sardinia, and Milan) were taken over by the Austrian Habsburgs. In 1720, Savoy exchanged Sicily for Sardinia. Following the extinction of the
During the war of the Spanish succession (1700-1714), Savoy acquired Sicily, while the remaining Spanish dominions in Italy (Naples, Sardinia, and Milan) were taken over by the Austrian Habsburgs. In 1720, Savoy exchanged Sicily for Sardinia. Following the extinction of the
 *
* Duchy of Massa and Carrara (in personal union with Modena from 1731)
* Duchy of Mirandola (in personal union with Modena from 1710)
* Prince-Bishopric of Brixen
*
*
* Duchy of Massa and Carrara (in personal union with Modena from 1731)
* Duchy of Mirandola (in personal union with Modena from 1710)
* Prince-Bishopric of Brixen
* Journal of the Private Life and Conversations of the Emperor, Vol. 3
Emmanuel-Auguste-Dieudonne comte de Las Cases. 1816. *
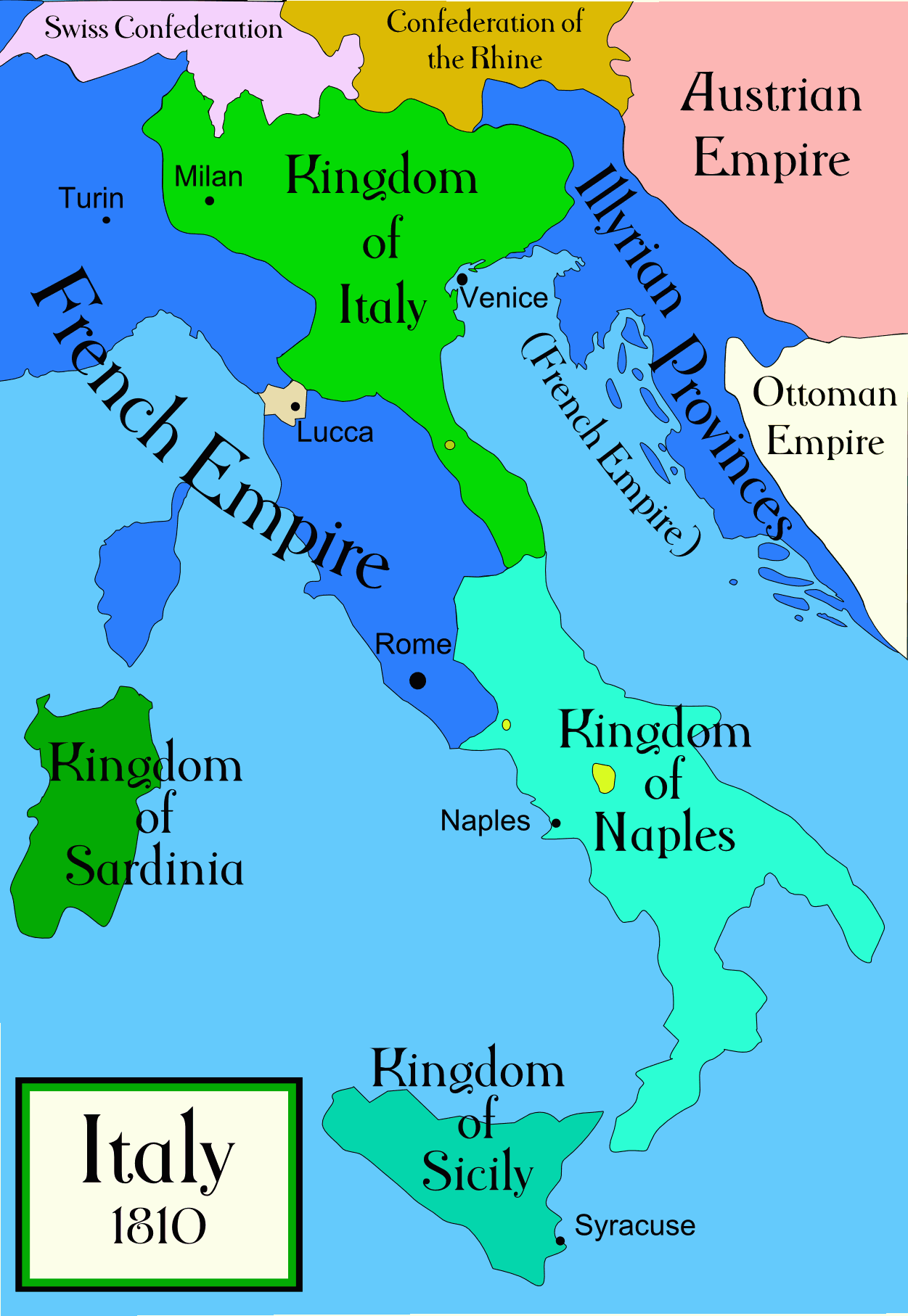
 Following the defeat of Napoleon's France, the
Following the defeat of Napoleon's France, the
 *
*
Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, up until its unification in 1861, was a conglomeration of city-states
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world throughout history, including cities such as Rome, ...
, republics, and other independent entities. The following is a list of the various Italian states during that period. Following the fall of the Western Roman Empire
In modern historiography, the Western Roman Empire was the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent imperial court. ...
and the arrival of the Middle Ages (in particular from the 11th century
The 11th century is the period from 1001 (represented by the Roman numerals MI) through 1100 (MC) in accordance with the Julian calendar, and the 1st century of the 2nd millennium.
In the history of Europe, this period is considered the early ...
), the Italian Peninsula was divided into numerous states. Many of these states consolidated into major political units that balanced the power on the Italian Peninsula: the Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
, the Venetian Republic
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
, the Republic of Florence, the Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan (; ) was a state in Northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti of Milan, Visconti family, which had been ruling the city since 1277. At that time, ...
, the Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples (; ; ), officially the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was established by the War of the Sicilian Vespers (1282–1302). Until ...
and the Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily (; ; ) was a state that existed in Sicily and the southern Italian peninsula, Italian Peninsula as well as, for a time, in Kingdom of Africa, Northern Africa, from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 until 1816. It was ...
. Unlike all the other Italian states of the medieval and early modern period, the republics of Venice and Genoa
Genoa ( ; ; ) is a city in and the capital of the Italian region of Liguria, and the sixth-largest city in Italy. As of 2025, 563,947 people live within the city's administrative limits. While its metropolitan city has 818,651 inhabitan ...
, thanks to their maritime power, went beyond territorial conquests within the Italian Peninsula, conquering various regions across the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
and Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
s.
Ancient Italy
 The ancient peoples of Italy are broadly referred to in historiography as
The ancient peoples of Italy are broadly referred to in historiography as Italic peoples
The concept of Italic peoples is widely used in linguistics and historiography of ancient Italy. In a strict sense, commonly used in linguistics, it refers to the Osco-Umbrian languages, Osco-Umbrians and Latino-Faliscan languages, Latino-Falisca ...
, although in modern linguistics this term is used to define only the speakers of the Italic languages
The Italic languages form a branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, whose earliest known members were spoken on the Italian Peninsula in the first millennium BC. The most important of the ancient Italic languages ...
, namely the Latino-Faliscans and the Osco-Umbrians. They include:
* Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization ( ) was an ancient civilization created by the Etruscans, a people who inhabited Etruria in List of ancient peoples of Italy, ancient Italy, with a common language and culture, and formed a federation of city-states. Af ...
* Italic peoples in the strict sense:
** Latino-Faliscans:
*** Latins
The term Latins has been used throughout history to refer to various peoples, ethnicities and religious groups using Latin or the Latin-derived Romance languages, as part of the legacy of the Roman Empire. In the Ancient World, it referred to th ...
**** Romans
***** Roman Kingdom
The Roman Kingdom, also known as the Roman monarchy and the regal period of ancient Rome, was the earliest period of Ancient Rome, Roman history when the city and its territory were King of Rome, ruled by kings. According to tradition, the Roma ...
*****Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
*****Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
*****Western Roman Empire
In modern historiography, the Western Roman Empire was the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent imperial court. ...
*** Falisci
The Falisci were an Italic peoples, Italic tribe who lived in what is now northern Lazio, on the Etruscan side of the Tiber River. They spoke an Italic languages, Italic language, Faliscan language, Faliscan, closely related to Latin. Origina ...
** Osco-Umbrians, also called Sabellians
Sabellians is a collective ethnonym for a group of Italic peoples or tribes inhabiting central and southern Italy at the time of the rise of Rome. The name was first applied by Niebuhr and encompassed the Sabines, Marsi, Marrucini and Vest ...
:
*** Umbrians
**** Marsi
The Marsi were an Italic people of ancient Italy, whose chief centre was Marruvium, on the eastern shore of Lake Fucinus (which was drained in the time of Claudius). The area in which they lived is now called Marsica. They originally spoke a l ...
**** Umbri
The Umbri were an Italic peoples, Italic people of ancient Italy. A region called Umbria still exists and is now occupied by Italian speakers. It is somewhat smaller than the Regio VI Umbria, ancient Umbria.
Most ancient Umbrian cities were sett ...
**** Volsci
The Volsci (, , ) were an Italic tribe, well known in the history of the first century of the Roman Republic. At the time they inhabited the partly hilly, partly marshy district of the south of Latium, bounded by the Aurunci and Samnites on the ...
*** Oscans
**** Marrucini
The Marrucini were an Italic tribe that occupied a small strip of territory around the ancient ''Teate'' (modern Chieti), on the east coast of Abruzzo, Italy, limited by the Aterno and Foro Rivers. Other Marrucinian centers included ''Ceio'' ( S ...
**** Osci
The Osci (also called Oscans, Opici, Opsci, Obsci, Opicans) were an Italic people of Campania and Latium adiectum before and during Roman times. They spoke the Oscan language, also spoken by the Samnites of Southern Italy. Although the langua ...
***** Aurunci
The Aurunci were an Italic tribe that lived in southern Italy from around the 1st millennium BC. They were eventually defeated by Rome and subsumed into the Roman Republic during the second half of the 4th century BC.
Identity
Aurunci is the n ...
***** Ausones
"Ausones" (; ), the original name and the extant Greek form for the Latin "Aurunci", was a name applied by Greek writers to describe various Italic peoples inhabiting the southern and central regions of Italy. The term was used, specifically, ...
***** Campanians {{Short description, Ancient Italic tribe
The Campanians (also Campani) were an ancient Italic tribe, part of the Osci nation, speaking an Oscan language.
Descending from the Apennines, the proto-Osci settled in the areas of present-day Campani ...
**** Paeligni
**** Sabines
The Sabines (, , , ; ) were an Italic people who lived in the central Apennine Mountains (see Sabina) of the ancient Italian Peninsula, also inhabiting Latium north of the Anio before the founding of Rome.
The Sabines divided int ...
*** Samnitics
**** Bruttii
**** Frentani
The Frentani were an Italic tribe occupying the tract on the southeast coast of the Italian peninsula from the Apennines to the Adriatic, and from the frontiers of Apulia to those of the Marrucini. They were bounded on the west by the Samnites, ...
**** Lucani
**** Samnites
The Samnites () were an ancient Italic peoples, Italic people who lived in Samnium, which is located in modern inland Abruzzo, Molise, and Campania in south-central Italy.
An Oscan language, Oscan-speaking Osci, people, who originated as an offsh ...
***** Pentri
***** Caraceni
***** Caudini The Caudini were a Samnite tribe that lived among the mountains ringing Campania and in the valleys of the Isclero and Volturnus rivers. Their capital was at Caudium, but it seems certain that the appellation was not confined to the citizens of ...
***** Hirpini
*** Others:
**** Aequi
300px, Location of the Aequi (Equi) in central Italy, 5th century BC.
The Aequi were an Italic tribe on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains to the east of Latium in central Italy who appear in the early history of ancient Rome. After a long stru ...
**** Fidenates
**** Hernici
The Hernici were an Italic tribe of ancient Italy, whose territory was in Latium between the Fucine Lake and the Sacco River (''Trerus''), bounded by the Volsci on the south, and by the Aequi and the Marsi on the north.
History
For many y ...
**** Picentes
The Picentes or Piceni or Picentini were an ancient Italic peoples, Italic people who lived from the 9th to the 3rd century BC in the area between the Foglia and Aterno rivers, bordered to the west by the Apennines and to the east by the Adriatic ...
**** Vestini
Vestini () were an Italic peoples, Italic tribe who occupied the area of the modern Abruzzo (central Italy), included between the Gran Sasso and the northern bank of the Aterno-Pescara, Aterno river. Their main centres were ''Pitinum ''(near mo ...
**** Sicels
The Sicels ( ; or ''Siculī'') were an Indo-European tribe who inhabited eastern Sicily, their namesake, during the Iron Age. They spoke the Siculian language. After the defeat of the Sicels at the Battle of Nomae in 450 BC and the death of ...
**** Venetics
* Ligures
The Ligures or Ligurians were an ancient people after whom Liguria, a region of present-day Northern Italy, north-western Italy, is named. Because of the strong Celts, Celtic influences on their language and culture, they were also known in anti ...
* Sardinians
Sardinians or Sards are an Italians, Italian ethno-linguistic group and a nation indigenous to Sardinia, an island in the western Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean which is administratively an Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special st ...
* Greek colonies in Magna Graecia
Magna Graecia refers to the Greek-speaking areas of southern Italy, encompassing the modern Regions of Italy, Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania, and Sicily. These regions were Greek colonisation, extensively settled by G ...
* Phoenician settlements in insular Italy
* Carthaginian settlements in insular Italy
*Cisalpine Gaul
Cisalpine Gaul (, also called ''Gallia Citerior'' or ''Gallia Togata'') was the name given, especially during the 4th and 3rd centuries BC, to a region of land inhabited by Celts (Gauls), corresponding to what is now most of northern Italy.
Afte ...
s
Early Middle Ages
*Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
* Ostrogothic Kingdom
The Ostrogothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of Italy (), was a barbarian kingdom established by the Germanic Ostrogoths that controlled Italian peninsula, Italy and neighbouring areas between 493 and 553. Led by Theodoric the Great, the Ost ...
* Lombard Kingdom
The Kingdom of the Lombards, also known as the Lombard Kingdom and later as the Kingdom of all Italy (), was an Early Middle Ages, early medieval state established by the Lombards, a Germanic people, on the Italian Peninsula in the latter part ...
* Duchy of Rome
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a country, territory, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or queen in Western European tradition.
There once existed an important difference between "sovereign ...
(under the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
)
* Exarchate of Ravenna
The Exarchate of Ravenna (; ), also known as the Exarchate of Italy, was an administrative district of the Byzantine Empire comprising, between the 6th and 8th centuries, the territories under the jurisdiction of the exarch of Italy (''exarchus ...
(under the Byzantine Empire)
* Exarchate of Carthage (under the Byzantine Empire)
* Thema of Sicily (under the Byzantine Empire)
* Catepanate of Italy (under the Byzantine Empire)
* Duchy of Benevento
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a country, territory, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or queen in Western European tradition.
There once existed an important difference between "sovereign ...
* Duchy of Spoleto
The Duchy of Spoleto () was a Lombards, Lombard territory founded about 570 in central Italy by the Lombard ''dux'' Faroald I of Spoleto, Faroald. Its capital was the city of Spoleto.
Lombards
The Lombards invaded northern Italy in 568 and b ...
* Duchy of Naples
The Duchy of Naples (, ) began as a Byzantine province that was constituted in the seventh century, in the lands roughly corresponding to the current province of Naples that the Lombards had not conquered during their invasion of Italy in the si ...
* Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
* Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
High Middle Ages
States in Central and Northern Italy
*Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
* Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
* Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Maritime republics, maritime republic from the years 1099 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italy, Italian coast. During the Late Middle Ages, it was a major commercial power in ...
* Republic of Pisa
The Republic of Pisa () was an independent state existing from the 11th to the 15th century centered on the Tuscan city of Pisa. It rose to become an economic powerhouse, a commercial center whose merchants dominated Mediterranean and Italian t ...
* Republic of Florence
* Republic of Lucca
* Republic of Siena
The Republic of Siena (, ) was a historic state consisting of the city of Siena and its surrounding territory in Tuscany, Central Italy. It existed for over 400 years, from 1125 to 1555. During its existence, it gradually expanded throughout south ...
* Republic of Ancona
The Republic of Ancona was a medieval commune and maritime republic on the Adriatic coast of modern-day Italy, notable for its economic development and maritime trade, particularly with the Byzantine Empire and Eastern Mediterranean, although som ...
* Republic of Noli
The Republic of Noli (; ) was an Italian maritime republic that was centred on the city of Noli, in Liguria, and existed from 1192 to 1797. The area is now in the province of Savona, Italy. To protect itself from possible attacks and invasion ...
* Republic of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa, or the Republic of Dubrovnik, was an maritime republics, aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' in Italian and Latin; ''Raguxa'' in Venetian) in South Dalmatia (today in southernmost ...
* Republic of San Marino
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a state in which political power rests with the public (people), typically through their representatives—in contrast to a monarchy. Although a ...
Principality of Salerno
The Principality of Salerno () was a Middle Ages, medieval Mezzogiorno, Southern Italian state, formed in 851 out of the Principality of Benevento after a decade-long civil war. It was centred on the port city of Salerno. Although it owed alle ...
* Catepanate of Italy (under the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
)
* Principality of Capua
The Principality of Capua ( or ''Capue'', Modern ) was a Lombards, Lombard state centred on Capua in Southern Italy. Towards the end of the 10th century the Principality reached its apogee, occupying most of the Terra di Lavoro area. It was ori ...
* Duchy of Gaeta
The Duchy of Gaeta () was an Early Middle Ages, early medieval state centered on the coastal Mezzogiorno, South Italian city of Gaeta. It began in the early ninth century as the local community began to grow autonomous as Byzantine Empire, Byzant ...
* Duchy of Naples
The Duchy of Naples (, ) began as a Byzantine province that was constituted in the seventh century, in the lands roughly corresponding to the current province of Naples that the Lombards had not conquered during their invasion of Italy in the si ...
* Duchy of Amalfi
The Duchy of Amalfi () or the Republic of Amalfi was a '' de facto'' independent state centered on the Southern Italian city of Amalfi during the 10th and 11th centuries. The city and its territory were originally part of the larger Duchy of Na ...
* Duchy of Sorrento
The Duchy of Sorrento was a small peninsular duchy of the Early Middle Ages centred on the Italian city of Sorrento.
Established in the 7th century as a fief of the Duchy of Naples, at the time still part of the Byzantine Empire.
Subsequently ...
* Emirate of Sicily
The island of SicilyIn Arabic, the island was known as (). was under Islam, Islamic rule from the late ninth to the late eleventh centuries. It became a prosperous and influential commercial power in the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean, with ...
(under the Fatimid Caliphate
The Fatimid Caliphate (; ), also known as the Fatimid Empire, was a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries CE under the rule of the Fatimids, an Isma'ili Shi'a dynasty. Spanning a large area of North Africa and West Asia, i ...
)
* County of Sicily
* County of Apulia
* Duchy of Apulia
The County of Apulia and Calabria (), later the Duchy of Apulia and Calabria (), was a Norman state founded by William of Hauteville in 1043, composed of the territories of Gargano, Capitanata, Apulia, Vulture, and most of Campania. It becam ...
* Duchy of Calabria
* Duchy of Apulia and Calabria
* Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily (; ; ) was a state that existed in Sicily and the southern Italian peninsula, Italian Peninsula as well as, for a time, in Kingdom of Africa, Northern Africa, from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 until 1816. It was ...
States of the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
* Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
* Commune of Milan
* March of Tuscany
* March of Verona
March is the third month of the year in both the Julian and Gregorian calendars. Its length is 31 days. In the Northern Hemisphere, the meteorological beginning of spring occurs on the first day of March. The March equinox on the 20 or 21 ...
* March of Treviso
* March of Ivrea
* March of Turin
* March of Montferrat
* March of Genoa
* Patriarchate of Aquileia
The Patriarchate of Aquileia was an episcopal see and ecclesiastical province in northeastern Italy, originally centered in the ancient city of Aquileia, situated near the northern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It emerged in the 4th century as a m ...
(including March of Friuli
The March of Friuli was a Carolingian frontier march, centered in the historical region of Friuli (corresponding mainly to the modern province of Friuli-Venezia Giulia in north-eastern Italy). Since the Frankish conquest and pacification of the ...
and March of Istria
March is the third month of the year in both the Julian and Gregorian calendars. Its length is 31 days. In the Northern Hemisphere, the meteorological beginning of spring occurs on the first day of March. The March equinox on the 20 or 21 ...
)
* Duchy of Spoleto
The Duchy of Spoleto () was a Lombards, Lombard territory founded about 570 in central Italy by the Lombard ''dux'' Faroald I of Spoleto, Faroald. Its capital was the city of Spoleto.
Lombards
The Lombards invaded northern Italy in 568 and b ...
* Bishopric of Brixen
* Bishopric of Trent
* County of Savoy
* County of Gorizia
* Marquisate of Saluzzo
* Marquisate of Ceva
* Marquisate of Incisa
* Marquisate of Finale
Cagliari
Cagliari (, , ; ; ; Latin: ''Caralis'') is an Comune, Italian municipality and the capital and largest city of the island of Sardinia, an Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Italy. It has about 146,62 ...
* Gallura
Gallura ( or ; ) is a region in North-Eastern Sardinia, Italy.
The name ''Gallùra'' is allegedly supposed to mean "stony area".
Geography
Gallùra has an area of . It is from the Italian peninsula and from the French island of Corsica.
...
* Logudoro
The Logudoro (; ) is a large historical region Sardinia, Italy. It is the namesake of the Logudorese dialect of Sardinian language, Sardinian, which covers a large area of northern-central Sardinia.
The first denomination of the area is contai ...
Late Middle Ages


Major states
*Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
* Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
* Republic of Florence
* Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples (; ; ), officially the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was established by the War of the Sicilian Vespers (1282–1302). Until ...
* Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan (; ) was a state in Northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti of Milan, Visconti family, which had been ruling the city since 1277. At that time, ...
* Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Maritime republics, maritime republic from the years 1099 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italy, Italian coast. During the Late Middle Ages, it was a major commercial power in ...
Minor states
* Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica *Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily (; ; ) was a state that existed in Sicily and the southern Italian peninsula, Italian Peninsula as well as, for a time, in Kingdom of Africa, Northern Africa, from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 until 1816. It was ...
* Duchy of Ferrara
The Duchy of Ferrara (; ; ) was a state in what is now northern Italy. It consisted of about 1,100 km2 south of the lower Po River, stretching to the valley of the lower Reno River, including the city of Ferrara. The territory that was part ...
* Lordship of Milan (before being raised to Duchy in 1395)
* Duchy of Modena and Reggio
The Duchy of Modena and Reggio (; ; ) was an Italian state created in 1452 located in Northern Italy, Northwestern Italy, in the present day region of Emilia-Romagna. It was ruled since its establishment by the noble House of Este, and from 1814 ...
* Prince-Bishopric of Brixen
* Prince-Bishopric of Trent
The Prince-Bishopric of Trent (; ) was an ecclesiastical principality roughly corresponding to the present-day Northern Italy, Northern Italian autonomous province of Trentino. It was created in 1027 and existed until 1803, when it was German m ...
* Marquisate of Bastia
* Marquisate of Ceva
* Marquisate of Finale
* Marquisate of Fosdinovo
* Marquisate of Incisa
* Marquisate of Mantua
* Marquisate of Massa
* Marquisate of Saluzzo
* Marquisate of Montferrat
* County of Asti
* County of Correggio
* County of Gorizia
* County of Guastalla
The County of Guastalla () was an Italian state, centered on the city of Guastalla in Northern Italy, which existed from 1428 to 1621, when it was then elevated to a Duchy.
History
The title of count was conferred in 1428 on Guido Torelli f ...
* County of Masserano
* County of Mirandola
* County of Montechiarugolo
* County of Novellara
* County of Pitigliano
* County of Santa Fiora
The County of Santa Fiora (), also known as State of Santa Fiora () was a small historical state of southern Tuscany, in central Italy. Together with the county of Sovana, it was one of the two subdivisions into which the possessions of the Aldobr ...
* County of Savoy (raised to Duchy of Savoy
The Duchy of Savoy (; ) was a territorial entity of the Savoyard state that existed from 1416 until 1847 and was a possession of the House of Savoy.
It was created when Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, raised the County of Savoy into a duchy f ...
in 1416)
** County of Nice
The County of Nice (; ; Niçard ) was a historical region of France and Italy located around the southeastern city of Nice and roughly equivalent to the modern arrondissement of Nice. It was part of the Savoyard state within the Holy Roman Emp ...
(in personal union
A personal union is a combination of two or more monarchical states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, involves the constituent states being to some extent in ...
with Savoy)
* County of Scandiano
* County of Sovana
* County of Tende
* County of Urbino (raised to Duchy of Urbino
The Duchy of Urbino () was an independent duchy in Early modern period, early modern central Italy, corresponding to the northern half of the modern region of Marche. It was directly annexed by the Papal States in 1631.
It was bordered by the A ...
in 1443)
* Golden Ambrosian Republic
The Golden Ambrosian Republic (; ; 1447–1450) was a short-lived republic founded in Milan by members of the University of Pavia with popular support, during the first phase of the Milanese War of Succession. With the aid of Francesco Sforza th ...
* Republic of Ancona
The Republic of Ancona was a medieval commune and maritime republic on the Adriatic coast of modern-day Italy, notable for its economic development and maritime trade, particularly with the Byzantine Empire and Eastern Mediterranean, although som ...
* Republic of Cospaia
The Republic of Cospaia (, local dialect: ''Republica de' Cošpäja'') was a small state in northern Umbria, now in Italy, that was independent from 1440 to 1826. It was in what is now the hamlet () of Cospaia, in the municipality () of San G ...
* Republic of Lucca
* Republic of Noli
The Republic of Noli (; ) was an Italian maritime republic that was centred on the city of Noli, in Liguria, and existed from 1192 to 1797. The area is now in the province of Savona, Italy. To protect itself from possible attacks and invasion ...
* Republic of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa, or the Republic of Dubrovnik, was an maritime republics, aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' in Italian and Latin; ''Raguxa'' in Venetian) in South Dalmatia (today in southernmost ...
* Republic of San Marino
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a state in which political power rests with the public (people), typically through their representatives—in contrast to a monarchy. Although a ...
* Republic of Siena
The Republic of Siena (, ) was a historic state consisting of the city of Siena and its surrounding territory in Tuscany, Central Italy. It existed for over 400 years, from 1125 to 1555. During its existence, it gradually expanded throughout south ...
* Rebel city-states in Papal States
After the Italian Wars
The Peace of Cateau Cambrésis ended theItalian Wars
The Italian Wars were a series of conflicts fought between 1494 and 1559, mostly in the Italian Peninsula, but later expanding into Flanders, the Rhineland and Mediterranean Sea. The primary belligerents were the House of Valois, Valois kings o ...
in 1559. The kingdoms of Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
, Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; ; ) is the Mediterranean islands#By area, second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, and one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. It is located west of the Italian Peninsula, north of Tunisia an ...
, Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of N ...
(inclusive of the State of Presidi) and the Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan (; ) was a state in Northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti of Milan, Visconti family, which had been ruling the city since 1277. At that time, ...
were left under the control of Spanish Habsburgs. France was in control of several fortresses and in particular of the Marquisate of Saluzzo. All the other Italian states remained independent, with the most powerful being the Venetian Republic
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
, the Medici's Duchy of Tuscany, the Savoyard state
The Savoyard state comprised the states ruled by the counts and dukes of Savoy from the Middle Ages to the formation of the Kingdom of Italy. Although it was an example of composite monarchy, it is a term applied to the polity by historians an ...
, the Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Maritime republics, maritime republic from the years 1099 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italy, Italian coast. During the Late Middle Ages, it was a major commercial power in ...
, and the Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
. The Gonzaga in Mantua, the Este in Modena and Ferrara and the Farnese in Parma and Piacenza continued to be important dynasties. Parts of the north of Italy remained a part of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
.
Major states
*Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
* Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
* Grand Duchy of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany (; ) was an Italian monarchy located in Central Italy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1860, replacing the Republic of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence. In the 19th century the population ...
* Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples (; ; ), officially the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was established by the War of the Sicilian Vespers (1282–1302). Until ...
* Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Maritime republics, maritime republic from the years 1099 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italy, Italian coast. During the Late Middle Ages, it was a major commercial power in ...
* Duchy of Savoy
The Duchy of Savoy (; ) was a territorial entity of the Savoyard state that existed from 1416 until 1847 and was a possession of the House of Savoy.
It was created when Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, raised the County of Savoy into a duchy f ...
* Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan (; ) was a state in Northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti of Milan, Visconti family, which had been ruling the city since 1277. At that time, ...
Minor states
*Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia, also referred to as the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica among other names, was a State (polity), country in Southern Europe from the late 13th until the mid-19th century, and from 1297 to 1768 for the Corsican part of ...
(under Spanish rule)
* Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily (; ; ) was a state that existed in Sicily and the southern Italian peninsula, Italian Peninsula as well as, for a time, in Kingdom of Africa, Northern Africa, from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 until 1816. It was ...
* Prince-Bishopric of Brixen
* Prince-Bishopric of Trent
The Prince-Bishopric of Trent (; ) was an ecclesiastical principality roughly corresponding to the present-day Northern Italy, Northern Italian autonomous province of Trentino. It was created in 1027 and existed until 1803, when it was German m ...
* Principality of Piombino
* Principality of Monaco
Monaco, officially the Principality of Monaco, is a sovereign city-state and microstate on the French Riviera a few kilometres west of the Italian region of Liguria, in Western Europe, on the Mediterranean Sea. It is a semi-enclave borde ...
* Duchy of Mantua
The Duchy of Mantua (; ) was a duchy in Lombardy, northern Italy. Its first duke was Federico II Gonzaga, member of the House of Gonzaga that ruled Mantua since 1328. In 1531, the duchy also acquired the March of Montferrat, thanks to the marr ...
* Duchy of Ferrara
The Duchy of Ferrara (; ; ) was a state in what is now northern Italy. It consisted of about 1,100 km2 south of the lower Po River, stretching to the valley of the lower Reno River, including the city of Ferrara. The territory that was part ...
** Duchy of Modena and Reggio
The Duchy of Modena and Reggio (; ; ) was an Italian state created in 1452 located in Northern Italy, Northwestern Italy, in the present day region of Emilia-Romagna. It was ruled since its establishment by the noble House of Este, and from 1814 ...
(In personal union
A personal union is a combination of two or more monarchical states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, involves the constituent states being to some extent in ...
with Ferrara)
* Duchy of Parma and Piacenza
** Duchy of Castro (in personal union with Parma)
* Duchy of Urbino
The Duchy of Urbino () was an independent duchy in Early modern period, early modern central Italy, corresponding to the northern half of the modern region of Marche. It was directly annexed by the Papal States in 1631.
It was bordered by the A ...
* Marquisate of Bastia
* Marquisate of Castiglione (raised to Principality of Castiglione in 1609)
* Marquisate of Finale
* Marquisate of Fosdinovo
* Marquisate of Massa (raised to Principality of Massa in 1568)
** Marquisate of Carrara (in personal union with Massa)
* Marquisate of Masserano (raised to Principality of Masserano in 1598)
* Marquisate of Montferrat (raised to Duchy of Montferrat in 1574; in personal union with Mantua)
* Marquisate of Sabbioneta (raised to Duchy of Sabbioneta in 1577)
* Marquisate of Torriglia
* County of Correggio (raised to Principality of Correggio in 1616)
* County of Guastalla
The County of Guastalla () was an Italian state, centered on the city of Guastalla in Northern Italy, which existed from 1428 to 1621, when it was then elevated to a Duchy.
History
The title of count was conferred in 1428 on Guido Torelli f ...
* County of Pitigliano
* County of Mirandola
* County of Montechiarugolo
* County of Novellara
* County of Santa Fiora
The County of Santa Fiora (), also known as State of Santa Fiora () was a small historical state of southern Tuscany, in central Italy. Together with the county of Sovana, it was one of the two subdivisions into which the possessions of the Aldobr ...
* County of Tende
* Monastic State of the Order of Malta
* Republic of Ancona
The Republic of Ancona was a medieval commune and maritime republic on the Adriatic coast of modern-day Italy, notable for its economic development and maritime trade, particularly with the Byzantine Empire and Eastern Mediterranean, although som ...
* Republic of Cospaia
The Republic of Cospaia (, local dialect: ''Republica de' Cošpäja'') was a small state in northern Umbria, now in Italy, that was independent from 1440 to 1826. It was in what is now the hamlet () of Cospaia, in the municipality () of San G ...
* Republic of Lucca
* Republic of Noli
The Republic of Noli (; ) was an Italian maritime republic that was centred on the city of Noli, in Liguria, and existed from 1192 to 1797. The area is now in the province of Savona, Italy. To protect itself from possible attacks and invasion ...
* Republic of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa, or the Republic of Dubrovnik, was an maritime republics, aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' in Italian and Latin; ''Raguxa'' in Venetian) in South Dalmatia (today in southernmost ...
* Republic of San Marino
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a state in which political power rests with the public (people), typically through their representatives—in contrast to a monarchy. Although a ...
After the Wars of Succession of the 18th century
 During the war of the Spanish succession (1700-1714), Savoy acquired Sicily, while the remaining Spanish dominions in Italy (Naples, Sardinia, and Milan) were taken over by the Austrian Habsburgs. In 1720, Savoy exchanged Sicily for Sardinia. Following the extinction of the
During the war of the Spanish succession (1700-1714), Savoy acquired Sicily, while the remaining Spanish dominions in Italy (Naples, Sardinia, and Milan) were taken over by the Austrian Habsburgs. In 1720, Savoy exchanged Sicily for Sardinia. Following the extinction of the House of Medici
The House of Medici ( , ; ) was an Italian banking family and political dynasty that first consolidated power in the Republic of Florence under Cosimo de' Medici and his grandson Lorenzo de' Medici, Lorenzo "the Magnificent" during the first h ...
, the Grand Duchy of Tuscany was ruled by the Habsburg-Lorraine
The House of Habsburg-Lorraine () originated from the marriage in 1736 of Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor, Francis III, Duke of Lorraine and Bar, and Maria Theresa of Habsburg monarchy, Austria, later successively List of Bohemian monarchs, Queen ...
. Later on, Southern Italy passed to a cadet branch of the House of Bourbon
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a dynasty that originated in the Kingdom of France as a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Kingdom of Navarre, Navarre in the 16th century. A br ...
, known as House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies
The House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies is a cadet branch of the House of Bourbon that ruled Southern Italy and Sicily for more than a century in the 18th and 19th centuries. It descends from the Capetian dynasty in legitimate male line through Phili ...
. Other states such as Genoa, Venice, Modena, the Papal States and Lucca remained with their governments unchanged.
Major states
*Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
* Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples (; ; ), officially the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was established by the War of the Sicilian Vespers (1282–1302). Until ...
(under the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
from 1714 to 1735; in personal union
A personal union is a combination of two or more monarchical states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, involves the constituent states being to some extent in ...
with Sicily under the Bourbon-Two Sicilies thereafter)
* Grand Duchy of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany (; ) was an Italian monarchy located in Central Italy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1860, replacing the Republic of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence. In the 19th century the population ...
(under Habsburg-Lorraine after 1737)
* Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan (; ) was a state in Northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti of Milan, Visconti family, which had been ruling the city since 1277. At that time, ...
(under Habsburg Monarchy)
* Duchy of Savoy
The Duchy of Savoy (; ) was a territorial entity of the Savoyard state that existed from 1416 until 1847 and was a possession of the House of Savoy.
It was created when Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, raised the County of Savoy into a duchy f ...
* Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Maritime republics, maritime republic from the years 1099 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italy, Italian coast. During the Late Middle Ages, it was a major commercial power in ...
* Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
Minor states
*Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia, also referred to as the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica among other names, was a State (polity), country in Southern Europe from the late 13th until the mid-19th century, and from 1297 to 1768 for the Corsican part of ...
(under Austrian monarchy from 1714 to 1720; in personal union with Savoy thereafter)
* Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily (; ; ) was a state that existed in Sicily and the southern Italian peninsula, Italian Peninsula as well as, for a time, in Kingdom of Africa, Northern Africa, from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 until 1816. It was ...
( under Savoy from 1713 to 1720; under Austrian monarchy from 1720 to 1734; in personal union with Naples under the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies
The House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies is a cadet branch of the House of Bourbon that ruled Southern Italy and Sicily for more than a century in the 18th and 19th centuries. It descends from the Capetian dynasty in legitimate male line through Phili ...
thereafter)
* Duchy of Mantua
The Duchy of Mantua (; ) was a duchy in Lombardy, northern Italy. Its first duke was Federico II Gonzaga, member of the House of Gonzaga that ruled Mantua since 1328. In 1531, the duchy also acquired the March of Montferrat, thanks to the marr ...
(under House of Gonzaga
The House of Gonzaga (, ) is an Italian princely family that ruled Mantua in Lombardy, northern Italy from 1328 to 1708 (first as a captaincy-general, then Margraviate of Mantua, margraviate, and finally Duchy of Mantua, duchy). They also ruled M ...
until 1708, Austrian Monarchy thereafter)
* Duchy of Parma and Piacenza (under Habsburg Monarchy from 1734 to 1748, under House of Bourbon-Parma
The House of Bourbon-Parma () is a cadet branch of the Spanish royal family, whose members once ruled as King of Etruria and as Duke of Parma and Piacenza, Duke of Guastalla, Guastalla, and Duke of Lucca, Lucca. The House descended from the Fre ...
thereafter)
* Duchy of Guastalla
The Duchy of Guastalla () was an Historical states of Italy, Italian state which existed between 1621 and 1748. It was bordered by the Duchy of Modena and Reggio and the Po River to the north, on the opposite bank of the Duchy of Mantua. Its place ...
(in personal union with Parma from 1748)
* Duchy of Modena and Reggio
The Duchy of Modena and Reggio (; ; ) was an Italian state created in 1452 located in Northern Italy, Northwestern Italy, in the present day region of Emilia-Romagna. It was ruled since its establishment by the noble House of Este, and from 1814 ...
Prince-Bishopric of Trent
The Prince-Bishopric of Trent (; ) was an ecclesiastical principality roughly corresponding to the present-day Northern Italy, Northern Italian autonomous province of Trentino. It was created in 1027 and existed until 1803, when it was German m ...
* Principality of Masserano
* Principality of Torriglia
* Principality of Piombino
* Principality of Monaco
Monaco, officially the Principality of Monaco, is a sovereign city-state and microstate on the French Riviera a few kilometres west of the Italian region of Liguria, in Western Europe, on the Mediterranean Sea. It is a semi-enclave borde ...
* Duchy of Montferrat, to House of Savoy
The House of Savoy (, ) is a royal house (formally a dynasty) of Franco-Italian origin that was established in 1003 in the historical region of Savoy, which was originally part of the Kingdom of Burgundy and now lies mostly within southeastern F ...
from 1708
* Marquisate of Fosdinovo
* Marquisate of Bastia
* Republic of Lucca
* Republic of San Marino
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a state in which political power rests with the public (people), typically through their representatives—in contrast to a monarchy. Although a ...
* Republic of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa, or the Republic of Dubrovnik, was an maritime republics, aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' in Italian and Latin; ''Raguxa'' in Venetian) in South Dalmatia (today in southernmost ...
* Republic of Noli
The Republic of Noli (; ) was an Italian maritime republic that was centred on the city of Noli, in Liguria, and existed from 1192 to 1797. The area is now in the province of Savona, Italy. To protect itself from possible attacks and invasion ...
* Republic of Cospaia
The Republic of Cospaia (, local dialect: ''Republica de' Cošpäja'') was a small state in northern Umbria, now in Italy, that was independent from 1440 to 1826. It was in what is now the hamlet () of Cospaia, in the municipality () of San G ...
* City of Fiume and its District
* Monastic State of the Order of Malta
Their populations and other vital statistics stood as follows in the late 18th century:Emmanuel-Auguste-Dieudonne comte de Las Cases. 1816. *
Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples (; ; ), officially the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was established by the War of the Sicilian Vespers (1282–1302). Until ...
(including Sicily): 6,000,000 (400,000 in Naples), army of 60,000 to 80,000, 2 ships of the lines and some frigates
* Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
: 3,500,000 (140,000 in the city of Venice itself), standing army and navy of 30,000, 12-15 ships of at least 54 guns plus frigates and brigs
* Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia, also referred to as the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica among other names, was a State (polity), country in Southern Europe from the late 13th until the mid-19th century, and from 1297 to 1768 for the Corsican part of ...
: 2,900,000 (2,400,000 on the mainland and 500,000 on the island), 12-15 fortified cities and towns (largest being Turin at 80,000), standing army of 25,000, which could be raised to 50,000 in a time of war and 100,000 with militia
* Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
: 2,400,000 (140,000 in the city of Rome), standing army of 6,000 to 7,000
* Austrian Lombardy (Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan (; ) was a state in Northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti of Milan, Visconti family, which had been ruling the city since 1277. At that time, ...
, Duchy of Mantua
The Duchy of Mantua (; ) was a duchy in Lombardy, northern Italy. Its first duke was Federico II Gonzaga, member of the House of Gonzaga that ruled Mantua since 1328. In 1531, the duchy also acquired the March of Montferrat, thanks to the marr ...
, and minor territories): 1,100,000 (40,000 in the city of Milan itself)
* Grand Duchy of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany (; ) was an Italian monarchy located in Central Italy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1860, replacing the Republic of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence. In the 19th century the population ...
: 1,000,000 (80,000 in Florence), standing army of 6,000, navy of 3 frigates
* Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Maritime republics, maritime republic from the years 1099 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italy, Italian coast. During the Late Middle Ages, it was a major commercial power in ...
: 500,000 (100,000 in the city of Genoa itself)
* Duchy of Parma: 500,000 (40,000 in the city of Parma itself), standing army of 2,500 to 3,000
* Duchy of Modena: 350,000 (20,000 in the city of Modena itself), standing army of 5,000 to 6,000
* Republic of Lucca: 100,000
Total: 18.3 million
During Napoleonic times (1792–1815)

Sister republics of Revolutionary France
* Republic of Alba * Anconine Republic * Astese Republic * Republic of Bergamo * Bolognese Republic * Republic of Brescia *Cisalpine Republic
The Cisalpine Republic (; ) was a sister republic or a client state of France in Northern Italy that existed from 1797 to 1799, with a second version until 1802.
Creation
After the Battle of Lodi in May 1796, Napoleon Bonaparte organized two ...
* Cispadane Republic
* Republic of Crema
* Italian Republic
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
* Ligurian Republic
* Jacobin State of Lucca
* Parthenopean Republic
The Parthenopean Republic (, ) or Neapolitan Republic () was a short-lived, semi-autonomous republic located within the Kingdom of Naples and supported by the French First Republic. The republic emerged during the French Revolutionary Wars after ...
* Republic of Pescara
* Piedmontese Republic
* Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
* Subalpine Republic
* Tiberina Republic
* Transpadane Republic
The Transpadane Republic () was a sister republic of France established in Milan from 1796 to 1797.
History
On 10 May 1796, the French army defeated the Austrian troops in the Battle of Lodi, and occupied the Duchy of Milan. Napoleon set up a ...
Client states of the First French Empire
*Kingdom of Etruria
The Kingdom of Etruria ( ; ) was an Italian kingdom between 1801 and 1807 that made up a large part of modern Tuscany. It took its name from Etruria, the old Roman name for the land of the Etruscans.
History
The kingdom was created by the ...
* Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
* Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples (; ; ), officially the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was established by the War of the Sicilian Vespers (1282–1302). Until ...
* Principality of Lucca and Piombino
* Principality of Benevento
* Principality of Pontecorvo
Other states
*Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia, also referred to as the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica among other names, was a State (polity), country in Southern Europe from the late 13th until the mid-19th century, and from 1297 to 1768 for the Corsican part of ...
* Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily (; ; ) was a state that existed in Sicily and the southern Italian peninsula, Italian Peninsula as well as, for a time, in Kingdom of Africa, Northern Africa, from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 until 1816. It was ...
* Principality of Elba (non-hereditary Monarchy under the exiled Emperor Napoleon)
* Republic of Cospaia
The Republic of Cospaia (, local dialect: ''Republica de' Cošpäja'') was a small state in northern Umbria, now in Italy, that was independent from 1440 to 1826. It was in what is now the hamlet () of Cospaia, in the municipality () of San G ...
* Republic of San Marino
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a state in which political power rests with the public (people), typically through their representatives—in contrast to a monarchy. Although a ...
From the restoration to the unification
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
(1815) was convened to redraw the European continent. In Italy, the Congress restored the pre-Napoleonic patchwork of independent governments, either directly ruled or strongly influenced by the prevailing European powers, particularly Austria. The Congress also determined the end of two millenary republics: Genoa was annexed by the then Savoyard Kingdom of Sardinia, and Venice was incorporated with Milan into a new kingdom of the Austrian Empire.
At the time, the struggle for Italian unification was perceived to be waged primarily against the Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
, since they directly controlled the predominantly Italian-speaking northeastern part of present-day Italy and were the most powerful force against the Italian unification. The Austrian Empire vigorously repressed nationalist sentiment growing in its domains on the Italian Peninsula, as well as in the other parts of Habsburg domains.
* Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th c ...
* Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia, also referred to as the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica among other names, was a State (polity), country in Southern Europe from the late 13th until the mid-19th century, and from 1297 to 1768 for the Corsican part of ...
* Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
The Kingdom of the Two Sicilies () was a kingdom in Southern Italy from 1816 to 1861 under the control of the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies, a cadet branch of the House of Bourbon, Bourbons. The kingdom was the largest sovereign state by popula ...
* Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia
The Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia (), commonly called the "Lombardo-Venetian Kingdom" (; ), was a constituent land (crown land) of the Austrian Empire from 1815 to 1866. It was created in 1815 by resolution of the Congress of Vienna in recogniti ...
(under Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
)
* Kingdom of Illyria
The Kingdom of Illyria was a crown land of the Austrian Empire from 1816 to 1849, the successor state of the Napoleonic Illyrian Provinces, which were reconquered by Austria in the War of the Sixth Coalition. It was established according to th ...
(under Austrian Empire)
* Grand Duchy of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany (; ) was an Italian monarchy located in Central Italy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1860, replacing the Republic of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence. In the 19th century the population ...
* Duchy of Parma, Piacenza and Guastalla
* Duchy of Modena and Reggio
The Duchy of Modena and Reggio (; ; ) was an Italian state created in 1452 located in Northern Italy, Northwestern Italy, in the present day region of Emilia-Romagna. It was ruled since its establishment by the noble House of Este, and from 1814 ...
* Duchy of Massa and Carrara
* Duchy of Lucca
* Principality of Monaco
Monaco, officially the Principality of Monaco, is a sovereign city-state and microstate on the French Riviera a few kilometres west of the Italian region of Liguria, in Western Europe, on the Mediterranean Sea. It is a semi-enclave borde ...
* Republic of San Marino
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a state in which political power rests with the public (people), typically through their representatives—in contrast to a monarchy. Although a ...
* Republic of Cospaia
The Republic of Cospaia (, local dialect: ''Republica de' Cošpäja'') was a small state in northern Umbria, now in Italy, that was independent from 1440 to 1826. It was in what is now the hamlet () of Cospaia, in the municipality () of San G ...
* Republic of San Marco
* Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
* United Provinces of Central Italy
Post-unification

Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
* Republic of San Marino
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a state in which political power rests with the public (people), typically through their representatives—in contrast to a monarchy. Although a ...
* Italian Regency of Carnaro
* Free State of Fiume
* Italian Social Republic
The Italian Social Republic (, ; RSI; , ), known prior to December 1943 as the National Republican State of Italy (; SNRI), but more popularly known as the Republic of Salò (, ), was a List of World War II puppet states#Germany, German puppe ...
* Kingdom of the South
The Kingdom of the South ( Italian: ''Regno del Sud'') is a term which is used in historiography to describe the Kingdom of Italy (initially Pietro Badoglio and later Ivanoe Bonomi as prime ministers) under the control of the Allied Military G ...
* Free Territory of Trieste
The Free Territory of Trieste was an independent territory in Southern Europe between Italy and SFR Yugoslavia, Yugoslavia, facing the north part of the Adriatic Sea, under United Nations Security Council Resolution 16, direct responsibility of ...
Italian Partisan Republics
The Italian Partisan Republics were the provisional state entities liberated by Italian partisans from the rule and occupation ofNazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
and the Italian Social Republic
The Italian Social Republic (, ; RSI; , ), known prior to December 1943 as the National Republican State of Italy (; SNRI), but more popularly known as the Republic of Salò (, ), was a List of World War II puppet states#Germany, German puppe ...
in 1944 during the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. They were universally short-lived, with most of them being reconquered by the Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the German Army (1935–1945), ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmac ...
within weeks of their formal establishments and re-incorporated into the Italian Social Republic.
* Republic of Alba (10 October - 2 November)
* Republic of Alto Monferrato (September - 2 December)
* Republic of Alto Tortonese
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a State (polity), state in which Power (social and political), political power rests with the public (people), typically through their Representat ...
(September - December)
* Republic of Bobbio (7 July - 27 August)
* Republic of the Cansiglio (July - September)
* Republic of Carnia (26 September - 10 October)
* (2 February - March)
* Republic of Oriental Friuli (30 June - September)
* Republic of Pigna (IM) (18 September - 8 October)
* Republic of the Langhe (September - November)
* (17 June - 1 August)
* Republic of Ossola (10 September - 23 October)
* (26 June - 27 November)
* Republic of the Ceno Valley (10 June - 11 July)
* Republic of the Enza Valley and the Parma Valley (June - July)
* Republic of the Maira Valley and the Varaita Valley (June - 21 August)
* (15 June - 24 July)
* Republic of the Lanzo Valley (25 June - September)
* Republic of the Sesia Valley (11 June - 10 July)
* Republic of Varzi (19/24 September - 29 November)
Current states
*Italian Republic
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
* Republic of San Marino
A republic, based on the Latin phrase ''res publica'' ('public affair' or 'people's affair'), is a state in which political power rests with the public (people), typically through their representatives—in contrast to a monarchy. Although a ...
* Vatican City State
Vatican City, officially the Vatican City State (; ), is a Landlocked country, landlocked sovereign state and city-state; it is enclaved within Rome, the capital city of Italy and Bishop of Rome, seat of the Catholic Church. It became inde ...
See also
*Italian city-states
The Italian city-states were numerous political and independent territorial entities that existed in the Italian Peninsula from antiquity to the formation of the Kingdom of Italy in the late 19th century.
The ancient Italian city-states were E ...
* Maritime republics
The maritime republics (), also called merchant republics (), were Italian Thalassocracy , thalassocratic Port city, port cities which, starting from the Middle Ages, enjoyed political autonomy and economic prosperity brought about by their mar ...
* Medieval commune
Medieval communes in the European Middle Ages had sworn allegiances of mutual defense (both physical defense and of traditional freedoms) among the citizens of a town or city. These took many forms and varied widely in organization and makeup.
C ...
* Signoria
References
States
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
*
*Italy
Historic states
Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...