Leading axle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
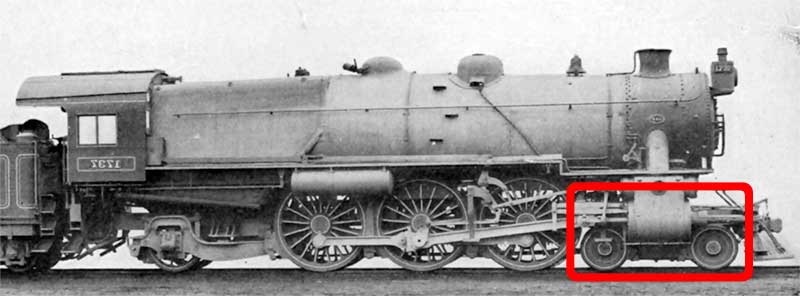 The leading wheel or leading axle or pilot wheel of a
The leading wheel or leading axle or pilot wheel of a
''Gladstone'' at the National Railway Museum, York
Accessed 22 December 2006. A single leading axle (known as a pony truck) increases stability somewhat, while a four-wheel leading truck is almost essential for high-speed operation. The highest number of leading wheels on a single locomotive is six, as seen on the 6-2-0 Crampton type and the
 The leading wheel or leading axle or pilot wheel of a
The leading wheel or leading axle or pilot wheel of a steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, Fuel oil, oil or, rarely, Wood fuel, wood) to heat ...
is an unpowered wheel
A wheel is a rotating component (typically circular in shape) that is intended to turn on an axle Bearing (mechanical), bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the Simple machine, six simple machin ...
or axle
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotation, rotating wheel and axle, wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In ...
located in front of the driving wheels. The axle or axles of the leading wheels are normally located on a leading truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport freight, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame construct ...
. Leading wheels are used to help the locomotive negotiate curves and to support the front portion of the boiler.
Overview
Many leading bogies do not have simple rotational motion about a vertical pivot. Bogies with a sliding motion controlled by springs was patented by William Adams in 1865. Other designs used swing links to take the weight of the bogie with a centering action. The first use of leading wheels is commonly attributed to John B. Jervis, who employed them in his 1832 design for a locomotive with four leading wheels and twodriving wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled t ...
s (a type that became known as the ''Jervis''). In the Whyte system of describing locomotive wheel arrangements, his locomotive would be classified as a 4-2-0, that is to say, it had four leading wheels, two driving wheel
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled t ...
s, and no trailing wheel
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle (Wheelset (rail transport), wheelset) located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels is usually located in a trailing Bogie, t ...
s. In the UIC classification
The UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements, sometimes known as the German classification''The Railway Data File''. Leicester: Silverdale, 2000. p. 52. . or German system,Kalla-Bishop P.M. & Greggio, Luciano, ''Steam Locomotives'', Cr ...
system, which counts axles rather than wheels and uses letters to denote powered axles, the ''Jervis'' would be classified 2A.
Locomotives without leading trucks are generally regarded as unsuitable for high speed use. The British Railway Inspectorate
Established in 1840, His Majesty's Railway Inspectorate (HMRI) is the organisation responsible for overseeing safety on United Kingdom, Britain's railways and light rail, tramways. It was previously a separate non-departmental public body, but ...
condemned the practice in 1895, following an accident involving two 0-4-4s at Doublebois, Cornwall, on the Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a History of rail transport in Great Britain, British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands (region), West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, ...
. Other designers, however, persisted with the practice and the famous 0-4-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement with no leading wheels, four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles and two trailing wheels on one axle. While the first locomotives ...
Gladstone class passenger expresses of the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway
The London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR (known also as the Brighton line, the Brighton Railway or the Brighton)) was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1846 to 1922. Its territory formed a rough triangle, with London at ...
remained in trouble-free service until 1933.Accessed 22 December 2006. A single leading axle (known as a pony truck) increases stability somewhat, while a four-wheel leading truck is almost essential for high-speed operation. The highest number of leading wheels on a single locomotive is six, as seen on the 6-2-0 Crampton type and the
Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad ( reporting mark PRR), legal name as the Pennsylvania Railroad Company, also known as the "Pennsy," was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. At its ...
's 6-4-4-6 S1 duplex locomotive and 6-8-6 S2 steam turbine. Six-wheel leading trucks were not very popular. The Cramptons were built in the 1840s, but it was not until 1939 that the PRR used one on the S1.
See also
*AAR wheel arrangement
The AAR wheel arrangement system is a method of classifying locomotive
A locomotive is a rail transport, rail vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. Traditionally, locomotives pulled trains from the front. However, Push–pu ...
* Adams axle
* Trailing wheel
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle (Wheelset (rail transport), wheelset) located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels is usually located in a trailing Bogie, t ...
* UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements
The UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements, sometimes known as the German classification''The Railway Data File''. Leicester: Silverdale, 2000. p. 52. . or German system,Kalla-Bishop P.M. & Greggio, Luciano, ''Steam Locomotives'', Cr ...
* Whyte notation
The Whyte notation is a classification method for steam locomotives, and some internal combustion locomotives and electric locomotives, by wheel arrangement. It was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte, and came into use in the early twenti ...
References
{{Locomotive running gear Train wheels